Class 12: Motivation
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Motivation
Psychological processes directing goal-directed behavior.
Why is motivation important?
its why you show up, engage, and do extra.
What are the four perspectives on motivation?
- Content
- Process
- Job design
- Reinforcement
Reinforcement
Using consequences to modify behavior.
what theory presents content perspective on employee motivation?
Maslow's Theory
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Theory categorizing human needs from basic to complex.
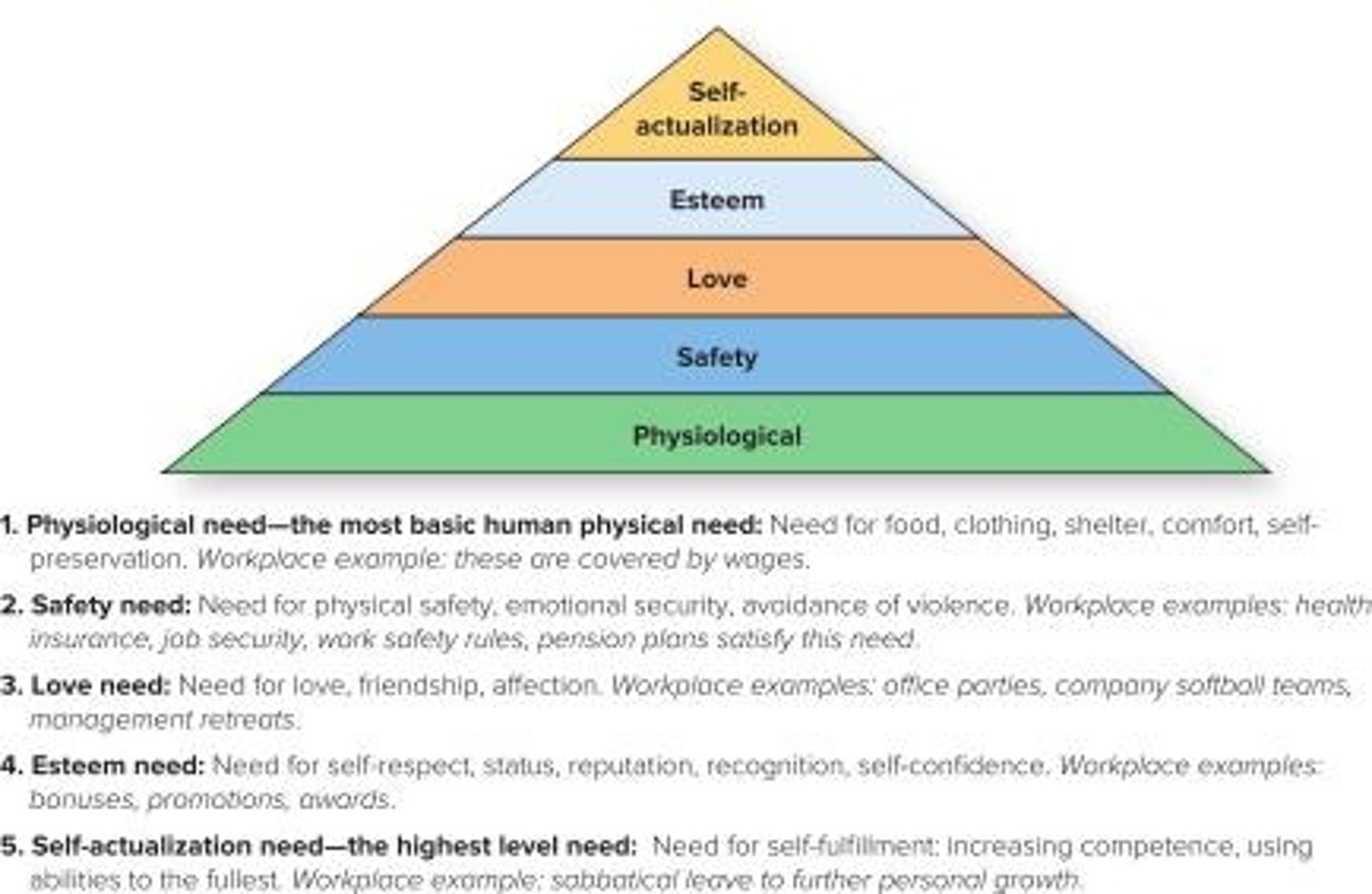
What perspectives are in Maslow's Theory ((1)Bottom to (5)top)
- Physiological
- Safety
- Love
- Esteem
- Self-Actualization
Physiological need in Maslow's theory
The most basic human need.
Ex: Food, clothing, shelter, comfort
Safety need in Maslow's theory
Need for physical safety, emotional security, avoidance of violence.
