Final - Primary Dentition
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
5 weeks
development of primary teeth begins as early as ____ in utero
after birth
primary tooth enamel is completed:
mandibular
which teeth erupt first, maxillary or mandibular?
female
whose teeth tend to erupt first, male or females?
premolars
which type of tooth is missing in the primary dentition?
lingually
permanent anterior teeth develop ______ to the primary anterior teeth
underneath
permanent posterior teeth develop ______ to the primary posterior teeth
mandible
Leeway space is greater in which arch?
root trunk
The distance from the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) to the root groove and from the CEJ to the root division
5 months in utero
calcification time for maxillary primary 1st molar:
12-16 month
eruption time for maxillary primary 1st molar:
4
#of cusps for maxillary primary 1st molar:
3
# of roots for maxillary primary 1st molar:
mesiobuccal
for maxillary primary 1st molar, there is a large bulge of enamel in the cervical region of the ________ root
lingually
the maxillary primary 1st molar's crown converges ____
triangular
the maxillary primary 1st molar occlusally takes a _____ shape
4
# of pulp horns for the maxillary primary 1st molar:
ML
what cusp on the maxillary primary 1st molar is the longest?
MB
what cusp on the maxillary primary 1st molar is the biggest?
maxillary primary 1st molar
what primary posterior tooth has an oblique ridge?
3
# of pits on the maxillary primary 1st molar:
4
# of cusps for maxillary primary 2nd molar:
primary maxillary 2nd molar
which primary tooth most resembles the permanent maxillary 1st molar
6 months in utero
calcification time for maxillary primary 2nd molar:
2-2.5 years
eruption time for maxillary primary 2nd molar:
primary maxillary 2nd molar
what primary tooth has a Cusp of Carabelli?
5 months in utero
calcification time for mandibular primary 1st molar:
12-16 month
eruption time for mandibular primary 1st molar:
6 months in utero
calcification time for mandibular primary 2nd molar:
2-2.5 years
eruption time for mandibular primary 2nd molar:
permanent
Congenitally missing teeth are much more common in the ______ teeth
mandibular 2nd premolars
what is the 1st most common congenitally missing primary tooth?
maxillary lateral incisors
what is the 2nd most common congenitally missing primary tooth?
maxillary 2nd premolars
what is the 3rd most common congenitally missing primary tooth?
primary
which teeth are whiter (less calcified), permanent of primary teeth?
primary mandibular central incisors
primary maxillary 2nd molars
which primary teeth contact only one tooth in the opposing arch?
wider
Mandibular Primary Molars are _____ mesiodistally than the Maxillary
occlusally
in primary teeth, enamel rods slope _____ from the DEJ
cervically
in permanent teeth, enamel rods slope _____ from the DEJ
primary mandibular 2nd molar
what is the most frequently retained deciduous tooth?
20
how many deciduous teeth are there?
A-J
the maxillary deciduous teeth are lettered ___ - __
K-T
the mandibular deciduous teeth are lettered ___ - __
E & F
what two teeth lie in the midsagittal plane in the deciduous maxilla?
O&P
what two teeth lie in the midsagittal plane in the deciduous mandible?
mandibular
which teeth erupt first, maxillary or mandibular?
mandibular central incisor
what is the first primary tooth to erupt?
central incisor
lateral incisor
1st molar
canine
2nd molar
looking at just one 1/2 arch of the mandible, what is the order that the primary teeth erupt?
1.5 years
about how long does it take the roots formations of primary teeth to complete?
overbite
Increased vertical overlap of the maxillary incisors
overjet
Horizontal projection of upper teeth over the lower.
mesial
