1- surgical instruments and materials
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What are the 2 types of instruments?
Simple- manual instruments directly activated by surgeon
Complex- high tech, activated by mechanism
Give examples of simple vs complex instruments
Forceps, needle holders
Electric scalpel, turbine
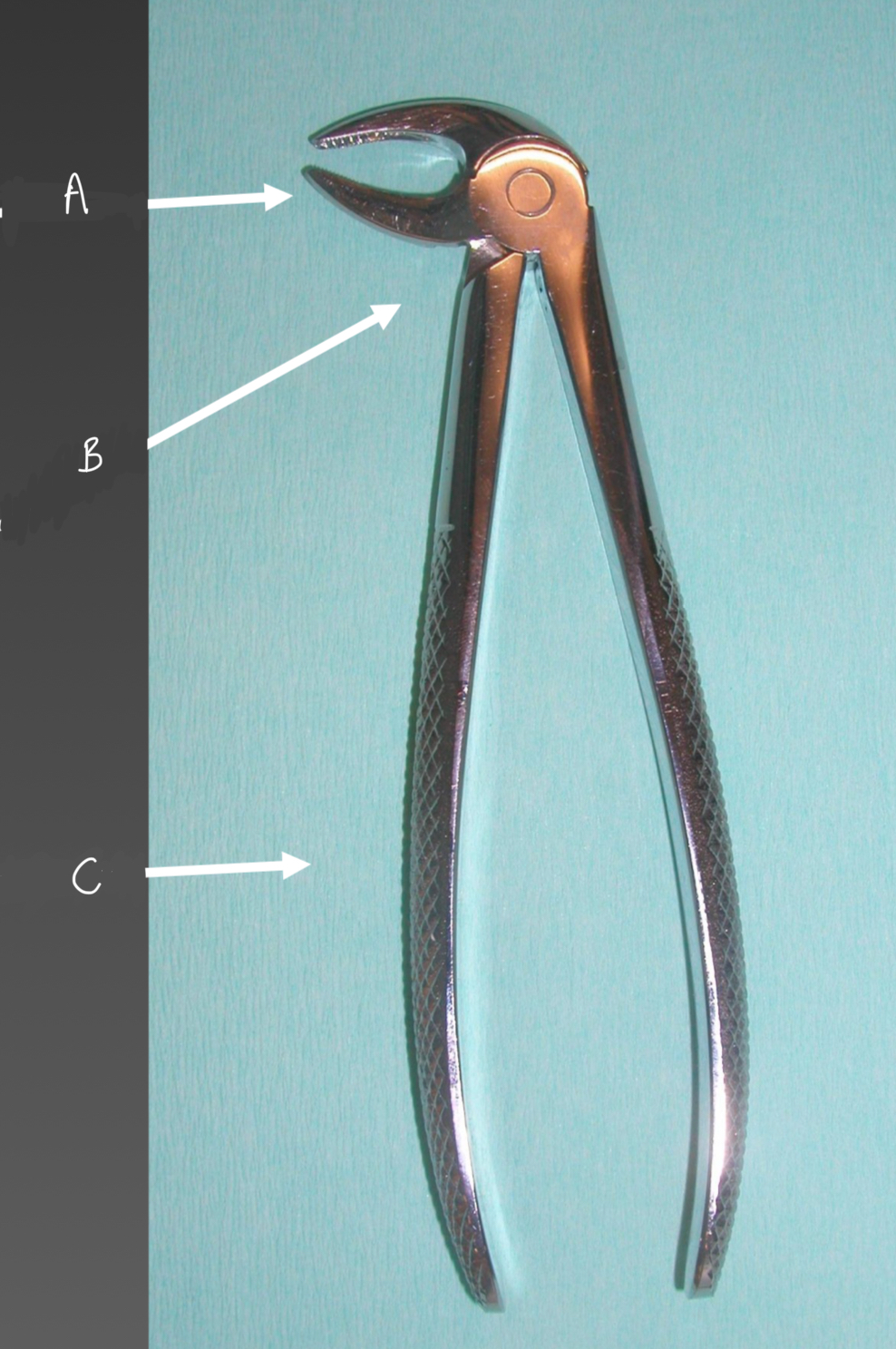
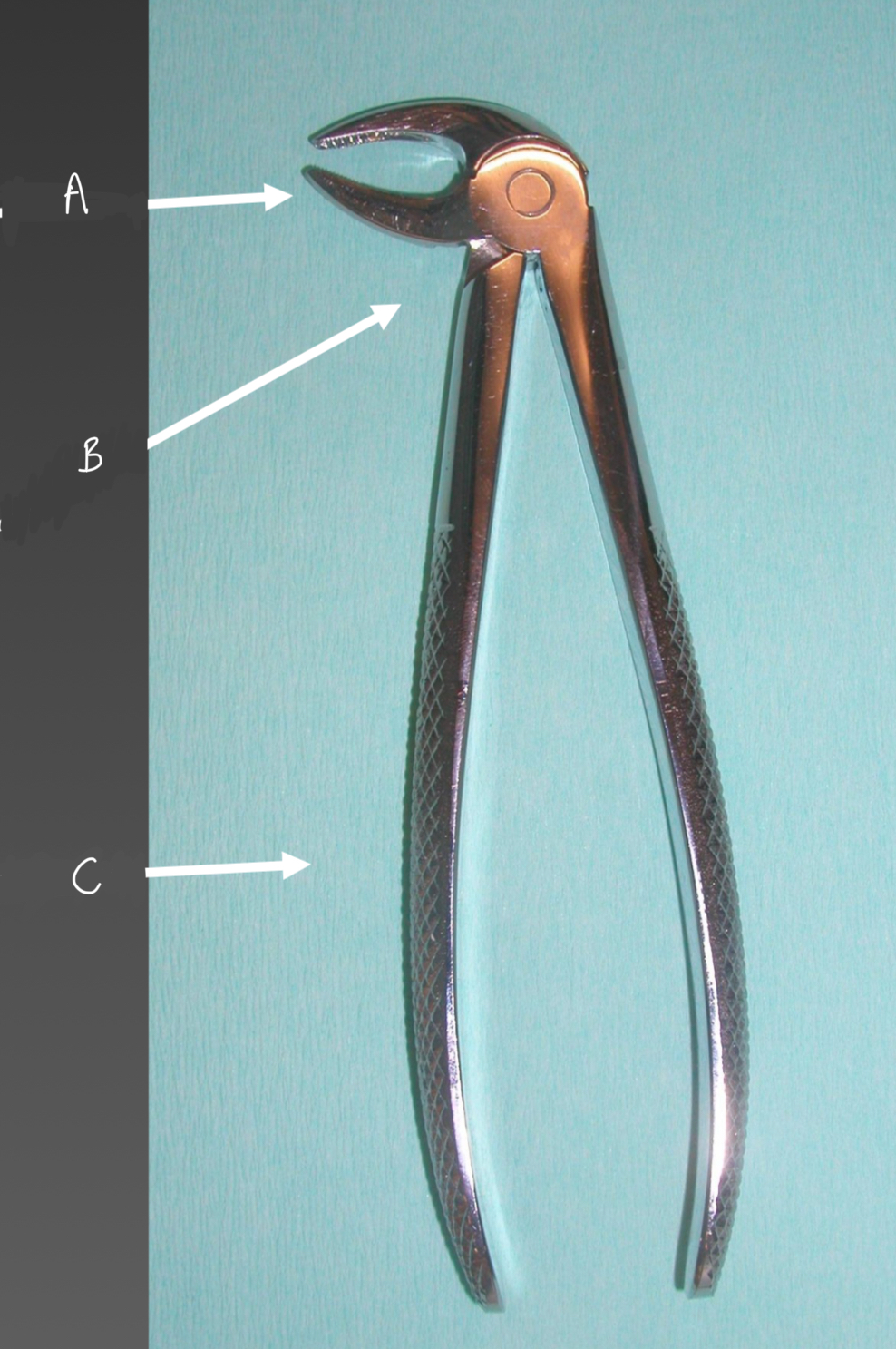
What are the parts of a simple surgical instrument?
Active area
Intermediate area, neck or stem
Passive area or handle
What instruments are used for local anaesthesia?
Metal cartridge syringe
Disposable plastic syringe
