Foundation of nursing Exam 4
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
What type of administration of medication goes directly into the blood stream that has an immediate effect?
Intravenous route
Intravenous route can have a increased risk for?
Infection or air embolism
What is the most dangerous route of administration?
Intravenous route
Has fewer solutes than cell components and results in fluid moving into the cell. - Water leaves the cells and interstitial fluid moves into the plasma
Hypotonic
A solution that has the same number of solutes than cell components and results in no fluid movement into or our of the cell.
Isotonic
A solution that has more solutes than are present within the cell and results in fluid movement out of the cell.
Hypertonic
A solution's ability to make water move in our out of cells; includes isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions.
Tonicity
List the solutions for isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic
Isotonic- 0.9% NaCl, LR
Hypotonic- 0.45% NaCl
Hypertonic- 10-15% Dextrose & 3% NaCl
Medications via Intravenous solution can be added to patient infusion solution, but
patient must receive it slowly over a long period, and check it Q1 hr
Involves a single injection of a concentrated solution directly into an intravenous line
Medication via an intravenous Bolus or Push
During administration medication via intravenous Bolus or push you should always
Consult a pharmacist or drug reference to confirm exact administration times
What is the term for administering a small amount of medication slowly into an IV catheter?
IV push
What should be followed when performing an IV push?
Medication manufacturer recommendations
What is IV push usually used for?
- Rapidly treat a life-threating condition
- To quicky achieve a therapeutic level of a medication
- To avoid fluid overload in clients who have cardiac or renal disease.
What should you do if an infusion pump is in use before administering medication?
Pause the pump
Which injection port should be used when administering medication?
Use the injection port closest to the patient
What should you do with the clamp on the administration set before using the injection port?
Close the clamp immediately above the injection port
How should you clean the injection port before administration?
Clean the port with an antimicrobial swab using friction
What is the mantra to remember for line cleaning?
EVERY LINE, EVERY TIME
What should you do after cleaning the port and before administering medication?
Flush the intravenous line
How should you flush the intravenous line in relation to the administered medication?
Flush at the same rate as the administered medication
What should you do after administering medication and flushing the line?
Unclamp the administration set above the injection port and restart the infusion pump if necessary
What should you do to make sure line is patent, and to clear line if not compatible with medication to be administered
You should flush
Medication is mixed with a small amount of intravenous solution and administered over a short period at the prescribed interval
Medication via intermittent intravenous infusion
intermittent Intravenous Infusion is often performed using a?
Infusion pump
Diluted in a large volume of IV fluid (50 to 200 ml) and infused over a period of time determined by the medications manufactueresdierctions
IV medication given intermittently via piggyback
What are the devices a patient with an intravenous line in place can receive the medication by?
Piggy back setup, Volume control administration set, and a mini-infusion pump (syringe pump)
