6. Primary Production and Eutrophication
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Definition and sources Process of eutrophication Eutrophication in Freshwater Ecosystems Eutrophication in Marine Ecosystems Ecosystem effects of eutrophication
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
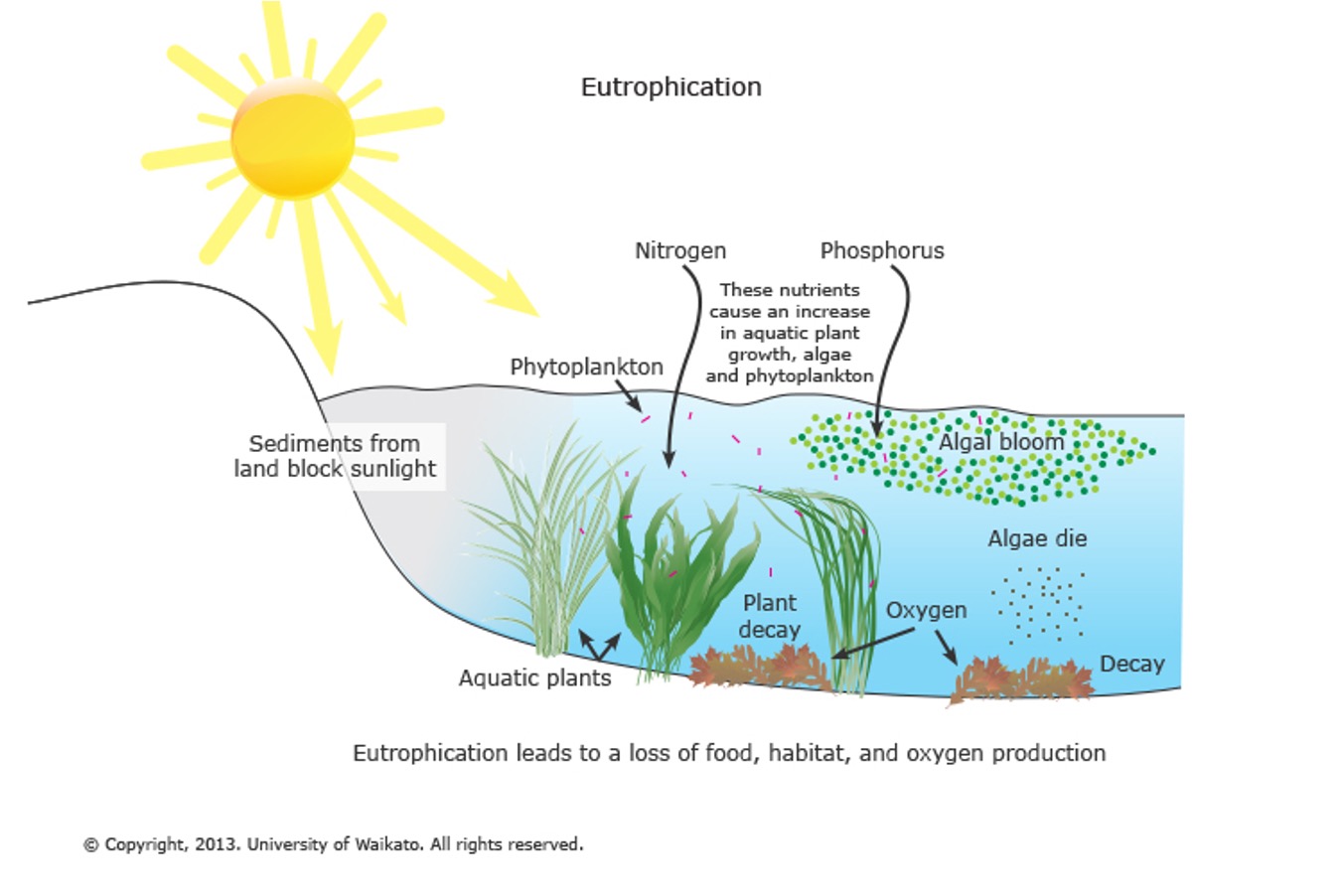
Eutrophication
«The increase of nutrients in an aquatic ecosystem that stimulates the growth of aquatic plants and algae»
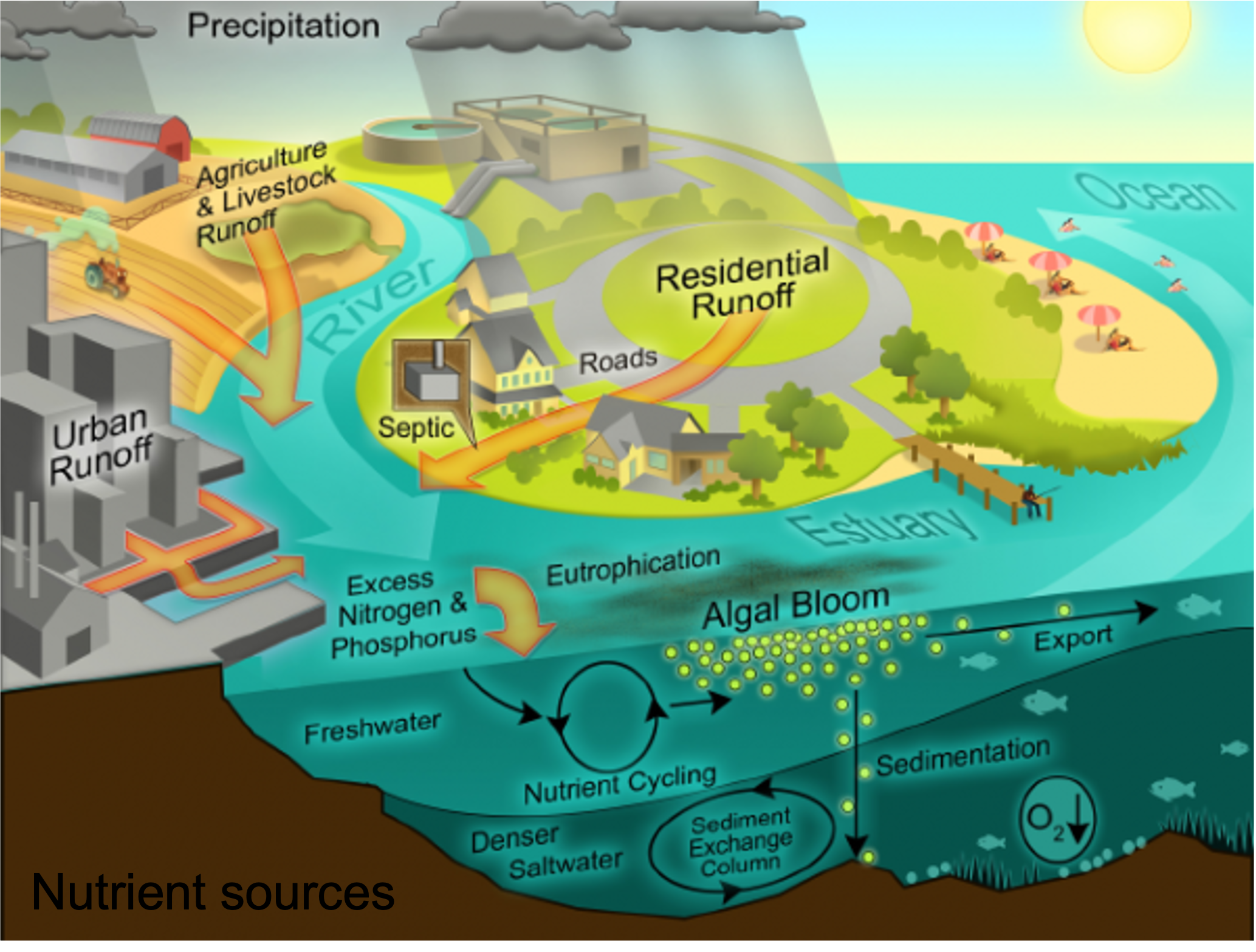
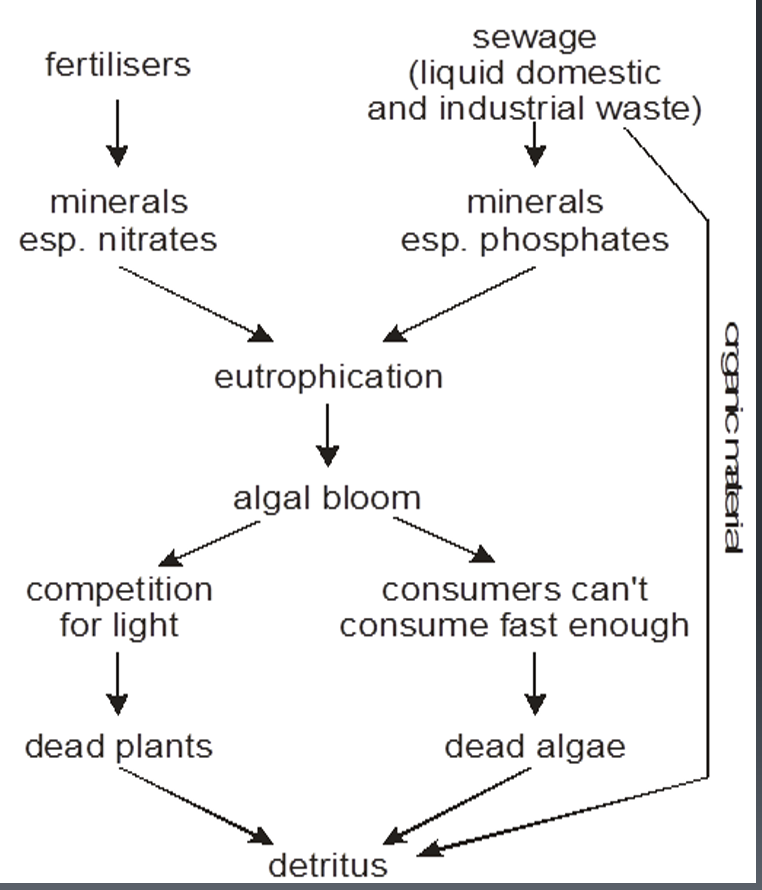
Process of Eutrophication