in the primary dentition, the primate space is ______ to the maxillary canine
distal
in the primary dentition, the primate space is ______ to the mandibular canine
Leeway space
Primary teeth are wider mesio-distally than the permanent teeth that replace them:
mesio-distally
Primary teeth are wider ____________ than the permanent teeth that replace them
tooth fusion
a rare developmental disorder characterized by the union of two adjacent teeth at the crown level (enamel and dentin), causing the formation of a tooth with an enlarged clinical crown:
tooth fusion
ID the tooth anomaly:
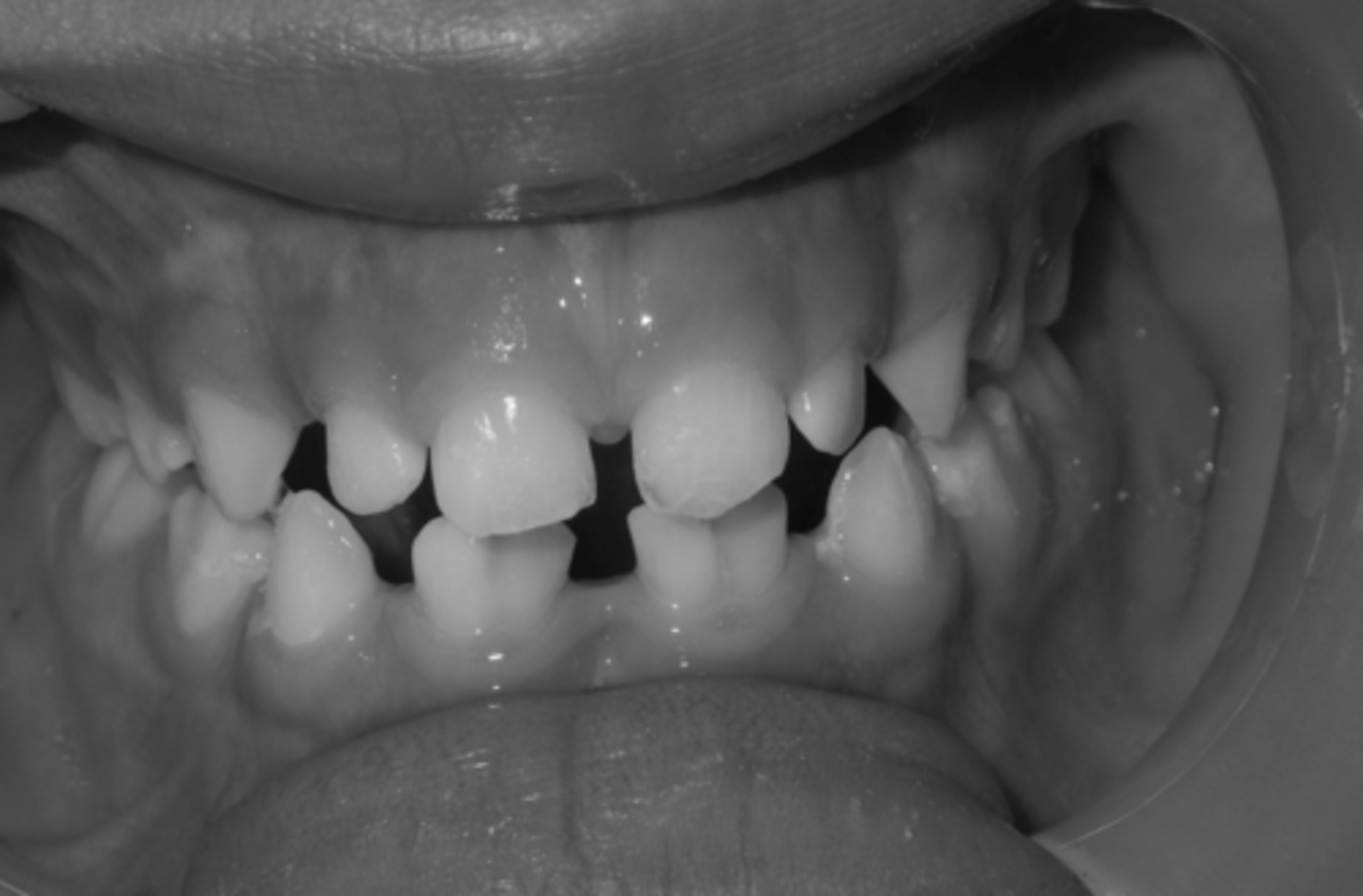
germination
occurs when a single bud splits and forms two teeth.
larger
in primary teeth, pulp chambers are ______ than those in permanent teeth
higher
in primary teeth, pulp horns are ______ than those in permanent teeth
mesio-distally
on the primary anterior teeth, the teeth are wider _______
more
the roots of the primary molar are slender and ______ flared than the premolars that replace them
false
t/f: primary teeth can have mamelons
3-4 months in utero
calcification for primary maxillary central incisor
4 months
crown completion for primary maxillary central incisor
7.5 months
eruption time for primary maxillary central incisor
2-3
# pulp horns for primary maxillary central incisor
mesial
on primary maxillary central incisor, there is usually a developmental groove on the _____ side of the root
2
# of pulp horns for primary maxillary lateral incisor
4-5 months in utero#
calcification for primary maxillary lateral incisor:
5 months
crown completion time for primary maxillary lateral incisor:
8-9 months
eruption time for primary maxillary lateral incisor:
primary maxillary canine
of the primary anterior teeth, what is the longest AND widest tooth?
rhomboid
from a facial aspect, the maxillary canine takes a ____ shape
triangular
the maxillary canine's root at a cross section takes a _____ shape
16-20 months
eruption time for primary maxillary canine:
9 months
crown completion for primary maxillary canine:
5 month in utero
calcification for primary maxillary canine:
0
# of pulp horns for primary maxillary canine:
at the same level
for primary maxillary canine, the mesial and distal height of contour are:
mesial
for primary maxillary canine, which incisal slope is longer, mesial or distal?
maxillary canine
what primary tooth has a root that is more than twice the length of its crown?
maxillary canine
what primary tooth has both on the lingual surface a mesial and distal fossa?
4-5 months in utero
calcification time for primary mandibular central incisor:
6.5 months
eruption time for primary mandibular central incisor:
2
# of pulp horns for primary mandibular central incisor:
4-5 months in utero
calcification time for primary mandibular lateral incisor:
7 months
eruption time for primary mandibular lateral incisor:
primary mandibular lateral incisor
that primary tooth labially, the crown is fan-shaped with a longer mesial side than the distal.
5 months in utero
calcification for primary mandibular canine:
16-20 months
eruption time for primary mandibular canine:
0
# of pulp horns for primary mandibular canine:
distal
which incisal cusp ridge slope is longer on the primary mandibular canine, mesial or distal?
2nd trimester
when do primary teeth show evidence of calcification in utero ?
at birth
when do 6-year molars show first evidence of calcification?
1/2
a tooth will erupt when its root is about _____ formed
1.5
The roots of primary teeth will complete about ___ years after eruption
2.5
the roots of the permanent teeth will complete about ___ years after eruption
centered
primary Maxillary incisors have incisal edges that are _____ over the long axis of the tooth
lingual
Mandibular incisors have incisal edges that are ______ to the long axis of the tooth