1/2 6.4 Cloning
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What is vegetative propagation?
Natural cloning/asexual reproduction in plants
What are the vegetative organs of plants?
- Root and shoot tips
- Axillary buds
- Vascular cambium
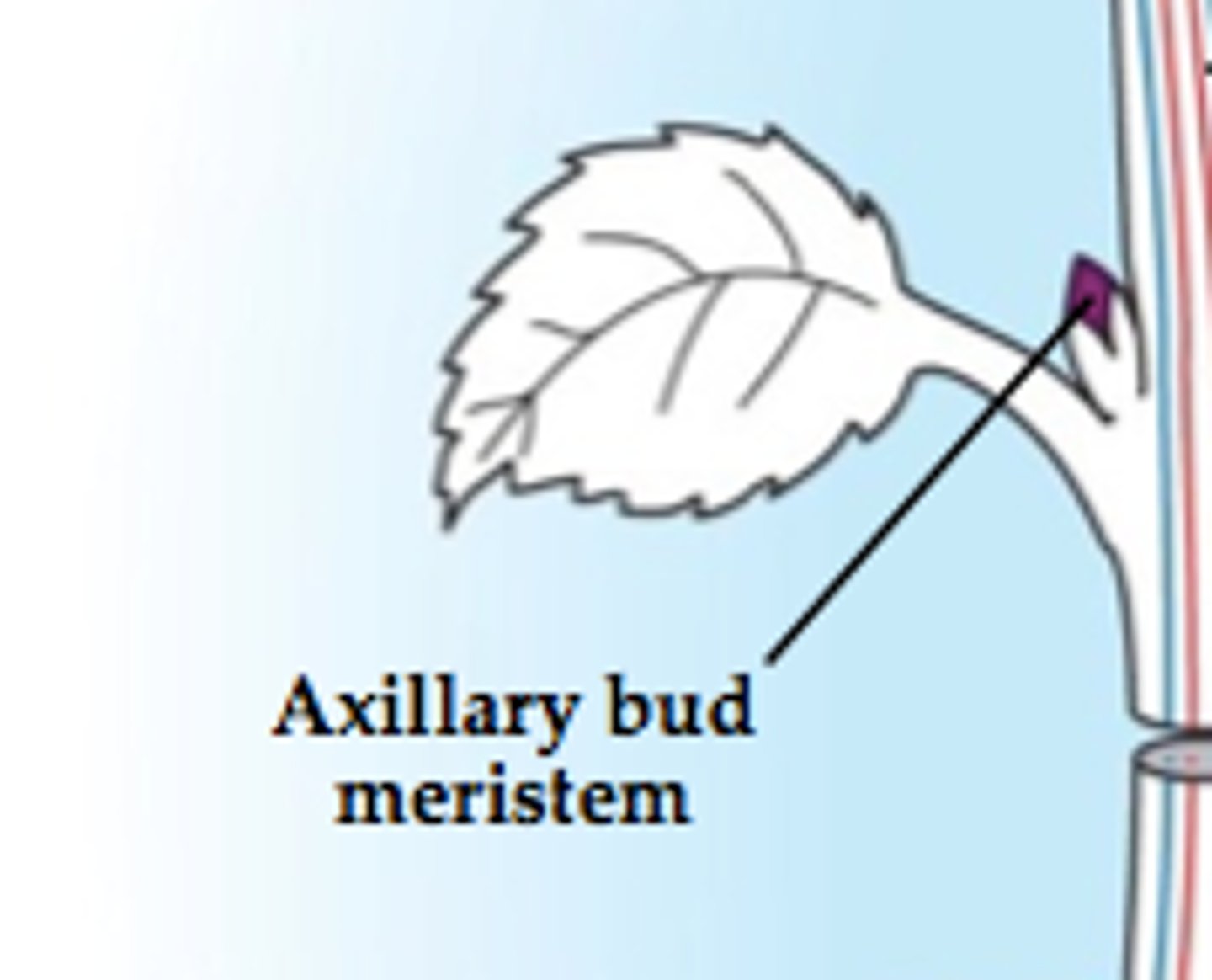
Where are axillary buds?