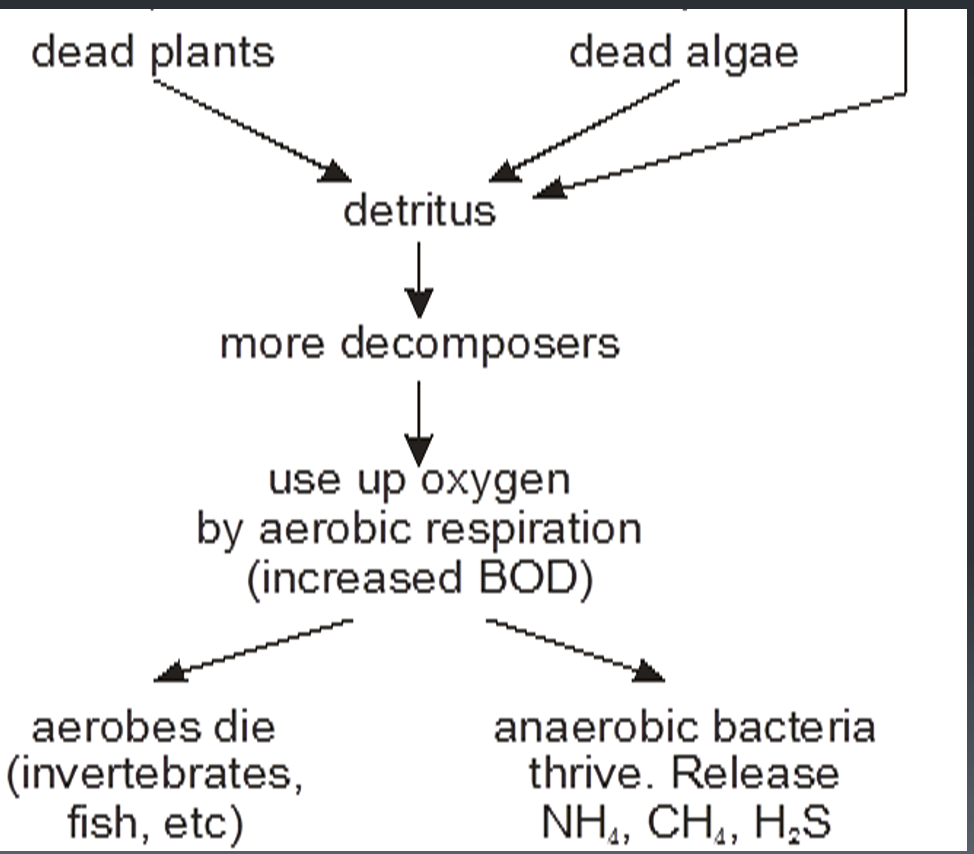
biological oxygen demand is the amount of dissolved oxygen needed (i.e., demanded) by aerobic biological organisms to break down organic material present in a given water sample at a certain temperature over a specific time period.
Eutrophication in freshwater systems
Eutrophic State
Extremely high concentrations of phosphorus and chl a and poorer water clarity
Shallow lakes often muddy and contain an abundance of aquatic plants
Eutrophication of lakes
natural
cultural
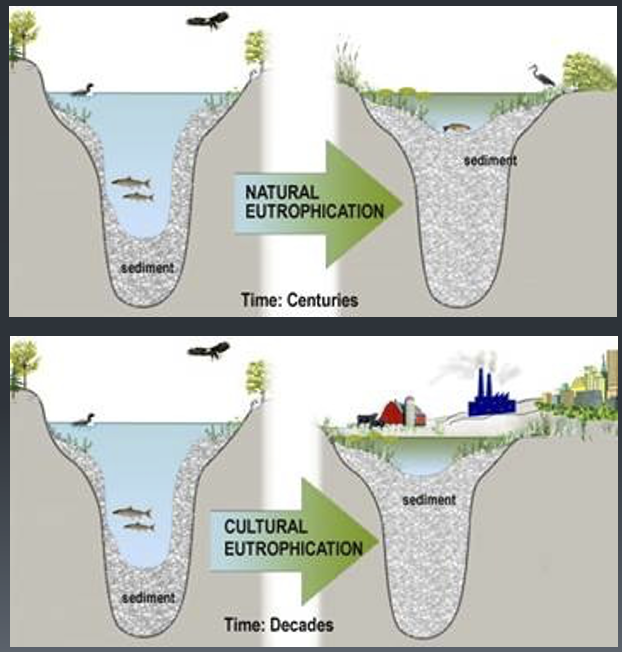
Eutrophication in experimental lake systems