Yutil metal syringe- doesn’t allow aspirating, high pressure, banned
Intraligamentary metal syringe
What are the advantages of a metal cartridge syringe?
Allows aspirating
Needles and cartridges easily changed
Easy to clean and sterilise
Controllable manual infiltration
What are characteristics of disposable needles for cartridges syringes?
Caliber- smaller number- thicker needle
Length- 25-27-30-38-40
Bevelled needle tip- short bevel of 45 degrees better than long- 5-7- produces less trauma
What instruments are used to facilitate visualisation and its subtypes?
Retractors maintain the flap-
Farabeuf
Minnesota
Tongue depressor
Mouth prop
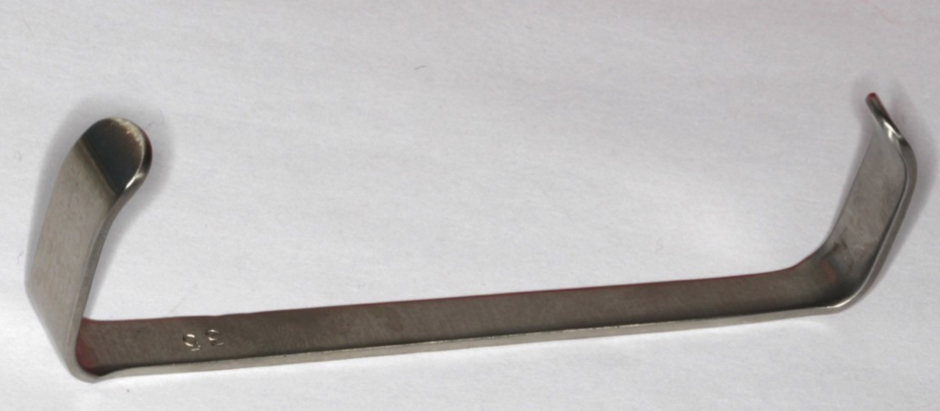

