cell signalling
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is signalling?
How cells talk to each other
What’re extracellular signal molecules?
Proteins, peptides, amino acids, nucleotides, steroids, fatty acid derivatives, dissolved gasses
Whats endocrine signalling?
Signals circulated through the body in the bloodstream
Hormones produced in endocrine cells
Whats paracrine signalling?
Signal molecules diffuse locally through extracellular fluid
Local mediators for nearby cells (close cells talking to each other)
Whats autocrine signaling?
Cells respond to signals they produced themselves
Ex: cancer cells that promote their own growth
What’s neuroscience signalling?
Fast signal with specificity to a single target cell
Very specific about which cell it wants to signal
Whats contact dependent signalling?
Cells make direct contact through signal and receptor molecules embedded in the plasma membrane
How selective are receptors?
Highly selective
What do cell surface receptors do?
Outside cell
Bind extracellular signals
Used for signals that are too large or hydrophilic to cross the membrane
What are intracellular receptors?
Inside cell
Bind signals that pass through the plasma membrane
Used for signals that are small and hydrophobic
What happens when receptors activate intracellular signaling molecules?
They can activate effector proteins which have an effect on cell behavior
Can one signal cause different effects in different cells? Provide an explanation if so
Yes, based on what type of receptor it binds to
Ex: Acetylcholine causes heart rate to decrease and causes salivary gland to release components of saliva
Explain how a cell response can be fast or slow
Muscle contraction is fast and occurs within milliseconds
Cell division requires hours
What happens in intracellular signaling pathways?
Transmembrane receptors detect a signal and relay the message across the membrane to the interior of the cell which is a primary step in signals transduction
Molecular relay race
Message is passed from one signaling molecule to the next
Final target molecule is reached
What’re components of the intracellular signaling pathway?
Relay the signal
Scaffolds to bring together other components
Amplify a signal
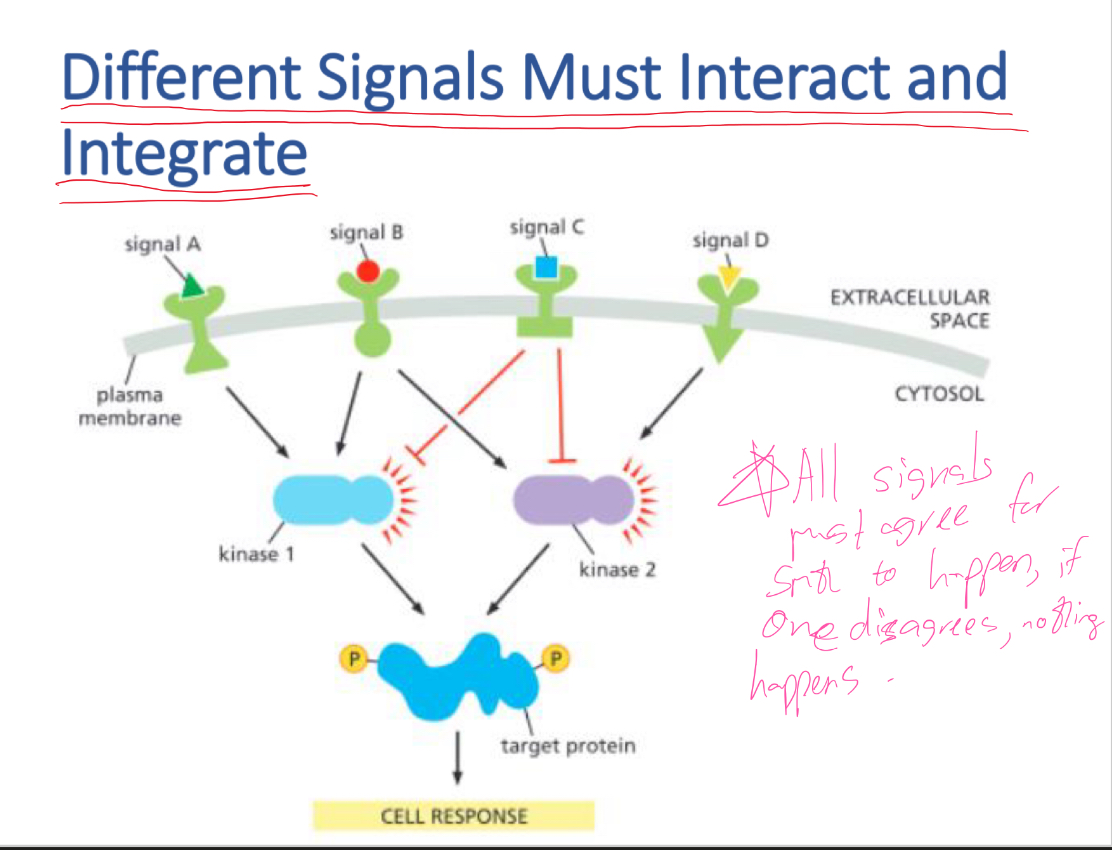
Integrate signals from multiple pathways
Distribute the signal to multiple effector proteins causing the pathway to branch
Regulate the activity of other components through feedback
+ve feedback enhances response
-ve feedback diminishes response
What’re most relay proteins and what do they do?