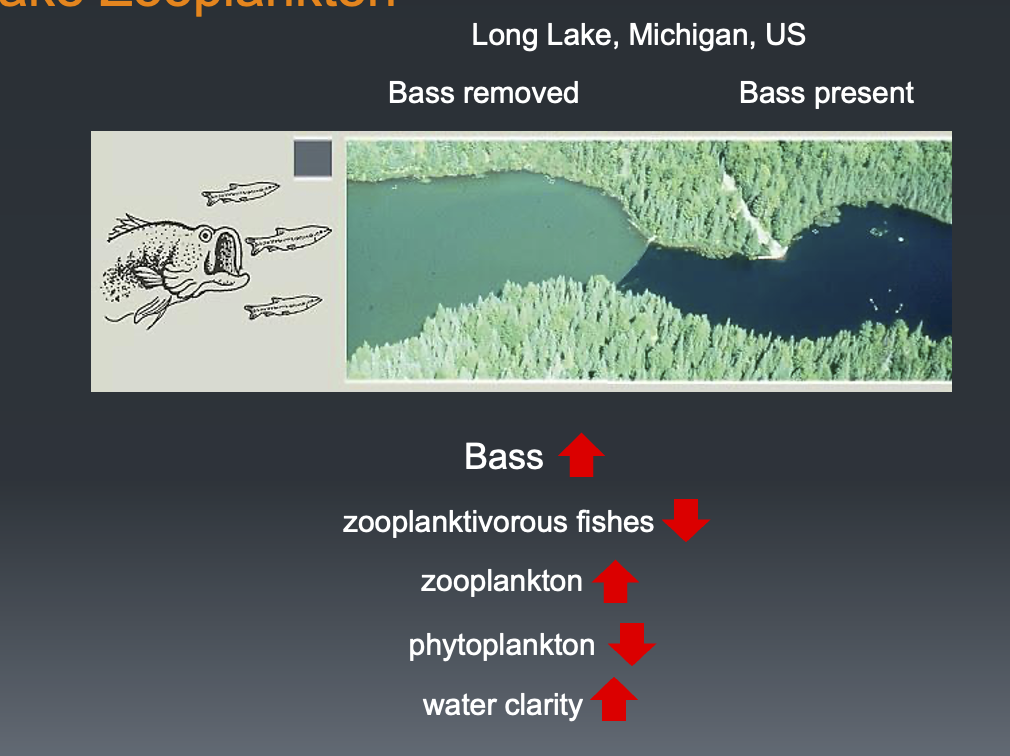
Bio-control of eutrohication in lakes
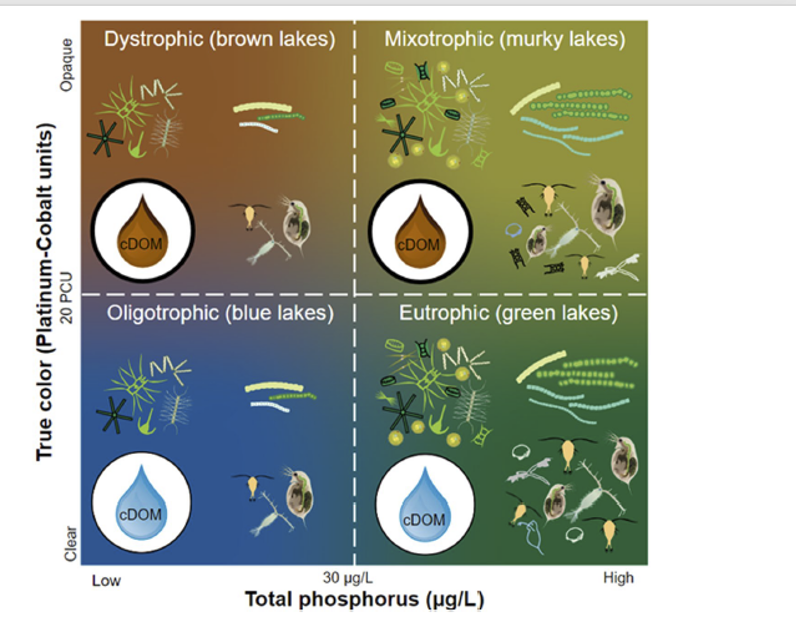
Types of Eutrophication in lakes
dystrophic
oligotrophic
mixotrophic
eutrophic
based on colour and level of phosphorous
Marine Eutrophication
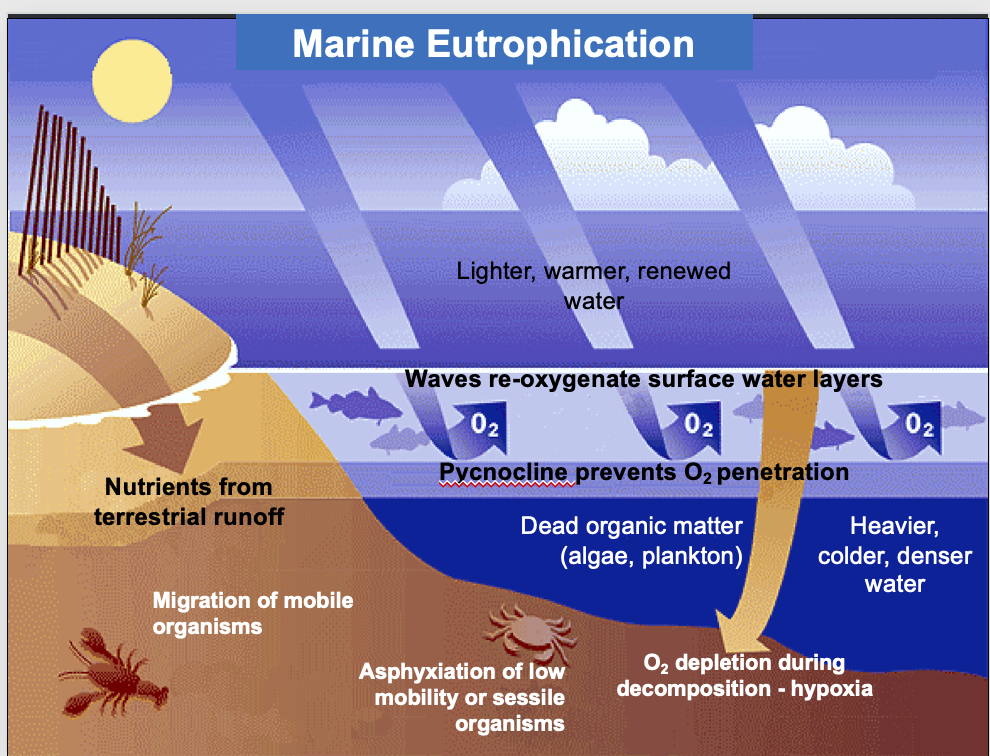
pycnocline forms causing stratification - preventing oxygen prnetration
waves on surface reoxygenate surface water
Nutrients from runoff and accumulation of dead orgainc matter on the bottom cause HYPOXIA
leads to asyphixyation of low mobility or sessile organisms
Called dead zones
