Urinary System Regulation 7B: GFR, Water Balance, and Hormonal Control
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is the purpose of renal handling in the urinary system?
Renal handling deals with the mechanisms by which various substances are processed by the kidney.
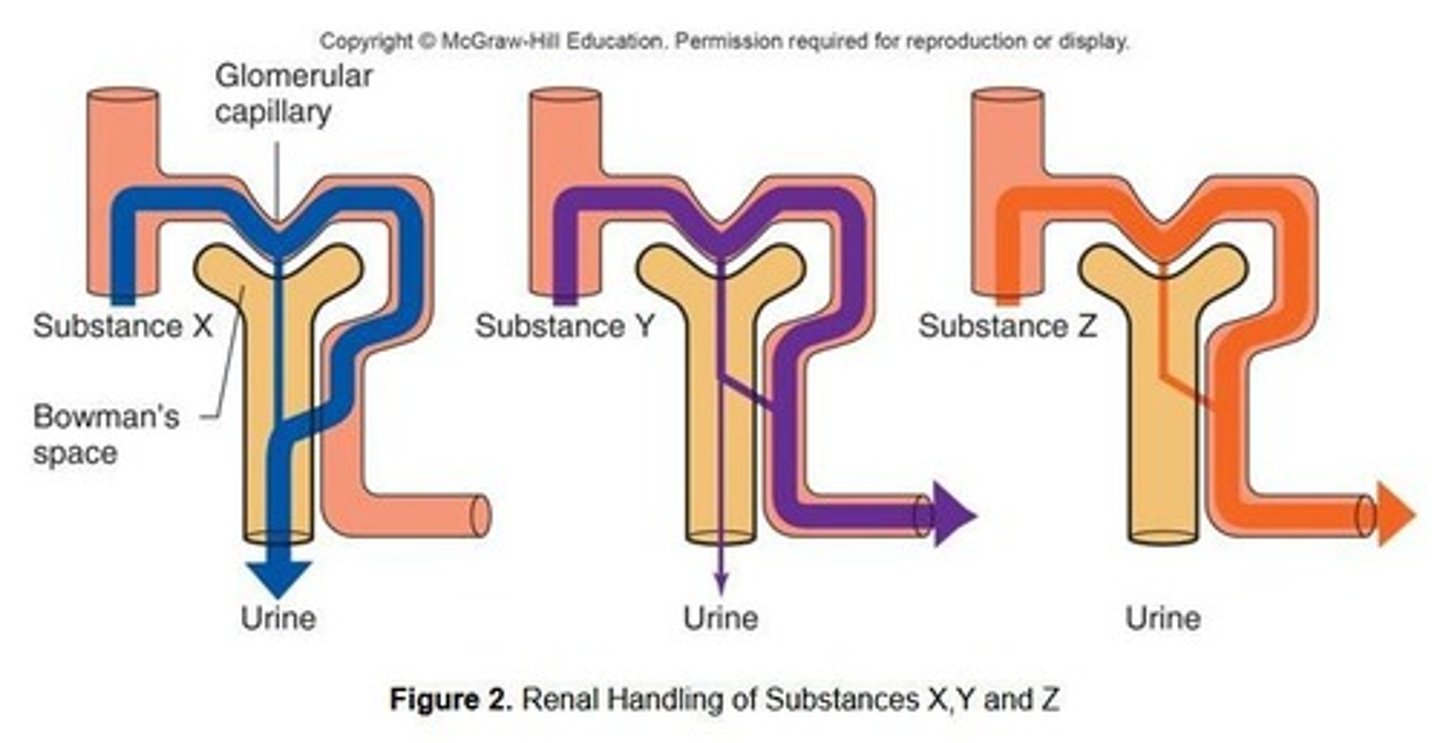
What are the three key questions regarding renal handling of substances?
1. Is the substance filtered out of the blood at the Renal Corpuscle? 2. Is the substance secreted from the peritubular capillaries into the nephron? 3. Is the substance reabsorbed back into the peritubular capillaries from the nephron?
What does renal clearance measure?
Renal clearance measures the rates at which various substances are removed from the blood by the kidney.
Give an example of a substance that is fully secreted by the kidneys.
Penicillin is an example of a substance that is partially filtered but fully secreted.
What is the primary function of inulin in renal studies?
Inulin is used to assess Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) as it is an inert polysaccharide injected and followed in research.
What is the myogenic response in the regulation of nephron function?
The myogenic response involves changes in blood pressure that modify the level of vasoconstriction or vasodilation of the afferent arteriole.
