31. Disorders of the penis and prepuce – hypospadias, phimosis, paraphimosis
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What is hypospadias?
A rare congenital condition where the urethral opening is abnormally located
What developmental failure leads to hypospadias?
Failure of urogenital folds to fuse and incomplete development of the penile urethra
How is hypospadias classified?
Based on the location of the urethral opening (glandular, penile, scrotal, perineal, anal)
What other congenital condition is commonly seen with hypospadias?
Cryptorchidism
Which dog breed has a predisposition for hypospadias?
Boston terriers

How is hypospadias typically diagnosed?
During the first puppy examination by observing urine output from an unusual orifice
What are the clinical signs of hypospadias?
Urinary incontinence, periurethral dermatitis, recurrent UTIs, excessive licking
What surgical treatments are available for hypospadias?
Scrotal or perineal urethrostomy (subpubic in cats) + castration and removal of prepuce and penile tissues
When might surgery not be required for hypospadias?
If the urethral opening is near the tip of the penis
What is phimosis?
Inability to protrude the penis
Is phimosis common or rare in dogs?
Rare
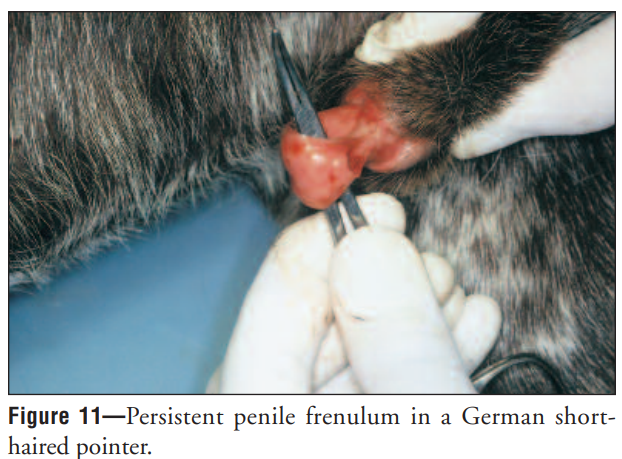
What are some causes of phimosis?
Persistent frenulum, short penis, small preputial opening or stricture (inflammation, neoplasia), trauma
What reproductive condition can predispose a dog to phimosis?
Cryptorchidism
What are the clinical signs of phimosis in dogs?
Licking, dermatitis (urine scalding), phallocampsis, inability to breed, pain
What are the clinical signs of phimosis in cats?
Dysuria, outflow obstruction, haematuria, distended bladder, balanoposthitis
How is phimosis diagnosed?
Physical exam (inability to protrude penis), potentially with sedation, semen collection in the presence of a bitch
What are the treatment options for phimosis?
Treating the underlying cause, surgery (cutting the frenulum or widening the preputial opening)
What is paraphimosis?
Inability to withdraw the penis into the prepuce
Is paraphimosis common or rare in dogs?
Common (especially in toy breeds due to masturbation)
What hormone is thought to mediate paraphimosis?
Testosterone
When is paraphimosis most likely to occur in relation to sexual maturity?
Prepubertal or during sexual arousal
What are some causes of paraphimosis?
Oedema of the penis (balanoposthitis), small preputial orifice, short prepuce, neurological issues, phenothiazine tranquillisers, being around bitches in heat, trauma
What preventative measure can be taken for paraphimosis?
Castration
What are the clinical signs of paraphimosis?
Dry, excoriated penis (ischaemia), self-mutilation, stranguria, haematuria, anuria
What factors influence the prognosis of paraphimosis?
Promptness of treatment and the degree of trauma or necrosis
How is paraphimosis diagnosed?
Physical exam, neurological exam, X-ray, MRI, CT (for IVDD), CSF check (for encephalitis)
What are the initial treatment steps for paraphimosis?
Lubrication, cold compress with hyperosmolar solution, repositioning the penis
What surgical interventions might be necessary for paraphimosis?
Surgical widening of the prepuce or amputation of the penis if necrotic or impossible to reposition
What is phallocampsis?
Abnormal curvature of the penis, sometimes seen with phimosis.
What does stranguria refer to?
Slow and painful urination, a potential sign of paraphimosis.
What is balanoposthitis?
Inflammation of the glans penis and prepuce, a potential cause of paraphimosis.
What is IVDD?
Intervertebral disc disease, a neurological condition that can contribute to paraphimosis.