CH1 - The Human Body: An Orientation
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Define Anatomy
Study of the structure of body parts and their relationship to one another
Define Physiology
Study of the function of body parts; how they work to carry out life-sustaining activities
List the Subdivisions of Anatomy
Gross or macroscopic anatomy
Microscopic anatomy
Developmental anatomy
Gross or Macroscopic Anatomy
The study of large, visible structures (see with the naked eye)
Example of Gross or Macroscopic Anatomy
Regional anatomy: all the structures (muscles, bones, bloods vessels, nerves, etc.) in a particular region of the body such as the abdomen or leg, are examined at the same time
System anatomy: body structure is studied system by system
Cardiovascular system → heart & blood vessels)
Surface anatomy: internal structures that relate to the overlaying skin surfaces
Use when identifying bulging muscles beneath a bodybuilder’s skin
Microscopic Anatomy
Deals with structures too small to be seem by naked eye
Example of Gross or Macroscopic Anatomy
Cytology
Study of cells
Histology
Study of tissues
Developmental Anatomy
Studies anatomical and physiological development throughout life
Example of Developmental Anatomy
Embryology
subdivision of developmental anatomy, concerns developmental changes that occur before birth
How to study anatomy?
To study anatomy one must know anatomical terminology and be able to:
Observe
Manipulate
Palpate
Auscultate
List the Subdivision of Physiology
Based on organ system
Renal physiology
Neurophysiology
Cardiovascular physiology
Often focuses on cellular and molecular levels of the body
How to study physiology?
To study physiology one must understand basic physical principles (electrical currents, pressure, and movements) as well as basic chemical principles
True/False: Anatomy and physiology are inseparable
TRUE → Anatomy and physiology are inseparable
Explain the Principle of Complementarity
Function always reflects structure
What structure can do depends on its specific form
Example(s) of Principle of Complementarity
Bones can support and protect body organs because they contain hard mineral deposit
Blood flows in on direction thorough the heart because the heart has values that prevent back flow
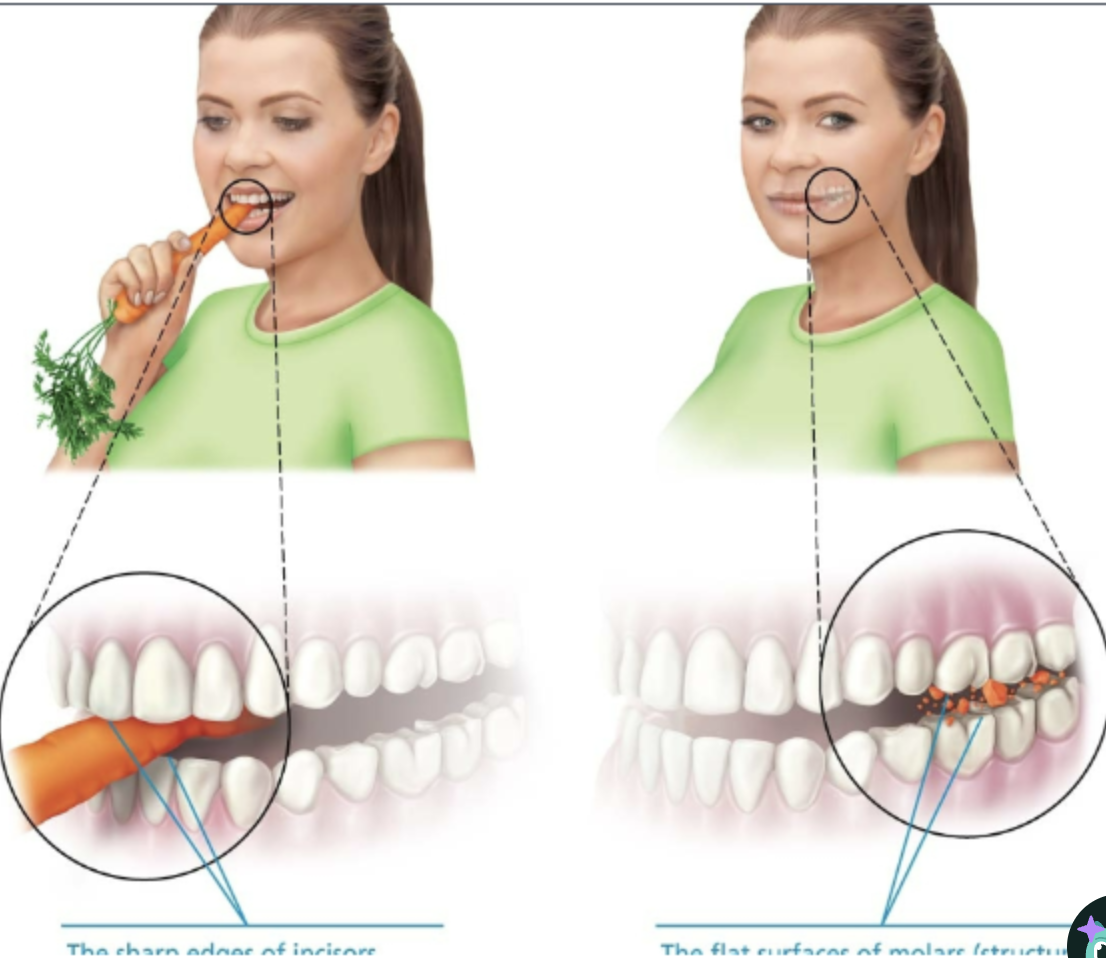
Various shape of our teeth reflect different actions
STRUCTURE = Sharp edges of incisors
FUNCTION = Cut food when you bite
STRUCTURE = Flat surfaces of molars
FUNCTION = Crushing, grinding, chewing
When the heart is cut in the frontal plane, the muscular walls of the left ventricle are visibly much thicker than those of the right ventricle. This extra muscle on the left side of the heart allows blood pressure in the systemic circuit to reach a normal peak of 120 mmHg. In contrast, the right side of the heart generally generates a peak pressure of approximately 15 mmHg in the pulmonary circuit. This observation is an example of …