Molecular Switches
For every activation there’s an inactivation step
Explain how molecular switches do their inactivation and activation
Through phosphorylation
Protein kinases attach a protein to the switch protein
Ser-Thr kinases phosphorylation ser or the
Try kinase phosphorylate tyrosine
Protein phosphate removes the phosphate
Organized in cascades
Whats an example of molecular switches and what do they do?
GTP binding proteins
Depend on whether GTP or GDP are bound to them
Shut themselves off with GTP-hydrolyzing activity (GTPase)
What’re the 3 types of cell surface receptors?
Ion channel coupled receptors
G protein coupled receptors
Enzyme couples receptors
What’re ion channel coupled receptors?
Change permeability of the membrane to specific ions which will change the membrane potential
What’re G protein coupled receptors?
They activate GTP-binding proteins to interact with an enzyme or ion channel to initiate an intracellular signalling cascade
Single polypeptide chain that passes through the membrane 7 times
Multipass transmembrane proteins
Receptors in processes that need to happen very quickly
What’re G proteins?
Each has 3 protein subunits (alpha, beta, gamma)
Alpha and gamma are bound to lipid tails
Altered receptor activates G protein by replacing GDP with GTP
Can break apart the subunits which can relay the signal to other molecules
What happens in G protein in unstimulated and stimulated states?
Unstimulated state: alpha subunits has a GDP bound
Stimulated: alpha subunit has GTP bound
What does the alpha subunit have in terms of GTP hydrolysis?
It has a GTPase (phosphatase) to hydrolyze GTP back to GDP
What does G proteins target?
Target of bacterial disease causing toxins
Ex: cholera
Explain control in G proteins
Controls gated ion channels (ex: in heart pacemaker cells)
Open channel when activating protein
Closed when not
What enzymes do G proteins activate?
They activate enzymes that produce small messenger molecules
Second messengers amplify and spread the intracellular signal
Whats an example of a G protein coupled receptors?
Adenylyl Cyclades activity
What happens in adenylyl cylase activity?
Activation makes the secondary messenger cAMP
AMP phosphodiesterase converts cAMP to AMP
AMP activates cyclic AMP dependent protein kinase (PKA)
What blocks AMP phosphodiesterase?
Caffeine blocks this enzyme which keeps the cAMP levels high in the cell
What gets activated and inactivated in adenylyl cyclase activity?
Activation of glycogen phosphorylase which breaks down glycogen
Inactivation of glycogen synthase
What’re the cell responses of adenylyl cyclase?
Increased heart rate
Glycogen breakdown
Fat breakdown
Cortisol secretion
What’re enzyme coupled receptors/ what they do?
They act as enzymes or associate with enzymes inside the cell to activate intracellular signalling pathways
Growth regulation, proliferation, differentiation, cell survival
Slow responses
Often lead to changes gene expression
What is the signal molecule in enzyme coupled receptors?
A dimmer
Whats an example of enzyme coupled receptors?
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs)
What do Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) Do?
Extracellular signal causes 2 receptors to dimerize
Intracellular tails are in close proximity which activates the kinase domains to phosphorylate each other on tyrosines
Phosphorylate tyrosines serve as docking sites for other proteins (interaction domain on the signalling proteins)
Signalling proteins bind the membrane and each other
Large aggregates - biomolecular condensates
Transmits signals along several routes simultaneously
How are Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) terminated?
Signal can be terminated when tyrosine phosphotases remove phosphate groups
Signal can also be terminated by endocytosis and destruction of RTK cuz sometimes phosphotases can’t get to cell
Is signal transduction a linear process?
No