Plant and animal breeding
1/37
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Why do breeders try to improve their produce (crops and/or livestock)?
Sustainable food production
In what two ways do breeders try to improve their produce (crops and/or livestock)?
Careful breeding or genetic technology
What are five improvements that can be made to crops and/or livestock?
Ability to thrive in certain conditions
Increase in nutritional value
Increase in yield
Resistance to disease
Resistance to pests
What are two examples of careful breeding?
Inbreeding, and cross breeding and F1 hybrids
Inbreeding
The fusion of two gametes from close relatives
Outbreeding
The fusion of two gametes from unrelated members of the same species
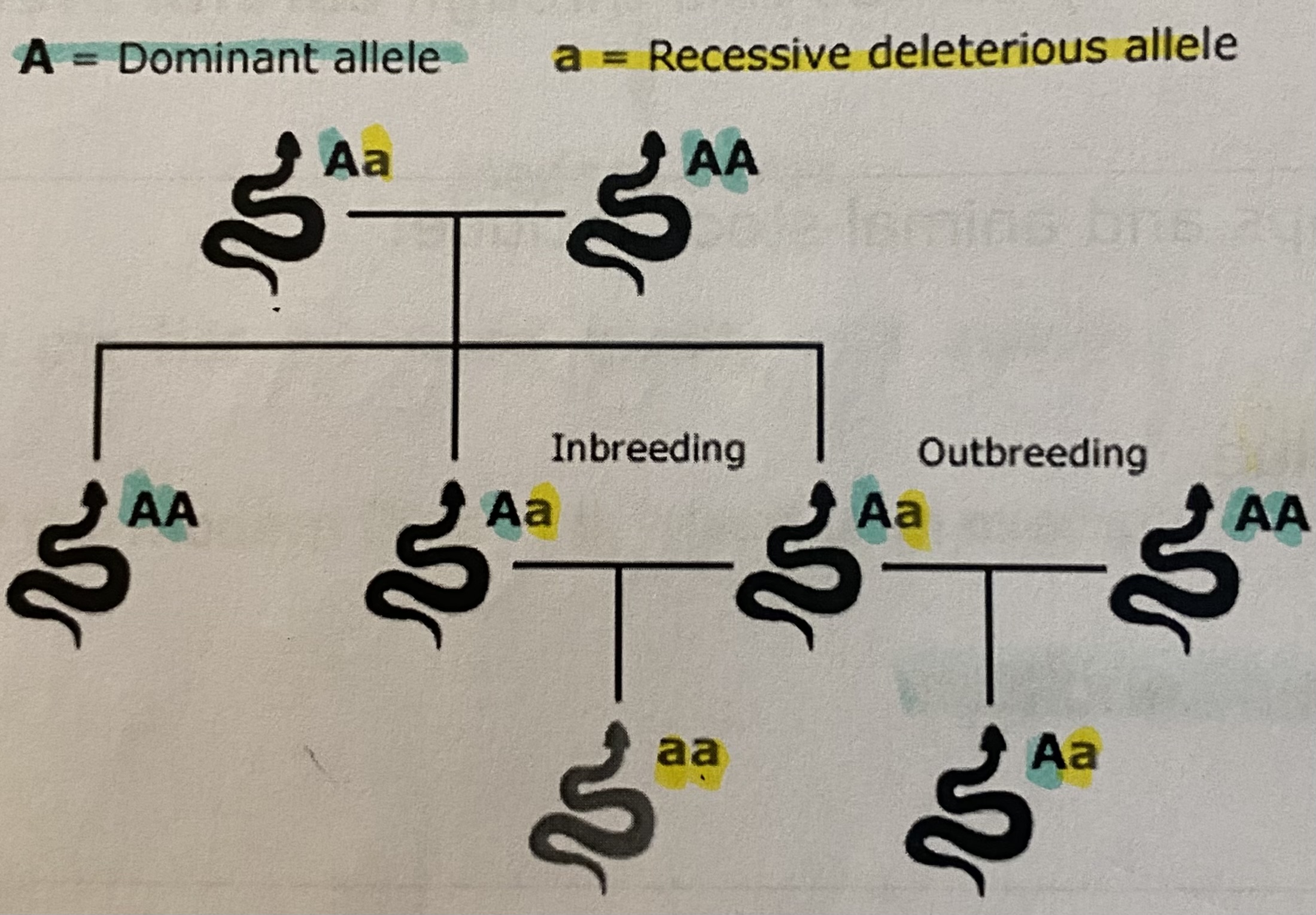
Diagram: breeding
Gametes
Sex cells
How many times are selected related animals or plants with desired characteristics bred for?