Deoxygenation
climate change - more intense thermoclines for longer
increase of deadzones world wide
Costal Waters
nitrogen is usually the limiting factor
include deltas and salt marshes are naturally eutrophic but have become more intense and frequent
coastal upwelling also increases the productivity of algae
examples: Mississippi delta , Black Sea
Dead Zones
areas in aquatic environments with low oxygen levels that can no longer support marine life
These regions, often caused by nutrient pollution and excessive algae growth, lead to hypoxia, making it difficult for fish and other organisms to survive. They can significantly impact biodiversity and local fisheries.
Harmful Algal Blooms
algae that produce toxins
Algae block light and suffocate fish
Toxic species
Pseudo-nitzschia : Amnesic, Shellfish. Poisoning
Alexandrium: Paralytic, Shellfish, Poisoning
Dinophysis: Diarrhetic, Shellfish, Poisoning
Ecological Impacts of Eutrophication
Toxic or non-edible phytoplankton species
Increase of gelatinous zooplankton
Decrease in biomass of benthic and epiphytic algae
Changes in macroalgal composition and biomass
Reduced water transparency
Water colouration and odour
Reduced Dissolved Oxygen – DO levels
Fish mass mortality
Loss of economically important fish stocks
Reduced aesthetic value of ecosystem
Sargassum Belt
in the middle of the atlanic
free floating
increase in surface temperature, and increase in nutrients from amazon river (caused by increased agriculture and deforestation)
Botswana Elephant Deaths
caused by cyanobacteria blooms
spillover - ripple effects
eutrophication effects terrestrial organisms
Remediation of Eutrophication
increase shellfish aquaculture - filter phytoplankton from water column
Increase seaweed aquaculture