Cell Structure and Function
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
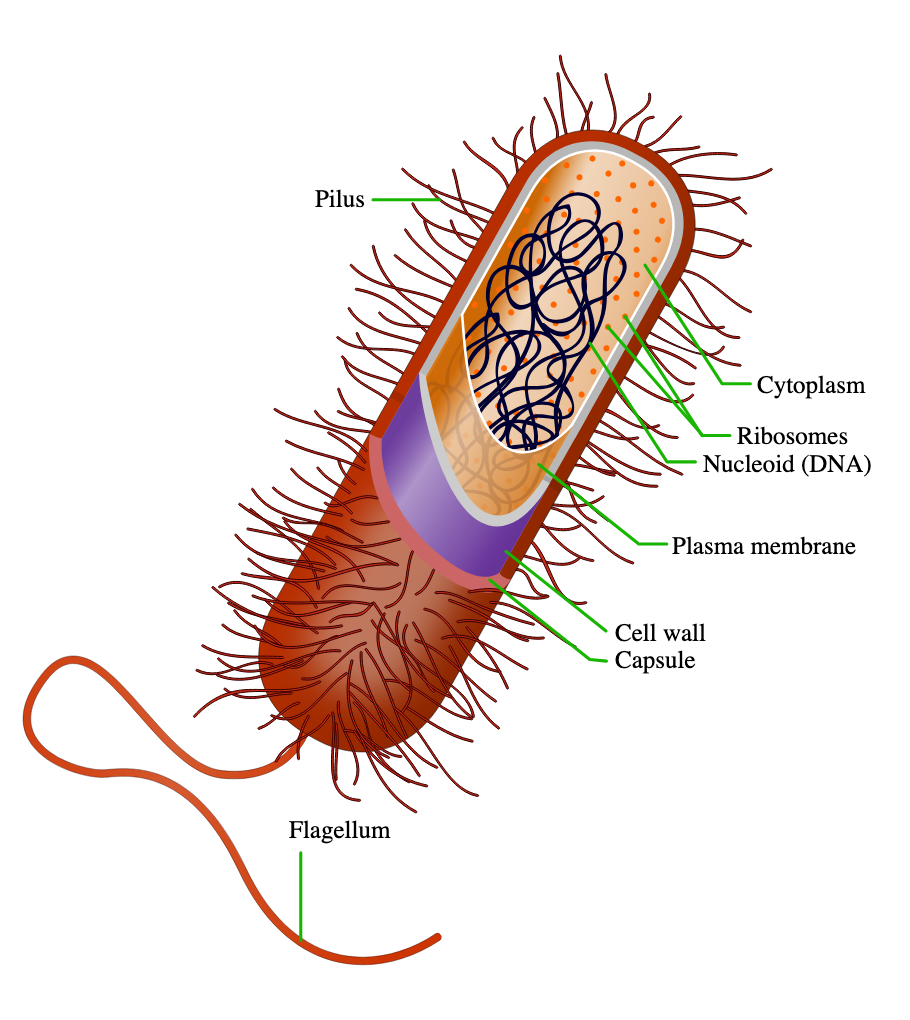
prokaryotic cells
simple cell
no nucleus, no membrane bound organelles - genetic information found in nucleoid region
circular chromosome
divide through binary fission
only found in Monera (bacteria) kingdom.
