The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lab
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
cerebrum
cerebral hemispheres
left and right (anatomical position)
divided down the middle by the longitudinal fissure.
cerebral cortex
Outer layer or cerebrum (gray matter - cell bodies/unmyelinated axons)
gyri
thick wrinkles of the brain.
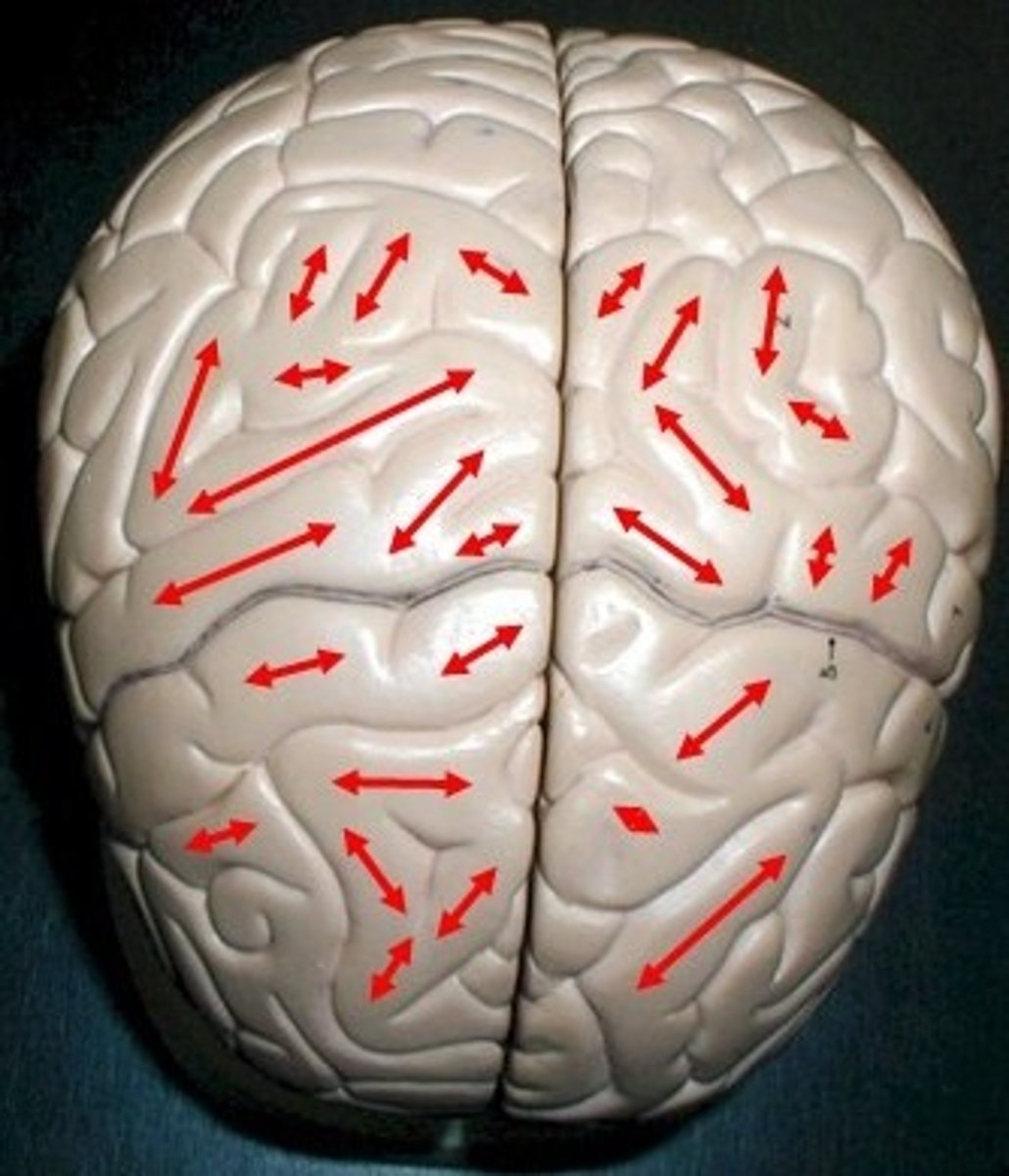
gyrus
one gyri. one thick wrinkle of the brain.
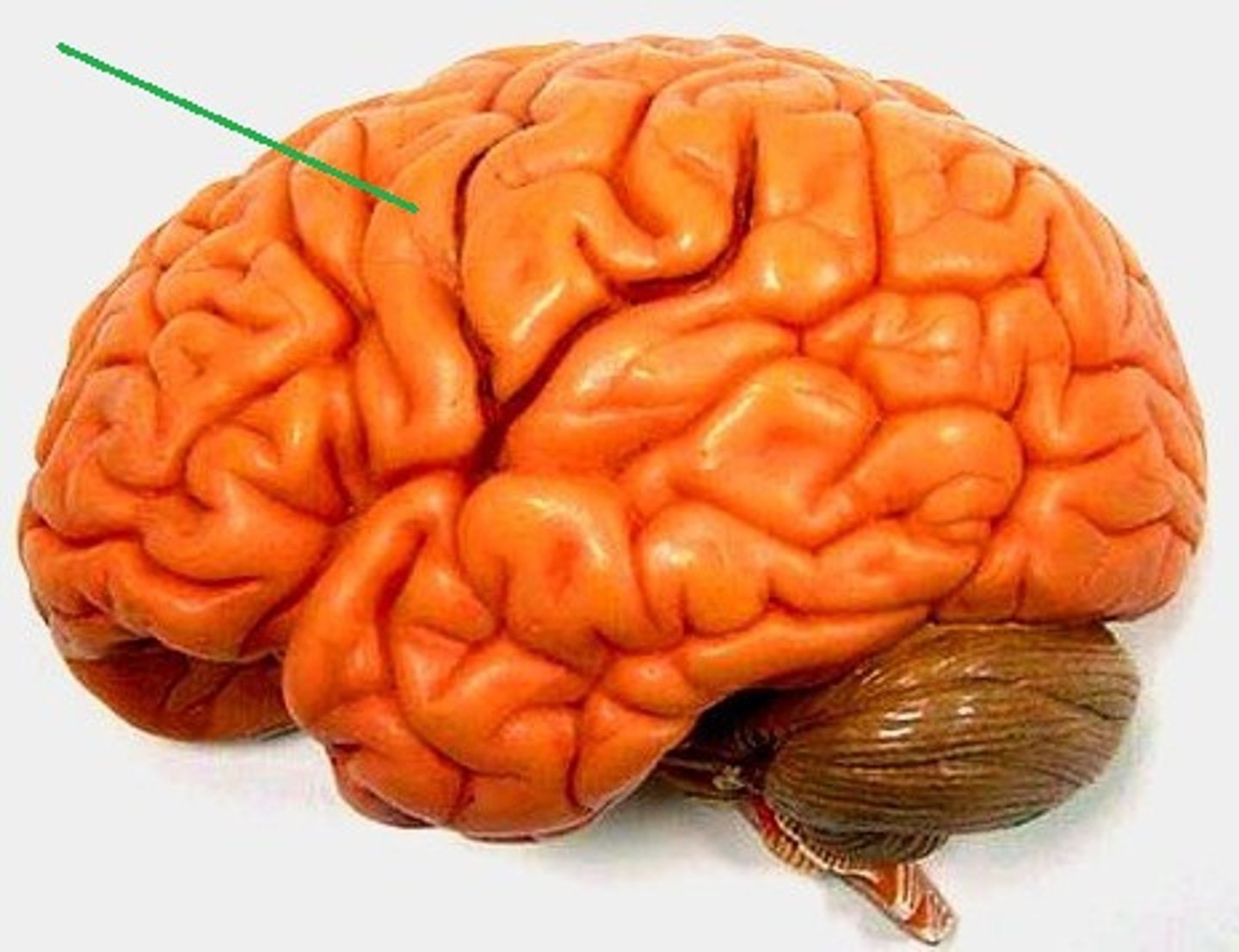
precentral gyrus
line that goes all the way across the front. Anterior to the central sulcus. In charge of primary motor.
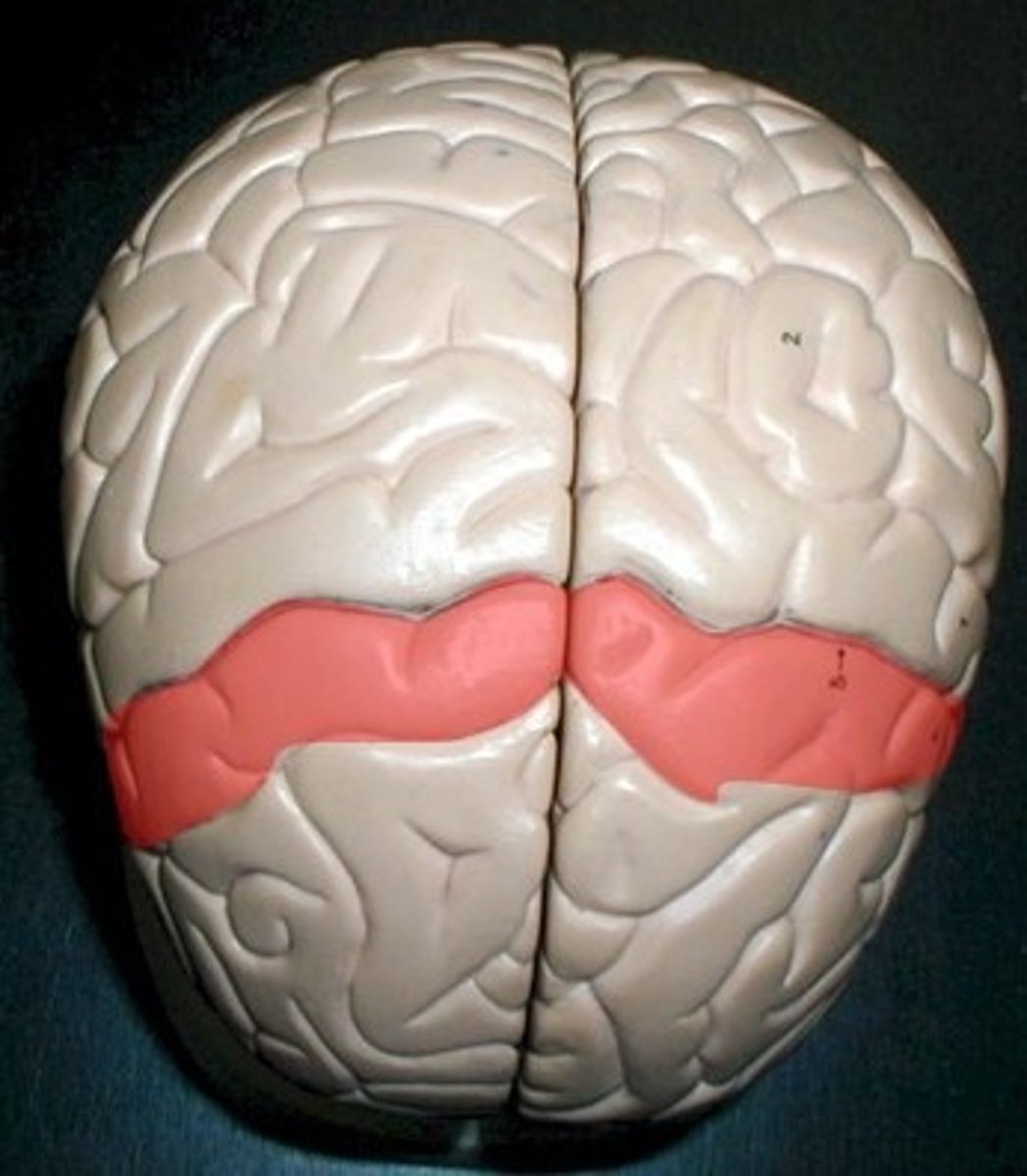
postcentral gyrus
posterior to the central sulcus. In charge of primary sensory.
sulci
the little cracks between the gyri (rivers/streams).
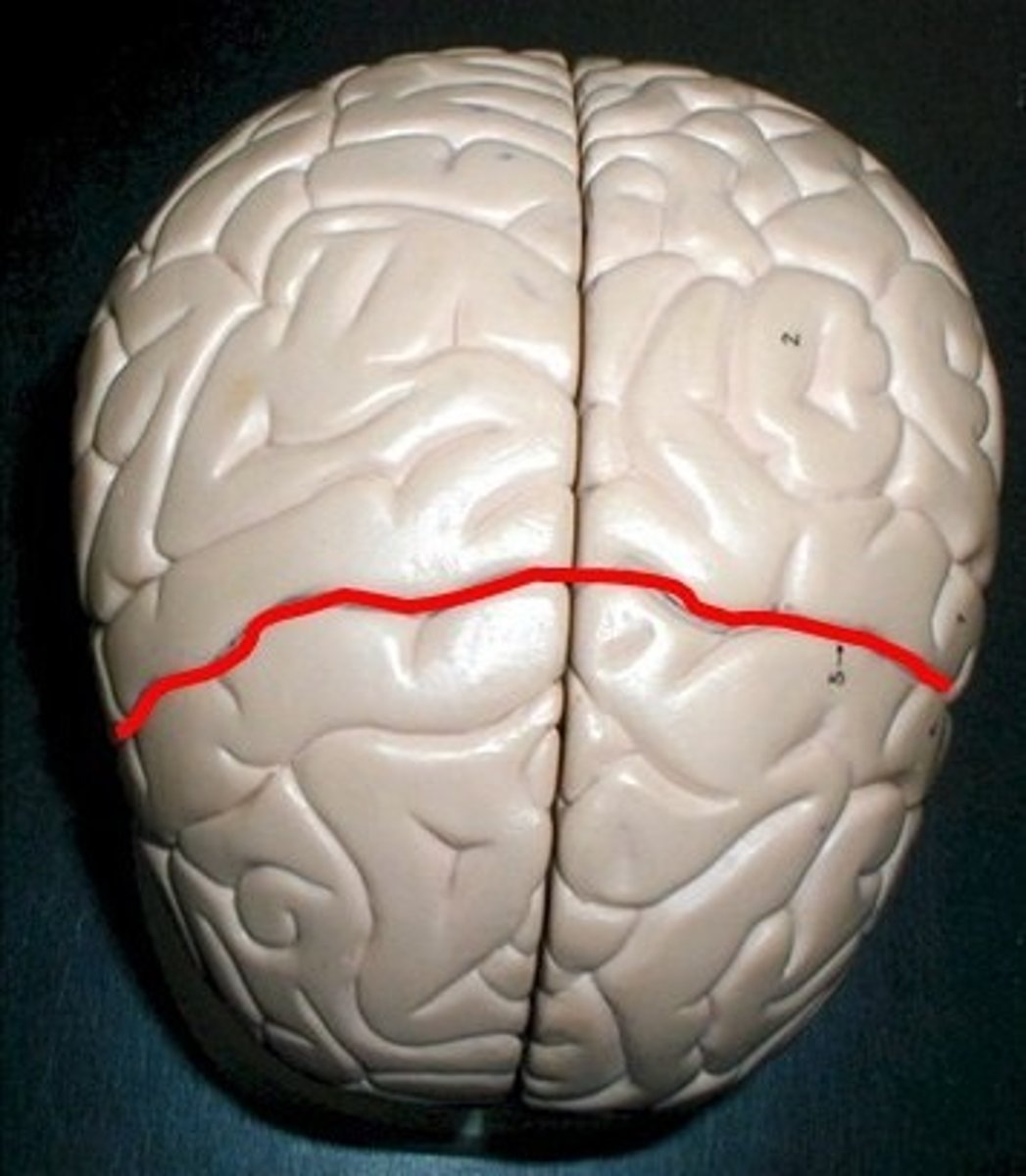
central sulcus
in between the precentral gyrus and postcentral gyrus.
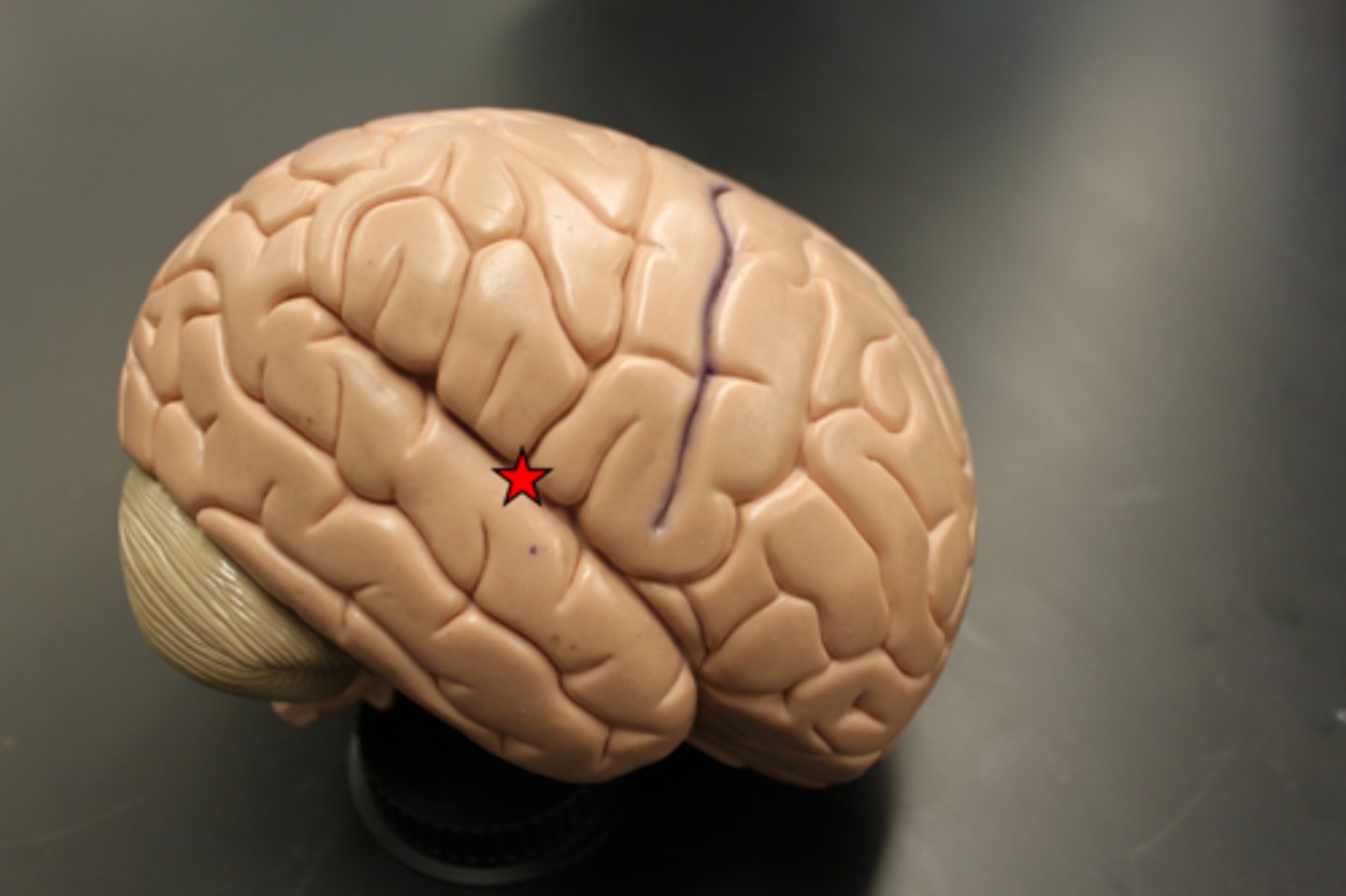
lateral sulcus
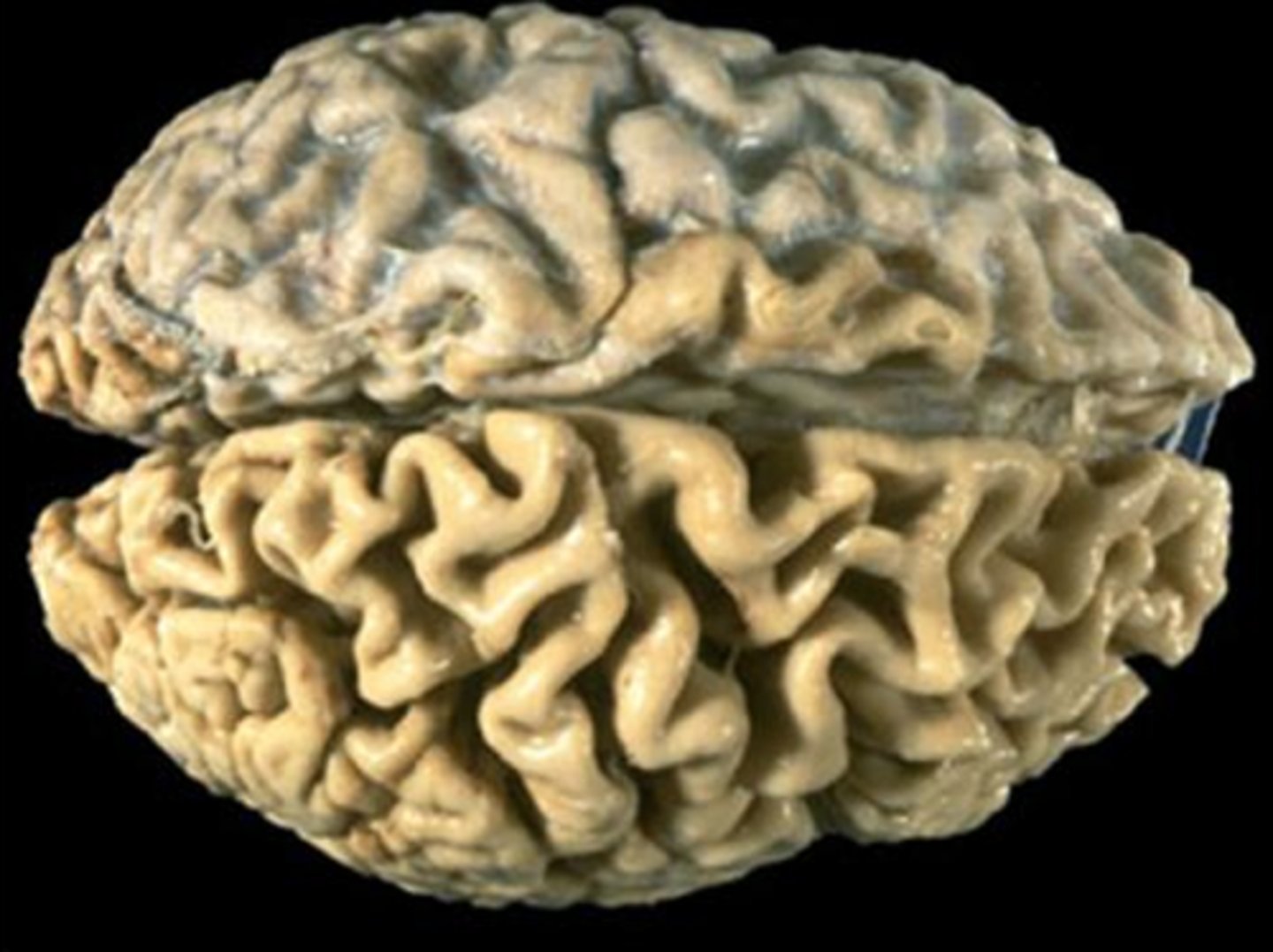
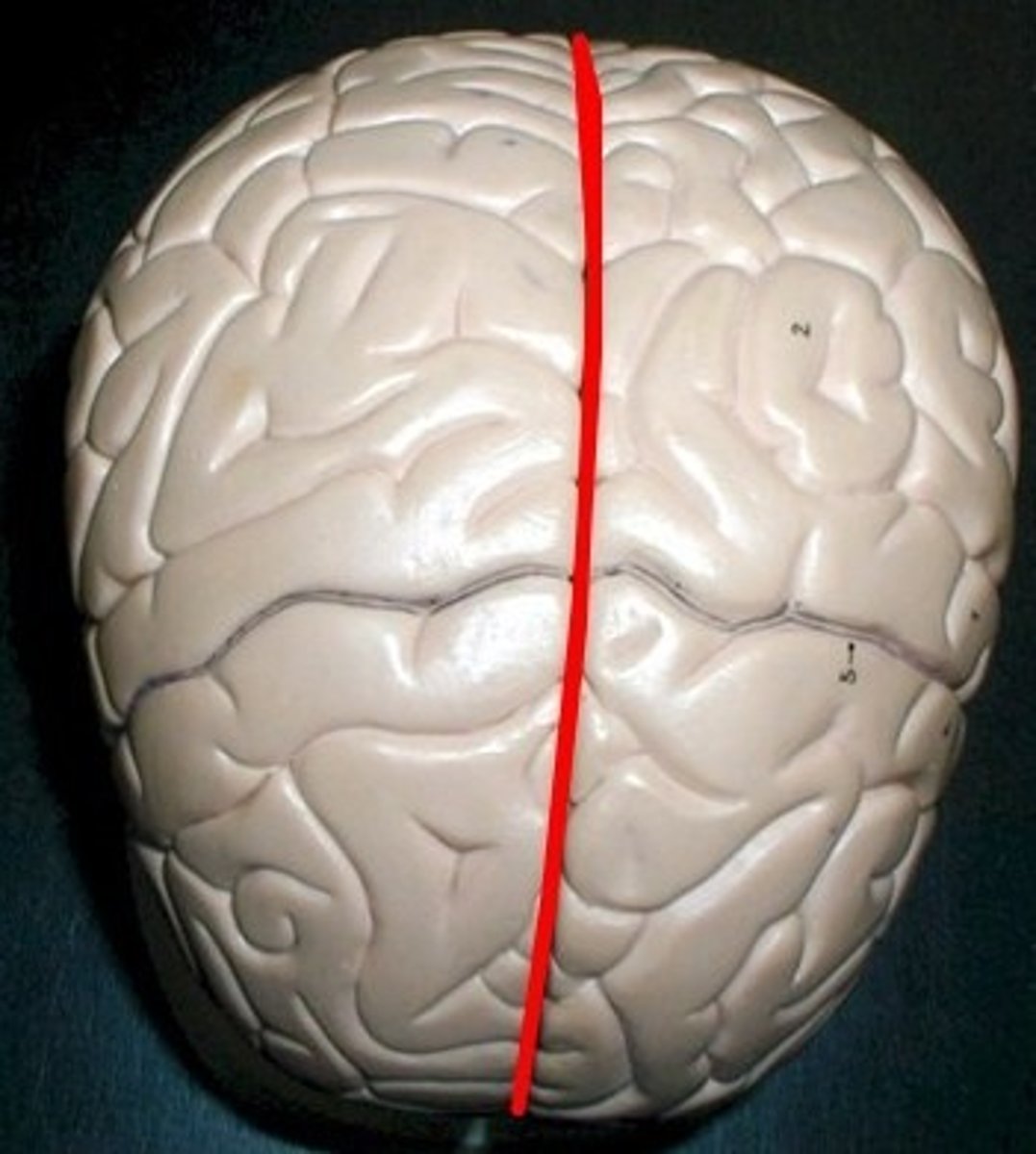
longitudinal fissure
divides the brain in half sagitally.