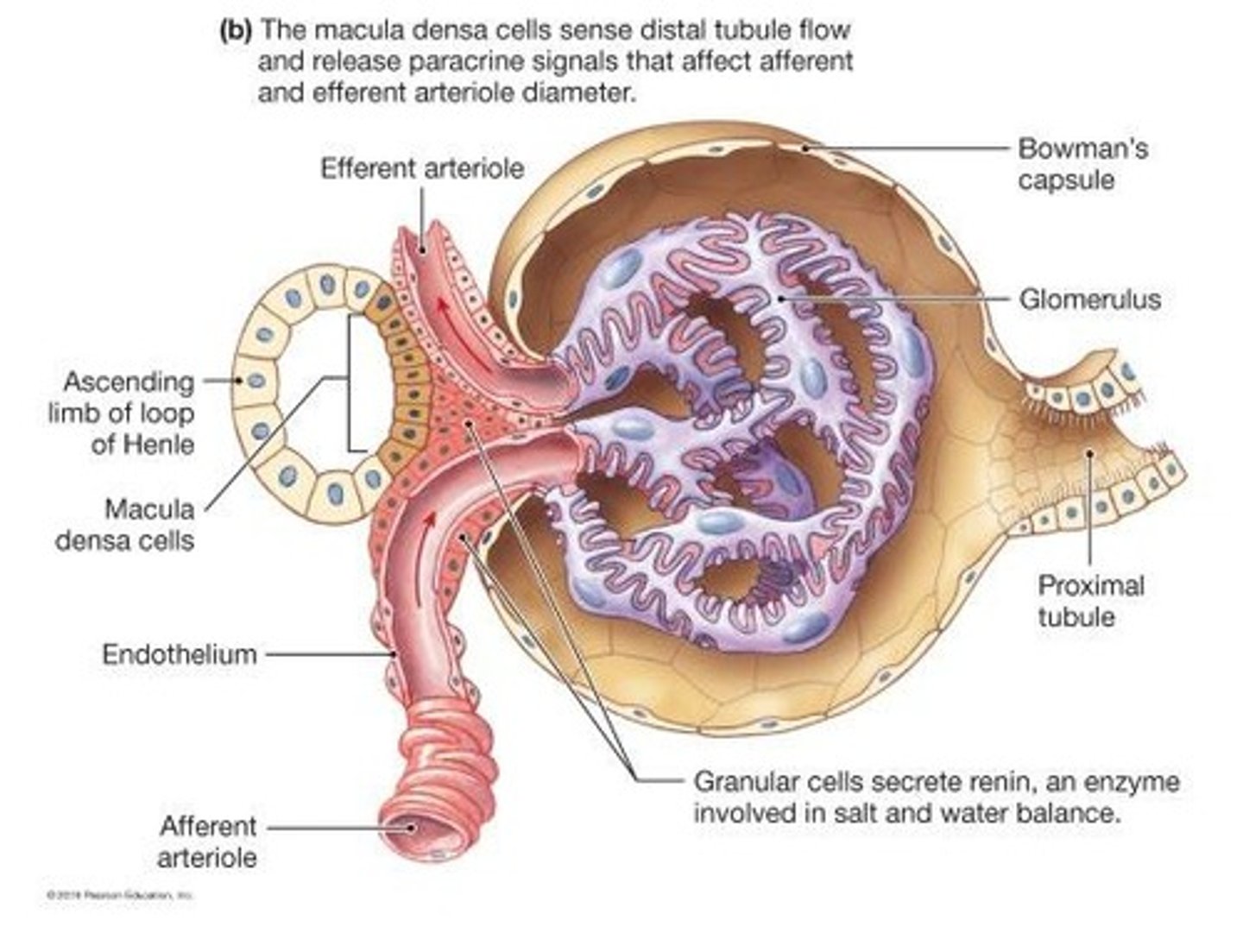
What is the role of the juxtaglomerular (JG) apparatus?
The JG apparatus facilitates communication between the distal convoluted tubule and the afferent arteriole, playing a role in regulating GFR.
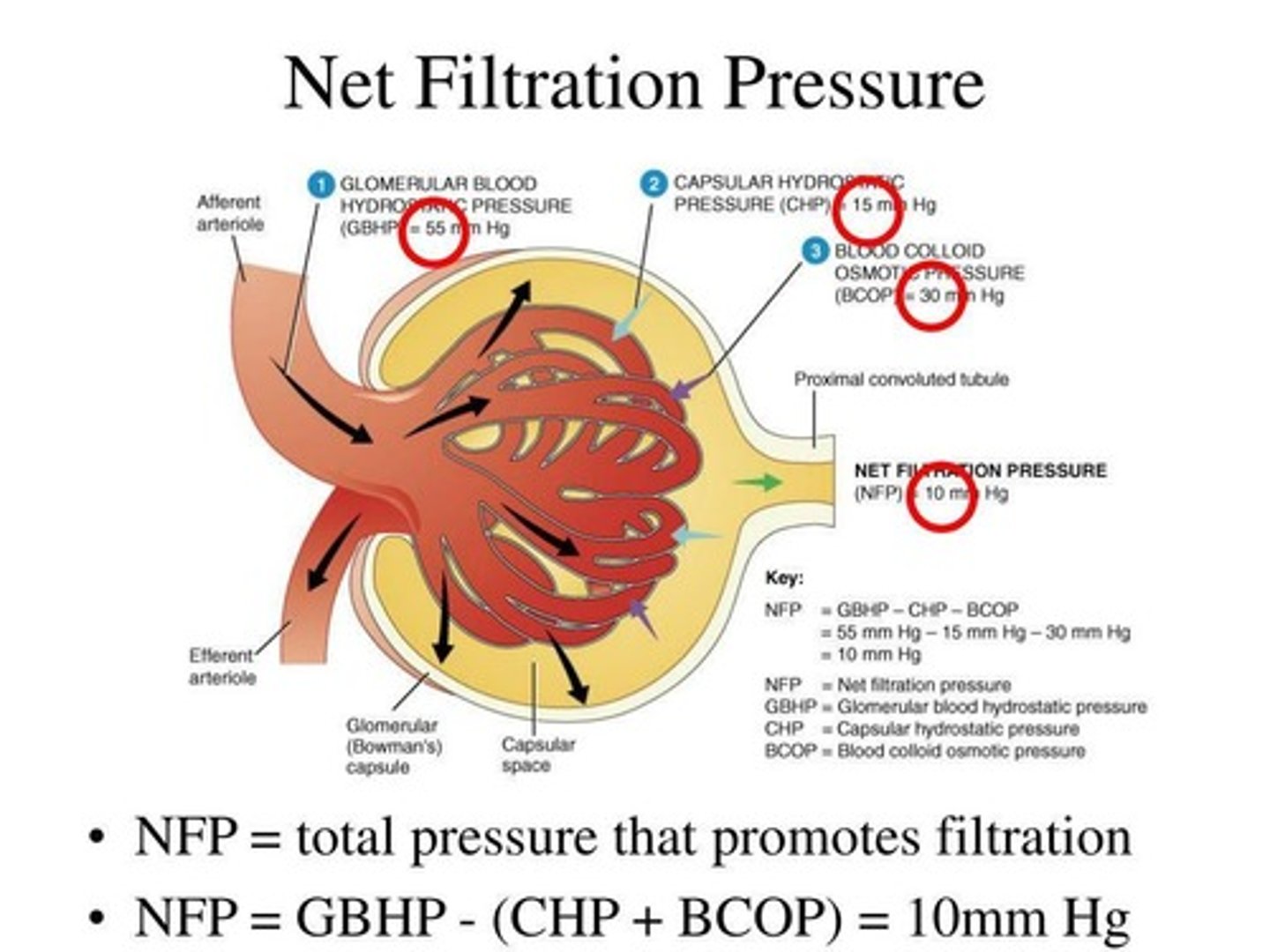
What is net filtration pressure (NFP)?
NFP is the force that drives filtration, determined by the balance of Glomerular Blood Hydrostatic Pressure, Capsular Hydrostatic Pressure, and Blood Colloid Osmotic Pressure.
