T18: hemodynamics, edema, hemorrhage, hemostasis
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
hemodynamics
how blood flows through your vessels
hemodynamic factors
things that affect how well your blood flows
hemodynamic instability
means body can't get enough blood flow (aka shock)
hyperemia and congestion refer to
an increase in blood volume within a tissue
hyperemia
active process resulting from arteriolar vasodilation and increased blood inflow
where does hyperemia occur
sites of inflammation and in exercising skeletal muscle
describe hyperemic tissues
redder than normal bc engorged with oxygenated blood
congestion
passive process resulting from impaired outflow of venous blood from a tissue
congestion in liver and extremities is caused by
right heart failure
congestion in lungs is caused by
left heart failure
describe congested tissues
abnormal blue-red color (cyanosis) that stems from accumulation of deoxygenated hemoglobin
2/3 of body water is
intracellular
1/3 of body water is
extracellular
extracellular blood is composed of
interstitial fluid
blood plasma
edema
an accumulation of interstitial (extravascular) fluid within tissues
effusion
accumulation of extravascular fluid in body cavities
hydrothorax/pleural effusion
fluid in the pleural cavity
hydropericardium / pericardial effusion
fluid in pericardial cavity
hydroperitoneum/free fluid/ascites
fluid in peritoneal cavity
anasarca
severe, generalized edema marked by profound swelling of SQ tissues and accumulation of fluid in body cavities
pitting edema
edema that retains an imprint when touched, commonly associated with left-sided CHF, usually LE
why does edema accumulate
increase vascular hydrostatic pressure
decreased plasma osmotic pressure
lymphatic obstruction
inflammation
fluid movement between vascular and interstitial spaces is governed by what
vascular hydrostatic pressure
colloid osmotic pressure
hydrostatic pressure
the pressure within a blood vessel that tends to push water out of the vessel
osmotic pressure
the external pressure that must be applied to stop osmosis
the edema fluid that accumulates due to high hydrostatic pressure or low colloid osmotic pressure is a _______
protein-poor transudate
inflammatory edema fluid is a _______
protein-rich exudate
why is inflammatory edema a protein-rich exudate
because increased vascular permeability
causes of edema
increased hydrostatic pressure
impaired venous return
arteriolar dilation
reduced plasma osmotic pressure
lymphatic obstruction
sodium retention
inflammation
hemorrhage
the leakage of blood from vessels
