Chemistry Midterm
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/126
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
1
New cards
Chemistry
The study of the composition, structure, and transitions of matter.
2
New cards
Inertia
How much force is required to move an object
3
New cards
condensation
Gas to liquid
4
New cards
Sublimation
Solid to gas
5
New cards
Density
The ratio of an object's mass to its volume.
6
New cards
The scientific method
problem solving process/method
7
New cards
A hypothesis is...
A suggested answer to a problem
8
New cards
What is true of theories?
They are part of the scientific method, they help organize a body of data, they are supported by experimental data.
9
New cards
What are four branches of chem?
Inorganic, organic, analytical, and biochemistry
10
New cards
What are the three major temperature scales?
Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin
11
New cards
What is the difference between a hypothesis, a theory, and a scientific law?
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested, a theory is a highly supported hypothesis, and a law is a mathematically proven theory.
12
New cards
What kinds of compounds are composed of carbon?
Organic
13
New cards
Qualitative analysis
Determination of composition
14
New cards
Quantitative
A determination of the % of each element in a cpd.
15
New cards
How many naturally existing elements are there?
92
16
New cards
Can a scientific law be proven mathematically?
Yes
17
New cards
List and explain the several different properties of matter.
Mass- the quantity of matter,
volume- how much space an object takes up,
inertia- the resistance force required to move an object,
impenetrability- 2 objects cannot occupy the same space simultaneously,
density- the ratio of an object's mass to its volume.
volume- how much space an object takes up,
inertia- the resistance force required to move an object,
impenetrability- 2 objects cannot occupy the same space simultaneously,
density- the ratio of an object's mass to its volume.
18
New cards
What are the four states of matter?
Solids, liquids, gases, and plasma
19
New cards
What is an example of heterogeneous matter?
Heterogeneous matter is either a mixture or a solution. For example, mixing salt and sand together.
20
New cards
List and explain the steps in the scientific method.
State the problem---what you are researching, Review the Literature---read the studies that have been conducted concerning your topic, Hypothesis---a statement that can be tested, Experimenting---gather data in order to make inferences, Theory---A likely explanation for a phenomenon, Law---Mathematically proven theory
21
New cards
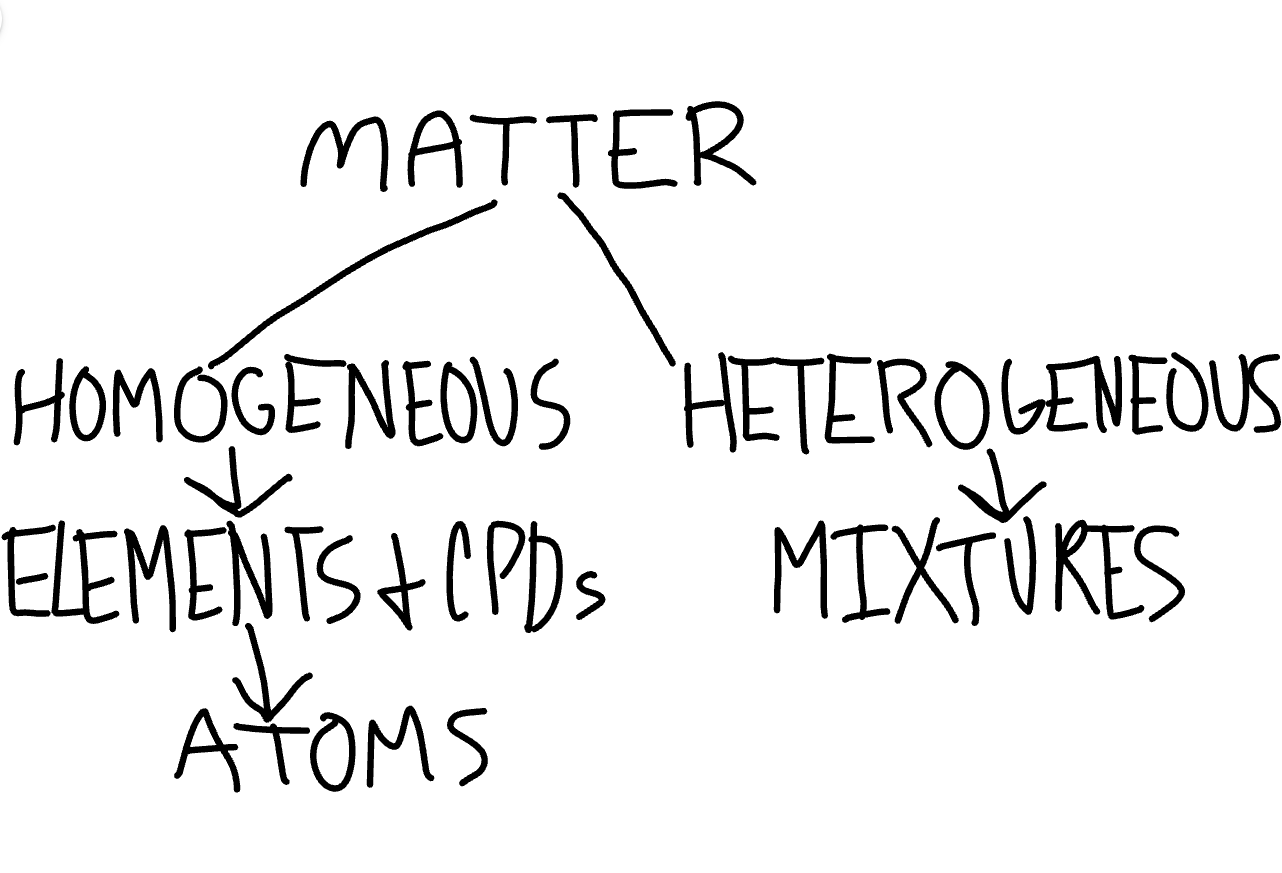
Show and explain the classification of matter.
