Lecture 13 Chromatic Aberration
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Lower Order Aberrations
defocus and astigmatism
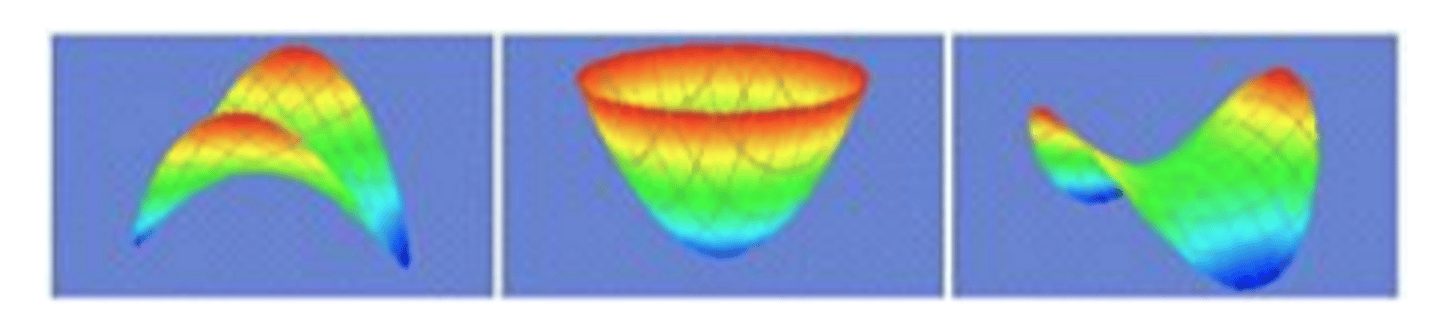
Higher Order Aberrations
-Spherical Aberration
-Coma
-Trifoil
Monochromatic aberrations are produced with
a single wavelength of light
chromatic aberrations occur when
a mixture of different wavelengths of light (polychromatic light) are considered
Dispersion
the transmission speed of light within a refractive medium depends upon the wavelength
-The refractive index is different for each wavelength [n=Vc/Vmed]
shorter wavelength of light are more
refracted than longer wavelengths
Chromatic dispersion
the separation of white light (polychromatic light) into its component elements by an optical element