Where leaves and the stem meet
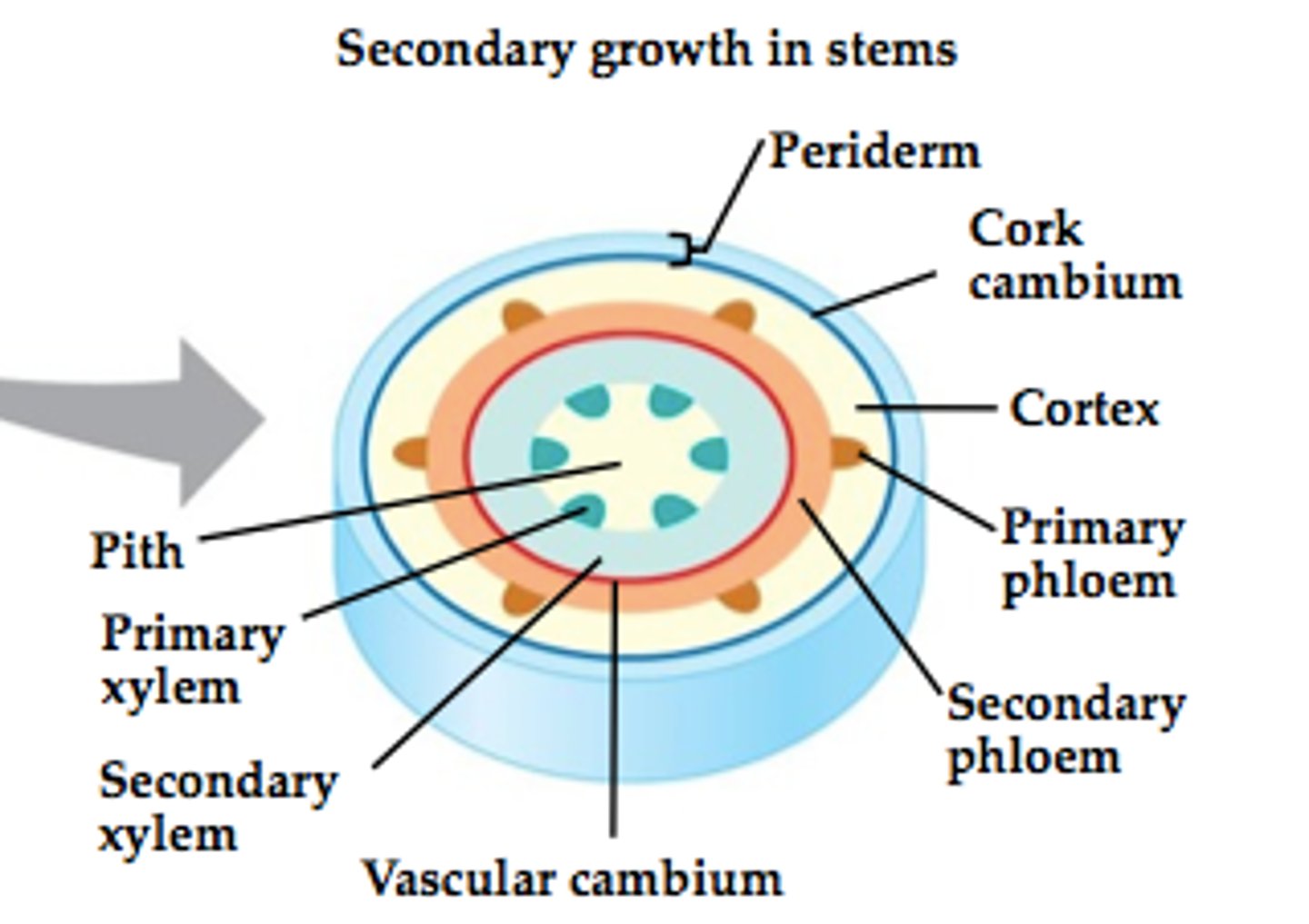
Where is vascular cambium?
Between xylem and phloem
Vegetative Reproduction Process
Over time, a plantlet forms at the vegetative organs and remains attached to its parent plant
These plantlets are clones of their parents as no other DNA has been introduced
At maturity, the plantlet becomes detached from its parent and can live independently, when it is capable of photosynthesising by itself
The new plants all have the same phenotype, so are uniform
What are runners/stolons?
Modified stems that grow horizontally above ground. The buds on these stems produce roots and shoots
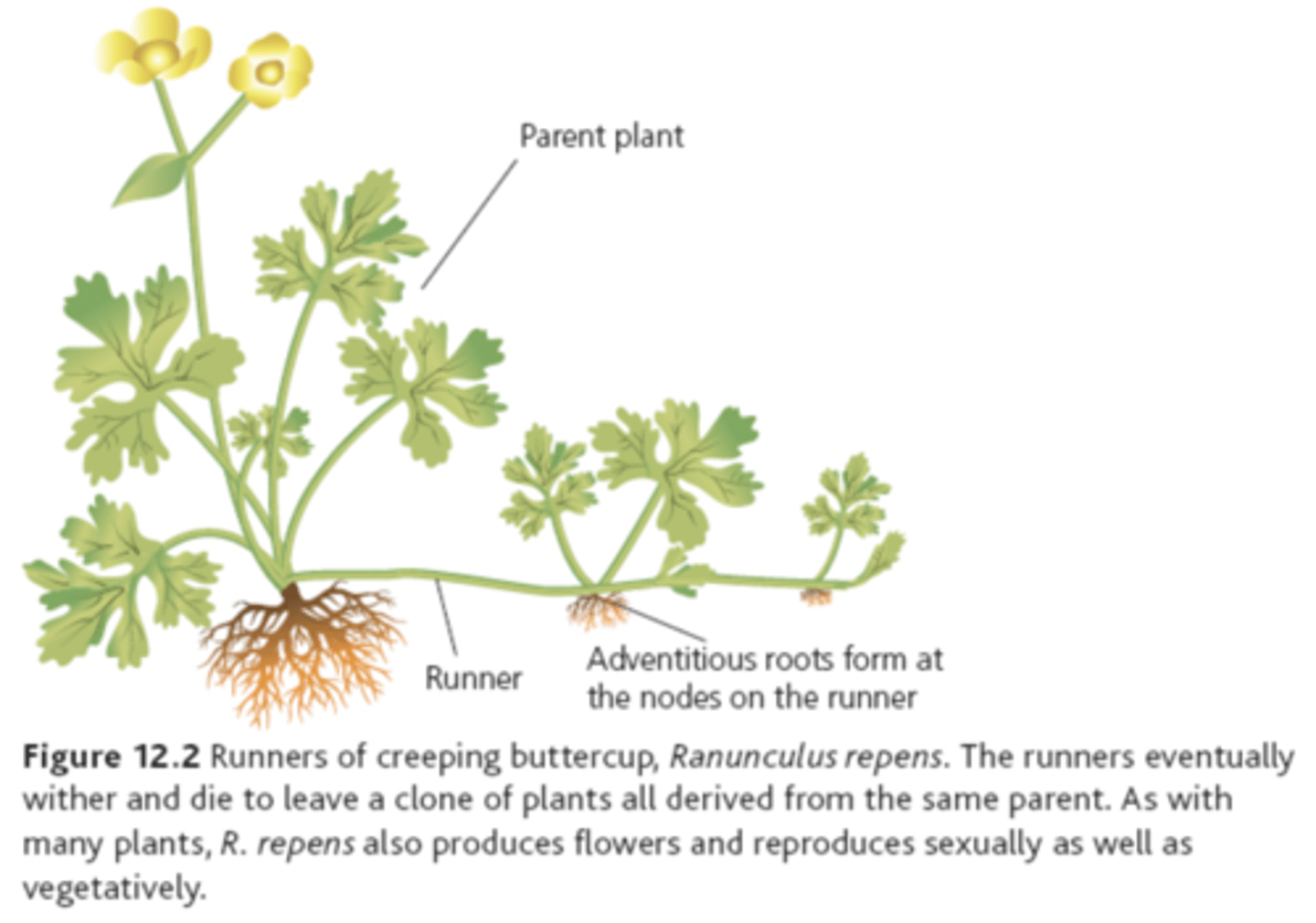
What are roots that form under the nodes of runner called?