binary fission
duplicate genetic material, divide in half, produce two identical daughter cell
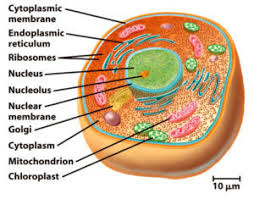
eukaryotic cells
has nucleus
can be unicellular or multicellular
linear chromosomeand membrane-bound organelles
endosymbiotic theory
eukaryotic cells originated from partnership of prokaryotes, focusing on mitochondria and chloroplasts
-same size as eubacteria
-reproduce like prokaryotes
-ribosomes similar to prokaryotes than eukaryotes
archezoa and diplomonads
eukaryotes without mitochondrias - Giardia is an infectious agent for the stomach
prokaryote organelles
plasma membrane, cell wall, ribosomes
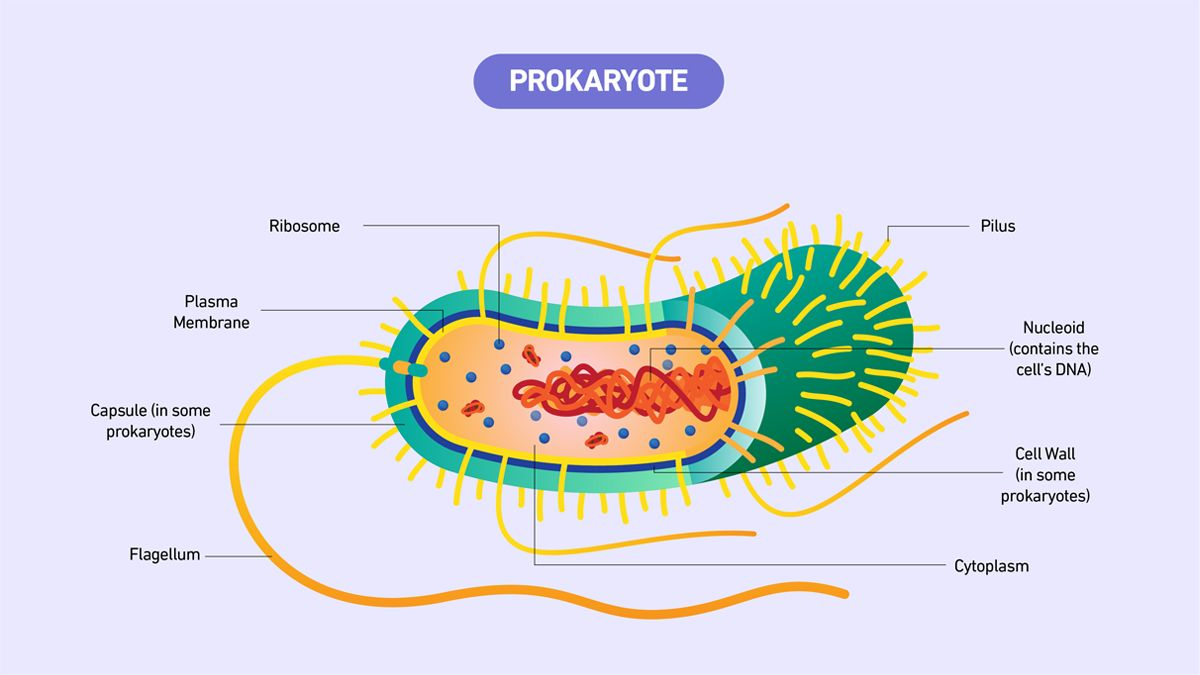
cell/plasma membrane
phospholipid bilayer - “fluid mosaic model”
barrier around the cell
cell wall
present in all prokaryotes
barrier that shapes and protects cell
ribosomes (prokaryotes)
host organelle for protein synthesis
cytoplasm
large and small subunit
eukaryotic organelles
cell/plasma membranes, cell walls (some), ribosomes, smooth ER, rough ER, golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes (some), nucleus, vacuole, peroxisomes, chloroplasts (some), cytoskeleton
ribosomes (eukaryotes)
bound organelles form proteins to be exported to membrane
free ribosomes in cytoplasm to form proteins for cytoplasm
built in nucleolus
smooth ER
lipid synthesis, detox, and carboyhrate metabolism
no ribosomes on surface of cytoplasmic cells
a lot in liver
rough ER
ribosomes on surface of cytoplasmic cells
proteins sent to Golgi
golgi apparatus
vessicle from ER and carry proteins around golgi sacs
macromolecules sent for modification, adding sugars and other molecules for glycoproteins
proteins sorted and sent to final destinations
protein path
nucleus sends out mRNA to ribosome
ribosome reads mRNA, creates polypeptide
