metallic bonding and crystallography
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
describe Hexagonal close packed structures (HCP)?
ABA arrangement
packing sequence of 1
third layer sisters directly over first
so here’s occupy 74% of total volume
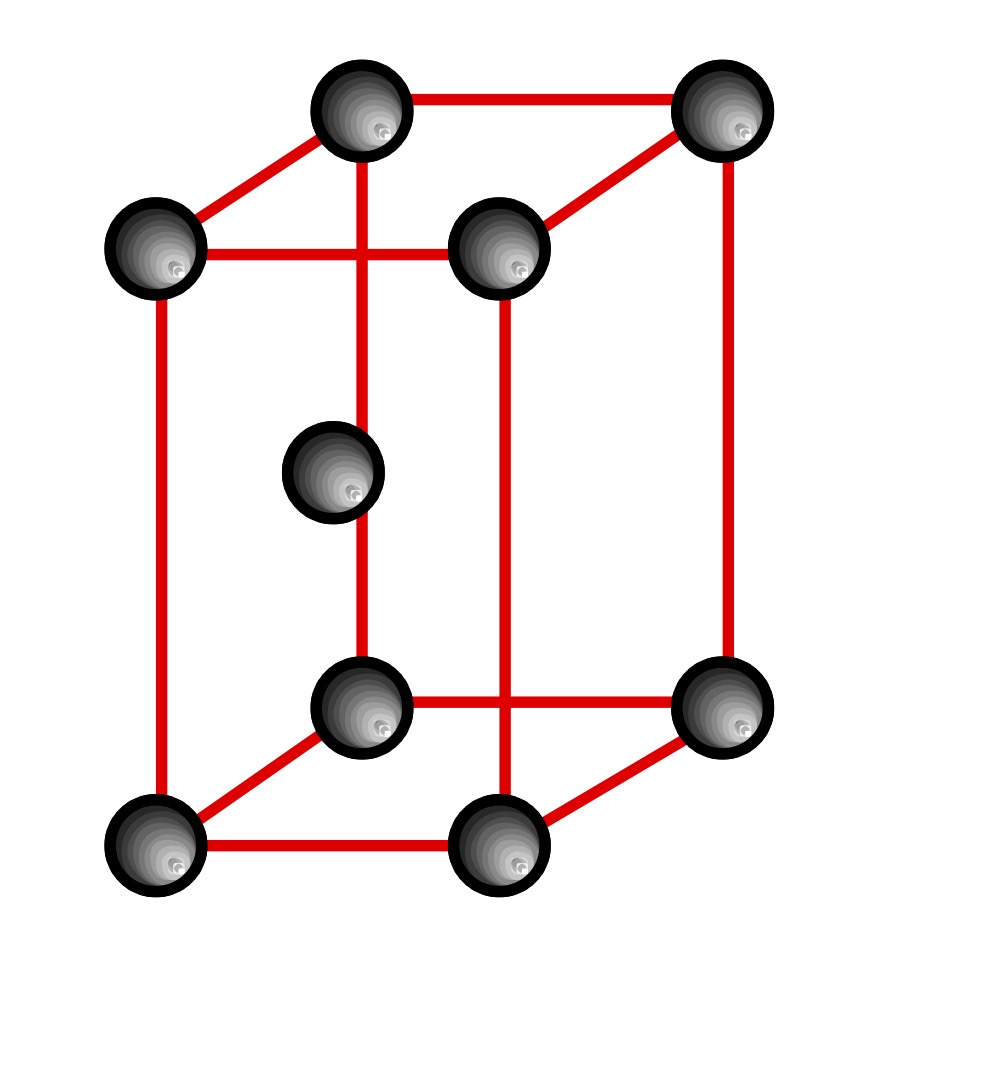
what is a HCP unit cell ?
the smallest parallel-sided volume element of a crystal structure (atom arrangement )
what does a HCP unit cell look like?
