Unit 4 - AP HUG
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Nation
a group of people with a common culture living in a territory and having a strong sense of unity. The Irish people, The German people, the Kurdish people
State
A country:
1. has defined boundaries
2. permanent population
3. sovereignty
4. recognized by other countries
nation-state
a sovereign state whose citizens or subjects are relatively homogeneous in factors such as language or common descent.
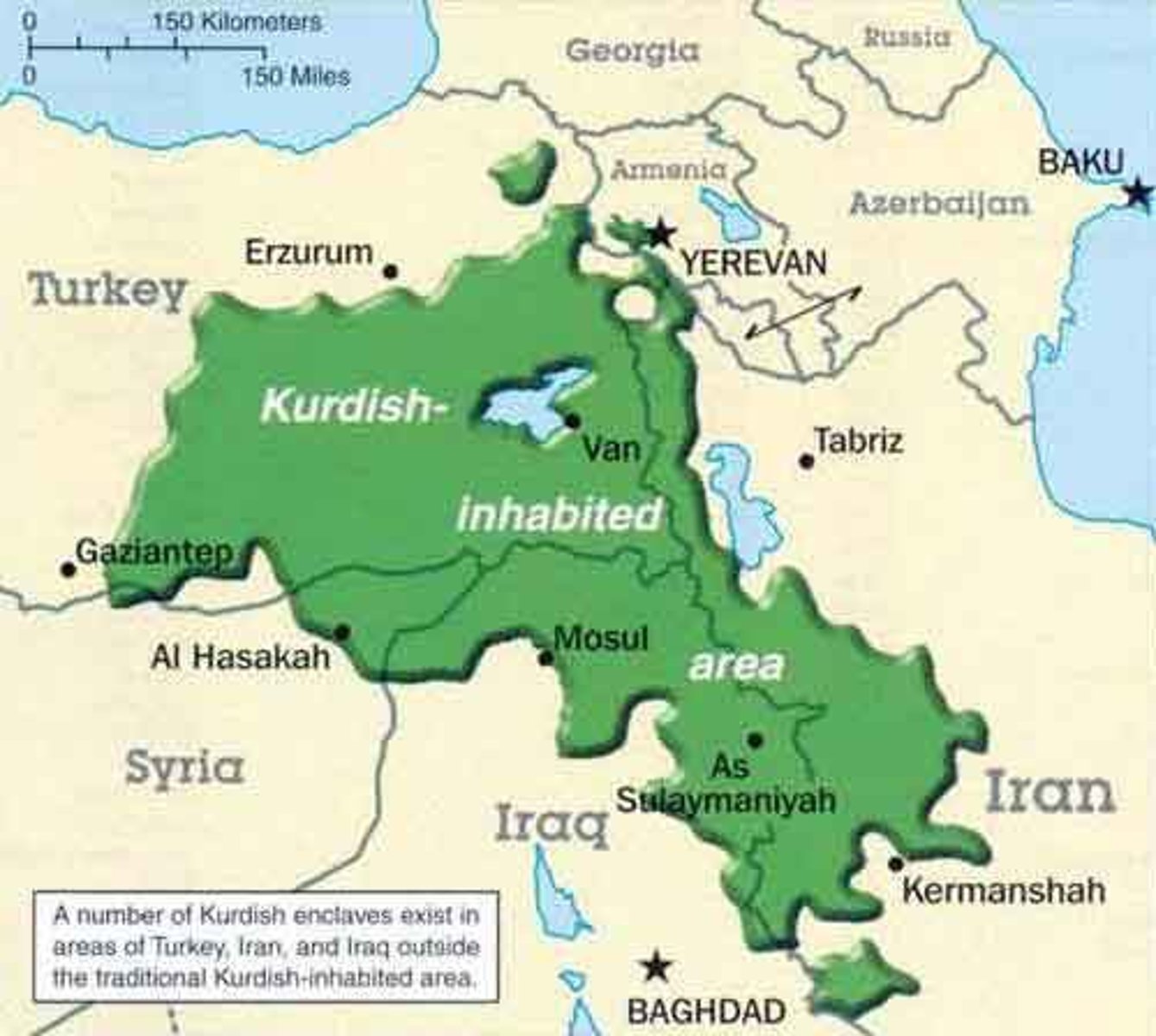
stateless nation
a group of people with a common political identity who do not have a territorially defined, sovereign country of their own.
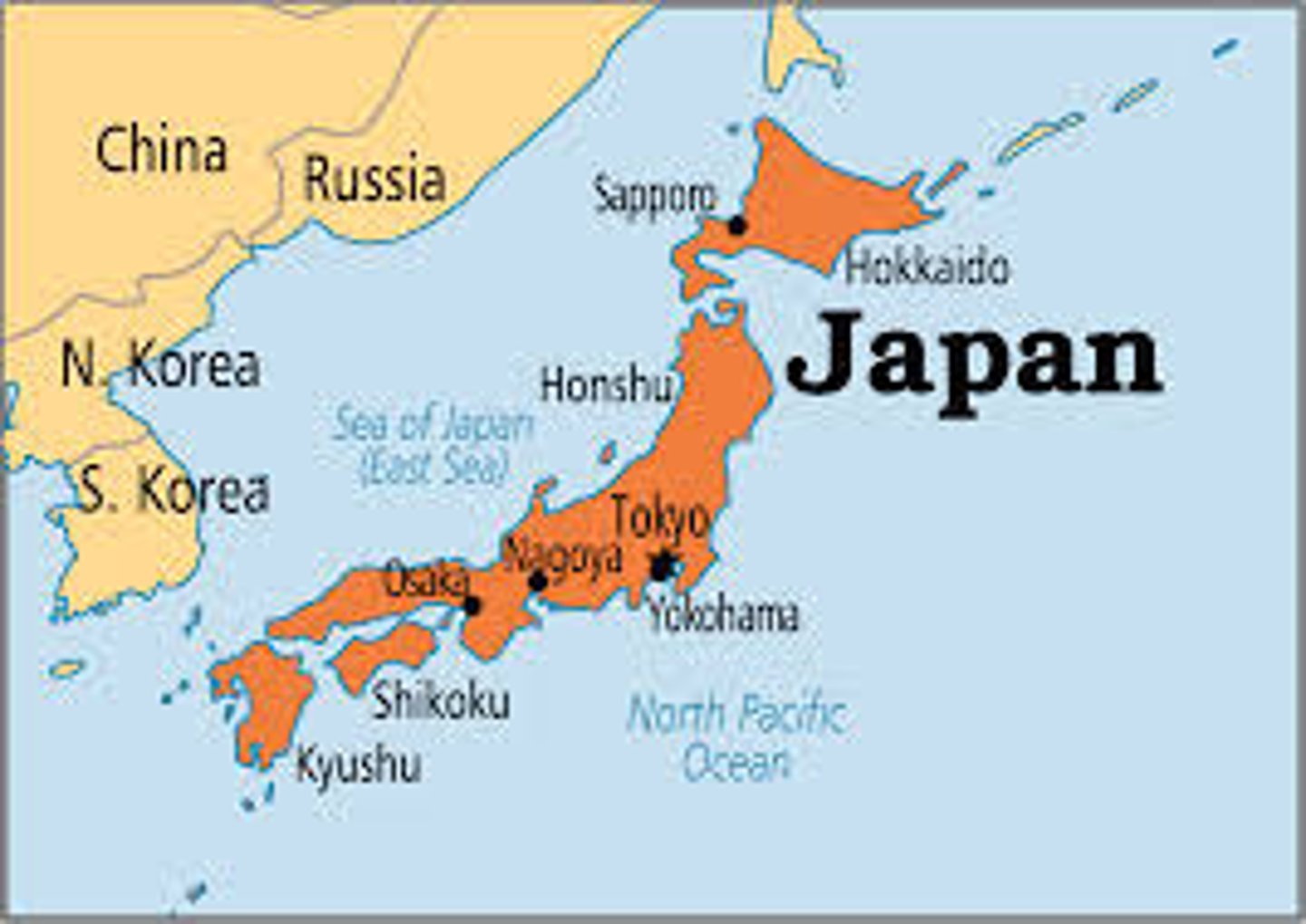
Nation-state example
Japan and Iceland
Stateless Nation Example
Kurds and Palestinians
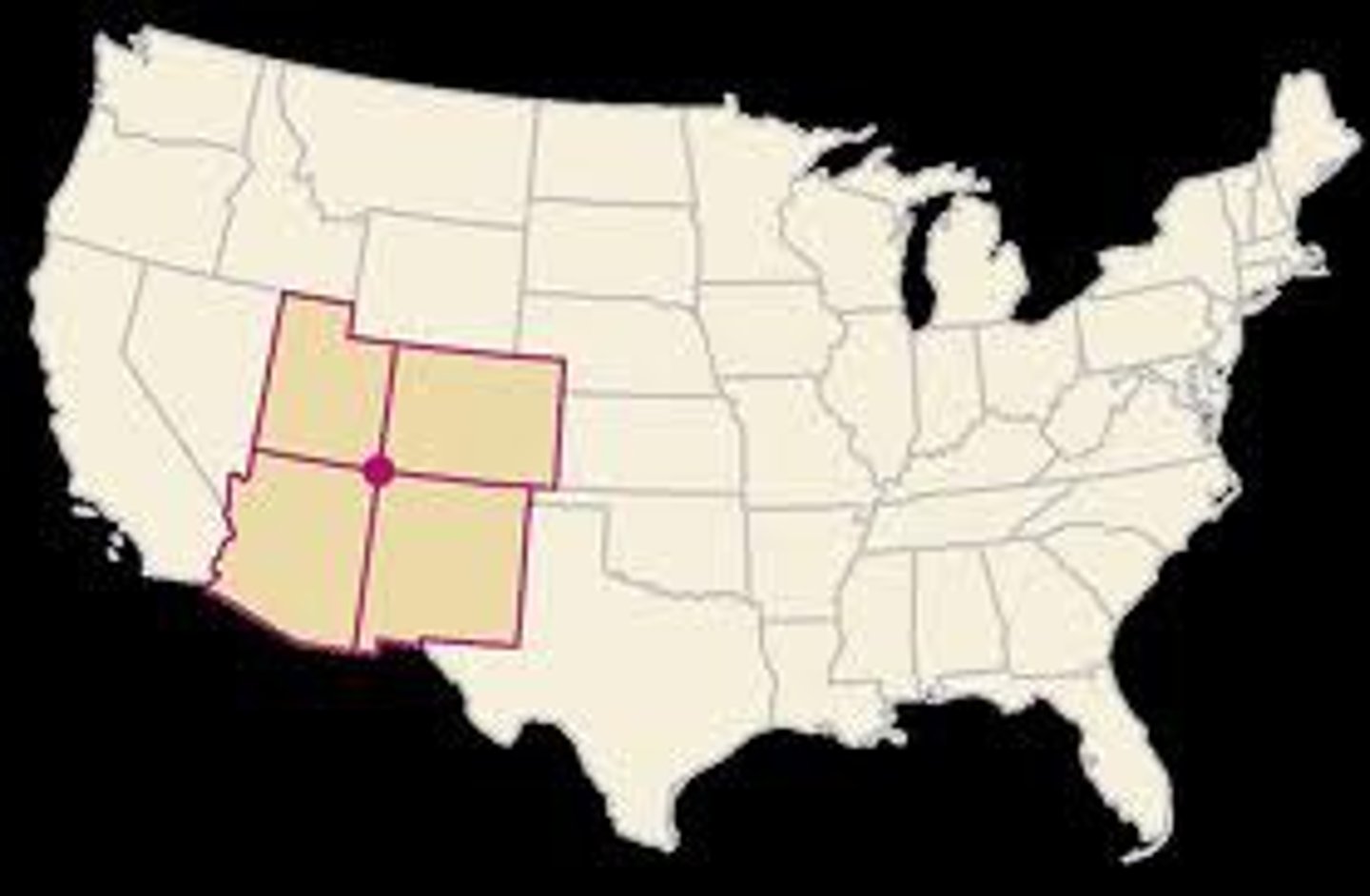
Multistate nation
a nation of people that transcends the borders of two or more states
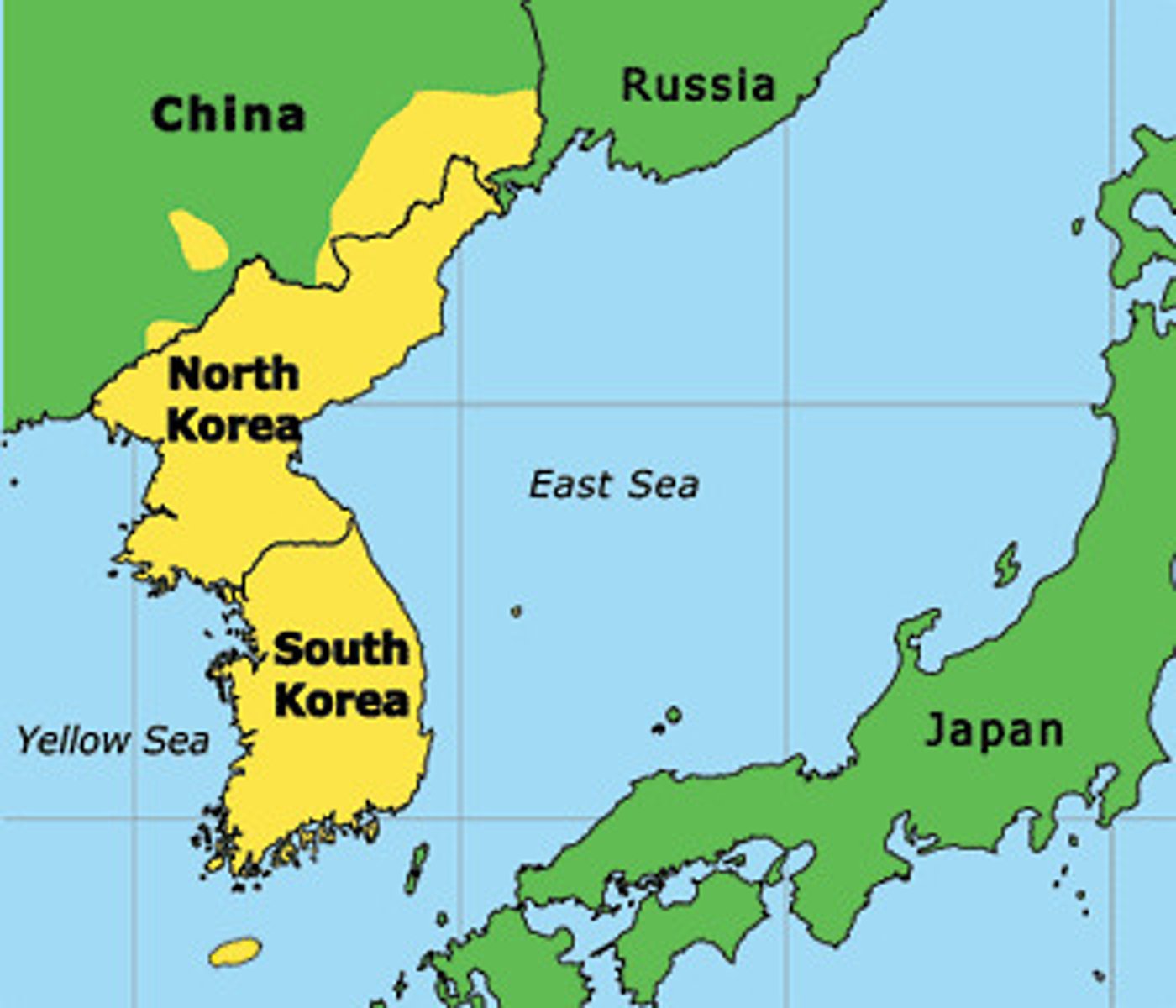
Multistate nation examples
Korean People (North and South Korea), German People (Germany, Austria, Switzerland)
Semiautonomous region
an area inside of a country that has some power to control itself more than other areas in the country