How does increased systemic blood pressure affect glomerular filtration?
Increased systemic blood pressure causes transient increases in afferent arteriole blood pressure, leading to constriction and decreased glomerular filtration rate to protect the capillaries.
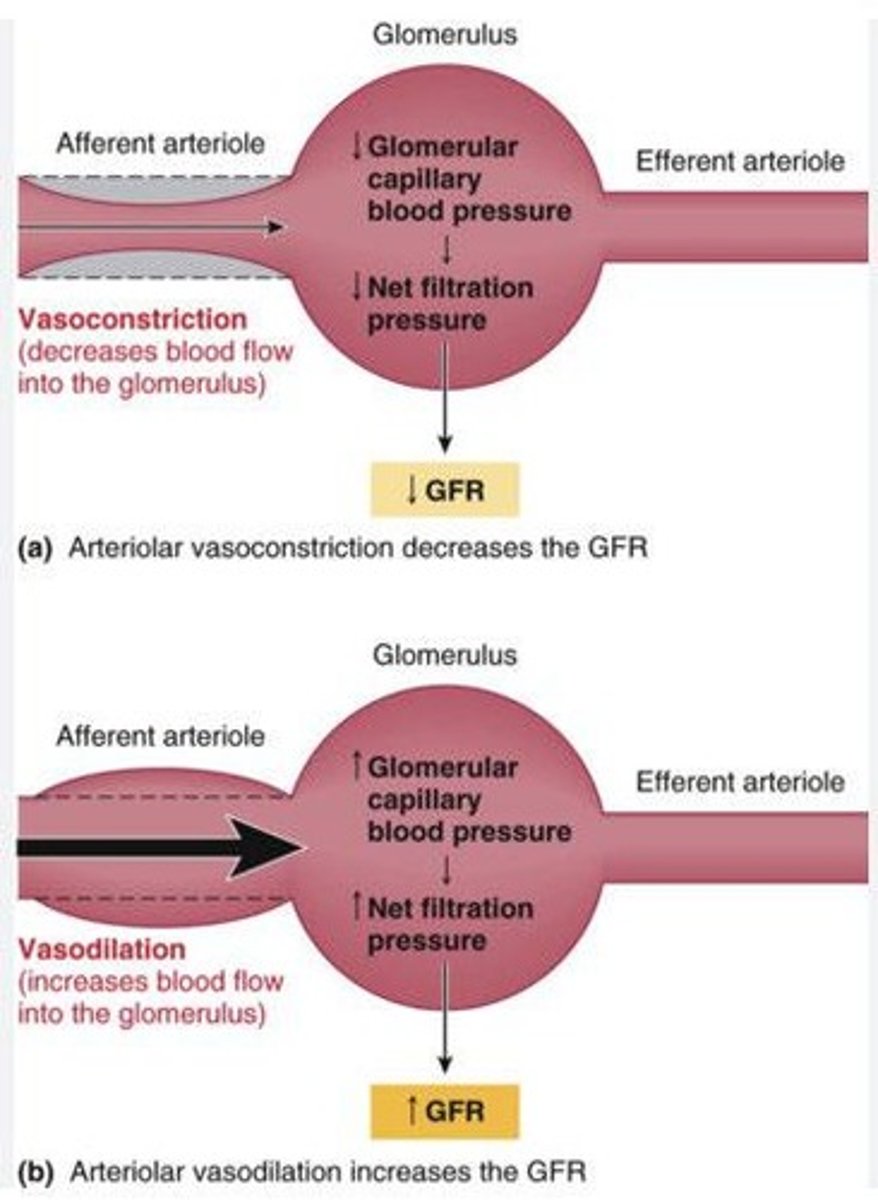
What happens to glomerular filtration rate during sympathetic nervous system activation?