A.) The Principle of Complementarity
B.) Organ System Interrelationships
C.) Necessary Life Functions
D.) Survival Needs
→ A.) The Principle of Complementarity
EXPLANATION: Linking how a structure looks (anatomy) to how it functions (physiology) is the bedrock of anatomy and physiology and is termed the principle of complementarity. The additional muscle on the left side of the heart (anatomy) allows the heart to pump blood to a higher pressure in the systemic circuit (physiology)
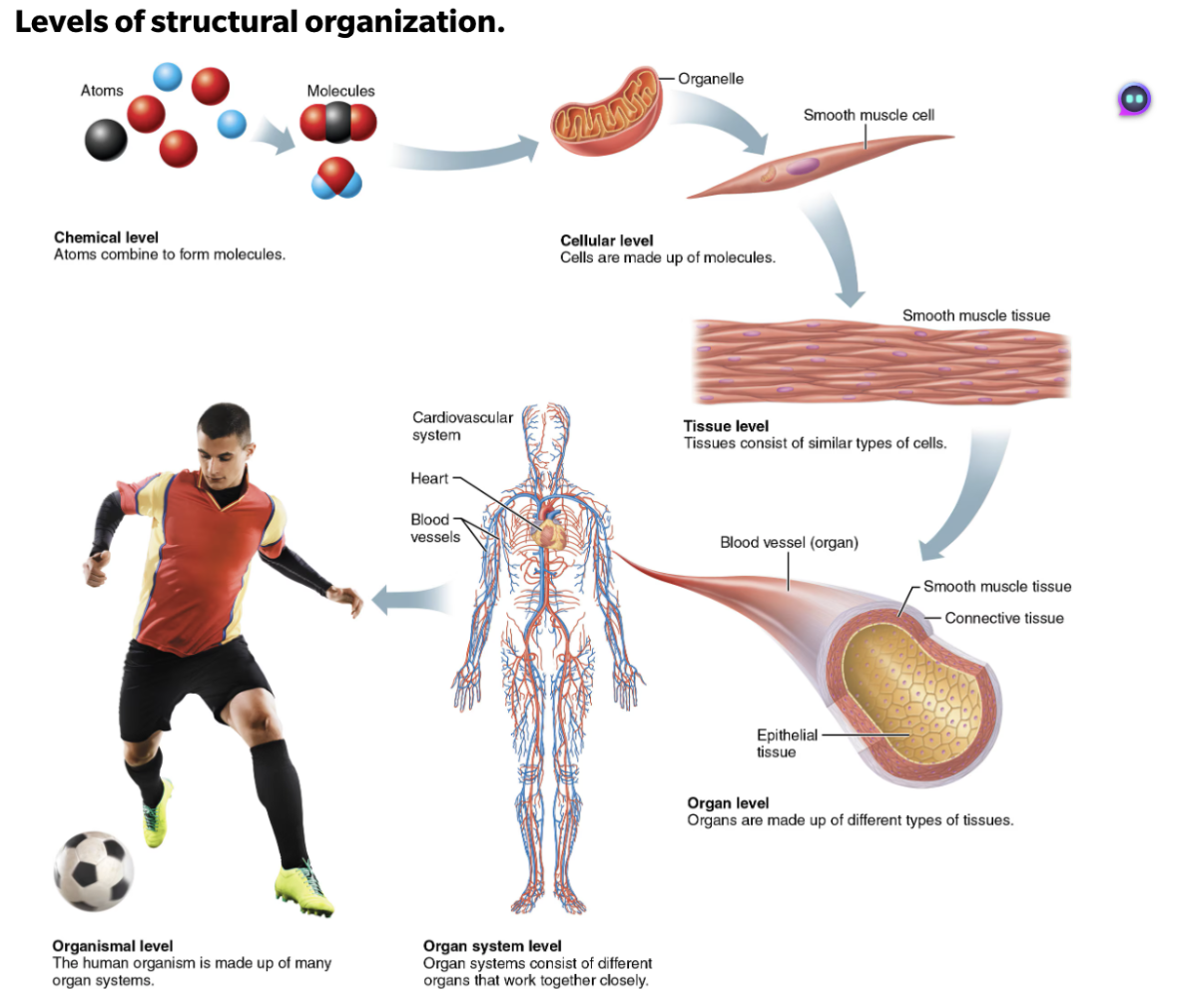
Name the different levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain their relationship
Chemical level
Atoms combine to form molecules (water & protein)
Cellular level
Cells are made up of molecules
Tissue level
Tissue consist of similar types of cells
Organ level
Organs are made up different types of tissue
Organ system level
Organ system consists of different organs that work together closely
Organismal level
The human organism is made up of many organ systems
Cellular
Organelles are the basic components
Smallest unit of life
Tissue
Similar group of cells that have a have a function
Epithelial, muscle, connective, and nervous tissue
Organ
Discrete structure composed of at least 2 tissue types