Adventitious Roots
Will the plantlet be okay when the runner dies?
The plantlet is self sustaining so yh
What is propagation?
The reproduction of organisms (like plants) through methods like cuttings
Why don't methods of propagation require seeds?
It is asexual reproduction
A well as runners/stolons, how else can plants can propagate asexually?
Using tubers, bulbs, suckers
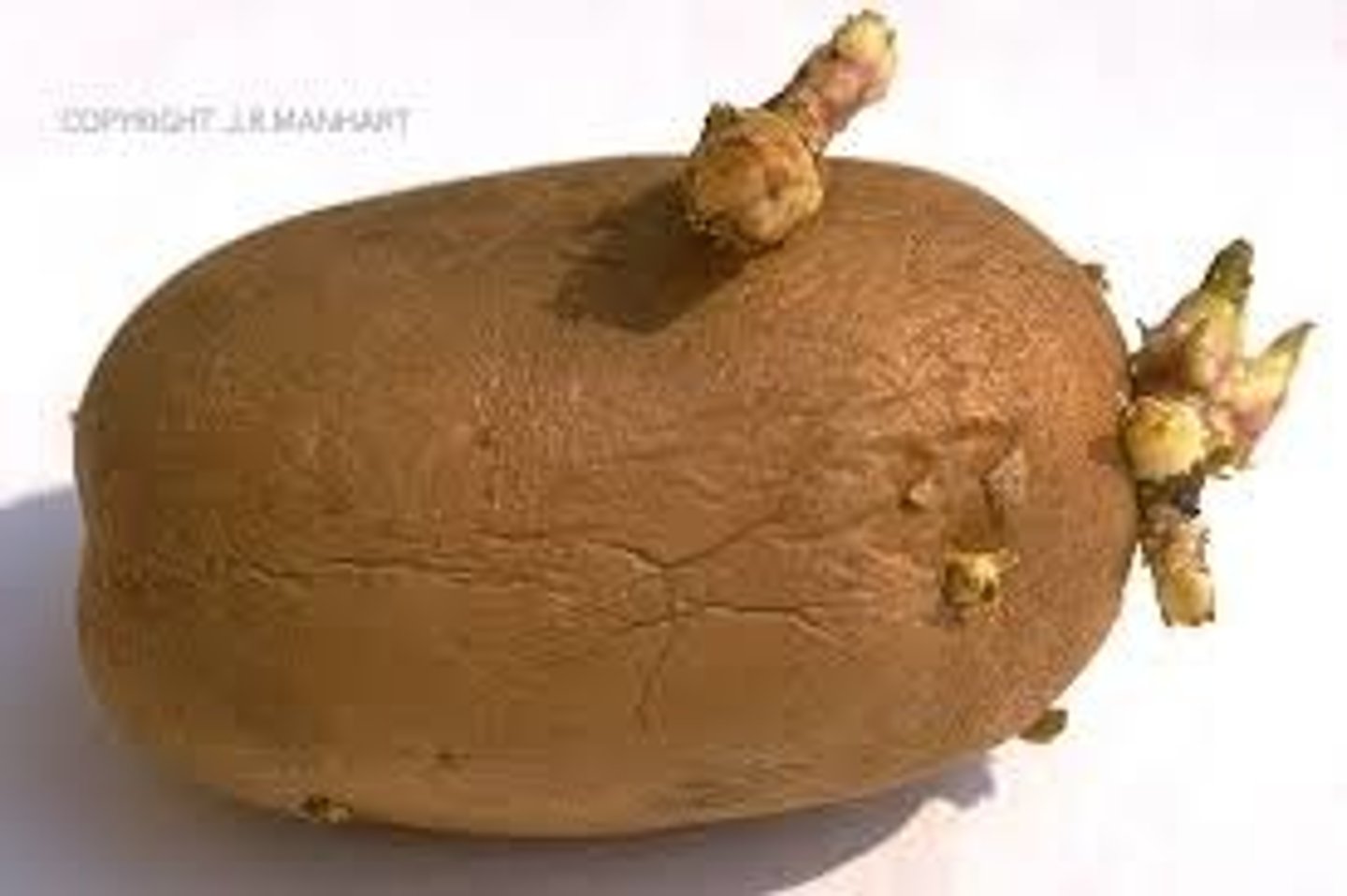
What is a stem tuber?