Increased sympathetic nervous system activation causes afferent arteriole constriction, decreasing glomerular filtration pressure and rate.
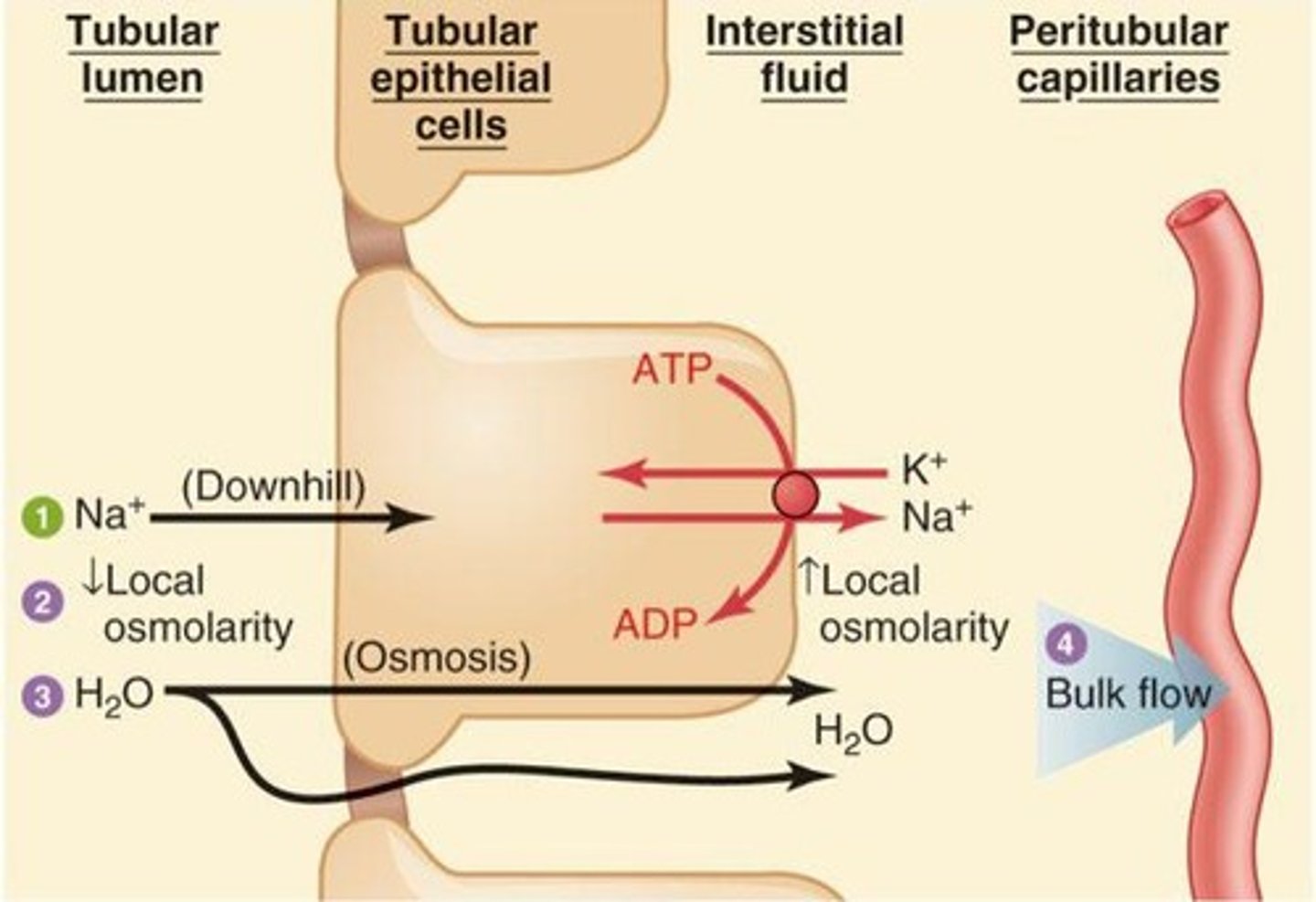
What is the primary mechanism for water reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule?
Water is reabsorbed passively following the sodium gradient from the lumen to the interstitial space and into the peritubular capillaries.
What hormone regulates water reabsorption in the collecting duct?
Vasopressin (ADH) regulates water reabsorption in the collecting duct.