Complex function
Organ system
Network of organs to accomplish a common goal
Cardiovascular system
Organism
Human
List the 11 organ system of the body
Integumentary system
Skeletal system
Muscular system
Nervous system
Endocrine system
Cardiovascular system
Lymphatic system/immunity
Respiratory system
Urinary system
Digestive system
Female/Male reproductive system
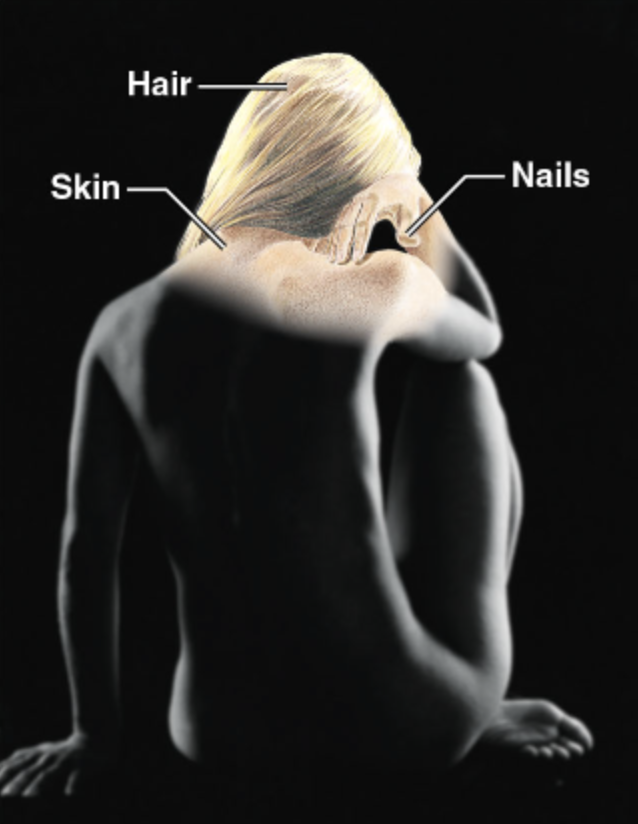
Explain the major function(s) of the Integumentary system
Forms the external body covering, and protects deeper tissues from injury
Synthesizes vitamin D
Houses cutaneous (pain, pressure, etc.) receptors and sweat and oil glands
Hair, Skin, Nails
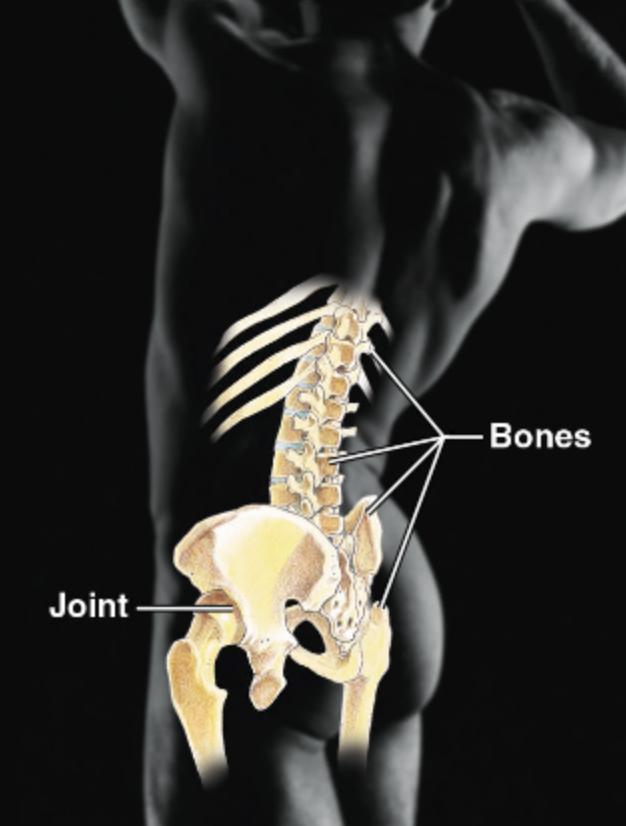
Explain the major function(s) of the Skeletal system
Protects and supports body organs
Proves a framework that muscles use to support movement
Blood cells are formed within bones
Bones store minerals
Joints and Bones
Explain the major function(s) of the Muscular System
Allows manipulation of the environment, location, and facial expression
Maintains posture, and produces heat
Skeletal muscles
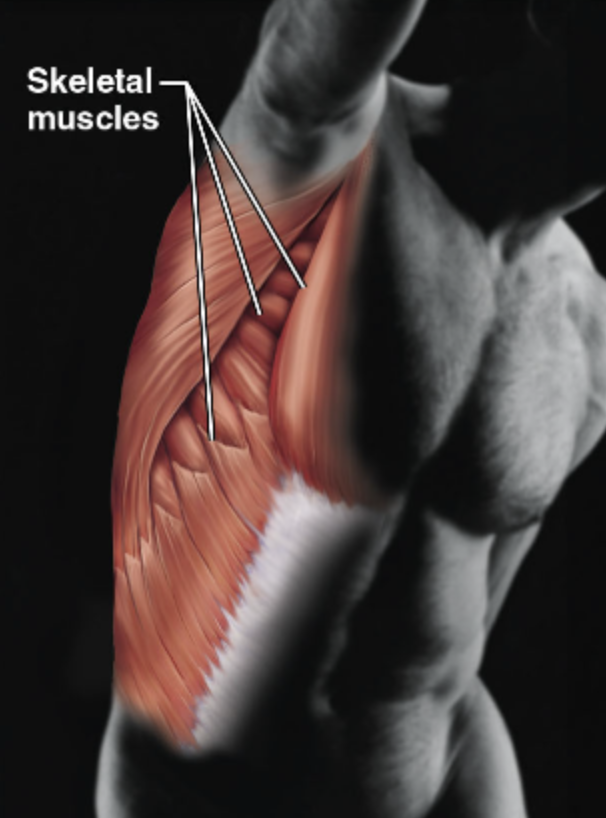
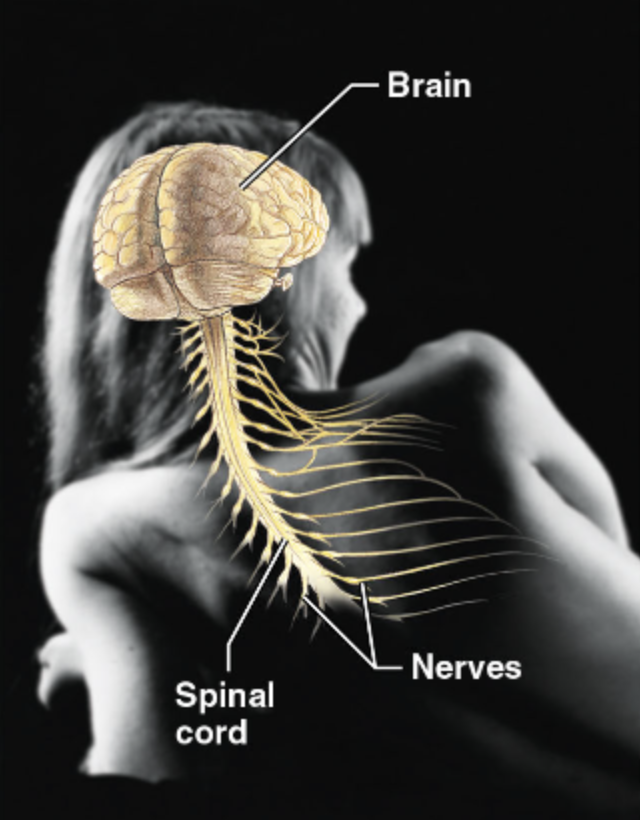
Explain the major function(s) of the Nervous System
As the fast-acting control system of the body, it responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands
Brain, Spinal cord, Nerves