Aetiology of Malocclusion in Orthodontics
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Malocclusion
Deviation from ideal occlusal relationship.
Aetiology
Study of causes or origins of conditions.
Skeletal Aetiology
Causes of malocclusion related to skeletal structure.
Dental Aetiology
Causes of malocclusion related to teeth.
Soft Tissue Aetiology
Causes of malocclusion related to soft tissues.
Genetic Factors
Inherited traits influencing malocclusion development.
Environmental Factors
External influences affecting occlusal abnormalities.
Combination Aetiology
Malocclusion caused by multiple factors.
Class I Skeletal Pattern
Normal anteroposterior relationship of jaws.
Class II Skeletal Pattern
Maxillary protrusion or mandibular retrusion.
Class III Skeletal Pattern
Maxillary retrusion or mandibular protrusion.
Vertical Skeletal Discrepancy
Variation in vertical jaw relationships.
Low Angle Skeletal Pattern
Characterized by a short face appearance.
High Angle Skeletal Pattern
Characterized by a long face appearance.
Transverse Skeletal Crossbites
Asymmetrical relationship of upper and lower jaws.
Anteroposterior Skeletal Discrepancy
Discrepancy in front-back jaw positioning.
Mild Asymmetries
Slight differences in facial structure.
Twin Studies
Research method for genetic influence analysis.
Mouth Breathing
Breathing through the mouth affecting dental health.
Syndromes
Genetic conditions influencing malocclusion.
Mandibular Condyle Fracture
Injury affecting jaw alignment and function.
Aetiology
Study of causes of dental conditions.
Malocclusion
Misalignment of teeth and jaws.
Multifactorial
Involving multiple factors or causes.
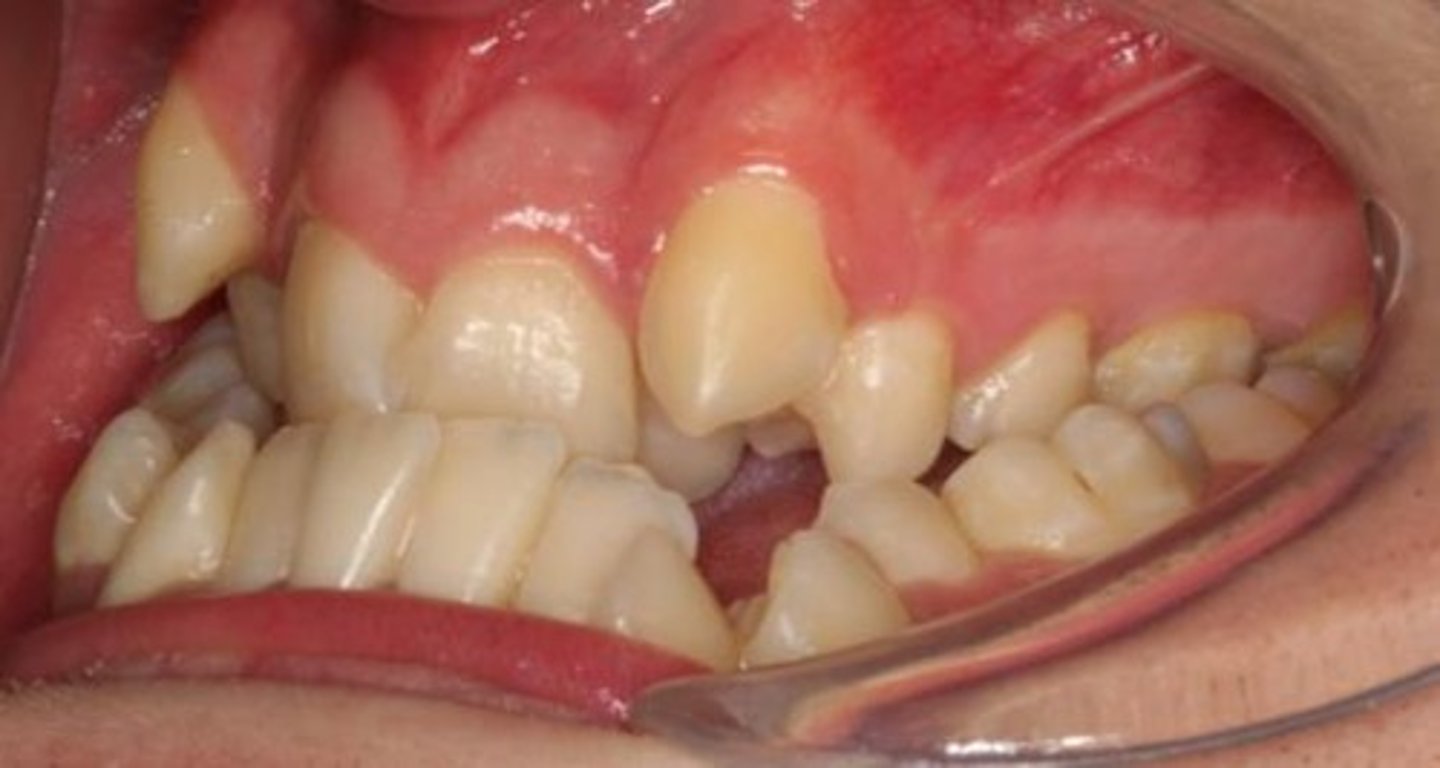
Supernumerary teeth
Extra teeth beyond the normal series.