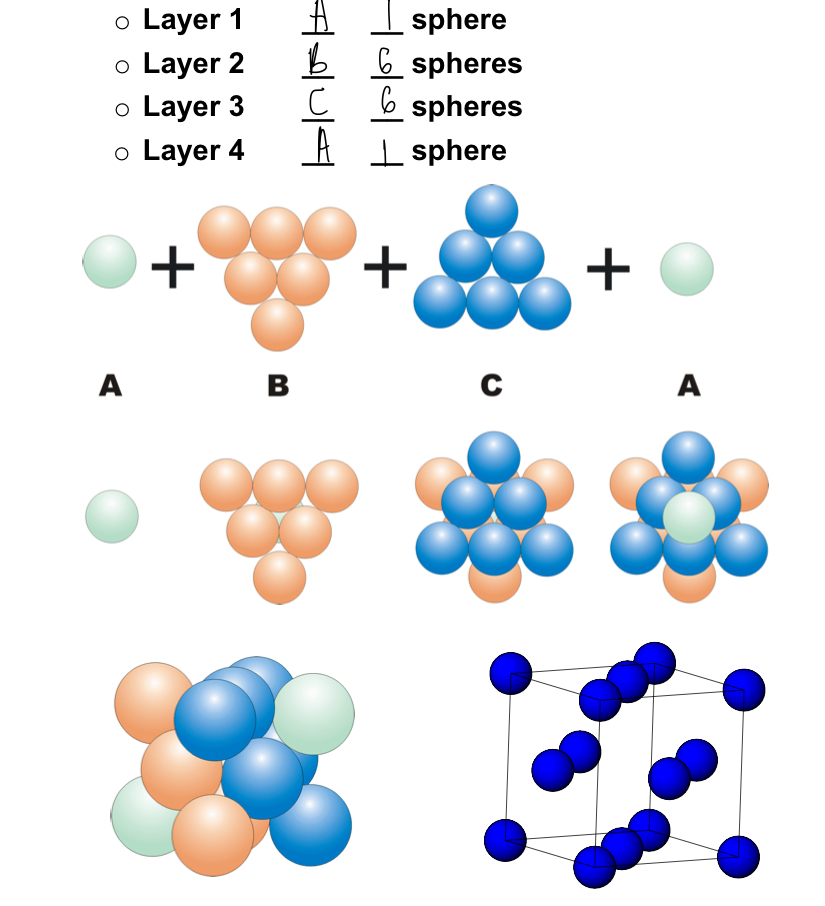
describe close cubic packing? (CCP)
ABC or ABCA
packing sequence of 2
third layer sits over holes in first layer
four layer sits directly over first layer
74% of the total volume is taken up by the spheres
what is a CCP unit cell?
the unit cell sits with one corner on an A layer and four (ABCA ) required to complete the cell
the CCP unit cell is also Face- centred cubic (FCC)
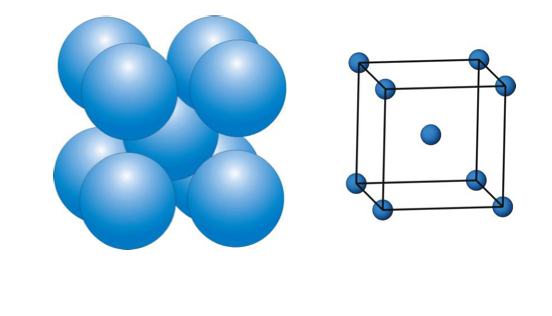
describe the Body-centred cubic (BCC) ?
spheres occupy 68% of the total volume
the arrangement spheres are in layers based on square rows NOT triangular
second layer sits so a sphere is directly over the gap in the first layer and pushes the spheres slightly apart
third layer sists DIRECTLY over first
what is the unit cell for a BCC ( body centred cubic )?
coordination number = 8
what is the overall definition of a unit cell ?
the smallest spatial segment of an entire crystal structure that fully represents the whole structure
what is the coordination number for an atom in a hexagonal close packed structure ?
12
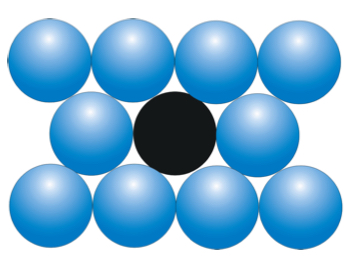
do HCP And CCP have the same coordination numbers ?
YES
what is the coordination number for BCC?
8
what is a crystalline solid
atoms , ions or molecules are in a lattice
have regular arrangement of atoms,ions or molecules
name examples of crystalline solids
NaCl
CuSO4.5H2O
diamond
any metak
what is an amorphous solid ?
non crystalline
atoms, ions or molecules have a random arrangement
similar in character to liquids
name examples of amorphous solids
charcoal , rubber, glass
what are the 5 types of crystalline solids?
atomic
molecular
ionic
metallic
network covalent
what is an atomic crystalline solid held together by and what is the strength of its bonding?
dispersion forces
weak bonding ∴ low melting boiling points
what is an example of an atomic crystalline solid?
noble gases
Identify the forces in molecular solids and their lattice structure
intermolecular forces
i.e dispersion, dipole, dipole, H bonds
lattice structure: lattice points are occupied by individual molecules
give one example of molecular crystalline solid and what is its lattice point
methane in an FCC structure
C on each lattice point
what bonding is an ionic crystalline solid and how is the solid held together?
ionic bonding : electrons are transferred between atoms to form cations and anions
solid is held together by electrostatic forces
give examples of ionic crystalline solids ?
NaCl, AgI , CdS, CaF2, ZnS
what is the structure of crystalline metallic solids and what is it held together by?
sea of electrons surrounding an array of cations held together by electrostatic interactions between electrons and cations
how do metals conduct electricity freely?
via motion of electrons
what is the structure of network covalent crystalline solids?
atoms joined by strong cov bonds enxtending throughout the solid forming a network
what materials do network covalent solids form?
hard rigid materials
give examples of network covalent solids?
diamond
graphite
what packing structure do metals adopt
HCP
CCP ( FCC)
BCC
in metallic structures what does delocalised electrons give rise to?
non directional bonding
why are metallic structures ductile and malleable?
delocalised electrons give rise to non directional bonding
why are metallic structures electrical conductors and thermal conductors?
their electrons are delocalised and mobile
what is an alloy
blend of metals ( and othe elements ) that is prepares by mixing molten components at an atomic level then cooling
what is a solid solution?
a solid with element mixed at the atomic level
what is the role of Zn in brass?
it increases the strength
what is the role of Cu in sterling silver
increases strength
what is the role of each Cr , Ni and C in stainless steel ?