Several generations until the population breeds true to the desired characteristic due to the elimination of heterozygotes
Example: heterozygotes (alleles)
Aa
Example: dominant homozygotes (alleles)
AA
Example: recessive homozygotes (alleles)
aa
Inbreeding depression
When a natural outbreeder is forcibly inbred
What causes inbreeding depression?
The genotypes that emerge are homozygous for an accumulation of recessive deleterious (harmful) alleles
What four things does inbreeding depression result in?
Decreased fertility
Decreased size
Decreased vigour (the size and speed of which a plant grows)
Decreased yield
Genotype
The alleles that an organism has for a particular characteristic
How can new alleles be introduced to animal and plant lines?
Crossing a breed or a cultivar with an individual with a different desired genotype
A crossbreed
When two individuals from different breeds are bred together to produce a new crossbred population with improved characteristics
Crossbreeding and F1 hybrids in animals
The two parent breeds can be maintained to produce more crossbred animals showing the improved desired characteristic
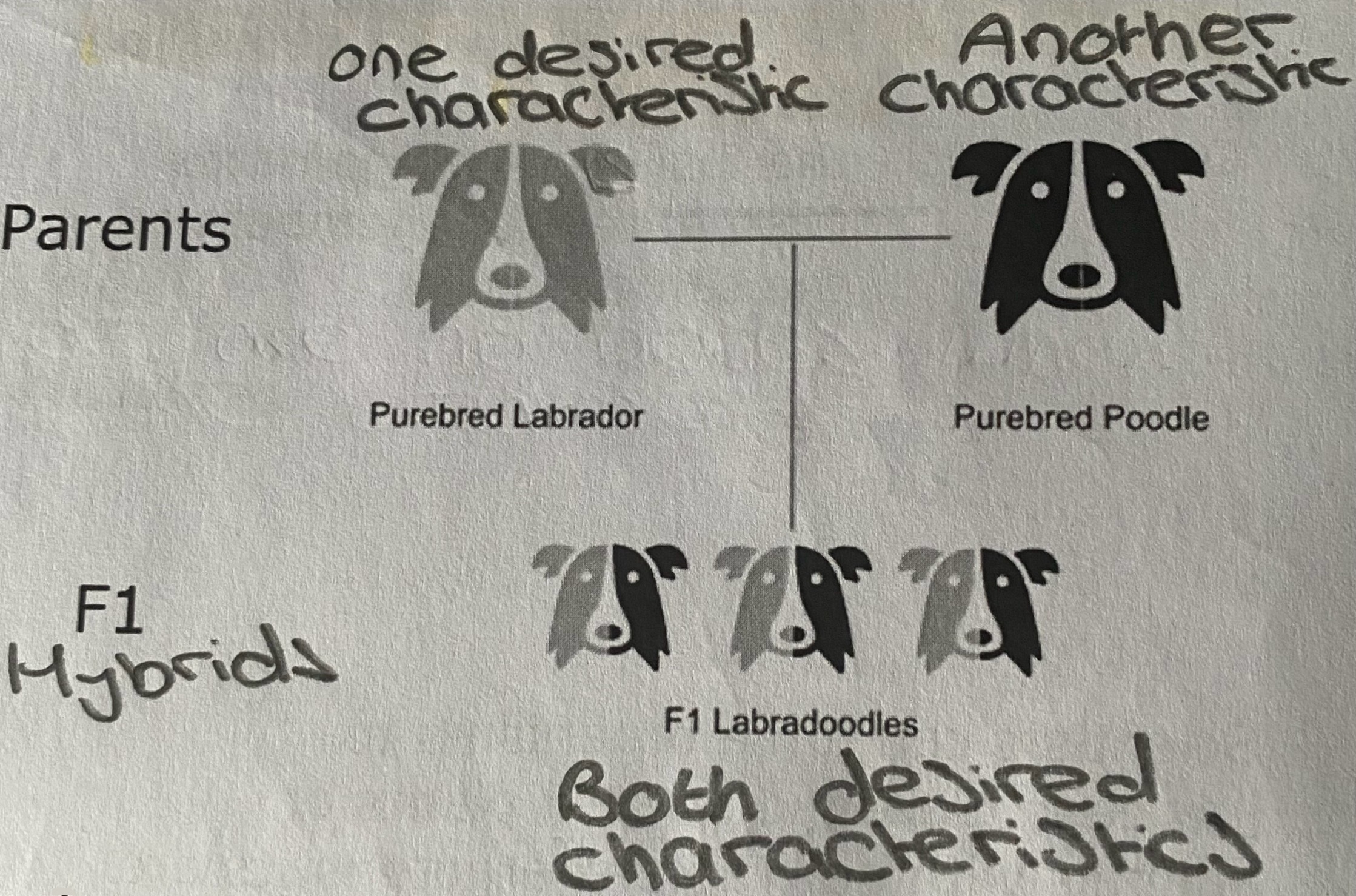
Diagram: cross breeding and F1 hybrids
Crossbreeding and F1 hybrids in plants
F1 hybrids produced by the crossing of two different inbred lines creates a relatively uniform heterozygote crop, often with increased vigour and yield
Why are F1 hybrids of animals and plants not usually bred together?
F2 generations show too much variation
Hybrid vigour
A phenomenon where hybrid offspring exhibit superior characteristics compared to their purebred parents
Genetic technology
Organisms with desired genes can be identified and used in breeding programmes as a result of genomic sequencing
Genetic transformation techniques
When the gene for a desired characteristic in one crop plant is inserted into the genome of another crop plant
Example: genetic transformation technique
DNA sealed in a bacterial plasmid which acts as a vector
Vectors
A DNA molecule used to carry foreign genetic information into another cell in recombinant DNA technology
What is the purpose of using genetic transformation techniques?
To make GM (genetically modified) plants with improved characteristics
What can breeding programmes involve?