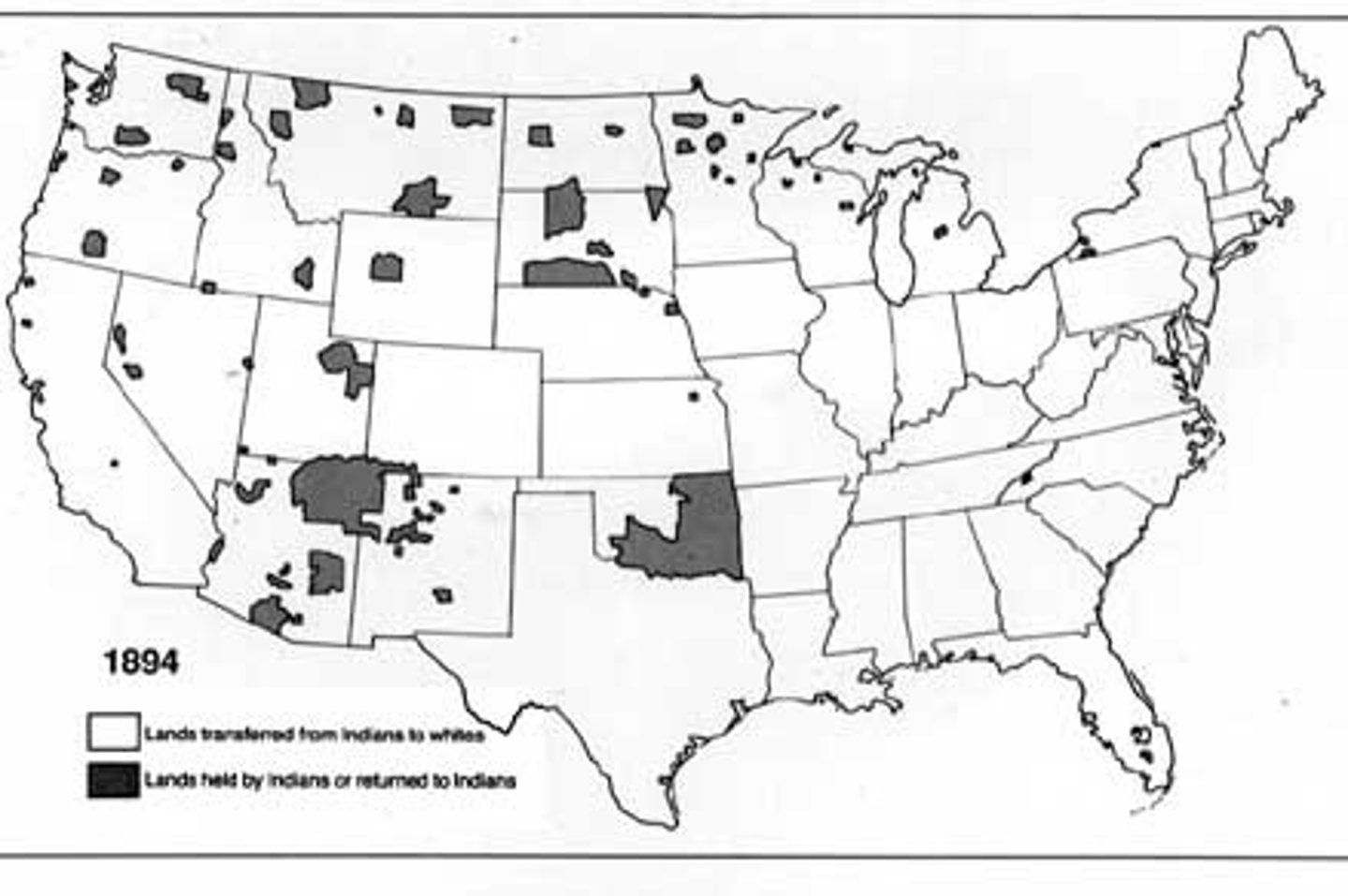
Semiautonomous region examples
Native American Reservations
Self-determination
the right of people to choose their own form of government
Colonialism
An attempt by one country to establish settlements and to impose its political, economic, and cultural principles in another territory.
Imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.

Independence Movements
a movement that is trying to gain political independence for some area that it thinks should be its own country
Sovereignty
Ability of a state to govern its territory free from control of its internal affairs by other states.
Devolution
The process whereby regions within a state demand and gain political strength and growing autonomy at the expense of the central government.
Neocolonialism
Also called economic imperialism, this is the domination of newly independent countries by foreign business interests that causes colonial-style economies to continue, which often caused monoculture (a country only producing one main export like sugar, oil, etc).

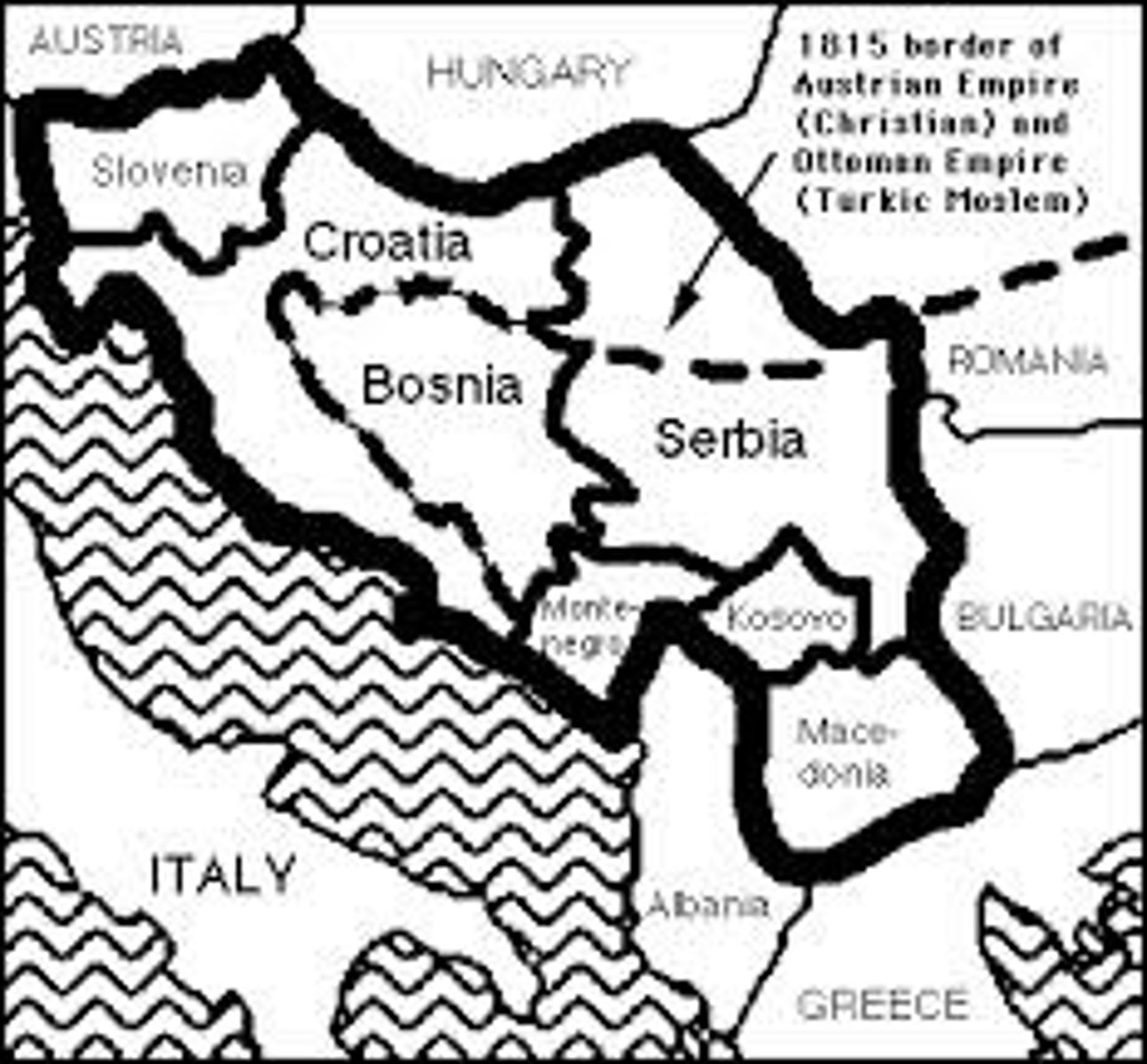
Shatterbelts are
politically fragmented areas often between two rival powers.