Dispersive power
quantifies the amount of dispersion produced by an optical element
-Normally, consider three wavelengths at 486, 589, and 656 nm.
-Their respective refractive indices are nf, nd, and nc.
-Then, the dispersive power (ω) = (nf-nc)/(nd-1)
As the dispersive power increases, the
dispersion of the optical element (prism of lens) increases.
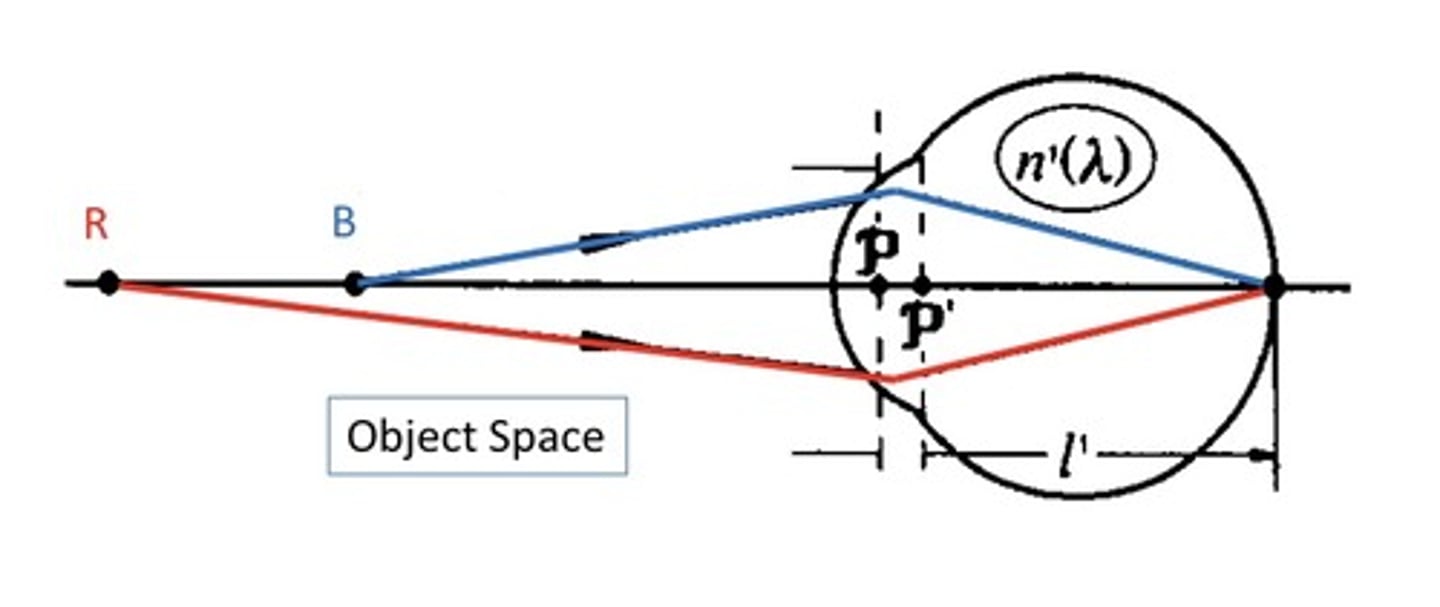
Longitudinal (or Axial) Chromatic Aberration (LCA)
When the chromatic dispersion occurs, the image of source formed by blue rays will be formed in front of the image formed by the red rays
LCA may be specified by
the 'distance' between image planes
-Measured in diopters (D)
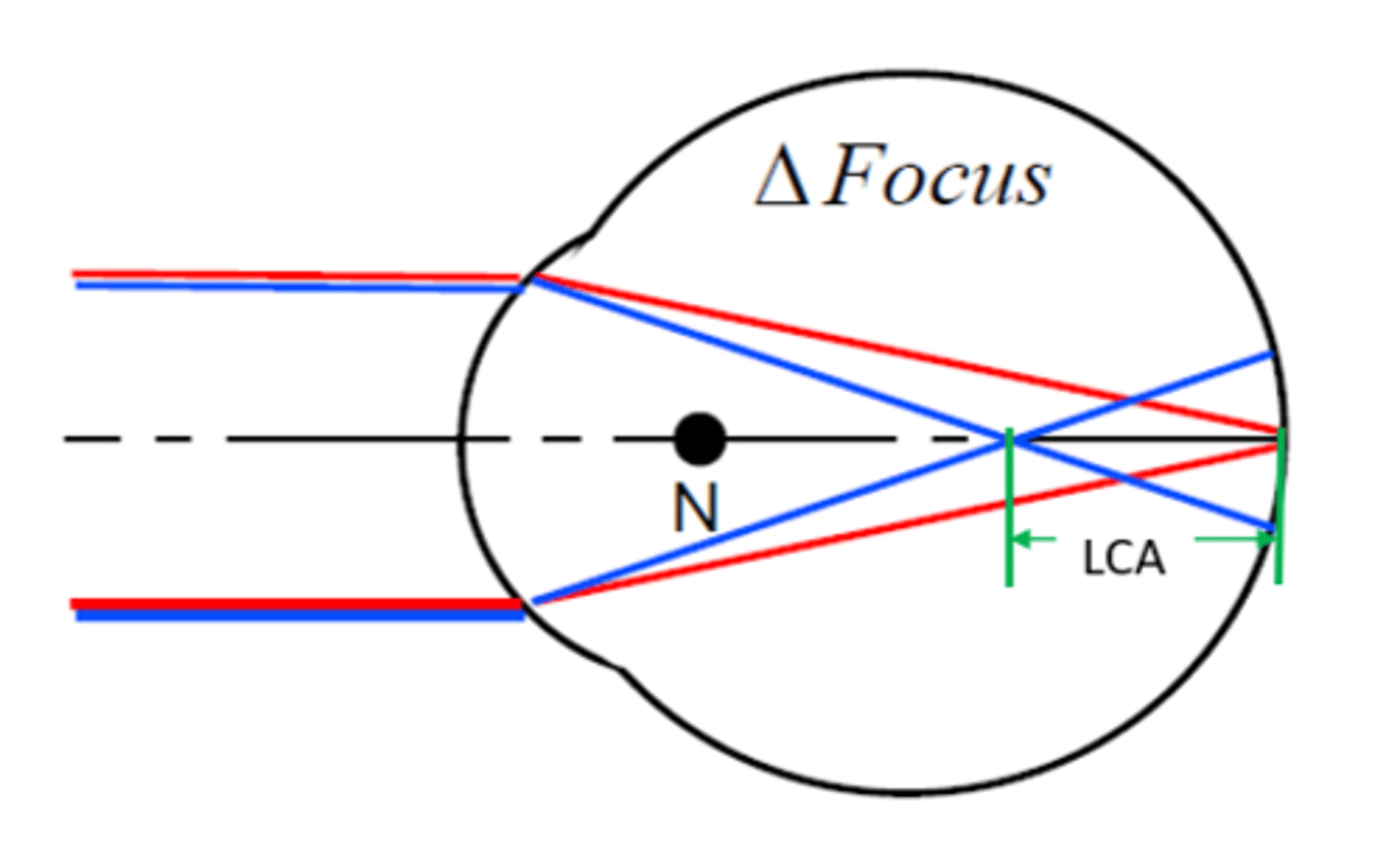