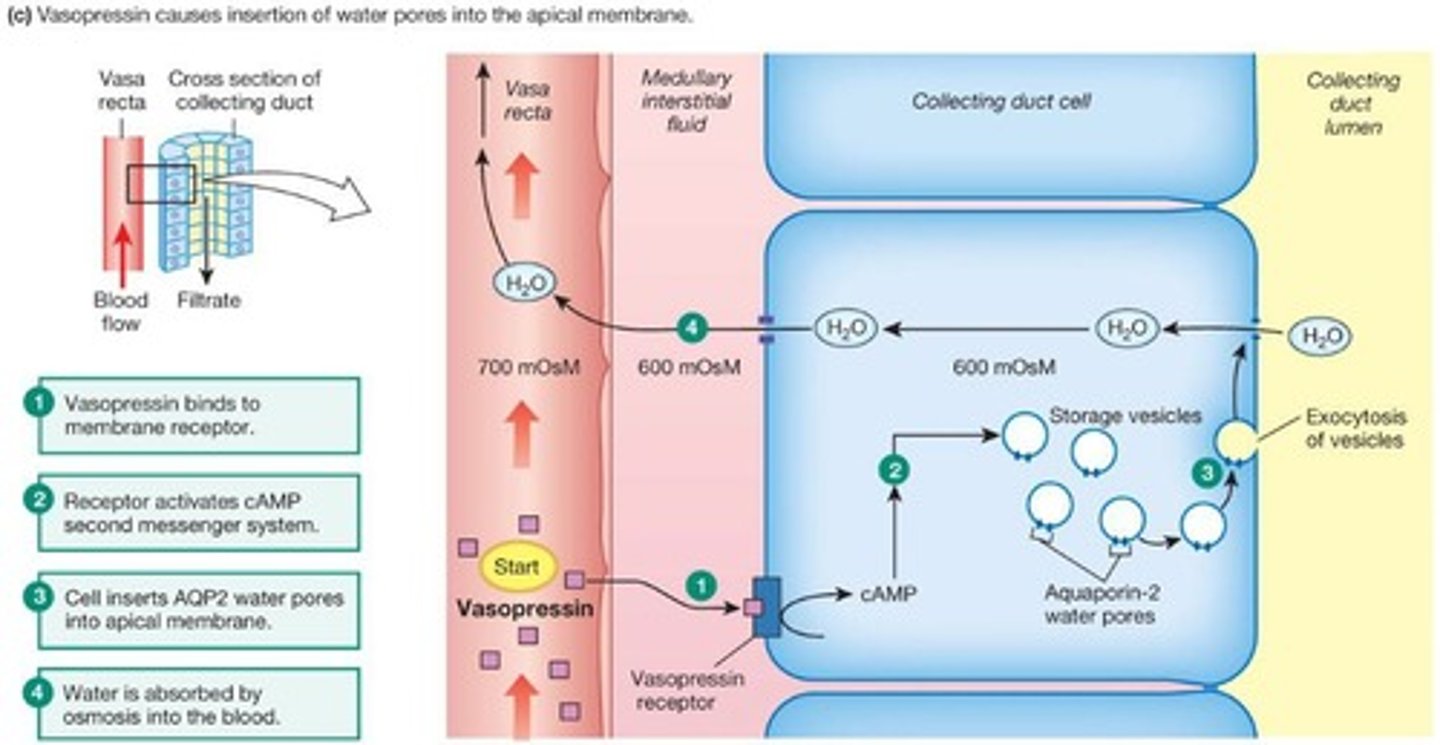
What factors increase the secretion of vasopressin?
Hypovolemia (low fluid volume) and hypernatremia (elevated sodium levels) increase vasopressin secretion.
What is the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system's role in blood pressure regulation?
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system responds to low fluid