Fusion and fission
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Theory of relativity
explain how space and time are linked for objects that are moving at a consistent speed in a straight line.
Einstein showed in his theory of relativity that matter can be considered a form of energy and hence, he proposed:
Mass can be converted into energy
Energy can be converted into mass
Some examples of mass-energy equivalence are:
The fusion of hydrogen into helium in the centre of the sun
The fission of uranium in nuclear power plants
Nuclear weapons
High-energy particle collisions in particle accelerators
The binding energy is equal to the amount of energy released in forming the nucleus, and can be calculated using:
E = (Δm)c2
E = Binding energy released (J)
Δm = mass defect (difference between the atoms mass and the sum of the masses of its protons and neutrons) (kg)
c = speed of light (m s-1)
The daughter nuclei produced as a result of both fission and fusion have a ____ binding energy per nucleon than the parent nuclei
higher
what does this therefore mean?
energy is released as a result of the mass difference between the parent nuclei and the daughter nuclei
Total binding energy of each nucleus = Binding energy per nucleon × Mass number
Since reaction 1 releases more energy than reaction 2, its end products will have a higher binding energy per nucleon
Hence, they will be more stable
This is because the more energy is released, the further it moves up the graph of binding energy per nucleon against nucleon number (A)
Since at high values of A, binding energy per nucleon gradually decreases with A
Nuclear reactions will tend to favour the more stable route, therefore, reaction 1 is more likely to happen
Annihilation is:
When a particle meets its equivalent anti–particle they both are destroyed and their mass is converted into energy in the form of two gamma ray photons

Pair production is the _____ of annihilation
oppposite
Pair production is:
When a photon interacts with a nucleus or atom and the energy of the photon is used to create a particle–antiparticle pair
The presence of a nearby ____ is essential in pair production so that the process conserves both energy and momentum + why?
neutron
A single photon alone cannot produce a particle–anti-particle pair or the conservation laws would be broken
Pair creation is a case of what conversion?
energy —> matter

This means the energy of the photon must be above a certain value to provide the ______________ of the particle–antiparticle pair
total rest mass energy
what equation is used for pair production:
ΔE = c2 Δm
Δm = rest mass of the particle (kg)
c = speed of light (m s–1)
ΔE = rest mass energy of the particle (J)
Therefore, in order to create a particle & anti-particle pair, the energy carried by a single photon must be at least twice the rest-mass energy required, i.e.
2ΔE = 2(c2 Δm)
This also means if a particle meets its anti-particle and annihilates, the energy carried away by each of the two photons Ephoton is given by:
Ephoton = hf = hc/λ= c2 Δm
Since the Planck constant is in Joules (J) remember to always convert the rest mass-energy from MeV to J.
Experiments into nuclear structure have found that the total mass of a nucleus is ___ than the sum of the masses of its constituent nucleons
less
What is this difference in mass is known as?
