Case study: Treatment of upper GI disease
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is Dyspepsia=
pain or discomfort in upper abdomen
hard or difficult digestion
Causes of dyspepsia
- stress
-alcohol
- smoking
- H pylori
- medicines
- spicy foods
2 presentations of dyspepsia
acute
chronic
Pain right-
duodenal ulcer
When to investigate dyspepsia (endoscope)?
if ‘alarm’ symptoms are present:
Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
Haematemesis (vomiting blood)
In patients aged 55+ with weight loss plus:
Upper abdominal pain
Reflux
Dyspepsia

What is a Barium swallow?
eat barium meal then x-ray, as barium is radium opaque so coats oesophagus for you to see shape
How to treat investigated dyspepsia?
treat underlying pathology but sometimes nothing found
If nothing found during investigation?
what is this called and what do we do?
Called functional, idiopathic dyspepsia
treat and test for H pylori
What if the H. pylori test is negative?
Offer low dose PPI or H2RA for 4 weeks.
h2ra ( histamine receptor antagonists).
If symptoms of investigated dyspepsia recur?
restart PPI or H2RA at lowest dose
People using PPIs or H2RAs should be offered an annual review
Examples of PPIs
esomeprazole, lansoprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole
Histamine receptor antagonists exmaples?
famotidine
histamine
ranitidine
cimetidine
What should you avoid doing with antacids?
long-term frequent use
Which is better PPIs or H2RAs?
PPI
How to test for H pylori?
test for antigens in blood- not accurate or pt accepted,
test for antigens in stool- not pt accepted,
Urea breath test least invasive
Treatment for uninvestigated dyspepsia
Give lifestyle advice (diet, smoking, alcohol, stress)
Review any current medications
Offer H. pylori test and treat, ensuring proper washout period
If H. pylori negative, give full-dose PPI for 4 weeks
If symptoms return, consider long-term acid suppression with PPI
If inadequate response to PPI, try H2RA (Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonist)
Dyspepsia
too much acid in stomach
Role of antacids/anglinates
quicker response than PPIs, but the effect doesn’t last long
They work by neutralising excess stomach acid
Oral first line therapy to eradicate h pylori for pt with no penicillin allergy
PPI + amoxicillin + clarithromycin/metronidazole (dependant on previous treatment) 7 days high dose

PPIs are used to treat
dyspepsia
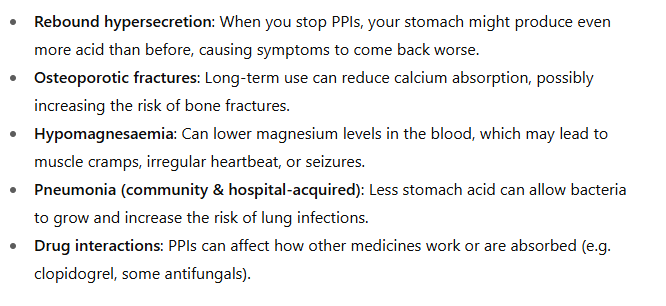
Safety of long-term PPI use
- rebound hypersecretion
- osteroporotic fractures
- hypomagnesaemia
- pneumonia
What is GORD?
retrograde passage of gastric contents from the stomach into the oesophagus
Symptoms of GORD
> heartburn
> pyrosis
> regurgitation of gastric contents into the throat
> early satiety
> belching
> hiccups
> nausea and vomiting
Therapeutic goals for treatment of GORD
> relieve symptoms
> promote oesophageal healing
> avoid long term complications
Barret's oesophagus=
pre-malignant complication of GORD in response to chronic acid exposure
What does barret's oesophagus look like?
dark red patches of tissue in lining- normal is pink
What can Barret's oesophagus develop into?
lower oesophageal cancer
Cause of GORD
abnormal relaxation of the lower oesophageal sphincter in combination with increased in stomach acid
Lifestyle modifications for pt with GORD
> avoid medication that relaxes the LOS
> avoid foods that relax the LOS
> lose weight
> avoid tight clothing
> stop smoking
> raise head of bed by 6-8 inches
> avoid eating within 3 hours of bedtime
Management of proven GORD:
- lifestyle advice
- full dose PPI for 4-8 weeks (depending on severity)
- in severe disease, consider full dose PPI long-term as maintenance-> step down where possible

Treatment for GORD if symptoms reoccur after initial treatment
offer PPI at lowest possible dose to control symptoms- even prn
Treatment in refractory cases of GORD
double dose PPI OR the addition of H2RA (taken at night) with a PPI can be tried on a short-term basis