volume and blood pressure, promoting retention of sodium and water to increase blood pressure.
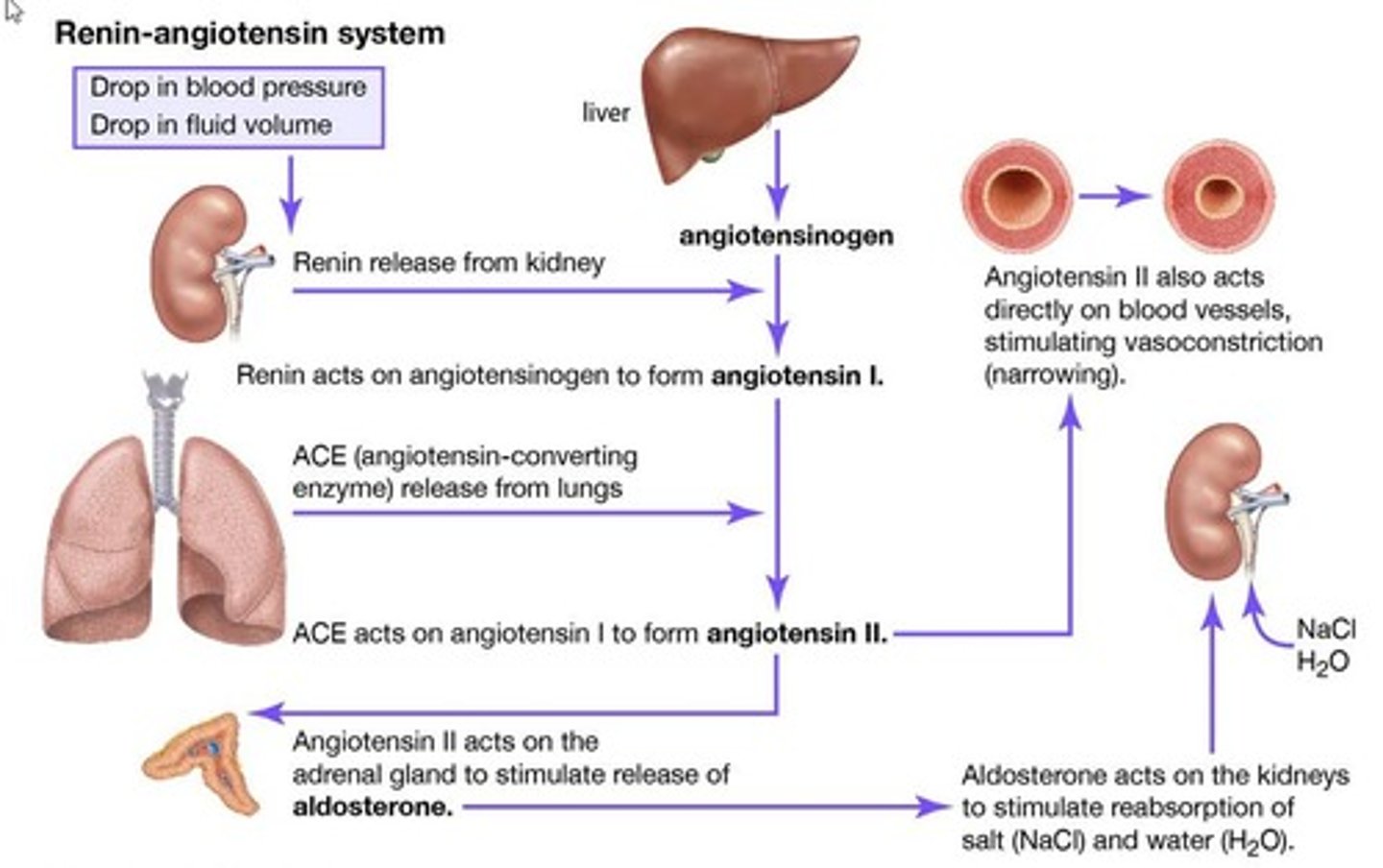
What is aldosterone and where is it produced?
Aldosterone is a steroid hormone produced in the adrenal cortex that increases sodium reabsorption in the kidneys.
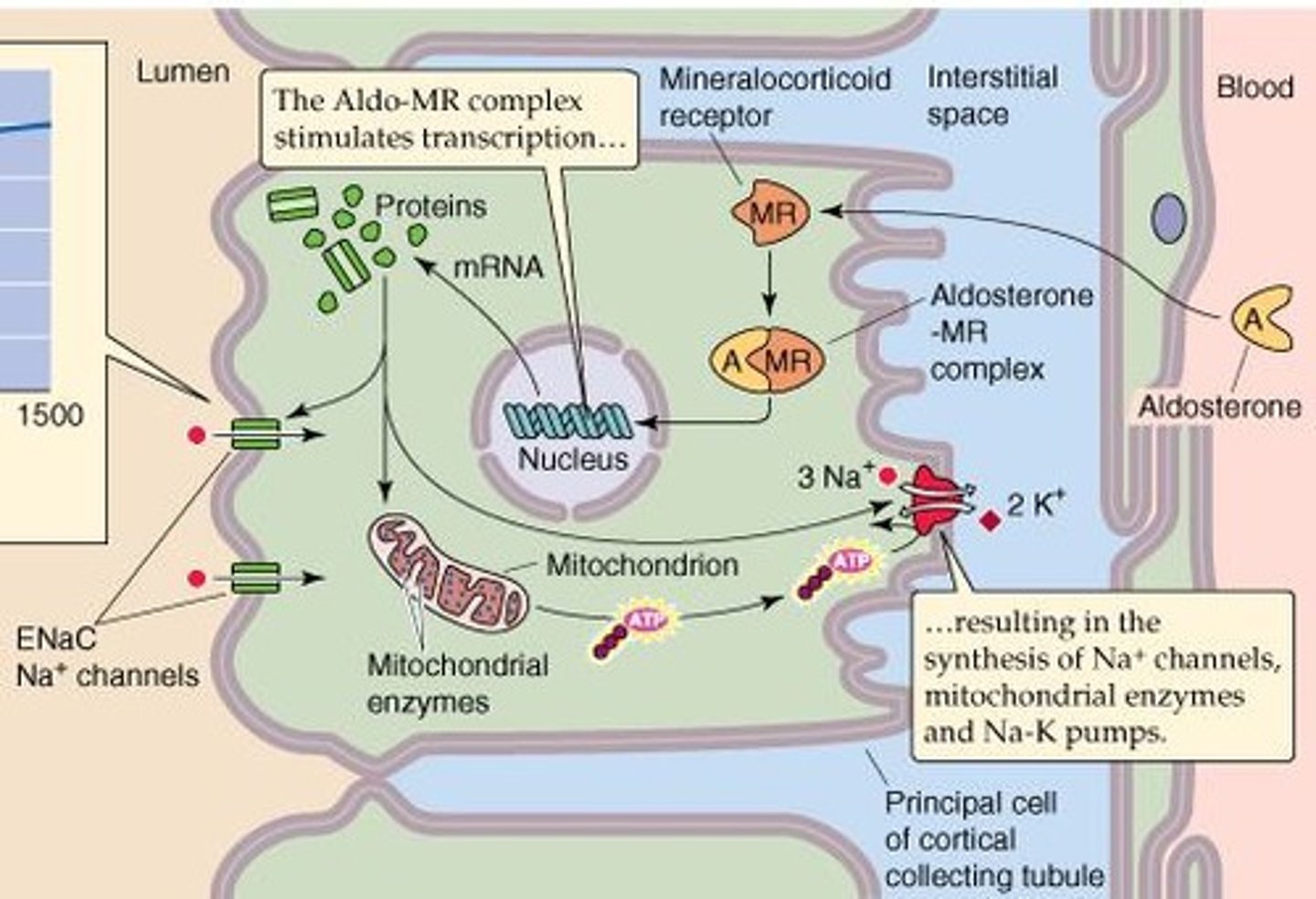
How does aldosterone affect sodium and water retention?
