Bio 1406 Lab Exam 3 UPDATED
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
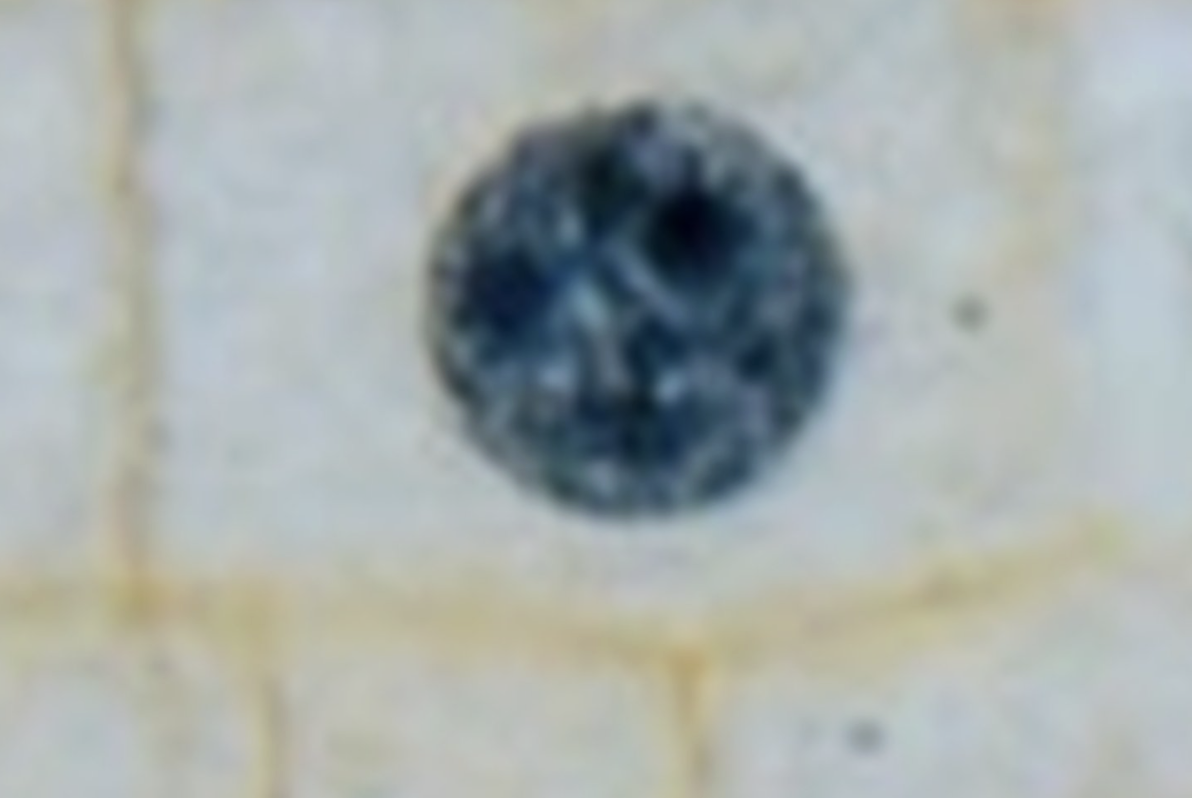

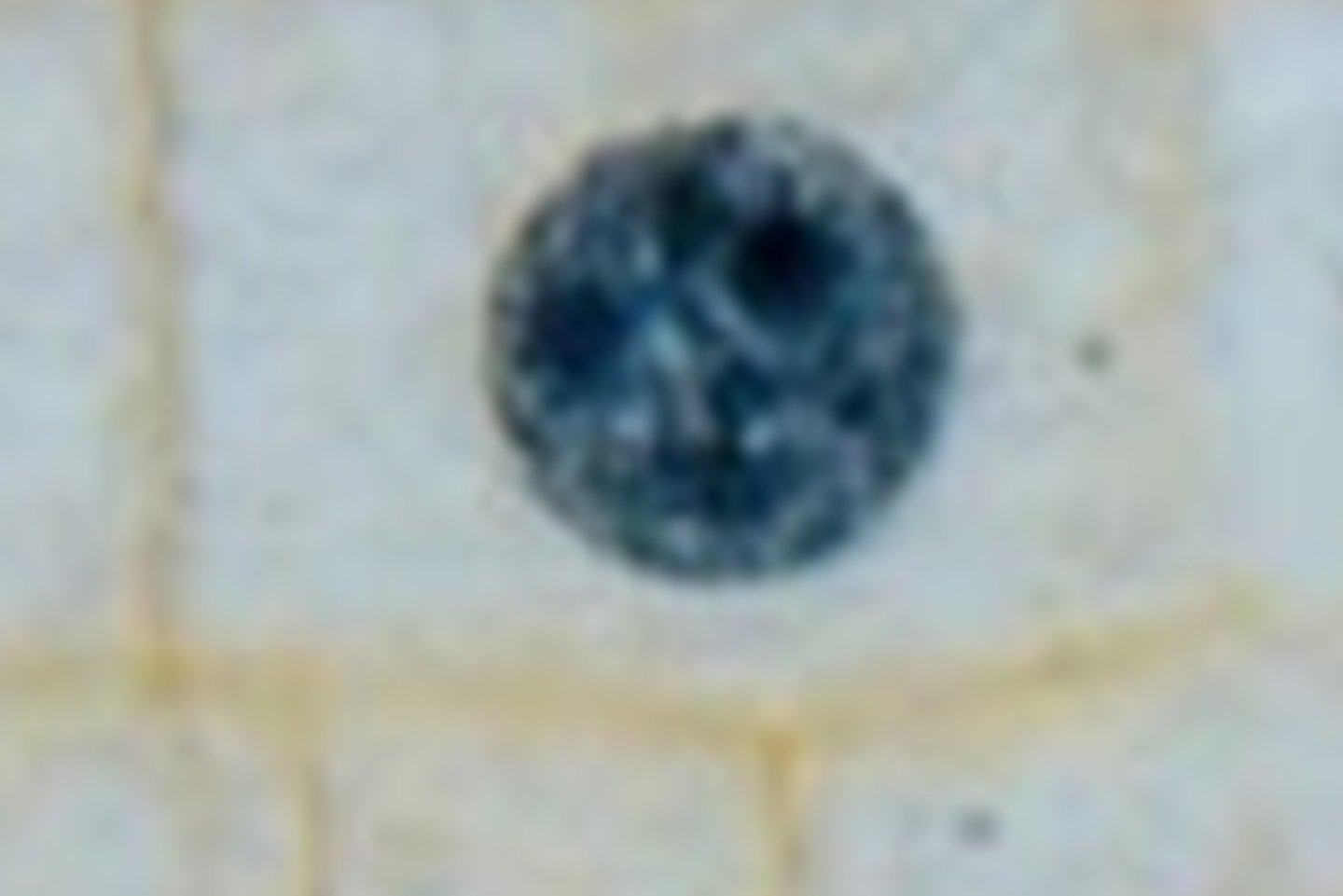
What is the image?
Interphase
What shows Interphase
Nucleus and nucleoli are visible. No chromosomes visible.
