Filtration
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the purpose of filtration?
to absorb low energy x-ray photons (thus reducing patient dose)
hardens the beam/improves beam quality
What effect does filtration have on the beam?
hardens the beam and improves beam quality
High x-ray frequency has ___ energy, ___ wavelength, and ___ penetrability
high energy
short wavelength
high penetrability
Low x-ray frequency has ___ energy, ___ wavelength, and ___ penetrability
low energy
long wavelength
low penetrability
Do low or high energy x-rays add useful information?
high (low energy x-rays just deliver more dose to patient)
Define attenuation
reduction in the number of x-ray photons in beam as it passes through matter
Does attenuation result in a gain or loss of energy?
loss
Define remnant beam
portion of beam that exits patient to strike the IR
What is another term for remnant beam?
exit beam
When filtration is applied and beam is hardened, how is the emission spectrum effected?
average energy is increased (shifts curve →)
# of photons in beam is decreased (amplitude of curve decreases)
What are the 3 factors that harden the beam? *IMPORTANT*
kVp
generator type (high efficiency generator produces a harder beam)
filtration (absorbs low energy photons to increase average energy and decrease photon quantity)
Define filter
any material designed to selectively absorb photons from x-ray beam
What is the standard filtering material?
Aluminum
What unit is filtration expressed in?
aluminum equivalency (Al/eq)
Define inherent filtration
permanently fixed filtration
What are the 3 kinds of inherent filtration, and which is the most important?
tube envelope
tube window
dielectric oil
Define added filtration
filtration outside of the tube
What are the 3 kinds of added filtration, and which is the most important?
thin sheet of aluminum
mirror w/ silver coating
collimator
Tungsten vaporization acts like ___ filtration
inherent
Total filtration = ___ + ___
inherent + added
What is the Al/eq range for inherent filtration?
0.5-1.0 mm Al/eq
What is the Al/eq for the collimator?
1.0 mm Al/eq
What is the Al/eq for the mirror?
1.0 mm Al/eq
What is the Al/eq range for added filtration?
1.0-2.5 mm Al/eq
The NCRP recommends ___ mm Al for equipment that operates above 70 kV
2.5
% of photons attenuated decreases as kV ___
increases
Should you raise or lower technique when filters are used?
raise (even with raised technique, patient dose is reduced)
Define Half-Value Layer
amount of absorbing material that reduces intensity of beam to ½ of its original value
Tubes operating above 80 kVp require an HVL of ___ (per the code of Federal Regulations)
2.3 mm Al/eq
If 4mm Al reduces an exposure from 5 mR to 2.5 mR, what is the HVL?
4 mm
If a 100 mR source has a HVL of 2mm Al, how many mm are required to reduce the exposure to 25 mR?
4mm
Explain compensating filters
filters added to the outside of the collimator head
evens out the beam intensity over a body part with unequal thickness (for a more uniform exposure)
made of aluminum or clear lead
What is a wedge filter used for?
foot or femur
How do you place a wedge filter?
the thicker end of the filter goes over the thinner body part
What is a trough filter used for?
mediastinum and lung
What is a ferlic filter used for?
shoot through hip and c-spine (swimmers)
Explain the boomerang filter (underpart)
compensates for variations in tissue density
placed beneath the patient
can produce artifacts
used for shoulders
does not decrease pt. dose
absorbs beam after it travels thru pt.
Define compound filters
filters with 2+ materials with complimentary absorbing properties
In compound filters, each layer absorbs characteristic radiation produced by ___
the previous layer
What is another term for a compound filter?
K-edge filter
Are compound filters used in diagnostic x-ray?
no
The Thoraeus filter is used in ___
radiation therapy
What 3 layers is the Thoraeus filter made up of?
tin, copper, aluminum
What is the atomic # of Tin?
50
What is the atomic # of Copper?
29
What is the atomic # of Aluminum?
13
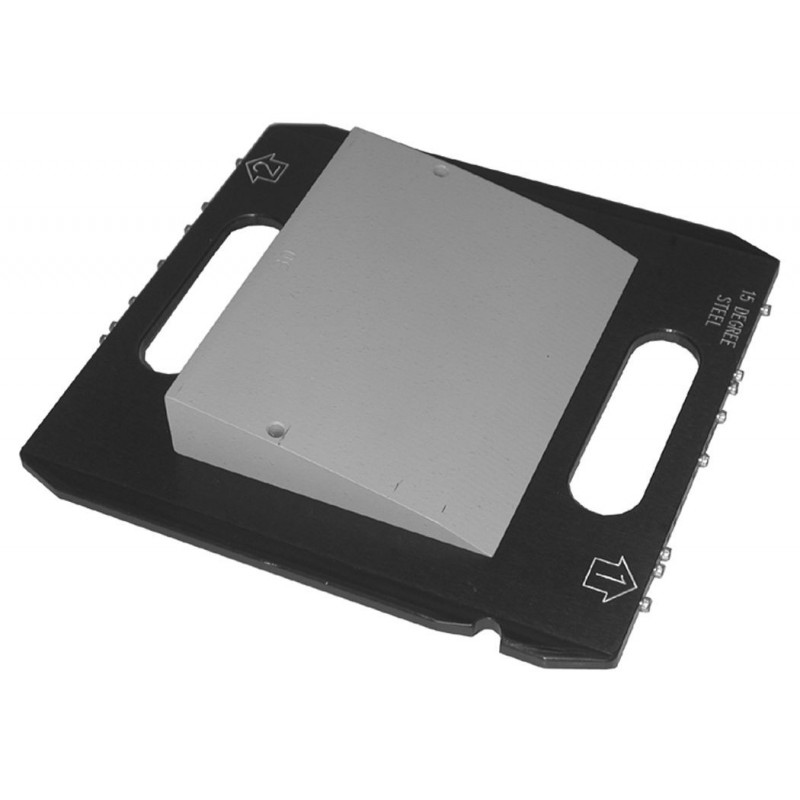

What type of filter is shown in the image?
wedge filter
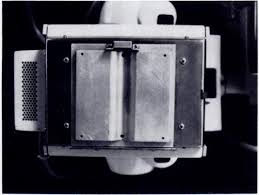
What type of filter is shown in the image?
trough filter

What type of filter is shown in the image?
ferlic filter

What type of filter is shown in the image?
boomerang filter