Choke Points
a strategic, narrow waterway between two larger bodies of water
Territorality
In political geography, a country's or more local community's sense of property and attachment toward its territory, as expressed by its determination to keep it inviolable and strongly defended.
relic boundary
a former boundary line that is still discernible and marked by some cultural landscape features

superimposed boundary
a boundary line placed over and ignoring an existing cultural pattern
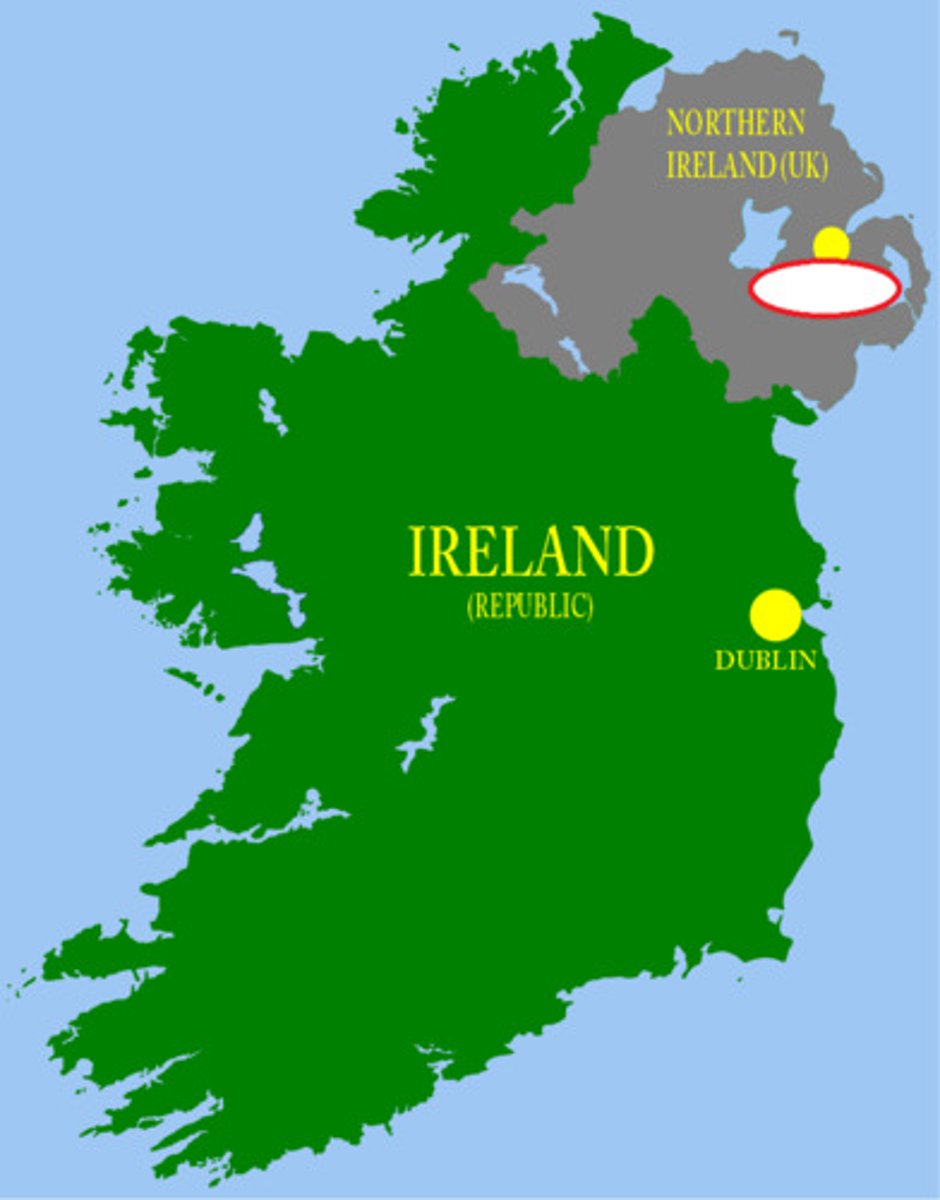
subsequent boundary
a boundary line that is established after the area in question has been settled and that considers the cultural characteristics of the bounded area
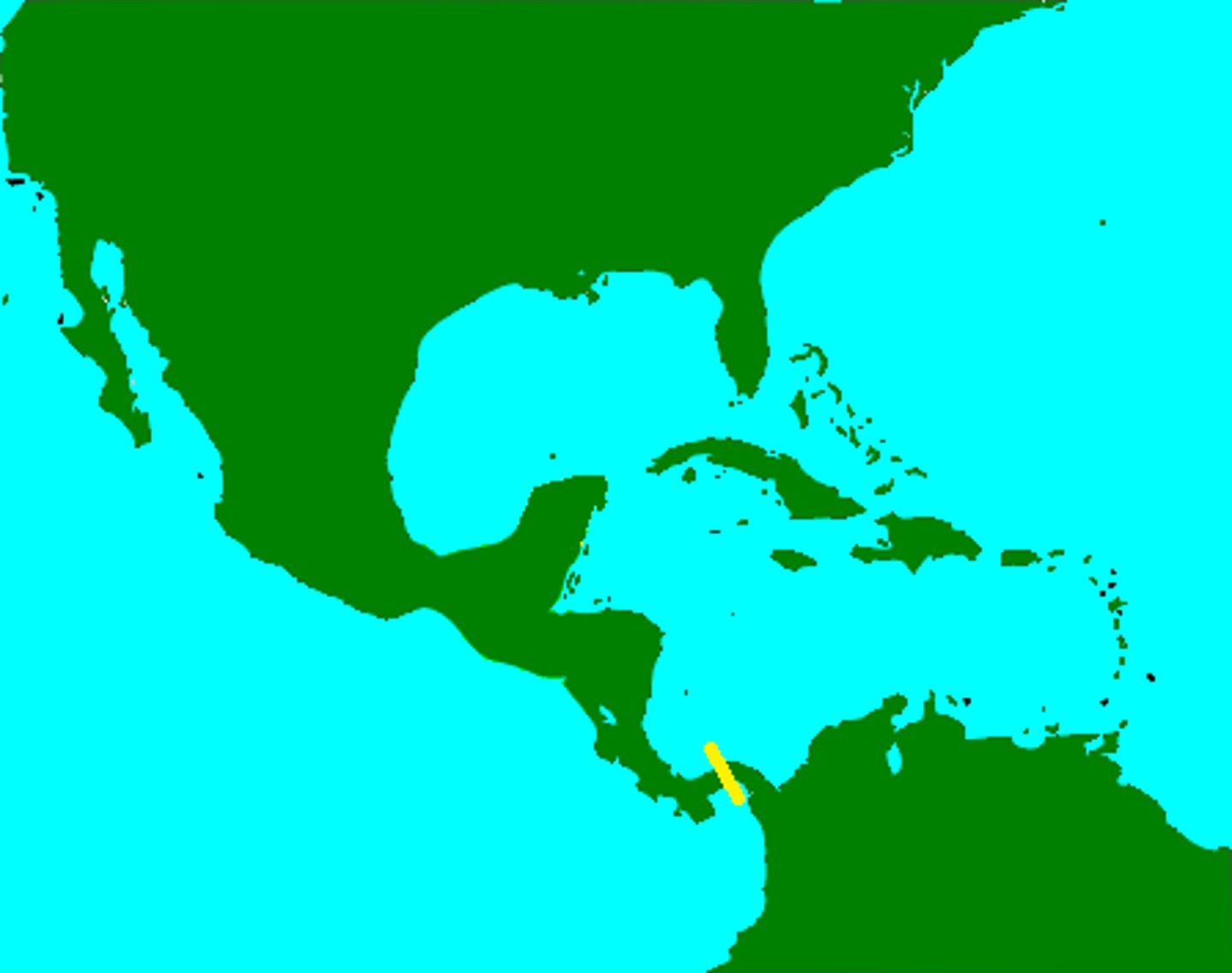
antecedent boundary
a boundary line established before the area in question is well populated
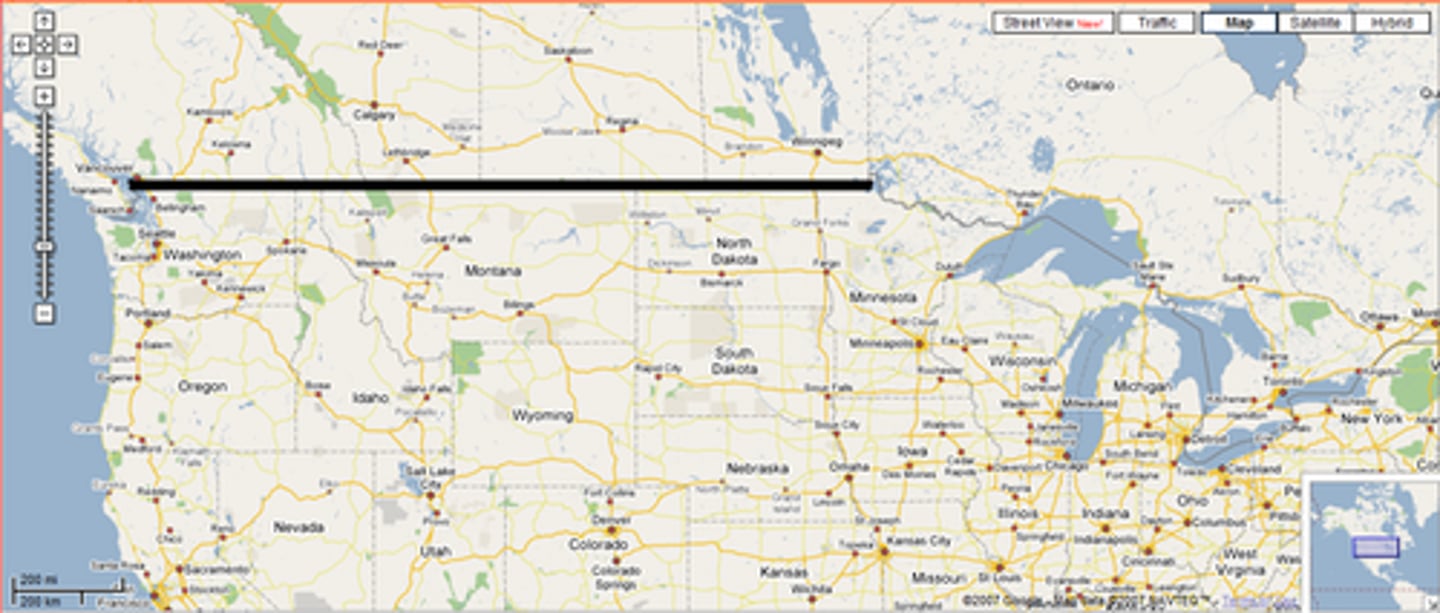
geometric boundary
Political boundaries that are defined and delimited by straight lines. (usually based on latitude or longitude)
consequent boundary
a boundary line that coincides with some cultural divide, such as religion or language
Defined Boundary
one established by a legal
document, such as a treaty.
Delimited Boundary
a line drawn on a map to show the limits of a space
Demarcated Boundary
A boundary demarcated (marked) by some visible means on the ground. Ex. wall posts, fences, etc.