Cr = helps stop corrosion
Ni = increases strength
C= improves strength in a diff way
what is a substitutional alloy ?
atoms of a solute metal randomly occupy sites in the solvent metal lattic
what is the criteria for a substitutional alloy?
metal radii must be similar within 15% of each other
solute metal must tolerate the coordination environment of the host lattice
elctropositivty of two metals must be similar
why must the electropositivity be similar of the two metals in substitutional alloy?
increased likely to be charge transfer and formation of a compound
what is an interstitial alloy?
holes ( interstices) between metals are occupied by another element
26% of space is available even in a close packed structure
what is a crystal structure?
name given to the unit cell and the particular arrangement of atoms within
what is a structure type?
a structure type is a defined arrangement of atoms
what are unit cells defined by?
three vectors ( a,b,c)
α, β and γ
how do you count atoms in a unit cell
by using their positions
corner : 1/8 per unit cell
edge : ¼ per unit cell
face: ½ per unit cell
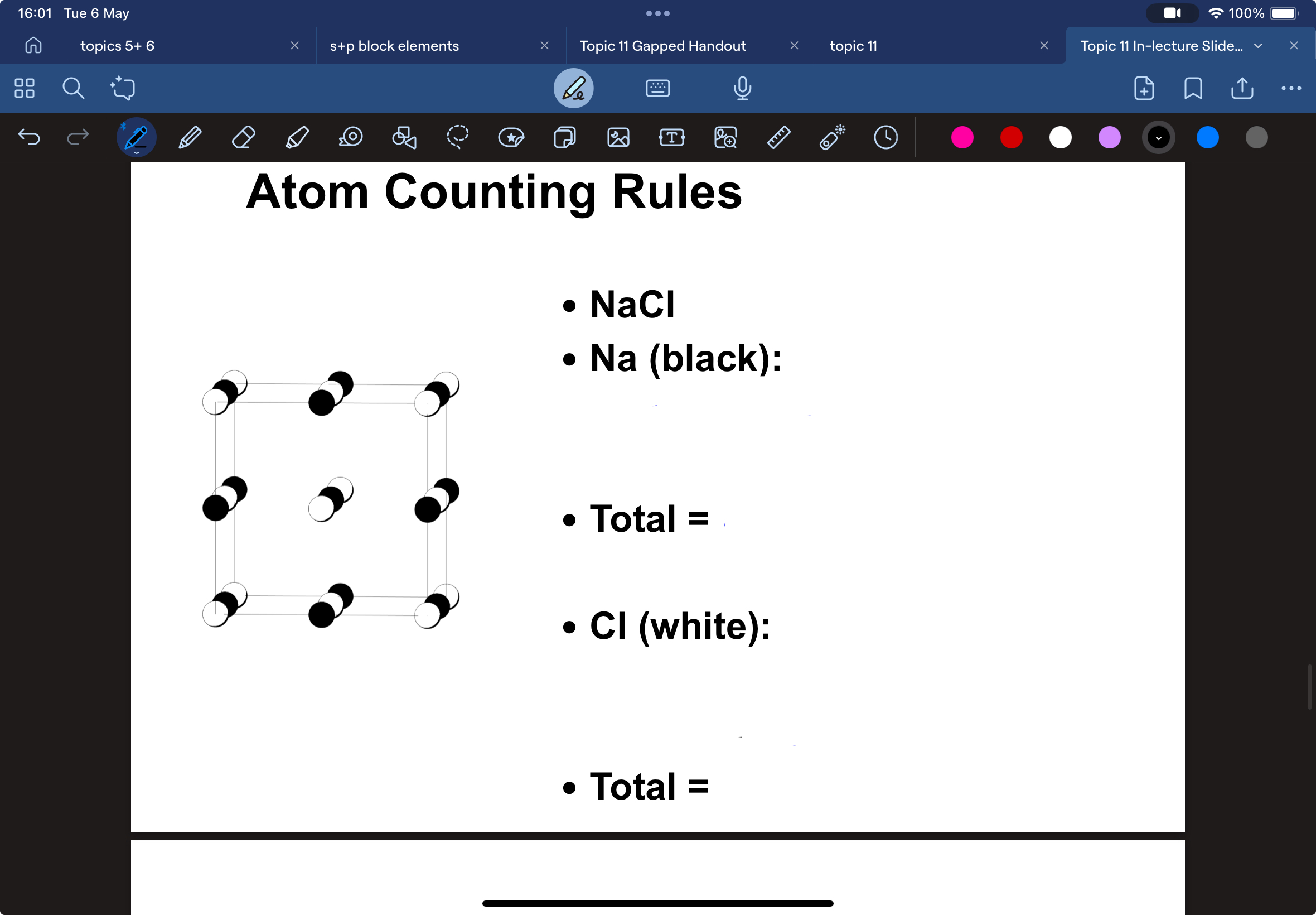
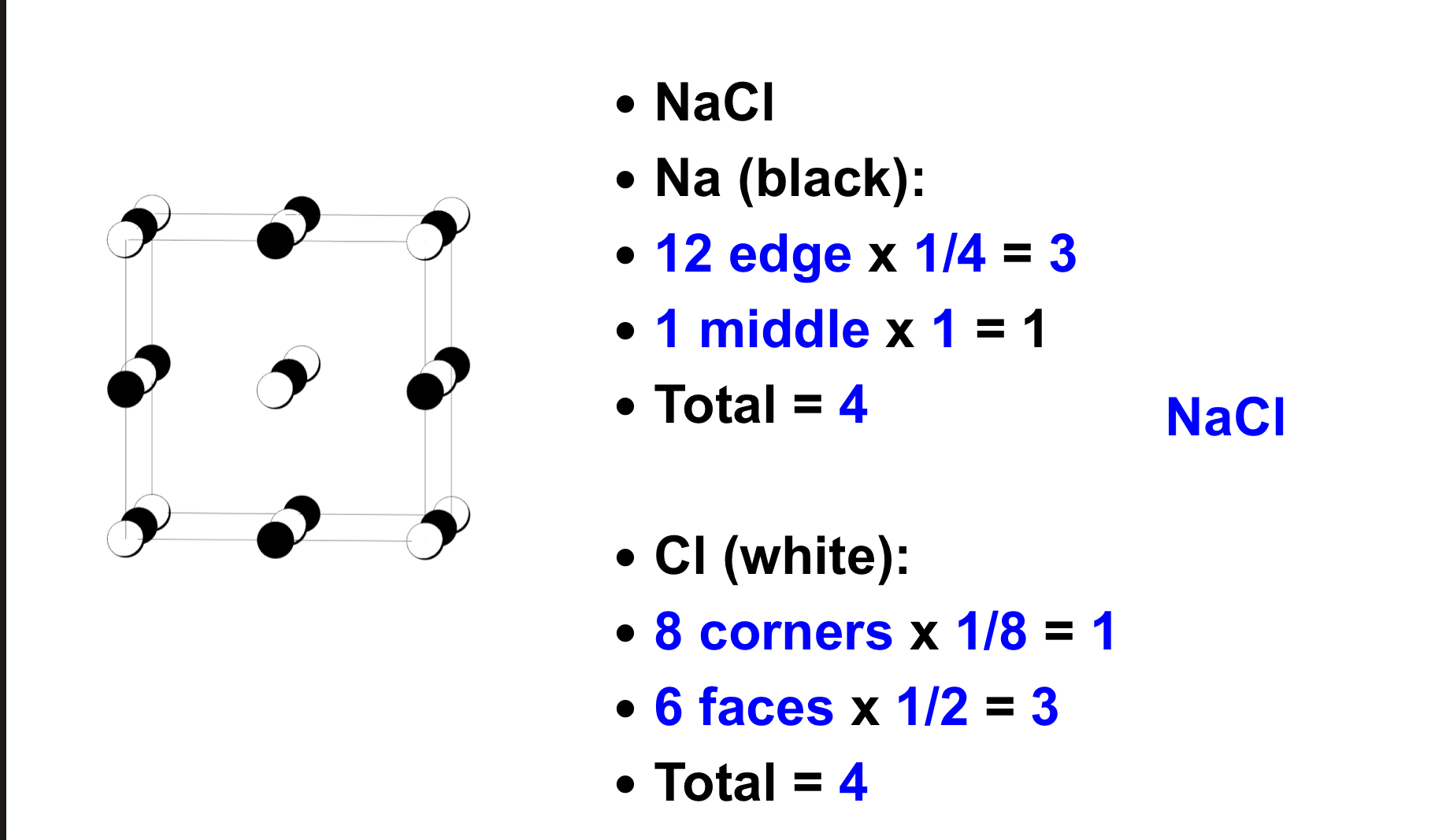
count the atoms of Na and Cl in NaCl
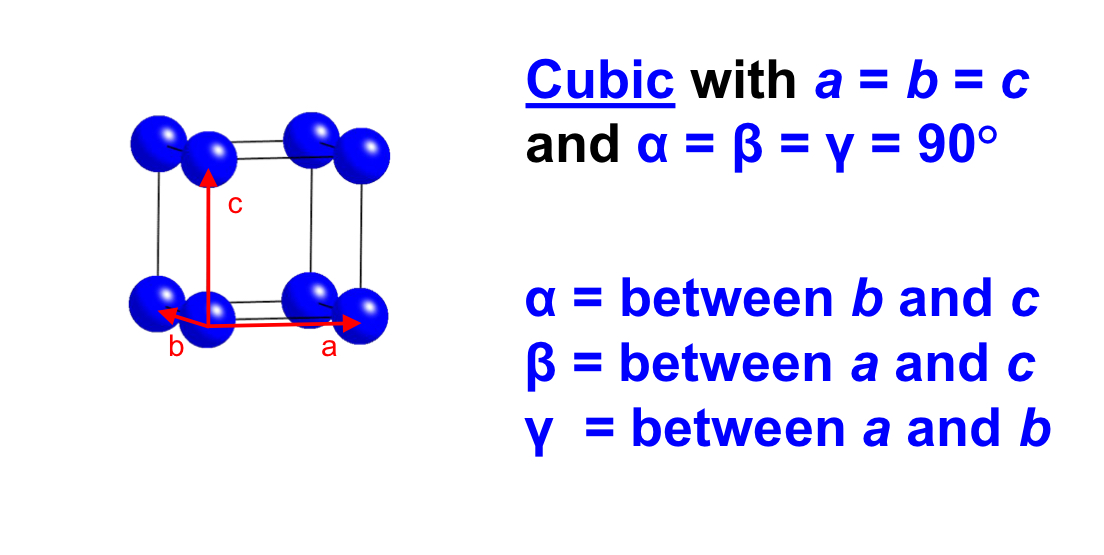
label the angles and sides in a cubic crystal system
Cubic (a = b = c, α = β = γ = 90°)
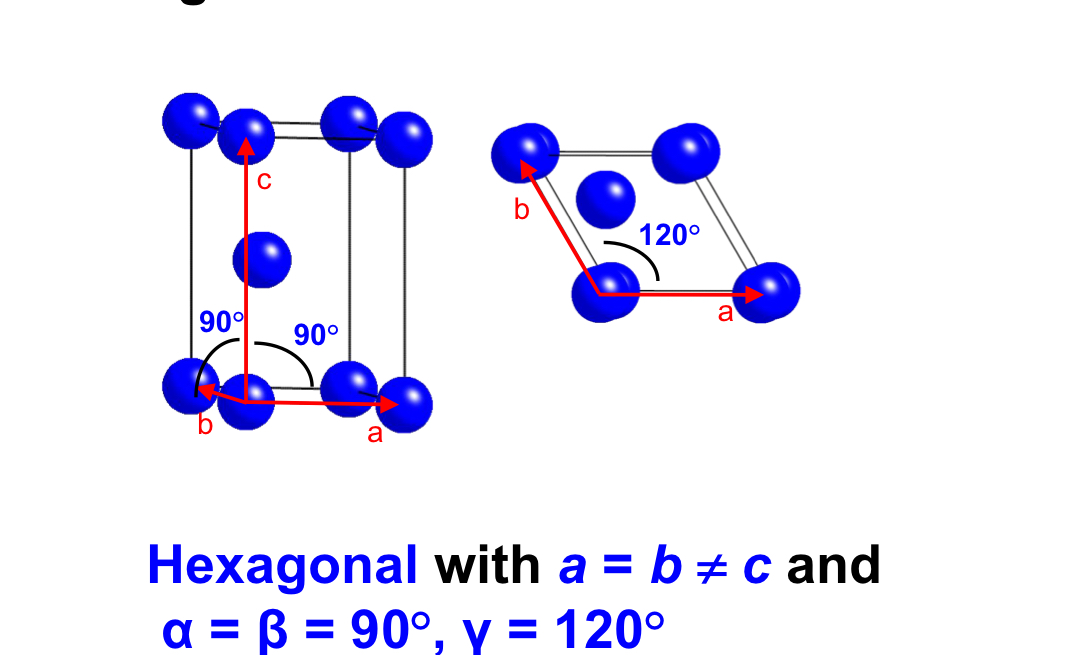