LCA can be quantified as
-Chromatic difference of power
-Chromatic difference of refraction
Chromatic difference of power
the variation of power with wavelength
-quantifies LCA
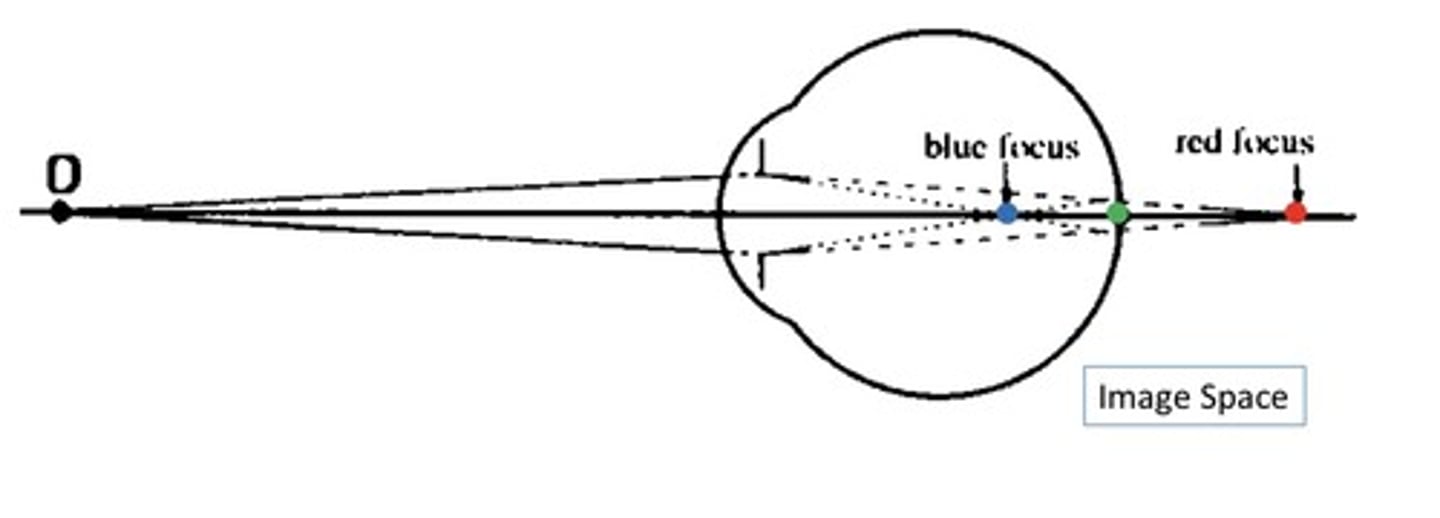
Chromatic difference of refraction
the vergences of source for which the source is focused at the retina for a range of wavelengths
-quantifies LCA
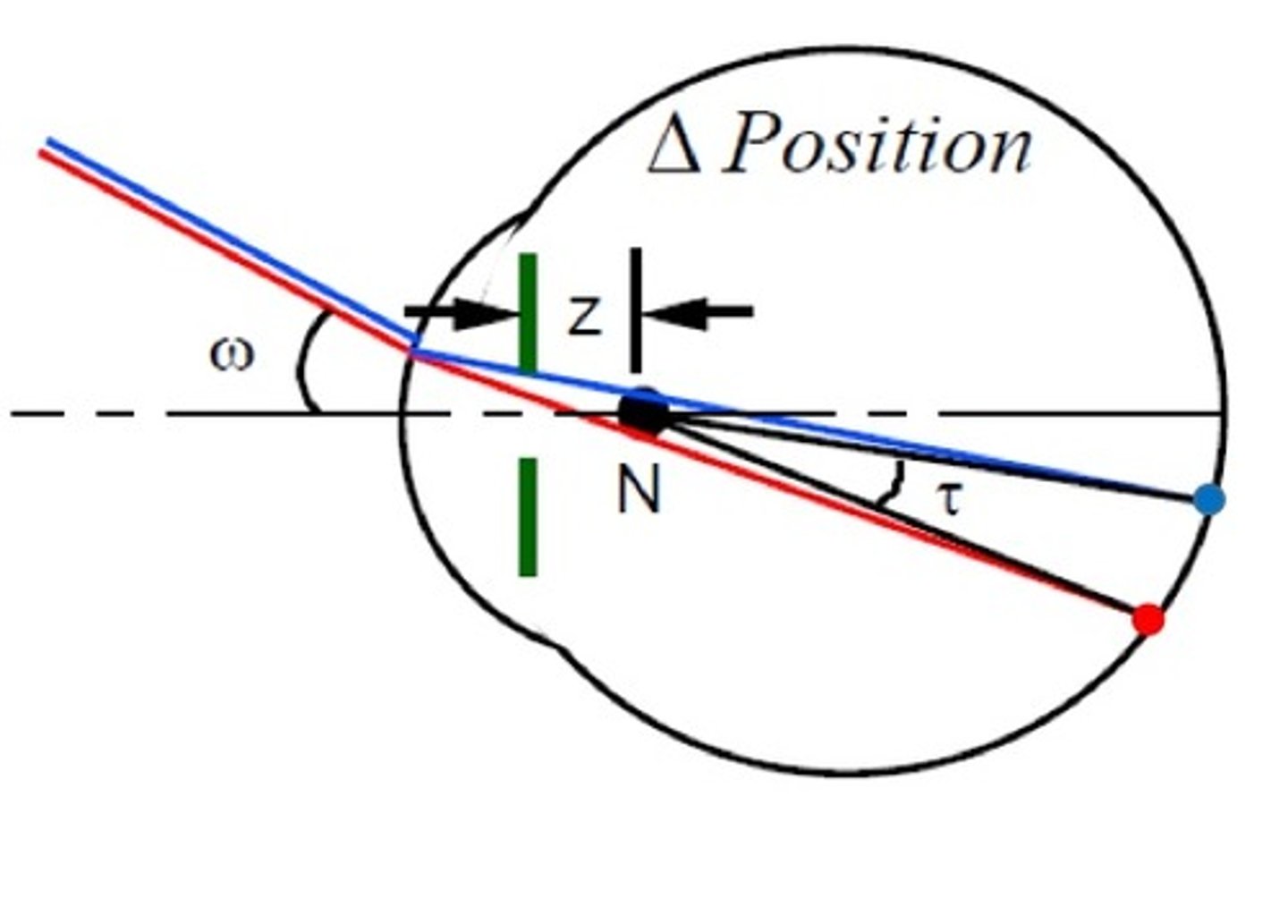
Transverse Chromatic aberration (TCA)
the variation of position of the image on the retina with wavelengths
-may be specified by the 'angle' between the refracted chief rays for different wavelengths
-oblique astigmatism= large angles
-coma = moderate angles
-LSA= on axis
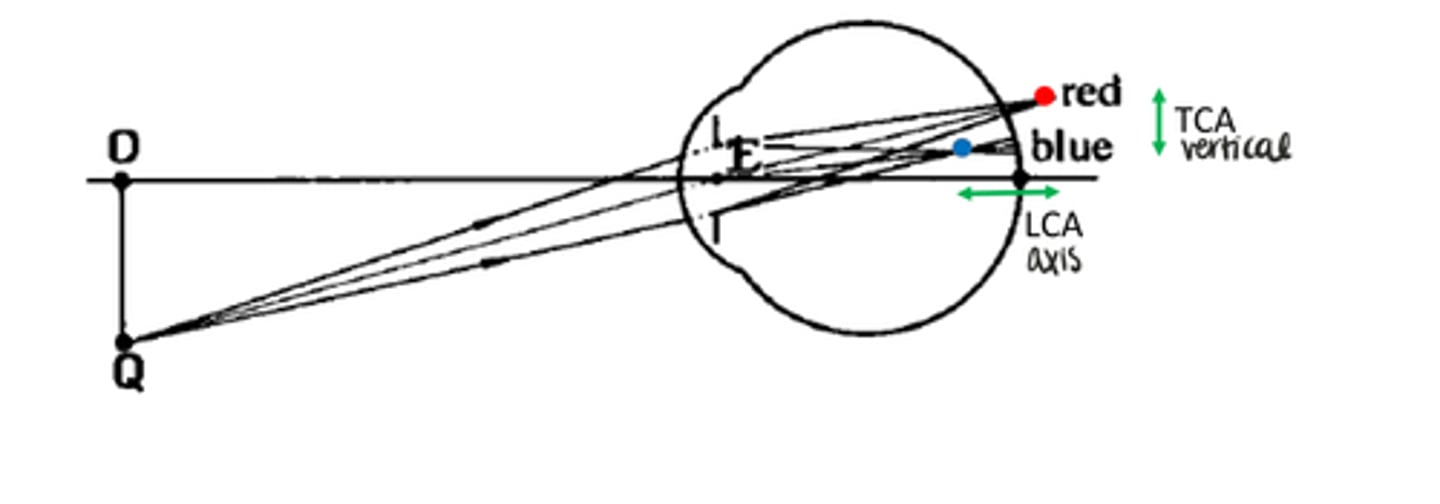
TCA can be quantified as