What’s this and what is it used for?
Farabeuf
Two blades- diff width and length
Retract lips and flap
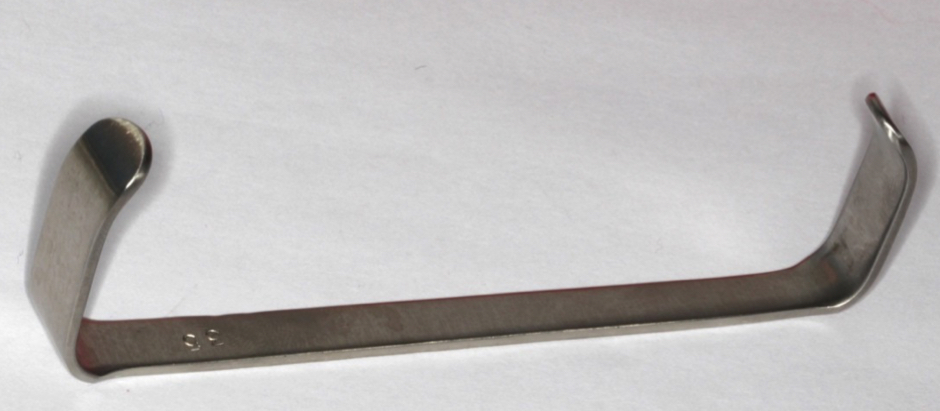