transverse fissure
area between the cerebrum and cerebellum.
corpus collosum
part of the cerebrum. white matter. Myelinated Axons. It's job is to allow communication between the left and right hemispheres.
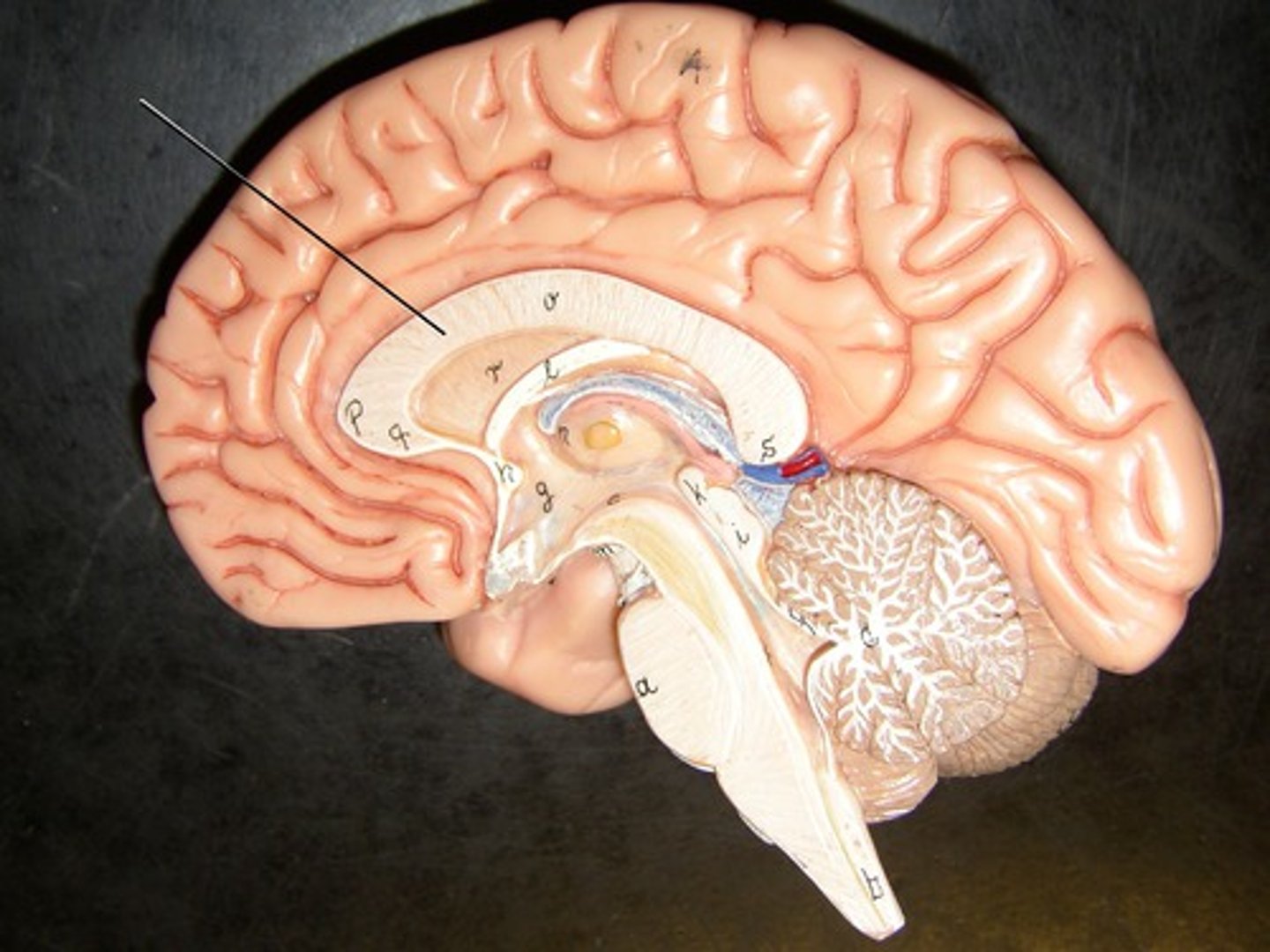
fornix
connects the hypothalamus and the hippocampus.
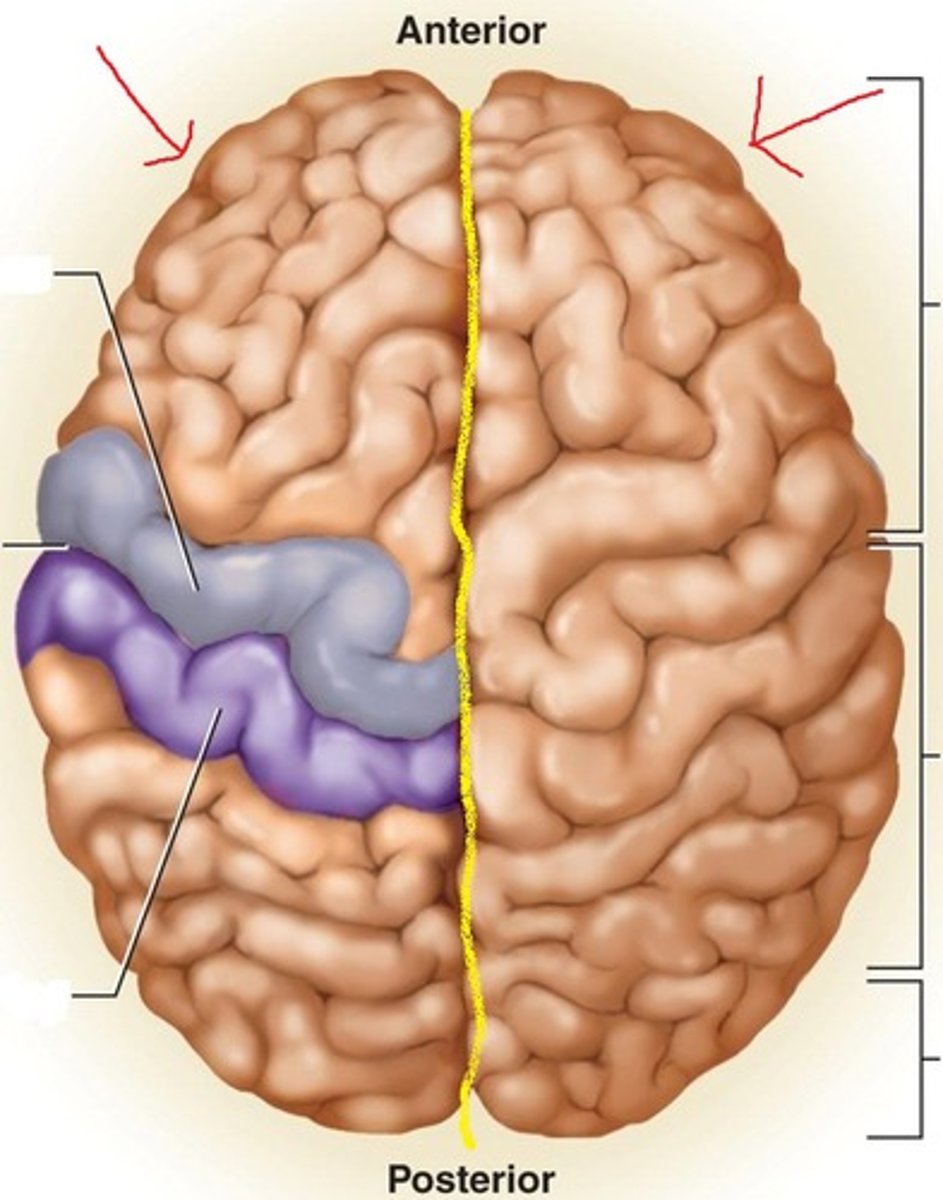
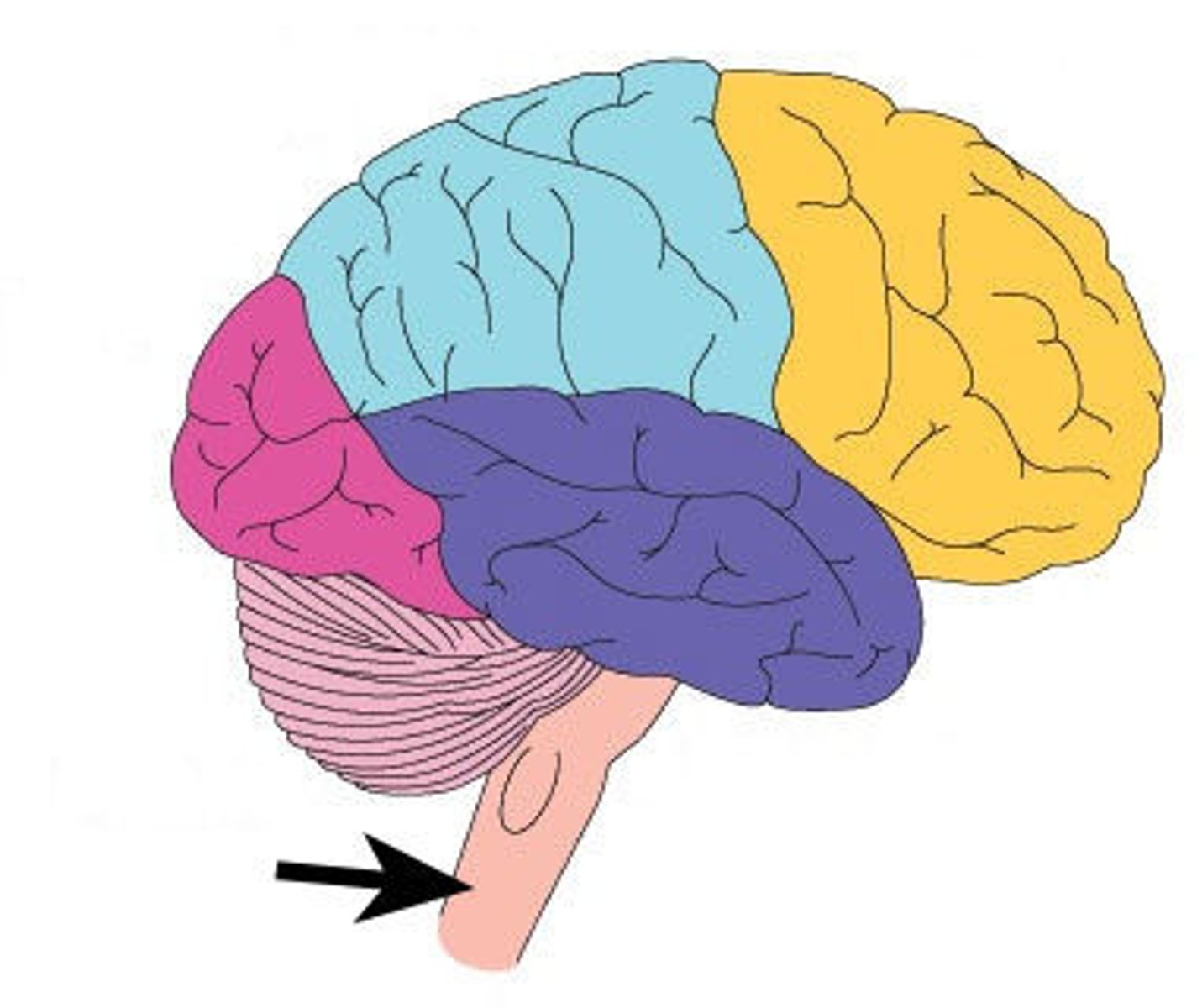
frontal lobe
from central sulcus to front of brain. Motor speech area (Broca area), primary motor cortex, higher intellectual functions, personality, verbal communication, voluntary motor control of skeletal muscles.
parietal lobe
Information like taste, temperature, and touch are integrated here. Part of Wernicke area, primary somatosensory cortex, sensory interpretation of textures and shapes, understanding speech and formulating words to express thoughts and emotions.
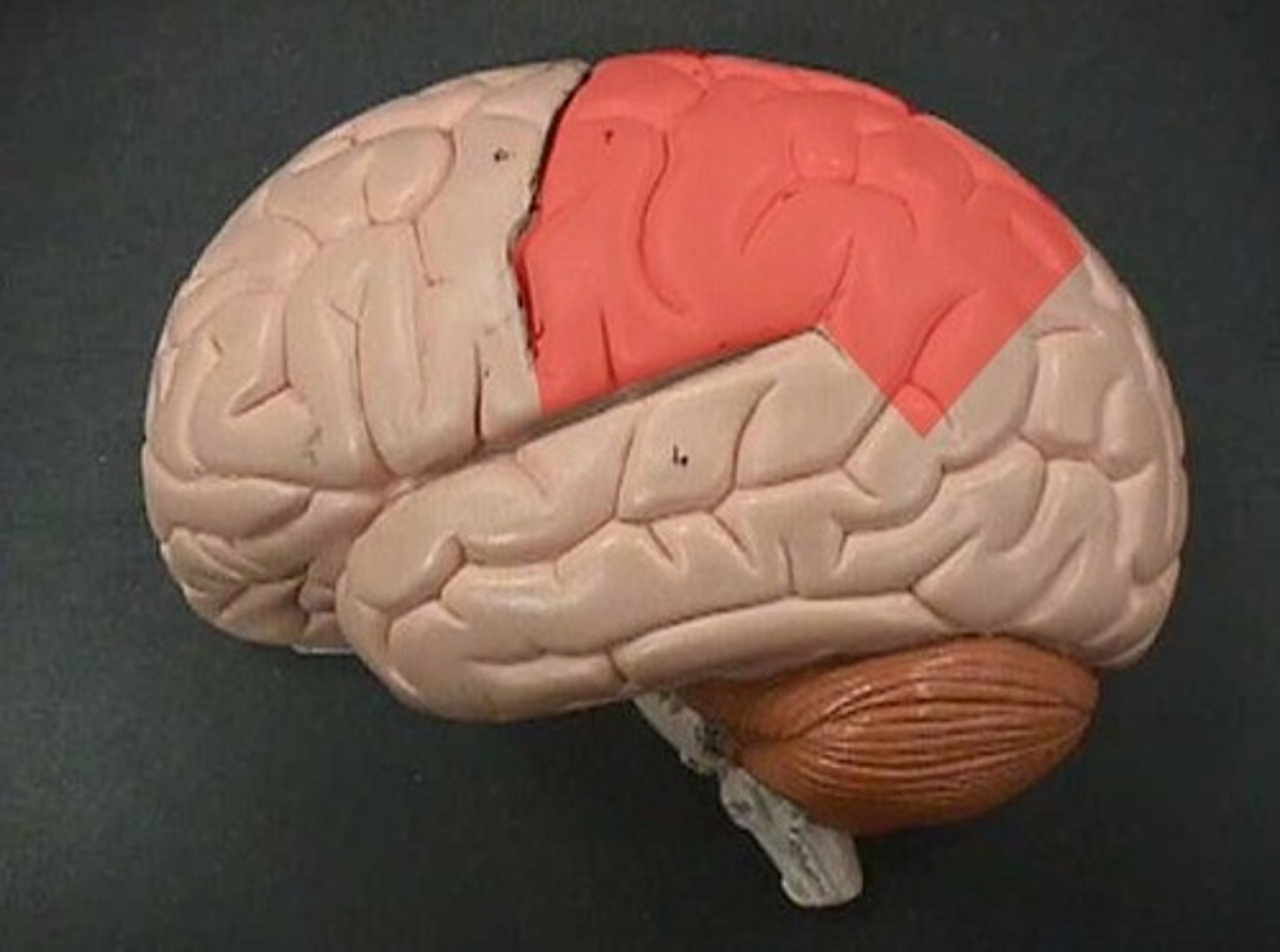
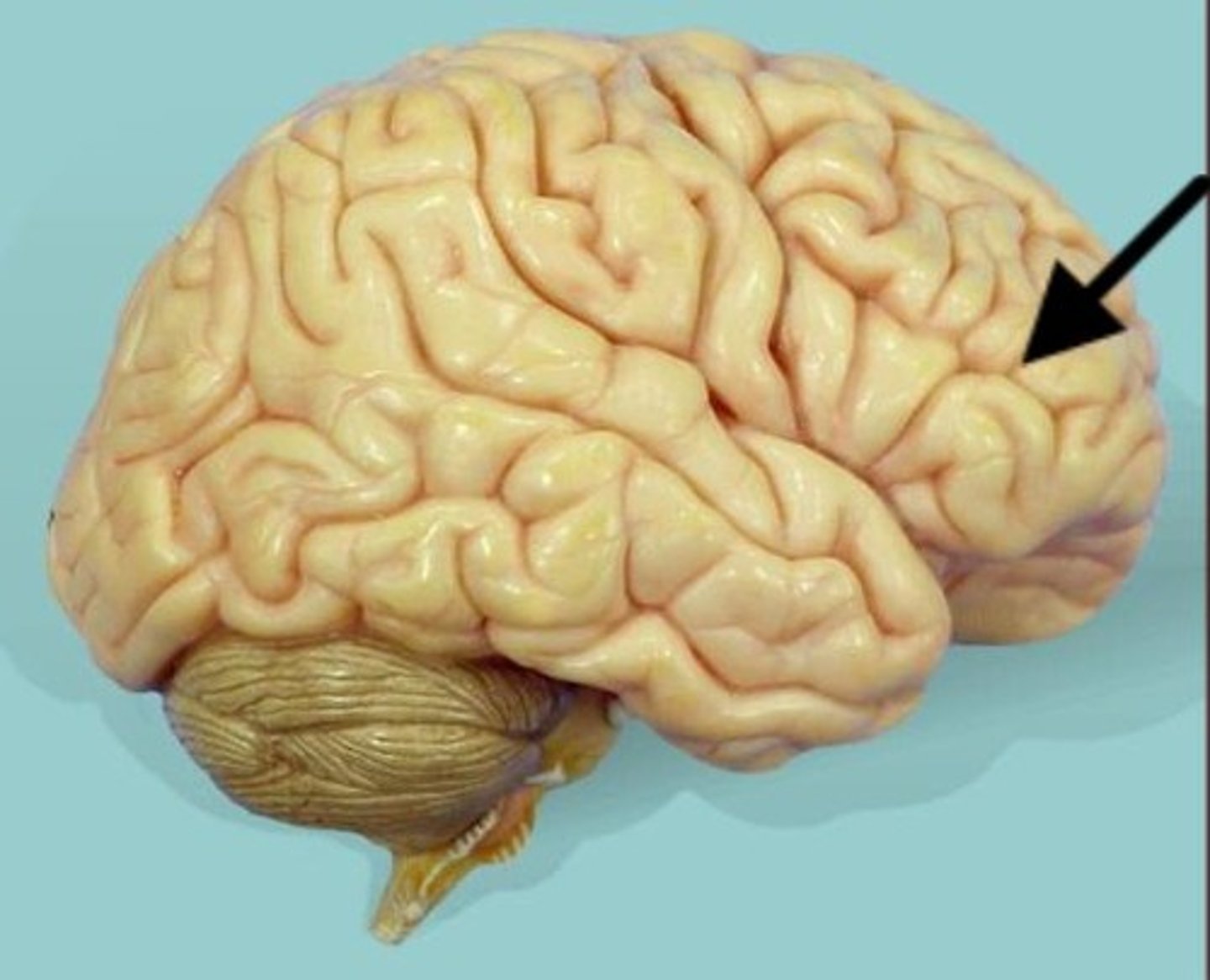
occipital lobe
This is where the visual cortex is.