mass defect or mass deficit
Mass defect is defined as:
The difference between the measured mass of a nucleus and the sum total of the masses of its constituents
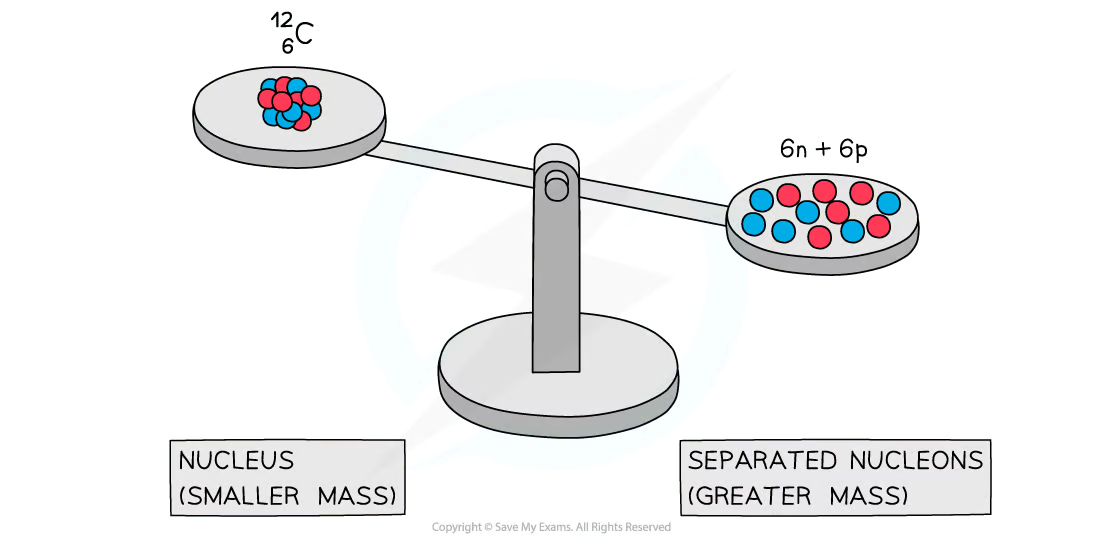
Due to the equivalence of mass and energy, this decrease in mass implies that energy is released in the process
Since nuclei are made up of neutrons and protons, there are forces of repulsion between the positive protons
Therefore, it takes energy, ie. the binding energy, to hold nucleons together as a nucleus
Binding energy is defined as:
The energy required to break a nucleus into its constituent protons and neutrons
(Avoid describing the binding energy as the energy stored in the nucleus – this is not correct – it is energy that must be put into the nucleus to pull it apart.)
Energy and mass are proportional, so, the total energy of a nucleus is less than the sum of the energies of its constituent nucleons
The formation of a nucleus from a system of isolated protons and neutrons is therefore an exothermic reaction - meaning that it releases energy
What is best for comparing nuclear stability?
binding energy per nucleon
The binding energy per nucleon is defined as:
The binding energy of a nucleus divided by the number of nucleons in the nucleus
A higher binding energy per nucleon indicates a ____ stability
higher
In other words, it requires more energy to pull the nucleus apart
What has the highest binding energy per nucleon, which makes it the most stable of all the elements?
Iron (A = 56)
graph of binding energy per nucleon against nucleon number:
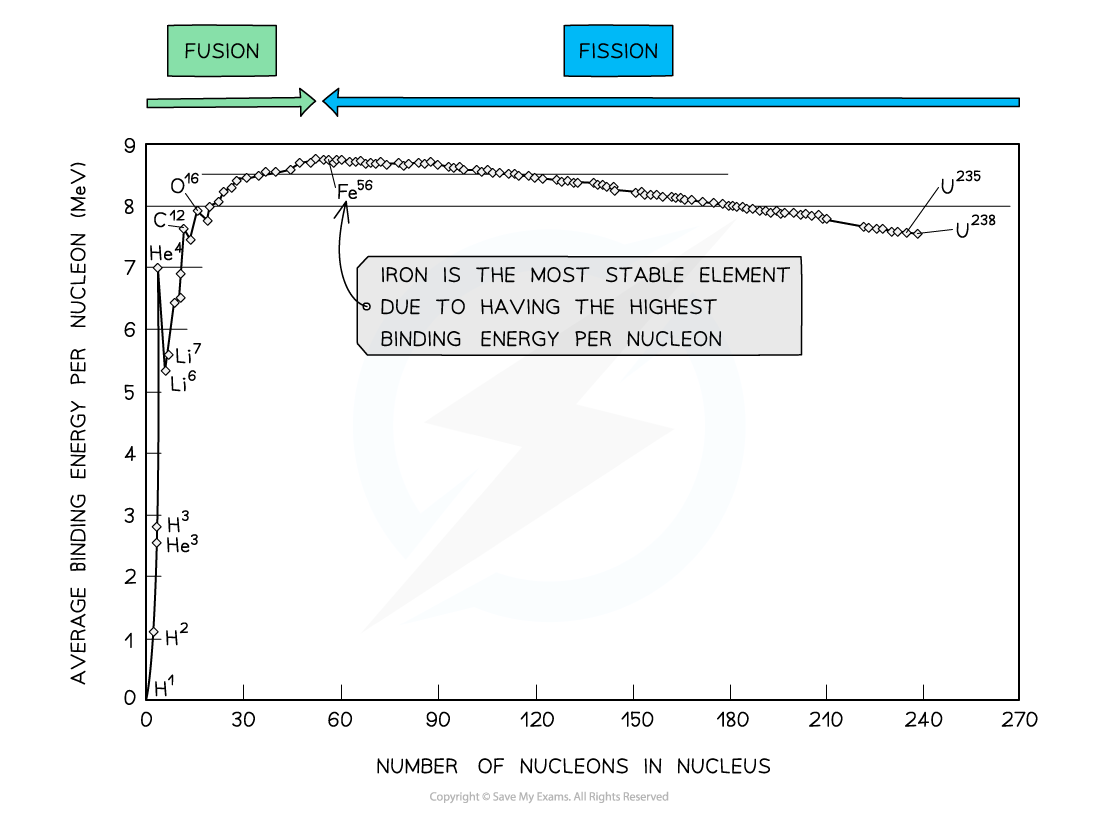