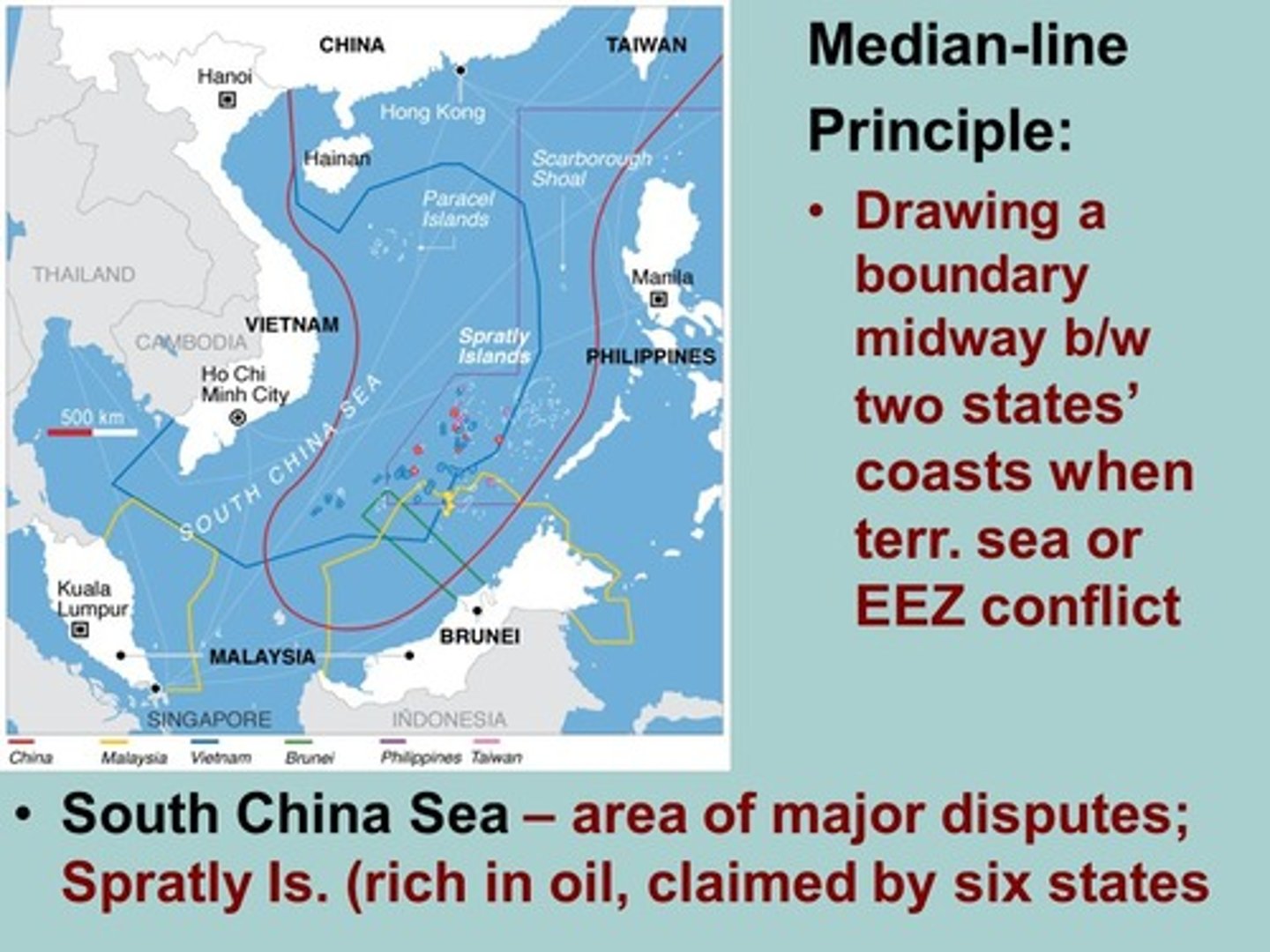
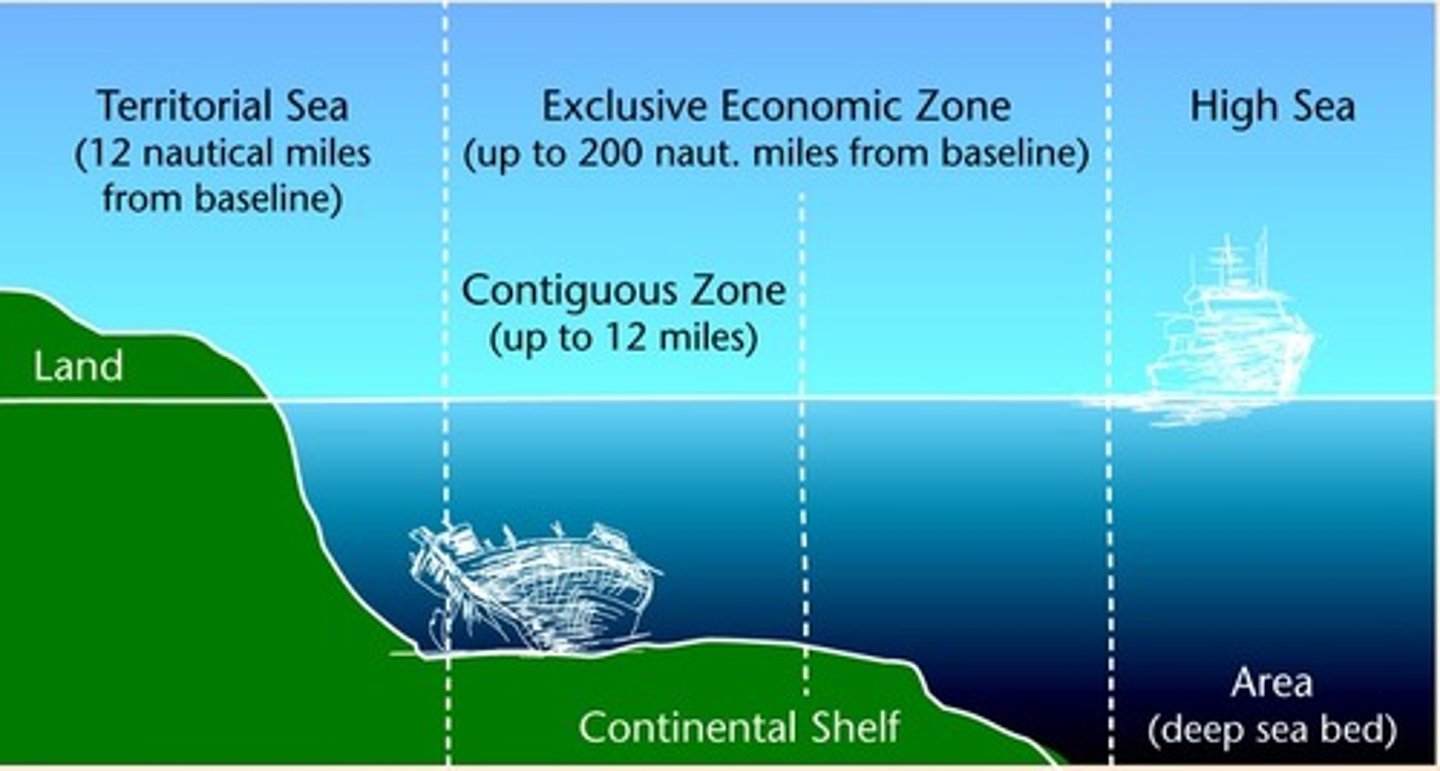
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
establishes how far into the ocean a state's influence extends.
12 Miles from shore - Territorial Sea (part of the country)
12-200 Miles from shore - Exclusive Economic Control (not part of the country, but only that country can fish or drill there)
200 miles from shore - High Sea (international waters)
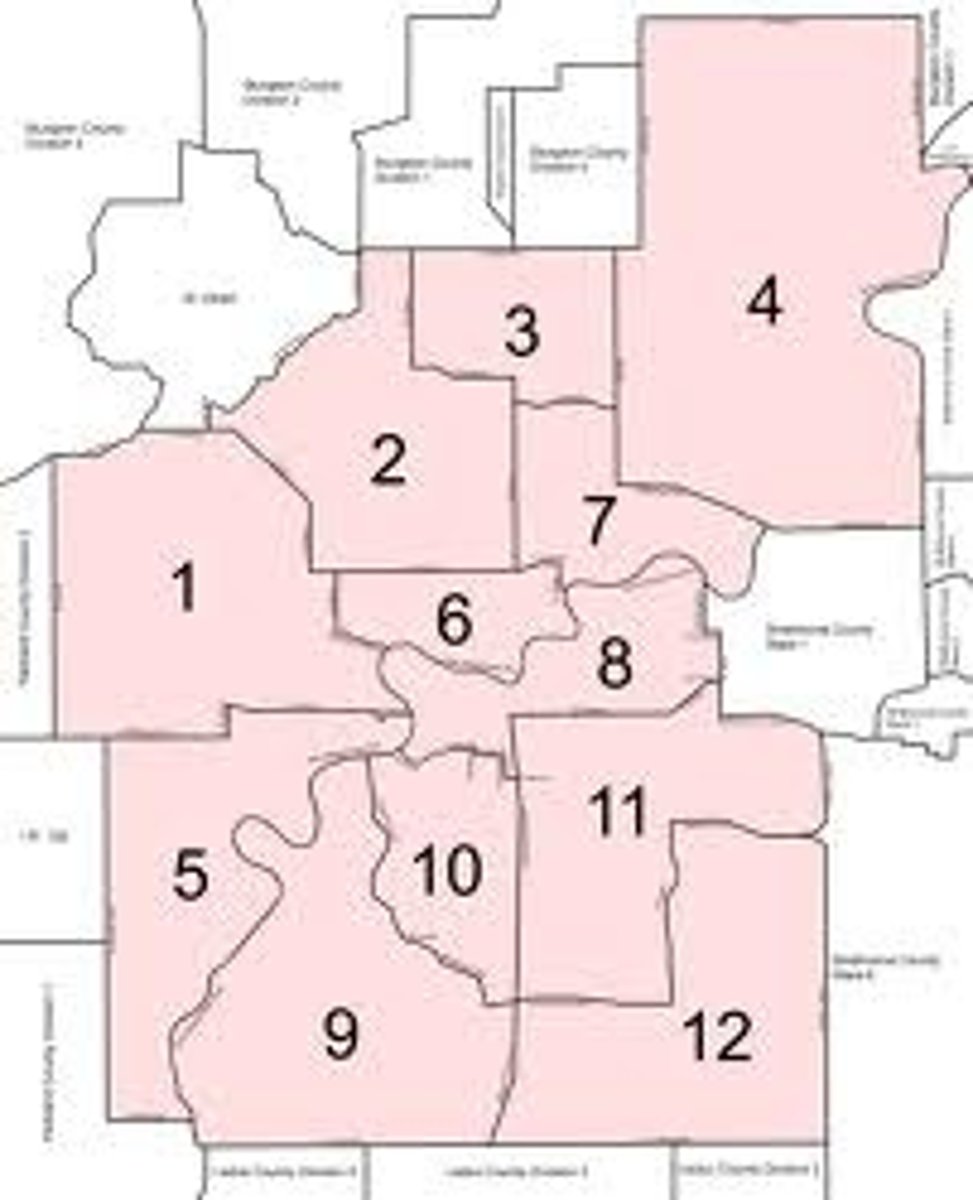
voting districts
House members represent a particular district of voters,
Gerrymandering
Process of redrawing legislative boundaries for the purpose of benefiting the party in power.