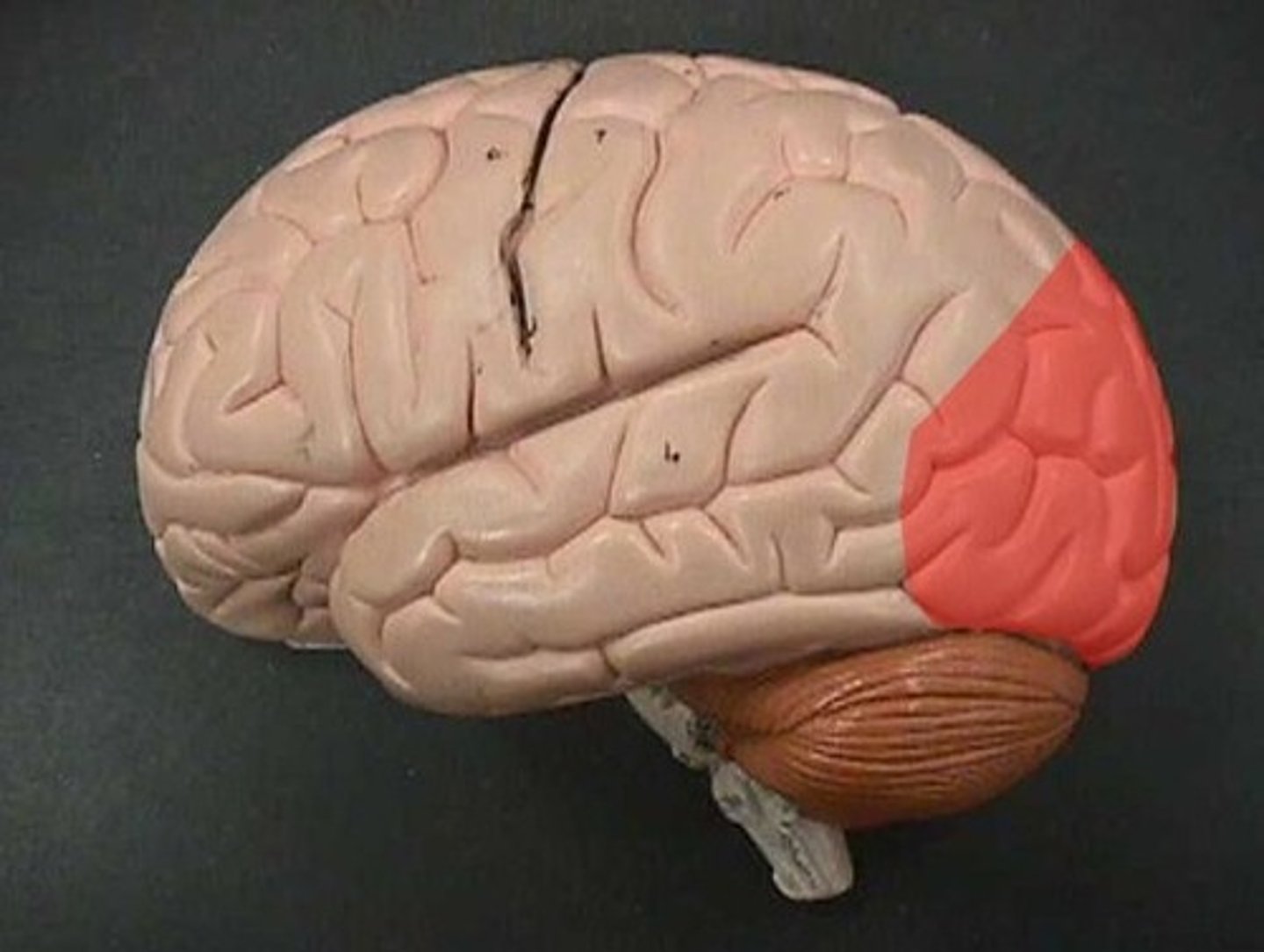
temporal lobe
This is where the primary auditory cortex is and the auditory association area. Primary auditory cortex, olfactory cortex, Part of Wernicke area.
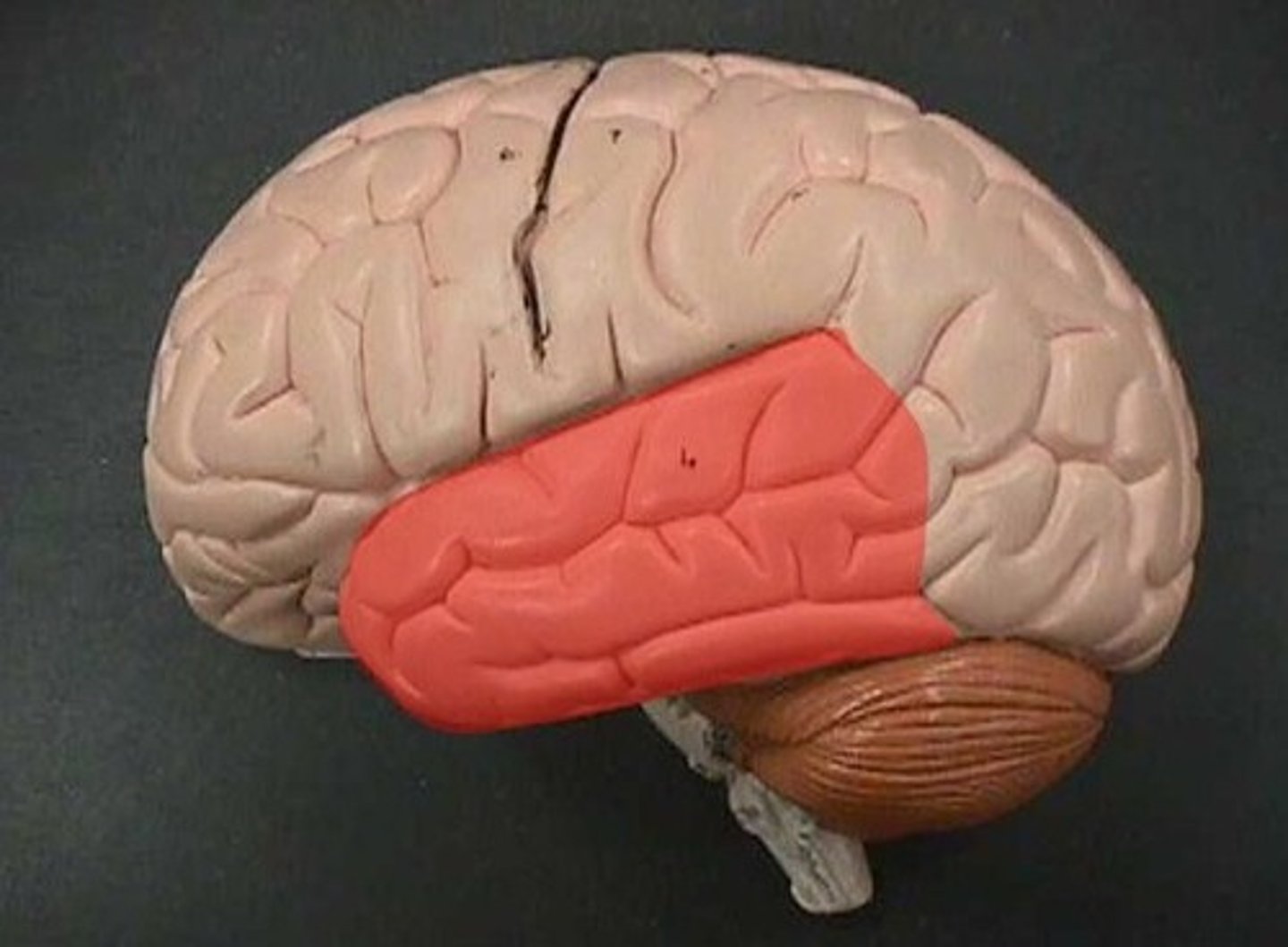
insula
The fifth lobe of the brain in the lateral sulcus. Primary gustatory cortex.
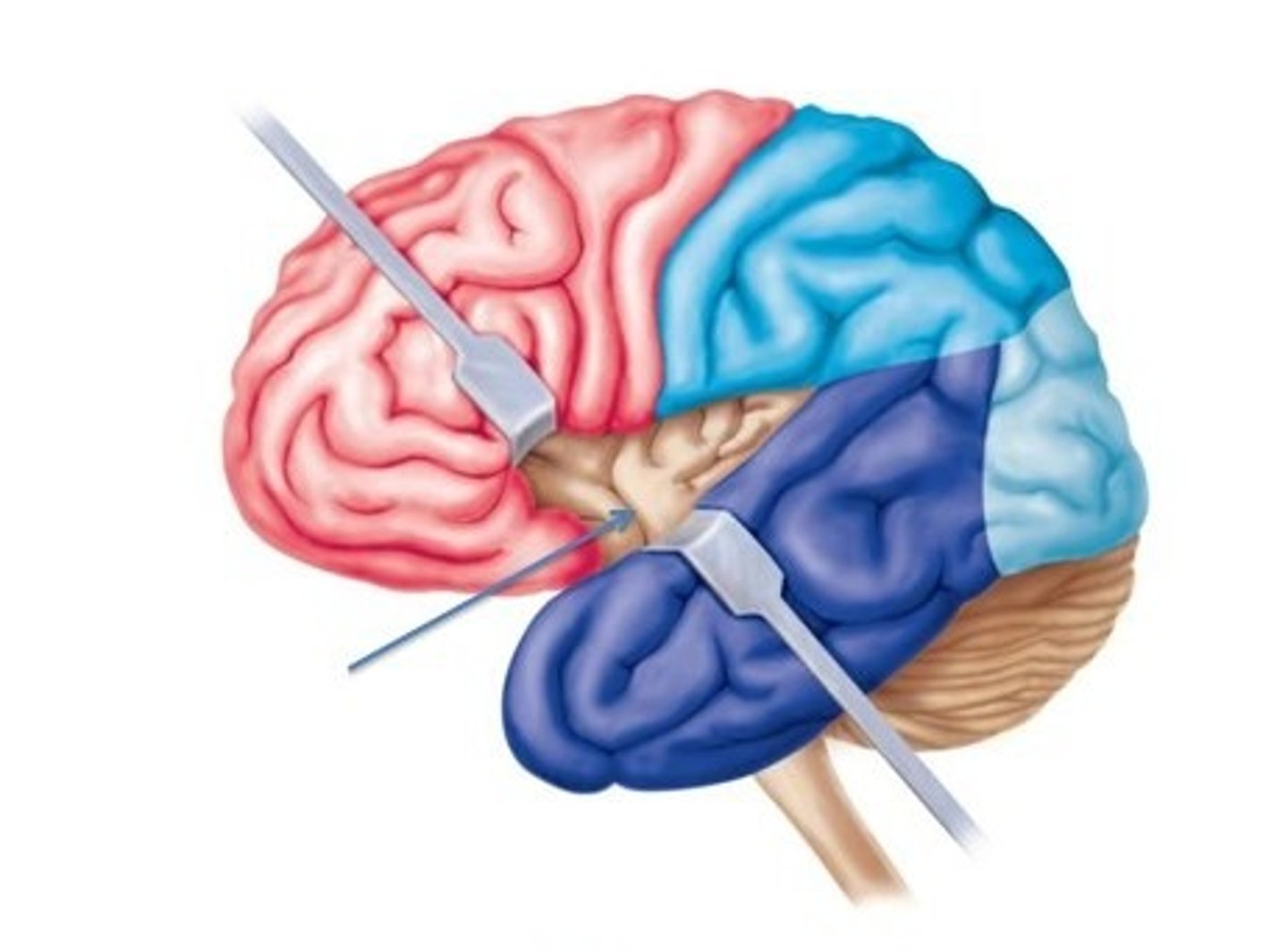
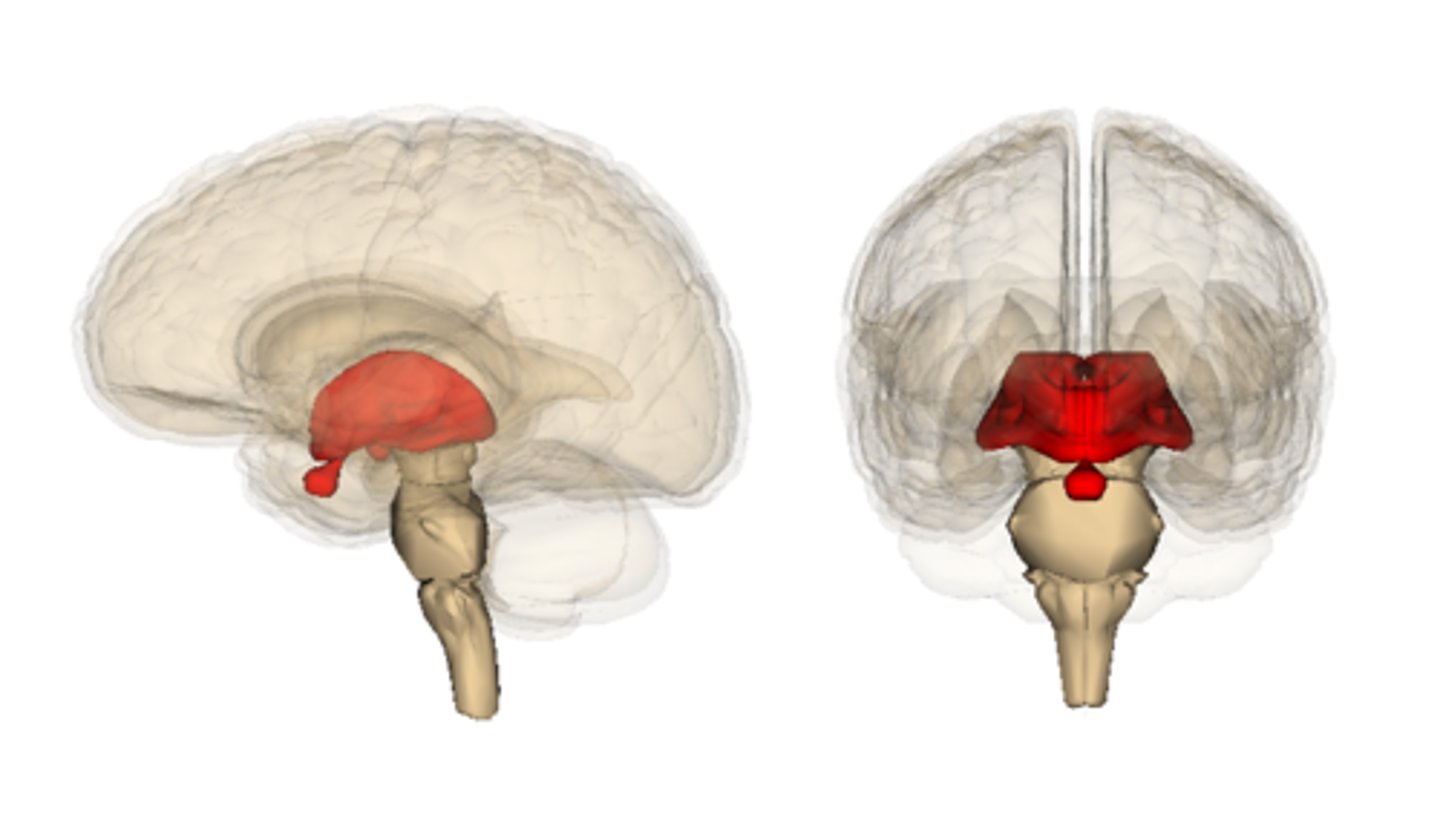
diencephalon
includes some of the area of the limbic system.
- acts as a connector in the brain.
- Connects cerebrum with the lower parts of the brain. Includes the pituitary gland, thalamus, hypothalamus, mammillary bodies, and pineal body.
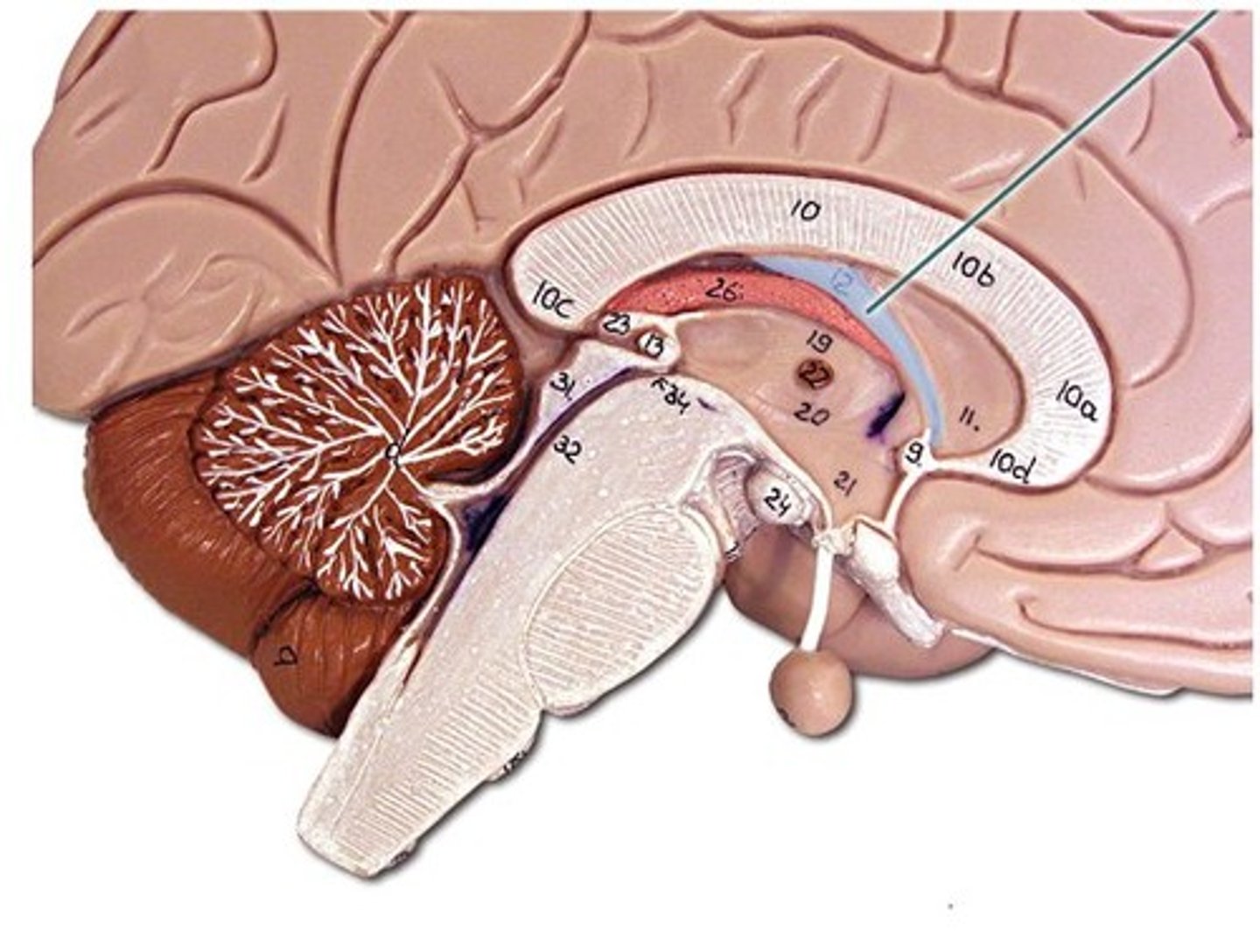
pituitary gland
the thing it hangs from is the infundibulum (the stalk that it hangs from. It regulates hormones. Releases hormones that control other endocrine glands. Releases tropic hormones.
