Radiography midterm study
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
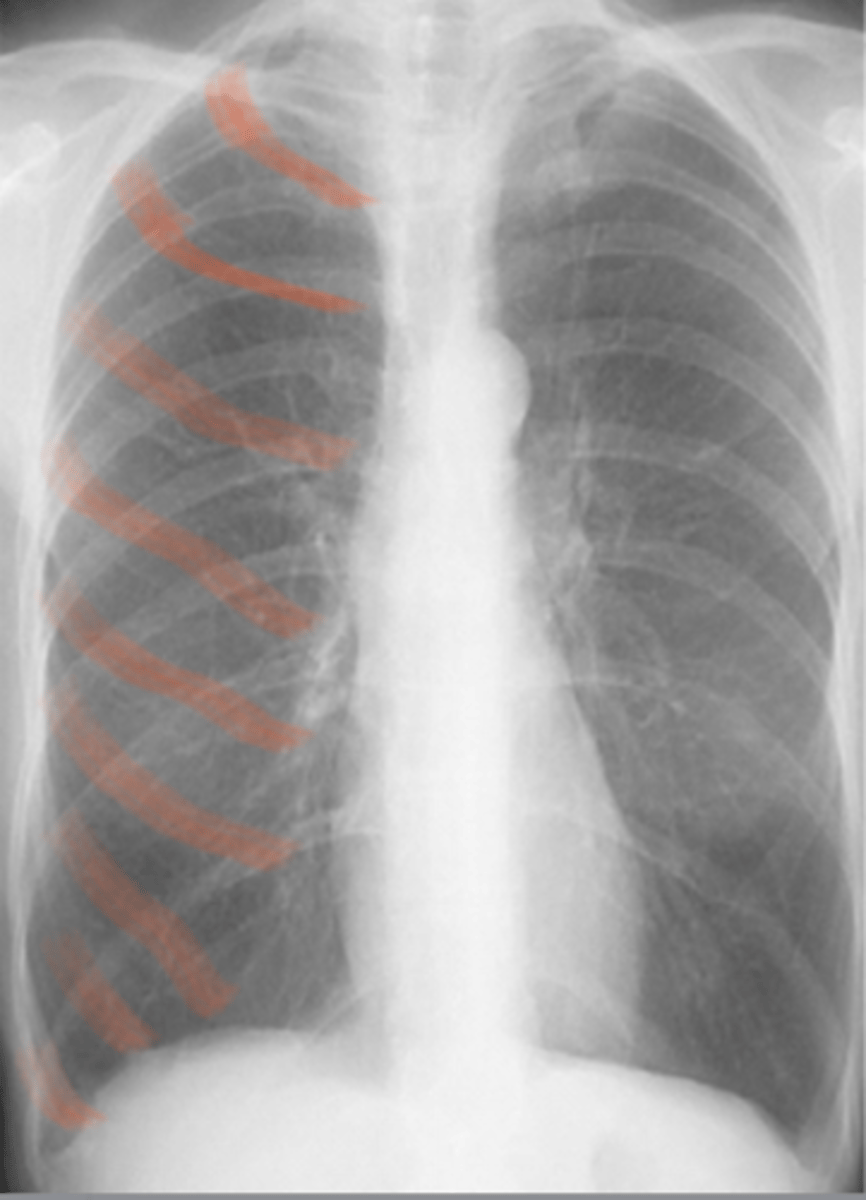
Pneumothorax
Hyperlucency
Trachea Shift →
Kerley B lines represent collapsed lung
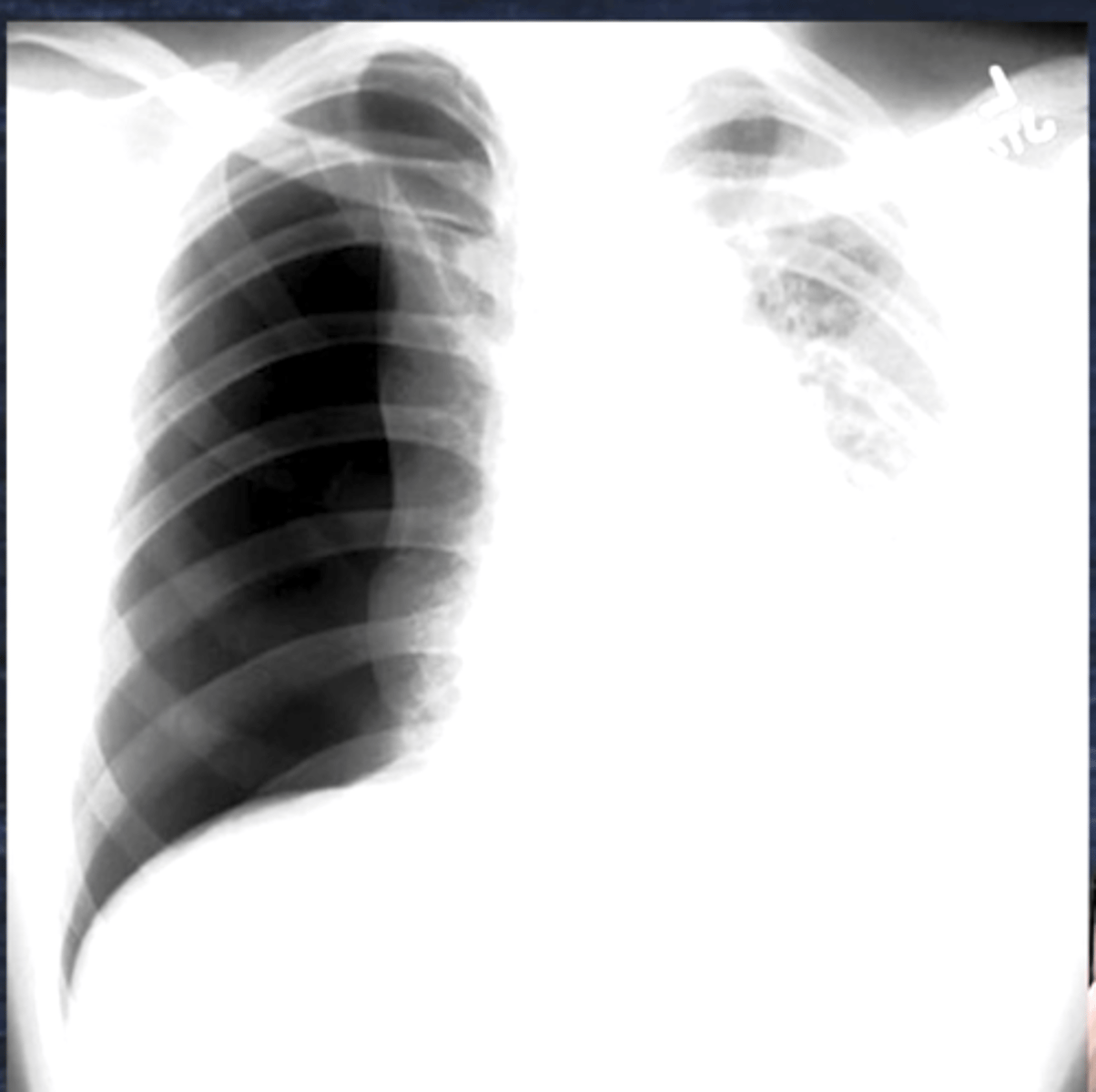
Pneumonia
Consolidation =Whiteness = Pneumonia
Blunted Costophrenic angles = consolidation secretions