label the angles and sides in a hexagon crystal system
Hexagonal (a = b ≠ c, α = β = 90°, γ = 120°).
what is centring in relation to a unit cell and what does it do?
translational symmetry
it generates new atom positions linked by the structural symmetry of the unit cell
what is a primitive cell?
has lattice points only on the corners of its unit cell
has no centring
EVERY LATTICE SYSTEM has a primitive lattice one within it
What is a Body-Centred Cell?
A body-centred cell (symbol I) has atoms shifted by ½ in all three directions (a,b,c), placing an atom at the body centre of the unit cell.
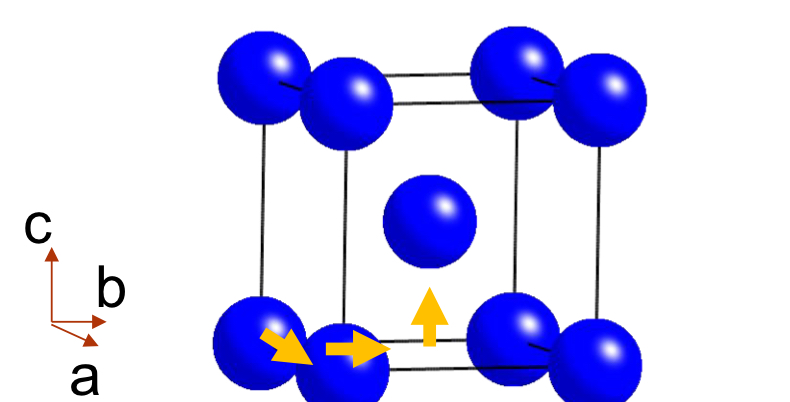
What is the translation vector for a Body-Centred Cell?
