Biology Final Flashcards
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Carbohydrate - Sugar
Provides short-term energy because it is digested quickly. (Simple)
Typically found in fruits such as apples and bananas. Exp. ATP
Carbohydrate - Starch
Provides prolonged energy because it is slowly digested. (Complex)
Potatoes, bread, rice, and pasta. Exp. ATP
Carbohydrate - Cellulose
Provides structure in the cell wall plats
Root and leaf vegetables such as celery, carrots, and lettuce.
Cell walls in plants.
Lipid
Long-term energy storage, insulation and makes up cell membranes.
Butter, avocado oil, beef fat, bacon, and yogurt.
Body fat and cell membranes
Protein
Builds or repairs cell structure, and speeds up chemical reactions.
Eggs, chicken, beef, quinoa, tuna, and nuts.
Exp. muscle, bones, skin, etc
What is the difference between a macromolecule and a monomer?
A macromolecule is more complex than a monomer, which is a single building block. Macromolecules are formed from many monomers linked together.
What is the monomer for carbohydrates?
Monosaccharide
What is the monomer for lipids?
Fatty Acid
What is the monomer for protein?
Amino Acid
What is the monomer for nucleic acid?
Nucleotide
‘Storage area’ for food, water, and air
Vacuole
Outer support structure of a plant cell
Cell Wall
Control center of the cell, “The brain.” Where DNA/chromosomes are found
Nucleus
Gives energy to the cell through the process of cell respiration
Mitochondria
Function as factories to make proteins
Ribosomes
Controls what enter and exits a cell
Cell membrane
Jellylike fluid that gives cells volume
Cytoplasm
Made of folded-up DNA
Chromosomes
Food making parts of plant cell filled with chlorophyll. Photosynthesis happens here.
Chloroplasts
Stores and transports food, fats and sometimes water to different parts of the cell.
Vesicles
Best describes a difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells?
The presence of membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cells indicates that they are more complex than prokaryotic cells.
The cells on your microscope slide appear to have a cell wall, green disks and nucleus. What type of cell do you think you are looking at and what are the green disks?
A eukaryotic plant cell and chloroplasts.
The cells on your microscope slide appear to have a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus. What type of cell do you think you are looking at and why?
A eukaryotic animal cell because of the presence of membrane-bound organelles. (Cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus. )
Name 3 organelles that are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes.
Name 3 structural (observable) differences between plant and animal cells.
Plant: Chloroplasts, cell wall, LARGE vacuole.
Name 3 structural (observable) differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic: More complex, nucleus, mitochondria
Pro: Flagellum
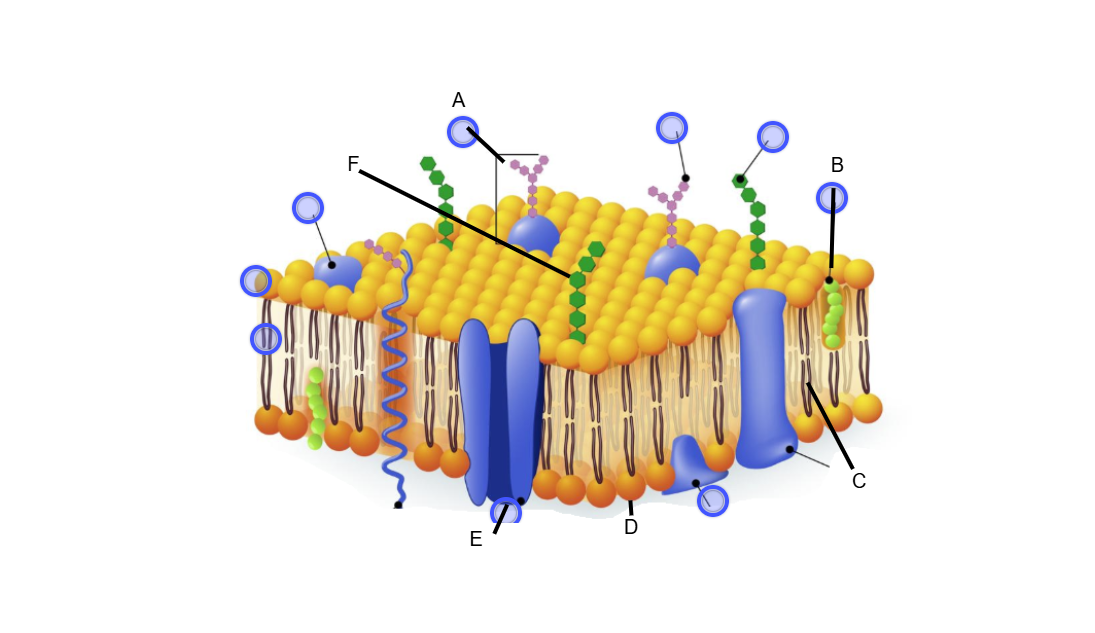
Name and describe the function of each part of the cell membrane.