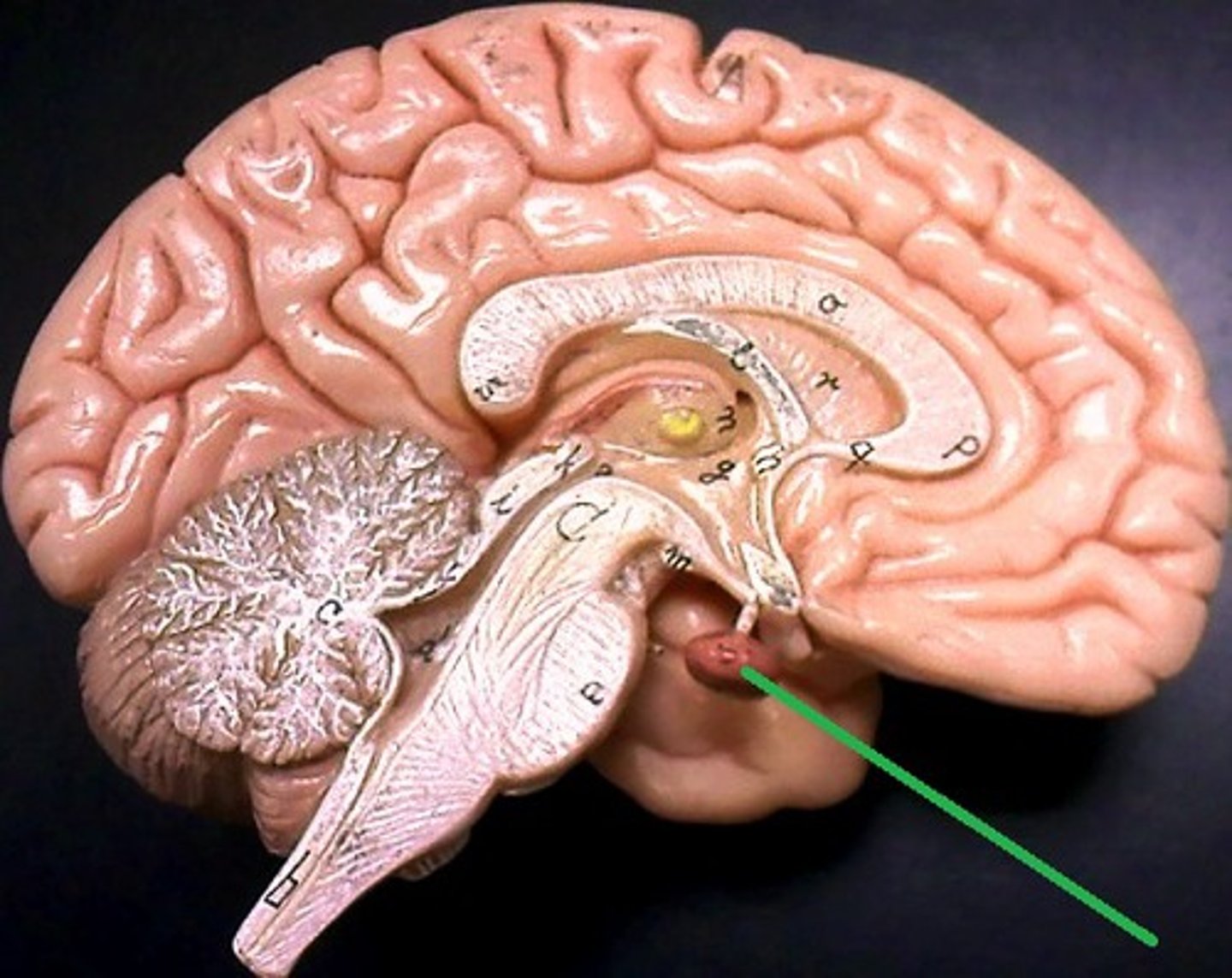
infundibulum
The stalk that the pituitary gland hangs from.
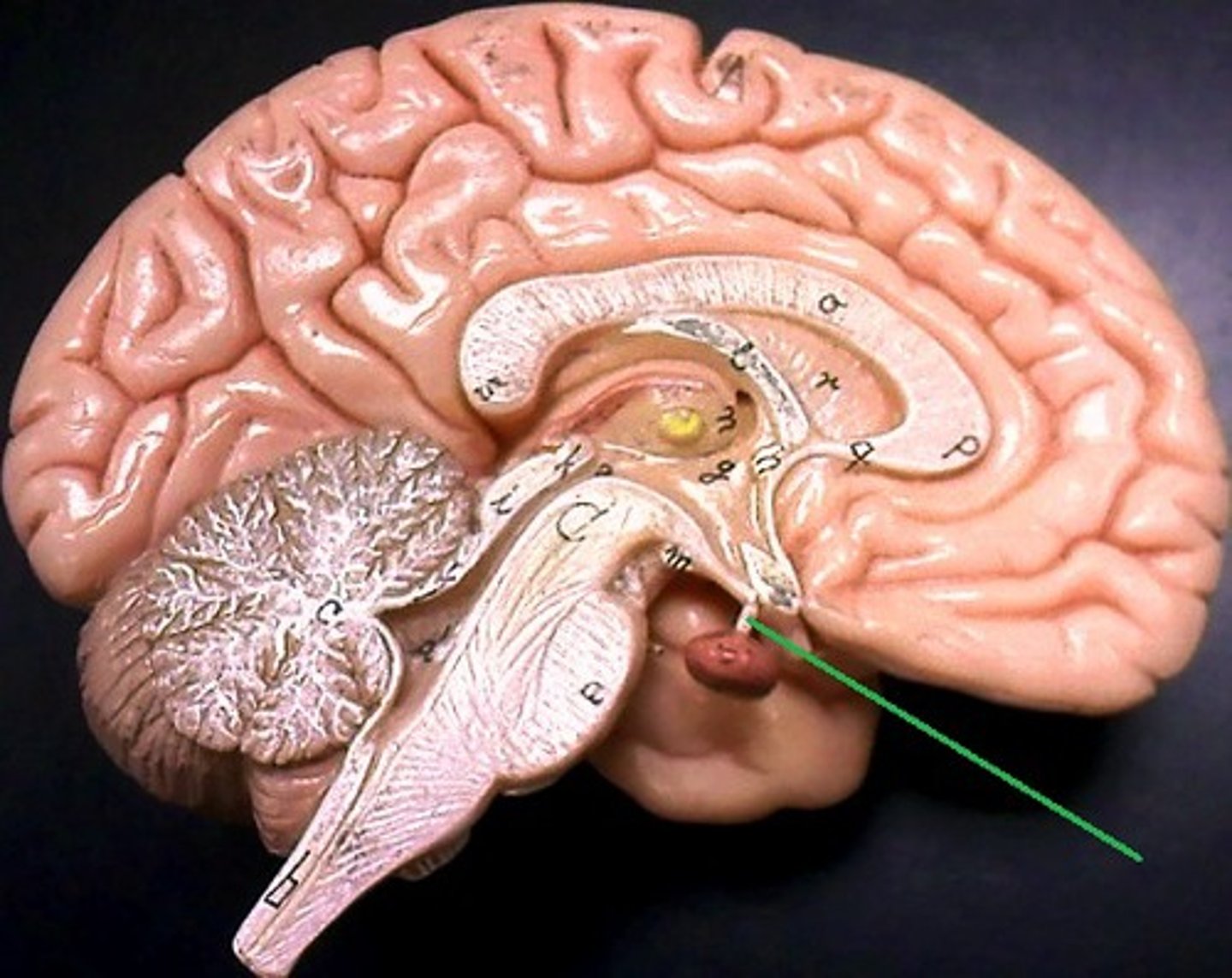
tropic hormones
hormones released from a gland and influence other glands.
thalamus
receives and filters incoming sensory information. All the senses except for smell hit thalamus first. With generalized and specified senses.
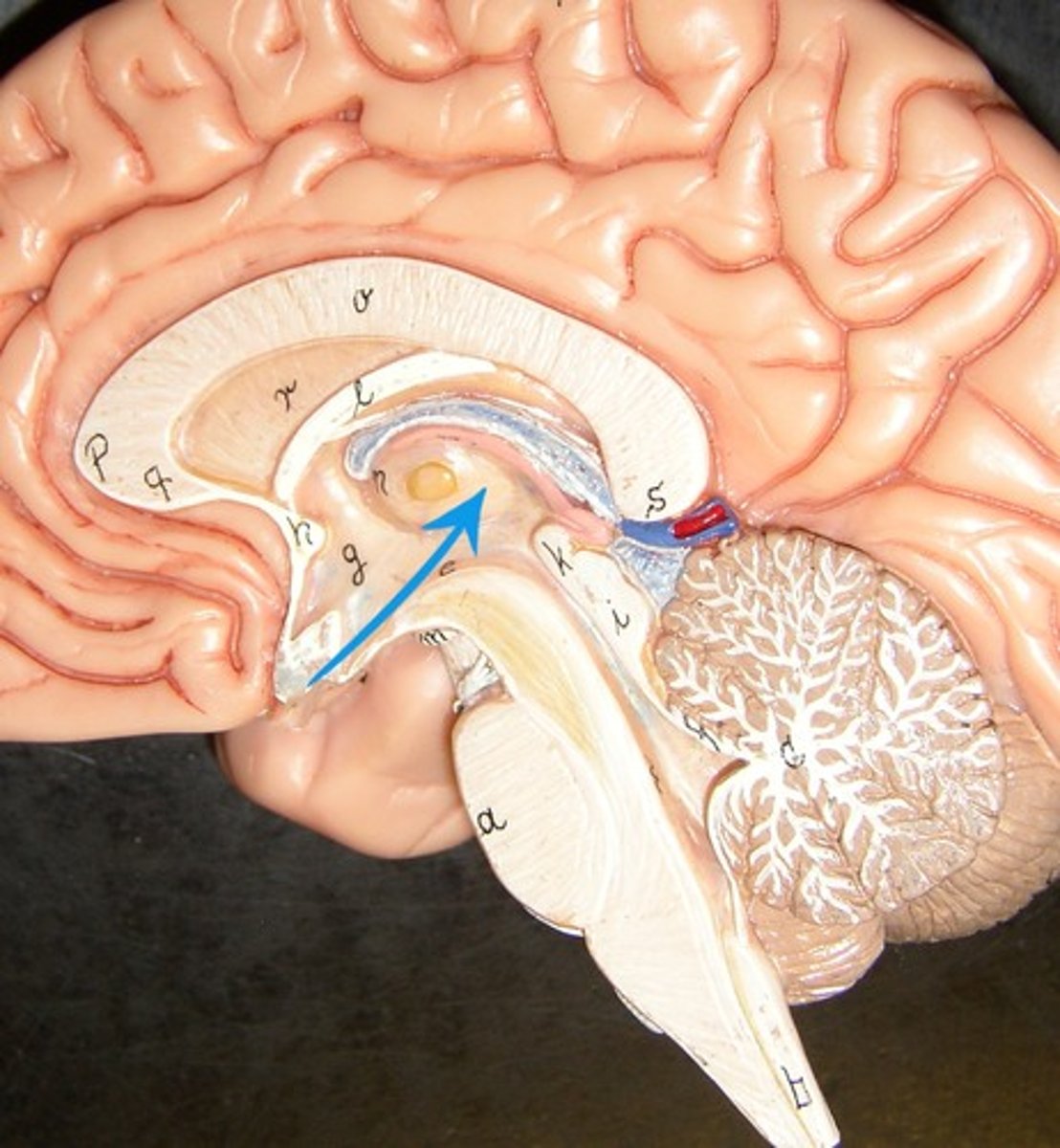
interthalamic adhesion
in the center of the thalamus. It connects the thalamus in the right and left hemisphere of the brain.
hypothalamus
This is the big cross roads. Master control of the autonomic nervous sytem (heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, parts of urination, respiration).
- Master control of the endocrine system - secretes hormones that tell the pituitary gland what to do. Pituitary gland cannot act unless it has orders from hypothalamus.
- Makes some hormones too that it stores in pituitary gland.
- Regulation of body temperature.
- Control of emotional behavior (seat of the limbic system). Center of it.
- Helps us to integrate feelings/ have complex feelings.
- Controls food and water intake (initiates thirst mechanism) . detects blood osmolality.
- Regulation of sleep-wake (circadian rhythms).
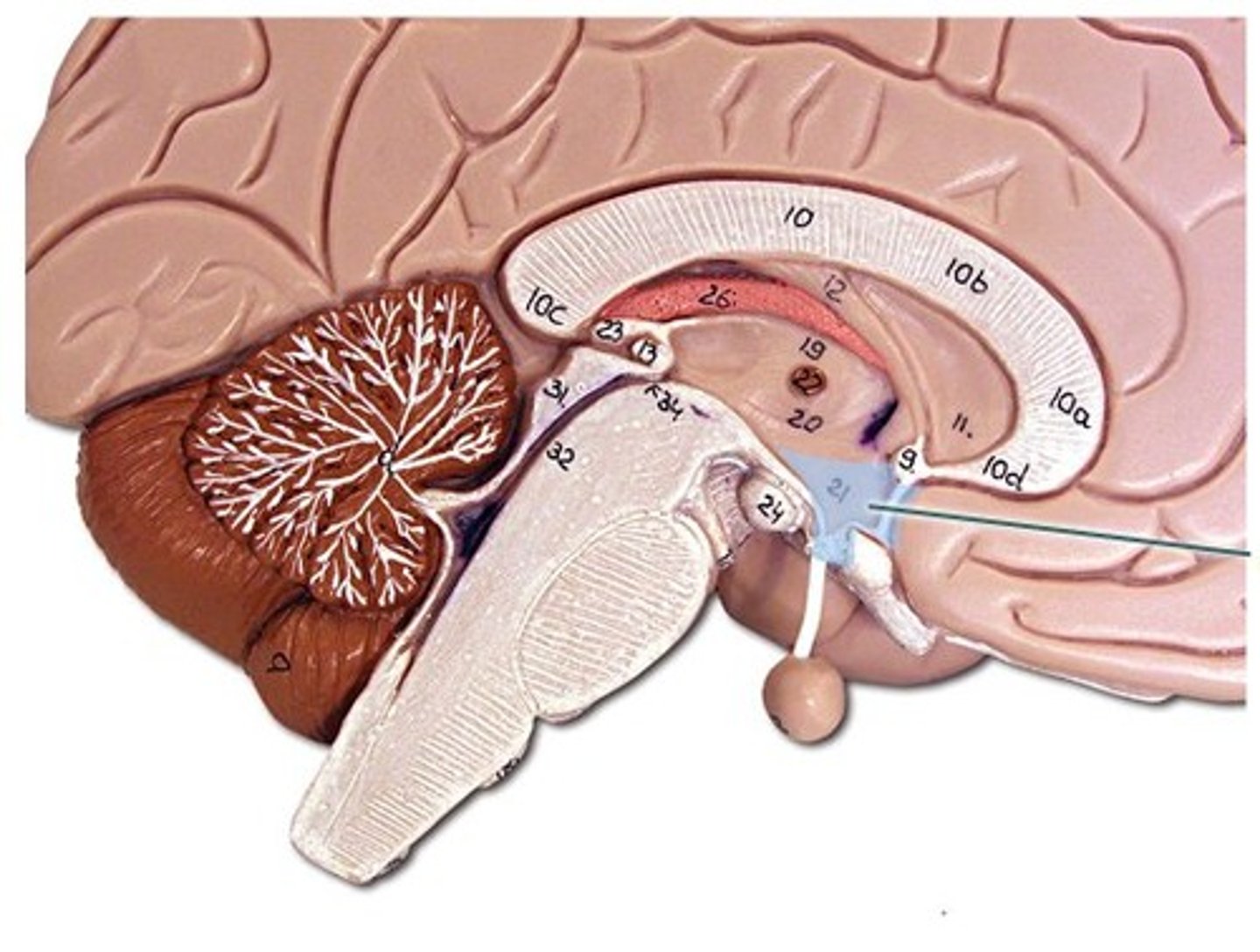
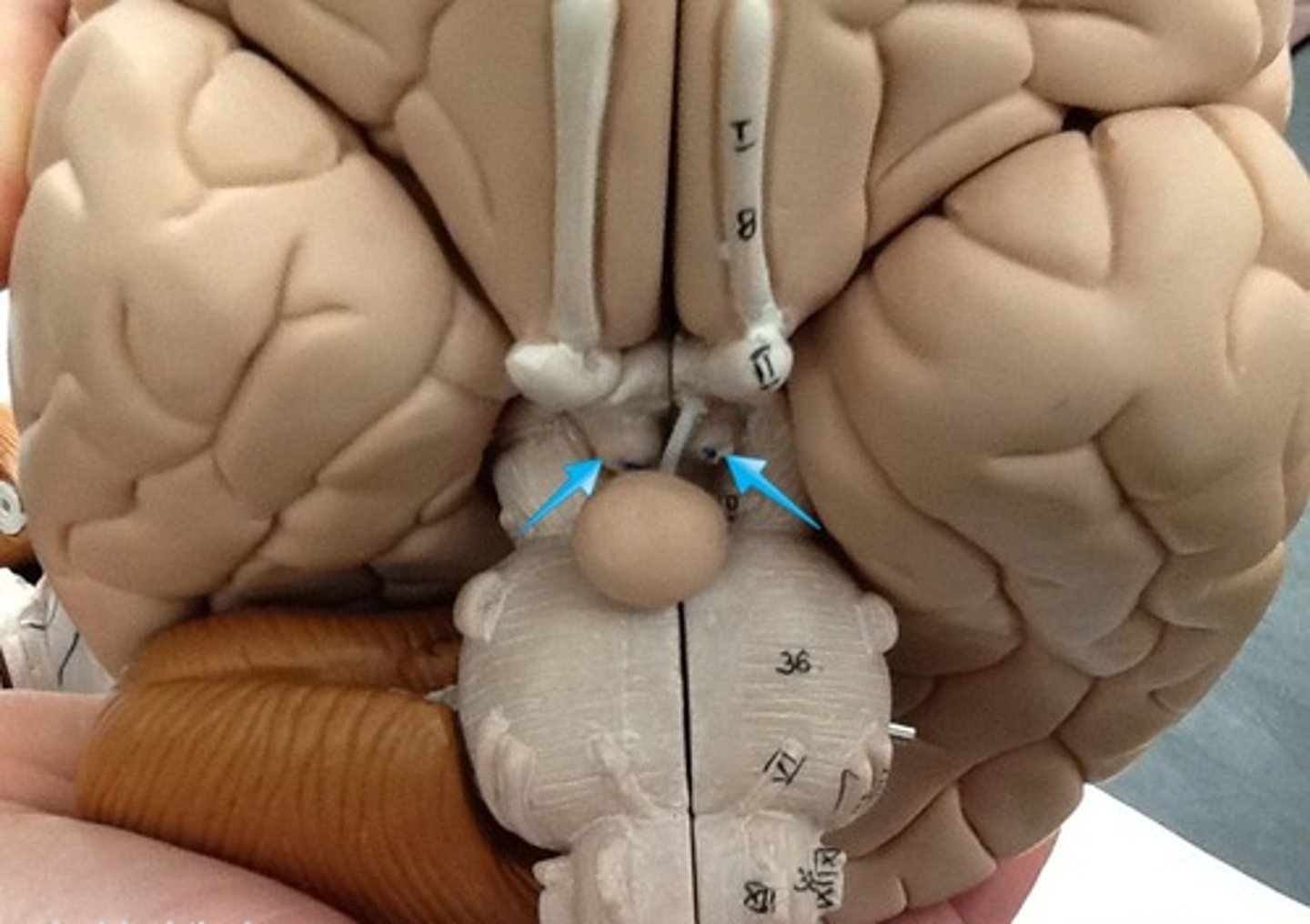
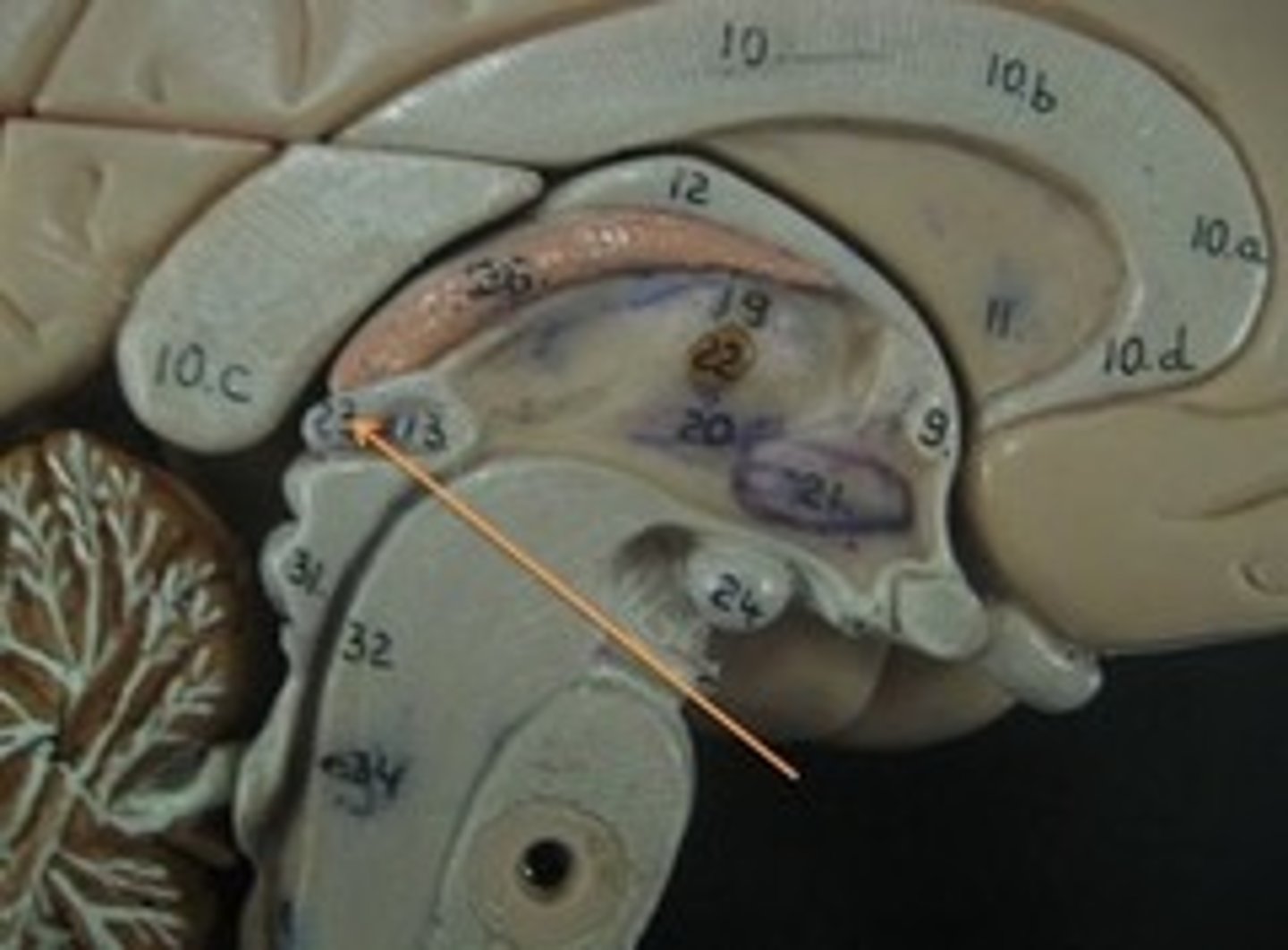
mammillary bodies
two bumbs between pituitary gland and brain stem. Part of limbic system. Contributes to functioning of limbic system.