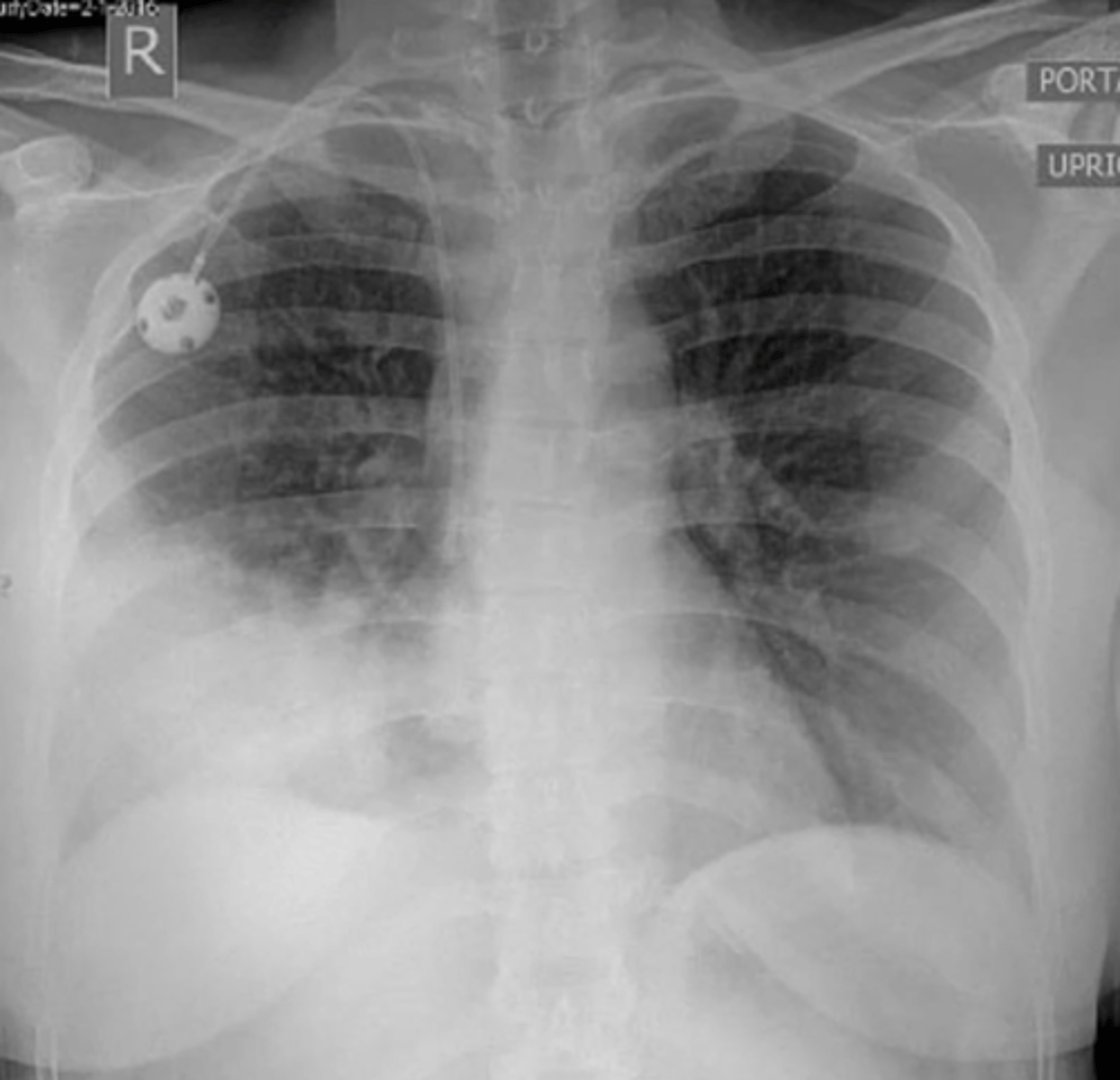
Pulmonary edema
Fluffy infiltrates = pulmonary edema
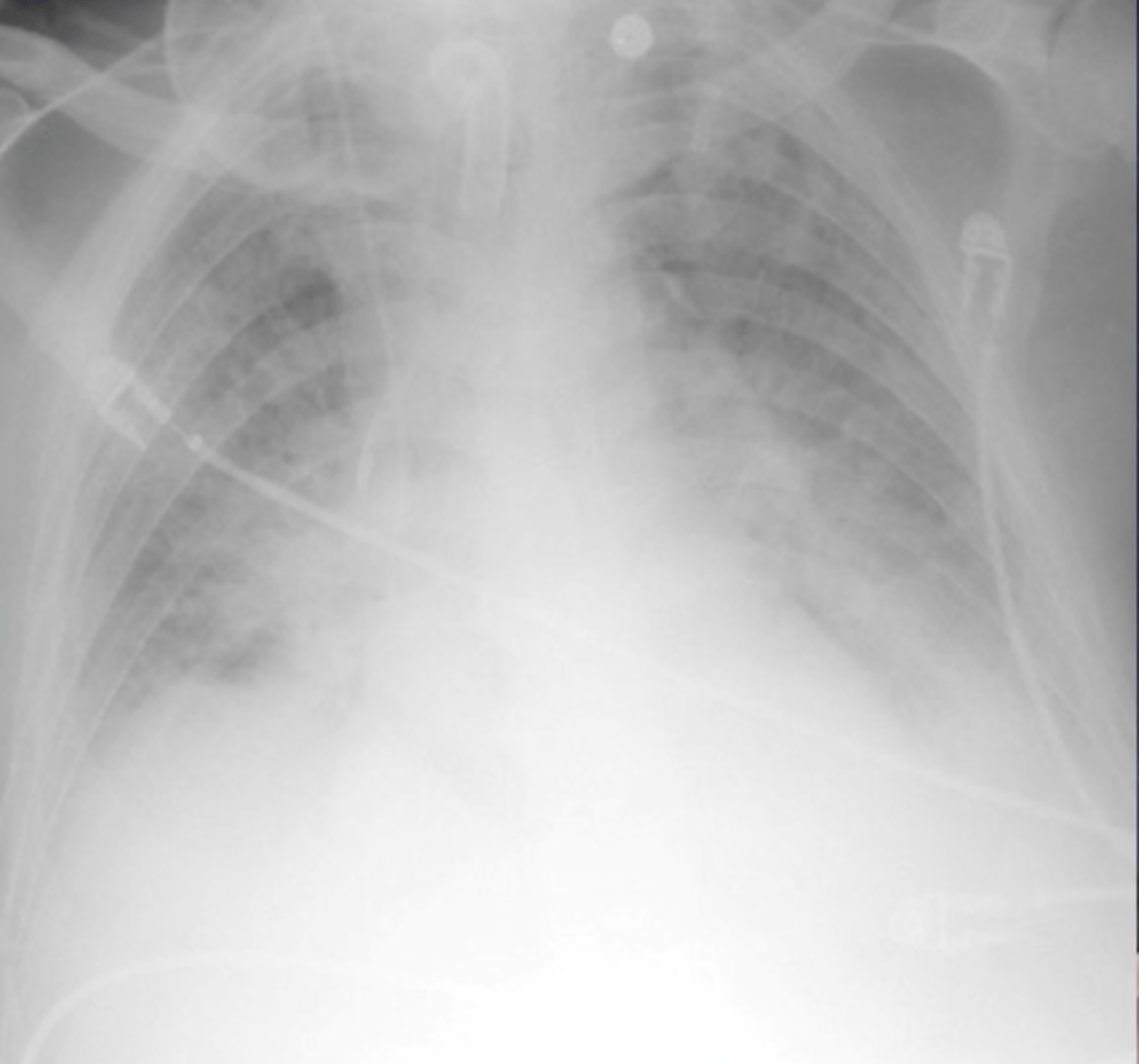
ARDS
Scattered patchy infiltrates
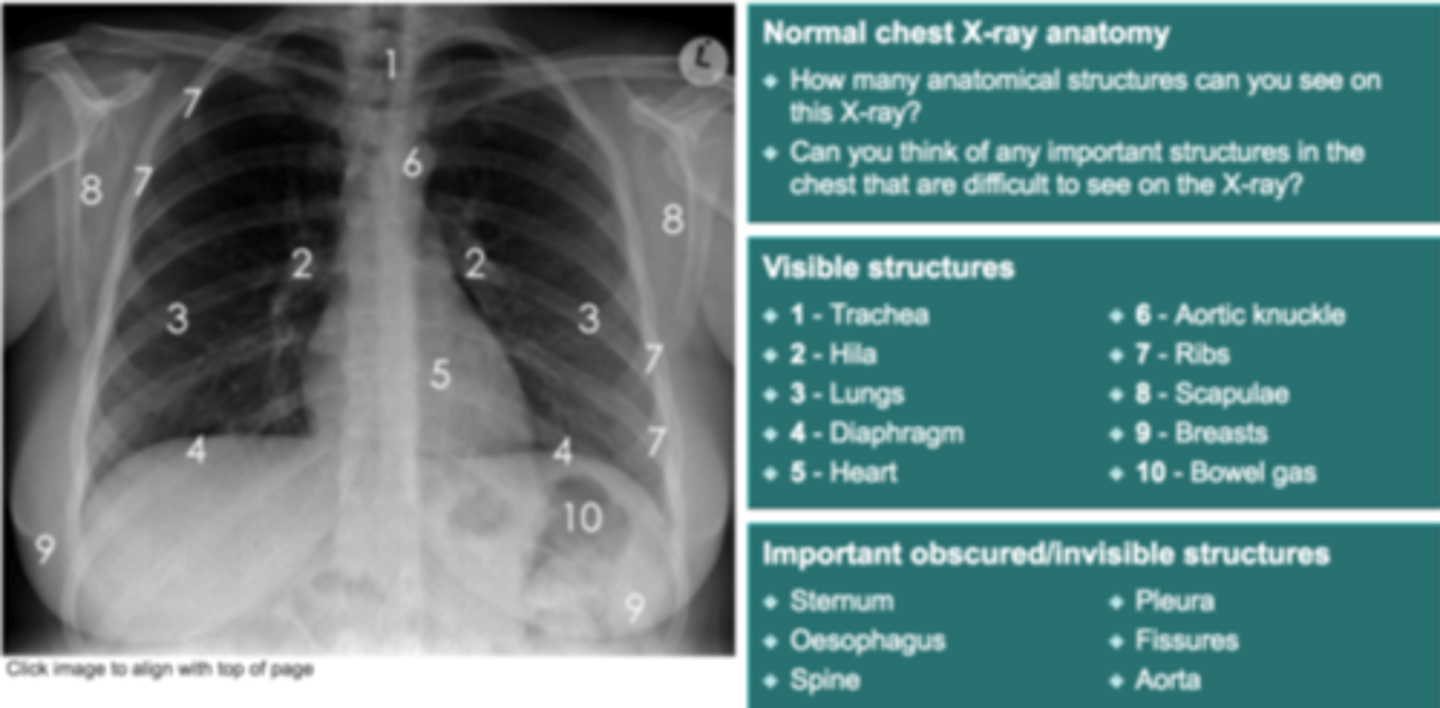
Proper ET tube placement may be described as
level with the __________ knob or ________
_______ cm above the carina
Level with ___
Aortic Arch
2-5
T4
Description
Tracheal shift from midline
Pneumothorax
Hemothorax
significant atelectasis
Description
Obliterated costophrenic angles
Pleural effusion
Description
Flattened Diaphragms
COPD
significant air-trapping
Description
Radiolucent
Normal
Fluffy infiltrates
Pulmonary edema
Wedge-shaped infiltrates
Pulmonary embolus
Air-bronchogram
Consolidation
Pneumonia
Butterfly or bat wing pattern
Pulmonary edema
Plate-like
patchy infiltrates
atelectasis
Scattered Patchy infiltrates
ARDS
Ground glass, honeycomb pattern
ARDS or IRDS
Reticulogranular
ARDS
Concave superior interface
Pleural effusion
What does radiopaque mean?
Radiopaque refers to substances or structures that appear white or bright on an X-ray because they block or absorb X-rays.
