D103 Mitochondria (ALS 8, Video 14)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
oxidative phosphorylation
AAs, simple sugars, fatty acids → high energy electron carriers (NADH and FADH2) → ATP
electrons move down the ETC, leading to the establishment of a electrochemical proton gradient that is then used to generate ATP
ATP syn requires a tight, proton impermeable inner mito membrane
ATP syn is able to convert chem energy into mech energy
atp production by mito
food breakdown, citric acid cycle, electron transport chain, atp synthase
food breakdown in mito
occurs in cytosol
via glycolysis
citric acid cycle in mito
occurs in mito matrix
acetyl coa is converted into high energy electron carriers (NADH)
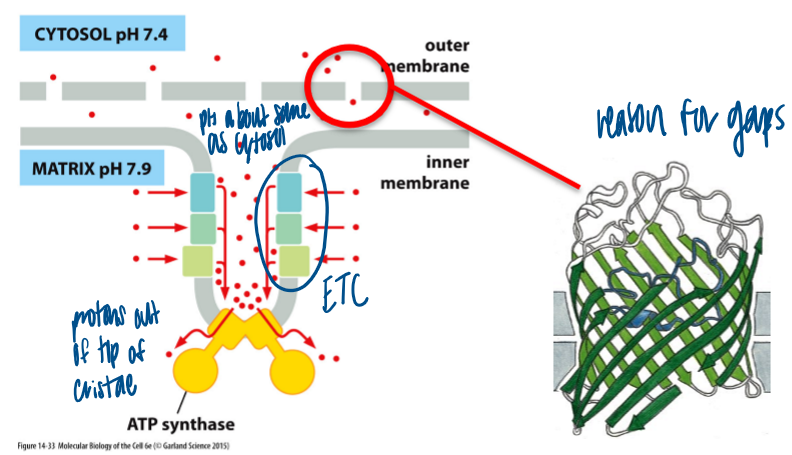
etc in mito
occurs in inner membrane of mito
electrons move between the complexes of the electron transport chain (arranged in order of increasing redox potential)
last electron acceptor: O2, which is reduced to H2O
electron movement generates a steep electrochemical gradient for protons (membrane potential + pH gradient)
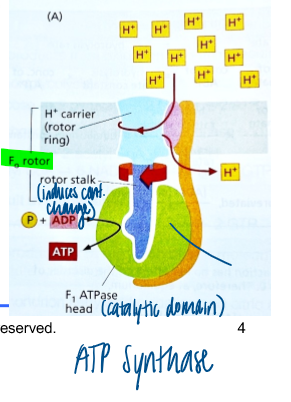
atp synthase in mito
occurs in inner mito membrane
uses steep electrochemical proton gradient to generate ATP
has a catalytic domain
hydrolysis of ADP → ATP causes conf change
what does atp production by mitos depend on
specialized inner membrane
highly permeable ions
high protein content (76% of the weight is protein, such as transporters)
cardiolipin
cristae arrangement generates proton sink
cardiolipin
diphosphatidyl glycerol with 4 fatty acid chains
controls membrane permeability
promotes high curvature of the membrame
mito outer membrane and atp production
porins make this membrane permeable to small molecules and proteins (>5kDa)
slightly basic pH in cytosol
mito behavior
highly dynamic
fission and fusion
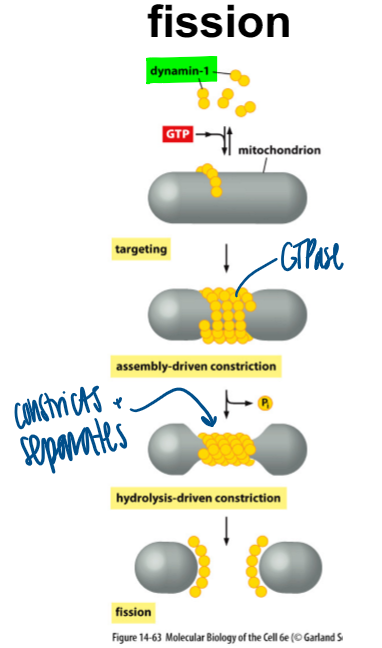
mito fission
dynamin-1 gets activated with GTP, then constricts to separate them
defective: elongated pieces bc it cannot break apart
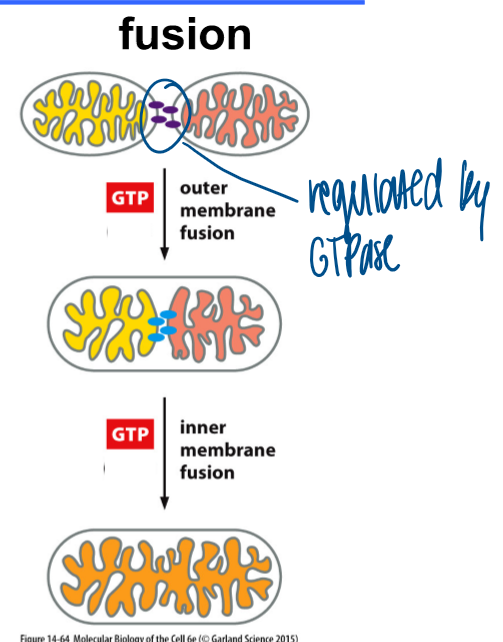
mito fusion
regulated by GTPase and requires 2 gtp inputs