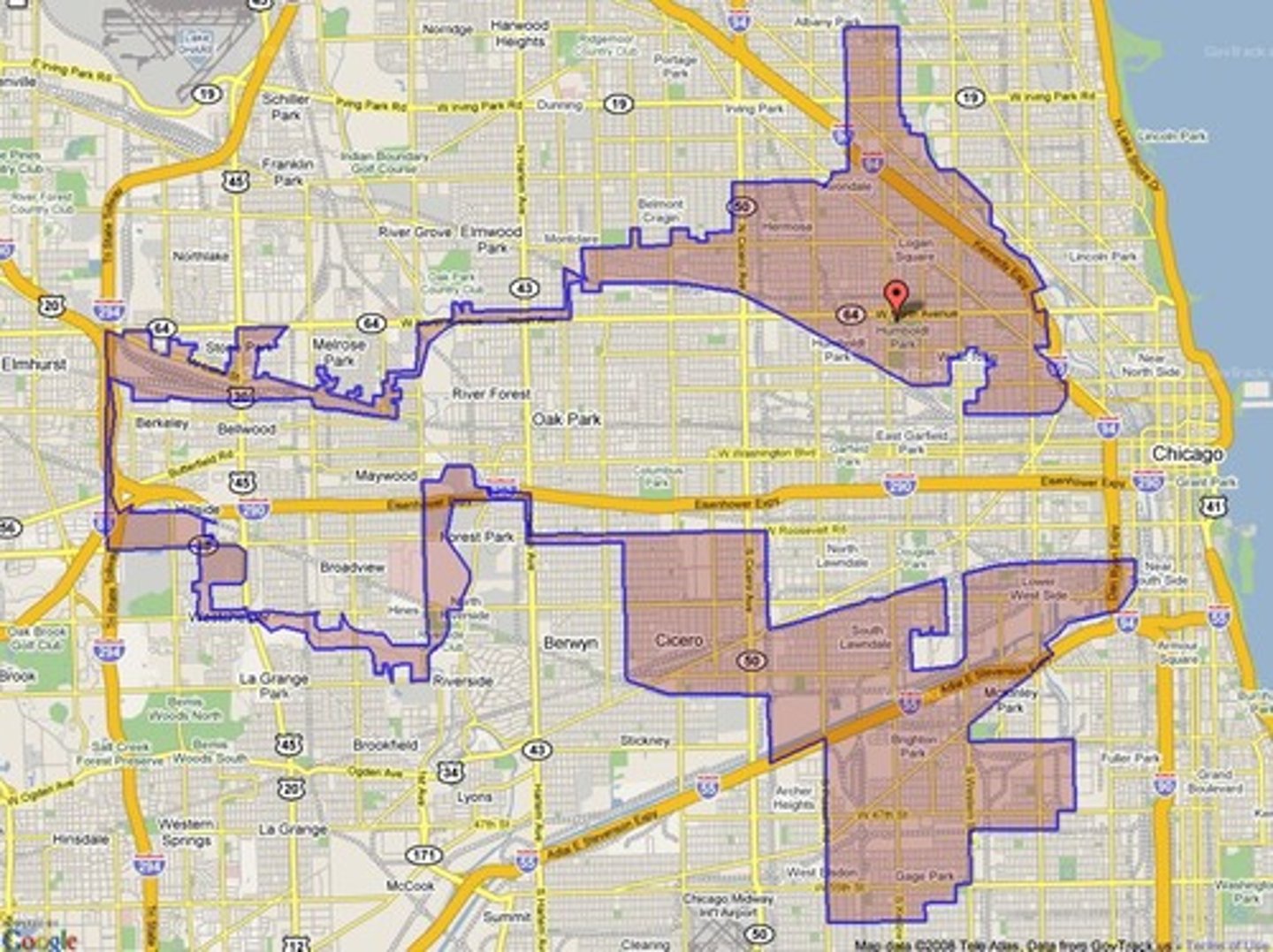
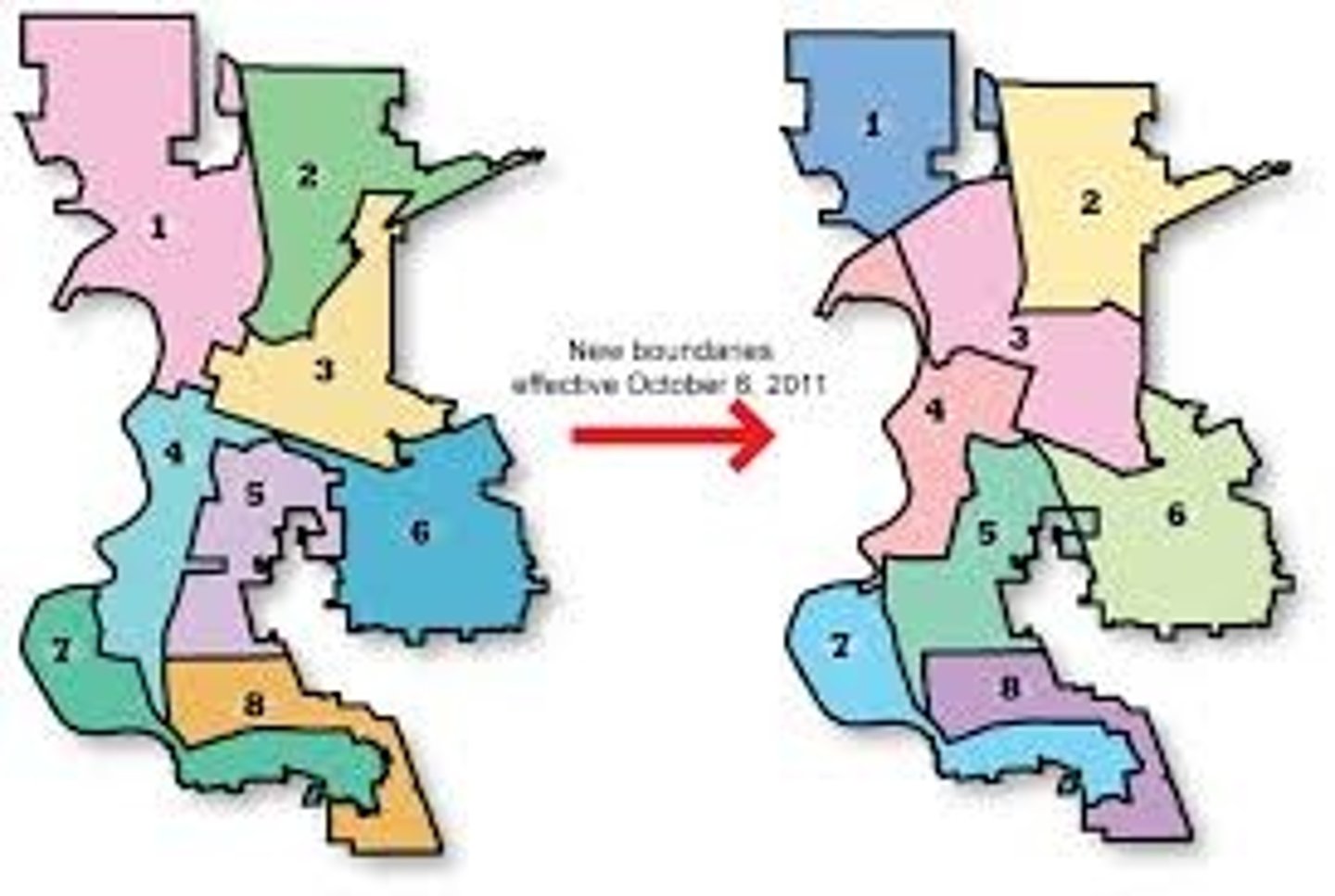
Redistricting
The redrawing of congressional and other legislative district lines following the census, to accommodate population shifts and keep districts as equal as possible in population. (Every 10 years)
Unitary State
places most power in the hands of central government officials.
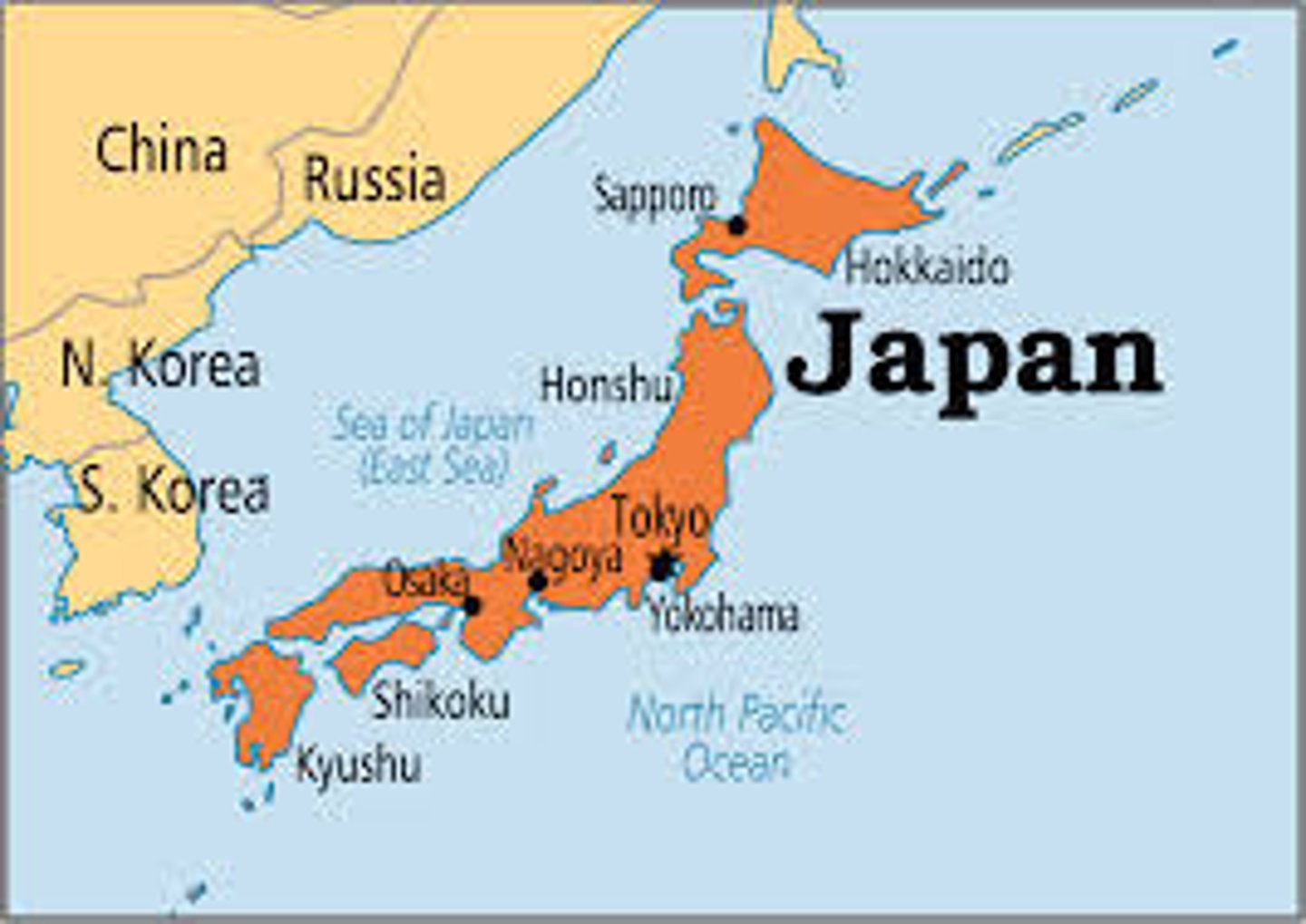
Federal State
An internal organization of a state that allocates powers to units of local government. (Example - America)

Advantages of Unitary Government
uniform policies, consistency, speed, efficiency
Advantages of Federalism
*Avoids concentration of power
*Keeps government close to people
*States serve as laboratories for new programs and training grounds for national leaders
*Allows adaption to regional differences
Causes of Devolution
ethnic separatism (religion, language, ethnicity), economic and social issues, irredentism, physical geography, centrifugal forces, terrorism, ethnic cleansing
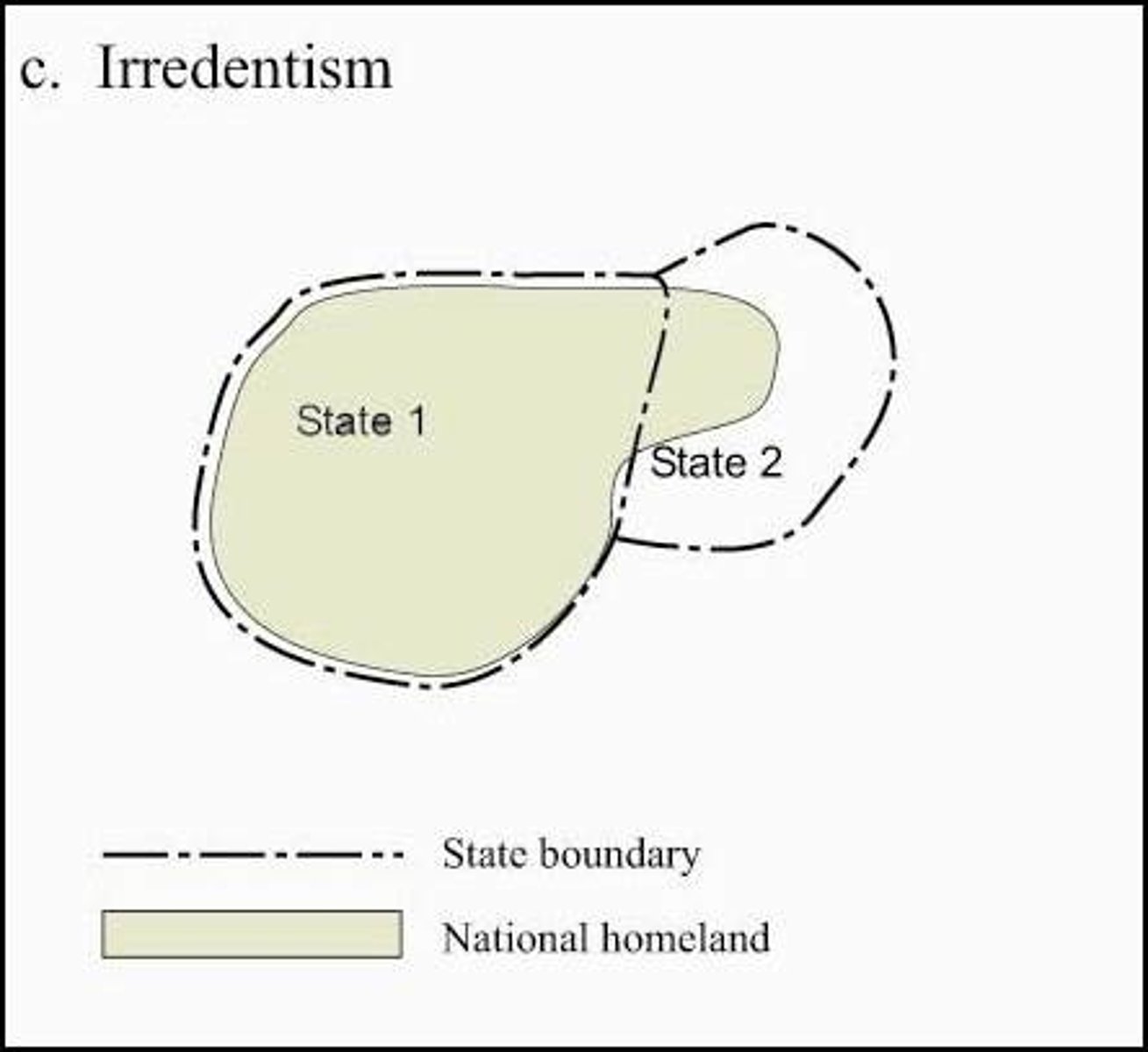
Irredentism