The tip of an underground stem becomes swollen with stored food to form a tuber or storage organ. Buds on the storage organ develop to produce new shoots (like eyes on a potato)

What is a stolon?
What is a bulb?
A thickened, underground stem with fleshy storage leaves attached at the base
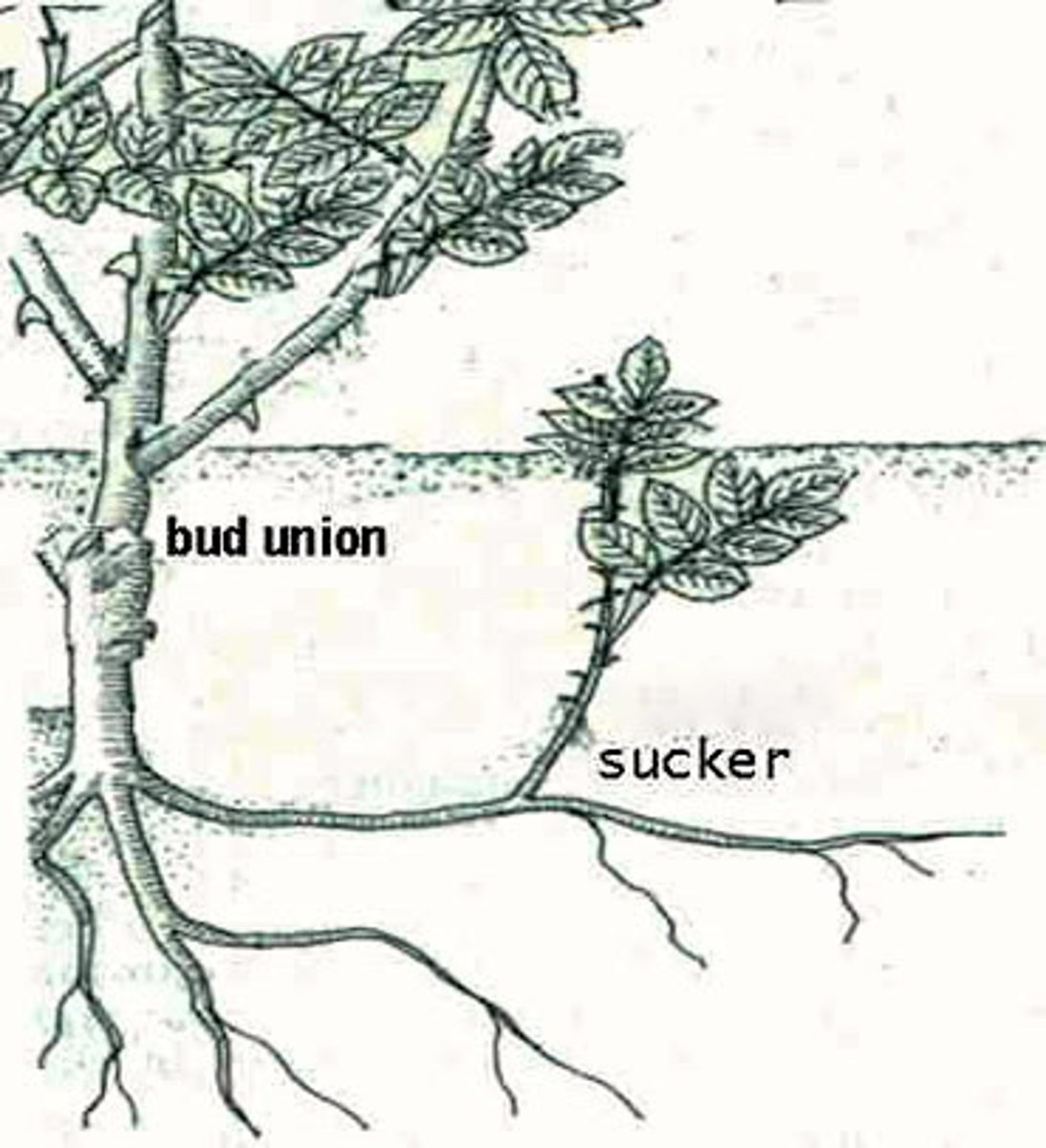
What are suckers?
Plant stems that arise from buds on the roots
What do onions and garlic produce?
- Bulbs
- Bulbs can grow adventitious roots underground and leafy shoots above ground
How the production of natural clones is exploited in horticulture.
- To propagate desirable species asexually, effectively, and at a lower cost than utilising sexual reproduction techniques.
- Splitting up bulbs, removing young plants from runners, and cutting up rhizomes all increase plant numbers cheaply, and the new plants have exactly the same genetic characteristics as their parents.
What are adventitious roots?