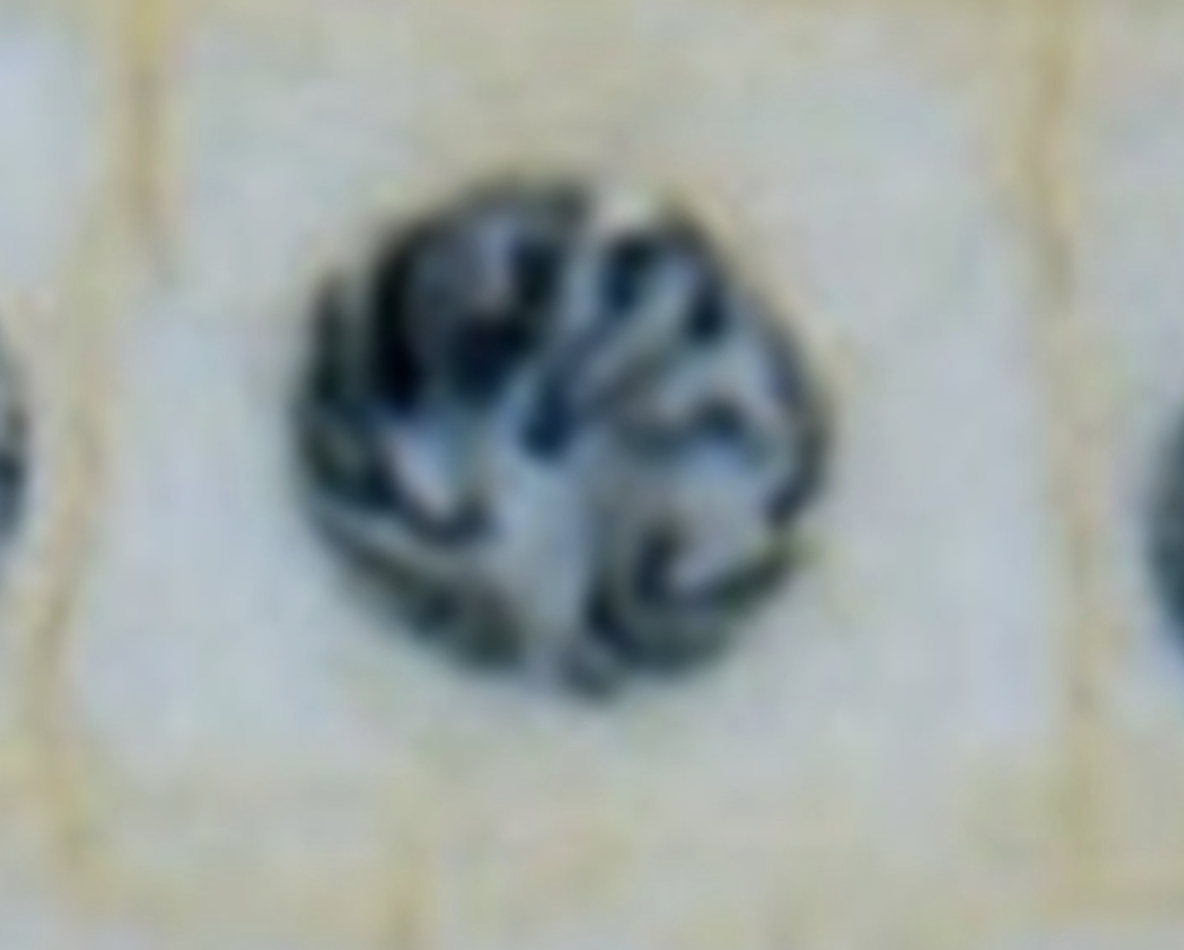


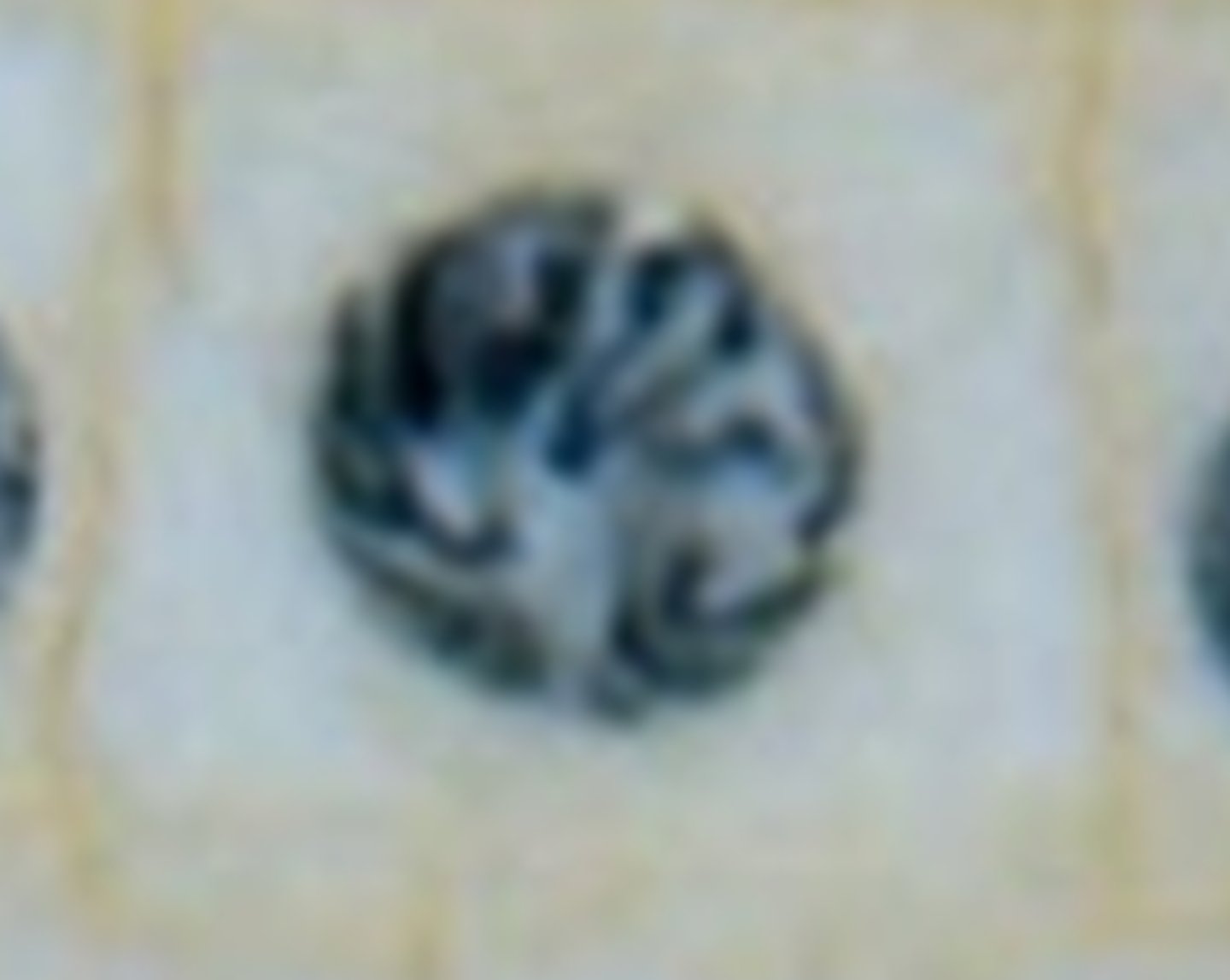
What is the image?
Prophase
What shows Prophase?
Chromosomes visible & disorganized. Nuclear membrane broken down.
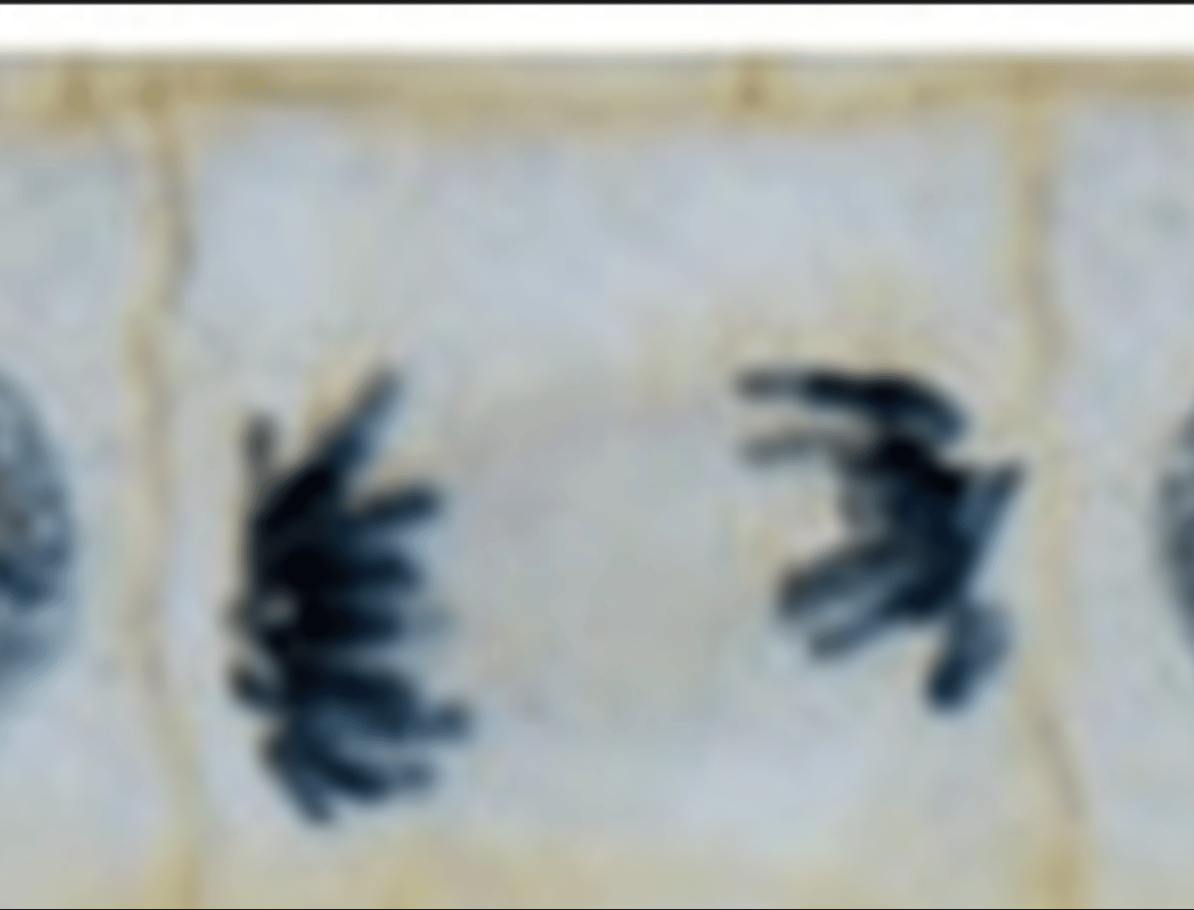


What is the image?
Telophase
What shows Telophase?
Chromosomes are at poles and decondensing, New cell wall is forming at midline of cell.