Can you give an example of radiopaque materials?
include bones, metal objects, Tubes
what is radiolucent?
substances or structures that appear dark or black on an X-ray.
Examples of Radiolucent Structures
Air:
Found in the lungs, trachea, and intestines.
Appears very dark due to minimal obstruction of X-rays.
Soft Tissues:
Organs Containing Gas:
Radiolucent Pathological Examples:
Pneumothorax: Air in the pleural cavity appears dark.
Emphysema: Overly air-filled lung spaces appear darker than normal.
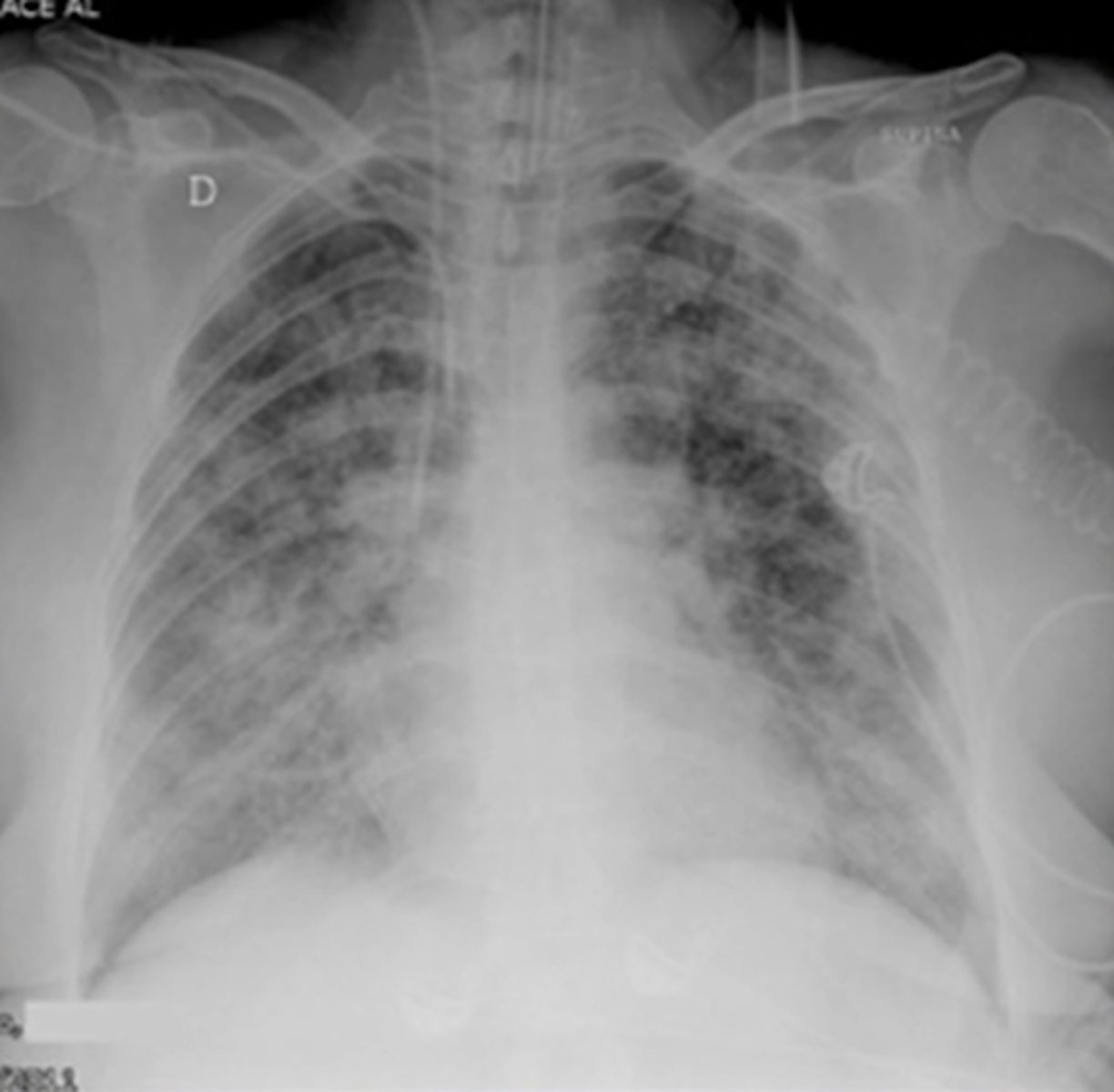
look at Xray
what can you identify?
What 3 typical pathologies do we look for when assessing breathing in X-rays?
Consolidation
Pneumothorax
Pleural effusion
What is consolidation of the lung - how is it caused?
Where alveoli and small airways fill with dense (WHITE) material (e.g. pus, fluid, cells, blood etc.)