(½, ½, ½) — this translates the origin lattice point to the body centre.
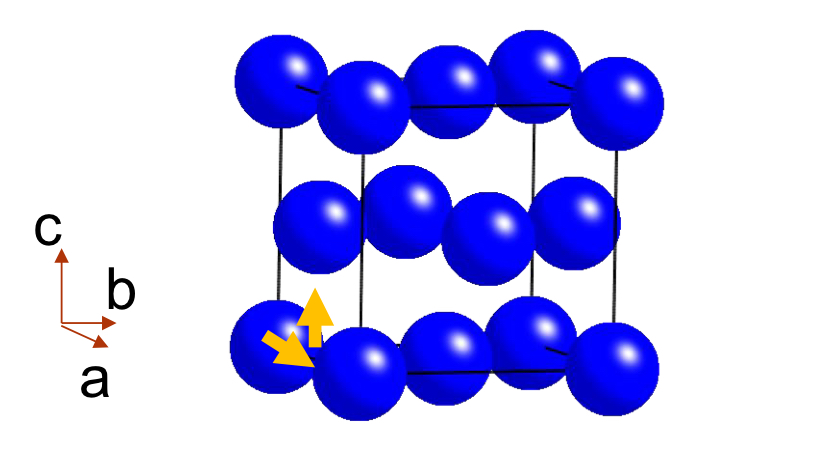
What is a Face-Centred Cell?
: A face-centred cell (symbol F) has atoms shifted by ½ along two axes ( a and b ) , (a and c ) ( b and c )
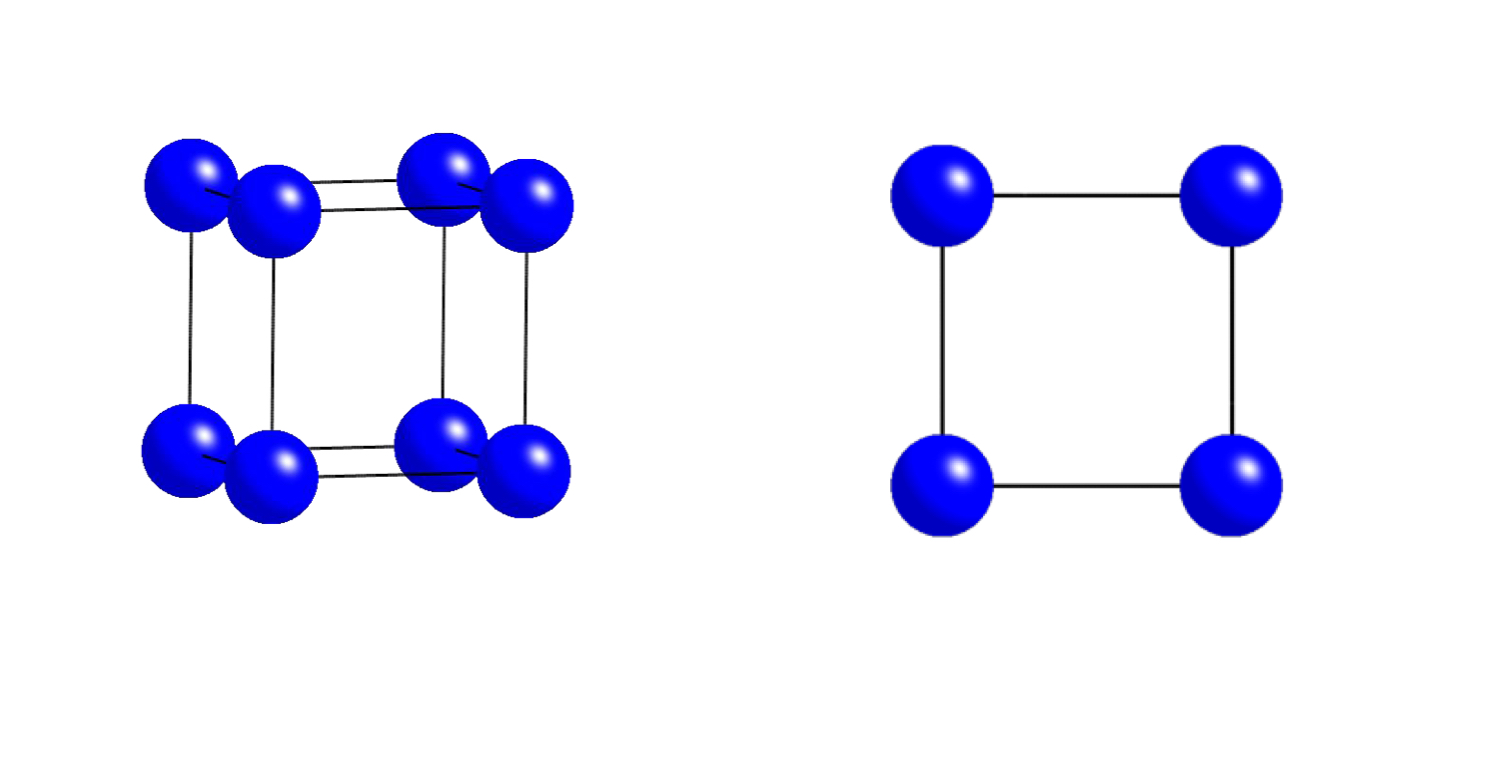
what unit cell does this plan view represent?