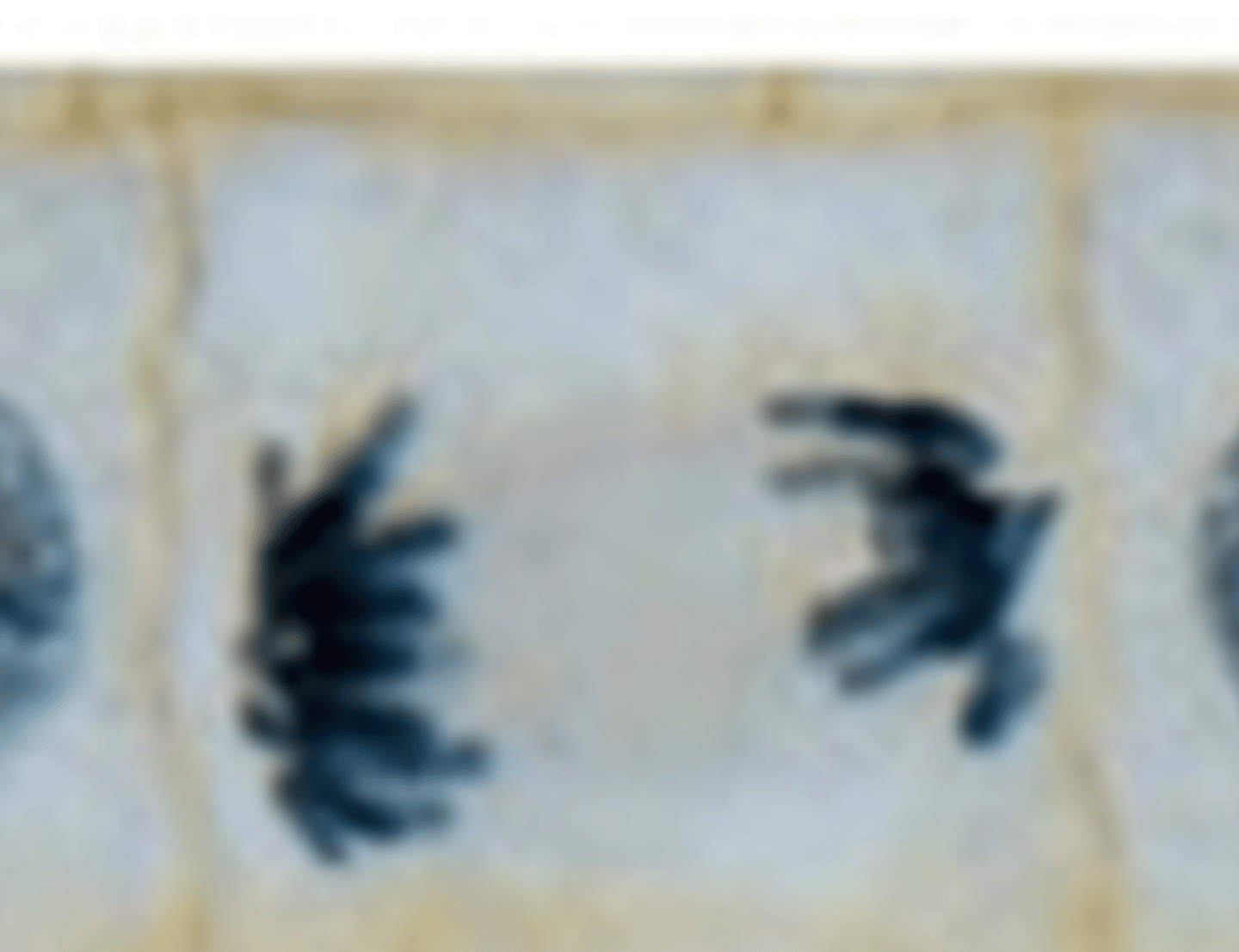


What is the image?
Metaphase
What shows Metaphase
Chromosomes at midline of cell (look like eyelashes)

What shows Anaphase?
Chromosomes moving to opposite sides of cell , look like < >
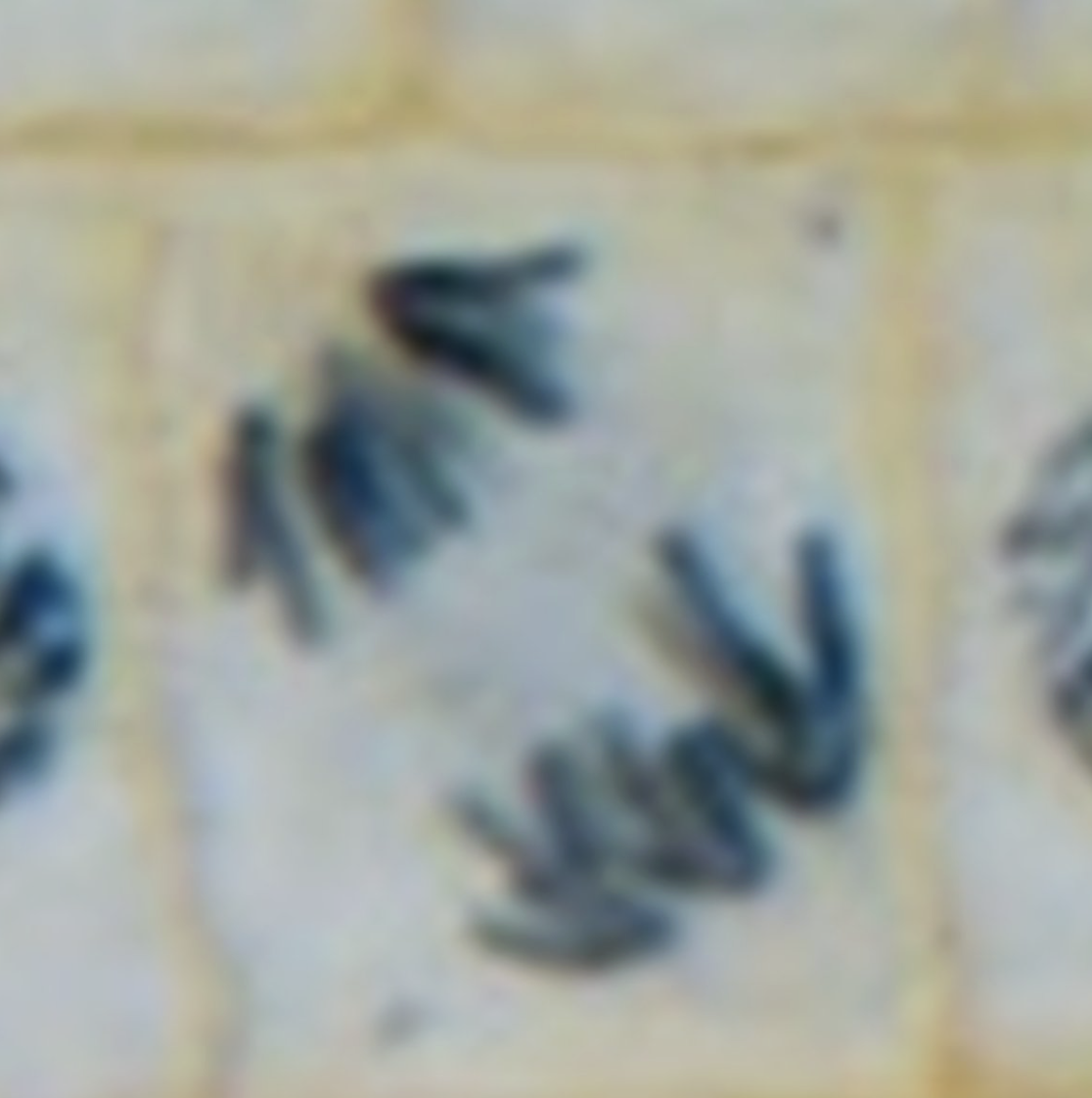
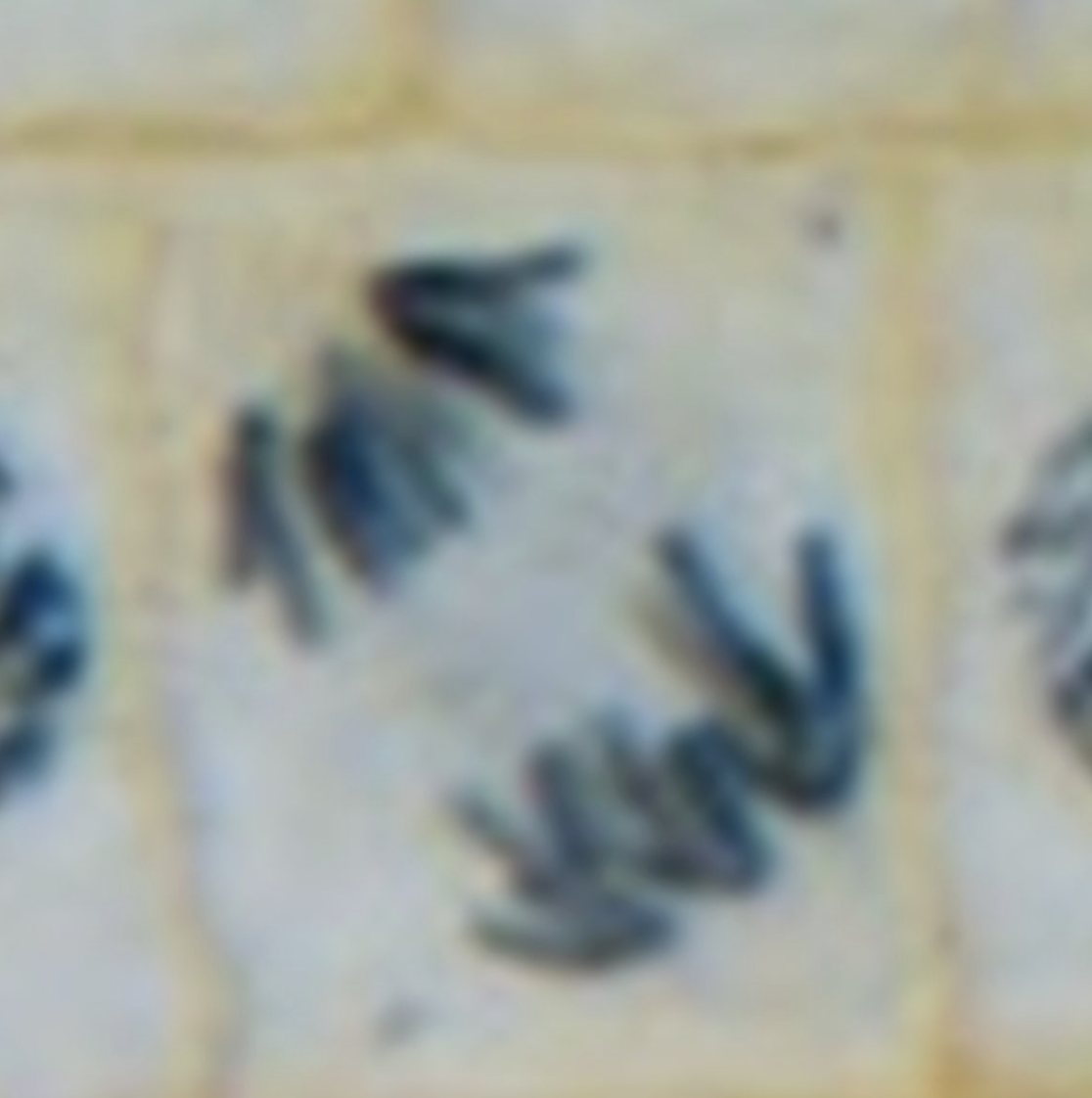


What is the image?
