CVPP Week 5: Autonomic Nervous System
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What spine levels are sympathetic fibers
T1-L2/L3
What spine levels are parasympathetics fibers
CN 3 7 9 10 and sacral plexus
Ultimate control of ANS is
Medulla oblongata
Sympathetic NS pre and post ganglionic axon lengths
Short pre-ganglionic
Long post-ganglionic
"Far from effector organ"
Parasympathetic NS pre and post ganglionic axon lengths
Long pre-ganglionic
Short post-ganglionic
"Close to effector"
Central control controlled by
CNS and PNS nerves
Local control is ____ and give 3 examples
Independent of nerves
1. Pacemaker potentials (SA node)
2. Heterometric autogeneration (starling's law)
3. Chemical secretions (NO, histamine, K+)
Two primary factors influencing local control
1. Hypoxia of tissues
2. Accumulation of cellular waste products (H+)
Other than central and local control, what is the last thing that controls circulation?
Hormones (epi/norepinephrine)
Where does sympathetic NS arise from
Reticular formation in brainstem
Sensory input and efferent output of sympathetic NS
Sensory input: goes to cerebral cortex and activates reticular formation
Efferent output: goes through thoraco-lumbar region and synapses
Parasympathetic NS arises from...
Dorsal medulla —> dorsal vagal nucleus
(Majority of parasymp activity is carried out by vagus nerve)
Autonomic NS controls what involuntary muscles and glands (3)
Cardiac muscle —> controls heart
Smooth muscle —> controls tunica media of vessels
Adrenal medulla—> release NT
T/F: generally, pattern of ANS is equal but opposite
True (but not in CV system!)
Does sympathetic or parasympathetic nerves control most of the blood vessels
Sympathetic
Where do blood vessels receive both symp and parasymp innervation from
Face, GI tract and external genitals
T/F: sympathetic nerves control the heart most of the time
False, its parasympathetic
Does parasympathetic nerves have direct influence over stroke volume?
No, only heart rate
What NT does somatic nervous system release
Acetylcholine
What NT does sympathetic nerve secrete
Norepinephrine
What NT does adrenal medulla secrete for sympathetic division
Epinephrine
What NT does parasympathetic divison secrete
Acetylcholine
Parasympathetic Right vagus nerve goes to....
SA node
Parasympathetic Left vague nerve goes to...
AV node
What does acetylcholine do when it's released from parasymp nerves
Increase K+ permeability —> decrease HR
What receptors do Ach act on in parasympathetic division
Muscarinic receptors
Where does sympathetic innervation go to
Both nodes and regular cardiac myocytes
What do sympathetic nerves release in the heart
Norepinephrine and epinephrine
What does Nor/epinephrine do to the heart when it is released
Increase Na and Ca permeability —> increase HR and SV
What receptors does Nor/epinephrine act on
Adrenergic receptors (sympathetic)
Sympathetic nerve release ______ to do what to blood vessels
Norepinephrine, Vasoconstriction
Adrenal medulla release _____ to do what do blood vessels
Epinephrine, Vasoconstriction
Parasympathetic nerves release ____ to activate _____ to do what to blood vessels
Release Ach to activate muscarinic receptors to cause vasodilation
Parasympathetic innervation of blood vessels to where they vasodilate happens where (3)
face, GI tract and external genitals
What're the two types of adrenergic receptors
Alpha
Beta
Where do we find alpha receptors
Blood vessels (vasoconstriction)
-mainly from norepinephrine
Where do we find beta receptors
Heart
Where to find Beta-1 receptors
Nodes —> increase HR
Myocardium —> increase in SV
Where to find Beta-2 receptors
Found in smooth muscle (coronary arteries and bronchioles)
When Beta-2 receptors are activated, what do they do to the smooth muscle?
Vasodilation from epinephrine
Norepinephrine bind to....