Ex: health insurance, job security
Love need in Maslow's theory
Need for love, friendship, and affection
Ex: office parties, company softball teams, management retreats.
Esteem need in Maslow's theory
Need for self- respect, status, reputation, recognition, self-confidence
Ex: bonuses, promotions, awards
What theory presents content perspectives?
McClellan Acquired needs theory
What are the 3 needs in McClellan Acquired needs Theory?
1. Need for achievement: "I need to excel at tasks"
2. Need for affiliation: "I need close relationships"
3. Need for power: " I need to control others"
What theory presents process perspectives?
Expectancy theory
Expectancy Theory
Motivation based on expected outcomes of actions.
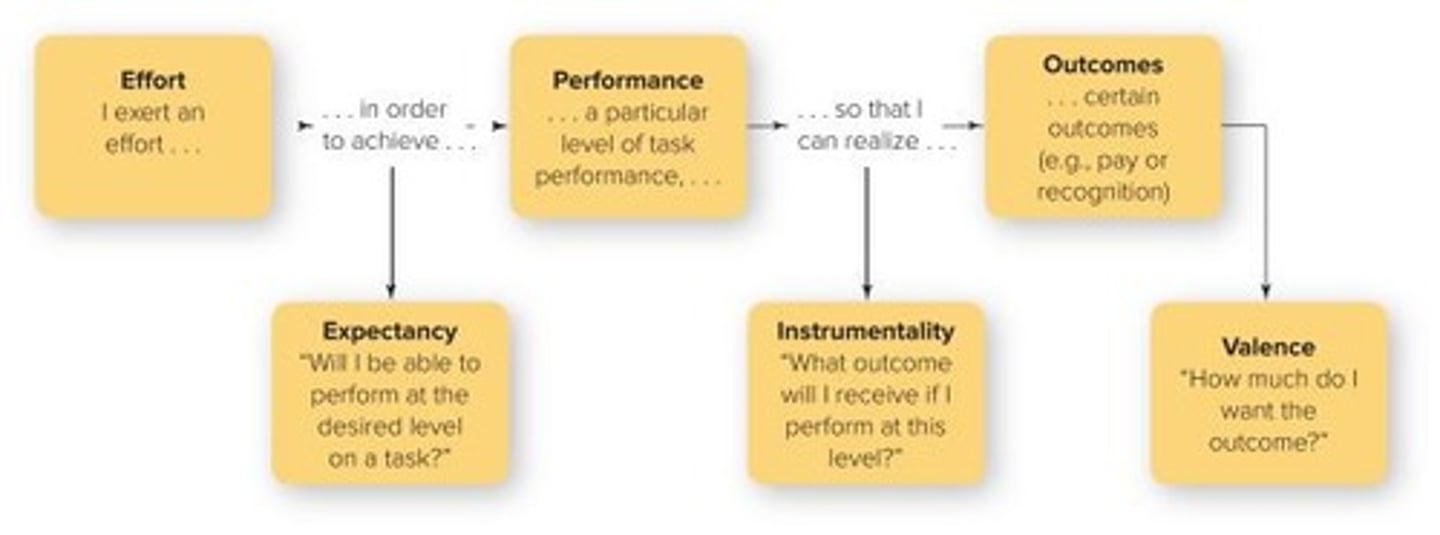
What perspectives are in Expectancy theory?
- effort
- expectancy
- performance
- Instrumentality
- Outcomes
- Valence
What theory presents process perspectives?
Goal-setting Theory
Goal-Setting Theory
Motivation through establishing specific, challenging goals.
What are the 2 types of goal orientations?
- Learning goal orientation
- Performance goal orientation
Learning Goal Orientation
Focus on acquiring new skills through goals.
Performance Goal Orientation
Focus on demonstrating existing competencies.
What theory presents fitting jobs to people?
Job design Theory
Job Enlargement
Adding variety to a job's tasks.
- Making the job larger
- Similar
Job Enrichment
Increasing responsibility in a job role.
- Making the job richer
- Different
What theory presents the job characteristics model?
Job design Theory
What characteristics are in the Job Design Theory
- Skill Variety
- Task Identity
- Task Significance
- Autonomy
- Feedback
Skill Variety
A job that requires different abilities
"how many different skills does your job require?"
Task Identity
Job requires all tasks from beginning to end
"How many different tasks are required to complete the work?"
Task Significance
Job affects lives of other people (Inside or outside the organization)
" How many other people are affected by your job?"
Autonomy
Job allows employee to make choices
"How much discretion does your job give you?"
Feedback
Workers receive clear, direct information about how they are performing.
"How much do you find our how well you're doing?"
What are the 4 reinforcement perspectives?