Anaphase
Haploid
Cells containing 1 copy of each chromosome
Diploid
Cells containing 2 copies of each chromosome
Gamete
Sperm or egg
Germ
Diploid body cells that become gametes
Meiosis
Cell division for germ cells to make gametes
Mitosis
Cell division of somatic cells
Somatic
Typical body cells
Syngamy
Fertilization, fusion of egg and sperm
G2
Cell preps for division, making needed components
Mitosis
Cell is dividing
G1
Part of interphase, cell enlarges, gets signal to replicate, preps for DNA replication
S
DNA replicates
Interphase
Cell is not dividing, made of 3 parts
Cytokinesis
Cytoplasm splits into 2 cells
Anaphase
Spindle separates daughter chromosomes to opposite ends of cell
Prophase
Centrioles move to opposite poles
Telophase
Chromosomes decondense
Prophase
Nuclear envelope breaks down
Telophase
Nuclear envelope reforms
Metaphase
Sister chromatids line up in center of cell
Prophase
Chromosomes condense
Prophase
Spindle fibers begin to form
Anaphase
Centromeres divide, sister chromatids become separate chromosomes
Telophase
Spindle apparatus breaks down completely
Prophase (chromosome duplicated or unduplicated?)
Duplicated
Metaphase (chromosome duplicated or unduplicated?)
Duplicated
Telophase (chromosome duplicated or unduplicated?)
Unduplicated
G2 (chromosome duplicated or unduplicated?)
Duplicated
G1 (chromosome duplicated or unduplicated?)
Unduplicated
Anaphase (chromosome duplicated or unduplicated?)
Unduplicated
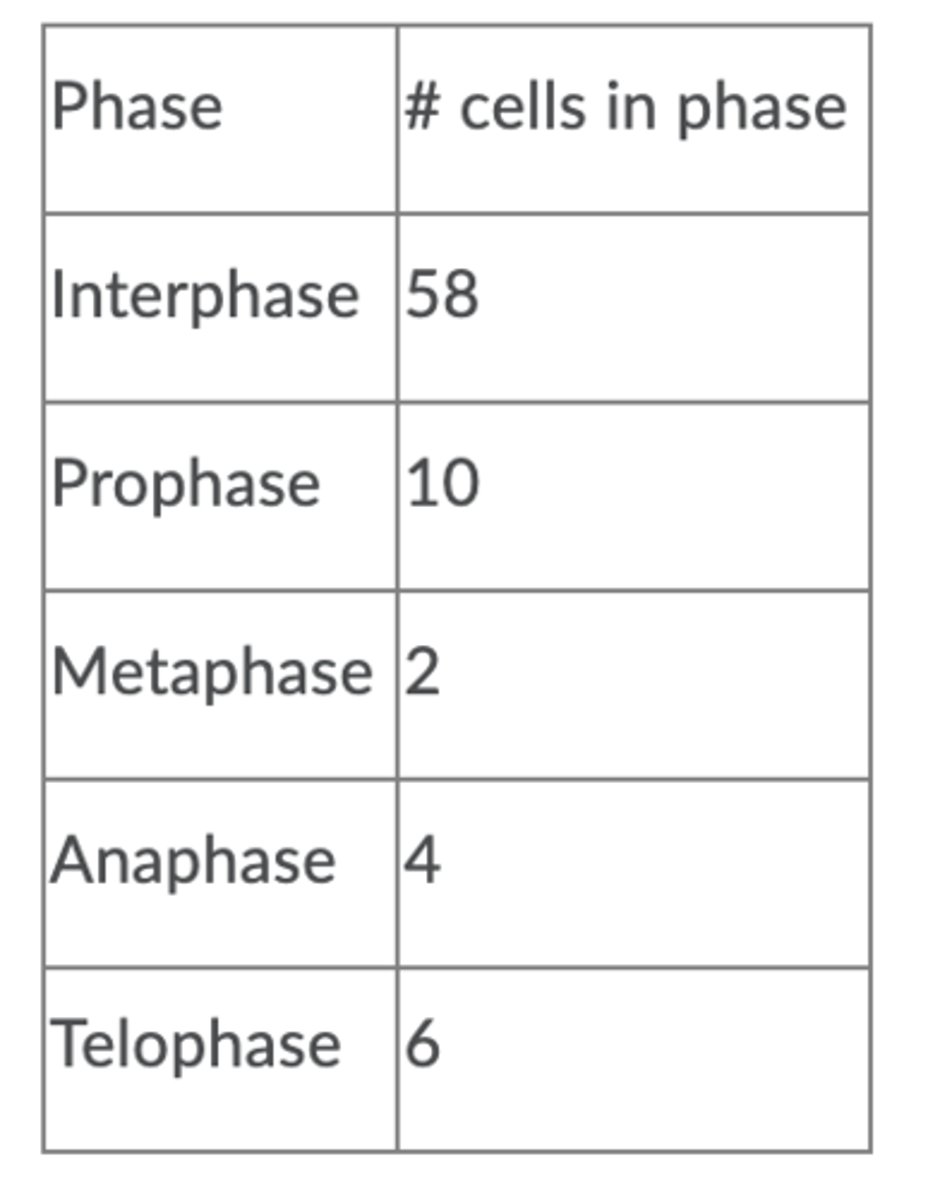
Anaphase
5%
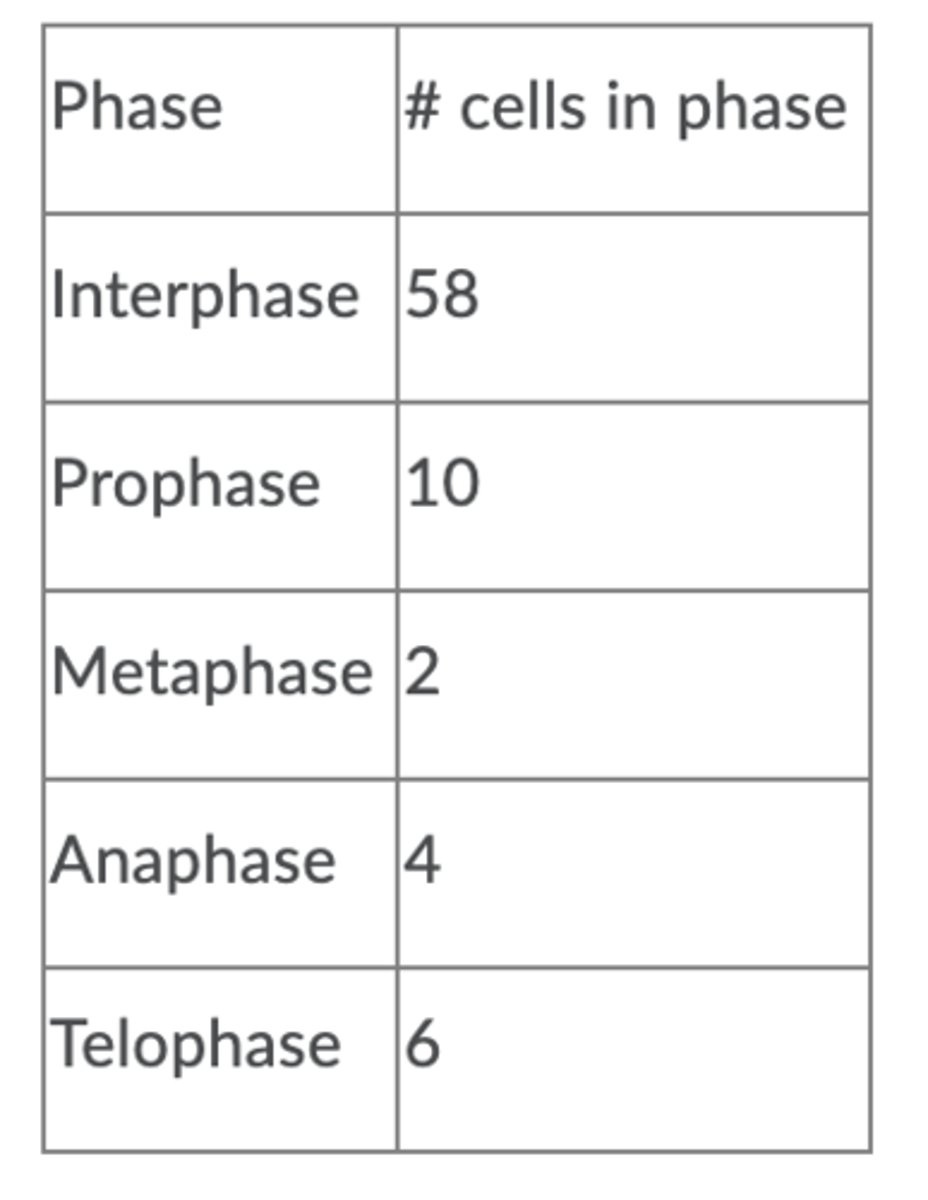
Interphase
72.5%
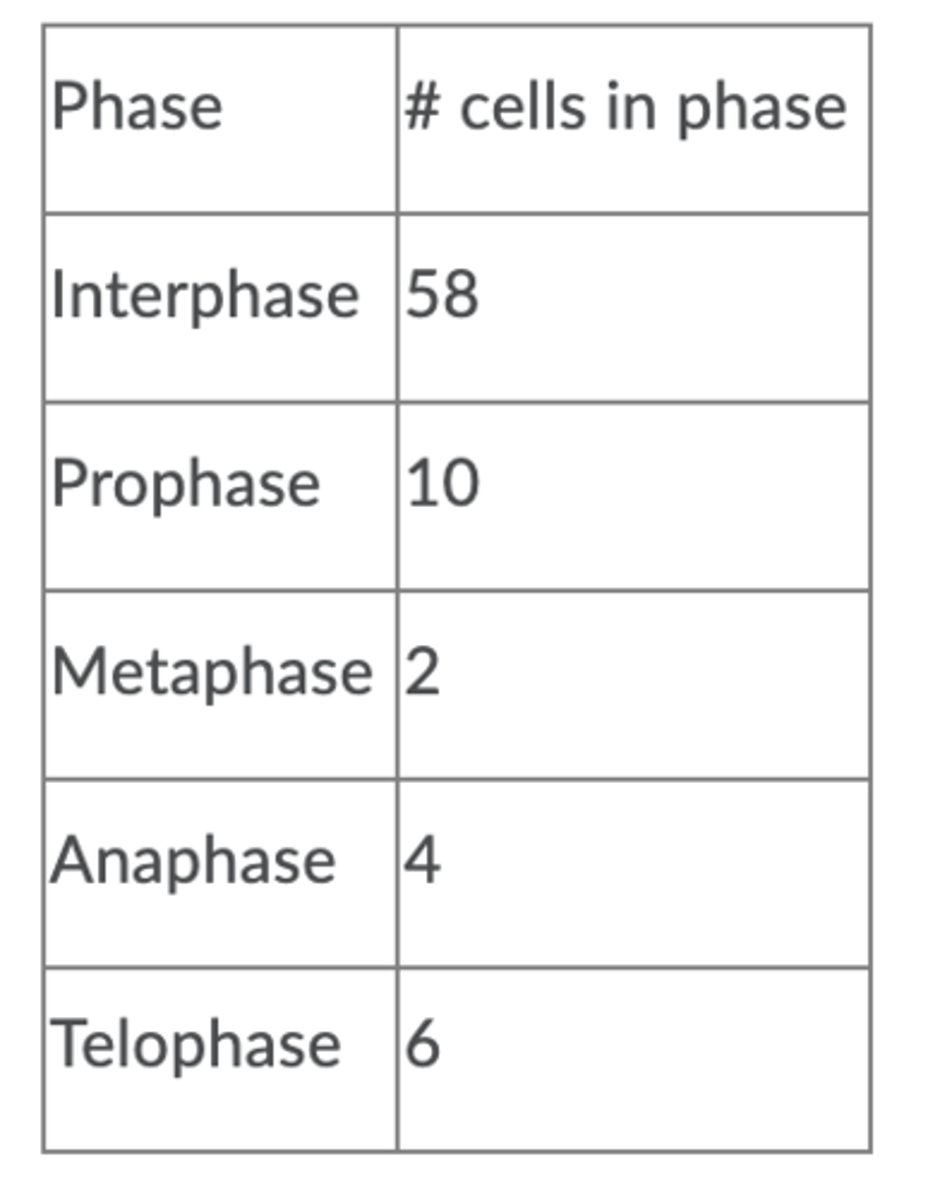
Metaphase
2.5%
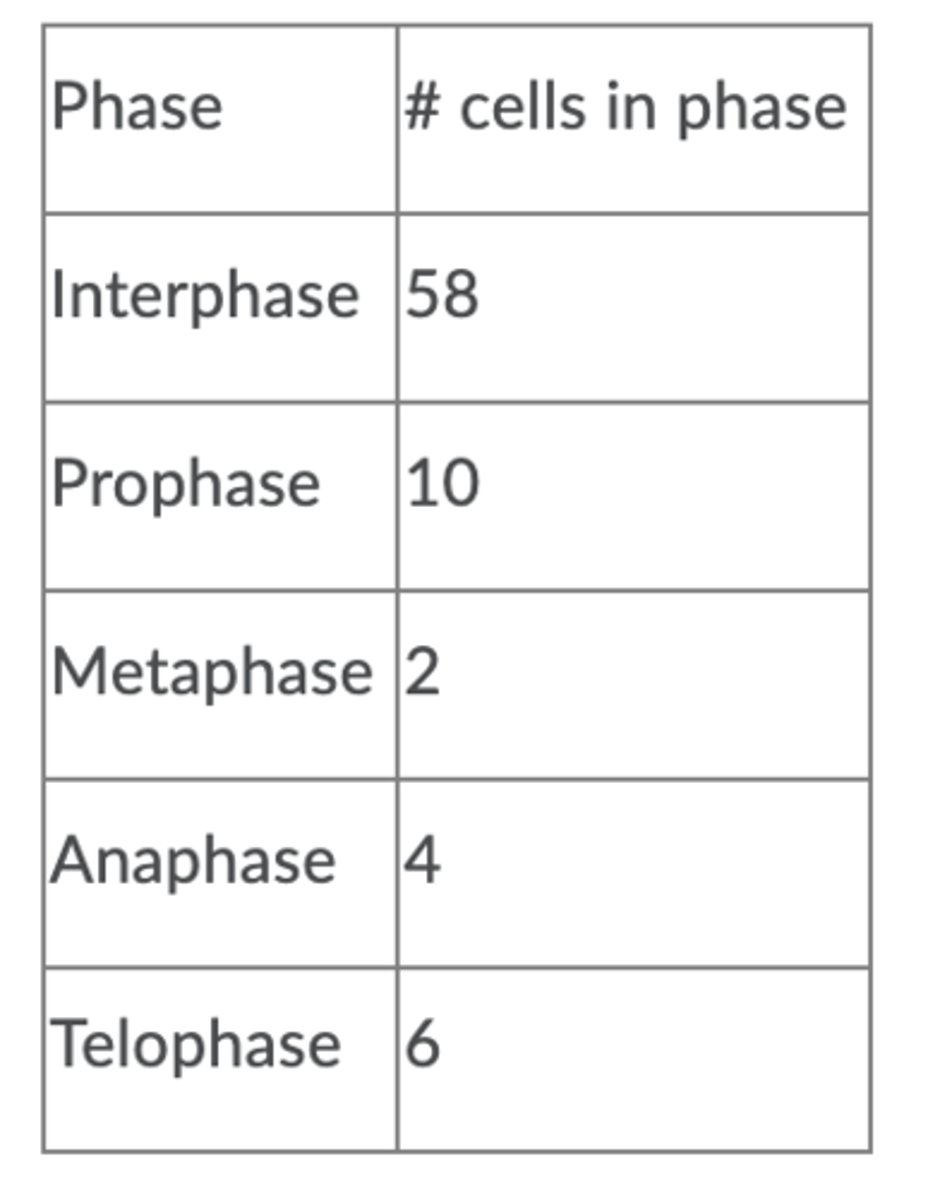
Prophase
12.5%
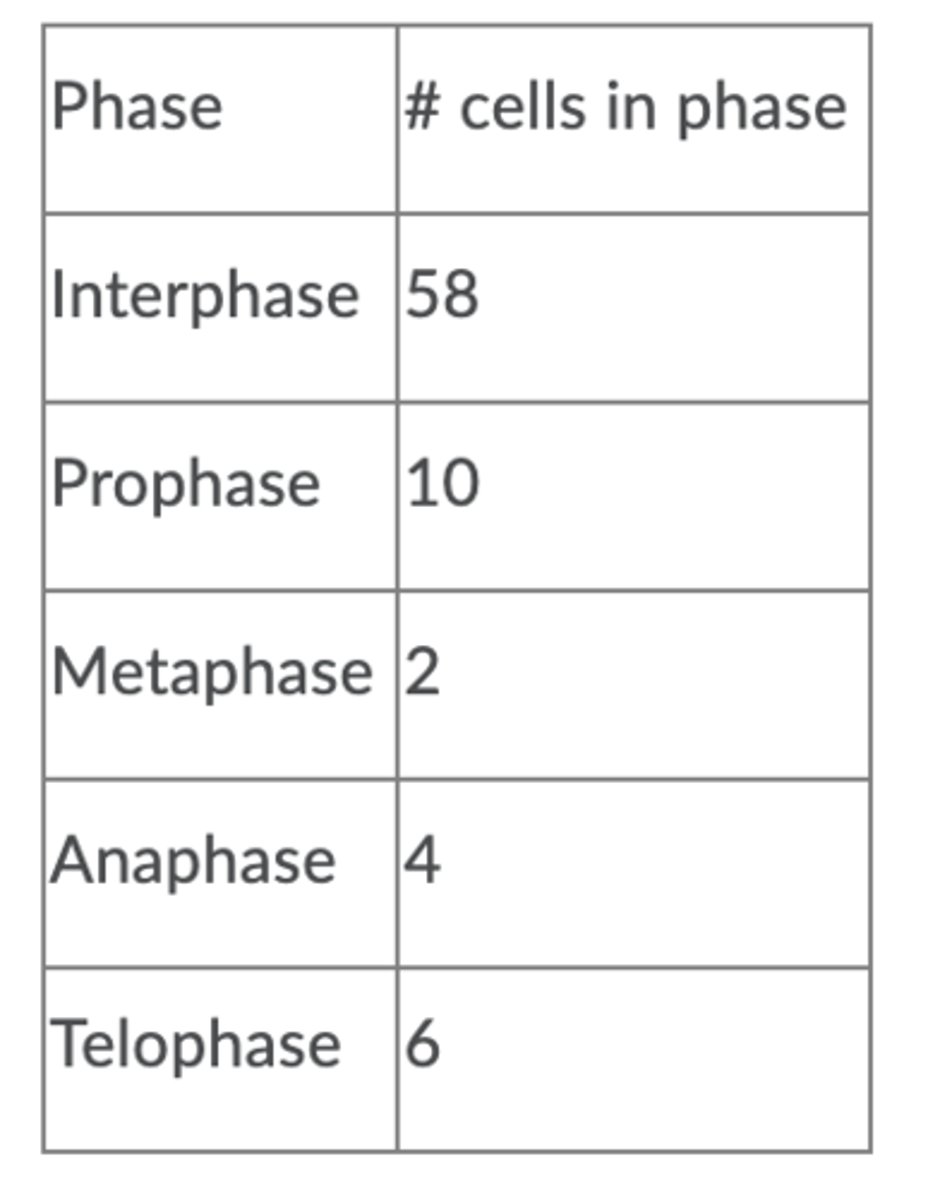
Telophase
7.5%
Mendel's law of independent assortment
Alleles of different genes sort independently of each other during gamete formation.