Key Features of the Graph:
At low values of A:
Nuclei tend to have a lower binding energy per nucleon, hence, they are generally less stable
This means the lightest elements have weaker electrostatic forces and are the most likely to undergo fusion
Helium (4He), carbon (12C) and oxygen (16O) do not fit the trend
Helium-4 is a particularly stable nucleus hence it has a high binding energy per nucleon
Carbon-12 and oxygen-16 can be considered to be three and four helium nuclei, respectively, bound together
At high values of A:
The general binding energy per nucleon is high and gradually decreases with A
This means the heaviest elements are the most unstable and likely to undergo fission
Do not begin your curve at A = 0, this is not a nucleus!
Binding energy can be calculated using the equation:
ΔE = c2Δm
Where Δm is the mass defect of a nucleus
Δm can be calculated using:
Δm = Zmp + (A – Z)mn – mtotal
Where:
Z = proton number
A = nucleon number
mp = mass of a proton (kg)
mn = mass of a neutron (kg)
mtotal = measured mass of the nucleus (kg)
Nuclear fission is defined as:
The splitting of a large, unstable nucleus into two smaller nuclei
What particularly undergoes fission?
Isotopes of uranium and plutonium both undergo fission and are used as fuels in nuclear power stations
What happens during fission?
a neutron collides with an unstable nucleus, the nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei (called daughter nuclei) as well as two or three neutrons
Gamma rays are also emitted
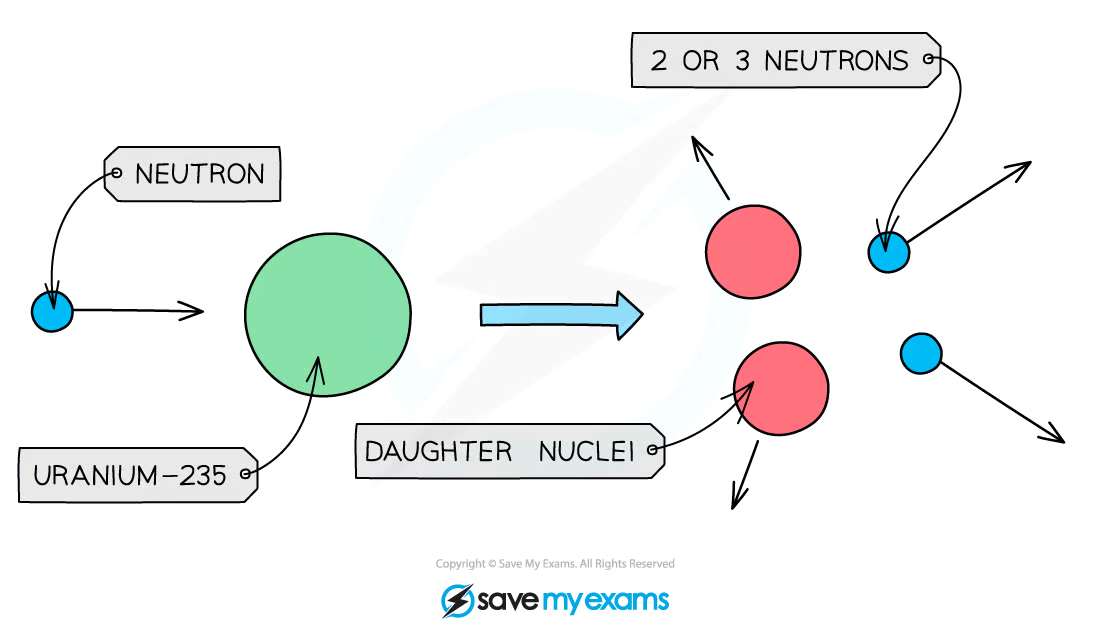
Why do the products of fission move away very quickly?