Hypodontia
Developmental absence of one or more teeth.
Microdontia
Abnormally small teeth.
Macrodontia
Abnormally large teeth.
Transposition
Position exchange of two teeth.
Impaction
Tooth unable to erupt properly.
Ectopic position
Tooth located in an abnormal position.
Delayed eruption
Later than normal tooth emergence.
Early loss of teeth
Premature loss of primary or permanent teeth.
Late loss of teeth
Delayed loss of primary or permanent teeth.
Talon cusp
Abnormal cusp on the tooth surface.
Ankylosed tooth
Tooth fused to bone, preventing eruption.
Space maintenance
Preserving space for future tooth eruption.
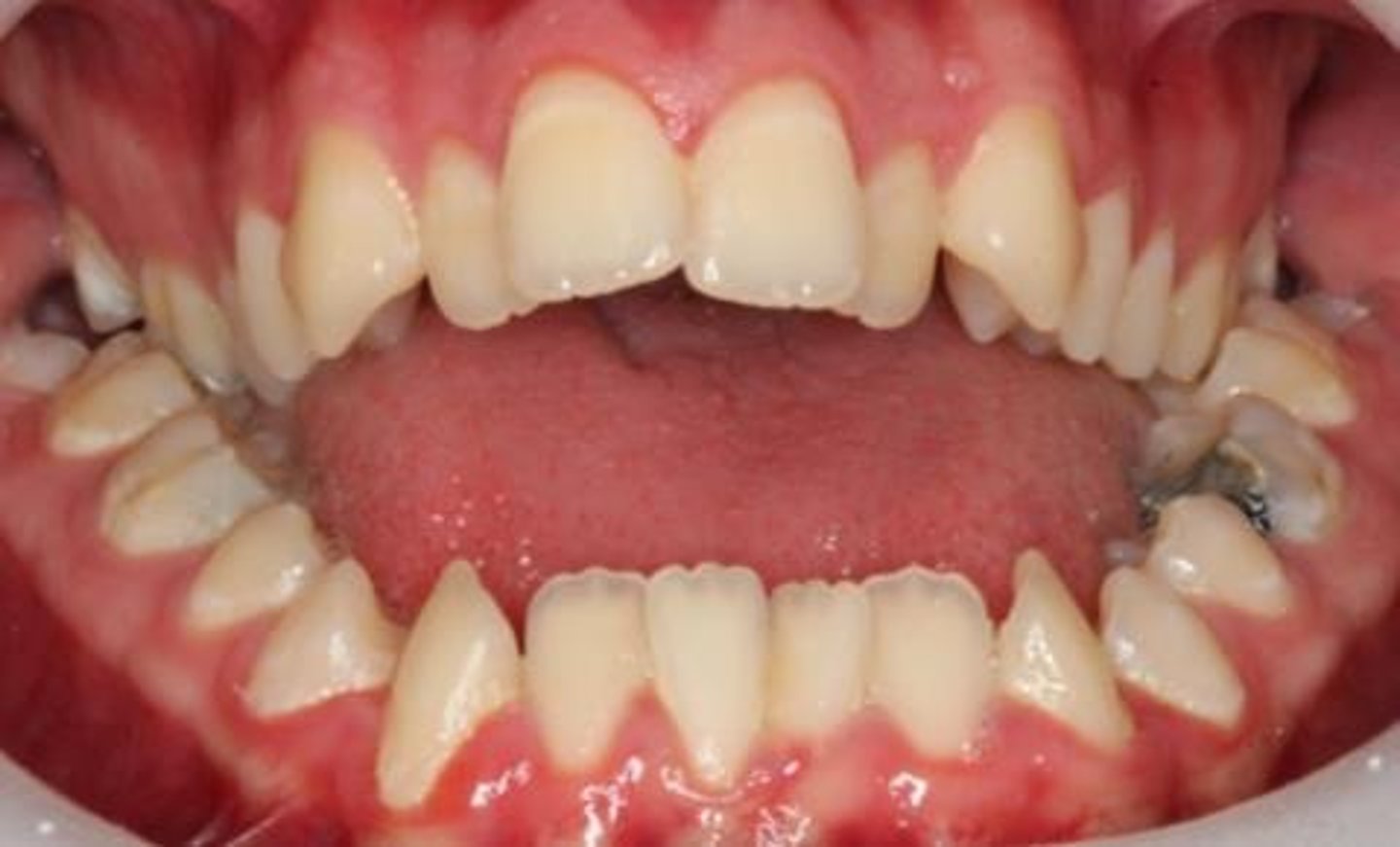
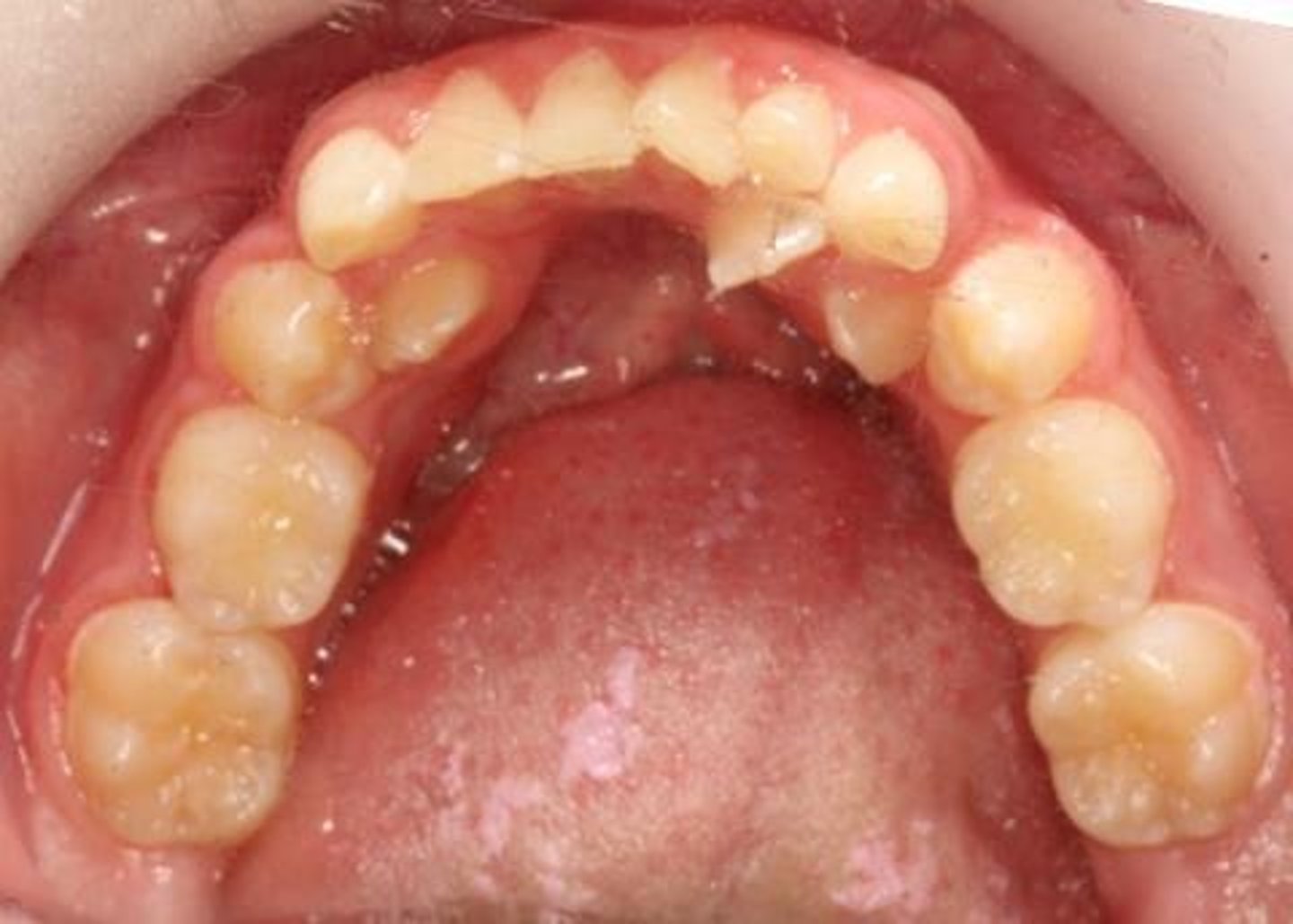
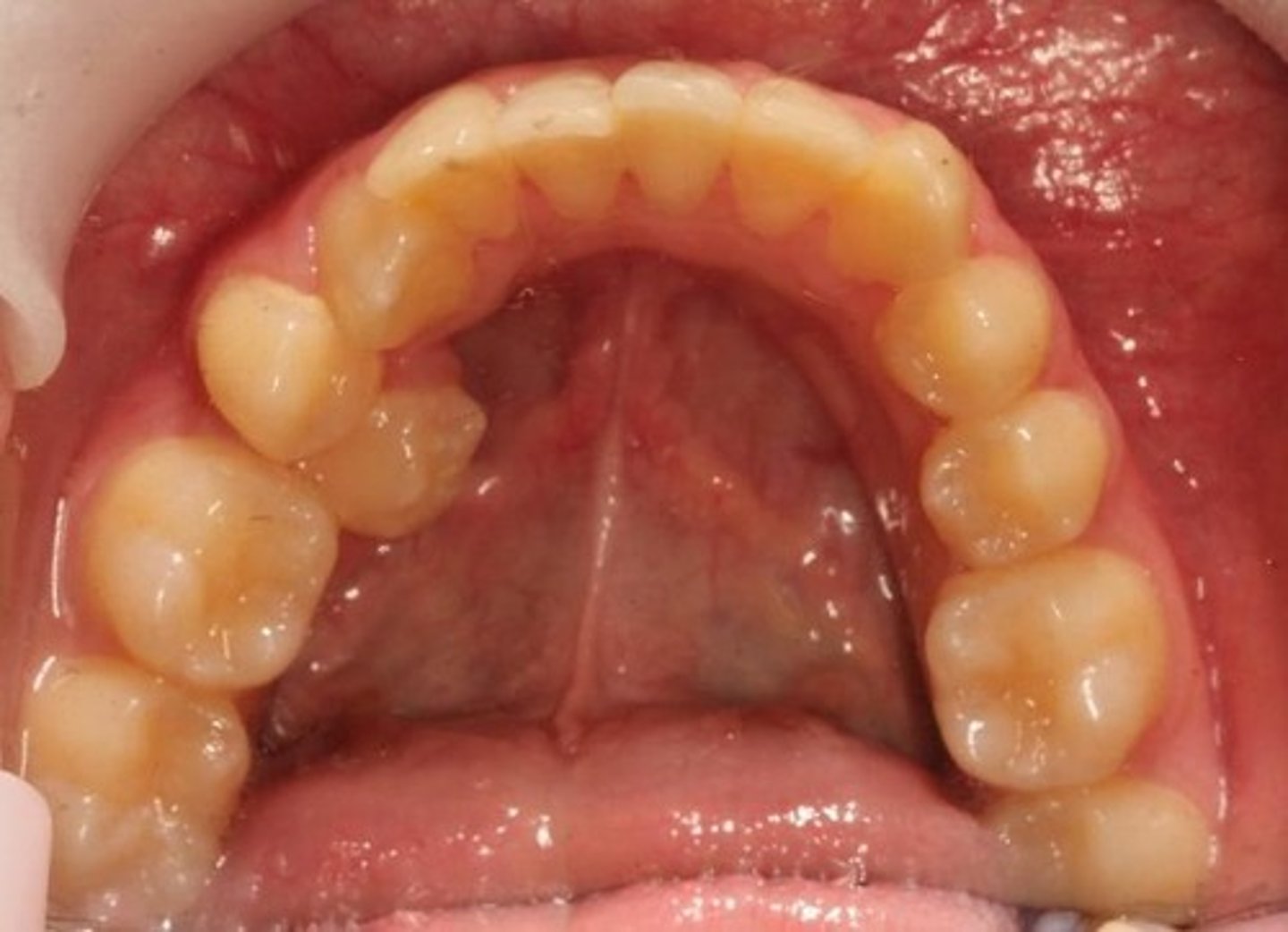
Crowded arch
Insufficient space for teeth in the jaw.