Alpha (tunica media) and Beta-1 (nodes and cardiac myocytes) receptors
Chronotropic effect =
Increase in HR (Beta-1)
Inotrophic effect
Contractility = increase in SV (Beta-1)
Epinephrine binds to...
Alpha (tunica media) and both Beta-1 (heart) and Beta-2 (coronary artery and bronchiole) receptors
Beta blockers are specific to which Beta receptor
Beta-1
What do beta blockers do
Block receptors so NT can't act on it
Slows down heart and reduce workload
For people with hypertention
Intrinsic rate of SA nose
60-100 BPM
Where is SA node located
Right atrium
AKA for SA node
Pacemaker
AV node is also known as...
SA node back up
Where is AV node located
Between atria and ventricles
Why is AV node slowest rate of conduction?
Give time for atria to fully contract to squeeze all of the blood into ventricle (but is second fastest at depolarizing!)
When threshold voltage is reached, cell depolarizes and what ions flow through voltage gated pores
Na flows in and K flows out of cell
T/F: Cardiac myocytes need a stimulus
False because SA node is pacemaker
Where is fastest leak of Na "funny" current
Fastest leak of Na is at SA node through hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide gated channels (HCN) = Na channels
Pacemaker potential AKA
Spontaneous diastolic depolarization
What is spontaneous diastolic depolarization
Leaky membranes that constantly leak Na and Ca into cell (funny current)
-mainly at SA node