polypeptide sent to ER, becomes vessicle for Golgi
Golgi sorts proteins and sent to final destination
mitochondria
double membrane organelles
inside is matrix, folds are cristae - increased surface area is more room for ETC
Krebs cycle (matrix) oxidative phosphorylation (cristae)
breakdown sugar to produce ATP, aerobic cellular respiration
has its own DNA, ribosomes, membrane
lysosome
digestion, enzymes to break down macromoleucles
stomach of the cell
absence leads to storage diseases like Tay-Sachs
cells no longer needed are destroyed
nucleus
storage site of DNA and how to build proteins
contains ribosome
has own membrane - nuclear envelope
nuclear pores - mRNA and others to enter and exit
vacuole
storage
large in plants, small in animals
peroxisomes
contain enzymes for breaking down fatty acids and detoxifying harmful substances
make hydrogen peroxide as by product and turn it into water
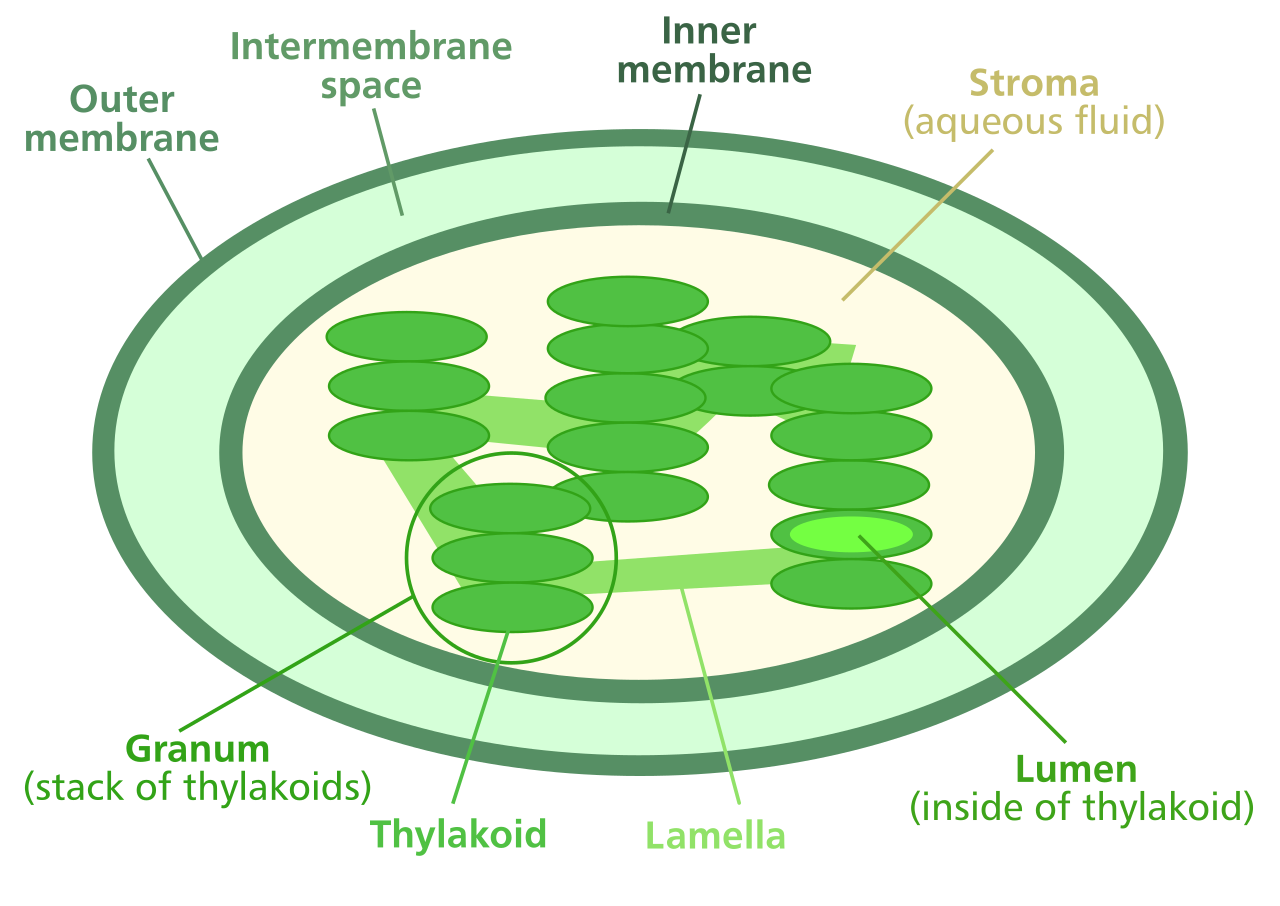
chloroplast
photosynthesis and energy production for plants
light energy → chemical energy
inner is stroma (light independent reactions), dark
outer is thylakoid membrane (light dependent reactions), light
has own membrane, ribosome
cytoskeleton
structure of cell
has microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments
microtubules: separate cells in cell division and movement of particles (flagella and cilia)
microfilaments: muscular contraction
intermediate filaments: keratins, maintain position of organelles
animal vs. plant
animals dont have chloroplasts or cell walls
plants dont have centrioles
fluid mosaic model
integral proteins, peripheral proteins, glycolipids, glycoproteins
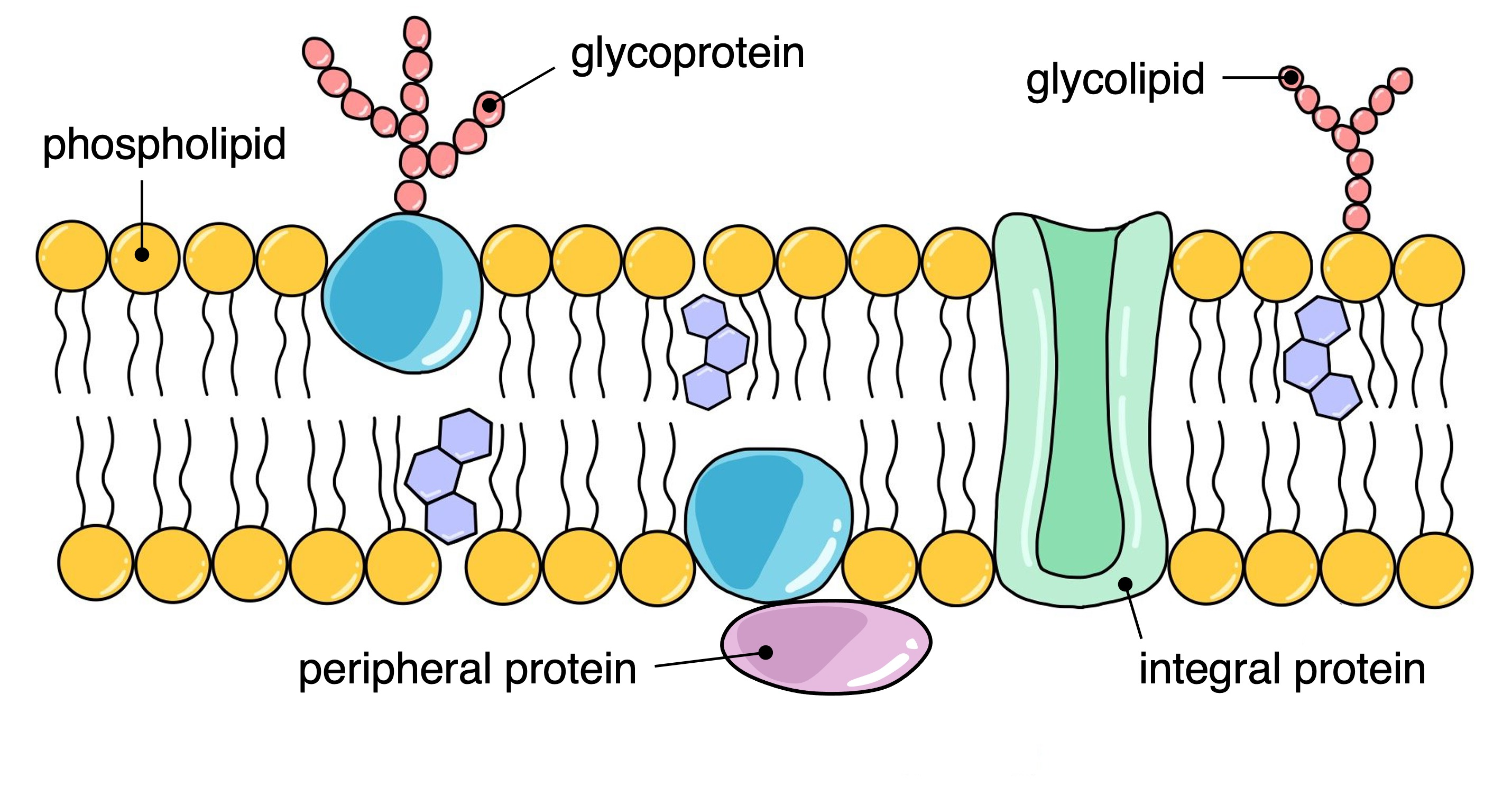
integral proteins
embedded in membrane
some can be transport/channel
can also function as enzymes to speed up rate of cellular reactions
