H.Bio - Photosynthesis Vocab Quiz.
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Jan 27, 2025.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
An energy carrying biological molecule.
ATP Energy, Adenosine Triphosphate.
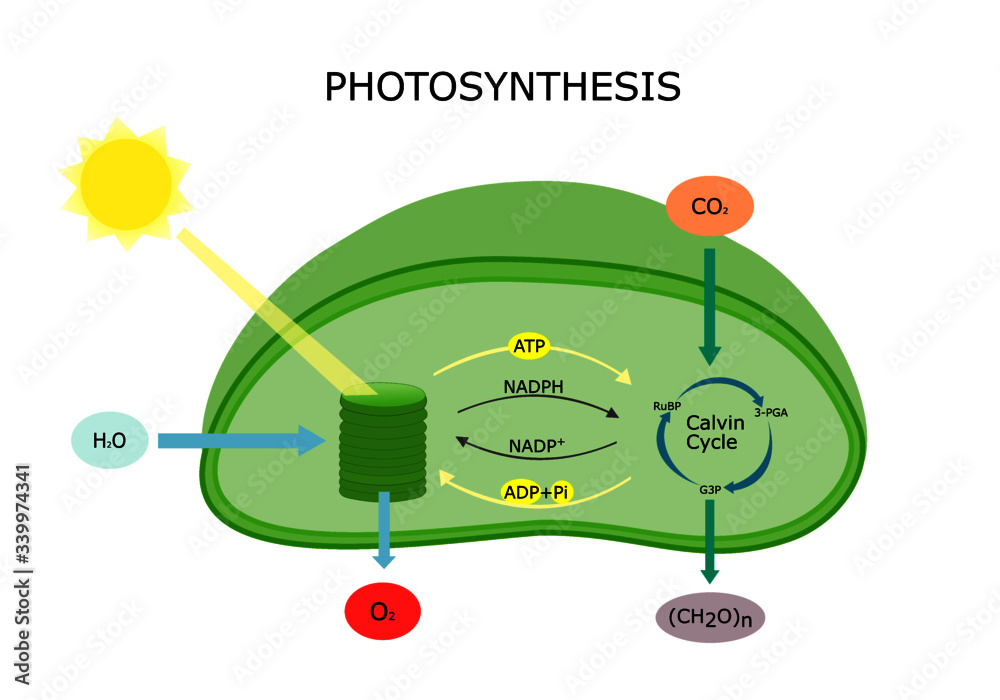
Photosynthesis Diagram
Photosynthesis.
A metabolic process in which pyruvate is broken down to produce ATP.
Aerobic Respiration.
Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration refers to the process where glucose in the presence of oxygen is completely oxidized and decomposed in cells to produce carbon dioxide and water, release energy, and synthesize large amounts of ATP.
Pyruvate
In anaerobic conditions, pyruvate converts to lactate through anaerobic glycolysis
Pyruvate is an organic molecule consisting of a 3-carbon atom backbone that plays a crucial role in both synthesis and breakdown pathways within organisms.
A light independent reaction during phase 2 of photosynthesis.
Calvin Cycle
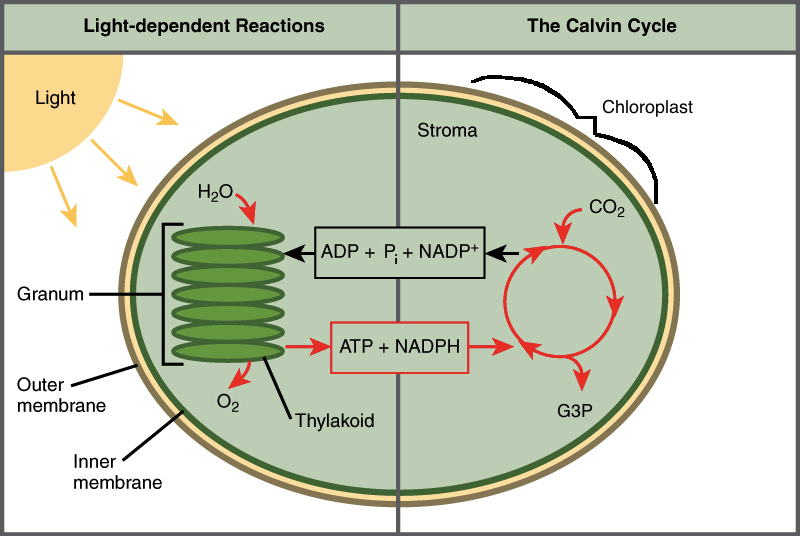
Calvin Cycle
The Calvin cycle is a process that plants and algae use to turn carbon dioxide from the air into sugar, the food autotrophs need to grow
Calvin cycle that take place in stroma of the chloroplasts during photosynthesis, is light-independent. But they usually do not occur in night because this cycle is dependent on the products of the light reactions
Pathway In which organic molecules are broken down to release energy for the cell.