Does spontaneous diastolic depolarization ever reach a stable membrane potential
No, spontaneous and slow decline in membrane potential during diastole causes it to not
What comes first in pacemaker potential: T-type or L-type Ca channels? And which one causes the upstroke
T-type opens first then L-type
-L-type causes upstroke (hella Ca in)
Do HCN channels open before Ca channels in pacemaker potentials?
Yes
HCN = hyper-polarization cyclic nucleotide gated channels
What happens in repolarization of pacemaker potential
HCN and Ca channels close and voltage gated K channels open so K goes out of cell
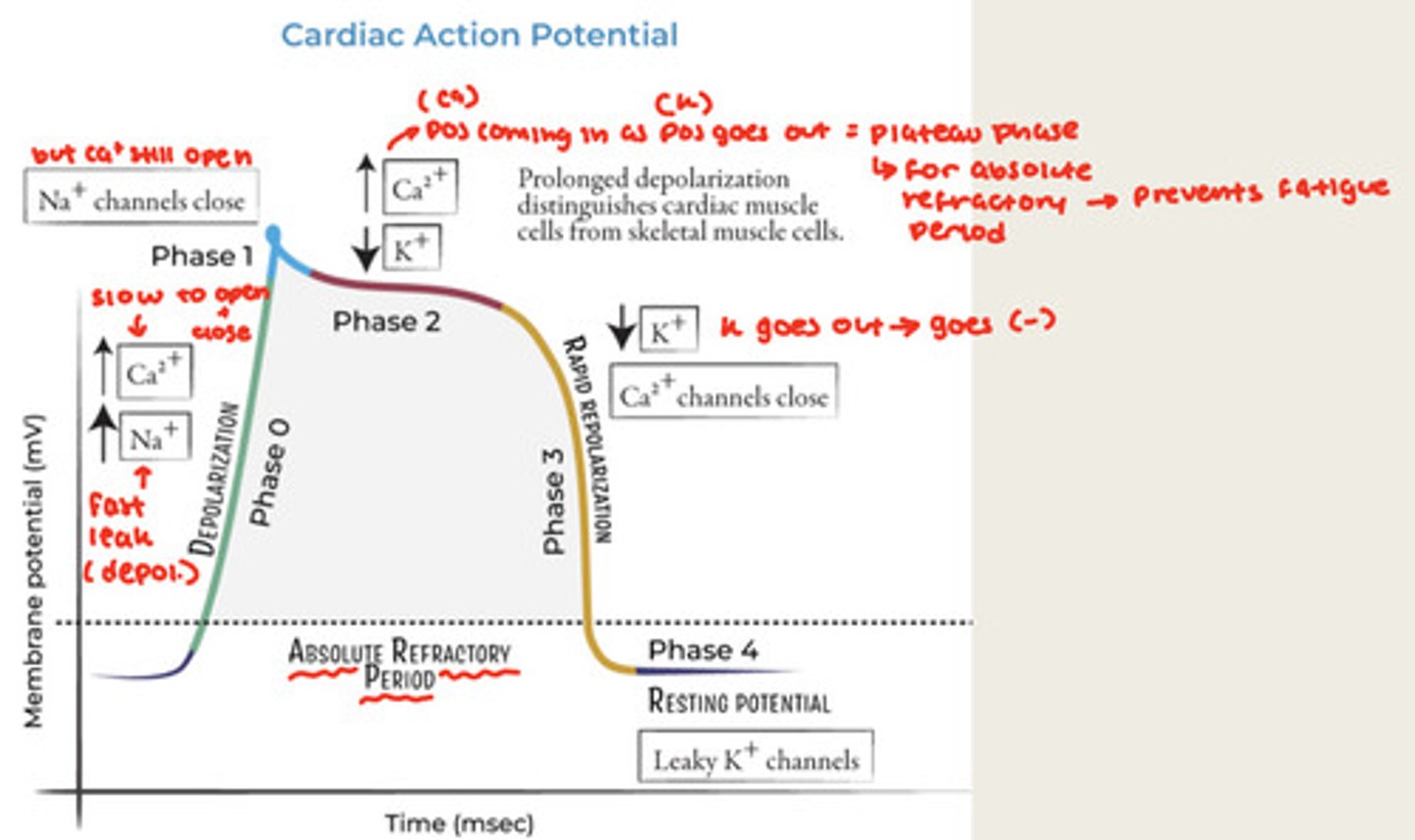
For regular cardiac muscle action potential look at graph on slide 22, better to study that then me trying to explain it
Where do you find pace maker potentials?
SA and AV node
Fast response myocytes AKA
Cardiac cells (not SA and AV node)
What does plateau phase and what does it do for myocytes
Caused by slow Ca channels and helps prevent fatigues (absolute refractory period)
What're the resting potentials for pacemaker potentials and myocytes
Pacemaker potentials = -60mV
Myocytes = -90mV
Where does stimulus start in our cardiac myocytes
SA node
EKG of heart
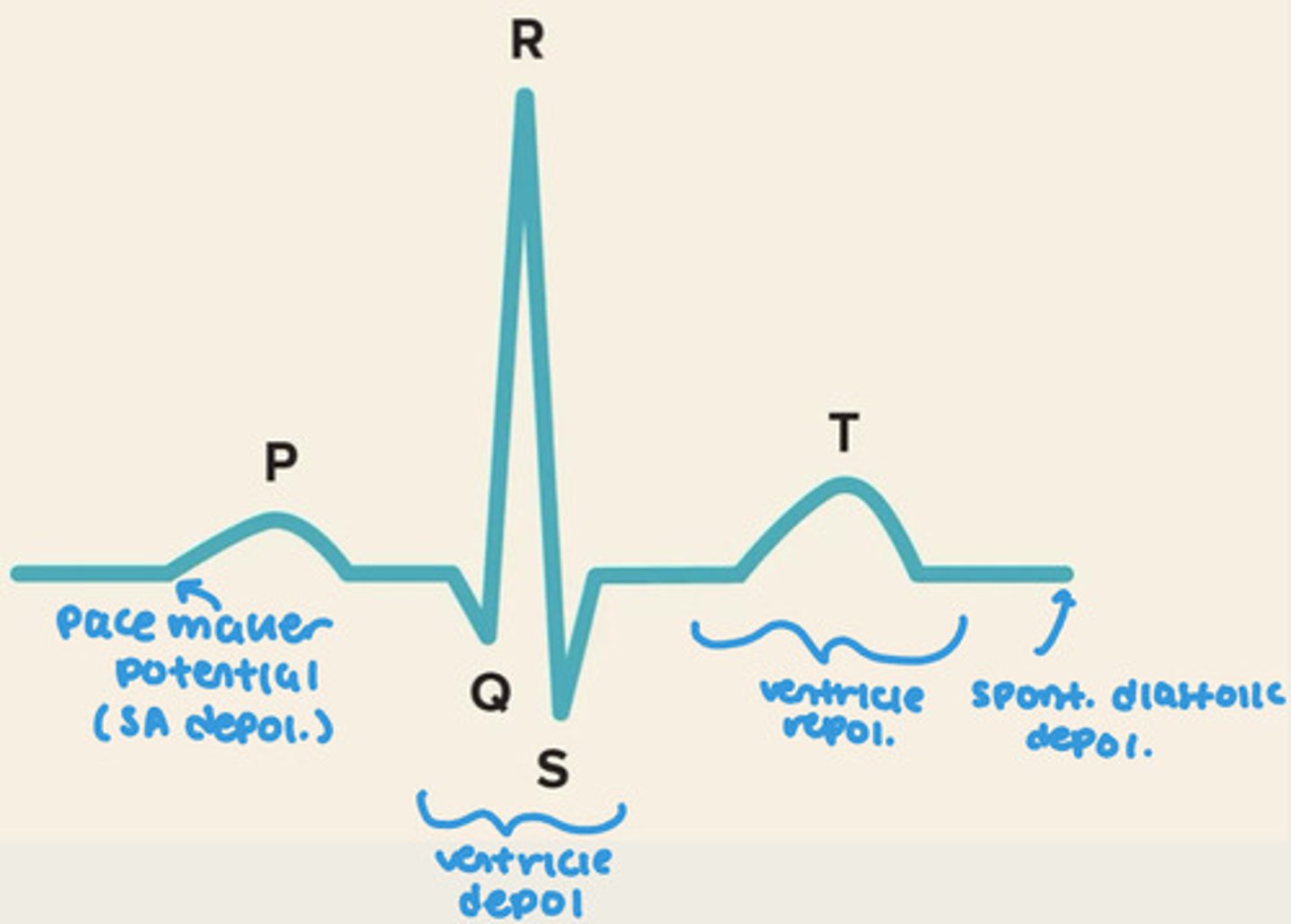
Av node is second fastest rate of depolarization but....
Slowest at conduction
-allows atria to squeeze all the blood into ventricle
Intercalated discs are also known as
Low resistance junctions
Conduction velocity def