primitive (P)
what unit cell does this plan view represent?
body centred cubic (BCC)
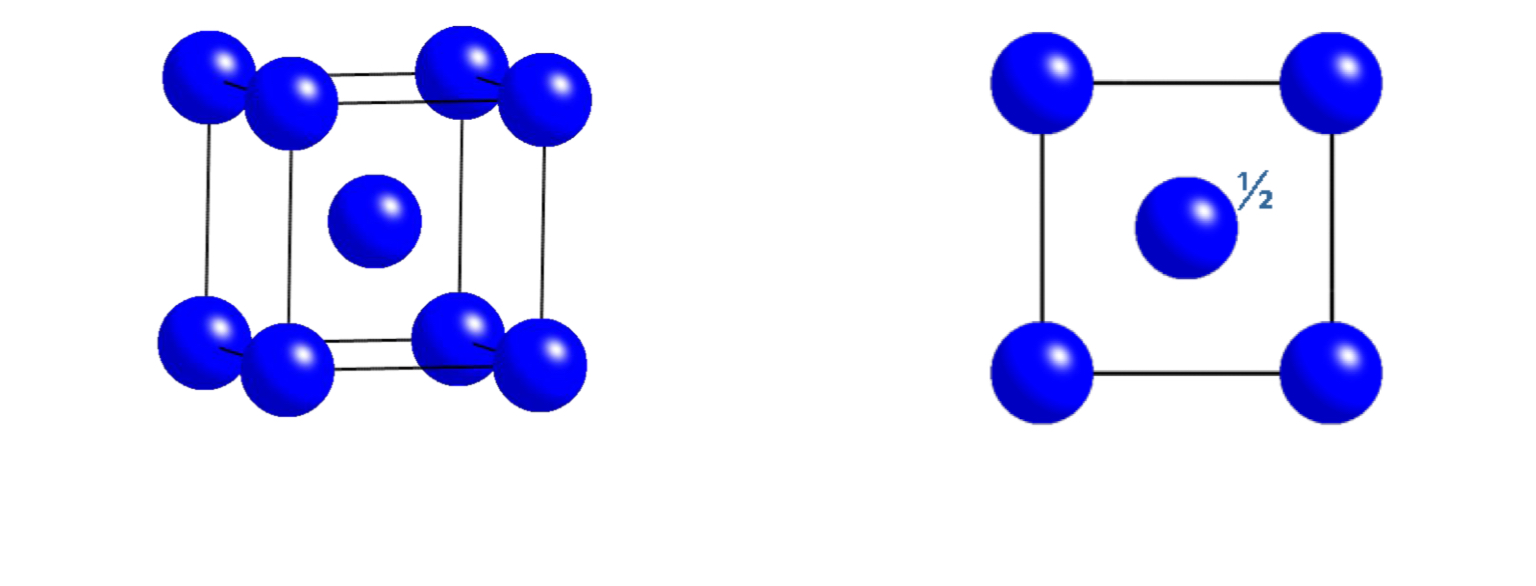
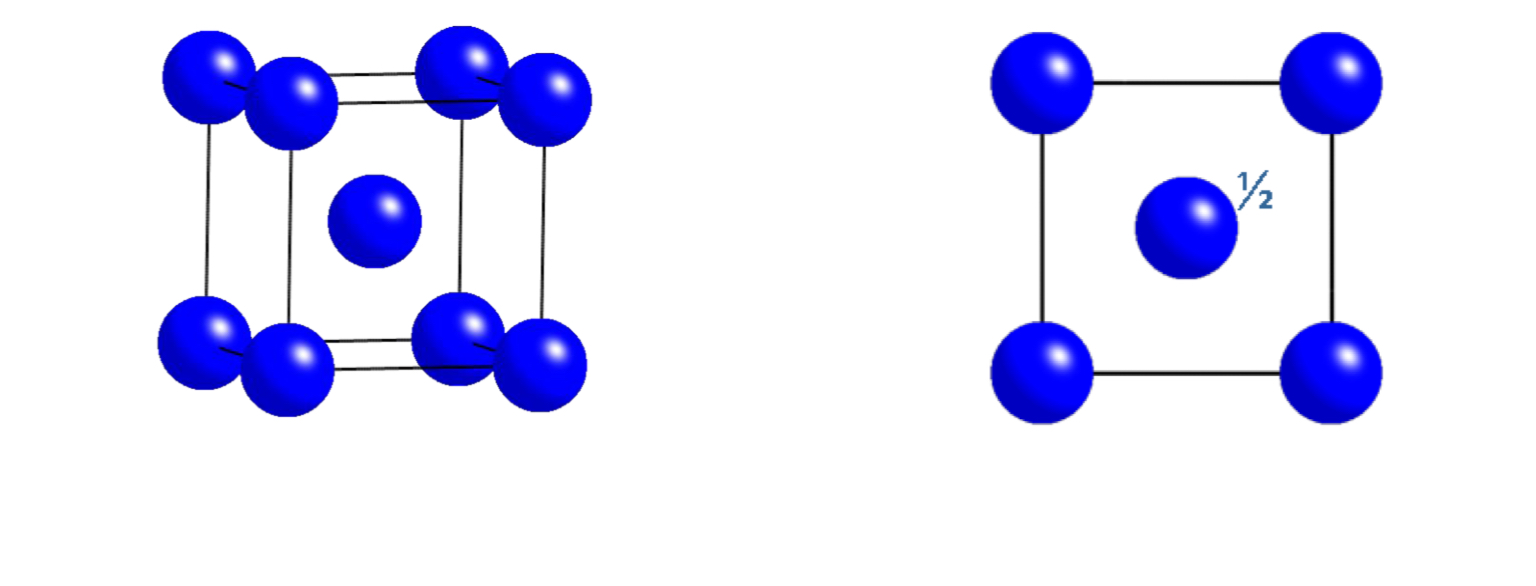