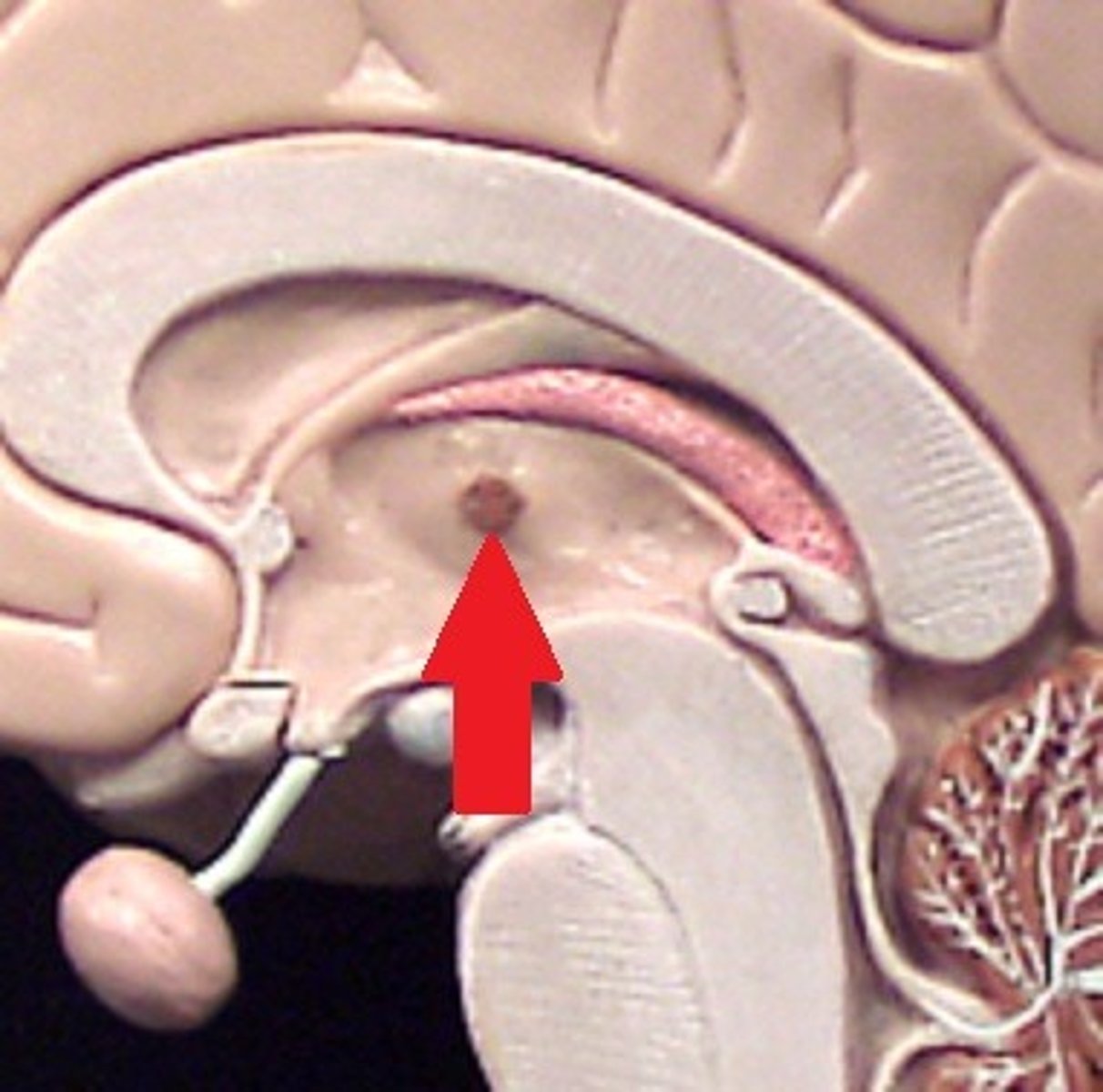
pineal body
considered an endocrine gland. Secretes melatonin. Plays a role in circadian rhythm - regulation of this. Sleep/wake cycles or night/day cycles. They don't know exactly how this works, but if the pineal gland does not release melatonin, you can have differences in circadian rhythm.
brain stem
Includes the mid brain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
midbrain
corpora quadrigemina,connector of cerebrum, diencephalon, and cerebellum to spinal cord. Connector in central nervous system.
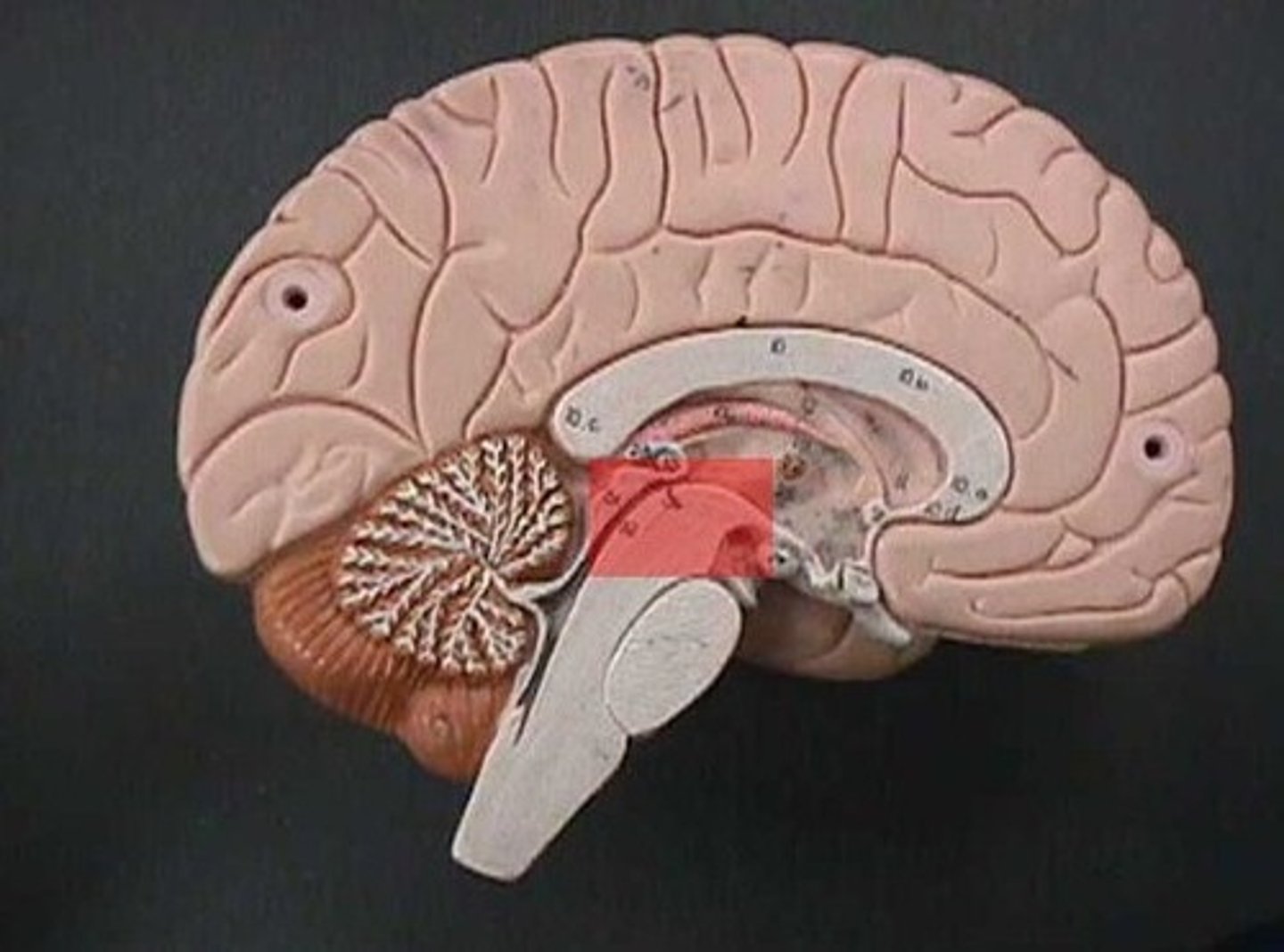
corpora quadrigemina
Also known as the tectal plate. Consists of the superior colliculi and the inferior colliculi.
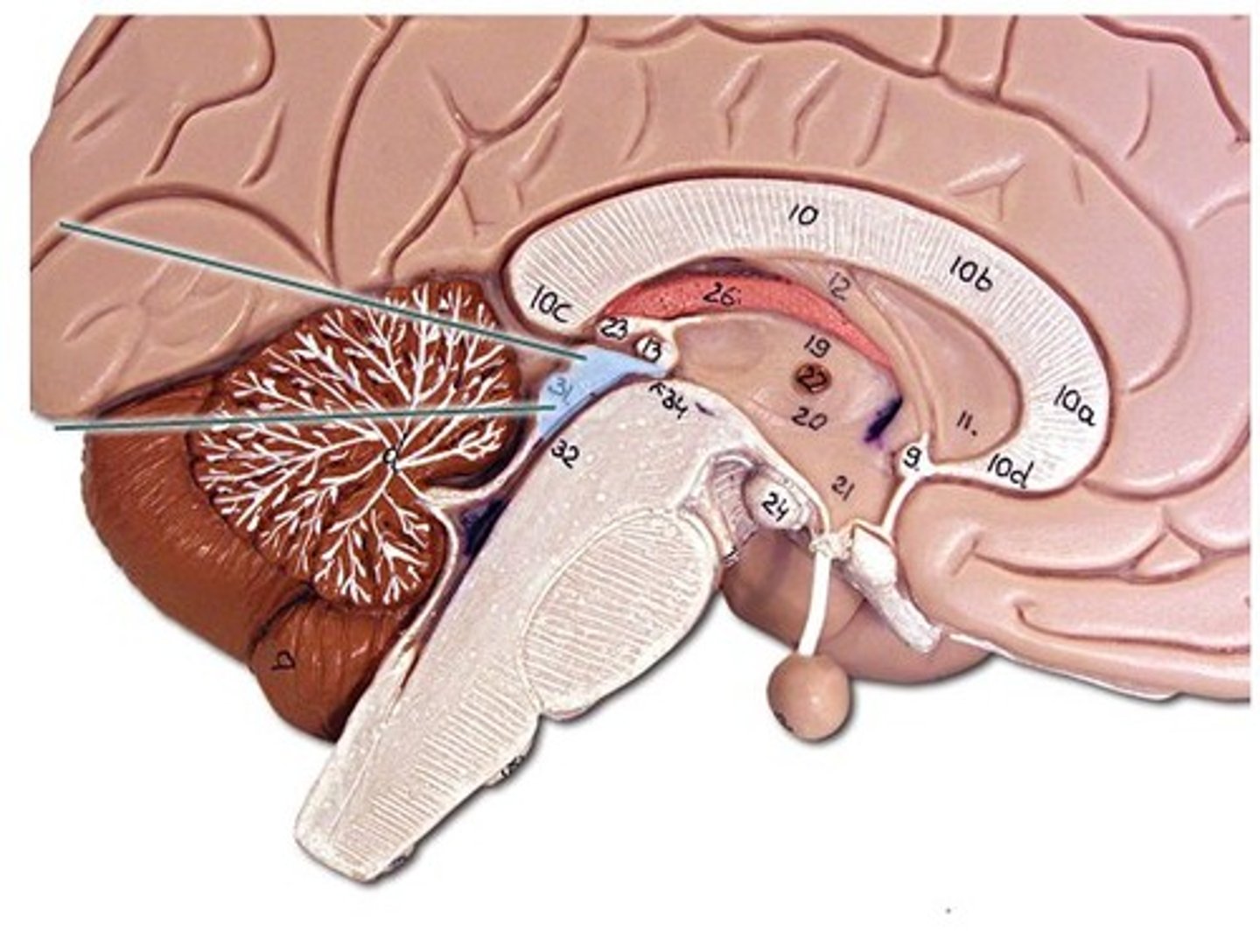
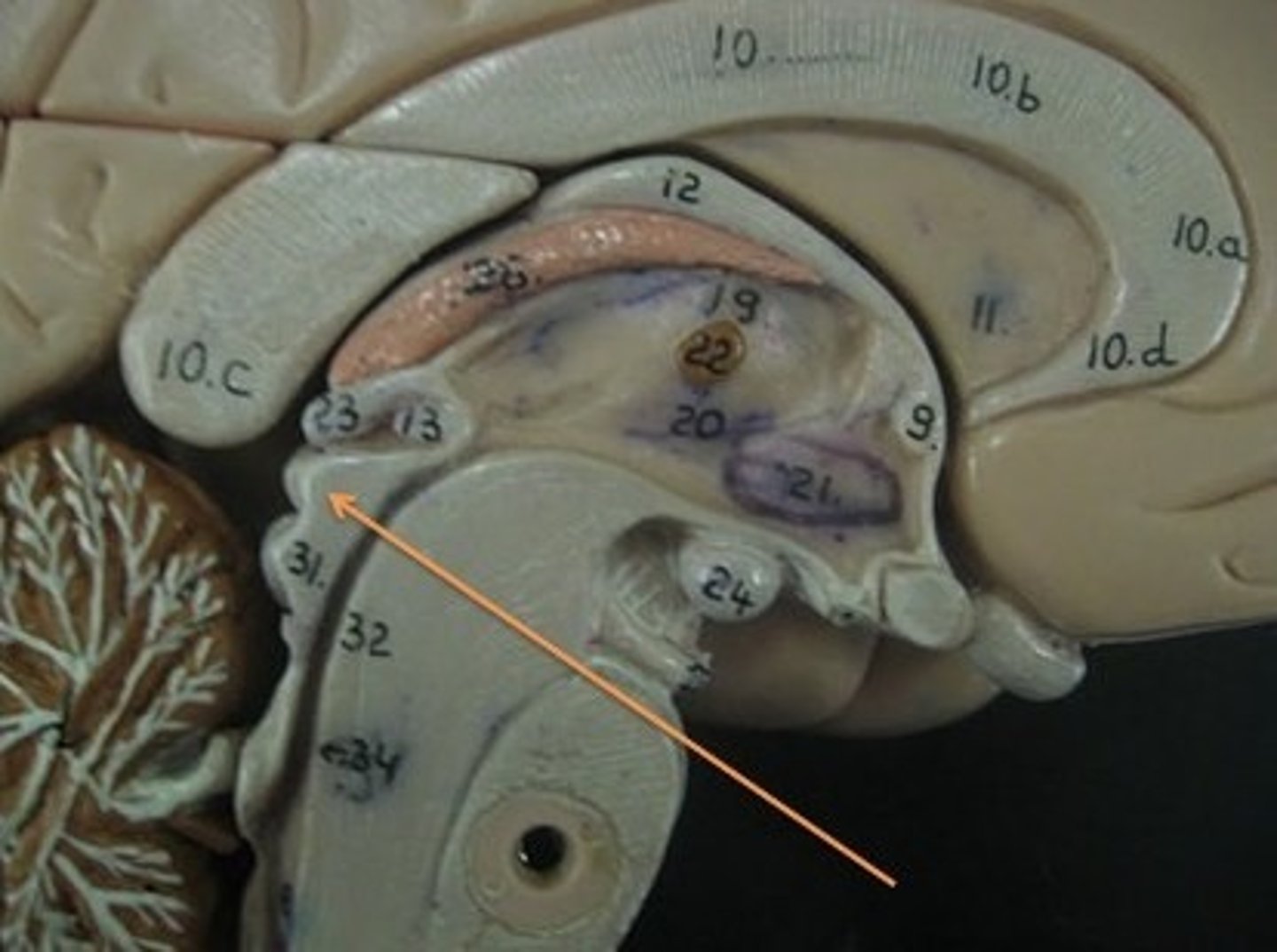
superior colliculi
bumby part on opposite side of pituitary gland. Top one. Responsible for visual reflex (track objects visually). If we see something in peripheray, we can turn towards object. Instinctive reflex.
inferior colliculi
bumpy part on opposite of pituitary gland. Bottom one. 31 auditory tracking. If we hear a loud noise, we can move toward it.
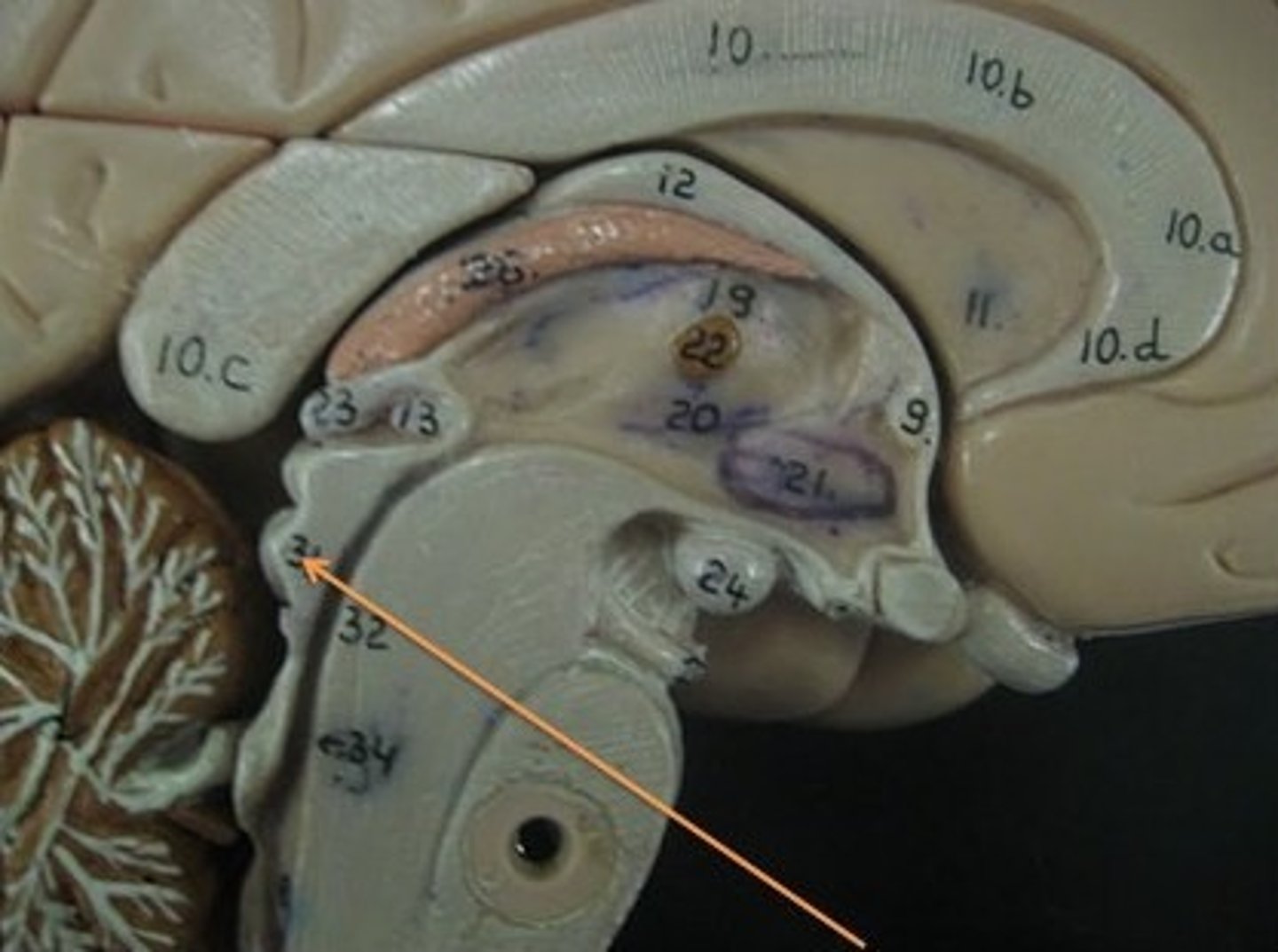
pons
contains parts of respiratory center. Plays a role in controlling breathing rate and depth.
medulla oblongata
has a cardiac center. Plays a role in influencing heart rate and the force of the contractions in the heart. In response to changes in blood pressure and oxygen levels.
- vasomotor center - helps to control blood pressure. Sends out signals that causes vasoconstriction or vasodilation of blood vessels. Contains parts of respiratory center.
- initiates inspiration and respiration.