Cellular Respiration.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
The chemical reaction for cellular respiration involves glucose and oxygen as inputs, and produces carbon dioxide, water, and energy (ATP) as outputs.
First stage of Cellular Respiration where glucose is broken down.
glycolysis.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is a set of reactions that converts glucose to pyruvate or lactate. This is the first metabolic pathway to be elucidated and hence is considered as a paradigm of metabolic pathways. Glycolysis is also called Embden-Meyerhoff pathway.
A stack of pigment containing thylakoids in a chloroplast.
Granum
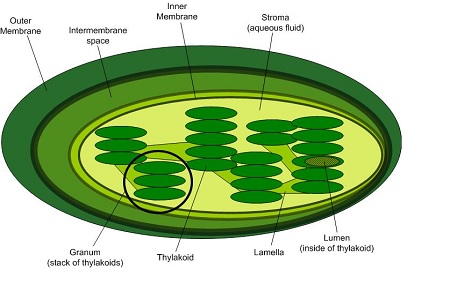
Granum
A stack of thylakoids where chlorophyll is stored.
Thylakoid
Thylakoids are pouch-like sacs that are bound to a membrane in the chloroplasts of a plant cell. They contain a pigment, called chlorophyll, that absorbs light. The light absorbed is used in photosynthesis and other processes that are light-dependent.
A series of reactions in which pyruvate is broken down inside the mitochondria, also called the citric acid cycle.
Krebs Cycle
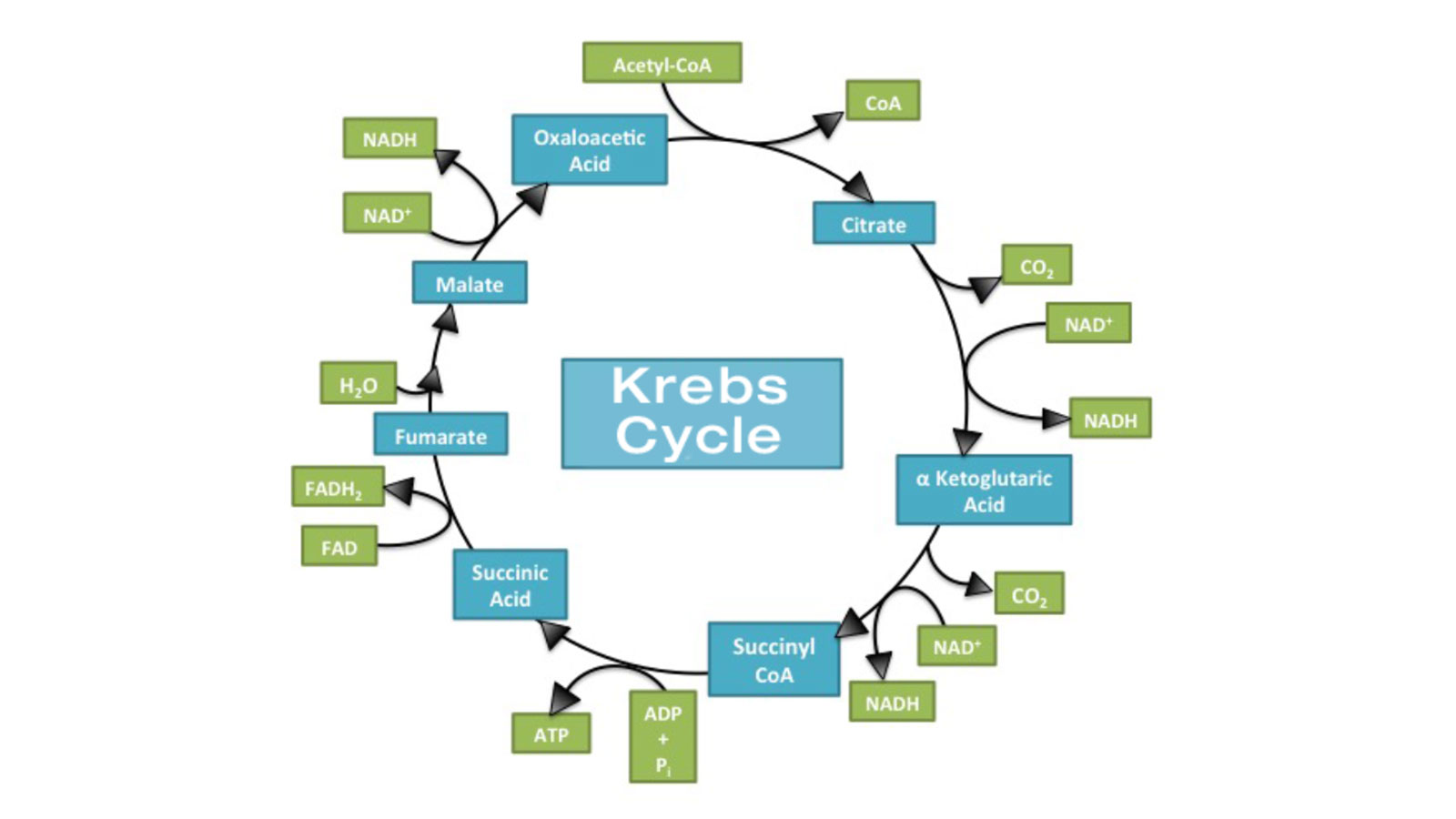
Krebs Cycle
What is the Krebs Cycle? Also known as the citric acid cycle, the Krebs cycle or TCA cycle is a chain of reactions occurring in the mitochondria, through which almost all living cells produce energy in aerobic respiration. It uses oxygen and gives out water and carbon dioxide as products.
Breaks down pyruvates
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism.
Metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the plant cell. On one hand, primary metabolism comprises all metabolic pathways that are essential to the plant's survival, generating compounds (metabolites) that are directly involved in the growth and development of the organism.
The major electron carrier in photosynthesis involved in electron transport.
NADP
NADP