Roots that develop from the shoot system instead of the root system
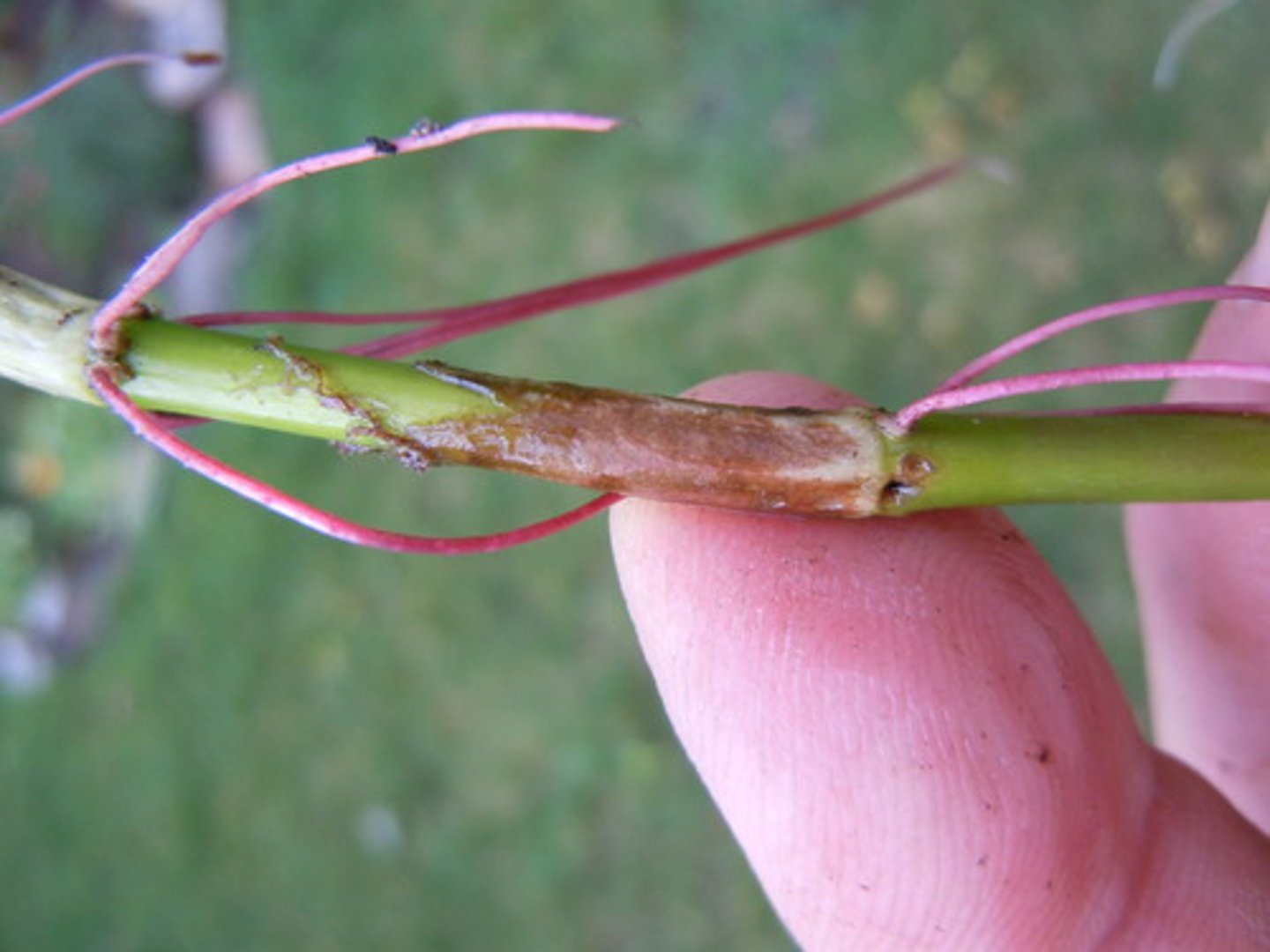

Perennials, shrubs, and herbs, can all what?
Grow adventitious roots from their cut stems
Why are cuttings used?
- It is a straightforward propagation technique
- Can expand the plant stock at a very low cost
- They can grow to full sized plants much quicker than from seeds
Equipment for Plant Cuttings
- Sharp scissors
- Potting compost
- Pots to house new plants
- Hormone rooting powder
- Plastic bag to cover cutting
What does hormone rooting powder contain?
Auxins
What do auxins do?
They promote mitosis and cell differentiation in the new root growth
What does mitosis produce in plants?
A mass of cells called a callus
Method for Plant Cuttings
Use a healthy shoot
Cut stem at a slant, between nodes
Dip in rooting powder
Place in soil/compost and add water
To reduce transpiration, cover with a plastic bag, or remove some leaves.