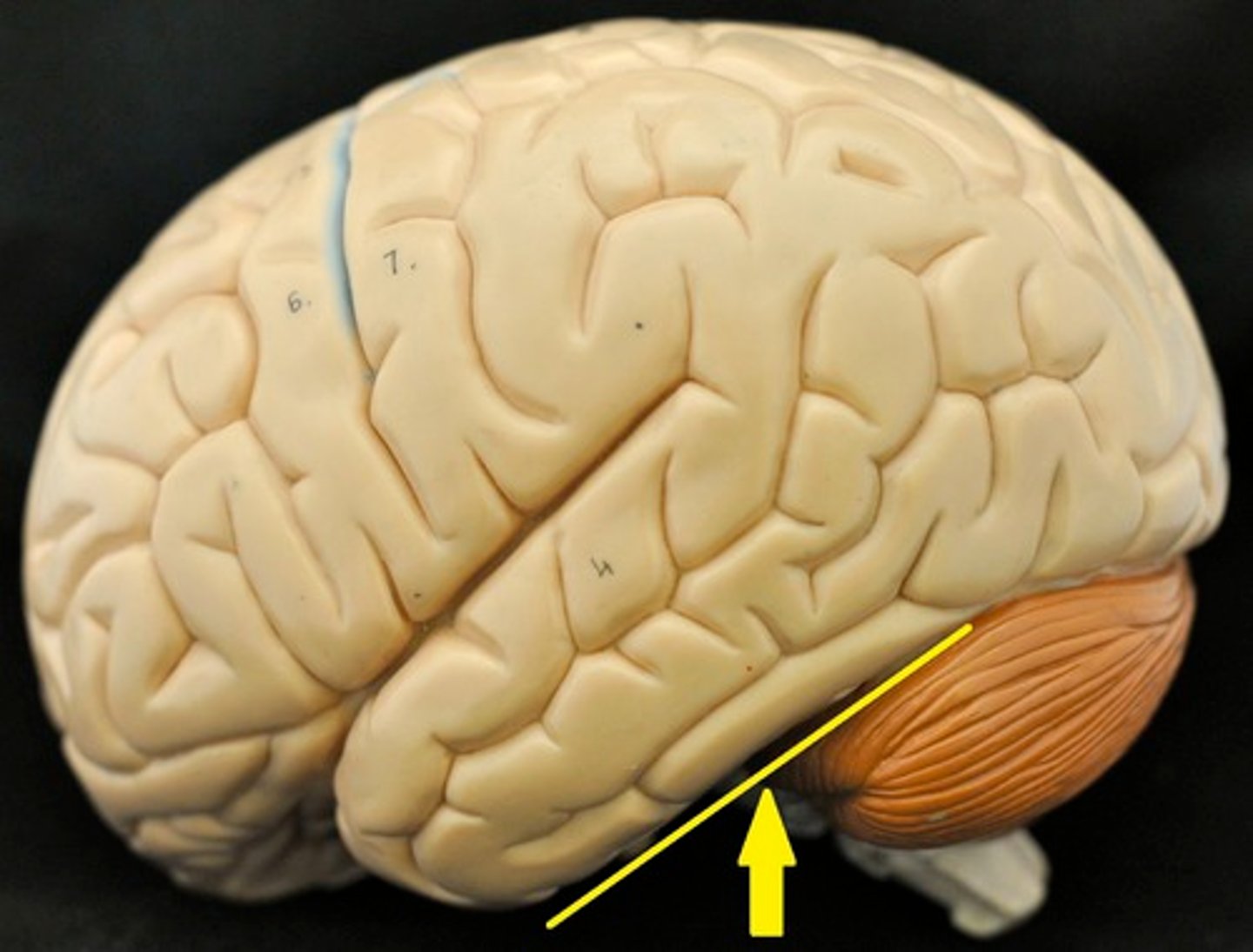
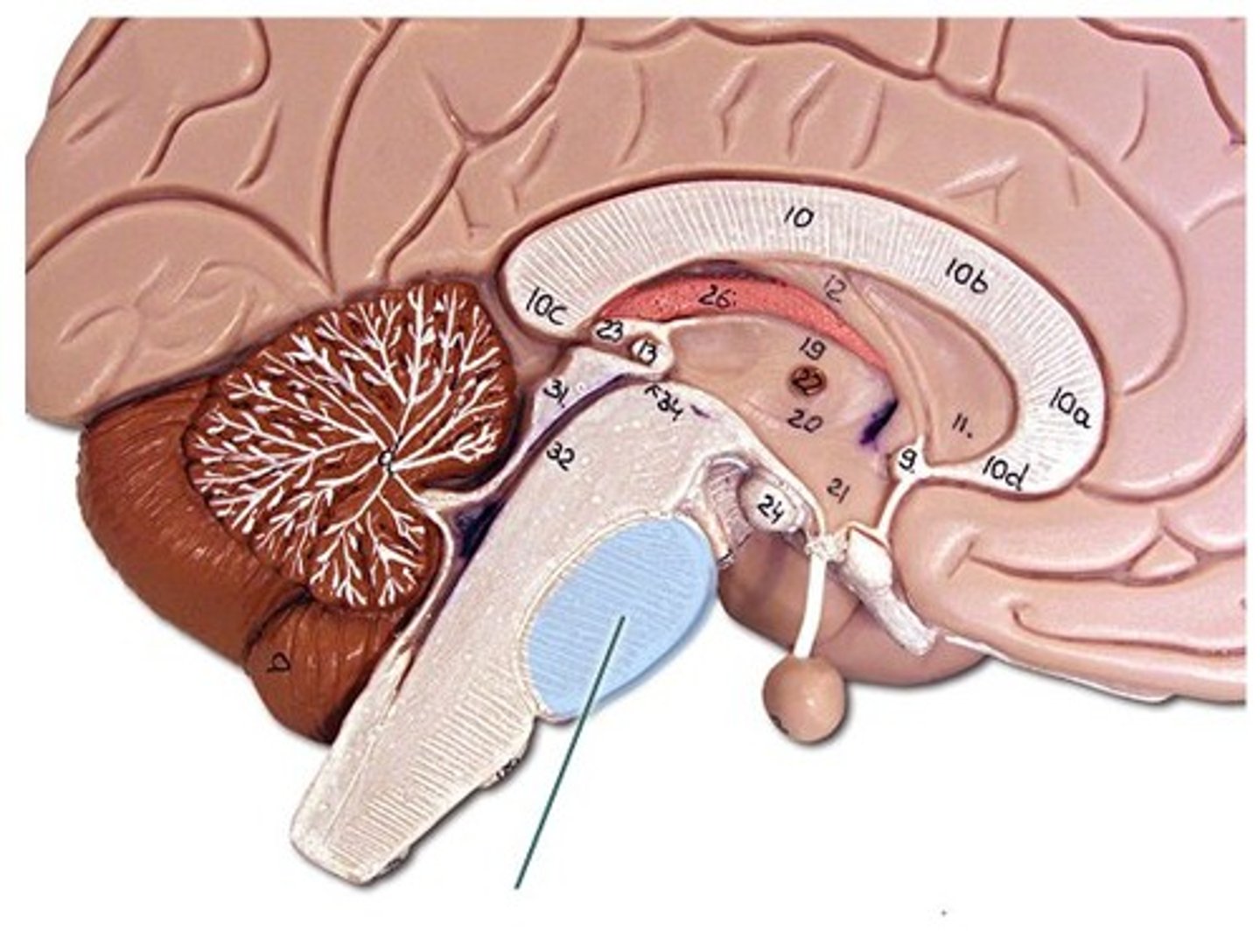
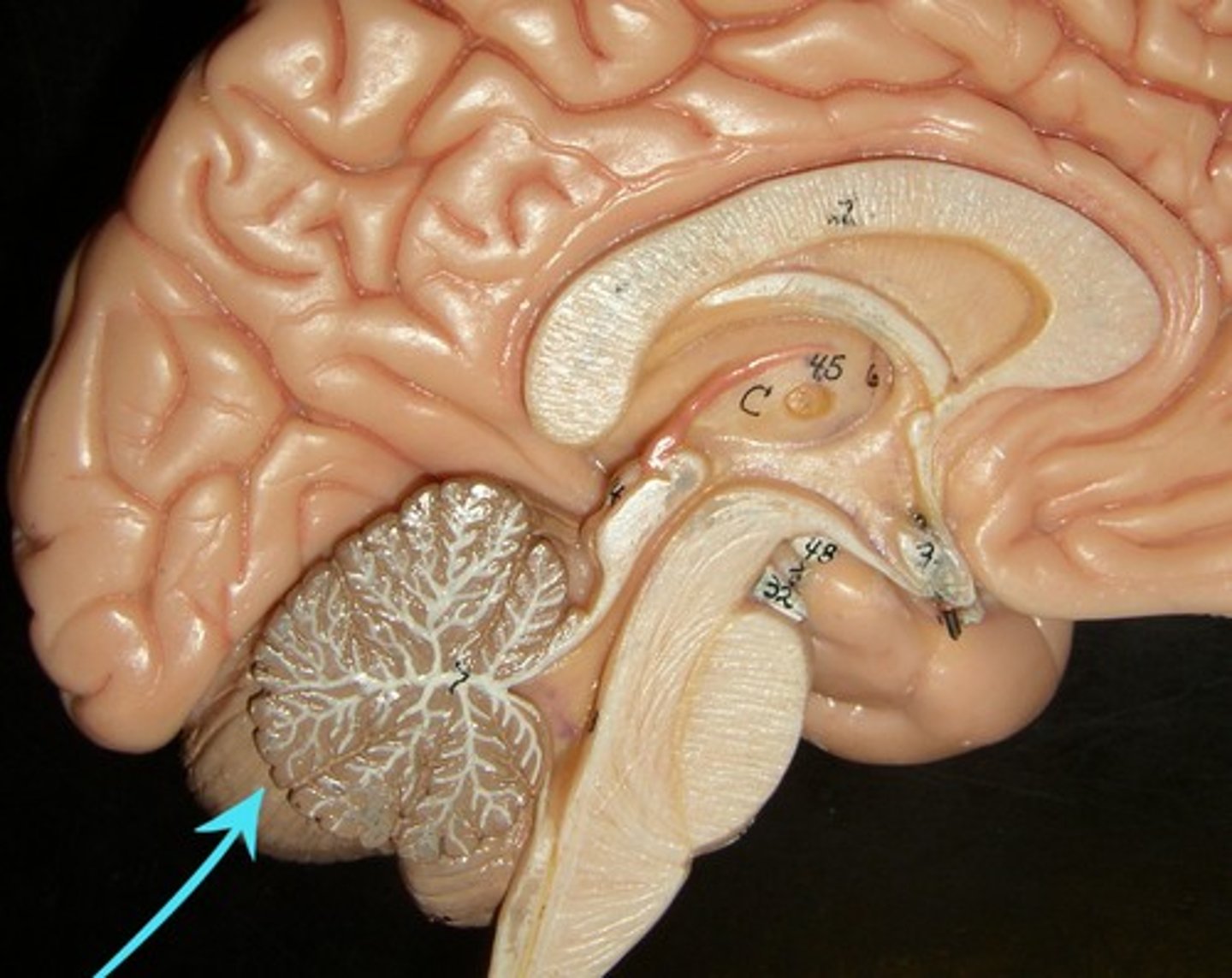
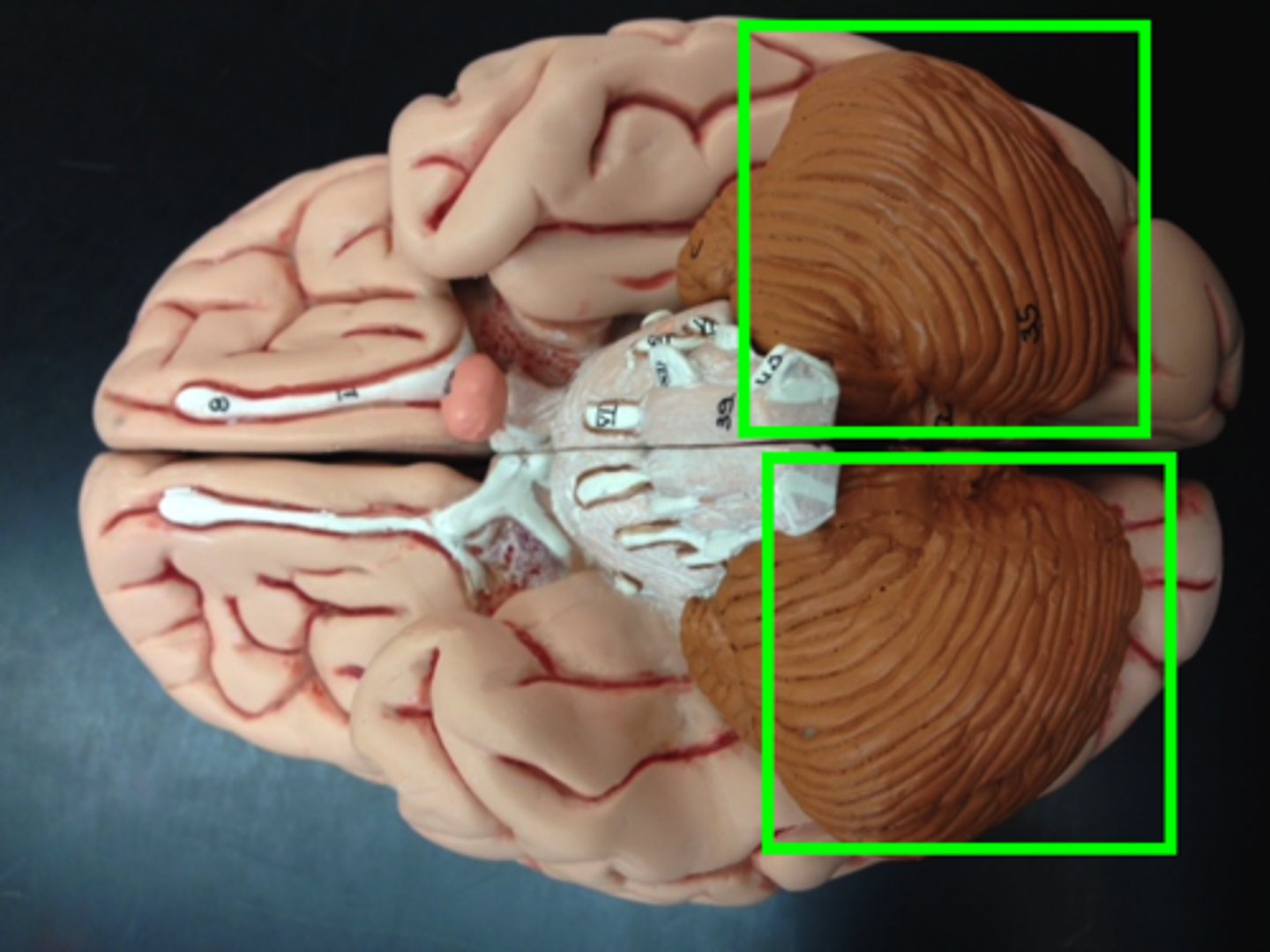
cerebellum
cerebellar hemispheres, cerebellar cortex, and arbor vitae.-
the little brain.
- Function: coordinates all voluntary movements. Ability to ride a bike, dance, anything complicated that calls for coordinating movement between left and right sides with skeletal muscles.
- Ability to move joints in a coordinated fashion- cerebellum in charge.
cerebellar hemispheres
divided by vermis.
cerebellar cortex
outer covering of cerebellum - gray matter.
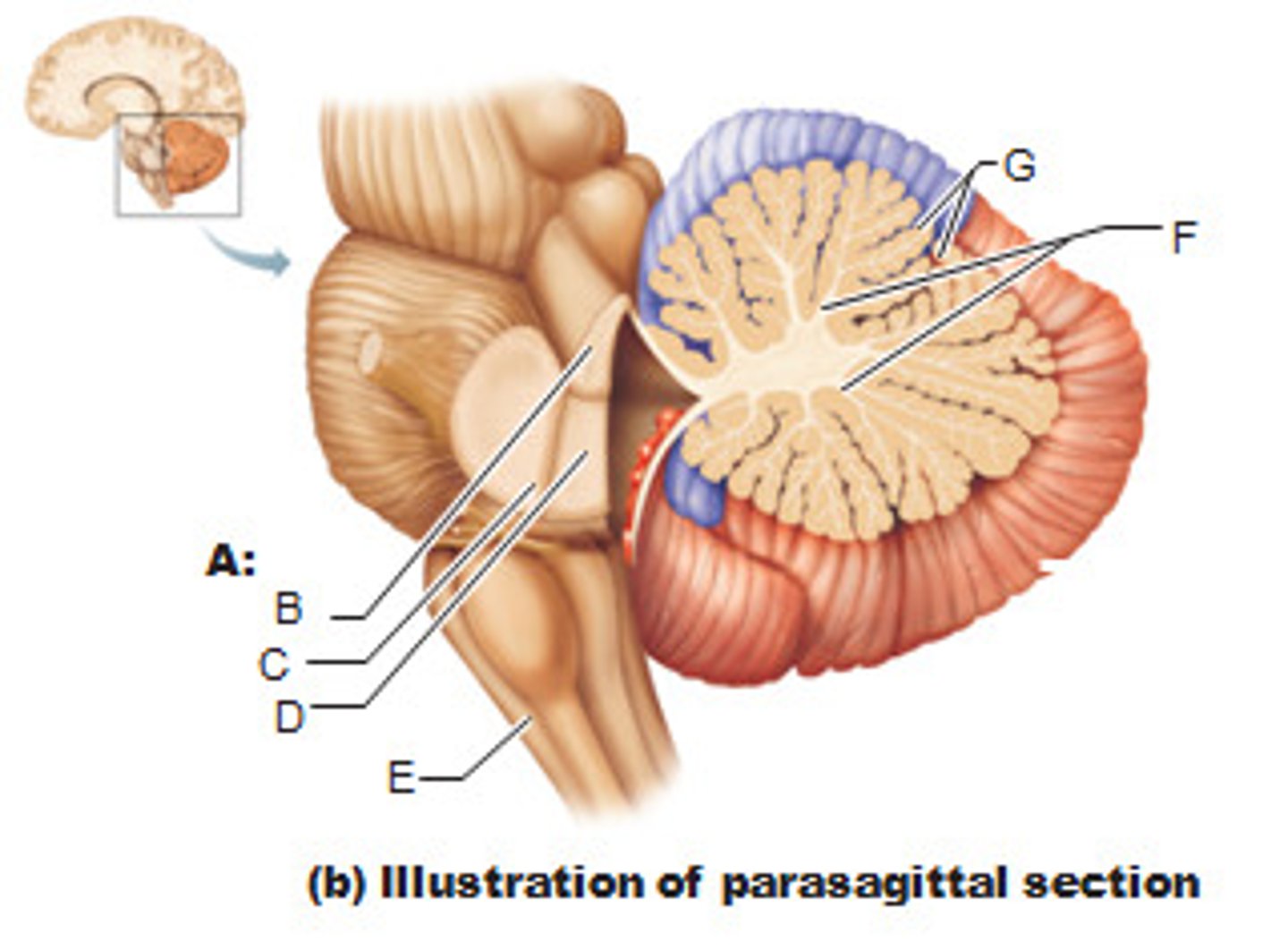
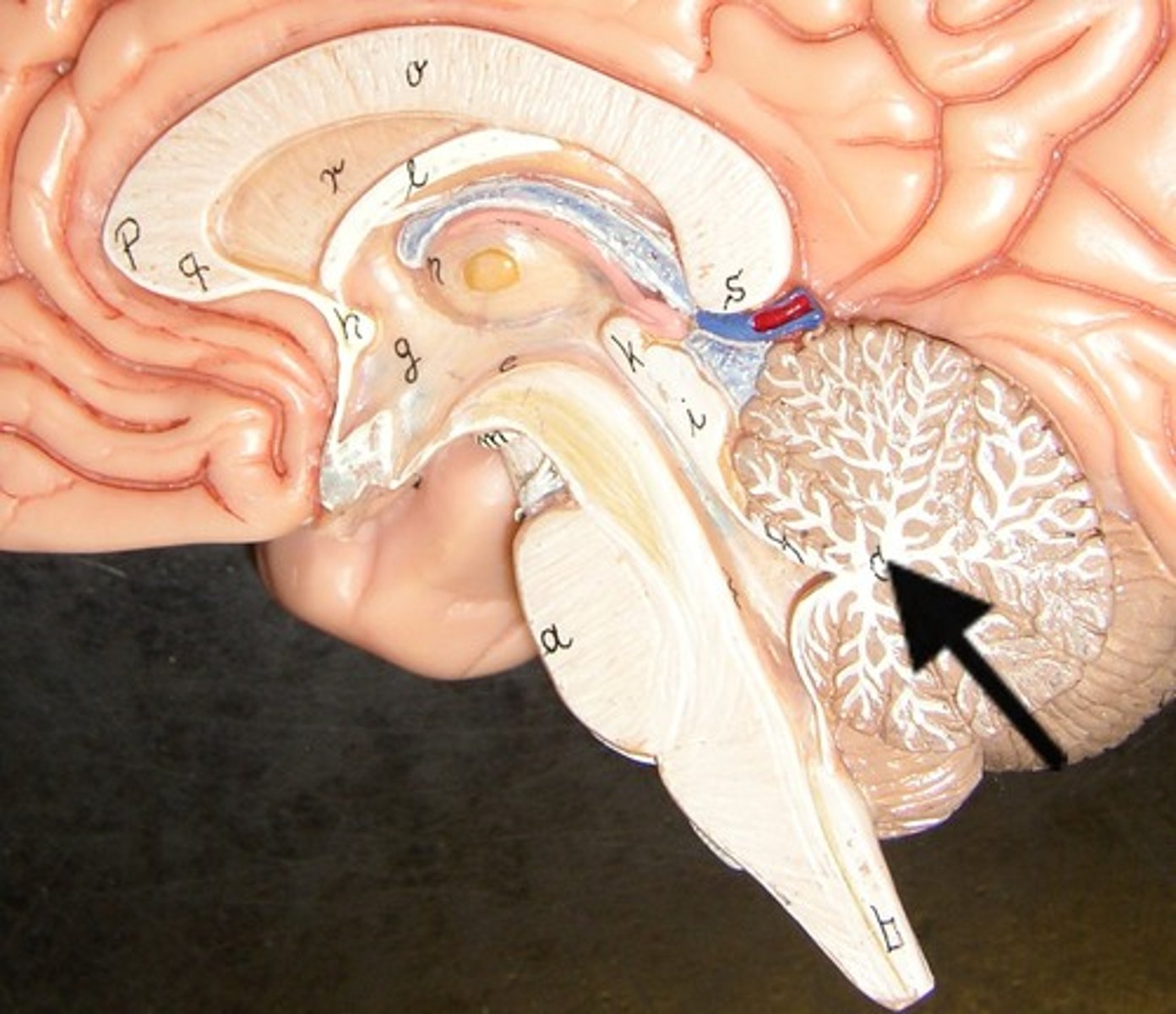
arbor vitae
"tree of life" white matter in cerebellum.
olfactory bulbs (I)
cranial nerve #1 (picking up information from outside). We transmit information to CNS and those portions below the bulb is the olfactory tract. Includes olfactory tracts
olfactory tracts
The portion below the olfactory bulb.
