Redox and electrode potentials
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
draw a diagram of how you would measure the standard electrode potential of Fe3+
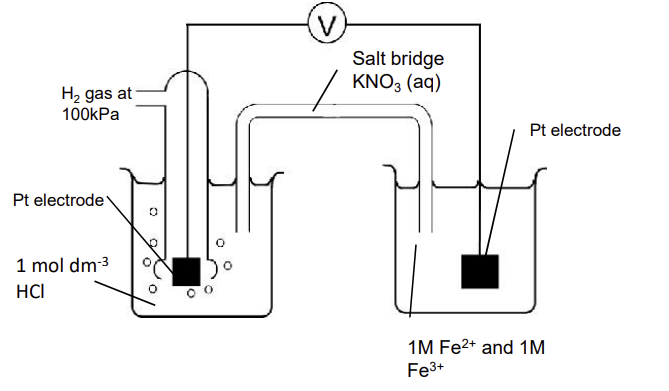
the more negative electrode potential…
is oxidised therefore the reducing agent
the more positive electrode potential…
is reduced therefore the oxidising agent
oxidising agent
gains electrons
reducing agent
loses electrons
Ecell =
more positive electrode potential - more negative electrode potential
P e N
what should be added to identify the end point of the titration between I2 and thiosulfate S2O3 2
A starch indicator is added near the end point when the iodine fades a pale yellow to emphasise it. With starch added the colour change is from blue/black to colourless
Observations during Fe2+ with MnO4 – titration
colour change from colourless to purple (Mn is in burette) vs purple to colourless (Mn is in conical flask)
electrons flow from…
half cell being oxidised (producing electrons) to half cell being reduced
advantages of hydrogen fuel cells
less pollution and CO2
greater efficiency
disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells
hydrogen is highly flammable, safety issues with storing it
high production costs + use of toxic chemicals in production
fuel cell
reacts with oxygen to give electrical energy
maintain a constant voltage
primary cells
non-rechargeable
secondary cells
rechargeable