AOS 5 - Biology - Adaptations
1/83
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Define gene pools
Gene pools are the complete set of all genes and alleles present within a particular population or species
What is the importance of a diverse gene pool?
Larger gene pools will contain a variety of genes and alleles, leading to a greater number of genotypes and phenotypes resulting in increased genetic diversity
Define mutations
Mutations involve permanent changes to the DNA sequence of an individual
What factors cause mutations?
Radiation (UV (from sunlight), X-rays)
Infectious Agents (Viruses, Bacteria)
Chemicals (Carcinogens (cigarettes), Processed foods + preservatives, Cosmetics + cleaning products)
How can mutations be catergorised?
As advantageous, neutral or disadvantageous based on the mutation’s overall effect on the survivability of the individual.
Where do mutations need to occur to make them heritable?
They need to occur in an individual’s germline cells (cells that generate gametes (sex cells), not somatic cells (body cells) as gametes contain the genetic information that is passed on to the offspring.
What are point mutations?
These describe the changes to a single nucleotide.
What are the types of point mutations?
Substitution
Silent (amino acid remains the same)
Missense (different amino acid)
Nonsense (introduces a premature stop codon, creating a termination sequence)
Frameshift Mutation
Insertion (nucleotide added to the sequence)
Deletion (nucleotide removed from the sequence)
What are block mutations? And the types of block mutations?
Involve changes to larger sections of DNA, potentially causing significant changes
Deletion - removal of a section of DNA
Duplication - replication of a section of DNA
Inversion - reversal of a section of DNA
Translocation - switching of two sections of DNA on different chromosomes
When do block mutations usually occur?
During the process of meiosis
Define aneuploidy
when an individual has either one extra or one too few chromosomes
Define polyploidy
when an individual has more than two sets of chromosomes
Define environmental selection pressures, and provide examples
factors within the environment that influence the survivability of a species.
Examples include predation, disease, competition, and climate change
What is natural selection?
A process in which organisms more suited to a particular environment are considered to have high genetic fitness due to the presence of their advantageous phenotypes
Overtime, because the fitter organisms have selective advantage they survive increasing the advantageous allele frequency in future populations
State the four conditions of Natural Selection
Variation
Selective pressure
Selective advantageous
Heritability
*discuss all four when explaining natural selection
What occurs at Variation?
Individuals in population vary genetically, which leads to phenotypic differences
What occurs at Selective Pressure?
An environmental selection pressure that impacts the survivability of organisms within a population and their ability to reproduce
What occurs at Selective advantageous?
Individuals with phenotypes that are fitter or more advantageous under the environmental selection pressure are given a selective advantage, allowing them to survive and reproduce
What occurs at Heritability?
The advantageous trait must be heritable, allowing it to be passed on from the parents ot their offspring. Therefore, over time, the frequency of the advantageous allele will increase
Define genetic variation
Differences in DNA sequences between individuals of the same species, leading to diverse traits/differences - this results from mutations, geneflow, sexual reproduction
How do selective pressure affect genetic diversity?
Selective pressures drive adaptations, and if a positive response is created, the frequency of advantageous traits will increase, at the expense of other disadvantages ones.
High genetic diversity increases the chance of possessing favourable alleles, aiding the species in surviving selection pressures.
Low genetic diversity exposes them to extinction due to the inability to adapt.
Define evolution
the change in genetic makeup of a population successive generations
define genetic drift
in response to random events, allele frequencies can change drastically and affect a population’s overall genetic diversity
What is the bottleneck effect?
When a large portion of a population is wiped out by a random event (natural disaster)
This decreases the population size, impacting allele frequencies - lower genetic diversity
What is the Founder effect?
when a smal, unrepresentative sample of individuals seperate from the larger population, colonising in a new region
The new populations genetic diversity is low
How does genetic drift reduce genetic diversity?
Through the random removal of alleles from the gene pool
It also increases the risk of inbreeding and lowers the adaptative potential
Bottleneck reduces through random events
Founder reduces through the establishment of a new population with a small un-representative sample
Define gene flow
The movement of alleles between different populations (either through migration or inbreeding)
Define immigration
When individuals enter a population, adding their alleles to the gene pool
Define emigration
Individuals exit a population, removing their alleles
Define a species
A group of individuals who are able to breed with eachother and produce viable offspring
Define speciation
The process by which populations genetically diverge until they become different species
→ this occurs when enough genetic differences have developed due to mutations, natural selection, gene flow and genetic drift
What are isolating mechanisms?
The pre-reproductive and post-reproductive mechanisms that prevent different species from interbreeding to produce fertile/viable offspring
What are the types of post reproductive mechanisms that isolate populations causing speciation?
geographical
ecological
temporal
behavioural
structural
What are the types of pre-reproductive mechanisms that isolate populations causing speciation?
gamete mortality
zygote mortality
hybrid sterility
Define allopatric speciation
involves the formation of new species as a result of a geographical barrier
How do geographical barriers cause the formation of new species?