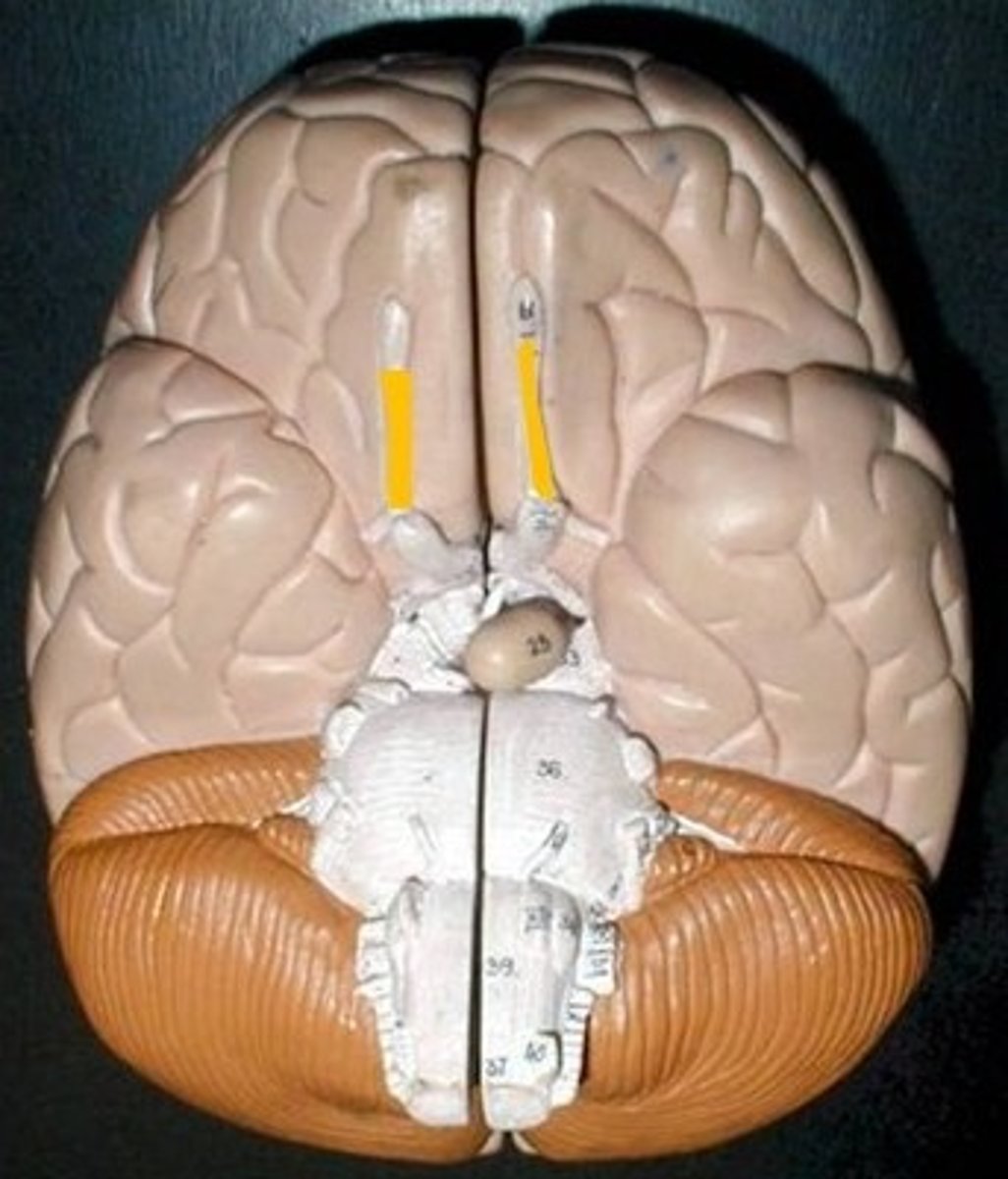
optic nerves (II)
Includes optic chiasma and optic tract. The X
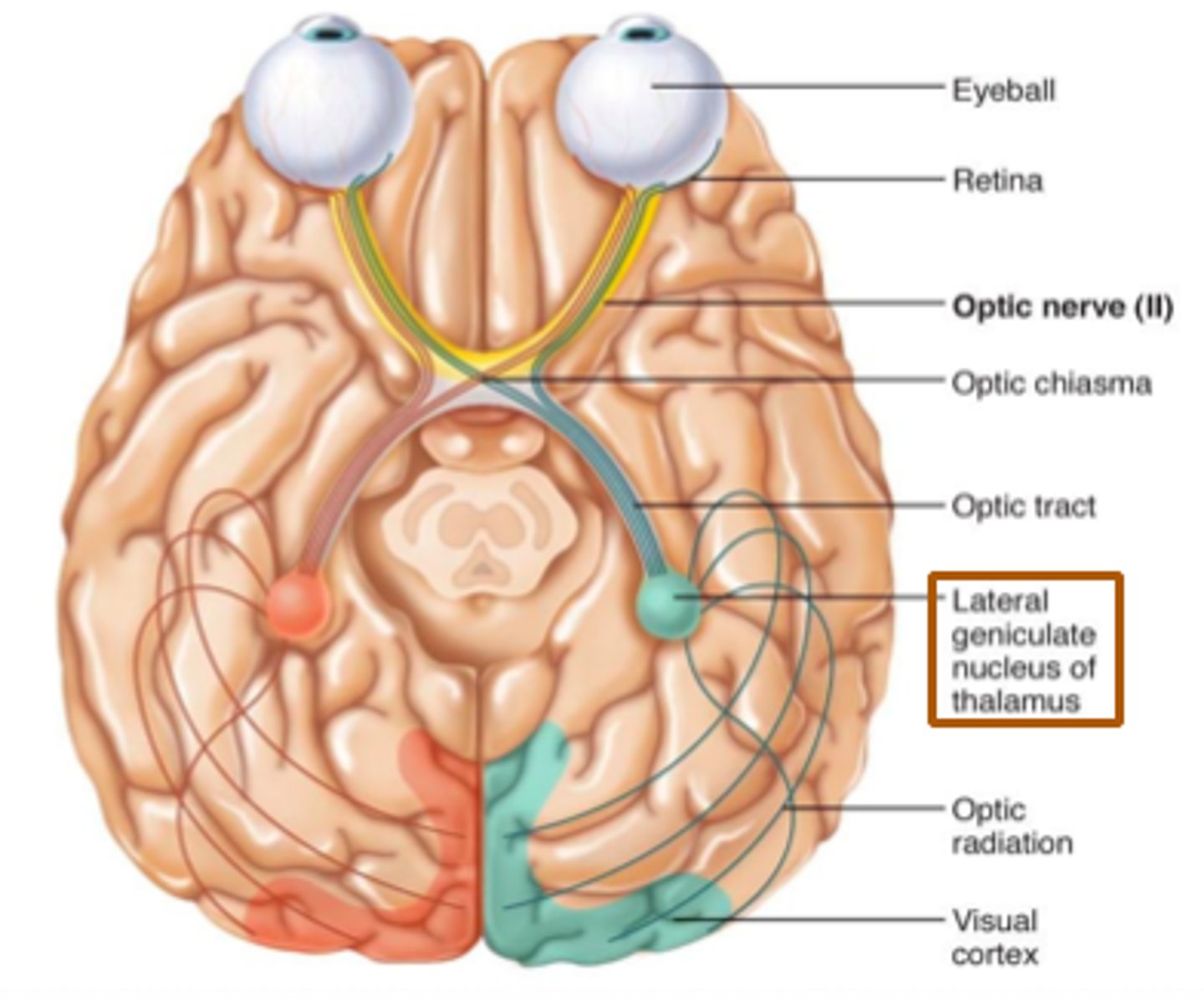
optic chiasma
portions of visual fields from both of eyes that cross here. Crossing over of information.
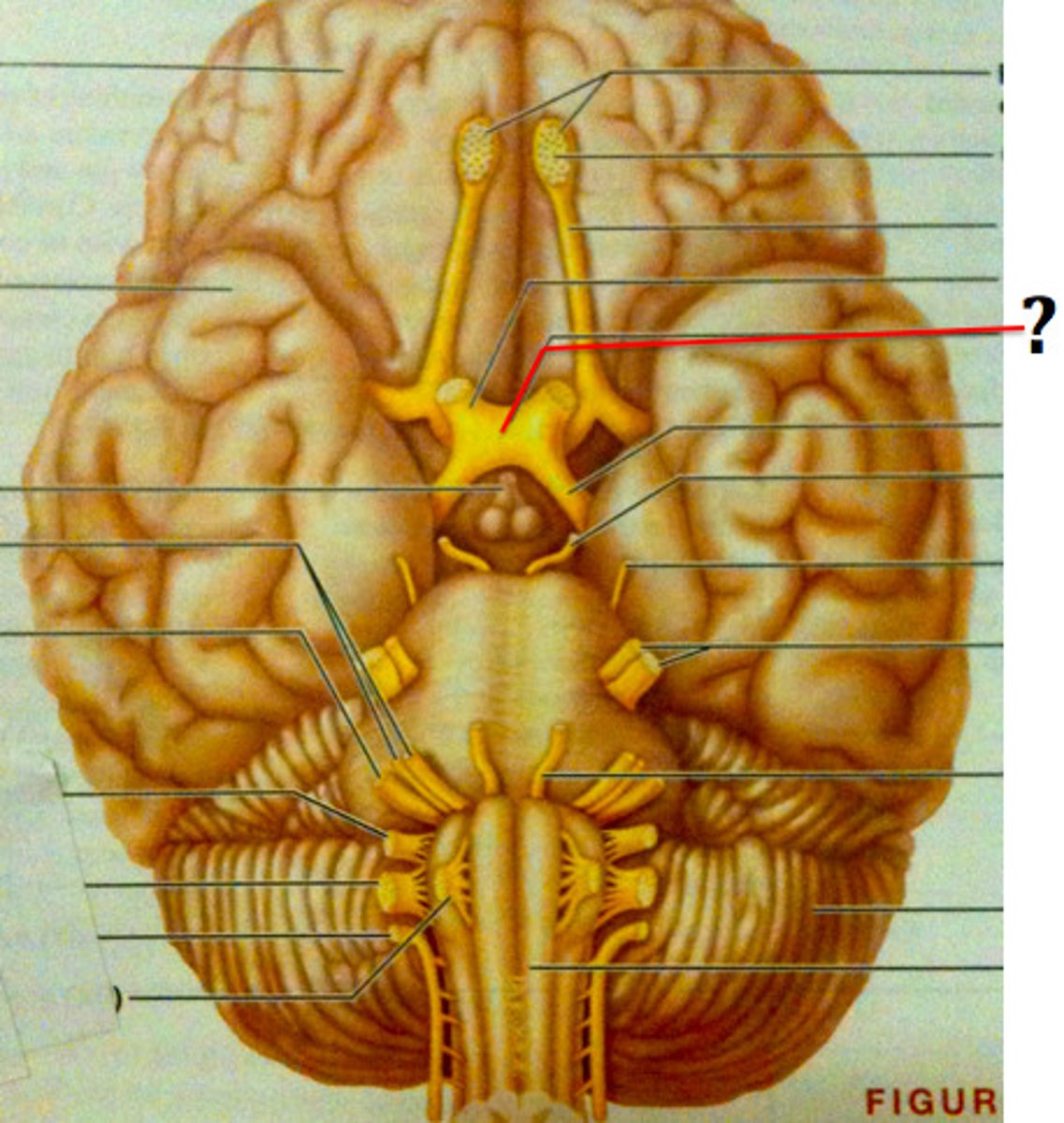
optic tract
bottom legs of the X. Goes to myelinated axons in CNS. This information should go to thalamus. It will go to occipital lobe.

ventricles
cavities in the brain. Includes lateral ventricles - right and left, third ventricle, fourth ventricle, cerebral aqueduct, and choroid plexus.
lateral ventricles (left and right)
right and left. Actual open space. Behind the corpus collosum.
- Cerebrospinal fluid circulates through these ventricles and underneath the meninges.
- Gives the brain buoyancy.
- brain floats a little bit and this prevents trauma.
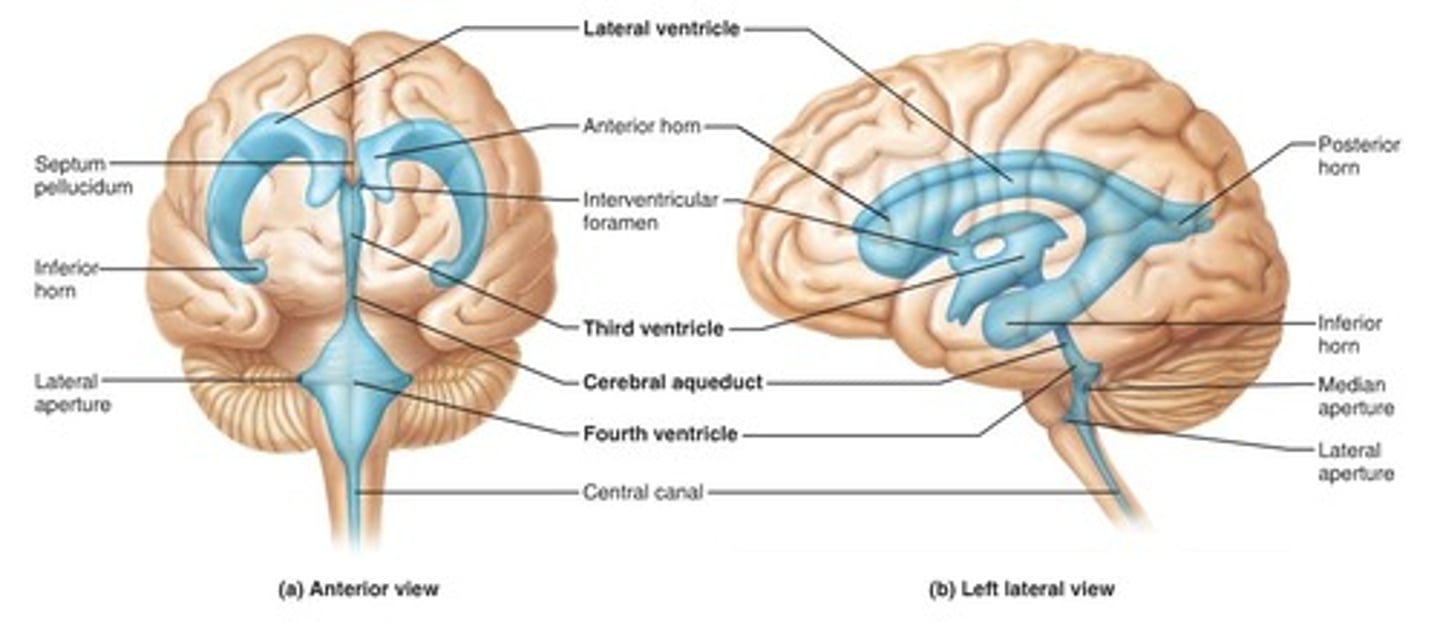
third ventricle
in the area where the hypothalamus is.
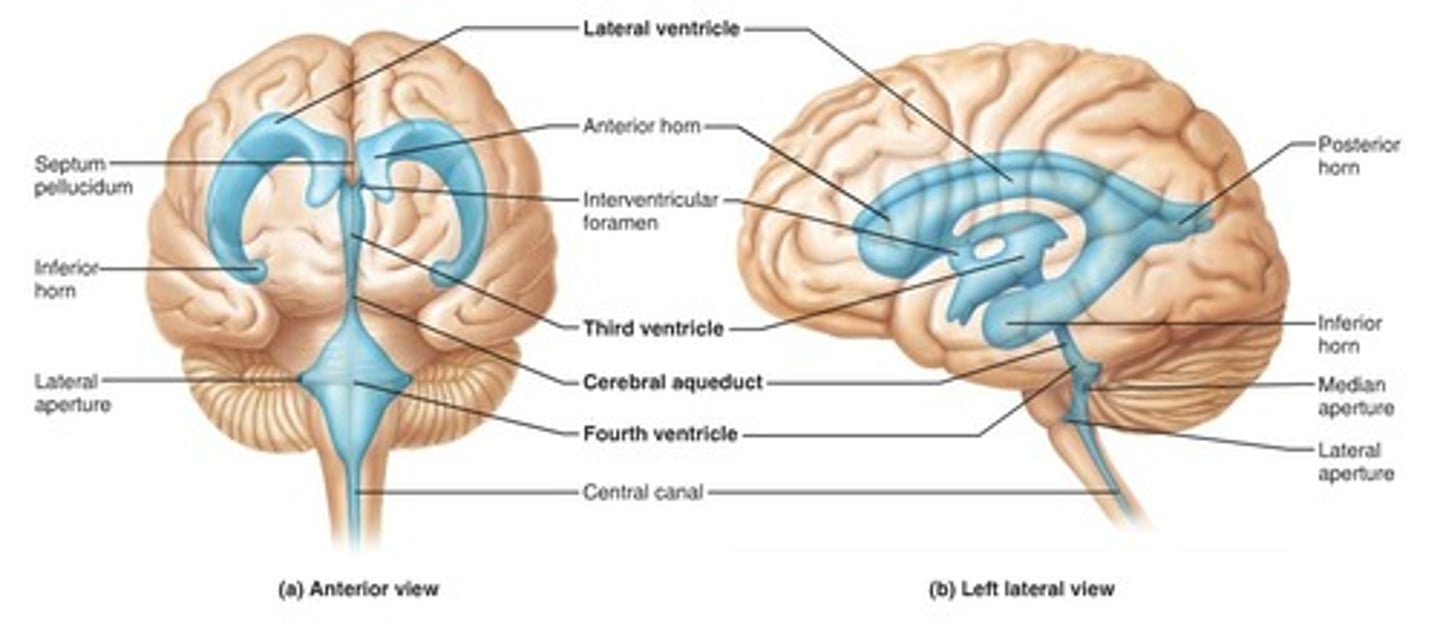
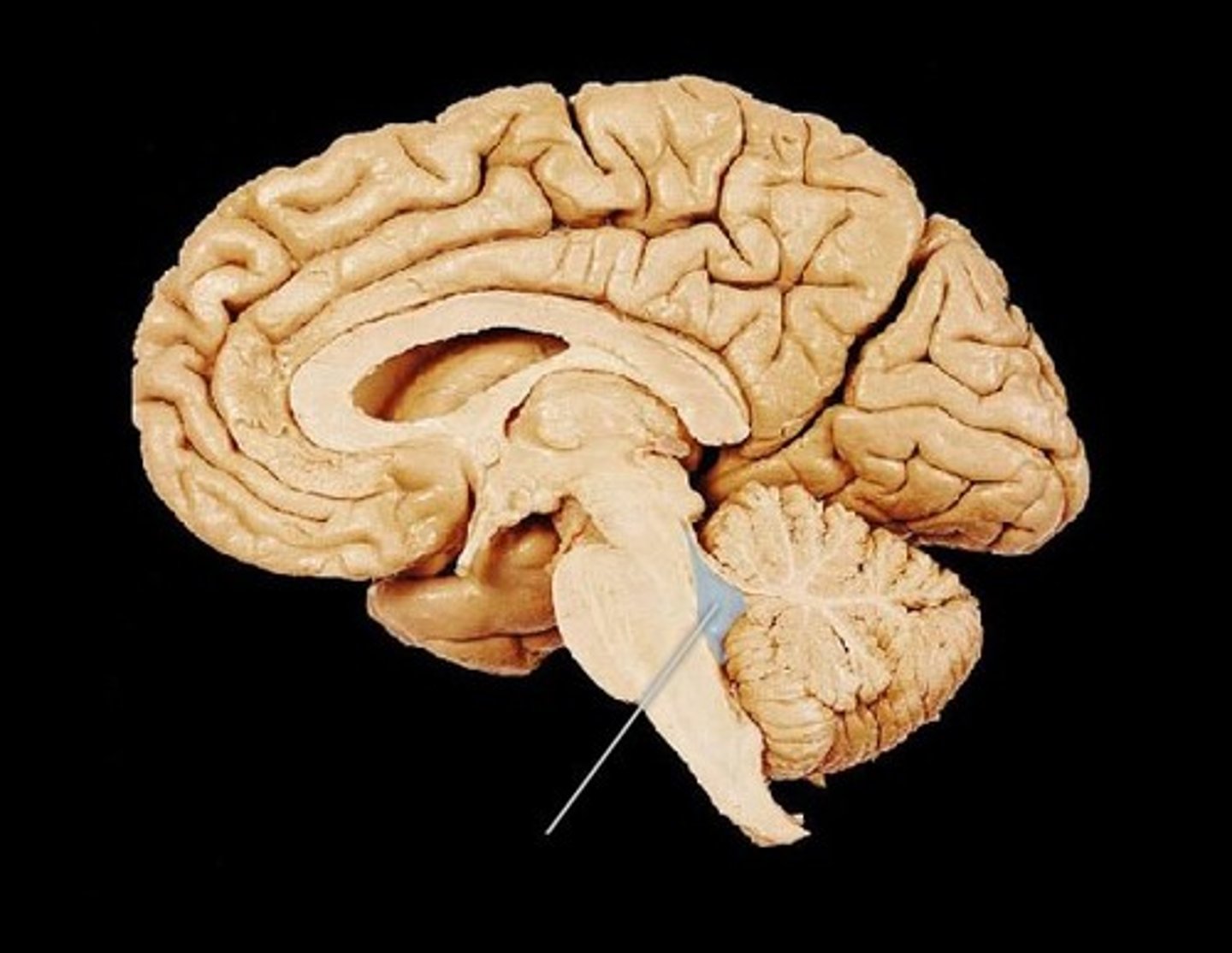
fourth ventricle
located beneath the arbor vitae in the cerebellum.