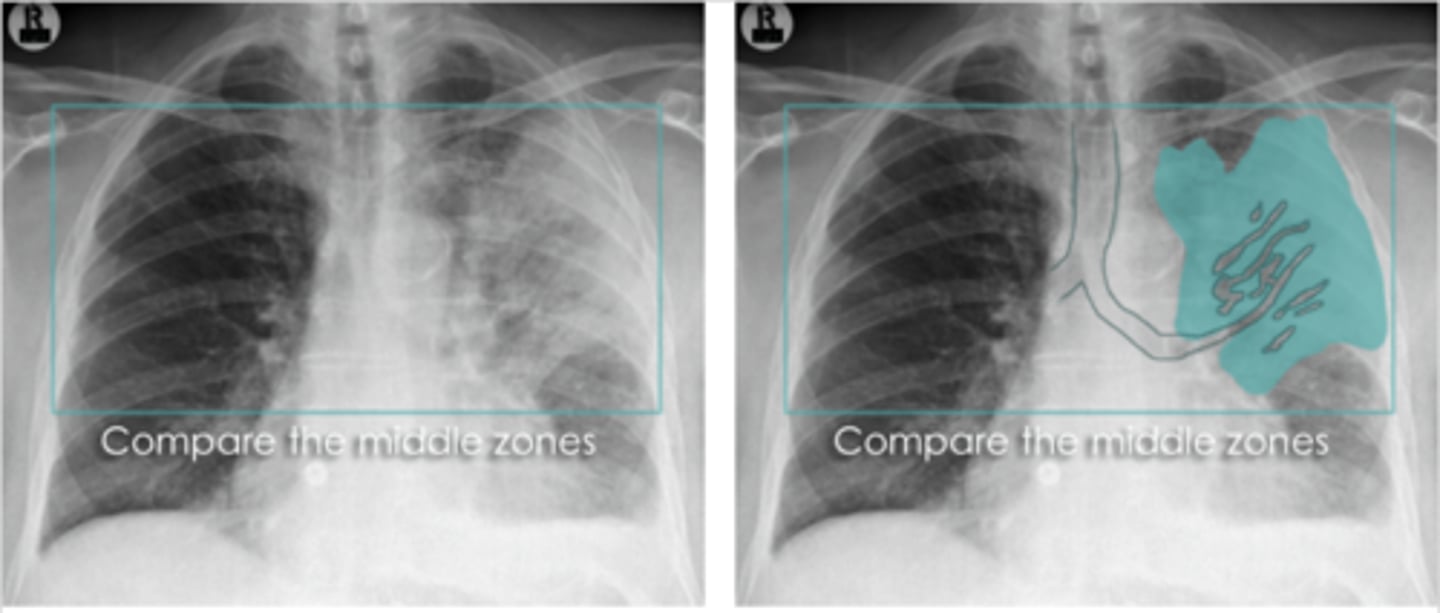
What is pneumothorax?
Hyperresonant and reduced tactile fremitus on the affected side
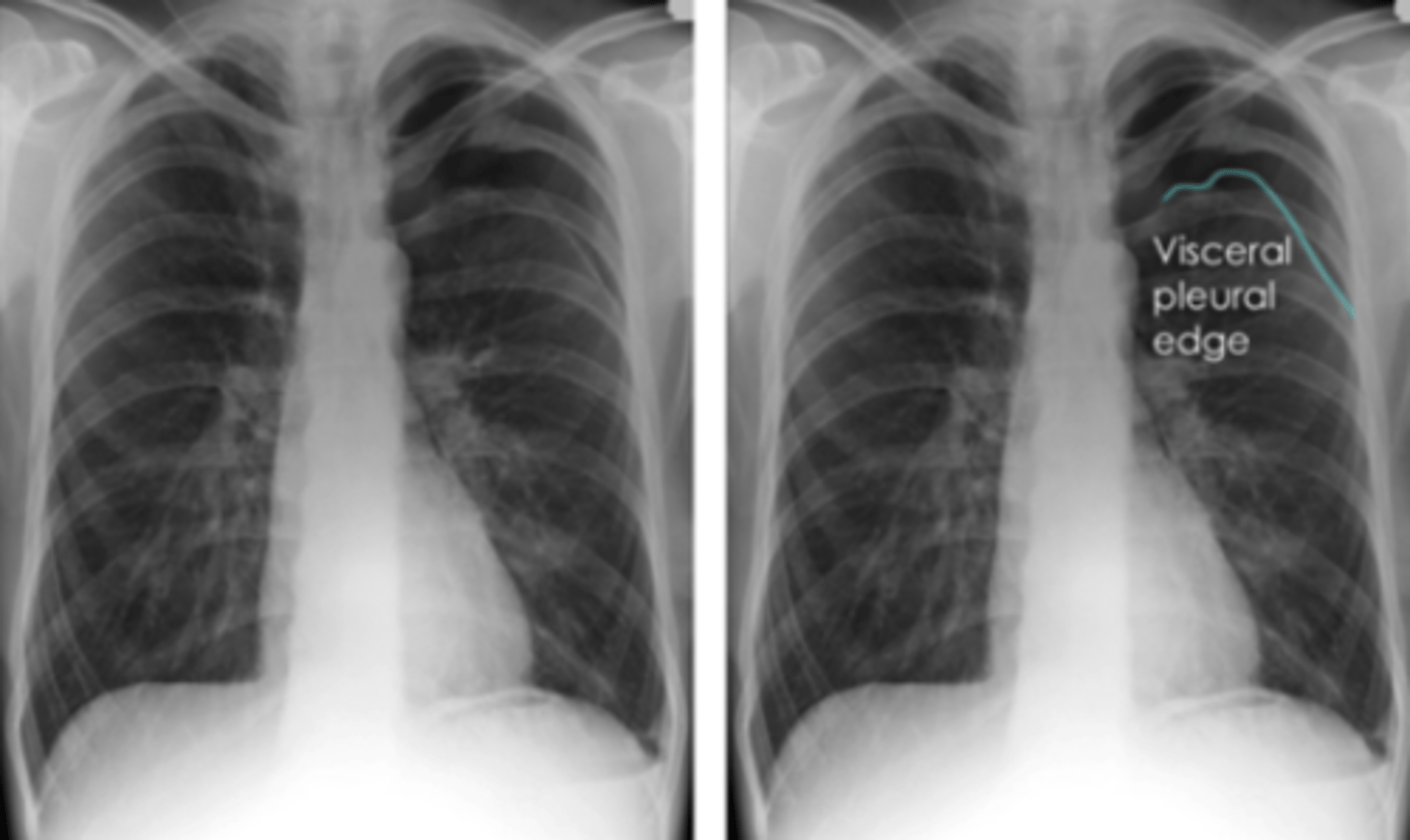
What is pleural effusion?
fluid gathers in lowest part of chest according to patient's position Affected, region appears white throughout