A. Glycoprotein
B. Cholesterol
C. Lipid Tails
D. Phosphate Head
E. Transport Protein
F. Glycolipid
Glycoprotein
Helps cells interact and identify each other
Cholesterol
Helps stabilize the phospholipids
Lipid Tails
Hydrophobic (water fearing)
Phosphate Head
Hydrophilic (water loving)
Transport Protein
Moves needed substances or wastes through the plasma membrane.
Glycolipid
Helps cells interact and identify each other.
Active Transport
Requires energy, low to high, moves large molecules
Passive Transport
Does not require energy, high to low, moves small and hydrophobic molecules.
Facilitated Transport
Does not require energy, high to low, moves small hydrophilic molecules.
Osmosis
The diffusion of WATER, will always be passive transport, high to low, water molecules.
Hypotonic
HIPPO=BIG, water moves in, cell swells or bursts
Hypertonic
HYPER=FAST=YOU SWEAT=LOSE WATER, water moves out, cell shrinks.
Isotonic
Cell does not change in size, equal concentration of solvent (liquid) in and out of cell.
What is ATP?
Adenosine Triphosphate: Chemical energy.
How is ATP different from ADP?
ATP has THREE phosphates while ADP has two, so ATP can create more energy.
When is energy released from ATP?
During hydrolysis.
List the reactants of photosynthesis:
Carbon and water
List the products of photosynthesis
Glucose and oxygen
Write the equation for photosynthesis
6CO2+6H2O—> C6H12O6+6O2
Photosynthesis produces what gas?
Oxygen
What is the organelle in which photosynthesis occurs?
Chloroplast
What gas is taken in by plant leaves? What gas is released?
Taken: Carbon
Released: Oxygen
As the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere decreases, the oxygen produced will ____
DECREASE
List the reactants of cellular respiration:
Oxygen and glucose
List the products of cellular respiration:
Carbon, energy, water
Write the equation for cellular respiration:
C6H12O6+6O2 —> 6CO2+6H2O
Cellular respiration produces what gas?
Carbon
What is the organelle in which cellular respiration occurs?
Mitochondria
What organisms do photosynthesis? Why?
Plants (producers) — For energy
What organisms do cellular respiration? Why?
All eukaryotic cells — For energy
How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration related?
Photosynthesis makes glucose which is used in cellular respiration for making ATP. (Equations are also reversed)
What macromolecule is involved with photosynthesis and cellular respiration? Name it.
Glucose
What do enzymes do?
Speeds up chemical reactions by lowering the amount of energy needed.
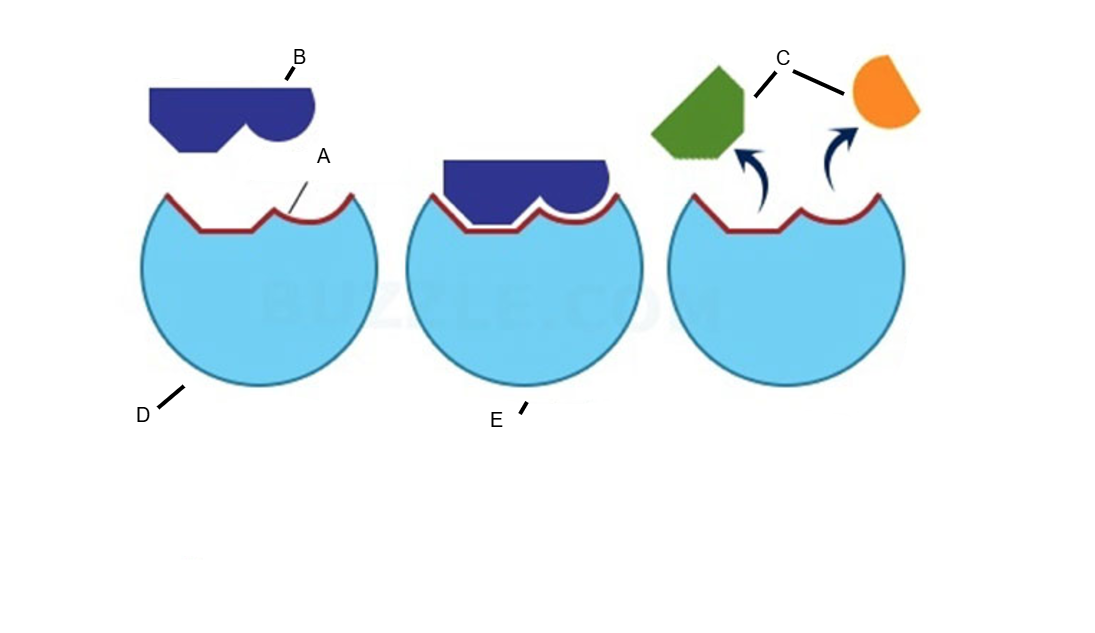
A. Active site
B. Substrate
C. Products
D. Enzyme
E. Enzyme substrate complex
Label the following diagram with the following: Enzyme, substrate, active site, product, enzyme substrate complex.