Aldosterone increases the expression of sodium channels and Na+/K+ pumps, enhancing sodium reabsorption and consequently increasing water retention.
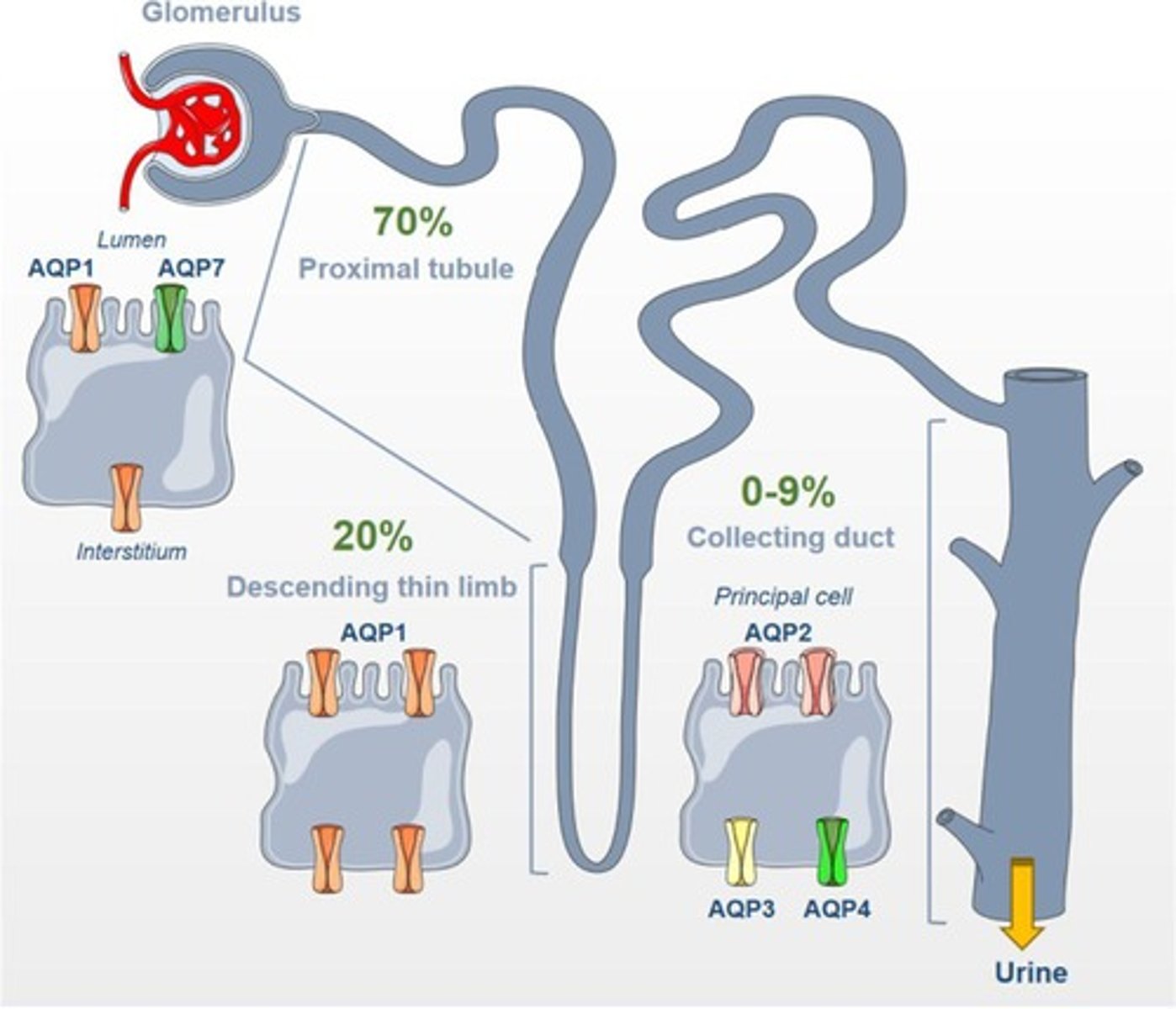
What is the significance of aquaporins in the urinary system?