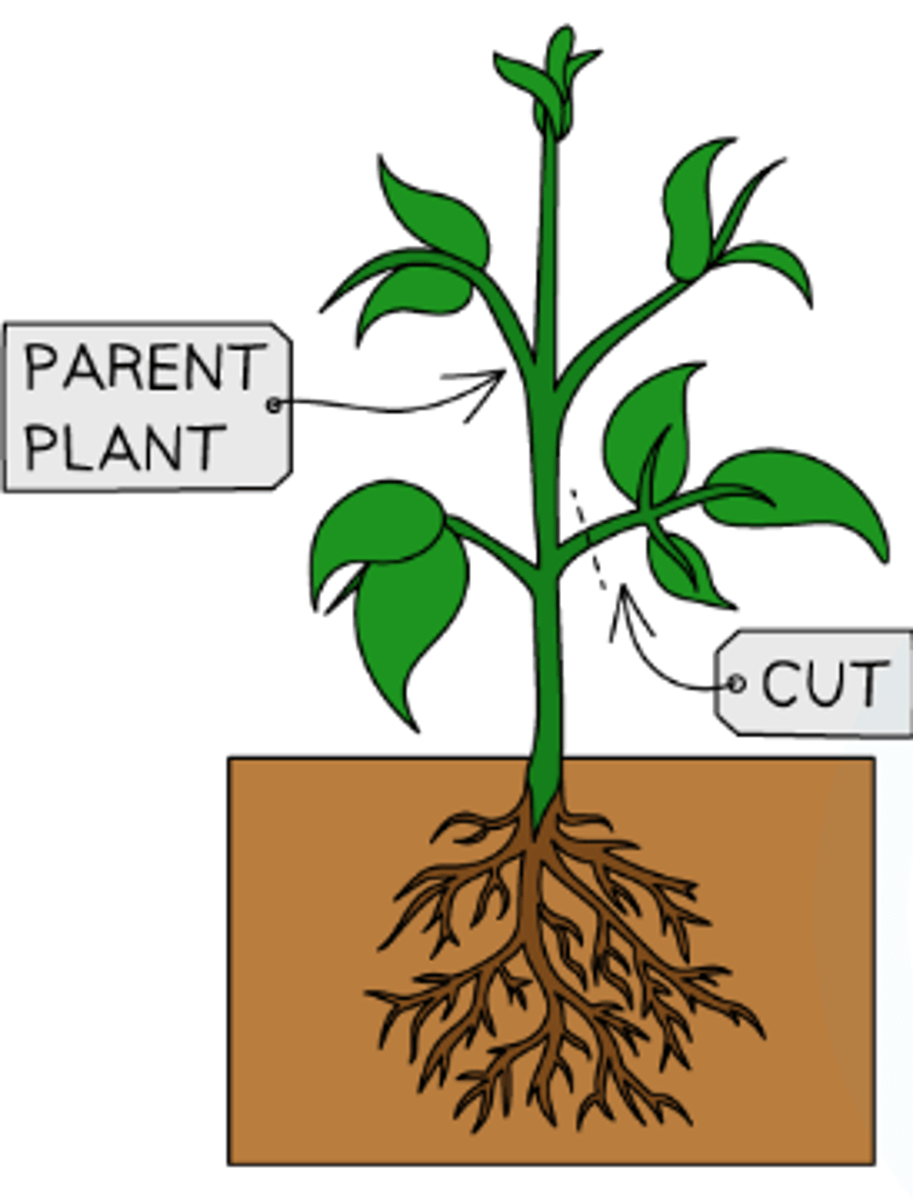
How to improve the Method for Plant Cuttings?
Select stem with no flowers to encourage root growth and reduce water loss
Remove most leaves to reduce water loss
Sterilise equipment to stop infection
Place in a greenhouse to control temperature, humidity, and moisture
Do not overwater the compost to allow air to reach the roots for root respiration
What is micropropagation?
The process of making large numbers of genetically identical offspring from a single parent plant using a tissue culture techniques
What are cultivars?
Plants that have been intentionally bred or selected by humans for specific traits like taste, size, colour, or disease resistance.
What are the benefits of plant cells being totipotent?
An entire plant can be reproduced from any of these cells
What is tissue culture?
Tissue culture is when cells are grown artificially, separate to the parent organism
Why is it possible that many clones can be produced from an original parent plant?
Many explants can be taken from the parent plant, and the calluses can be subdivided.
What practices must be taken during micropropagation?
- The explant must be disinfected
- Aseptic techniques must be used
- This is to avoid fungi from colonising the growth medium and causing the micropropagation to fail
Why is micropropagation used?
To reproduce endangered species of plants where relatively little source material exists
Method for Micropropagation:
Wear eye protection.
Wipe all surfaces with disinfectant.
Soak all apparatus in sterilant
We do all this to ensure a sterile environment so that no fungi will contaminate the experiment, as that would result in seeing a fungal growth rather than an explant growth
Cut the plant material into explants (e.g. a leaf/bud/root)
Sterilise the explant with alcohol. This is to ensure only the plant cells are present.
Place the explant on agar containing glucose and amino acids.
Glucose is used for aerobic respiration
Amino acid used to make proteins
A callus will form
We can treat this callus by inducing high auxin and cytokines. The callus can be sub divided into different sizes. We are treating it to induce the roots.
Transfer to a greenhouse
What does this micropropagation experiment show?
This shows that the cells in the explant have the capability to produce all the different cell types that make up a full cauliflower plant, hence they are totipotent.
Differences between cuttings and micropropagation:
Cutting requires less expensive equipment than micropropagation
Cutting requires less staff than micropropagation
Cutting produce less clone offspring than micropropagation.
How can natural cloning occur?
- Embryo splitting
- Fragmentation
- Budding
- Parthenogenesis
What is budding?