What is a synthesis reaction?
Joining of 2 reactants to produce a complex product
What is a decomposition reaction?
Compound breaks down in to 2 or more simpler substances.
In which organelle is DNA found?
Nucleus
What are the monomers (building blocks) of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA?
Nucleotides
What are the four nitrogen bases?
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine.
In DNA, A always pairs with what?
T
In DNA, C always pairs with what?
G
A nucleotide is made up of what three parts?
Phosphate group, nitrogenous base, sugar.
What does DNA tell cells to make?
Proteins
What is a gene?
A segment of DNA that codes for a trait.
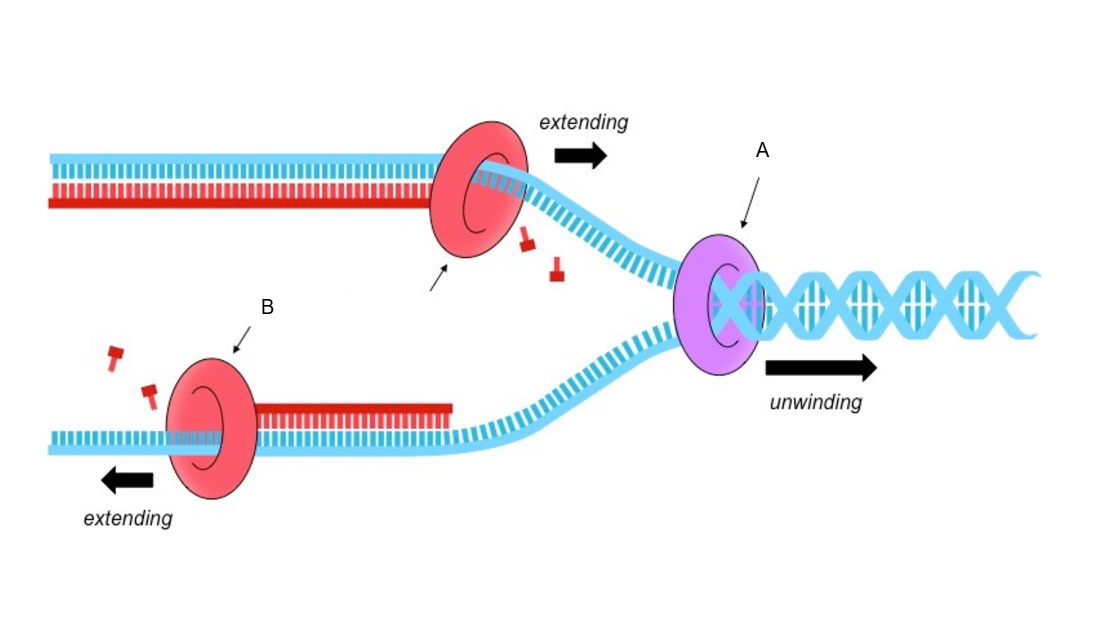
A. Helicase: Unzips the DNA
B. DNA polymerase: Replicates and synthesizes DNA.
Label the enzymes.
What are the steps to replication in DNA?
Hydrogen bonds between nucleotides break, strands of DNA separate, hydrogen bonds between nucleotides form, free nucleotides are attracted to exposed bases on the loose strands of DNA
Why is DNA replication called semi-conservative replication?
One original and one new strand.
What organelle makes proteins?
Ribosomes
What are the monomers (building blocks) of proteins?
Amino Acids
Why is mRNA able to leave the nucleus when DNA can’t?
mRNA is single stranded, therefore smaller.