The policy of a state wishing to incorporate within itself territory inhabited by people who have ethnic or linguistic links with the country but that lies within a neighboring state. (This is why Russia invaded Ukraine)
Supranationalism
a venture involving 3 or more national states political economic or cultural cooperation to promote shared objectives. Examples: European Union, Nato, UN

Causes of Supranationalism
Global efforts to address transnational and environmental challenges and to create economies of scale, trade agreements, and military alliances help to further supranationalism.
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
a group of 28 countries that has agreed to protect each other in case of attack; founded in 1949. Led by the USA.
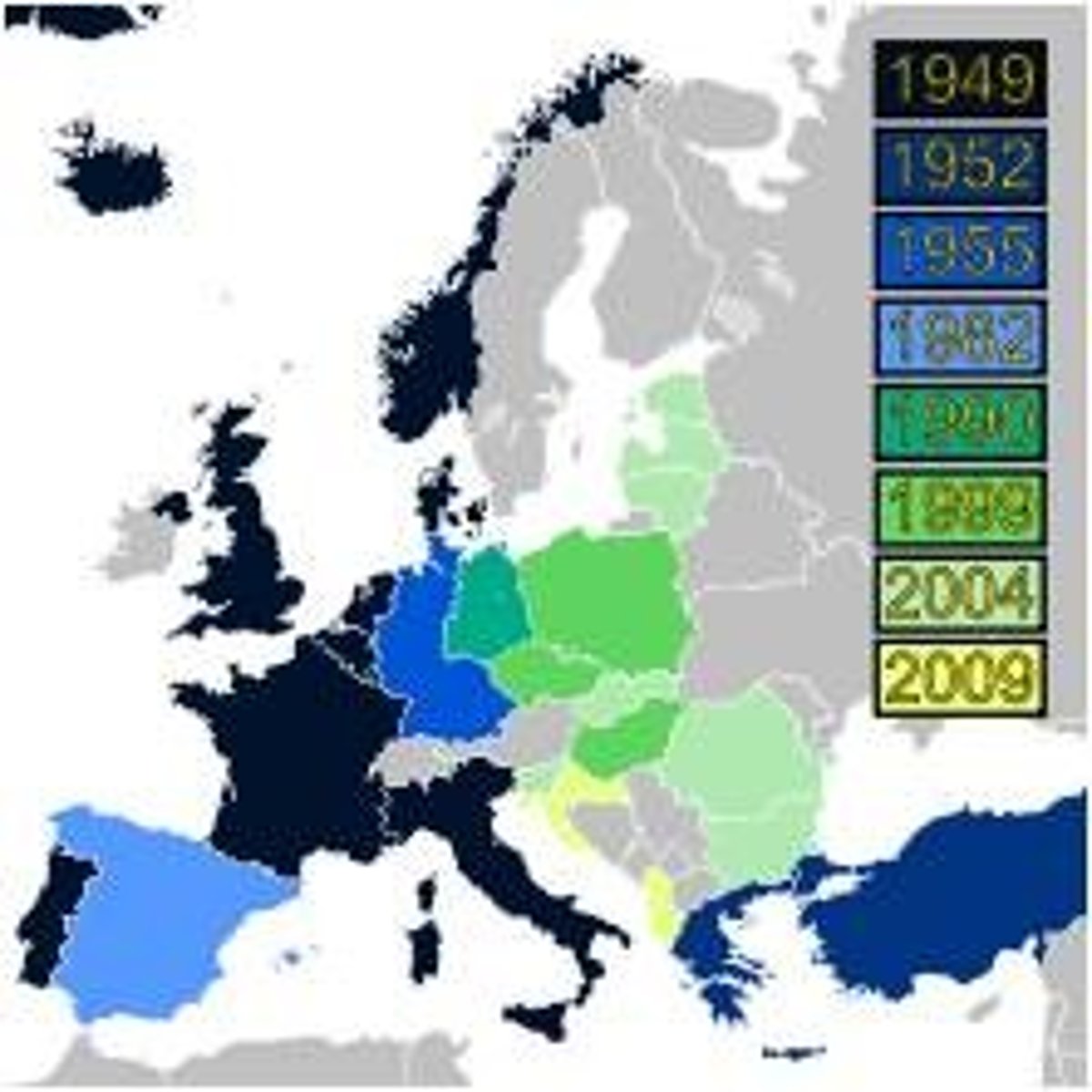
United Nations (UN)
an organization of independent states formed in 1945 to promote international peace and security

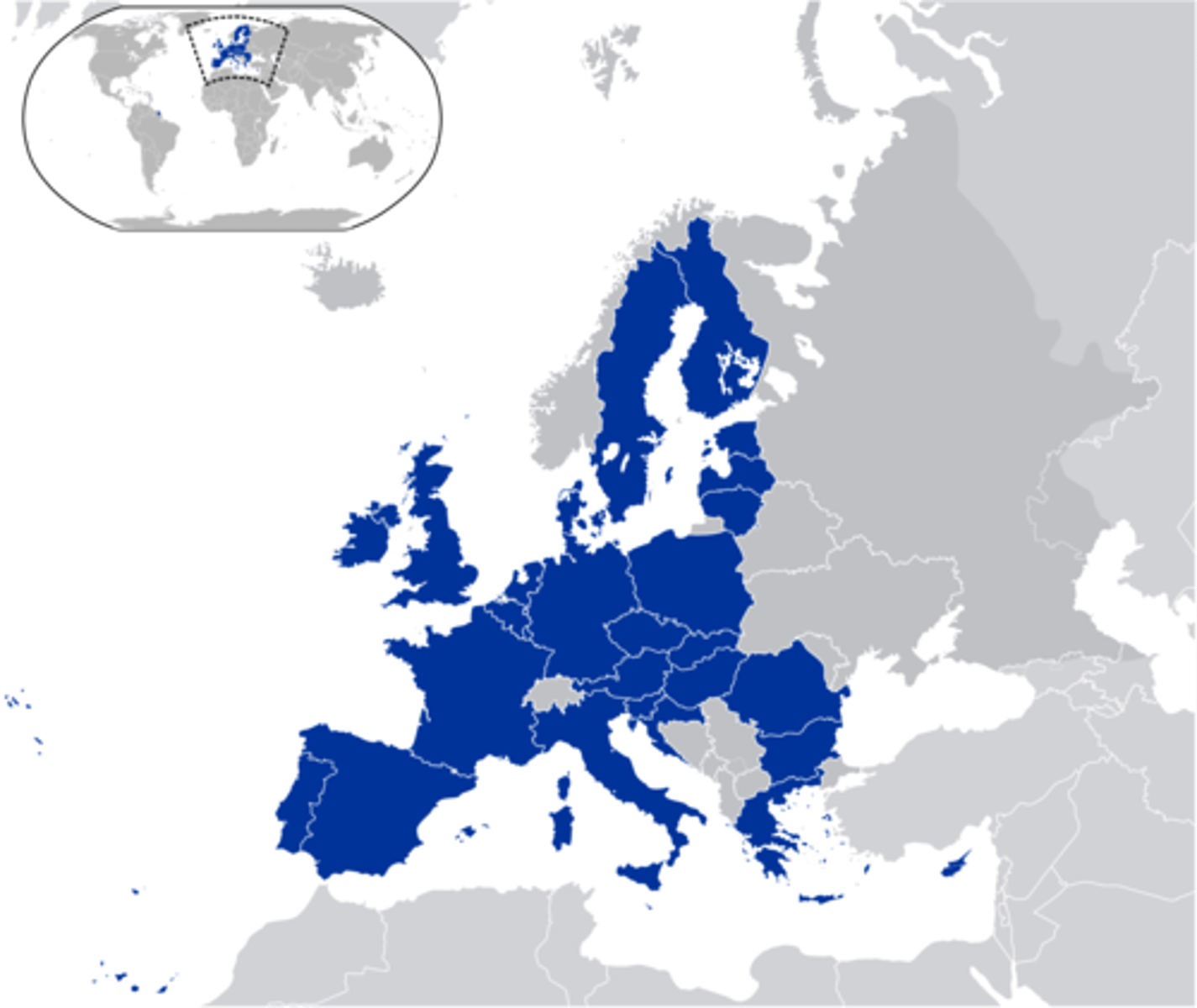
European Union (EU)
a free trade zone encompassing 27 European countries. Also allows for free movement of people. United Kingdom (UK) recently left the EU in what was called Brexit (British Exit)
