Honors Chemistry - Unit 2: Atoms, Isotopes, Periodic Table
1/48
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Democritus
around 400 BC, proposed that matter was made of small, hard, and indivisible particles called atoms. no real evidence, not widely believed

Dalton
1803 - 1808 - defined atom. atom was indivisible, and matter is made of atoms. atoms of one element are identical.

Thomson
1904 - “Plum Pudding” model of the divisible atom. discovered the existence of the electron.
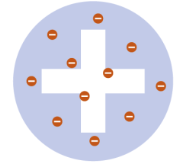
Rutherford
1911 - gold foil experiment. atom had a very small, positively charged nucleus containing most of the mass. electron # = proton # and electrons move around the nucleus.

Bohr
1913 - “Planetary” model. electrons move around the nucleus in fixed orbits. electrons can move to different orbits based on energy level.
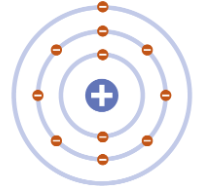
Present model
electrons occupy orbitals which are volumes of space around the nucleus. different energy levels and sublevels which contain sets of orbitals.

matter
anything that has mass and takes up volume
what are physical properties?
a characteristic of a substance that can be seen or observed without changing the identity of the substance
what are chemical properties?
describes the ability of a substance to undergo a specific chemical change
chemical property ex.
corrosiveness, rusting, acidity, toxicity, flammability
physical property ex.
color, odor, melting & boiling point, density, taste
element
a pure substance that cannot be broken down further than it is
compound
two or more elements chemically combined. the elements lose their identities and take on new properties.
mixture
two or more substances physically combined together
Law of Conversion of Matter
matter cannot be created or destroyed, only changed.
physical change
changing the form of particles without changing what the substances are made of. usually reversible
physical change ex.
melting, evaporating, condensing, freezing
chemical change
two or more different substances combine/break apart to form a new, different substance. usually NOT easily reversible.
atom
basic unit of an element that still retains the properties of that element
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus
atomic mass
number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
isotope
same element but a different number of neutrons/mass
average atomic mass
weighted average mass of an atom based on abundance.
valence electrons
electrons in the outer most energy level/shell which are involved in bonds and reactions
ions
atoms without a charge
octet rule
all atoms “want” 8 valence electrons
duet rule
1st energy level has 2 electrons
cation
PAWsitively charged atom (lost electrons)
anion
onions = tears. negative charged atom (gained electrons)
metal characteristics
lustrous (shiny). malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity, high melting point
nonmetals
not lustrous, brittle if solid, poor conductors of heat and electricity, low melting points, can be any state of matter at room temperature
transition metals
elements in the middle of the table. changed from metallic properties to nonmetallic properties.
metalloids
have both metallic and nonmetallic properties
alkali metal properties
extremely reactive (especially in water), silver colored and shiny, density is extremely low.
alkaline earth metal properties
slightly less reactive than alkali metals, silver colored and harder than alkali.
transition metal properties
moderate range of reactivity and a wide range of properties. usually shiny and good conductors of heat and electricity, higher densities and melting points than groups 1 & 2.
lanthanides and actinides properties
transition metals, elements in each of the two periods share many properties. lanthanides are shiny and reactive. all actinides are radioactive and unstable.
halogen properties
all nonmetals, very reactive, poor conductors of heat and electricity, form salts with metals.
noble gases
unreactive nonmetals, colorless, odorless gases at room temperature. all found in earth’s atmosphere. stable and don’t combine with other elements.
group 1A
alkali metals
group 2A
alkaline earth metals
group B
transition metals
group B at the bottom
lanthanides and actinides
group 7A
halogens
group 8A
noble gases
Aufbau principle
electrons enter orbitals of lowest energy first
Pauli exclusion principle
an atomic orbital can only have a max of two electrons
Hund’s rule
when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy level, one electron enters each orbital until all orbitals contains one e- with parallel spin
most reactive nonmetals
halogens