what unit cell does this plan view represent?
face centred cubic (FCC)
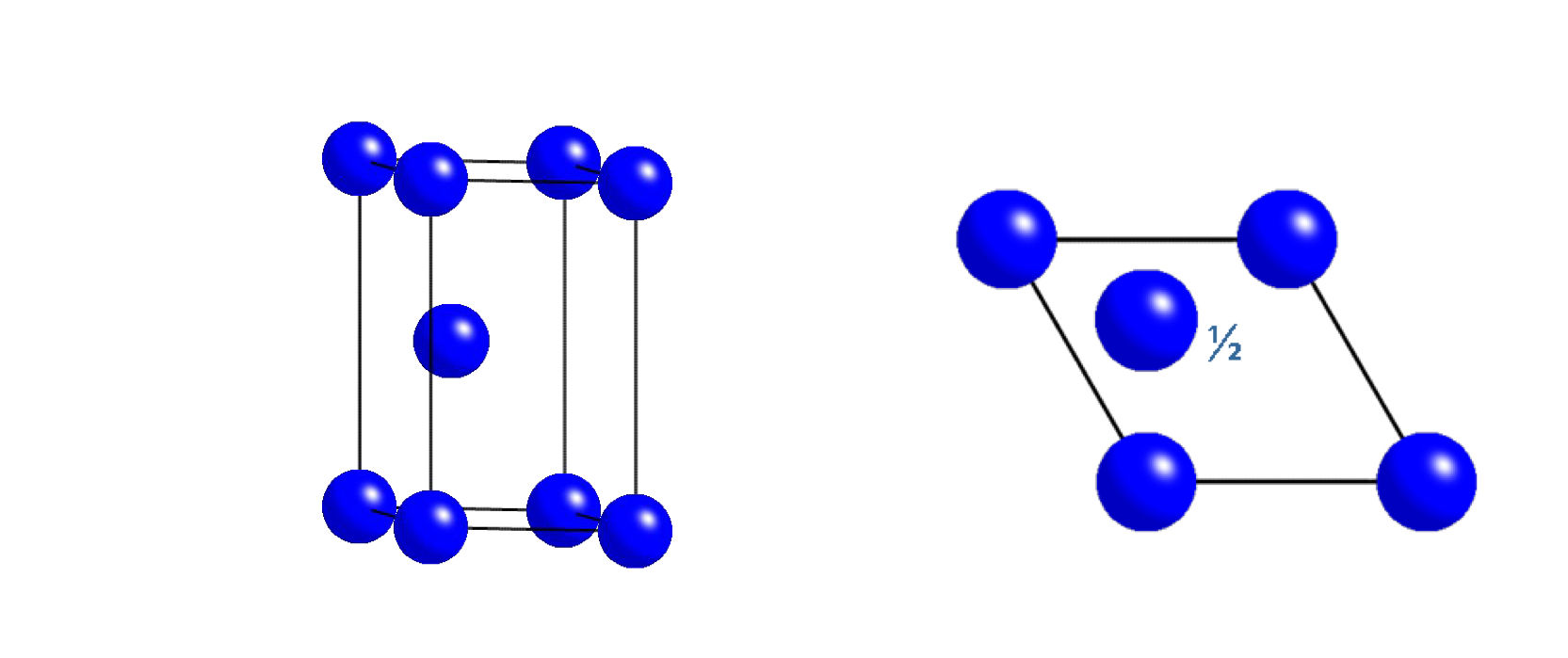
what unit cell does this plan view represent?
hexagonal close packed (HCP)