F2
2nd generation of offspring, from cross of two F1
Allele
A version of a gene that codes for a protein (Blonde vs Brown hair)
Dominant
Alleles express the dominant phenotype if at least one of this type of allele is present in genotype (unless incomplete or codominance). Indicated with capital letter
Genotype
Allele combination, such as homozygous dominant, heterozygous, homozygous recessive
Heterozygous
Alleles are different: one dominant other recessive
Monohybrid cross
Case of 1 character inheritance when both parents are heterozygous
Recessive
Alleles that express the recessive phenotype only if homozygous
Homozygous
Both Alleles are identical; both recessive or both dominant
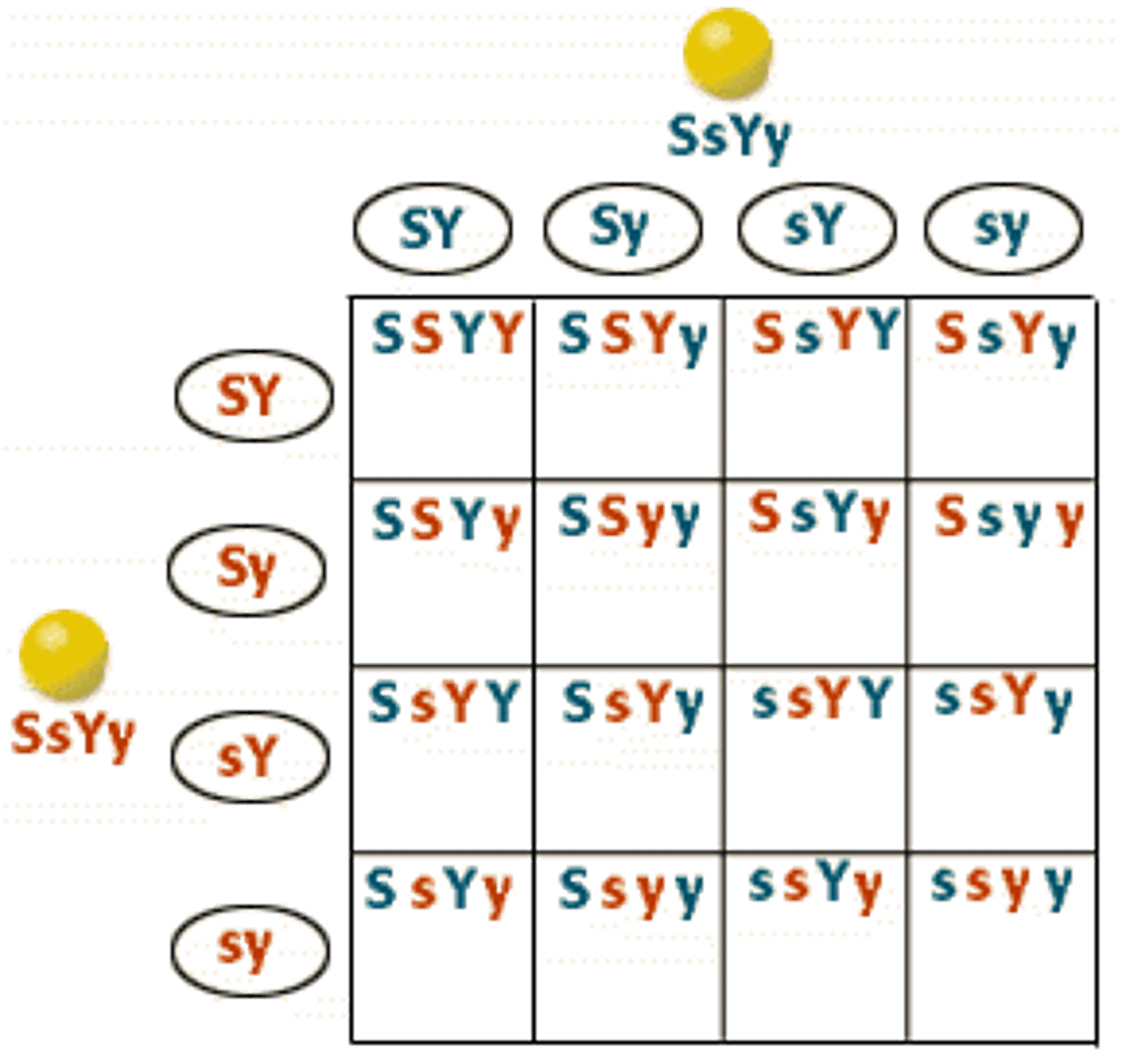
Dihybrid cross
Case of 2 character inheritance when both parents are heterozygous in both characters
F1
First generation of offspring
Gene
Specific DNA nucleotide sequence that codes for a protein when expressed
True breeding
Parents with particular phenotype produce offspring with only the same phenotype, so parents homozygous for trait
Mendel's law of segregation
When individual makes gametes, 2 copies of gene separate, so each gamete gets 1 copy
Test cross
Organism with unknown genotype is crossed with homozygous recessive
Phenotype
Physical or behavioral expression of a gene
If parent is BB, gametes are
B
If parent is Bb, gametes are
B or b
If parent is TtGg, gametes are
TG, Tg, tG, tg
If parent is heterozygous for blood type A, what gametes will they make? (imagine the superscripts are working)
IA and IO
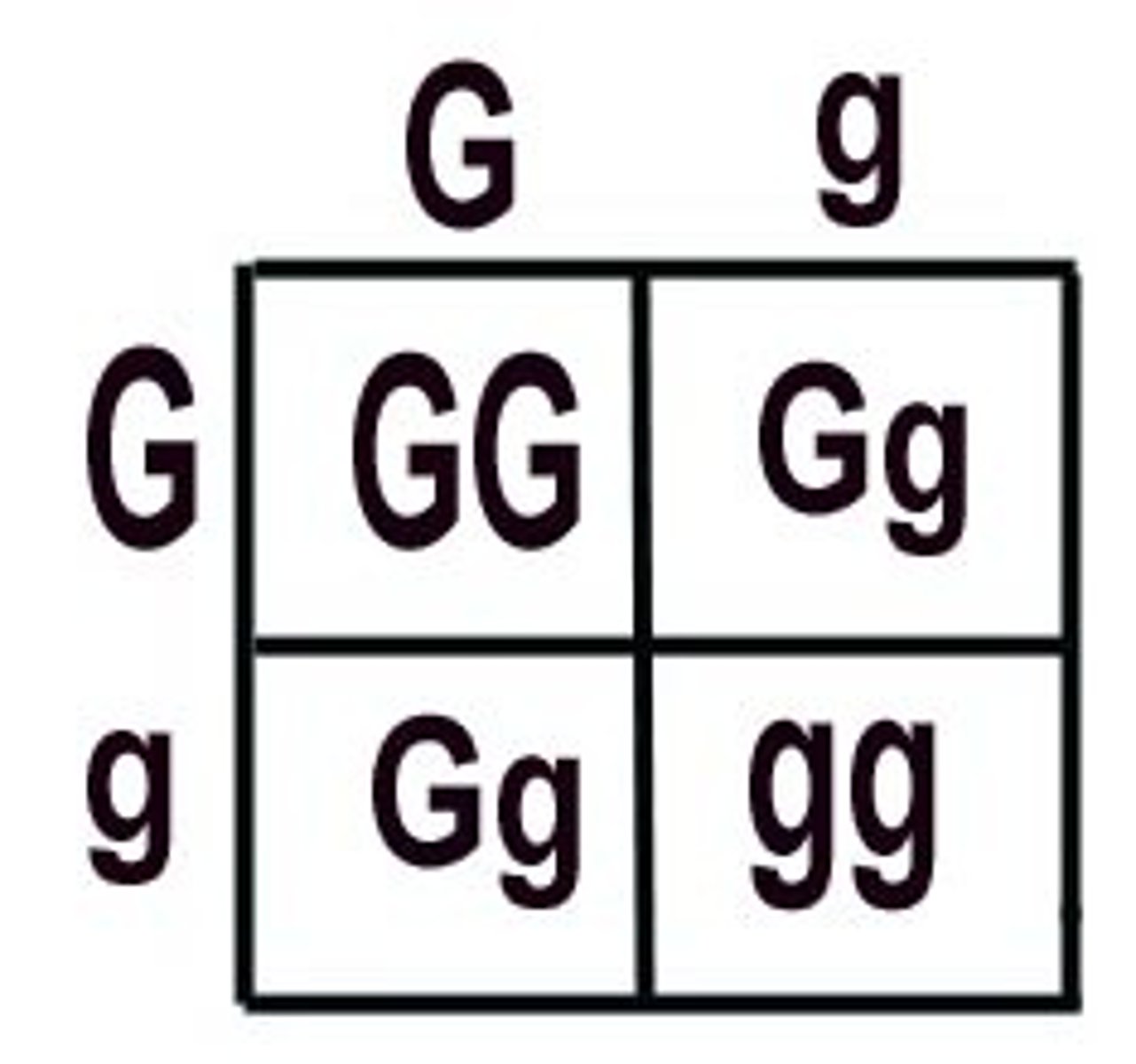
Make PUNNETT square for a cross between a male heterozygous with brown eyes and a woman with blue eyes.
Genotypic ratio: 0 BB : 2 Bb : 2bb
Phenotypic ratio: 2 Brown : 2 blue
The cross is aaBbCcDd x aaBbCCDD
What fraction of children will be aaBbCcDd?