The intermittent or additive solution (secondary) is placed higher than the primary solution
- an extension hook is used to lower the primary intravenous fluids
Piggy back set up
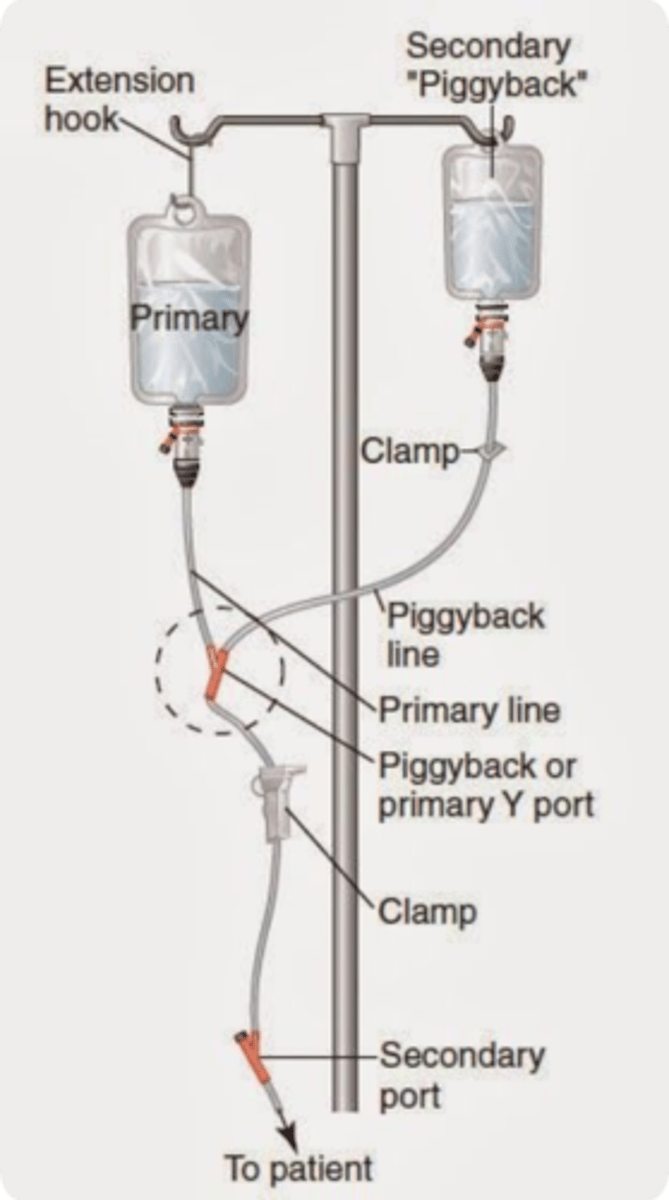
Device that allows flow in one direction and automatically prevents reverse flow if the fluid in the line reverses direction.
Back check valve
Concurrent programming of primary and secondary piggyback lines
- allows for more secondary/piggyback lines
IV pump

Formula for flow rate
Volume (mL)/ time (hrs)
Used for infusing solutions into children, critically ill, and older adults when the volume of fluid infused is a concern
Volume control Administration set
A pump for intermittent infusion that is battery operated and allows medication to be mixed in a syringe to be connect to the primary line
Mini-infusion pump (syringe pump)

Mini-infusion pump (syringe pump) is usually used for
kids
What is an alternative way to prime the secondary tubing?
Backfill Method for gravity infusion
What should you attach to the secondary infusion tubing?
The medication bag
What should you do with the medication bag in relation to the primary IV infusion?
Lower the medication bag below the primary IV infusion
What should you do after opening the clamp on the secondary infusion tubing?
Allow the solution to enter the drip chamber until it is ½ full
What should you do after the drip chamber is ½ full?
Close the clamp on the secondary tubing and hang the medication container on the pole
What is the next step after hanging the medication container?
Proceed with administration by lowering the primary IV container
Vary in drops per ml but usually 10-20 drops per mL
Macro drops
Delivers 60 drops per mL
Micro drip
What is an infusion lock used for?
Patients who require intermittent intravenous medications or bolus/push.
What advantage does an infusion lock provide to patients?
It allows patients more freedom than a continuous intravenous infusion.
Should IV push medications be diluted or reconstituted using a pre-filled flush syringe of 0.9% sodium chloride?
No, do not dilute or reconstitute IV push medications this way.
When should clinician-prepared syringes of IV push medications or solutions be labeled?
They should be labeled unless prepared at the patient's bedside and immediately administered.
What should be done if an adverse effect is suspected after administering IV push medications?
Notify the patient's primary care provider.
What determines the additional intervention after an adverse effect is suspected?
The type of reaction and assessment of the patient.
Documentation must include
Date, time, dose, route of administration, site of administration, and rate of administration
T/F PRN medications require documentation of the reason for administration
True
T/F A refused or omitted medication does not need to be documented
False
What are some local complications associated with central venous catheters?
Infiltration, phlebitis, and thrombophlebitis
What are some systemic complications associated with central venous catheters?
Fluid overload, embolus, and sepsis
Which complications are more serious and may be life threatening?
Systemic complications
What type of central venous catheters are available for patients at high risk for infection?
Anti-infective CVADs (impregnated with antiseptics and coated with antibiotics)
What is a key consideration for using anti-infective CVADs?
Patients with expected dwell time of more than 5 days or those with enhanced risk of infection
Who are considered to be at enhanced risk of infection when using central venous catheters?
