CHEM 232- Classifying Nucleophiles
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are characteristics of a good nucleophile and strong base
-C -, N -, O -
-Trapped charge (no resonance, no conductive effect, etc.)
-Small R group
What are characteristics of a poor nucleophile and strong base
-N -, O -
-Bulky R group
What are characteristics of a good nucleophile and weak base
- Charge is delocalized
- More polarizable and less electronegative than neutral oxygen
- conjugate base that are more stable than good Nu/strong base
What are characteristics of a poor nucleophile and weak base
Neutral oxygen species
For neutral nucleophiles, as we go ___________ a column, our atom gets ____________ and becomes more polarizable. As polarizability increases, it becomes a ______________ nucleophile.
down; bigger; better
What is solvolysis?
when the solvent acts as the nuceophile
During SN2 as substitution increases, relative rate becomes.....
slower
What is hydrolysis?
When H2O is both solvent and nucleophile
Define hyper conjugation
The stabilizing interaction that results from an interaction between the electrons in a sigma bond (usually C-C or C-H) and an adjacent empty or partially filled p orbital or pi orbital.
In SN1, only __________ ____________ _________ is active in the RDS, which makes it a _______ step reaction coordinate.
electron leaving group; two
SN1 Mechanisms:
Better leaving groups ______________ rate.
Changing the nucleophile has ______ __________ on rate.
More substitution at reactive (alpha) carbon ____________ rate.
If the reactive (alpha) carbon is a stereo center, the ________ stereoisomers form.
increases
no effect
increases
two
What are characteristics of radical halogenation?
sp2 hybridized
hyper conjugation stabilize
trigonal planar
flat
Carbocations are always:
- ________ hybridized
- The p orbital is ______
- _________ _________, flat
- __________ deficient, ___________ charged
- ___________ energy species
sp2
empty
trigonal planar
electron; positively
high
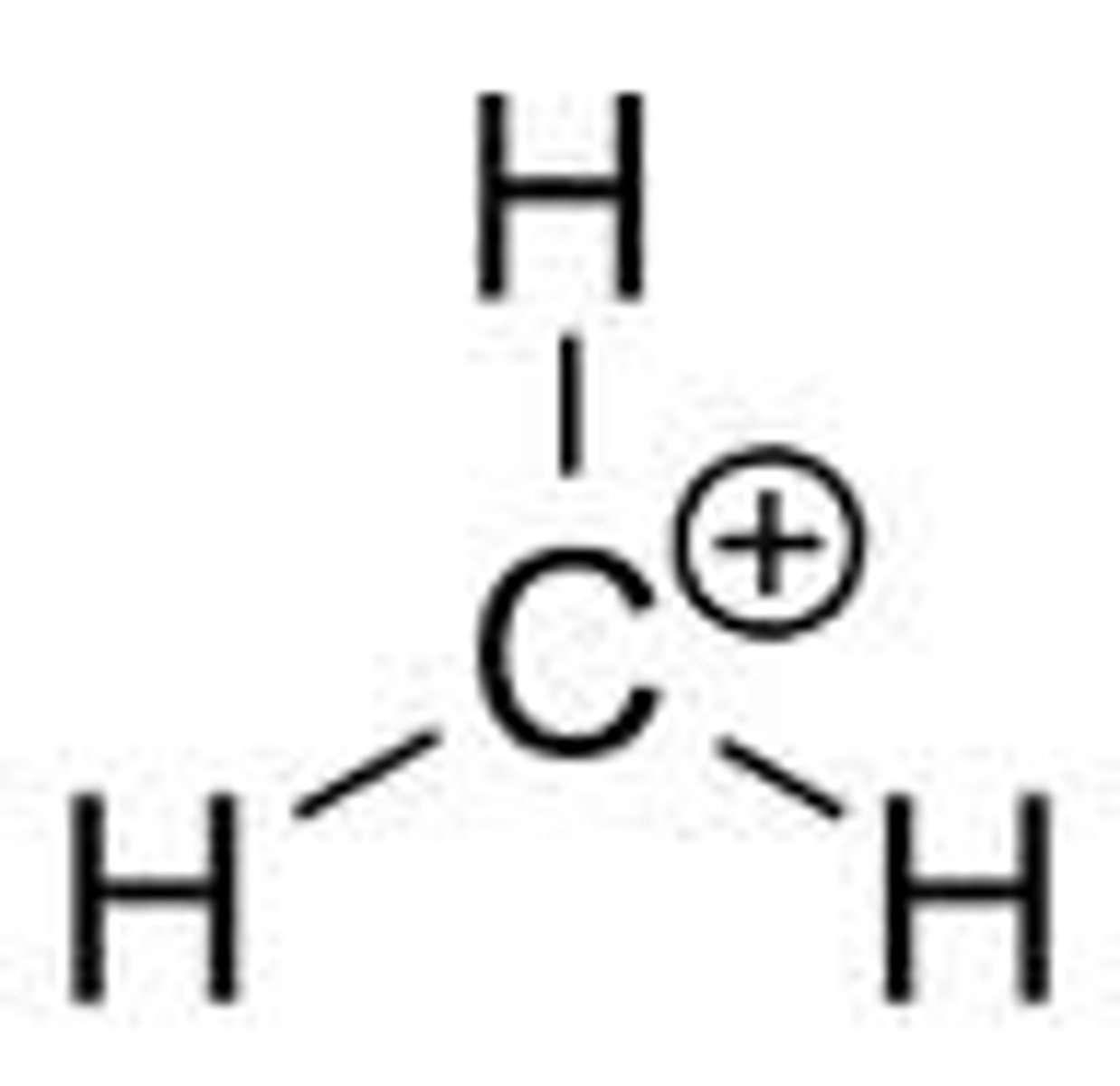
What is the first step of SN1?
What happens?
Dissociation
Leaving group leaves, bond breaks, and rate determining step happens
What is the second step of SN1?
What happens
Does the nucleophile attack from one or both sides?
Coordination
Nucleophile attacks, bonds made
Both
What is the third step of SN1?
What happens?