Name the 4 nitrogen bases in RNA
Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine.
What are three differences between RNA and DNA
RNA is single stranded, DNA is double stranded. RNA has ribose while DNA has deoxyribose. DNA uses Thymine while RNA uses Uracil.
Where is DNA found?
Nucleus
Where is RNA found?
Cytoplasm
Where does transcription occur?
Nucleus
Where does translation occur?
Cytoplasm
Protein synthesis events:
DNA serves as a template for RNA, RNA moves to cytoplasm, tRNA bonds to a specific codon, amino acids bond together.
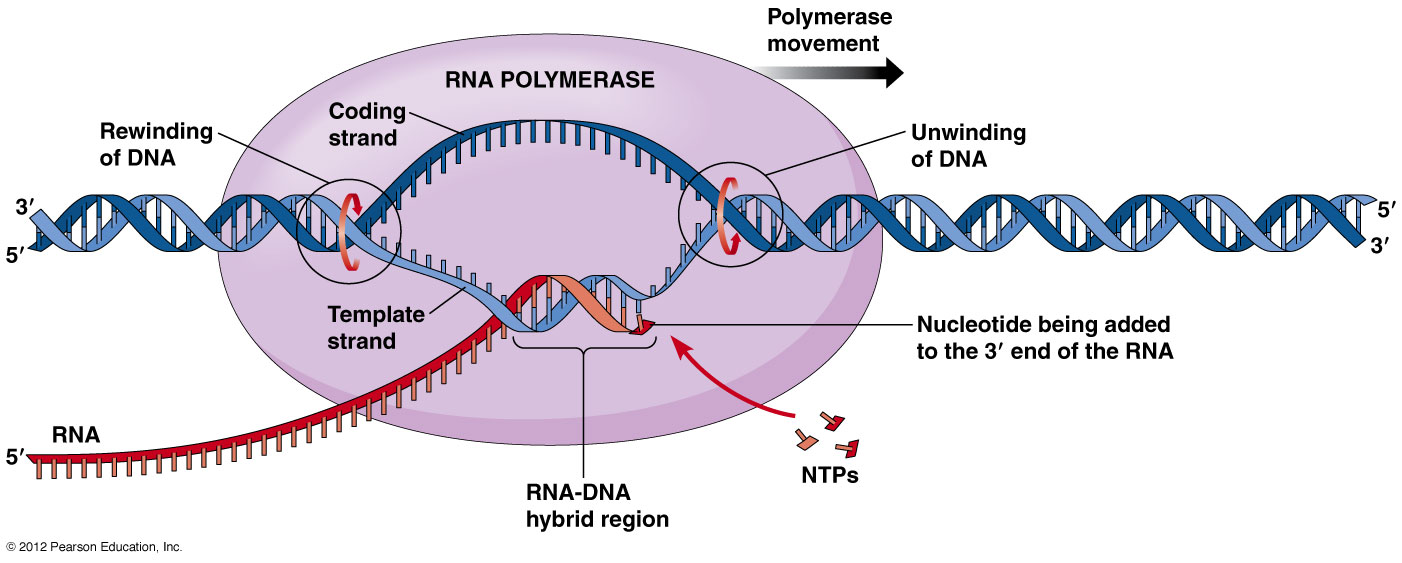
Transcription or Translation?
Transcription
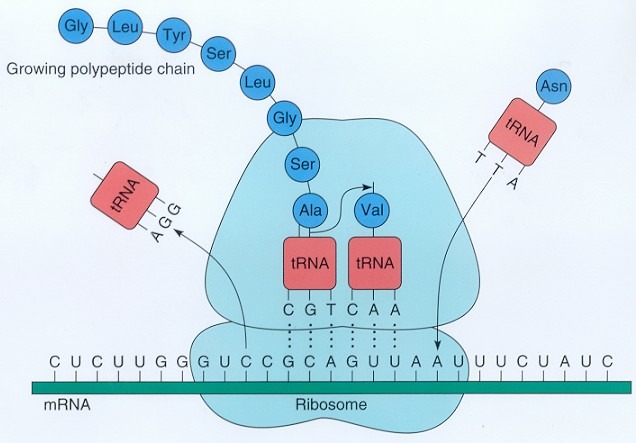
Transcription or Translation?
Translation.
What is a mutation?
A change in genetic material.
Point mutation
Involve changes in 1 or few nucleotides
Deletion
Section of chromosome is missing
Insertion
Sections of genes are reversed