- Positive reinforcement
- Negative reinforcement
- Extinction
- Punishment
Positive Reinforcement
AKA: positive strengthening.
Giving something good because they did something good.
This counts as "Good behavior."
Negative Reinforcement
AKA: Negative strengthening.
Taking away something bad.
This counts as "Good behavior."
Extinction
Weakening behavior by removing positive outcomes.
This counts as a "Bad behavior"
Punishment
Weakening behavior by introducing negative consequences.
This counts as a "Bad behavior"
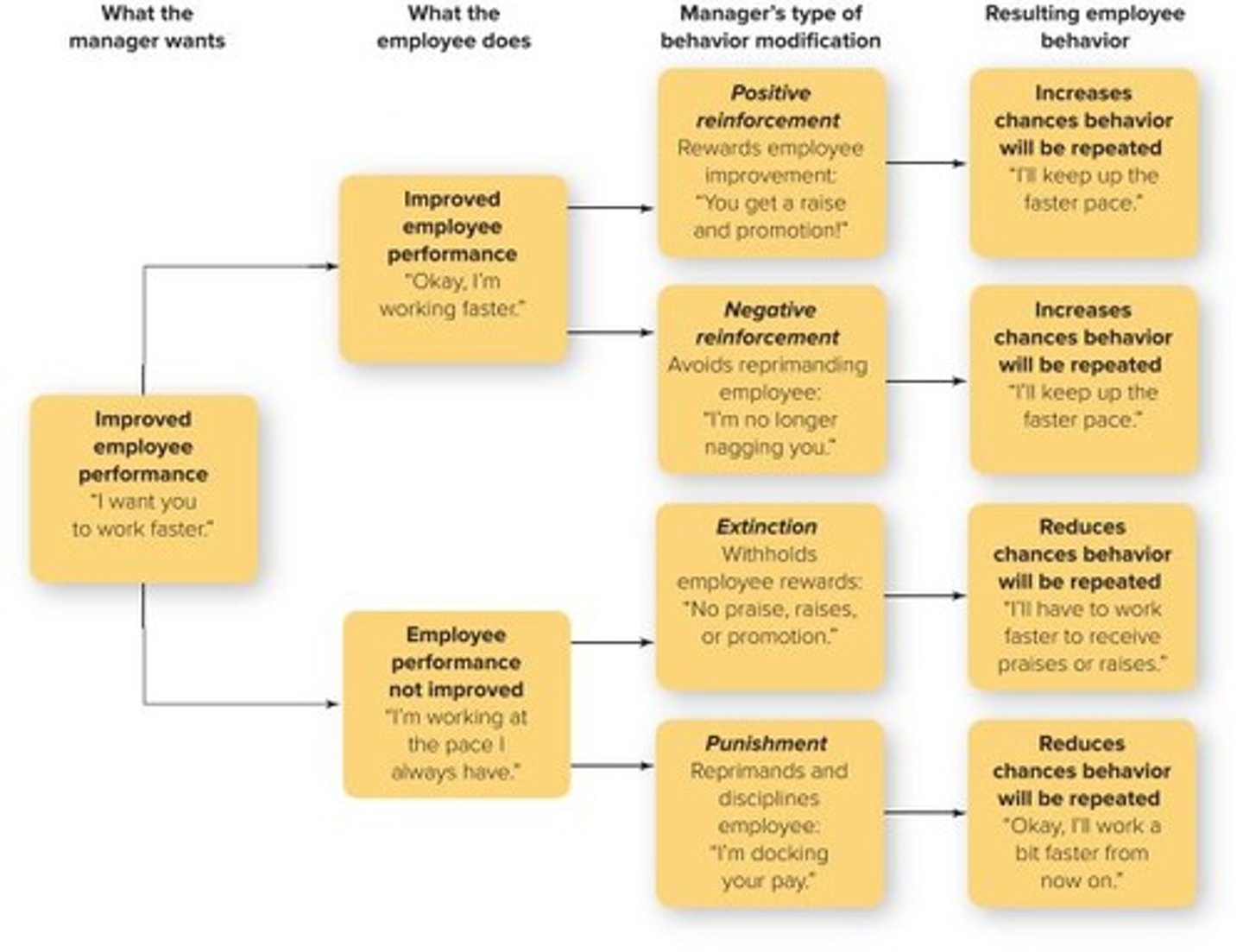
what are the 2 good behaviors?
- Positive reinforcement
- Negative reinforcement
What are the 2 bad behaviors?
- Extinction
- Punishment
what thing is not necessarily the best motivator
Money
What are the 4 motivators?
- need for Work - life balance
- need for personal growth
- need for a positive work environment
- need for meaningful work