Blunting of the costophrenic angles:
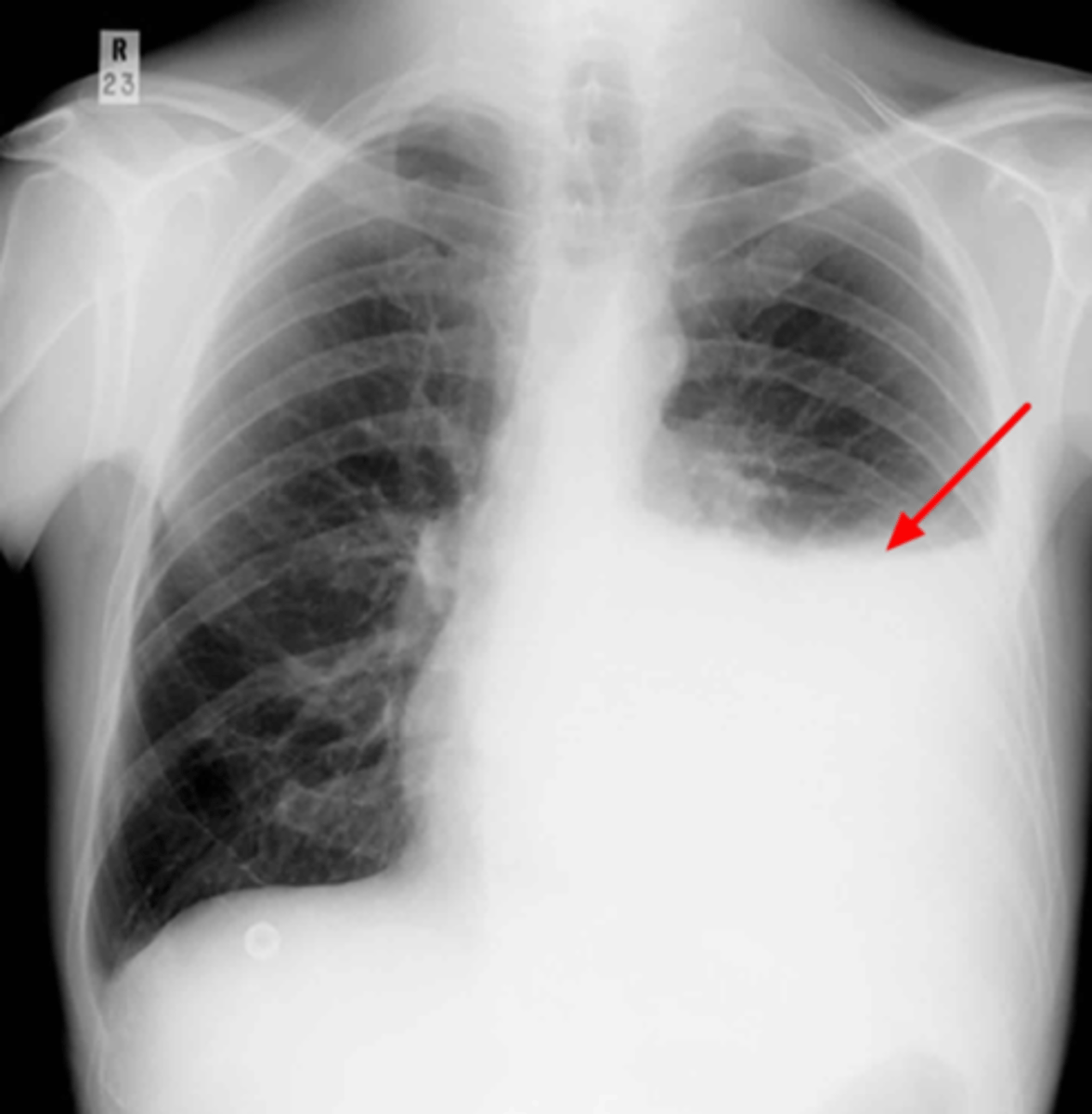
Notice the blunted costophrenic angles
Indicates effusion but not too severe
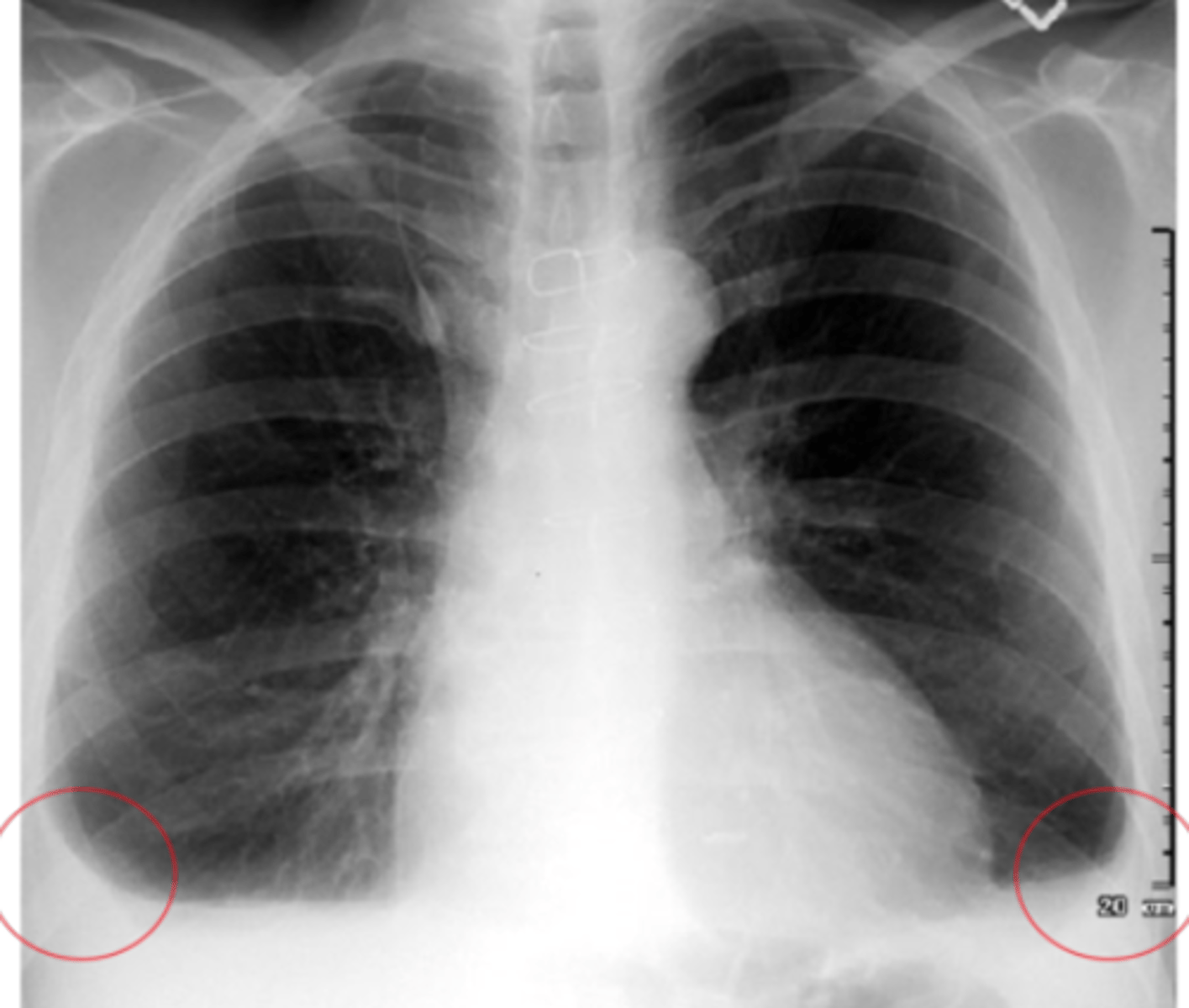
When do we see the pleura in an x-ray?
ONLY visible when there is an abnormality present - pleural thickening, fluid/air in pleural space
What are the features of COPD on a chest X-ray?
COPD = emphysema/ chronic bronchitis CXR features: Hyperinflation more than 6 anterior ribs/ 8 posterior visible Flattening of hemidiaphragm