The growth of a new animal out of the side of the original animal by mitosis
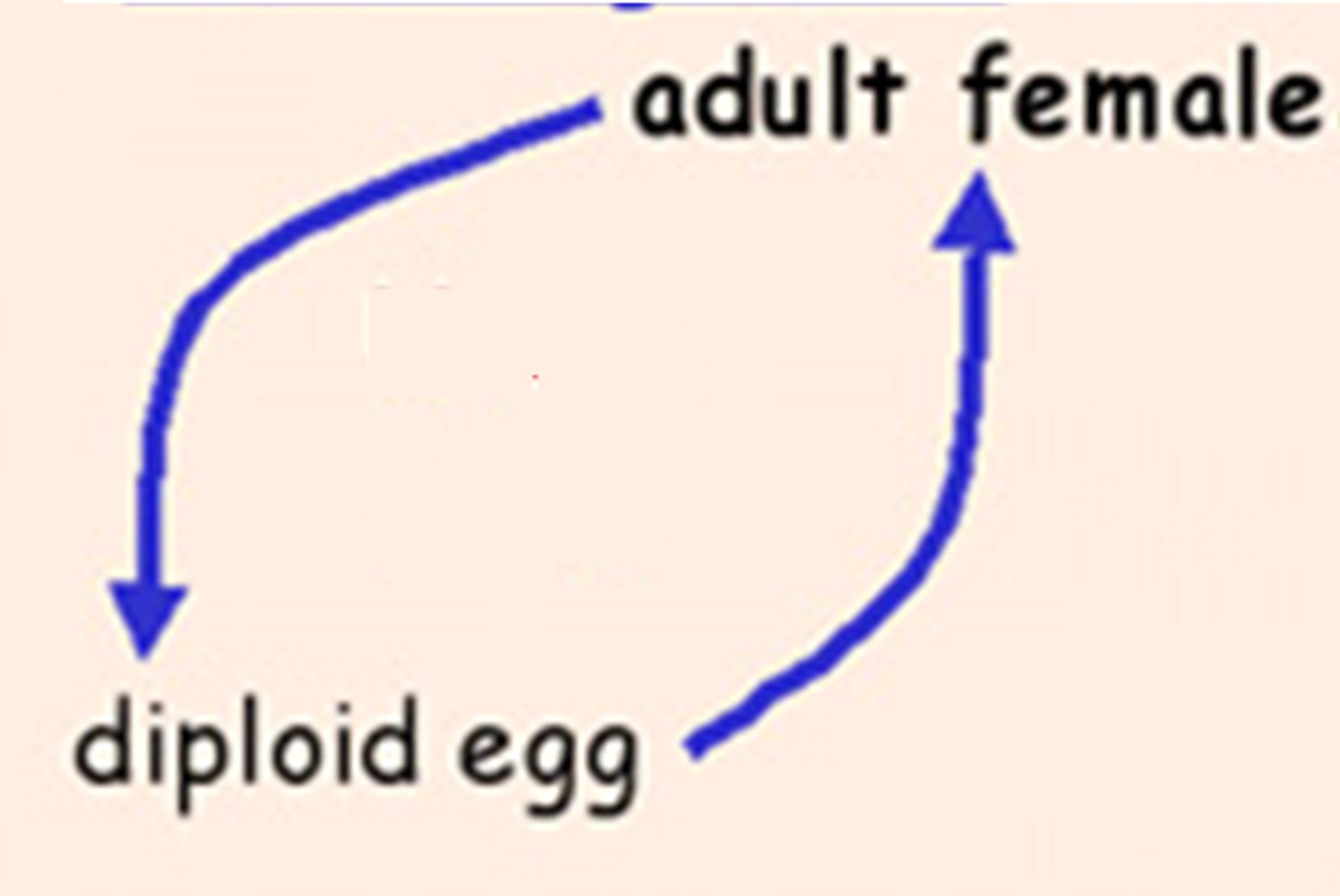
What is parthenogenesis?
A natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and development of embryo clones occur without fertilisation by a male gamete
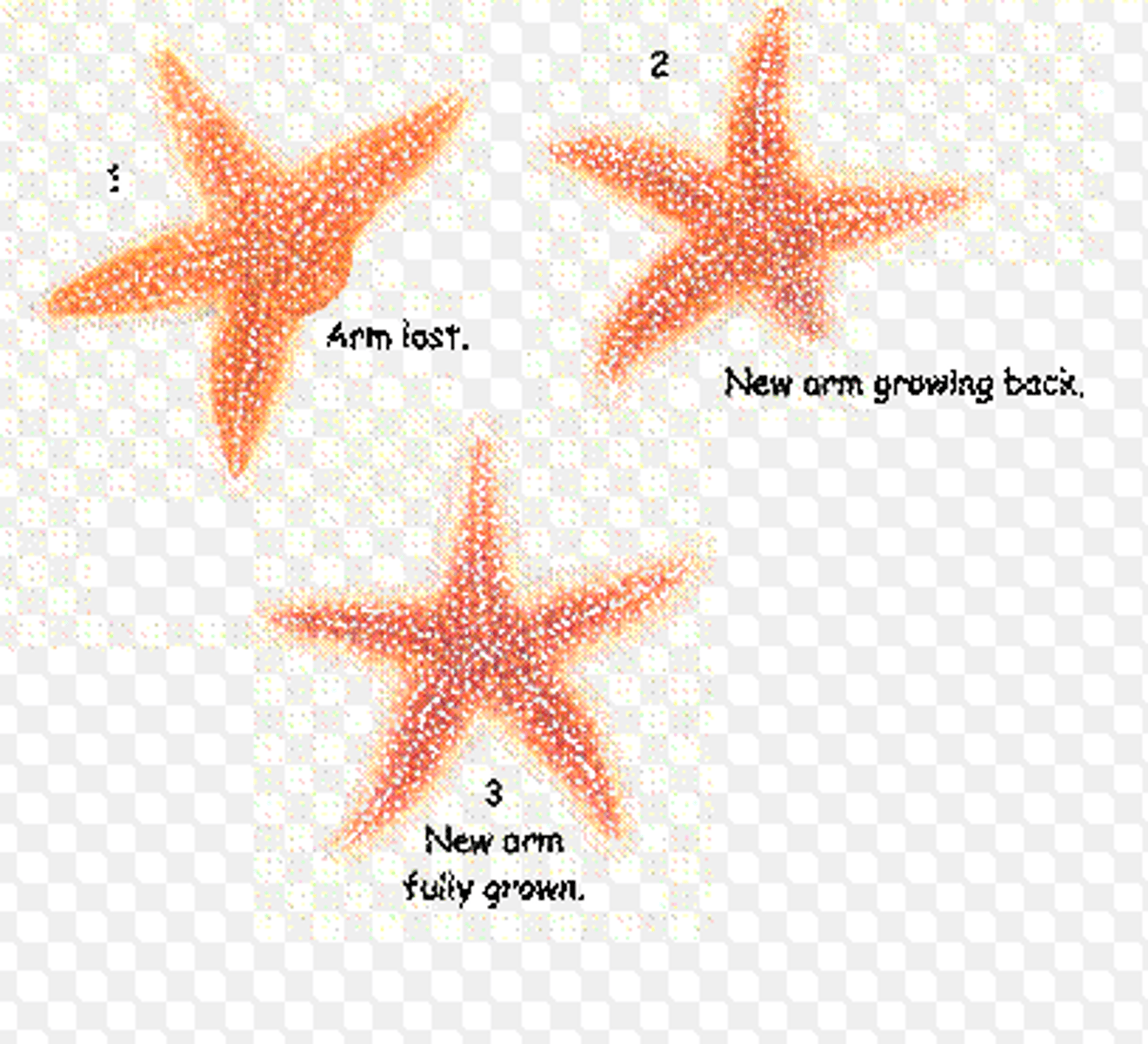
What is fragmentation?