Neutropenic, transplant, burn, or critically ill patients
what are some Signs/sympots of fluid overload systemic complication
increase in blood pressure, moist crackles, coughs with rapid b reaths, restless, distended neck veins and edema/weight gain
How can you manage fluid overload
By decreasing rate of IVF, monitoring VS and keeping patient in high fowlers position
What are some signs/symptoms of Air Embolism (rare)
palpations, dyspnea/excessive coughing, altered mental status, rapid pulse
How to manage Air embolism
Clamping cannula, put them on left side and in Trendelenburg position, and check vital signs & oxygen.
What are some signs or symptoms of Infection?
Temperature elevation as well as increased pulse/resp rate.
Nausea and vomiting
How to manage infection?
Trying to prevent is KEY
- call physician for further order
How can medication escape into tissue
By the cannula puncturing the wall of the vein or by fluid leaking from vein at insertion site
phlebitis and extravasation are examples of
Medication escaping the tissue
What are sign/symptoms of Iniltration
edema, leakage, discomfort and cool to touch
How to manage infiltration
stop infusion, relocate site, warm compresses, and elevate extremity
What are signs/symptoms of Extravastion?
Blistering, inflammation, and necrosis
How to manage extravasation
Stop infusion, discontinue the IV site, Agency protocol, and notify physical
What are signs/symptoms of phlebitis
Red/warm area, and a painful vein
How to manage a phlebitis
D/C/IV site, relocate IV, warm, moist compress
Erythema at access site with or without pain
Grade 1 of phlebitis Scale
Pain at access site with erythem and/or edema
Grade 2 phlebitis scale
Pain at access sit with erythem and/or edema streak formation
- palpable venous cord
Grade 3 phlebitis Scale
Pain at access site with erythema and/or oedema
Streak formation
Palpable venous cord>1 ich in length purulent drainage
Grade 4 Phlebitis scale
What are signs/symptoms of thrombophlebitis?
Pain, red, swelling, warm to touch, and fever, general malaise
How to manage Thrmobophlebitis?
check on D/C IV, warm compress, elevate patient and do not massage site
What are signs/symptoms of Hematoma
Ecchymosis, immediate swelling around insertion site
How to manage Hematoma
Removal of IV, light pressure, ice prn for 24 hrs, elevate patient and assess for damage movement and circulation.
What are sign/symptoms of Clotting and obstruction
Slow infusion rate, unable to flus, blood backflow
How to manage clotting and obstruction
d/c IV site, never aspirate blood clot, never force flush and prevent
Identified safety as an organizational priority and emphasized that medical errors are more frequently due to system problems rather than human error
The institute of medicine
Every individual has the opportunity to be heard, feel important, and be valued team member for the contribution offered
Team empowerment
Open and honest lines of communication are needed between the tea members and form the team to other hospital units
Communication
Teach members are united in their efforts to eliminate rumors and operate with only the facts
transparency
Staff claim ownership for human error and are willing to disclose the error and help prevent similar errors
Accountability
Are errors in medical care that are clearly identifiable, preventable, and serious in their consequences for patients, and that indicate a real problem in the safety and credibility of a health care facility.
"Never events"
•Foreign object left in patient
•Surgery on the wrong body part
•Mismatched blood transfusion
•Air embolism
•Severe pressure ulcers acquired in hospital
•Infant discharged to the wrong person
These are all examples of?
Serious reportable events (SREs)
What are factors affecting safety
Age and development, lifestyle, social behavior, environment, mobility, sensory perception, awareness of safety, and ability to communicate
Immediate pause by entire surgical team to confirm the correct patient, procedure and site
Procedural
What are the three elements for a procedural time out
right patient, right procedure, right location
What is the reason many falls with injuries go unreported for older adults?
older adults fear activity restriction, loss of independence, or placement in long-term care facility if they report their injury
CDC states a client answering yes to any of these questions indicates the need for more extensive assessment and intervention. What are these questions.
- Have you falling in the past year
- Do you feel unsteady when standing or walking
- do you worry about falling
PASS
Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep
RACE
Rescue, Alarm, Confine, Extinguish
What are signs of carbon monoxide poisoning
Headaches, nausea, dizziness, breathlessness, collapsing, and loss of consciousness
Never put anything in mouth when a patient has a?
Seizure
In what position do you place the patient in after seizure?
Side lying
death of a baby less than 1 year old in which the cause not obvious before investigation
Sudden unexpected infant death (SUID)
Devices used to limit physical activity of a client or part of body
Restraints