Crop plants that have been genetically modified using recombinant DNA technology
Recombinant DNA technology
A technique used to mass produce proteins like insulin by genetically altering bacteria to incorporate the necessary human genes to express the desired hormones
Example: recombinant DNA technology (Bt toxin)
The bacterial gene for Bt toxin is extracted from one crop and inserted into another which will then produce their own Bt toxin, making them resistant to certain insects
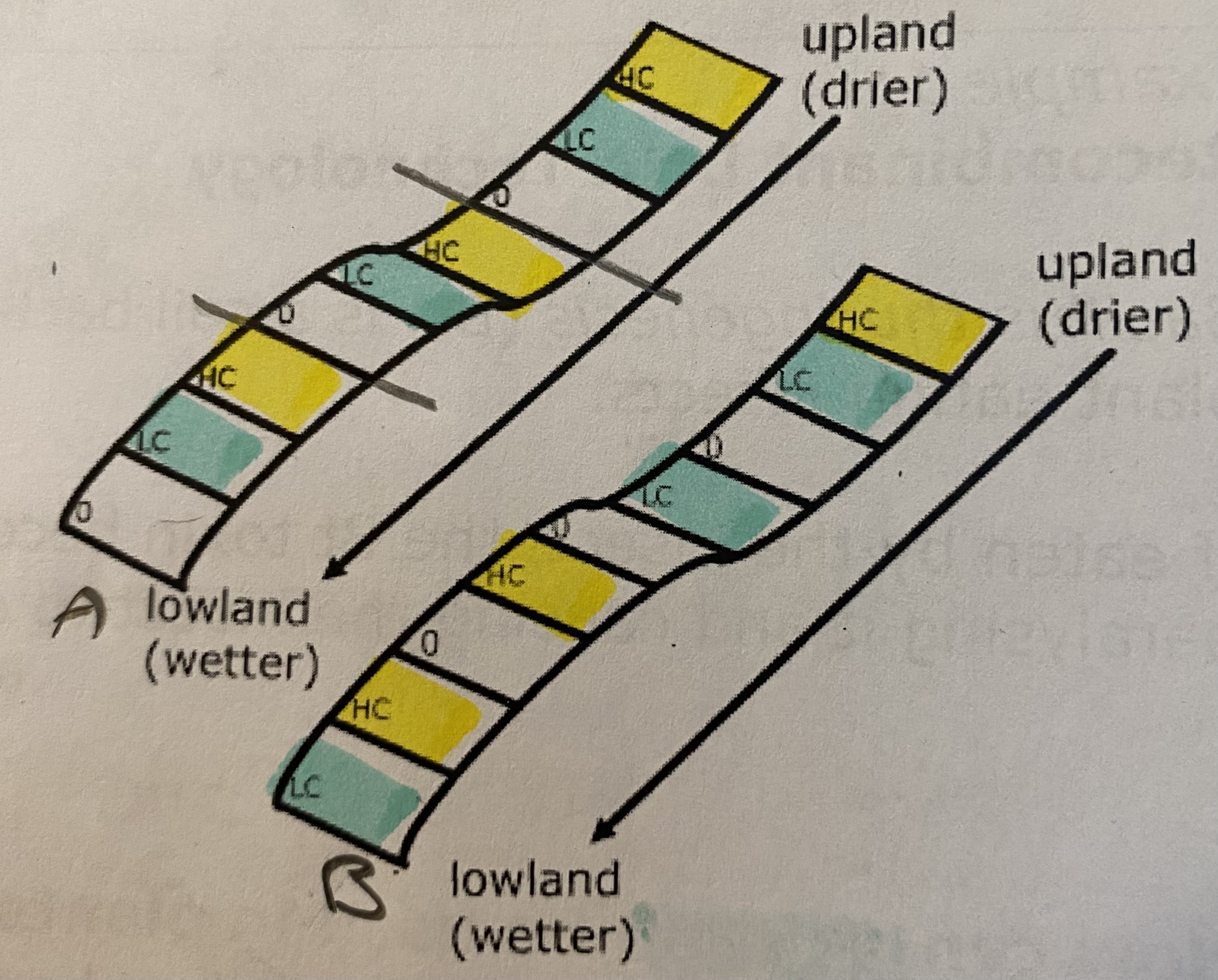
Diagram: a plant field trial
What three things are plant field trials used for?
To compare the performance of two different plant cultivars under the same set of environmental conditions
To evaluate GM crops
To see the effect of different environmental conditions or treatments on a new cultivar of crop plant
Cultivar
A crop plant that has been produced in cultivation by selective breeding
Selective breeding
Choosing two parents with particular characteristics and breeding them together to produce offspring with a variety of desired characteristics
What are the three design features of a plant field trial?
Inclusion of several replicates - takes account of the variability within the sample
Randomisation of treatments - prevents bias when measuring the treatments affects
Selection of treatments - ensures a valid comparison
Alleles
A different form of the same gene
What determines an individuals alleles?
By the individuals parents inheritance