It involves the breaking up of the original animal into small parts, each of which can then grow into a whole animal as seen in some corals, sea anemones and starfish.
Monozygotic Twins Process
An egg is fertilised by a sperm as in a singleton birth
This forms a zygote
The single zygote undergoes a few cell cycles (mitotic divisions) to become an embryo. This is why identical twins are referred to as monozygotic
At the embryo stage, the embryo splitting occurs.
Two embryos that form are identical, with the same genotype and develop in utero together
The result is the birth of identical offspring, always of the same gender, with identical phenotype
Why are non identical twins not considered twins?
Because non-identical twins are formed from separate eggs and sperm, they are not considered clones
Arguments for Artificial Plant Cloning
Desirable genetic characteristics always pass on to clones (doesn't always happen when plants reproduce sexually)
It produces lots of plants quickly, compared to the time it would take to grow them from seeds
Used to reproduce seedless fruit/plants
Propagation can be done at any time of the year
All the plants produced will be uniform
Arguments against Artificial Plant Cloning
Undesirable characteristics passed on
Low genetic diversity, so disease can easily wipe them out
Contamination by microorganisms during tissue culture can be disastrous and result in complete loss of the plants being cultured
What is Artificial twinning?
A process that produces offspring that are clones of each other but not of their parents
Why is Artificial twinning carried out?
It boosts yields of livestock and promotes desirable characteristics
Artificial Twinning Process
Animal with the desired trait is given hormone treatment to release more eggs
The ova can then be fertilised naturally or by artificial insemination
The totipotent blastocysts split to produce several smaller zygotes in vitro
The zygotes are grown in the lab for a few days to ensure they are good, before being implanted into a surrogate mother.
The surrogate mother gives birth to identical twins
Why are the two split embryos usually put into different surrogate mothers rather than both placed in one surrogate mother?
A single pregnancy carries fewer risks than twin pregnancies
What are the benefits of Artificial twinning?
Guarantees desirable characteristics in the offspring
However, what is the problem with Artificial twinning?
It is not possible to predict how many offspring will be produced
What is reproductive cloning?
Producing an individual who is genetically identical to another
What is reproductive cloning also known as?
Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer
What is a somatic cell?
Body cell
Dolly the Sheep
First livestock animal that was cloned from an adult somatic cell
What number of animals are required for reproductive cloning?
1 - An animal to be cloned donates a cell
2 - A female donates an egg cell
3 - A surrogate mother
SCNT Process
The animal to be cloned donates a somatic body cell
The nucleus from the somatic cell is removed
An unfertilised egg cell is extracted from the female egg donor.
The unfertilised egg cell is enucleated (nucleus is removed)
The nucleus from the somatic body cell is fused with the enucleated egg cell using an electric current.
The hybrid zygote cell is now treated to encourage it to divide by mitosis
The embryo is implanted into the surrogate mother for gestation and birth
What is the result of reproductive cloning?
The surrogate mother gives birth to a cloned animal with identical DNA to the original animal that donated the somatic body cell.
What variables must be kept the same when comparing SCNT results?
- The age of the nuclear donor
- The conditions the surrogate mother were kept in
- The health of the surrogate mothers
Arguments For Animal Cloning
Embryo cloning is well accepted and noncontroversial in the field of livestock farming
Cloning can remove less desirable characteristics from the gene pool over time, much in the way that selective breeding has done
Many animals with desirable characteristics can be cloned, ideal for maximising agricultural output eg. milk yield in cattle
Cloning can help preserve endangered species, ahead of possible reintroduction of those species to the wild
Cloning can provide regenerated organs for patients suffering from degenerative disease.
Such organs will be a direct genome match to the patient so would have no risk of rejection by the immune system
Arguments Against Animal Cloning
The process of somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is very variable
Subsequent cloning attempts have led to a high number of early deaths and genetic abnormalities in the clones
Cloning destroys embryos which could in theory develop into a healthy adult animal
Definition of Monozygotic
Organisms that originate from a single zygote (fertilized egg).