Matter is either homogeneous or heterogeneous. Homogeneous matter is a pure substance consisting of elements and cpds. It is also the physical composition of atoms. Heterogeneous matter is impure, and consists of mixtures and solutions.
22
New cards
Accuracy
The nearness of a measurement to its accepted value
23
New cards
Precision
the agreement between measurements using the same apparatus and materials
24
New cards
know how to convert
Kilo-hecto-deca- |standard| -deci-centi-milla
25
New cards
Equivalents
1K= 2.2 lbs
1L= 1.06 qts
1L= 1.06 qts
26
New cards
V r.s.=
l x w x h
27
New cards
V cyl. =
πr²h
28
New cards
Vcube=
e³
29
New cards
Vsphere (s)=
4/3 πr³
30
New cards
Density formula
Mass/volume
31
New cards
Fahrenheit formula
==F= 9/5 c +32==
32
New cards
Celsius formula
==C=5/9 (F-32)==
33
New cards
Kelvin formula
==K=C +273==
34
New cards
electromagnetic radiation
Forms of NRG that travel as waves at the speed of light
35
New cards
Frequency
the number of cycles per second
36
New cards
electron dot notation
a means of expressing valence electrons
37
New cards
Valence electrons
The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom
38
New cards
Octet
a stable atom having a full orbital of 8 electrons
39
New cards
spectra
The characteristic wavelength emitted by an excited atom
40
New cards
What is the unit for wavelength
angstrom
41
New cards
This particle has mass of 9.11 x 10⁻²⁸
electrons
42
New cards
What form of radiation is highest in NRG
Gamma Rays
43
New cards
An atom that gain an electron will have a _____ electric charge
negative
44
New cards
Which particles are found in the nucleus of an atom
protons & neutrons
45
New cards
What is the relationship between NRG of waves and wavelength?
The longer the wavelength, the lower the NRG
46
New cards
The _____ is the unit for frequency
Hertz (Hz)
47
New cards
State the Aufbau principle
Electrons must enter orbitals of lowest NRG first
48
New cards
Definition of the term “atom”
The smallest unit of an element/matter
49
New cards
The speed of electromagnetic radiation (light) is
186,000 mi/sec
50
New cards
State Hund’s Rule
Within a sub-level, each orbital must have one electron before they start pairing up
51
New cards
What are isotopes?
Atoms of the same element having a different atomic mass
52
New cards
List the four kinds of atomic orbitals
S, P, D, F
53
New cards
Explain the relationship between the energy of a wave and frequency
The higher the frequency, the higher the energy of a wave
54
New cards
What is the difference between the terms atomic mass and mass number?
The mass number is the mass of an atom’s protons plus it neutrons, while the atomic mass is the total mass of an atom’s protons, neutrons, and electrons
55
New cards
What is the formula for calculating the velocity of electromagnetic waves?
V= f x λ (velocity = frequency x wavelength)
56
New cards
The atomic number of an atom represents the quantity of ______
protons
57
New cards
List and explain the energies of the electromagnetic spectrum from highest to lowest
As you go towards the left side of the list, NRG is extremely high, frequency is extremely high, and wavelength is shorter. As you go to the right side of the list, the frequency decreases, NRG decreases, and wavelength is longer. Gamma Rays have the highest NRG and radio waves have the lowest. Everything to the left of the squiggly line is called ionizing radiation. Visible light is what humans can see, including red, orange, yellow, green, indigo, and violet.

58
New cards
Explain the term “hybridization” and its significance in atomic structure
Hybridization is the combination of two orbitals of near equal NRG to form a single orbital that is more stable. This is significant because hybridization provides a more simple way for atoms to become stable.
59
New cards
What is the difference between the continuous vs. bright line spectra of an excited atom?
The continuous spectrum is the summation of all wavelengths emitted by an excited atom, while the bright line spectrum is the individual wavelengths emitted by an atom.