1/8%
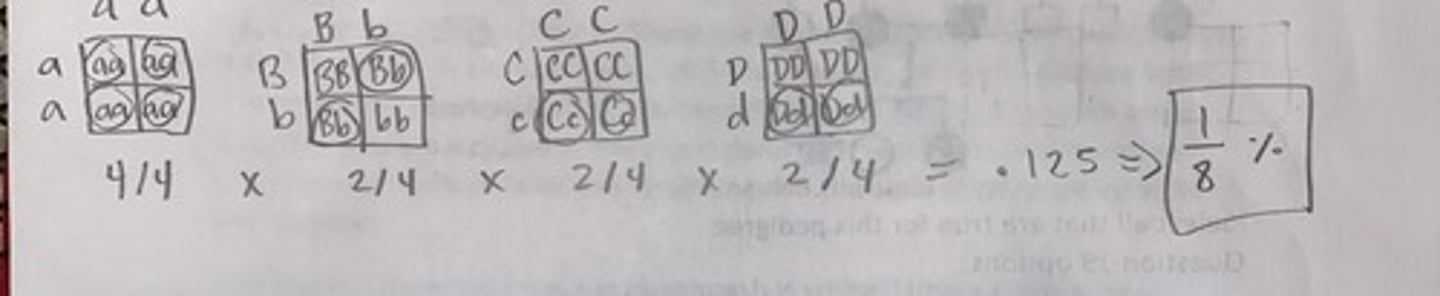
Dad can pass an X linked trait to his daughter
True
Dad can pass an X linked trait to his son
False
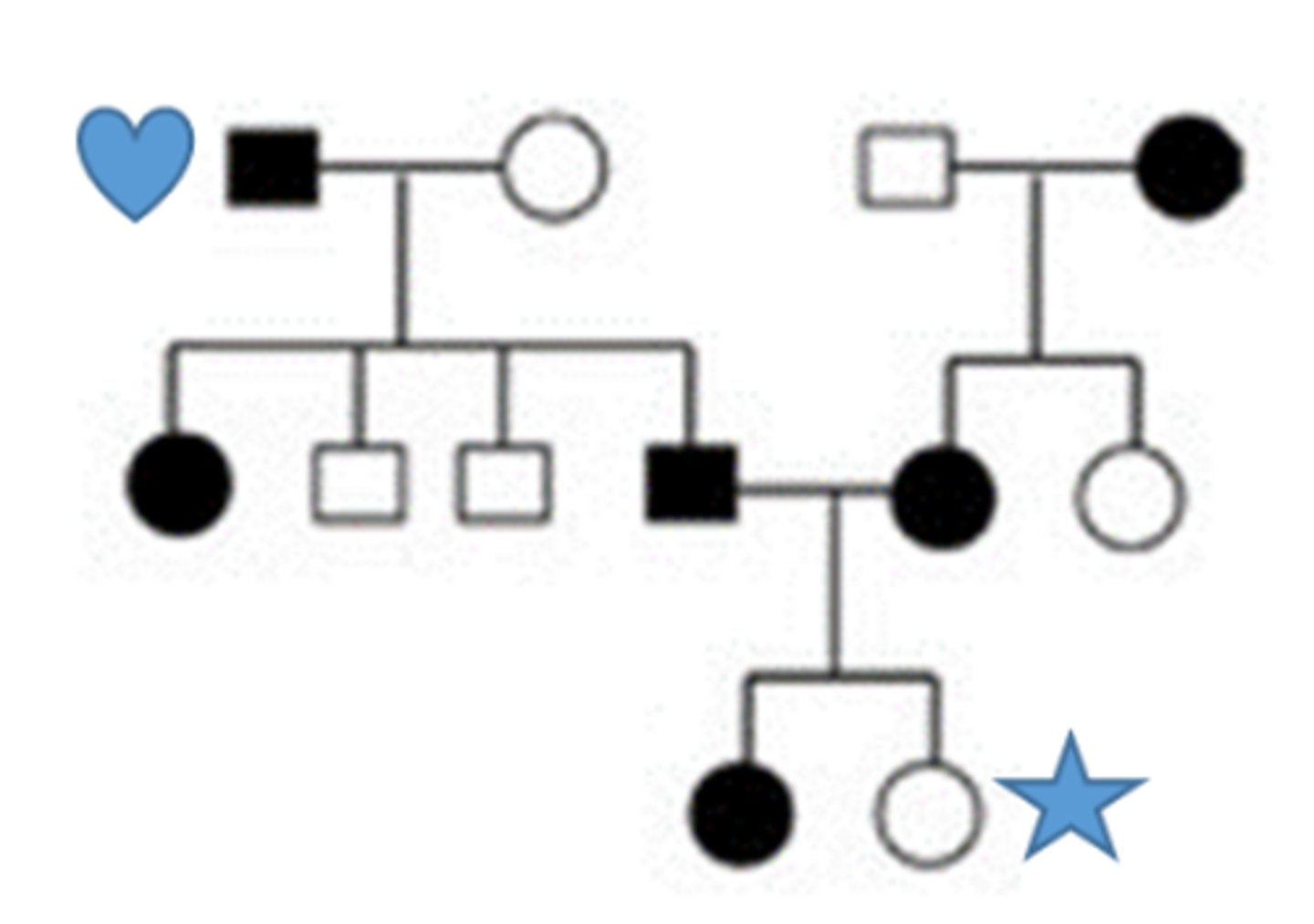
For this Pedigree:
Question options:
The trait is dominant, every affected person has affect parent
The trait is recessive, it skips a generation
The trait is Y linked, passing only from father to son
The trait is X linked, Dad passes to daughter but not to son
The star person is male
The star person is female
The star person is heterozygous
The star person is homozygous recessive
The heart person is male
The heart person is female
The heart person is heterozygous
The heart person is homozygous dominant
For squash Dominant A means the squash is white. Little aa means the squash can produce color. Y means yellow squash and yy means green squash. If 2 heterozygous squash cross, how many of the offspring are likely to be ____white ____yellow ____green
11 white, 12 yellow, 4 green

What is it called when one gene allows another gene to express?
Epistasis
Lysis of membranes
Detergent in homogenization buffer dissolved phospholipid bilayer
Precipitation
Ice cold ethanol removed DNA from solution
Purification
Cheese cloth filtered out big chunks, then centrifugation separated debris from solution
Homogenization
Mortar & Pestle broke tissues into individual cells and broken open plant cell walls
In DNA, Adenine pairs with
Thymine (T)
.
In DNA, Cytosine pairs with
Guanine (G)
In RNA, Adenine pairs with
Uracil (U)
In RNA, Guanine pairs with
Cytosine (C)
Why do restriction endonucleases cut certain DNA segments?
sequence of nucleotides give unique shape
IF EcoRI has restriction (cut) sites at GAATTC, how many times would this DNA be cut _____ and how many fragments would be produced _____. Remember, you always have 1 more fragment than restriction site. 1 piece of string with 1 cut site will make 2 fragments.
5' TAGAATTCCTAGAATTCCG3'
2/3
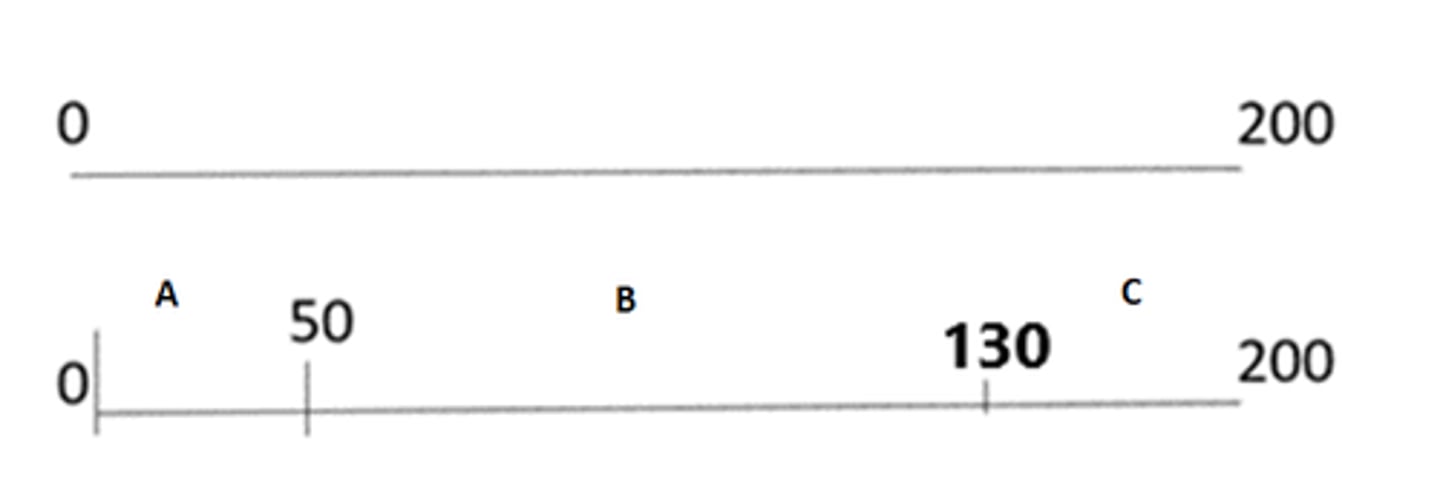
Given this data, select all that are true.