hemorrhagic diatheses
bleeding disorders
4 types of hemorrhage
petechiae
purpura
eccymoses
hematoma
large bleeds into body cavities are described according to their _____
location
why do large hemorrhages occasionally result in jaundice
RBC and hemoglobin are broken down by macrophages
petechiae
minute hemorrhages into skin, mucous membranes, or serosal surfaces
causes of petechiae
low platelet counts
defective platelets
loss vascular wall-support
increased vascular pressure
(1-2mm diameter)
purpura
3-5mm hemorrhages and usually raised
causes of purpura
vascular inflammation
trauma
increased vascular fragility
same disorders that cause petechiae
petechiae (picture
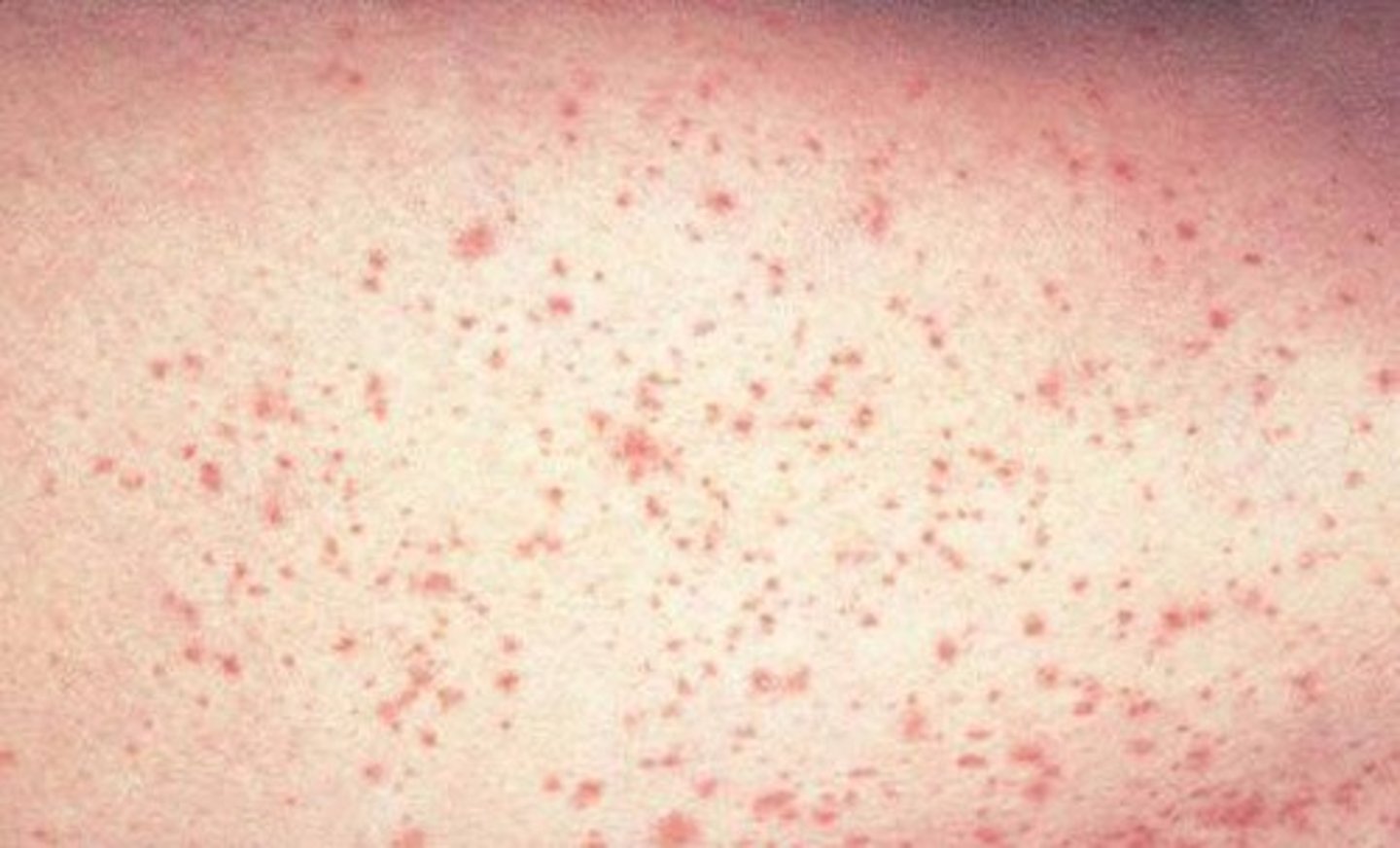
purpura (picture
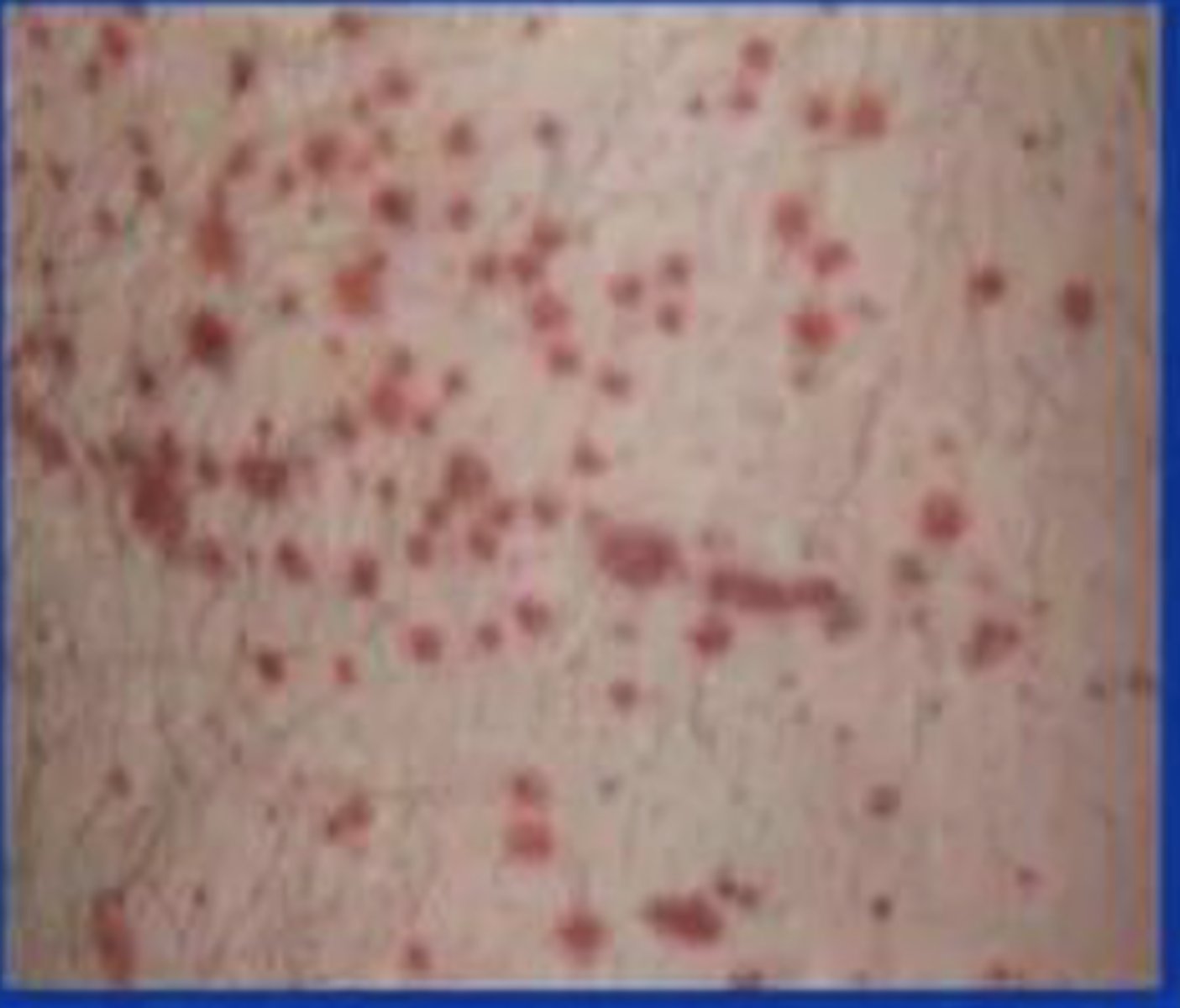
ecchymosis
1-2 cm SQ hematomas (bruises)
extravasated
let or forced out from the vessel into the surrounding area
cause of ecchymosis
trauma
early bruising appears
red-blue to blue-green
bruising eventually turns what color
golden-brown
ecchymosis (picture)
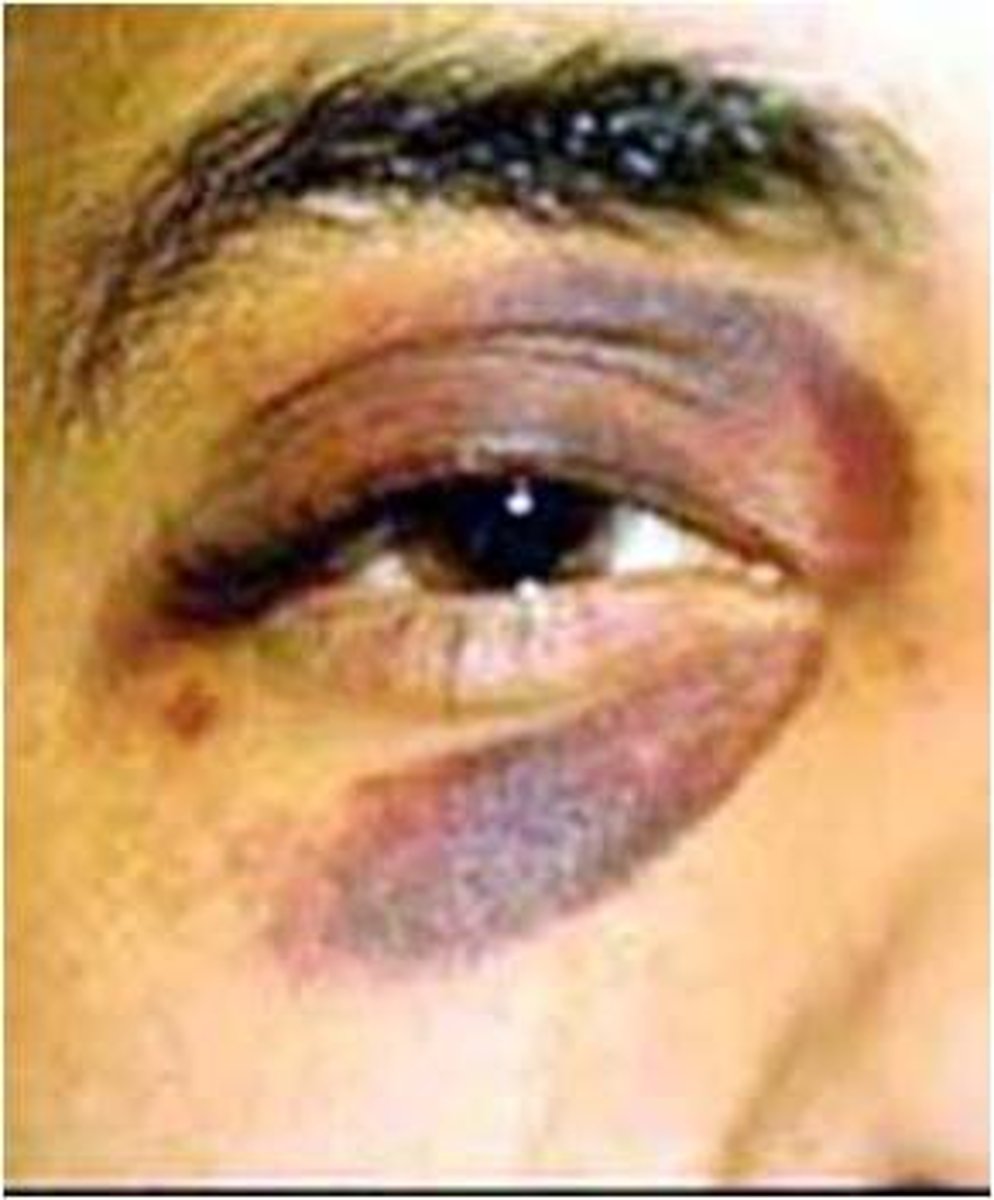
hematoma
hemorrhage that accumulates within a tissue
clinical impact of a hemorrhage depends on:
1. volume blood lost
2. rate of bleeding
3. location of bleed
4. health of individual
hemostasis
process initiated by a traumatic vascular injury that leads to the formation of a blood clot
pathogenic counterpart of hemostasis
thrombosis
thrombosis
formation of a clot (thrombus) within vessels that is inappropriate
thrombus
blood clot
thrombus is formed of
platelets, fibrin, +/- RBC
when does a thrombus occur
when procoagulant component of hemostasis escapes the regulatory factors and fibrinolysis (when disruption of factors that contsitute Virchow's triad)
virchow triad
the primary abnormalities that lead to intravascular thrombosis
components of virchow's triad
endothelial injury
stasis/turbulent blood flow
hypercoagulability
how does abnormal blood flow lead to arterial/cardiac thrombosis
-by causing endothelial injury/dysfunction
-by forming countercurrents and local pockets of stasis
hypercoagulability
an abnormally high tendency of the blood to clot
hypercoagulability is an important risk factor for
venous thrombosis (occasionally contributes to arterial or intercardiac thrombosis)
what is hypercoagulability caused by
alterations in coagulation factors
arterial thrombosis commonly present as
myocardial infarction or stroke
venous thrombosis commonly present as
DVT in smaller veins of legs/arms
embolize
when venous thrombi can detach and travel elsewhere
what happens to thrombi?