The speed at which a cardiac action potential moves from one part of the heart to another
Based on size, the ____ the ____
Based on size, the bigger the faster
-Ex: AV node is the smallest so its the slowest
Norepinephrine (_____) and Epinephrine (______) = Increases permeability to _____ and _____ (FILL IN THE BLANK)
Norepinephrine (nerves) and Epinephrine (adrenal medulla) = Increases permeability to Na and Ca
-gets to threshold faster
Acetylcholine = _____ permeability to ______ (FILL IN THE BLANK)
Acetylcholine = Increases permeability to K
Adrenergic effect =
Increased HR and SV (sympathetic)
Cholinergic effect =
Decreased HR, no effect on SV (parasympathetic)
Length tension relationship
The more a muscle is stretched - to a point - the more tension it develops
Starling's law of the heart AKA (2)
Heterometric autoregulation and Frank/Starling mechanism
Ejection fraction equation
Stroke volume / EDV
- % of blood that leaves ventricles with each contraction
Normal EF vs Heart failure EF
Normal = 55-70%
Heart failure = less than 40%
Things that would increase EJ in normal heart (2)
1. Sympathetic activation = increase in SV
2. Increase in venous return —> increase EDV —> greater stretch (starling's) —> greater contraction (increase in SV)
In heart failure, the ____ in venous return ____ejection fraction
In heart failure, the increase in venous return decreases ejection fraction (heart too weak to create greater contraction)