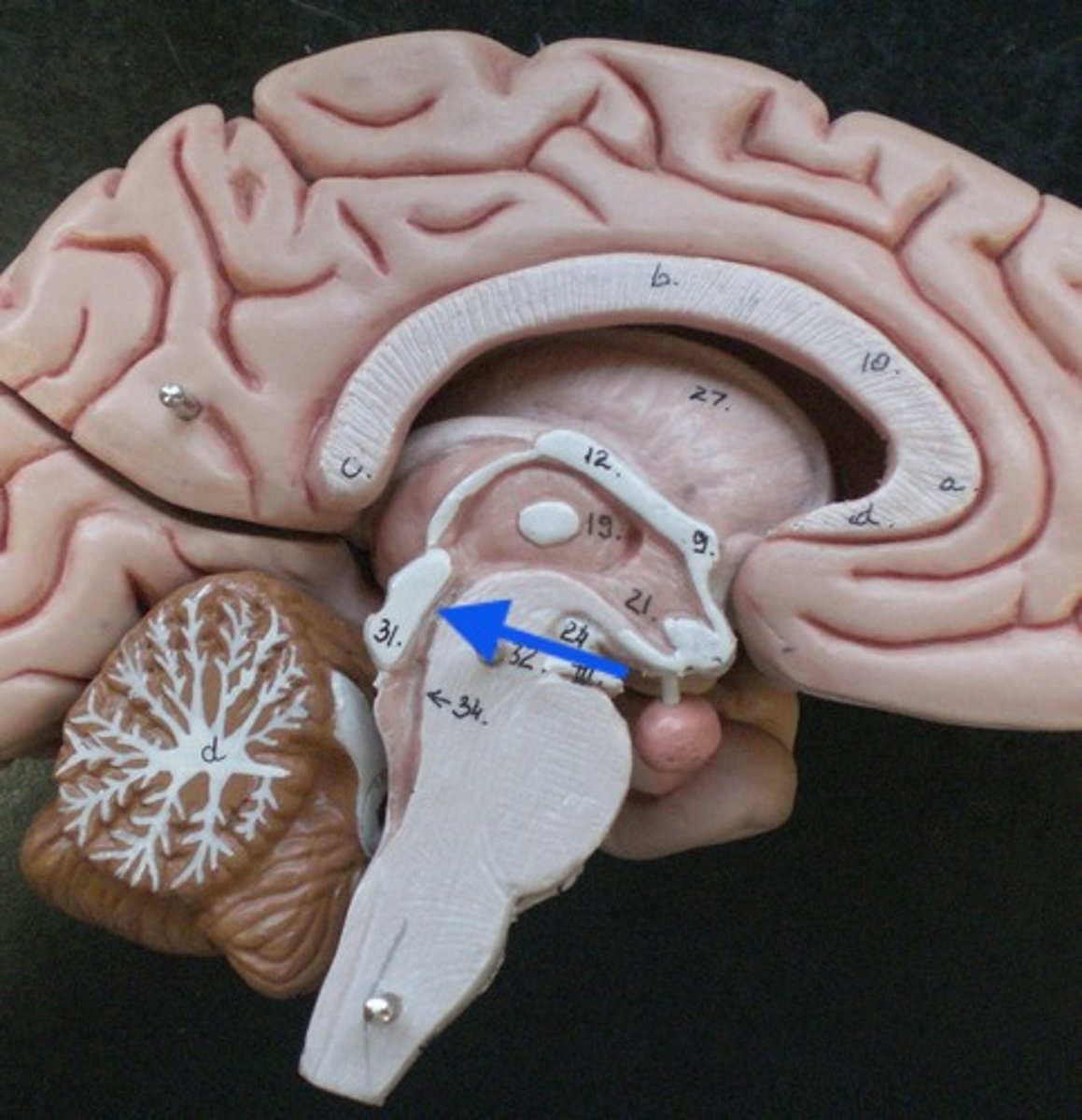
cerebral aqueduct
connector between third and fourth ventricle in front of colliculi.
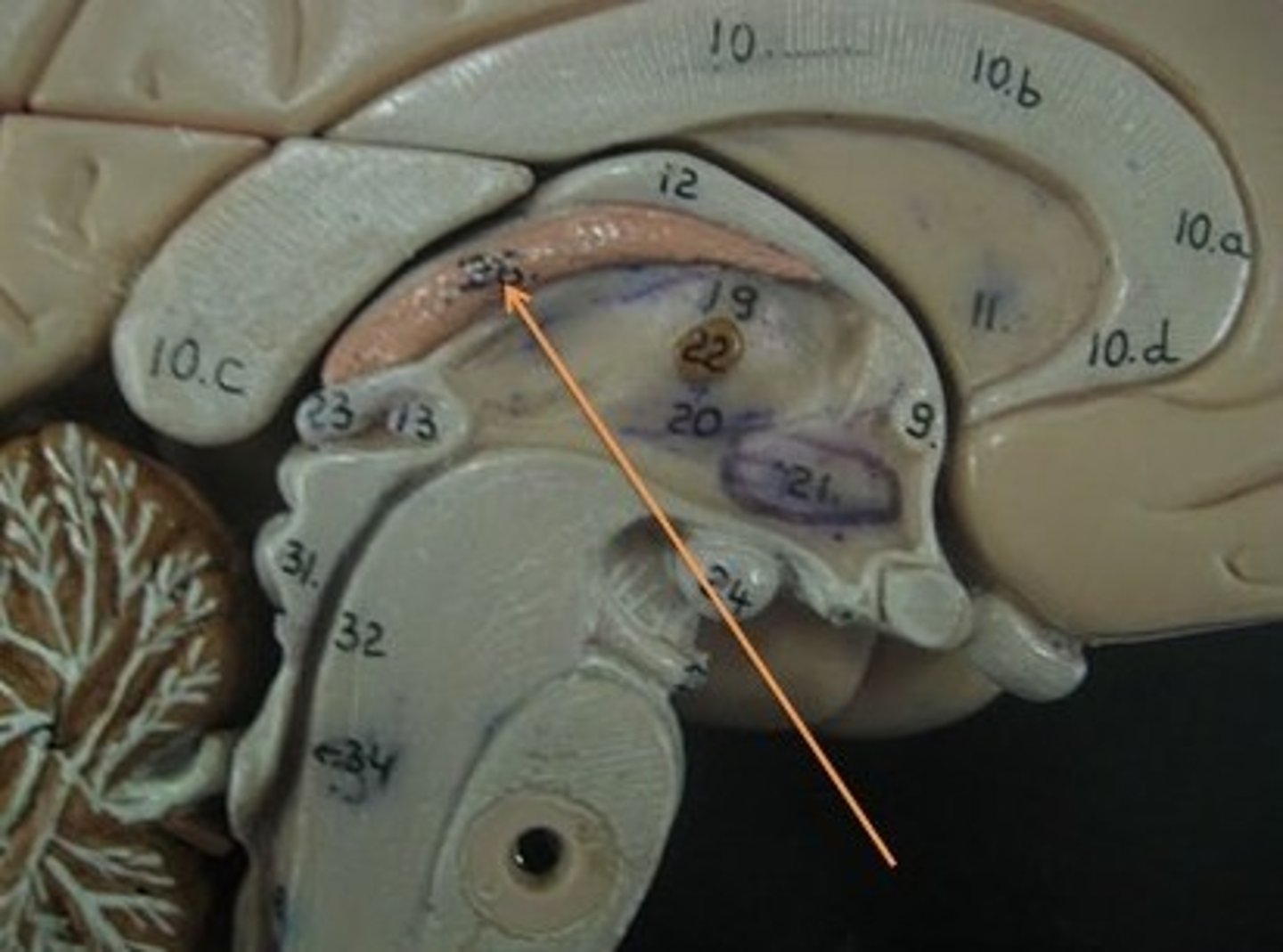
choroid plexus
ependymal cells - line ventricles and central canal of spinal cord.
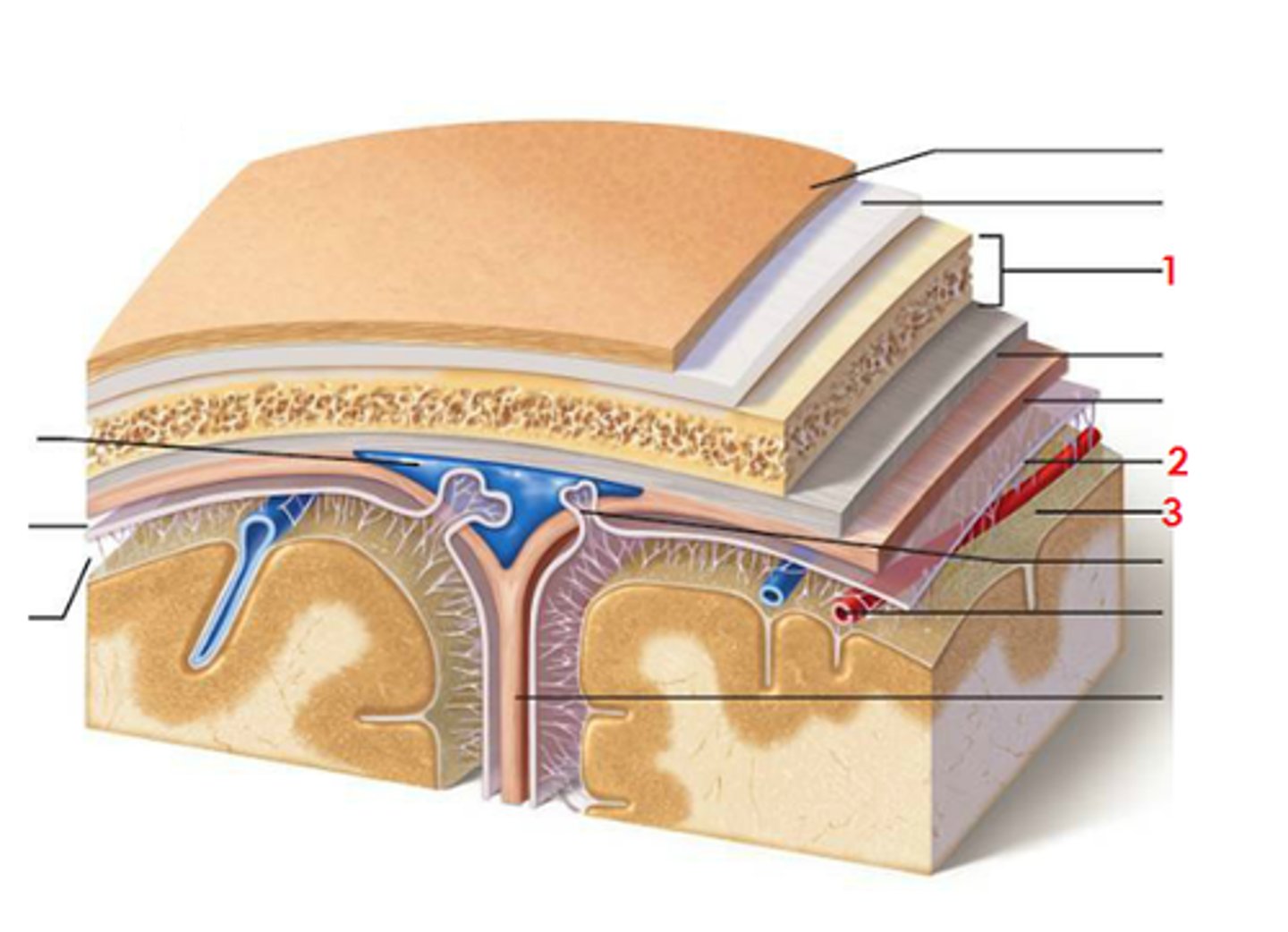
meninges
scalp, periosteium, then, 1st meningeal layer. Includes dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater.
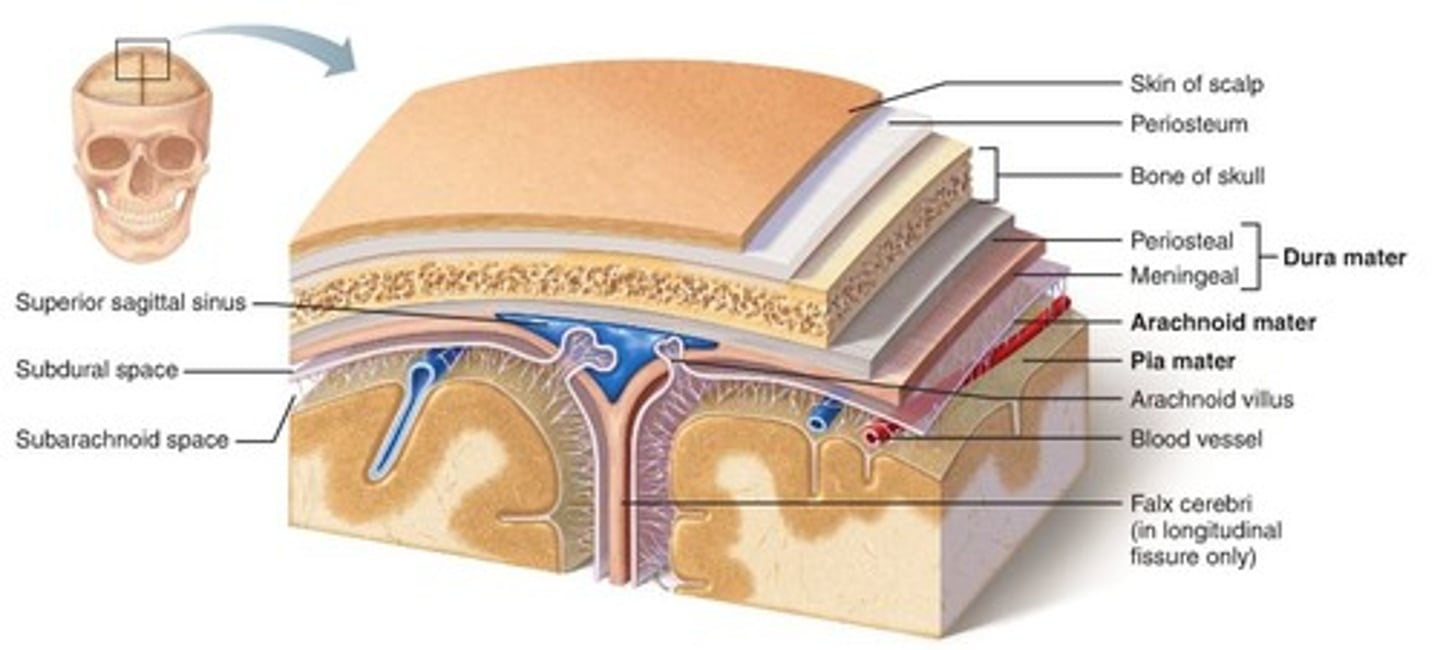
dura mater
2 layers. Periosteal layer (outer layer) and the meningeal layer - closest to next meningeal layer. This can create the dural venous sinus. right below 1 in this picture
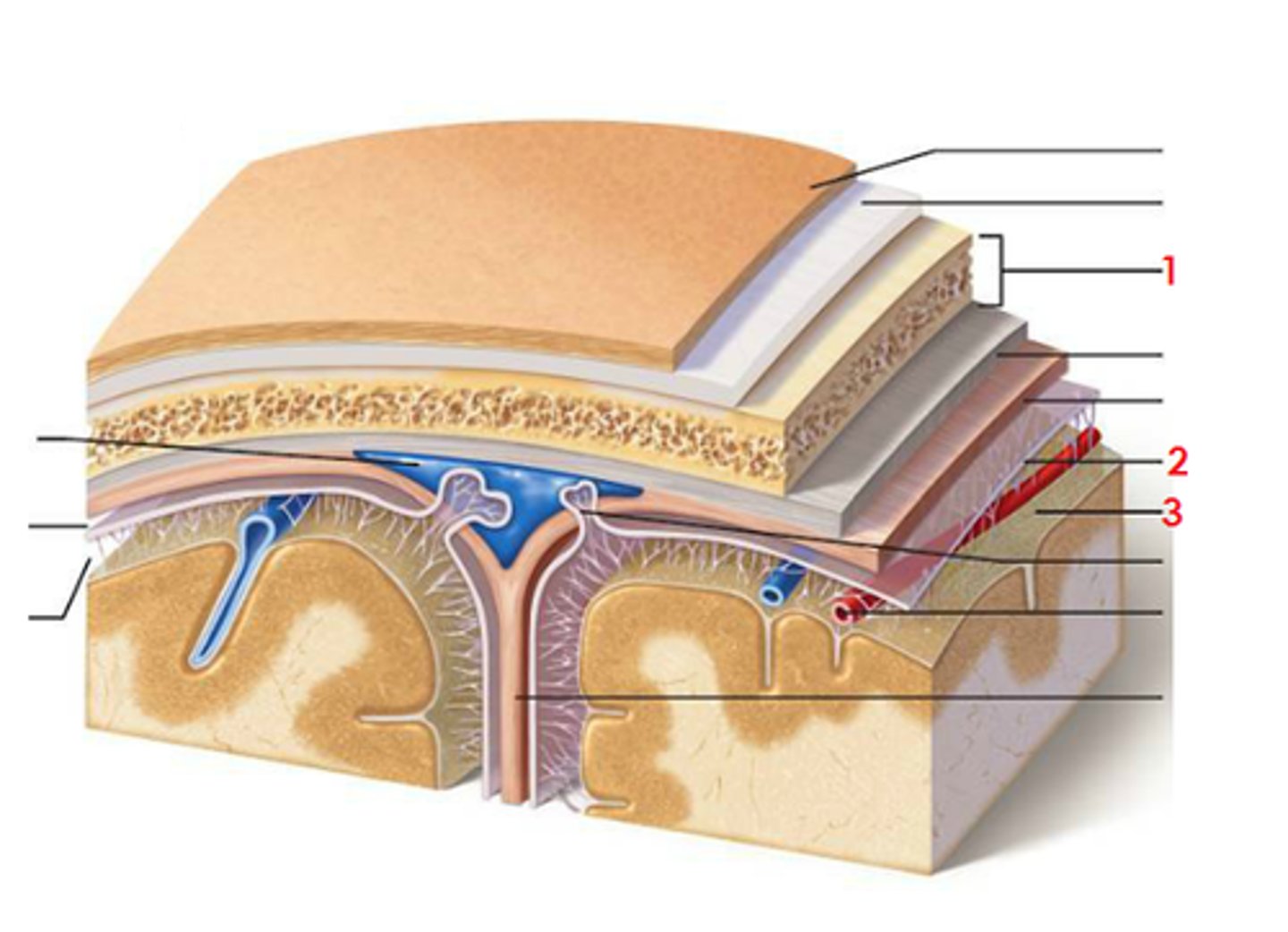
arachnoid mater
meningeal layer on top. 2 in this picture
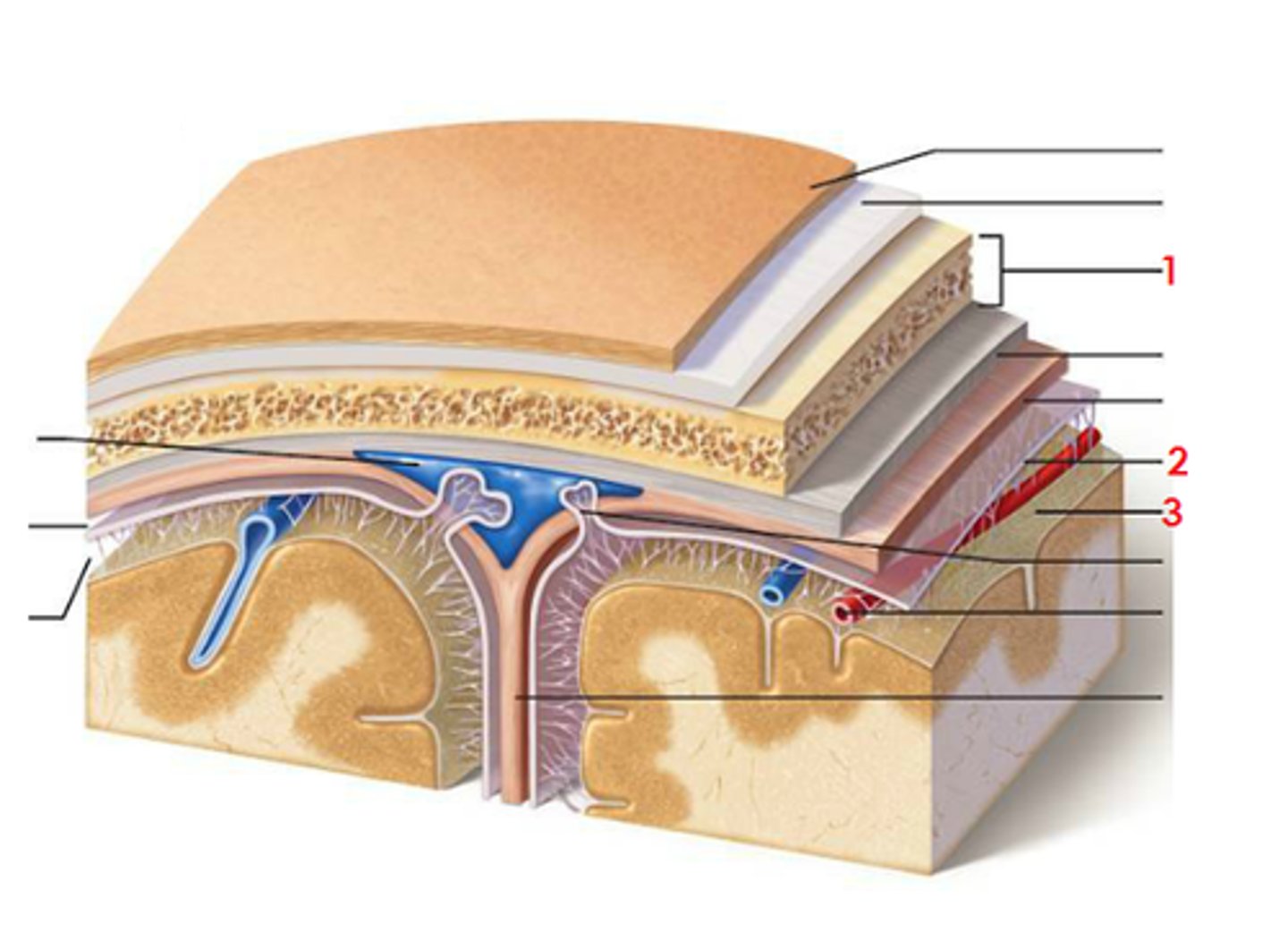
pia mater
sits directly on top of brain tissue. When CSF circulates, it circulates on top of brain tissue. If you try to tear pia mater away, you'll tear brain tissue. 3 in this picture