Energy transferred is from nuclear potential energy to KE
what is spontaneous fission?
nuclei to undergo fission without additional energy being put into the nucleus (rare)
Usually, for fission to occur the unstable nucleus must first absorb a ____
neutron
fission of uranium-235:
Take, for example, uranium-235, which is commonly used as a fuel in nuclear reactors
It has a very long half-life of 700 million years
This means that it would have low activity and energy would be released very slowly
This is unsuitable for producing energy in a nuclear power station
During induced fission, a neutron is absorbed by the uranium-235 nucleus to make uranium-236
This is very unstable and splits by nuclear fission almost immediately
What is the significance of in fission, producing two or three neutrons which move away at high speed?
Each of these new neutrons can start another fission reaction, which again creates further excess neutrons
what is this process called?
chain reaction
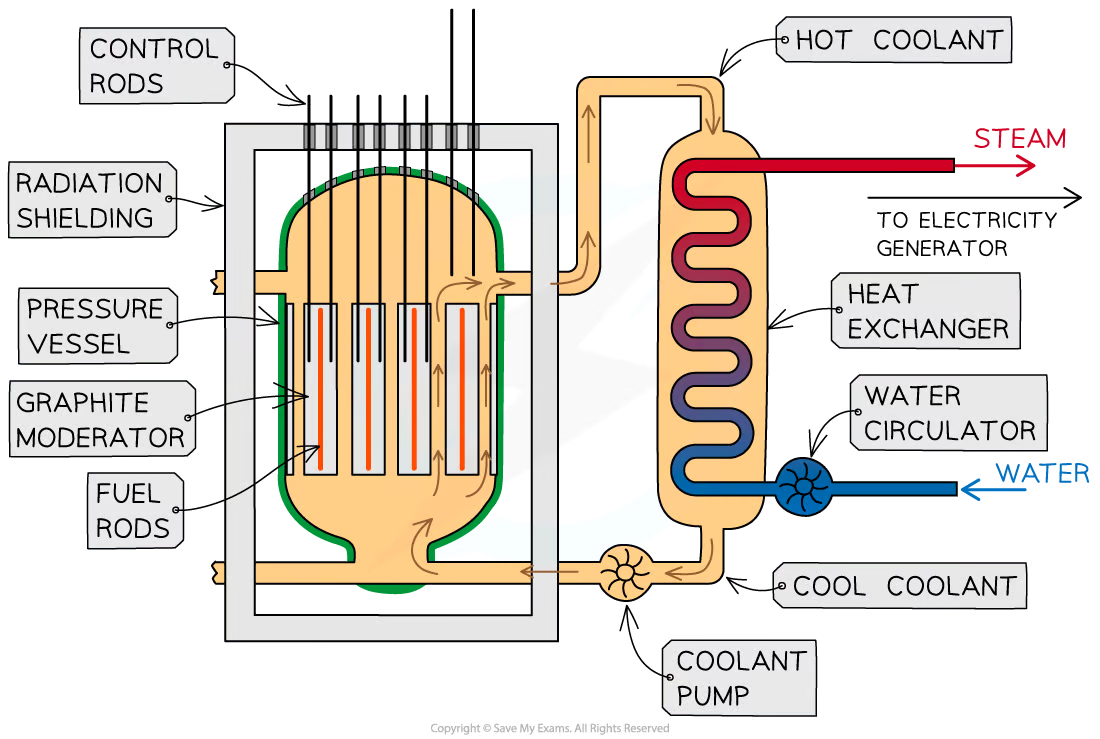
What is the purpose of the moderator?