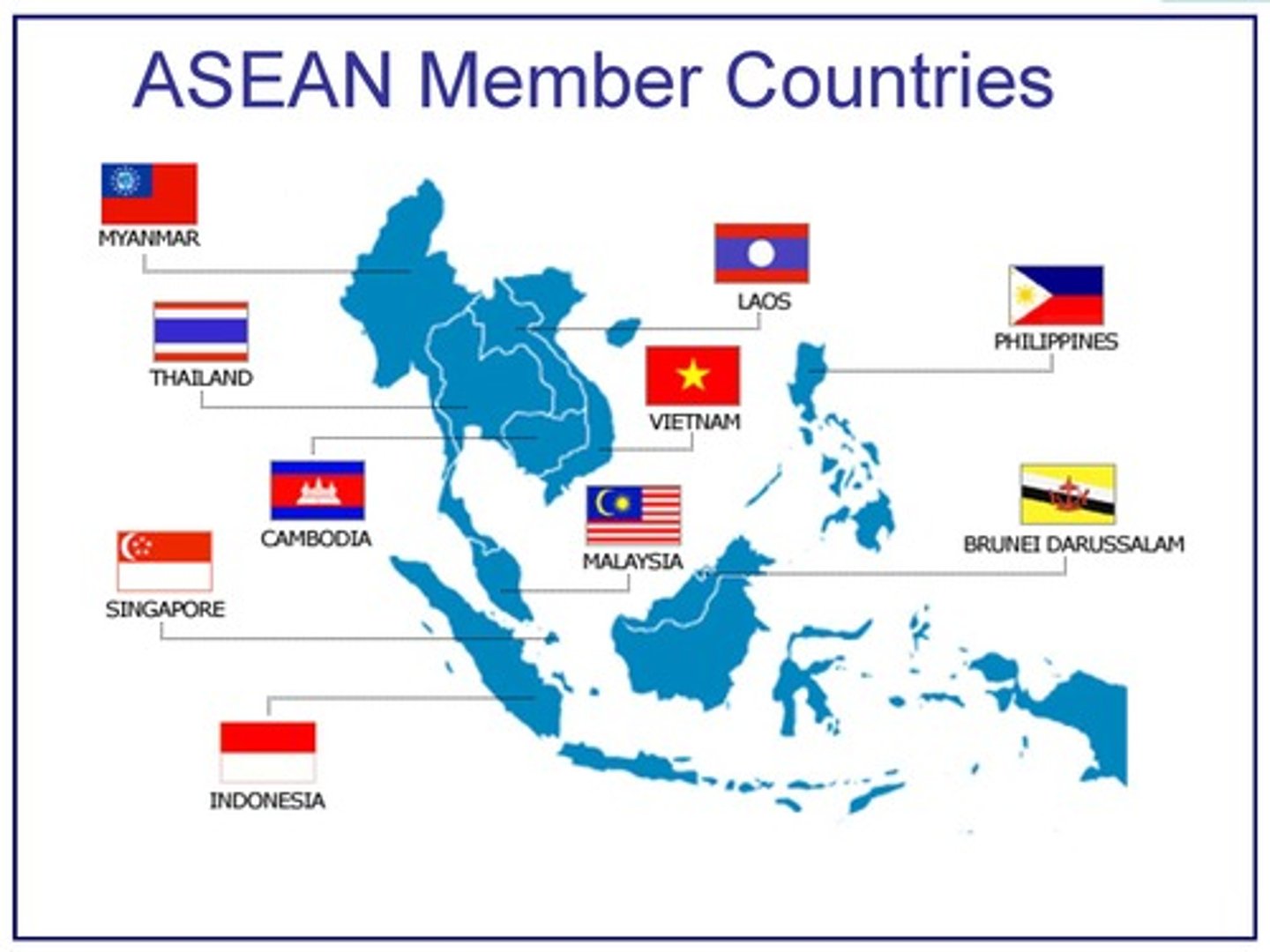
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
a trade alliance that promotes trade and economic integration among member nations in Southeast Asia
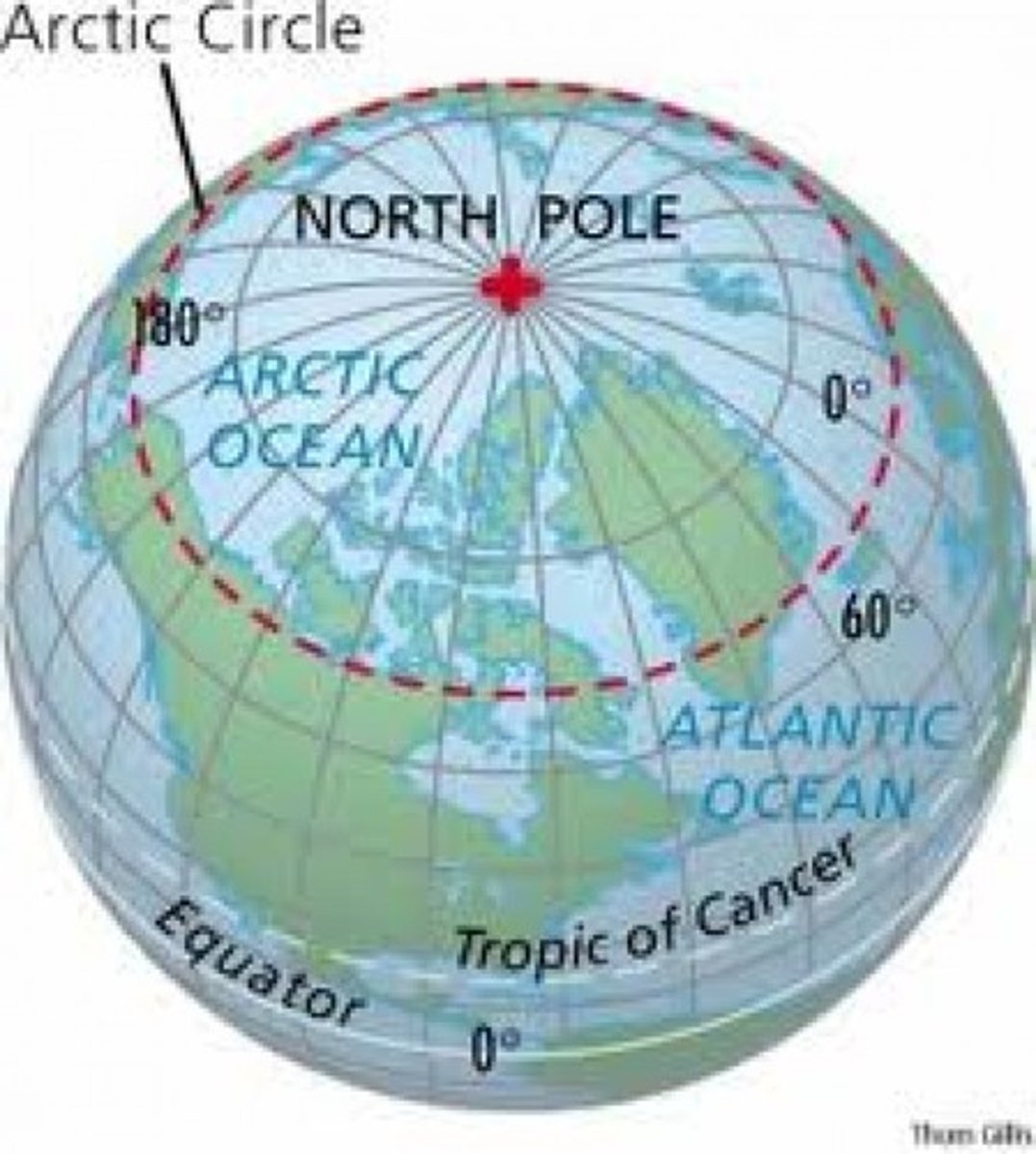
Arctic Council
: A multilateral organization composed of representatives
from the eight circumpolar states and six indigenous organizations.
African Union
organization formed in 2002 to promote unity among African states and to foster development and end poverty

Effects of Supranationalism
countries may have to cede some sovereignty to the organization.
Centripetal Forces
Forces that tend to unite or bind a country together. (common language, religion)

centrifugal force
a force that divides people and countries. (ethnic differences, economic inequality)
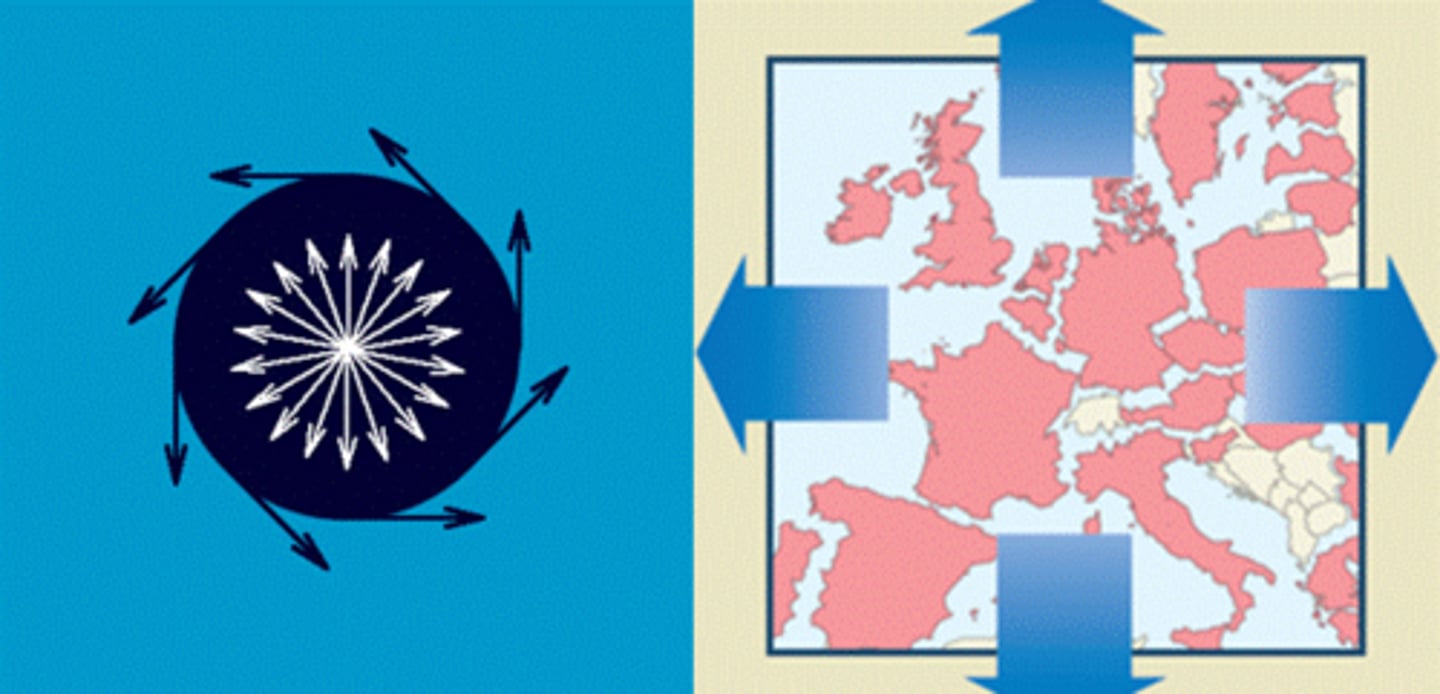
Territoriality
In political geography, a country's or more local community's sense of property and attachment toward its territory, as expressed by its determination to keep it inviolable and strongly defended.