-Chromatic difference of position
-Chromatic difference of Magnification
Chromatic difference of position
The variation of position with wavelength
-quantifies TCA
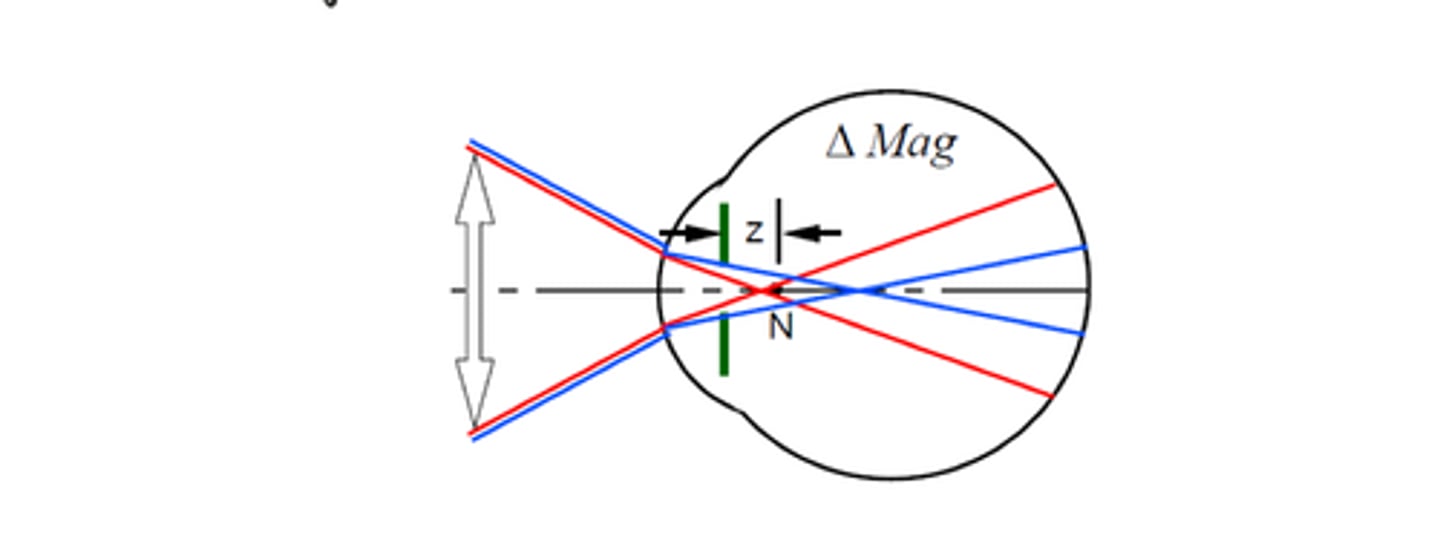
Chromatic difference of Magnification
the variation of magnification with wavelength
-A wavelength-dependent deviation of the ray that lead to a difference in magnification, with blue light being less magnified than the red light
-Quantifies TCA
foveal longitudinal chromatic aberration
if the pupil is decentered using an artificial pupil on axis
-Many eyes have TCA in the fovea due to the naturally decentered surfaces
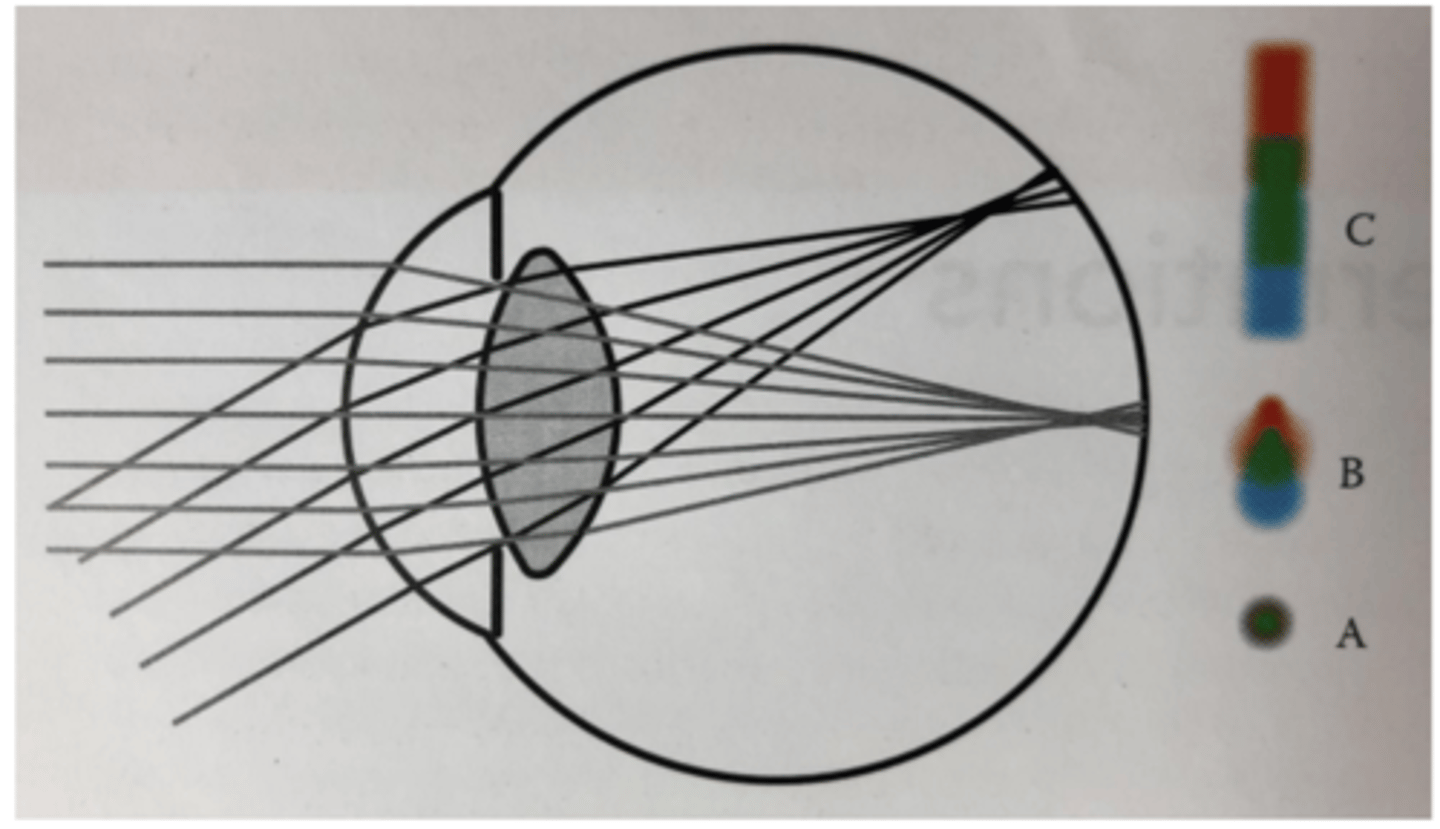
LCA between 400-700 nm range is
~2.1 D
-13 different studies over 50 years using variety of experimental methods show only a "little" variation among studies or individuals
-The small variation in CA is because the main constituent of the ocular media is water, whose dispersion cannot vary between subjects
The human eye has too much power for shorter wavelengths.
Human eye is more myopic for shorter wavelength and so a negative spectacle lens is required to correct this focusing error (LCA)
LCA does not change significantly over the life span
Small changes in the refractive indices of the eye's media which occurs with age leads to age-dependent changes in refractive error. However, the eye's chromatic aberration is determined by the dispersion of the media rather than by the refractive index
How is the eye's chromatic aberration determined?
by the dispersion of the media rather than by the refractive index
What if chromatic aberration does change with age?
Important consequences for (i) ocular measurement (optometers) and (ii) vision itself.
The magnitude of the aberration is assume to be that of young subjects, and any age-dependent changes would then invalidate the instrument calibration for older people.
what does the magnitude of TCA depend on?
the field angle of the object (TCA varies with angle linearly)
-Unlike LCA, TCA varies in magnitude among studies and subjects.
-average TCA across population is zero, but, for any given eye it is not zero.
what is the mean magnitude of foveal TCA for red and blue light (produced by a computer monitor)?