To slow down neutrons
What is the moderator?
a material that surrounds the fuel rods and control rods inside the reactor core
How does a moderator slow down reactions?
fast-moving neutrons produced by the fission reactions slow down by colliding with the molecules of the moderator, causing them to lose some momentum
The neutrons are slowed down so that they are in thermal equilibrium with the moderator, hence the term ‘thermal neutron’
This ensures neutrons can react efficiently with the uranium fuel
Purpose of a control rod
To absorb neutrons
How do control rods work?
number of neutrons absorbed is controlled by varying the depth of the control rods in the fuel rods
Lowering the rods further ________ the rate of fission, as more neutrons are absorbed
Raising the rods _____ the rate of fission, as fewer neutrons are absorbed
decreases
increases
what does it do?
This is adjusted automatically so that exactly one fission neutron produced by each fission event goes on to cause another fission
In the event the nuclear reactor needs to shut down, the control rods can be lowered all the way so no reaction can take place
What is the purpose of the coolant?
To remove the heat released by the fission reactions
How does the coolant work?
The coolant carries the heat to an external boiler to produce steam
This steam then goes on to power electricity-generating turbines
structure of nuclear reactor
Within the fuel rods, nuclei of uranium-238 quickly decay into nuclei of _______
These nuclei are ______
They have a long half-life of ____ years
plutonium-239
extremely radioactive
24,000
What is the use of plutonium-239 decaying slowly?
It will remain radioactive for a very long time
So, it presents a risk of contamination for a long time
It is classified as high-level radioactive waste
What are the three main types of nuclear waste?
Low level
Intermediate level
High level
What is low-level waste?
This is waste such as clothing, gloves and tools which may be lightly contaminated
This type of waste will be radioactive for a few years, so must be encased in concrete and stored a few metres underground until it can be disposed of with regular waste
What is intermediate-level waste?
This is everything between daily used items and the fuel rods themselves
Usually, this is the waste produced when a nuclear power station is decommissioned and taken apart
This waste will have a longer half-life than the low-level waste, so must be encased in cement in steel drums and stored securely underground
What is High-level waste?
This waste comprises of the unusable fission products from the fission of uranium-235 or from spent fuel rods
This is by far the most dangerous type of waste as it will remain radioactive for thousands of years
As well as being highly radioactive, the spent fuel roads are extremely hot and must be handled and stored much more carefully than the other types of waste
How is high-level waste is treated?
The waste is initially placed in cooling ponds of water close to the reactor for a number of years
Isotopes of plutonium and uranium are harvested to be used again
Waste is mixed with molten glass and made solid (this is known as vitrification)
Then it is encased in containers made from steel, lead, or concrete
This type of waste must be stored very deep underground
Where can Isotopes with long half-lives not enter?
water and food supplies
Where must these locations be?
geologically stable, secure from attack, and designed for safety
Fusion is defined as:
Small nuclides combine together to make larger nuclei, releasing energy
Low mass nuclei (such as _________) can undergo fusion and release energy
hydrogen and helium
What do the nuclei need to have to fuse?
both nuclei must have high kinetic energy
Why do they need high KE?
protons inside the nuclei are positively charged, which means that they repel one another
It takes a great deal of energy to overcome the electrostatic force
When two protons fuse, the element _____ is produced
deuterium
In the centre of stars, the deuterium combines with a tritium nucleus to form a helium nucleus, plus the release of energy, which provides fuel for the star to continue burning
In the fusion process, the mass of the new heavier nucleus is ___ than the mass of the constituent parts of the nuclei fused together, as some mass is converted into energy.
LESS
What happens with this energy?
Not all of this energy is used as binding energy for the new larger nucleus, so energy will be released from this reaction. The binding energy per nucleon afterwards is higher than at the start.
fission e.g