Definitional boundary dispute
Conflict over the language of the border agreement in a treaty or boundary contract
Locational Boundary Dispute
Conflict over the location or place of a boundary
Operational Boundary Dispute
Conflict over the way a boundary should operate or function, such as the conflict over allowing migration across the border
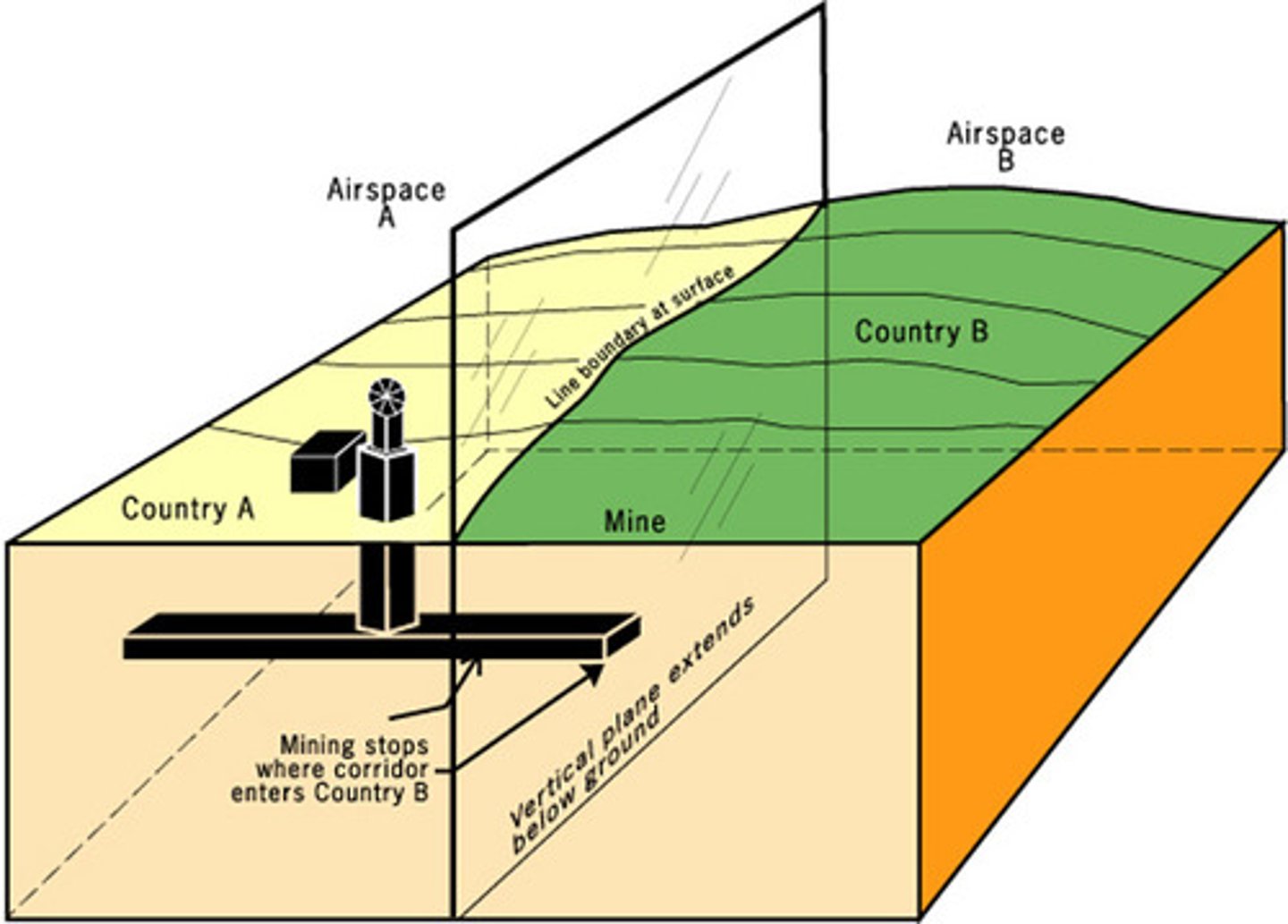
Allocational Boundary Dispute
A boundary dispute that involves conflicting claims to the natural resources of a border region.
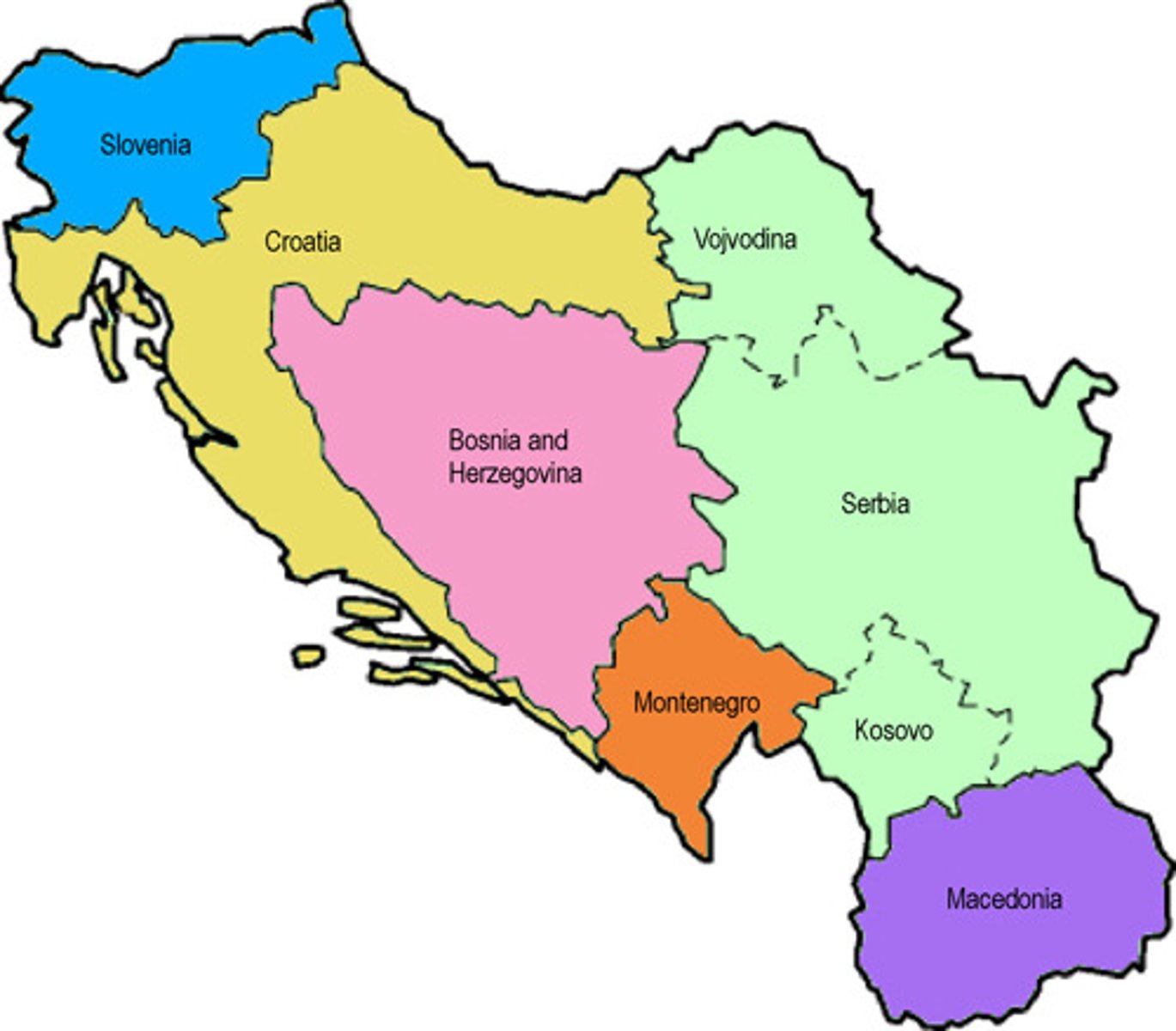
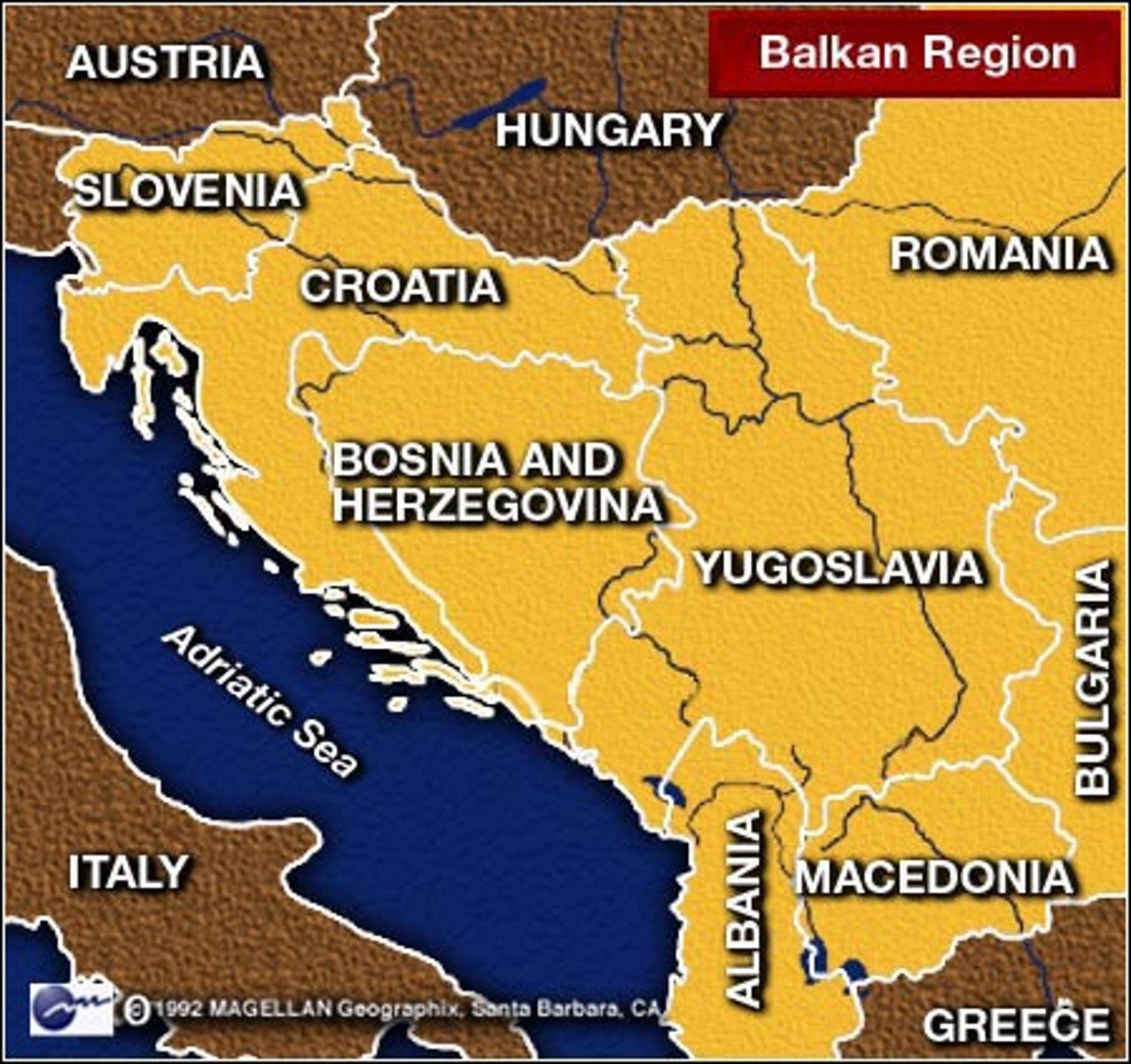
Balkanization
Process by which a state breaks down through conflicts among its ethnicities.
Examples: USSR and Yugoslavia
Median-line principle
lines made to distribute water ways when states are within 200 miles of each other