gtp input to fuse the outer membranes
gtp input to fuse inner membrane
defective: small fragments bc it cannot fuse together to make bigger parts
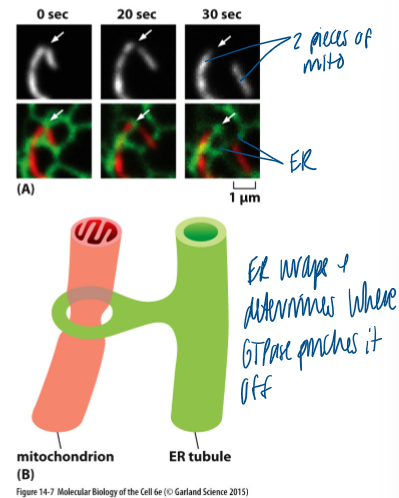
what determines mito organization
contact sites with the ER
ER wraps and determines where GTPase pinches it off
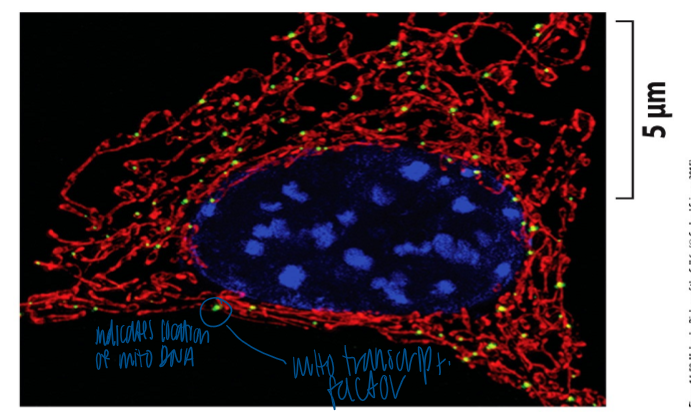
mitochondria and dna
mito contain their own dna
mito dna is organized as clusters (=nucleoids)
clusters are anchored to the inner membrane
10-1000s nucleoids/cells
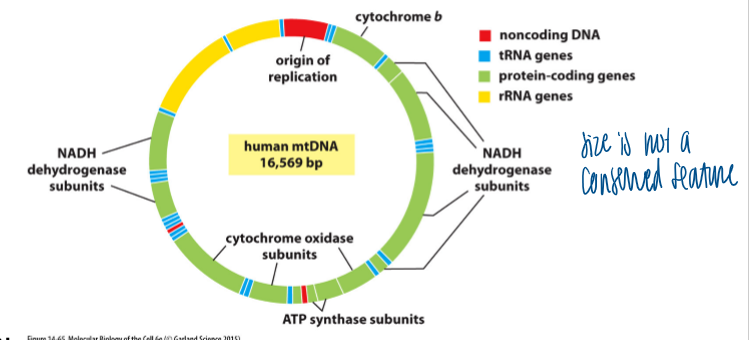
significance of mito DNA
humans: 37 genes which encode 13 mito proteins
other organisms: varying size of the mito genome
ex: yeast = 80,000 bp; plants = 200,000 bp
mito dna vs nuclear dna
mito dna has dense gene packing = no introns
does not replicate in parallel ot nuclear DNA during s-phase (as needed)
uses a different genetic code (4 out of 64 codons are different)
no proofreading and DNA repair mech (mutation rate is 1000x higher than for nDNA)
endosymbiont theory
primordial eukaryotic cells without ability to use oxygen
colonized by aerobic bacteria
gene traensfer of 1000+ genes to nucleus
13 structural proteins encoded by bacterial/mito DNA
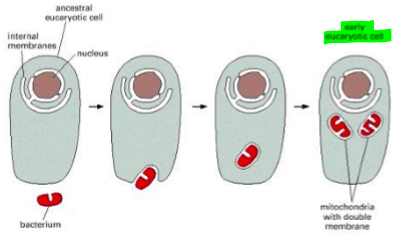
supportive evidence for the mito endosymbiont theory
double membrane that surrounds the mito matrix
circular dna
transcription and translation machinery of mitos are similar to those of bacteria
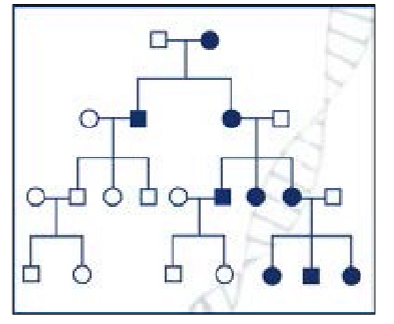
how are mito inherited
maternal inheritance
egg contributes the majority of cytoplasm to the zygote; mitochondria are contained in the cytopalsm
a mutation in mtDNA is only transmitted from the motherl it is passed on to all offspring
symptoms of leigh syndrome
normal at birth, but progressive loss of mental and motile ability
brain lesions that are detectable by mri
caused by at least 26 mutations that affect mito energy production
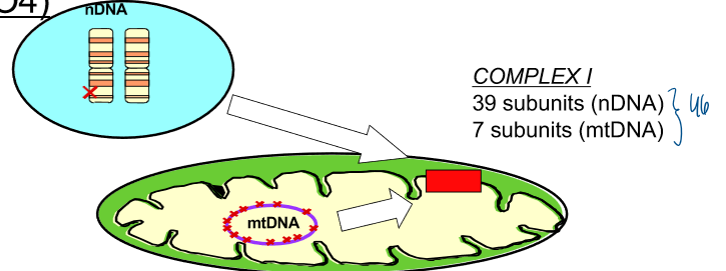
causes of leigh syndrome
mutations in genes that encode for complex i subunits
complex i: 39 subunits (mDNA), 7 subunits (mtDNA)
