How to Teach Relativity to Your Dog - Chapter Notes
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
State Science UIL Chapter Notes (Chapter 10 - Chapter 12)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Event Horizon
The boundary around a black hole beyond which no light or other information can escape. It represents the point of no return for matter and energy.
Hawking Radiation
Radiation emitted from the event horizon of a black hole due to virtual particles created near the event horizon. When one particle from a virtual particle - antiparticle pair falls into the black hole, the other escapes as Hawking Radiation, and the block hole loses mass. Given time, the black hole evaporates entirely into this radiation.
Stephen Hawking
Proved back in the 1970s that black holes emit radiation.
Black Hole Information Paradox
To preserve the information content of the universe, the Hawking Radiation from an evaporating black hole must somehow contain all the information about the objects that fell into the black hole, but it is not clear how.
Black Hole Characteristics
Black holes warp spacetime in their vicinity. Time passes much more slowly near a black hole than out in space. Even light cannot escape a black hole.
If you were to take an orbit around the event horizon of a black hole, then returned to a point far from it, you might find that people watching you say you take your trip _______ as long as you thought it took.
hundreds or thousands
__________ relationships we are used to in flat space can behave in different ways around a black hole.
Fundamental Geometric
Einstein’s most famous equation
E=mc²
“The Einstein Equation” - Einstein’s field equation from general relativity.
It describes the way spacetime bends in response to the presence of matter.
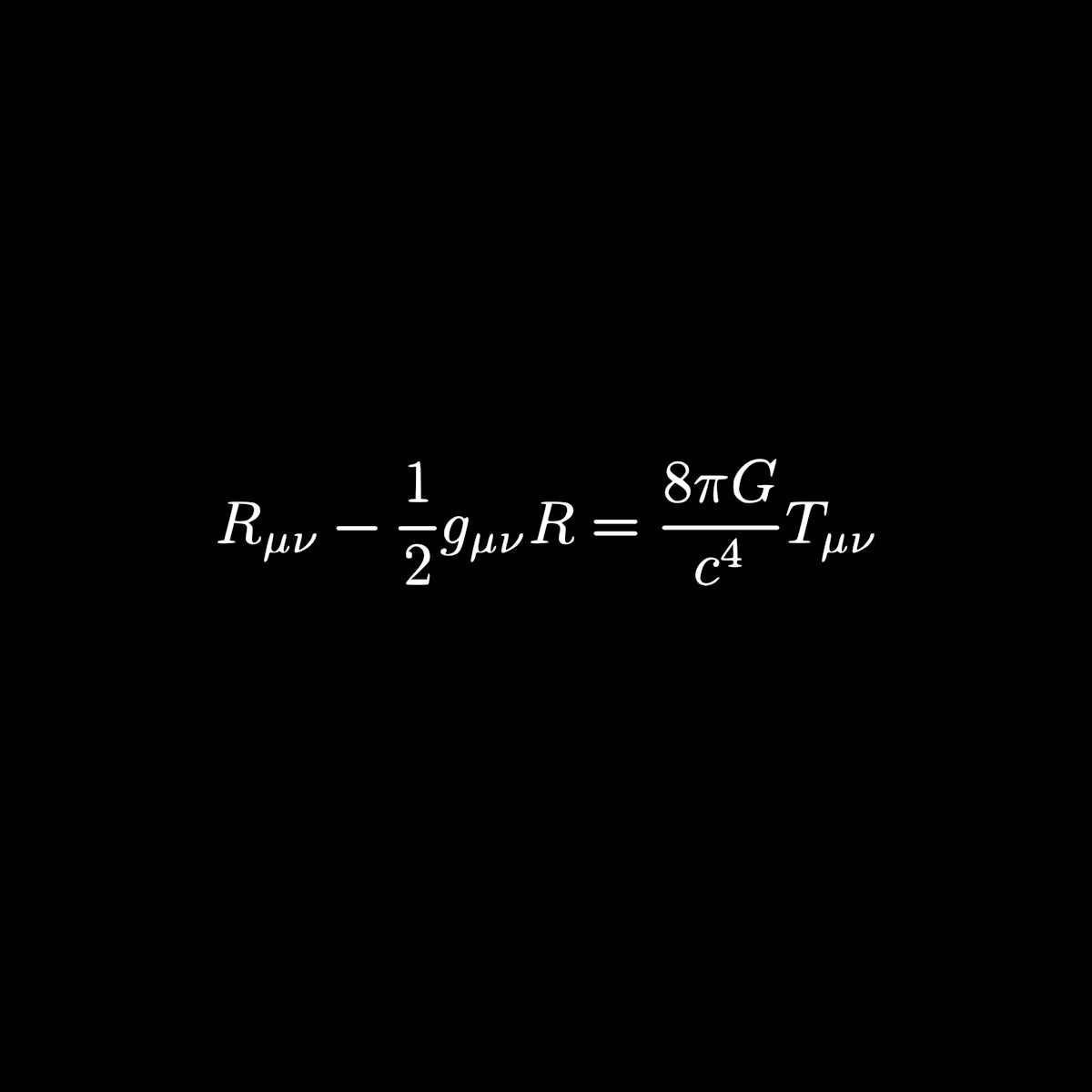
This _____ of spacetime is the mathematical core of general relativity.
curvature
Who said this quote: “Matter tells space how to curve, space tells matter how to move.”
John Archibald Wheeler
The _____ of an observer through space affects the rate at which they move through _____, but the right combination of space and time lets us reconcile all the observations of _______.
speed, time, different moving observers
Equivalence Principle
tells us that one effect of gravity is to change the rate at which observers move through time in different places.
Clocks at _______ altitudes tick ______ than those at low altitudes.
higher, faster
The changing of space and time is the manifestation of _____, which is one of those laws.
gravity
The rules for understanding how spacetime is bent by a massive object are mathematically very similar to the rules for describing the geometry of objects on a ________.
curved surface
The most obvious consequence is that _______ lines in a curved geometry will eventually ______.
parallel, cross