propagation
organization
recanalization
dissolution
embolization
primary complication of thrombi
occlusion of BV > leading to ischemia
embolus
detached intravascular solid/liquid/gaseous mass that is carried by the blood from its point of origin to a distant site (where it often causes tissue dysfunction or infarction)
the vast majority of emboli derive from _____
dislodged thrombi (blood clot)
fat emboli
emboli composed of fat droplets
air emboli
bubbles of air/nitrogen
cholesterol emboli
atherosclerotic debris
primary consequence of systemic embolization (arterial)
ischemic necrosis (infarction) of downstream tissues
primary consequence of pulmonary embolization (venous)
hypoxia, hypotension, R sided heart failure
infarct
area of ischemic necrosis (dead cells) caused by occlusion of vascular supply of affected tissue
effects of vascular occlusion are influenced by
- anatomy of vascular supply
- rate of occlusion
- tissue vulnerability to hypoxia
most important factor in determining whether occlusion of an individual BV causes damage
presence or absence of an alternative blood supply
organs that can withstand infarction due to dual blood supply
lungs, liver
organs that cannot withstand infarction due to end-arterial circulations
kidneys, spleen
why are slow developing occlusions less likely to cause infarction
because they allow time for the development of collateral blood supplies
neurons and hypoxia
die after 3-4 minutes of ischemia
mycardial cells and hypoxia
die after 20-30 minutes of ischemia
thromboembolism underlies 3 major causes of morbidity and death:
mycardial infarction
pulmonary embolism
stroke
primary hemostasis
formation of platelet plug
steps of hemostasis
1. vasoconstriction
2. primary hemostasis
3. secondary hemostasis
4. clot stabilization
what happens in arteriolar vasoconstriction
injured endothelial cells release endothelin > vessels contract
steps of primary hemostasis
1. platelet adhesion
2. shape change
3. granule release
4. recruitment
5. aggregation
platelet adhesion
platelets bind to von willebrand's factor (released by endothelial cells) on collagen
how do platelets bind to vWf
GP1b receptor on platelets binds to vWf on collagen
platelet shape change
platelets change from small and round to flat, spiky protrusions that increase SA
granule release and recruitment
platelets release granules (vWf, serotonin, ADP, thromboxane A2) to attract more platelets
aggregation
aggregation of platelets at site of injury to form a platelet plug
secondary hemostasis
deposition of fibrin
tissue factor (factor 3)
membrane-bound procoagulant glycoprotein normally expressed by subendothelial cells in vessel wall (ie smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts)
extrinsic and intrinsic pathways lead to activation of _______ at the ______ pathway
factor Xa
common pathway
activation of factor Xa leads to what?
formation of fibrin mesh
tissue factor binds and activates factor 7 that lead to
thrombin generation
functions of thrombin
-activates platelets
-activates 5a (commmon) and 8 (intrinsic)
-cleaves fibrinogen > fibrin
-cleaves stabilizing factor (8a)
prothrombin
factor 2
thrombin
factor 2a
fibrin
factor 1a
fibrinogen
factor 1