nuclear dna mutations leigh’s syndrome (autosomal recessive inheritance) + mt dna mutation leigh’s syndrome (maternal inheritance) → progressive degeneration of the CNS
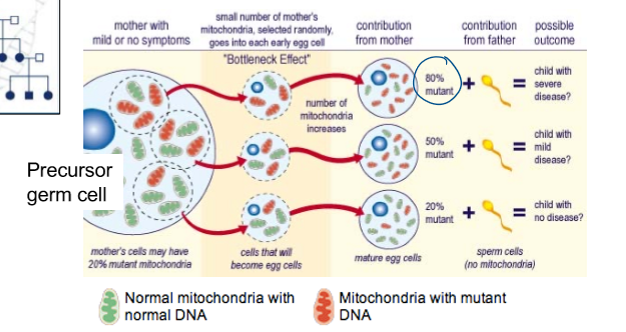
sibling inheritance of mito
siblings may have different mito and a different degree of severity of a mito disease
the offspring from a mother can display different severities of a mito disease phenotype
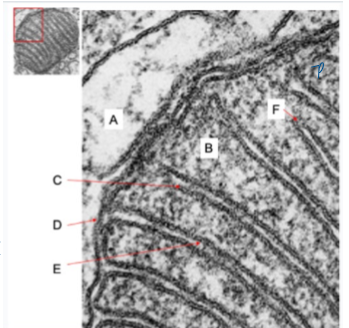
what happens where inside mitochondria
A = cytosol
B = tca cycle enzymes
D = porins (gives permeability)
F = high conc of atp-syntahse
you have identified a compound that makes the inner mitochondrial membrane permeable to ions. which of the following describes the most direct consequences of incubating your cells with this compound?
proton gradient and atp synthase become uncoupled
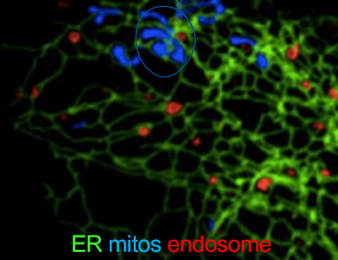
you have learned that mito and er form membrane contact sites. which of the following experiments would be allow you to determine if the er controls the morphology of mito
alter er organization and observe mitochondria morphology by immunofluorescence microscopy
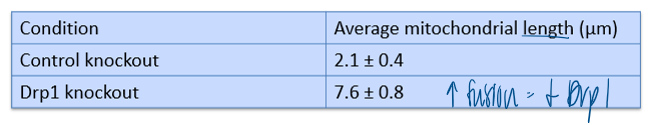
mito constantly undergo fusion and fission, processes regulated by the gtoases Drp1 and Mfn1/2. A researcher knocks down Drp1 in cultured cells and stains mito wiht a fluorescent dye. the average mito length was measured from confocal micrographs. based on the data, which conclusion is best supported?
Drp1 promotes mitochondrial fission
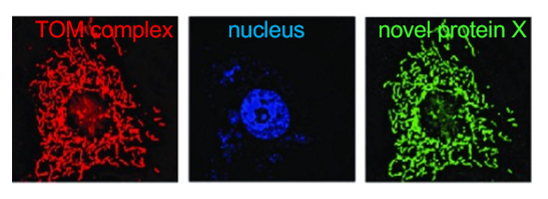
you have identified a novel protein (x) thru a functional screen. since you dont have an antibody, you tag the cDNA of this protein with GFP. In colocalization studies in which you also use an antibody to the TOM complex (together with the correct secondary antibody with a red fluorophore. which of these conclusions is best supported by result?
x localizes to mito
where do mitochondria come from; which of the following facts provides strong support for the endosymbioent theory for the origin of mitochondria?
mitochondrial dna is circular
who in this family has differnet mitochondrial dna
maternal, so not in the father