NADP is an electron carrier. It stands for Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate. NADP works with numerous enzymes to supply energy to the numerous processes in a cell
A light absorbing colored molecule in a chloroplast.
Pigment
Pigment
In biology, a pigment is any coloured material found in a plant or animal cell. Pigments are what give colour to our skin, hair and eyes. They are also what colour plants. Pigments make things appear to be certain colours because they absorb and reflect different wavelengths of light
The fluid filled space in a chloroplast.
Stroma
One of the stacked flattened membranes in the chloroplast.
Thylakoid.
Stroma
Stroma is the liquid material found throughout the cavity of the chloroplast. The function of the stroma is to provide volume around the different structures inside the chloroplast for protection. The stroma is where the light-independent reaction process of photosynthesis, also called the carbon cycle, takes place.
Process in which sunlight is turned into energy.
Photosynthesis
Light Independent reaction
The light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle) use stored chemical energy from the light-dependent reactions to “fix” CO2 and create a product that can be converted into glucose. The ultimate goal of the light-independent reactions (or Calvin cycle) is to assemble a molecule of glucose.
Light dependent reactions
The light-dependent reactions convert light energy into chemical energy. The goal of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis is to collect energy from the sun and break down water molecules to produce ATP and NADPH. These two energy-storing molecules are then used in the light-independent reactions.
There are two light dependent reactions: the first occurs at photosystem II (PSII) and the second occurs at photosystem I (PSI). PSII absorbs a photon to produce a so-called high energy electron which transfers via an electron transport chain to cytochrome b6f and then to PSI.