Question options:
Fragment A 50bp
Fragment B 130bp
Fragment B 80bp
Fragment C 200bp
Fragment C 70bp
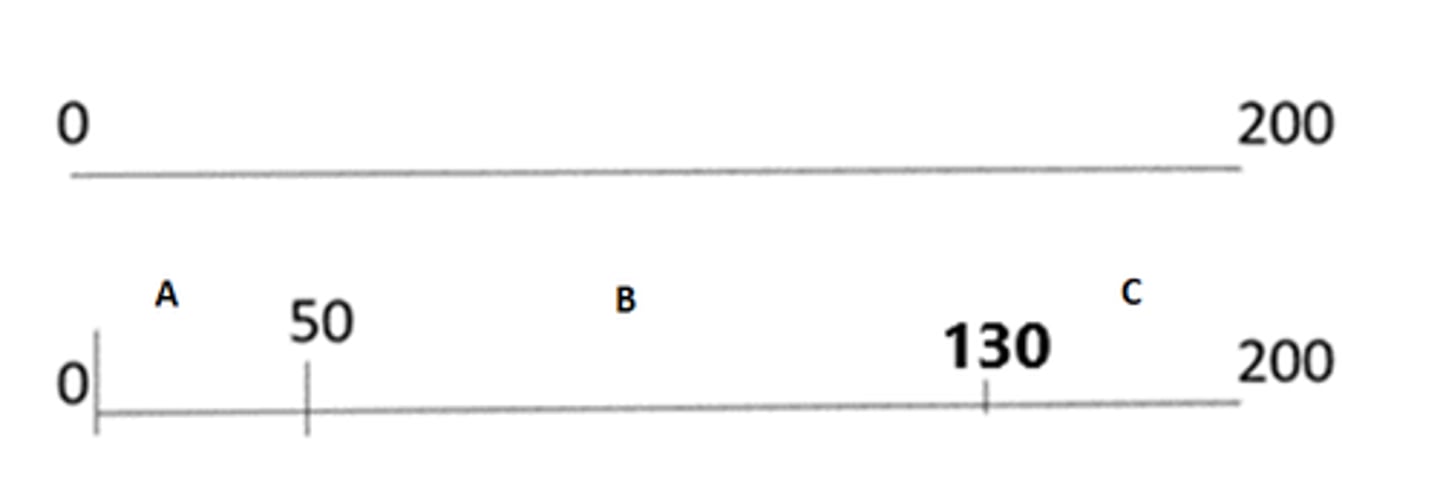
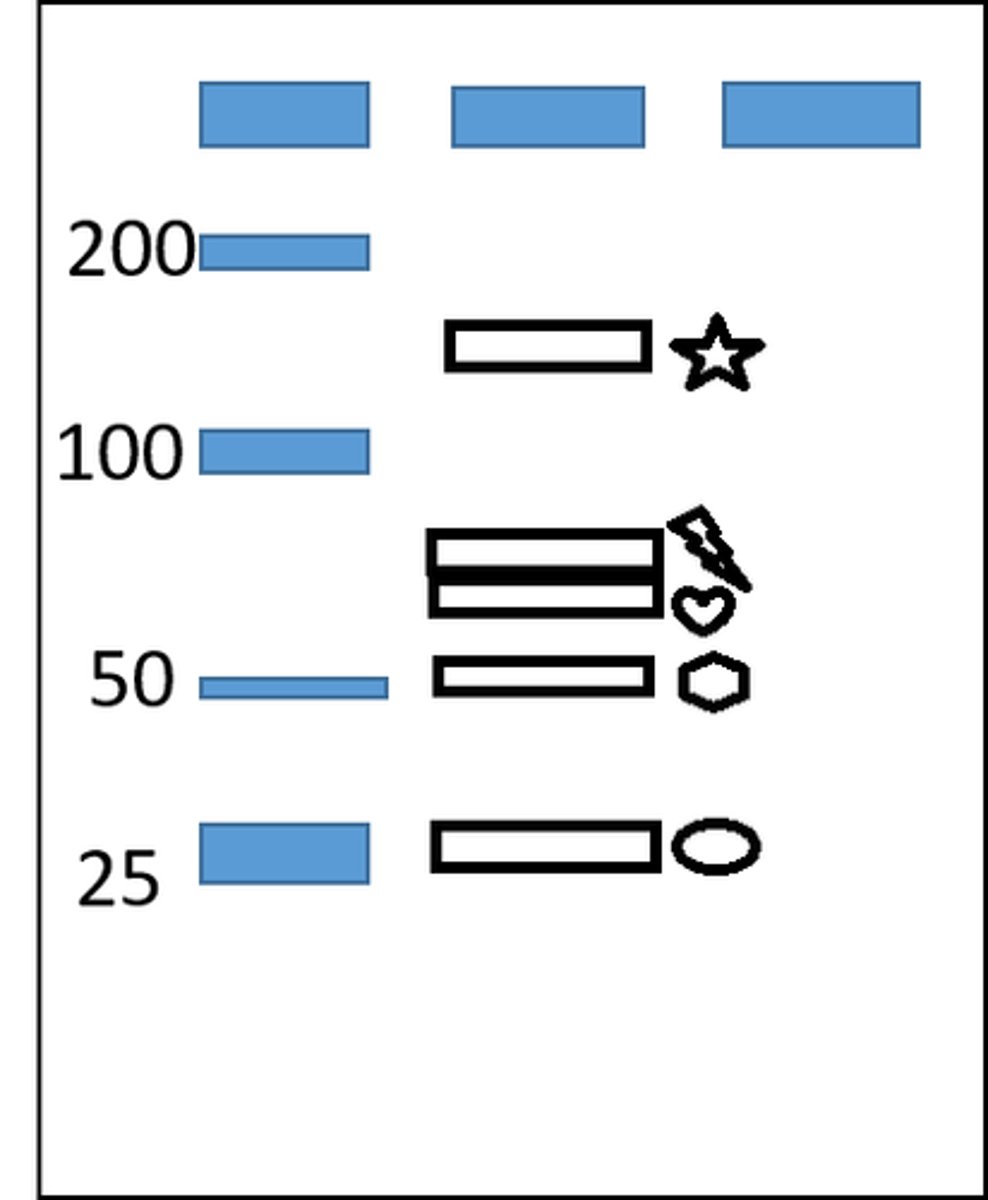
Given this gel, if DNA fragments are A 50bp, B 80bp and C 70bp, select all that are true of this gel.
Fragment C aligns at star
Fragment B aligns at lightning bolt
Fragment C aligns at heart
Fragment A aligns at hexagon
Fragment A aligns at oval
Given these data, if a person has a 1/10 chance of having Fragment A; 1/30 chance of having Fragment B; and 1/50 chance of having Fragment C, what is the chance someone having this exact DNA fingerprint?
1/15000
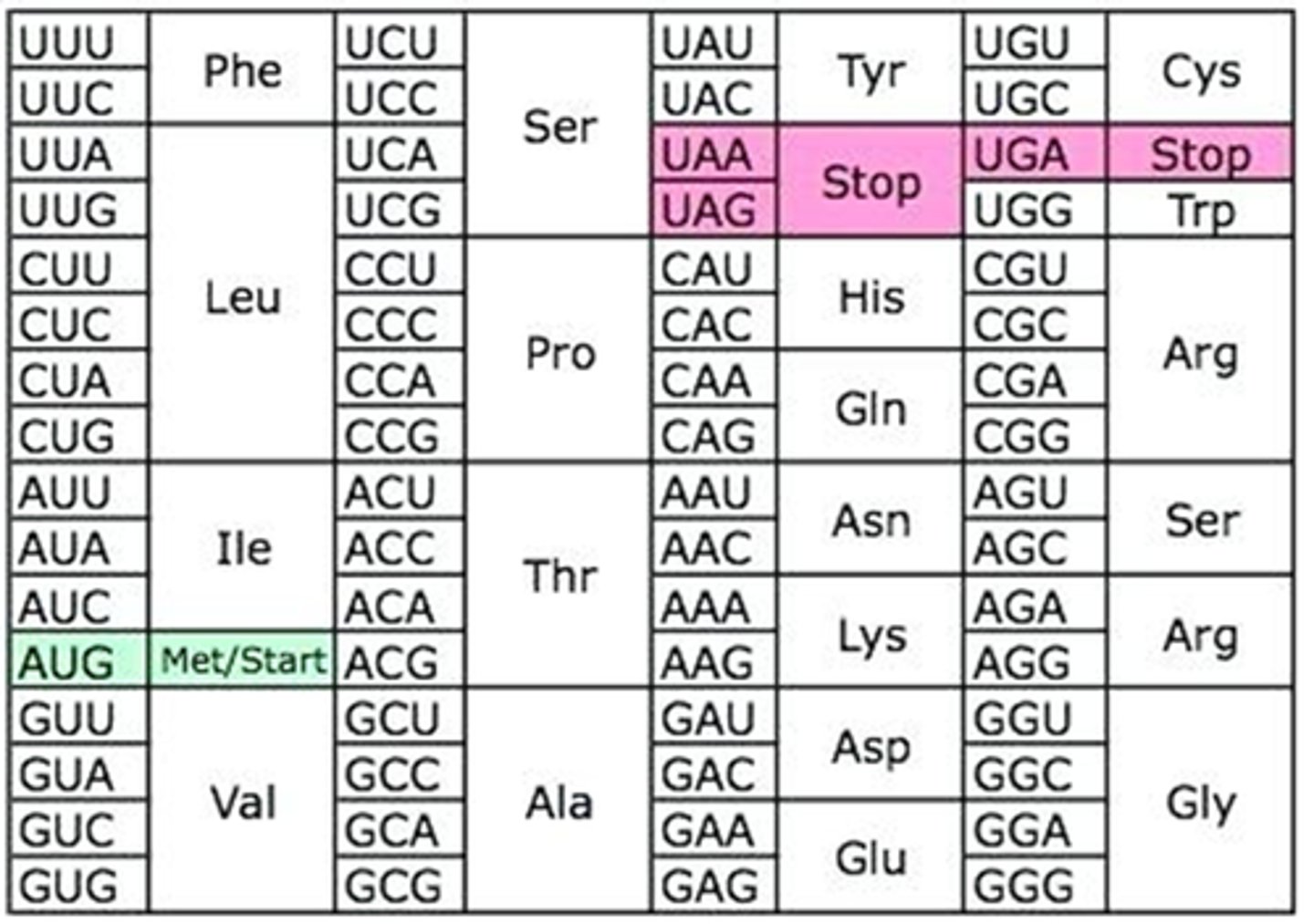
Transcription is
using nucleotide sequence of DNA to determine nucleotide sequence of RNA, occuring throughout the life of the cell
Transcribe this DNA to mRNA. Remember DNA uses ATGC. RNA uses AUGC. They will be antiparallel to each other.
5'ATCCGAT3'
3'UAGGCUA 5'
Translation is
using mRNA to determine amino acid sequence of proteins, in the cytoplasm of eukaryotes, two of these are correct
Given this mRNA sequence, select all that are true. 5'GACAUGCCCUGCUAG3'
Question options:
The first amino acid is ASP
Ignore all nucleotides from 5' until AUG
First amino acid is Met
Second amino acid is Pro
Third amino acid is Pro
Third amino acid is Cys
UAG is stop codon