Asymmetric retention
Unequal retention of teeth affecting alignment.
CL shifts
Changes in dental midline due to tooth loss.
Incidence of supernumerary teeth
4-6% prevalence excluding third molars.
Types of supernumeraries
Conical, tuberculate, supplemental, and odontomes.
Dental Aetiology
Study of dental disease causes and factors.
Microdontia
Variation in tooth size; prevalence 2.5%.
Macrodontia
Variation in tooth size; prevalence 1%.
Supernumerary Teeth
Extra teeth beyond the normal count.
Hypodontia
Congenital absence of one or more teeth.
Impaction
Tooth blocked from erupting by a barrier.
Transposition
Positional interchange of adjacent teeth.
Ectopic Position
Tooth erupts in an abnormal location.
Talon Cusp
Abnormal tooth form resembling a talon.
Delayed Eruption
Later than normal emergence of permanent teeth.
Early Loss of Deciduous Teeth
Premature loss of primary teeth.
Late Loss of Deciduous Teeth
Delayed loss of primary teeth.
Early Loss of Permanent Teeth
Premature loss of adult teeth.
Crowded Arch
Insufficient space for teeth in the dental arch.
Genetic Factors
Influence of genes on dental abnormalities.
Environmental Factors
Impact of external conditions on dental health.
MSX1 Gene
Gene linked to hypodontia and microdontia.
PAX9 Gene
Gene associated with tooth development issues.
Sonic Hedgehog Gene (Shh)
Initiates tooth formation; absence causes agenesis.
Ectopic Tooth
Tooth following an abnormal eruption path.
Prevalence of Maxillary Canines
Impaction occurs in 2-3% of cases.
Aetiology
Study of causes of malocclusion.
Multifactorial
Involves multiple contributing factors.
Soft tissue aetiology
Influence of soft tissues on dental alignment.
Equilibrium theory
Teeth position stabilizes with surrounding tissues.
Pressure from the tongue
Tongue forces affect tooth positioning.
Pressure from the lips
Lip forces influence dental alignment.
Pressure from the cheeks
Cheek forces impact tooth positioning.
Lip competence
Ability of lips to maintain closure.
Lower lip position
Position affects upper incisors' retroclination.
Incompetent lips
Inability to maintain lip closure, causing issues.
Lower lip trap
Condition exacerbating increased overjet.
Adaptive tongue thrust
Tongue thrusting due to malocclusion.
Endogenous tongue thrust
Primary cause of malocclusion from tongue posture.
Non-nutritive sucking habits
Sucking behaviors affecting dental alignment.
Thumb sucking
Type of non-nutritive sucking habit.
Dummy sucking
Sucking on pacifiers; impacts dental structure.
Maxillary arch length
Length of upper dental arch; can increase.
Mandibular arch width
Width of lower dental arch; can widen.
Labial frenum
Tissue connecting lip to gums; affects spacing.
Low frenal attachment
Frenum attachment causing potential midline diastema.