0.82 arcmin of visual angle
Chromatic diplopia
a point object emitting two wavelengths of light will produce a double retinal image which gives rise to the perception of a double object
-a phenomenon, which is the basis for chromo stereopsis
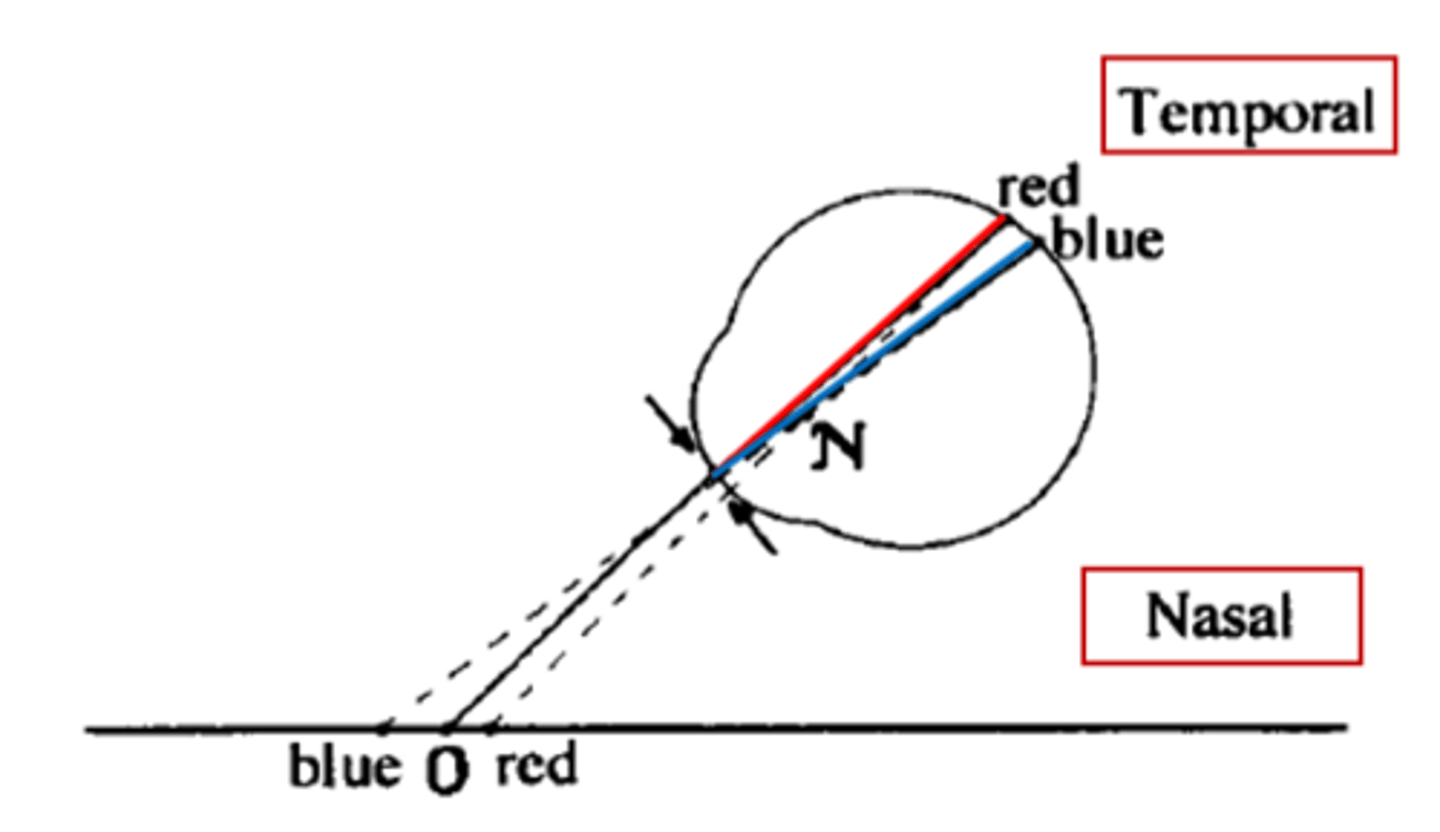
Chromo steropsis
a stereoscopic illusion in which differently colored objects located at the same viewing distance appear to lie at different distances
-Reddish objects appear closer than bluish objects
-an effect of TCA combined with binocular vision

If pupils are displaced temporally relative to the visual axis
red will appear closer
if pupils are displaced nasally relative to the visual axis
blue will appear closer
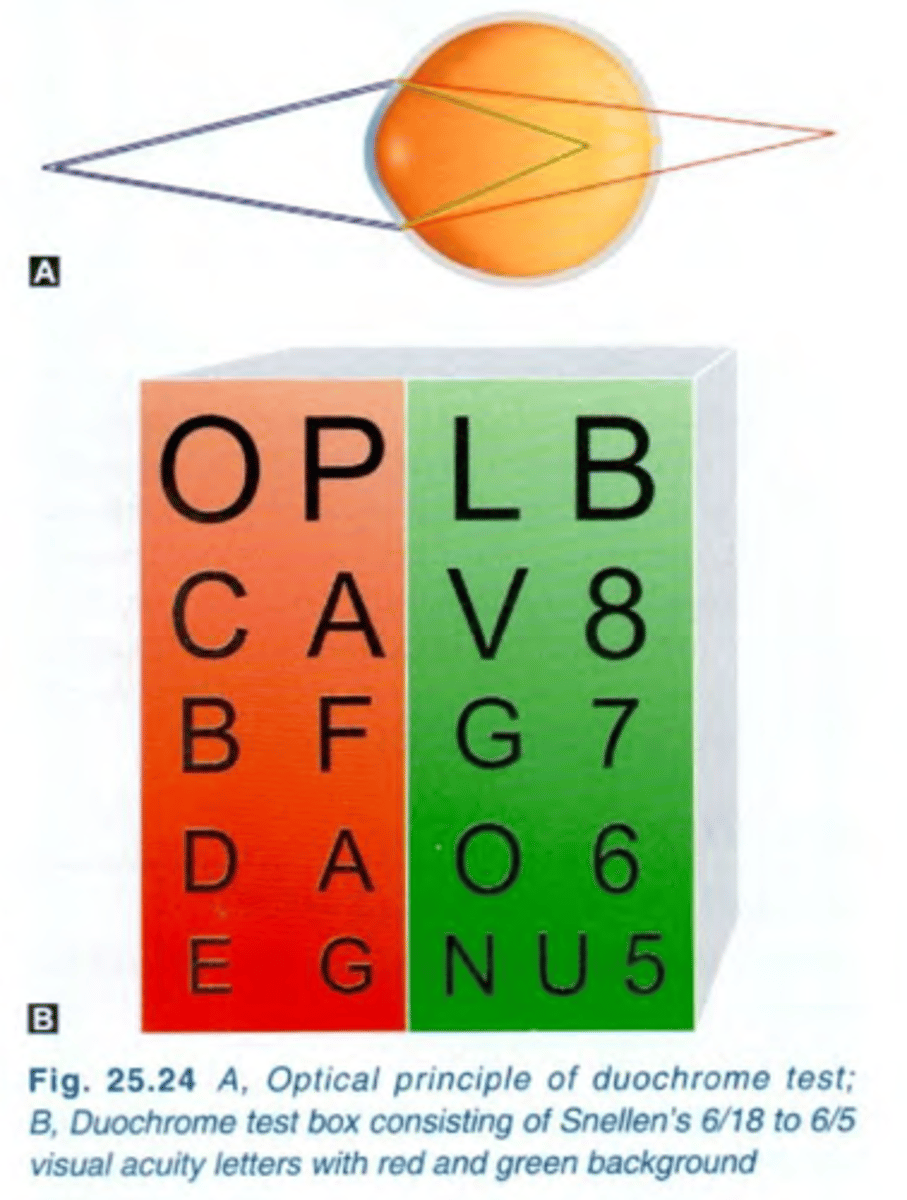
Duochrome test
test that uses the eye's chromatic aberration in the determination of the near end of the refraction.
-In this test, patient compares the sharpness of letters presented on red and green backgrounds.
-Refraction is adjusted until the letter on the two colored backgrounds appear equally clear, or until the letters on one of the backgrounds are slightly clearer.
The separation of white light (polychromatic light) into its component elements by an optical element is referred to as
chromatic dispersion
The variation of power with wavelength – ‘Chromatic difference of
Power
TCA may be specified by the __________ for different wavelengths
Angle
Human eye is __________ for shorter wavelength source.
More myopic
The half width of the diffraction limited PSF is 3.23. If spherical Aberration of 0.5 microns is added to this PSF, What would happen to the PSF?
Increase
Calculate the Strehl Ratio, If the maximum light level of the diffraction limited PSF is 65 lumens (or whatever units), and the maximum light level of the Aberrated PSF is 40 lumens.
0.61