Acid/Base (deprotonation)
Proton transfers
Is water is a weak or strong nucleophile?
WEAK !!!
In SN1:
Nucleophile is the attacking ___________ _________
The electrophile is the _______________
electron pair
carbocation
You can only make stereoisomers if _______________ a stereo center
attacking
SN1 reaction rate:
A better _________ (more _____ conj. base) leaves faster.
leaving group; stable
SN1 reaction rate:
What is the Hammond Postulate?
More __________ at the alpha carbon _____________ the carbocation intermediate through ______________.
Share electron density to stabilize the carbocation/ late TS ++
substitution; stabilizes; hyper conjugation
Which two cannot SN1:
Methyl and primary or secondary and tertiary?
Why?
Methyl and primary because they are too high in energy and less stable
Hyperconjugation:
involves an interaction between.....
it stabilizes both ___________ and ______________.
is a ___________ effect than conjugation.
the interacting orbitals must be aligned on ___________ atoms.
p and sigma orbitals
radicals; carbocations
weaker
aligned
What is the most effective way to share electrons?
Both resonance and hyperconjugation do what?
Resonance
Share electron density
What do polar aprotic solvents do to the reaction rate? How do they stabilize the carbocation?
increase the reaction rate
through H-bonding
The nucleophile in SN1 is _________, which makes it a two step reaction.
The nucleophile in SN2 is ________, which makes it a one step reaction.
weak
strong
Which mechanism is this rate for:
rate= k [Nu][e-LG]
Sn2
What are the 5 key characteristics to SN2 mechanisms?
- 1 step reaction, concerted
- inversion, backside attack, stereospecific
- needs a good leaving group and a strong nucleophile
- less hindered (less crowded) electrophile (methyl, primary) is best
- max rate with polar parotid solvent
What mechanism is this rate for:
rate= k [e-LG]
SN1
What are the four key characteristics of SN1 mechanisms?
- 2 step mechanism, carbocation intermediate
- may form 2 stereoisomers
- needs to have a good leaving group and a stable carbocation (secondary or tertiary alpha carbons are best)
- maximize rate with polar protic solvent
If you have a secondary carbon leaving group, what determines what mechanism it will be?
if the nucleophile is strong then it is.......
if it is weak then it is.....
the nucleophile
SN2
SN1