60
New cards
periodic table-
a listing of all known elements
61
New cards
Cation-
a positively charged atom
62
New cards
Ionization NRG
the NRG used to lose an electron
63
New cards
noble gases
elements in group 8 that have an octet structure and are ==__extremely__== stable
64
New cards
transition elements
elements that have more than one oxidation state
65
New cards
who based the periodic table on atomic number?
Moseley
66
New cards
What are the elements in group II called?
Alkaline earth
67
New cards
What indicates the quantity of valence electrons?
Group
68
New cards
T/F: Cations are generally larger in radii compared to their “parent” atom
False
69
New cards
T/F: Group VII are called halogens
True
70
New cards
T/F: The unit of the atomic radii is the millimeter
False
71
New cards
T/F: The noble gases were discovered by Sir William Ramsey
True
72
New cards
T/F: Halogens have very high electron affinity
True
73
New cards
State the periodic law
when elements are arranged by their atomic number
74
New cards
What is the difference between a group and a period?
A group is a vertical row and has 8
A period is a horizontal row and has 7
A period is a horizontal row and has 7
75
New cards
List five non-metals
Oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, neon, and fluorine
76
New cards
The _____ is the unit for atomic radii and is equal to ______
picometer; 10⁻¹⁰m
77
New cards
Which elements generally have “high” ionization energies?
Non-metals
78
New cards
Ionization NRG (increases or decreases) as one goes down a group.
DECREASES
79
New cards
List several synthetic materials
Cerium, europium, plutonium, curium
80
New cards
list several gaseous elements
Oxygen, helium, carbon, sulfur,
81
New cards
What are the metalloids?
metalloids are elements that have properties of both metals and non-metals
82
New cards
what is the unit for ionization NRG and electron affinity
kcal/mole
83
New cards
what is \[Xe\]6s²4f⁷
Eu
84
New cards
what is the difference between atomic number, mass number, and atomic weight?
the atomic # is the number of protons in an atom. The mass # is the amount of protons + neutrons in an atom. Atomic weight is the total mass of the atom
85
New cards
What are the lanthanide and actinide series of the elements?
continuation of periods six and seven
86
New cards
electronegativity-
an atom’s desire to share electrons
87
New cards
A + ____ → A⁺ + _ _ _ (explain)
NRG; 1e⁻; An atom plus NRG reacts and creates an atom with a positive charge and has one valence electron
88
New cards
Discuss the 8 major groups of elements.
Group I: Alkali Metals- oxidation #: +1, 1 valence electron, extremely active, extremely low ionization NRG, Xs¹
Group II: Alkaline Earth Metals- oxidation #: +2, Xs², very low ionization NRG
Group III: The Aluminum Family- oxidation #: +3, Xs²px¹, high ionization NRG
Group IV: The Carbon Family- oxidation # varies, Xs²px¹py¹, high ionization NRG
Group V: The Nitrogen Family- oxidation #: +3, -3, +5, very high ionization NRG
Group VI: The Oxygen Family- oxidation #: -2, very high ionization NRG
Group VII: The Halogens- oxidation #: -1, extremely high ionization NRG
Group VIII: The Noble Gases- oxidation #: 0, extremely stable, extremely high ionization NRG
Group II: Alkaline Earth Metals- oxidation #: +2, Xs², very low ionization NRG
Group III: The Aluminum Family- oxidation #: +3, Xs²px¹, high ionization NRG
Group IV: The Carbon Family- oxidation # varies, Xs²px¹py¹, high ionization NRG
Group V: The Nitrogen Family- oxidation #: +3, -3, +5, very high ionization NRG
Group VI: The Oxygen Family- oxidation #: -2, very high ionization NRG
Group VII: The Halogens- oxidation #: -1, extremely high ionization NRG
Group VIII: The Noble Gases- oxidation #: 0, extremely stable, extremely high ionization NRG
89
New cards
Discuss the concept of electron affinity and explain the periodic trends for electron affinity on the table.
Electron affinity is the NRG released when an atom loses or gains an electron. The periodic trend is as you go down the periodic table, electron affinity decreases, and as you go more right it increases
90
New cards
Chemical bond-
an attractive force between atoms, causing them to bond
91
New cards
Molecular geometry-
3-D shape of a bond
92
New cards
Diatomic molecule-
2 of the same atom that bond
93
New cards
Polyatomic ion-
2 or more atoms that bond to form an ion
94
New cards
Ionic character-
a formula used to calculate the polarity of a covalent bond
95
New cards
A negatively charged ion
anion
96
New cards
what does a polar bond produce?
an unequal distribution of charge on a cpd (a positive and a negative region)
97
New cards
If two covalently bonded atoms are identical, the bond is ….
nonpolar
98
New cards
The electrons involved in the formation of chem bonds are called
valence electrons
99
New cards
When the octet rule is satisfied, the outermost _____ are filled
s & p orbitals
100
New cards
What molecule has a shape related to a tetrahedron (or has sp³) bonding?
CBr4