peripheral proteins
on one side of cell membrane
receptor proteins - signaling and attachment from molecule
glycolipids & glycoproteins
surface of cell membrane
receptors on cell surfaces
immune response
permeability of membrane
semi-peremable
small, non-charged molecules
basic types of cell transport
diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, active transport, endocytosis, exocytosis
diffusion
movement of molecules down concentration gradient without use of energy
high concentraiton → low concentration
passive
osmosis
passive diffusion of water down concentration gradient
high concentraiton → low concentration
water goes hypotonic (swell, low solute) to hypertonic (shrink, high solute)
isotonic is middle ground, ideal for animals
hypotonic is ideal for plants
facilitated diffusion
like diffusion but with help of channel/transport proteins
specific
active transport
against concentration gradient, so low → high
requires ATP
NaK pump: diffusion wants Na in and K out—pump moves Na out and K in, maintaining cell potential
affected by temp, number of transport molecules, ATP, and ion concentration
endocytosis
membrane folds in to form vessicle and escorts into cell
phagocytosis and pinocytosis
receptor-mediated endocytosis: receptor brings in molecule
active transport
exocytosis
exported out of the cell, vessicle becoming part of cell membrane
active transport
water potential
how freely water molecules can move
determining water potential
a. cell walls exert pressure in opposite direction of turgor
b. predict water movement from solute potential
c. add presure + solute potential
turgor/pressure potential
physical pressure on cell membranes, increases with increasing pressure
solute potential
decreases as concentration of solute increases