A geographical barrier prevents gene flow, with different selection pressures causing genetic differences to develop until the two populations can no longer interbred
What is sympatric speciation?
Doesn’t rely on geographical barriers to prevent gene flow, it occurs within populations sharing the same locations where different selection pressures act on different phenotypes causing new species to develop.
Define selective breeding
When the selection pressure is human-induced, and there is a desired trait that humans are selecting for (or removing from the populations)
What are the requirements for selective breeding?
Variation: natural phenotypic variation within the population
Selection Pressures: the favourable trait is selected by humans, who they pressure and establish a breeding population with the trait-genetically controlled
Heritability: as the favourable trait is heritable, it will increase in allele frequency due to repeated selection reinforcements.
What is the main type of selective breeding, and the others?
Main: selecting for a trait you want
Others: selecting against the trait you want + selecting against the trait you don’t want
What are antimicrobial agents (examples, and role)
Eg: antifungals, antivirals, antibiotics
Play an important role in protecting against harmful pathogens, except new antimicrobial agents need to constantly created because pathogens are becoming better at resisting them
How is antibiotic resistance developed?
The formation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria can be attributed to the process of natural selection, where the exposure to antibiotics serves as an environmental selection pressure
Explain the process of natural selection in the context of developing antibiotic resistance
Variation - A population of bacteria has individuals that are resistant to an antibiotic, and those susceptible/sensitive to it
Selection pressure - exposure to the antibiotic acts as an environmental selection pressure
Selective advantage - this is given to the bacteria resistant to the antibiotic
Heritability - Bacteria resistant to the antibiotic are able to continue replicating and pass on the allele for resistance to other bacteria via bacterial conjugation, increasing it allele frequency
Do antibiotics cause bacterial resistance?
No. The evolution and development of this resistance is an example of natural selection, where this resistance to certain antibiotics already exists within the population, and the exposure to the antibiotics acts to highlight those resistant.
How is this variation in genes created that allows the resistance to antibiotics?
Mutations. Variation and the emergence of new alleles are largely caused by mutations. These can include:
Inactivation (addition of a phosphate group to the antibiotic, reducing its ability to bind to bacterial ribosomes)
Pumping out (increasing active efflux of drugs)
Modification (changing the shape of the protein targeted by the antibiotic)
Are there any other factors that contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance?
Inappropriate compliance with a treatment plan (patient not completing their course of antibiotics)
Inappropriate use of antibiotics
Widespread use of antibiotics in general = overexposure
Define antigenic drift
This involves small and gradual changes in the genes encoding for viral antigens (in the beginning, memory cells will still be able to recognise the virus, but if enough changes accumulate, they may not)
Define antigenic shift
This involves the sudden and significant changes to the genes encoding for viral antigens, commonly due to two or more different strains of a virus combing, meaning little immunity will exist.
List the key events in history of life on earth
Emergence of prokaryotes
Widespread photosynthesis
First eukaryotes
First multicellular organisms
The Cambrian Explosion
Animals on land
Mammals
Flowering plants
What is a fossil?
Sometimes, given the right set of conditions, the remains of a body can be preserved and form a fossil - all fossils both discovered and undiscovered are referred to as the fossil record
Outline the process of fossilisation
A body/dinosaur dies in a river
The body is covered with sediment, the soft tissues decompose and the hard body structures become fossilised by permineralization
The sedimentary layers accumulate and the resultant pressure forms sedimentary rock
The earth’s movements raise the layers of the rocks to the surface
The rock erodes, exposing the fossilised body structures
Define trace fossils
Trace fossils are indirect evidence of an organisms existence, such as their footprints or nests
What are the conditions that increase the likelihood of fossilisation?
Physical protection from decomposers/scavengers (fungi, bacteria)
Areas of rapid sediment accumulation
Constant cool temperatures - slows down decomposition
Low oxygen availability and light exposure - slows down decomposition
Define relative dating
Relative dating involves estimating a fossil’s age by comparing it to the known age of other fossils and/or rocks.
The law of succession states that the closer to the surface a fossil is, the younger it is, due to sedimentary rock being laid in layers based on time.
What are index fossils?
Index fossils are fossils that are widespread, physically distinctive, existed for a short period of time and have a know age - they and be used to determine the relative age of another fossil in the same layer, or below or above. Trilobites and ammonoids are good examples.
Define transitional fossils
Transitional fossils show traits that are common to both its ancestral group and its descendant group, showing certain features that have changed and evolved over time
What is absolute dating and what aer radioisotops?
Involves calculating the age of a fossil in years
An example is radioactive dating
Radiometric dating involves measuring amounts of radioisotopes and their products
A radioisotope is an unstable form of an element, that will spontaneously break down into a more stable product (eg carbon 14 → nitrogen 14)
Define what a ‘half-life’ is
The half-life of a particular radioisotope is the amount of time before half the original mass is broken down into its products
How does radioactive dating work?
It works by comparing the ratio of a radioisotope to its broken-down product - using the known half-life of the radioisotope, we can calculate how old the object we are dating is
What is comparative anatomy, and what does it involve?
Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the structural morphology of fossils
It includes homologous, analogous and vestigial structures
Define homologous structures
A homologous structure is a structure present in many species that may look or function very differently, but is derived from a common ancestor
Evidence of DIVERGENT EVOLUTION - common ancestor
Define analogous structures
They are structures present in two or more species that fulfil the same function but do not originate from a common ancestor
CONVERGENT EVOLUTION - distantly related species have independently evolved similar traits due to similar selection pressures
Define vestigial structures
Vestigial structures in an organism that have lost their original function, but once did serve a purpose for its ancestors
They are evidence of divergent evolution
What is molecular homology, and why do we study it?
DNA sequences, and amino acid sequences, in a species change over time, due to an accumulation of mutations
For this reason, it is expected that if two species diverged a long time ago, they would have more differences in their DNA that two species that diverged more recently.
What are the main amino acid sequences studied?
Hemoglobin
Cytochrome C
More similarities = more recent common ancestor = more closely related, this also applies to similarities in DNA sequences when comparing them at corresponding gene regions
Why is determining the relatedness using mitochondrial DNA better?
Mitochondria contain their own genome
The mutation rate in mtDNA is much higher than in nuclear DNA, this means that for very closely related species, the mutation rate still ensures that there are enough differences in DNA sequences for use to compare.
There is no recombination in mtDNA because it’s only inherited from the mother, this means that mtDNA remains unchanged from generation to generation, making it easier to trace back to past ancestors.
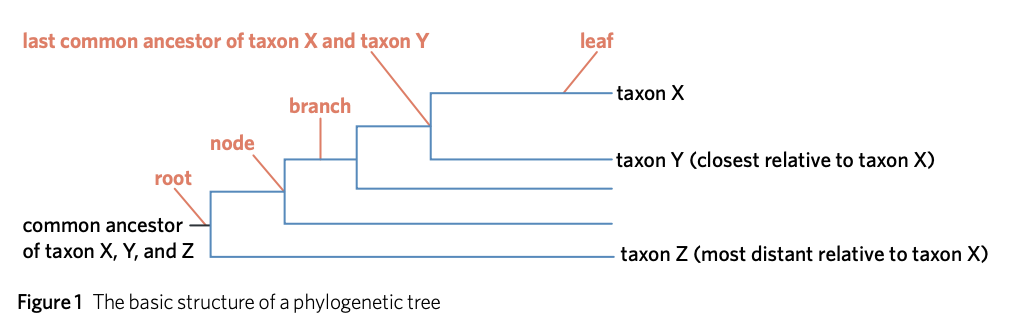
What are phylogenetic trees?
They show the evolutionary relationship between organism structures
What are the key structures of a phylogenetic tree?
Root - a line at the origin, representing the earliest ancestor
Branch - each line of the tree
Node - point where branch splits, divergence between taxa
Leaf - end of branch, where present-day species is
State the order of taxa (King Phillip Came Over For Good Soup)
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
What are hominoids, and their distinguishing factors
The superfamily hominoidea - apes
Increased cranium size
Shorter spine
Molar teeth
Longer arms
Lack of tail
Broader rib cage
What are hominins, and their distinguishing factors
The taxonomic point at which humans seperated from other species
Key characteristic: bipedalism - distinguishes use from chimps/gorillas
Canine teeth (ours are smaller)
Brow ridge (ours is smaller)
Spine curve (we has an S shaped spine, gorilla’s is C shaped)
Increased cognitive abilities
What characteristics define mammals?
Hair/fur
Variety of teeth
Mammary glands
Single/lower jaw
What characteristics define primates?
Flexible spines + hip rotation
Prehensile hands/feet
Opposable thumb/big toe
Sensitive touch receptors
What are the general patterns of hominin evolution?
Moving from an arboreal (living in trees) lifestyle to complete bipedalism
Shortening of arms and lengthening of legs
Faces becoming flatter
Skulls becoming rounder
What changes occur in the brain size?
The brain size is estimated from the volume of an extinct hominin’s cranium
Improved diet of the hominin leads to increased brain size. With the creation of fire allowing meat to be eaten, meats contain a large amount of fats that provide increased brain development and more energy for this growth
Specifically the cerebrum of hominin brains become more folded, increasing the TSA so more neurons and enhanced cognitive ability
What are the positives of increased brain size?
Cognitive benefits lead to improved social outcomes
Lower predation vulnerability
Group care + shared mothering
Cooking + stable food production
What are the negatives of increased brain size?
The morphological changes = higher energy cost
higher energy needs
higher complexity of childbirth
larger diet
How did a larger brain size impact culture development?
Written and verbal language skills allowed their culture to be passed on via cultural evolution
Other changes produced in hominin evolution
A more centralised foramen magnum
Lessening of the brow ridge
A decreasing arm to leg ratio
What changes in limb structure occured?
Shorter arms due to less contact with the ground, and allowing the carrying of children, preparing food
Longer legs makes walking more efficient
Shorter, more bowl-shaped pelvis provides upright walking support