Aquaporins are integral membrane proteins that facilitate the passive movement of water across cell membranes, crucial for water reabsorption.
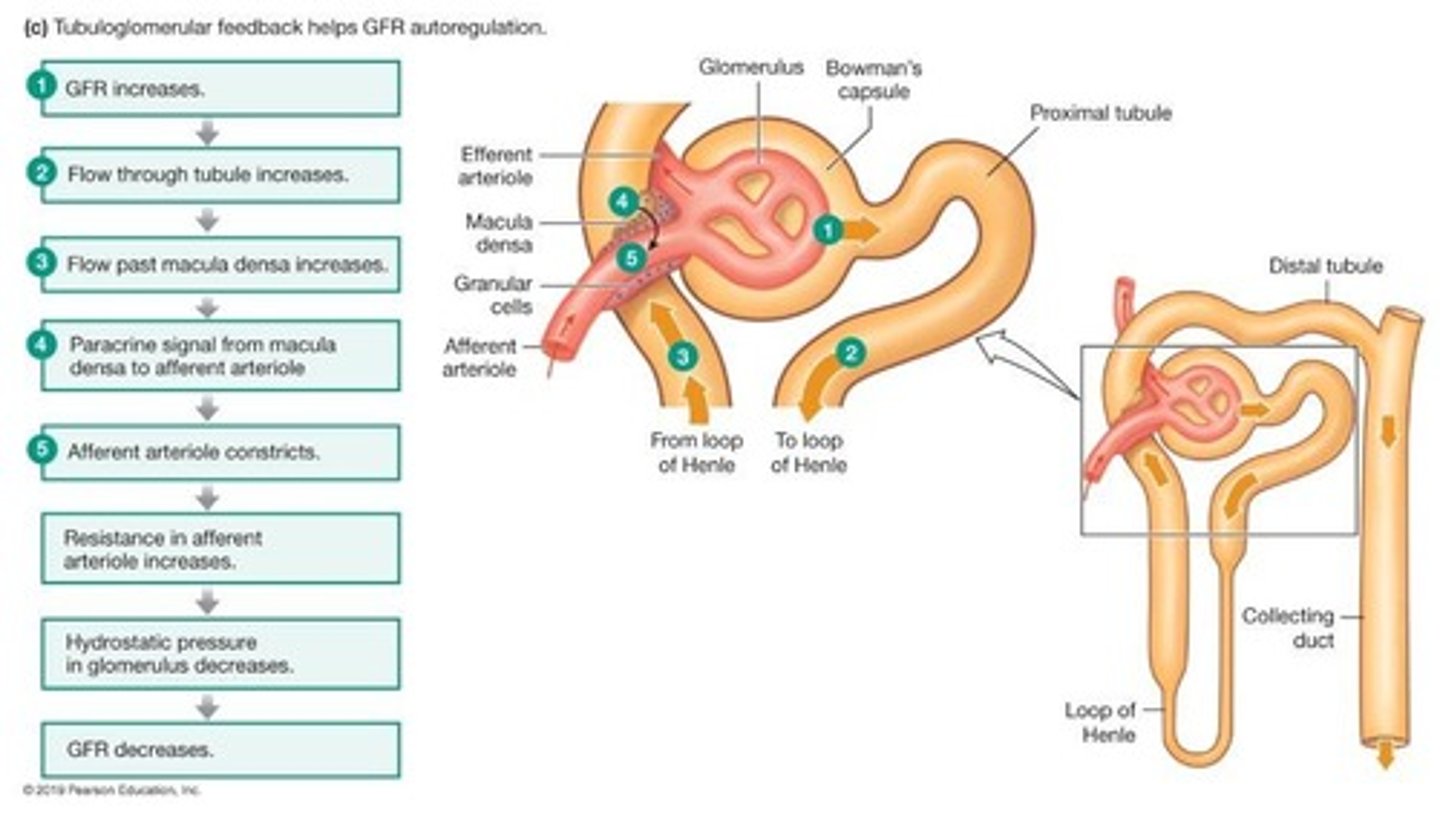
How does tubuloglomerular feedback regulate GFR?
Tubuloglomerular feedback involves the macula densa cells detecting increased NaCl in the distal convoluted tubule, leading to afferent arteriole constriction and normalization of GFR.
What is the effect of decreased systemic blood pressure on glomerular filtration?
Decreased systemic blood pressure causes afferent arteriole dilation, increasing glomerular capillary pressure and glomerular filtration rate.
What is the primary site for water reabsorption in the nephron?
About 70% of water is reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule.
What is the role of the macula densa in renal function?
The macula densa cells respond to changes in sodium chloride concentration, influencing the regulation of glomerular filtration rate.
What is the impact of vasopressin on urine volume?
Vasopressin decreases urine volume by increasing water reabsorption in the kidneys.
What are the two main mechanisms for regulating water reabsorption at the collecting duct?
1. ADH (vasopressin) 2. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System.
What happens to urine volume during the 'fight or flight' response?
During the 'fight or flight' response, sympathetic activation decreases urine volume by constricting the afferent arteriole.
What is the consequence of increased glomerular capillary pressure?
Increased glomerular capillary pressure assures adequate filtration despite low systemic blood pressure.