What’s this, used where?
Minnesota
Retract flaps
Any part of oral region

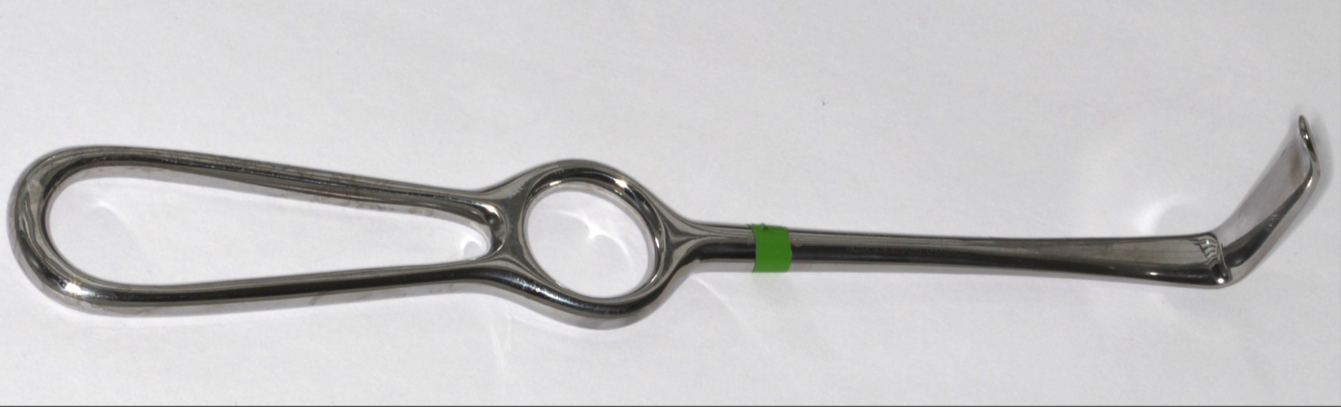
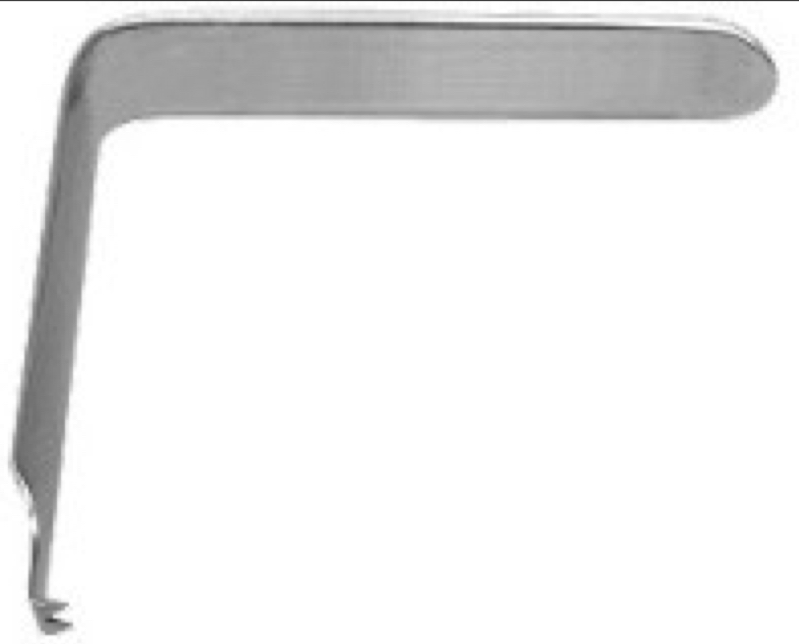
What’s this, used for?
Langenbeck
Retract, retain, protect flaps and cheeks
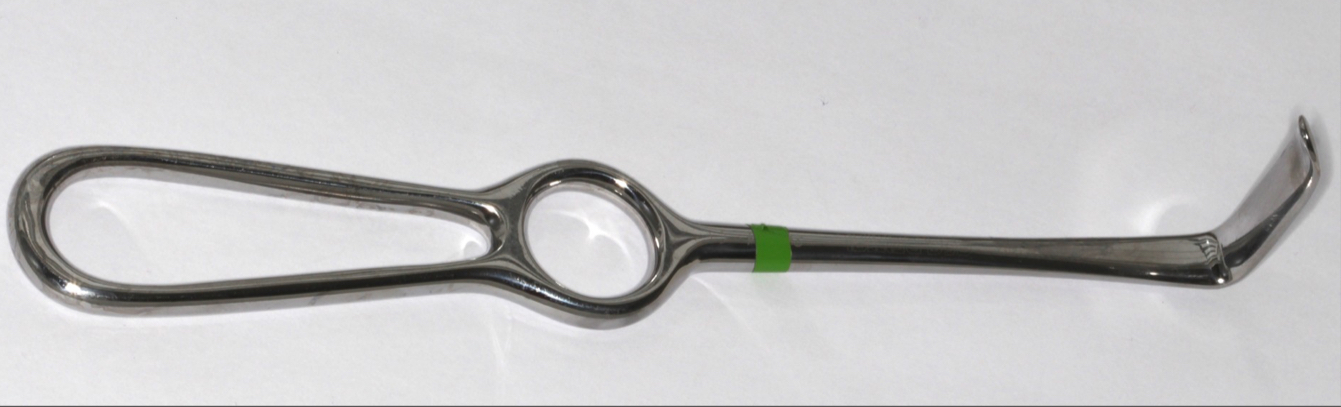

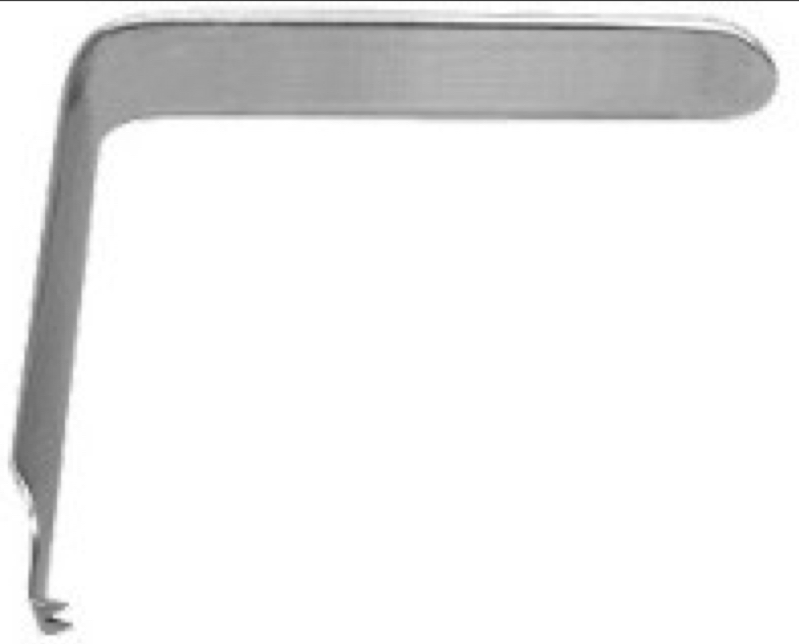
What’s this?
Austin


What’s this?
Middeldorf


What’s this?
Tongue depressor- could also use spoon


What’s this?
Branemark retractor

What are scalpels?
Sharp- for incisions
Handle no 3
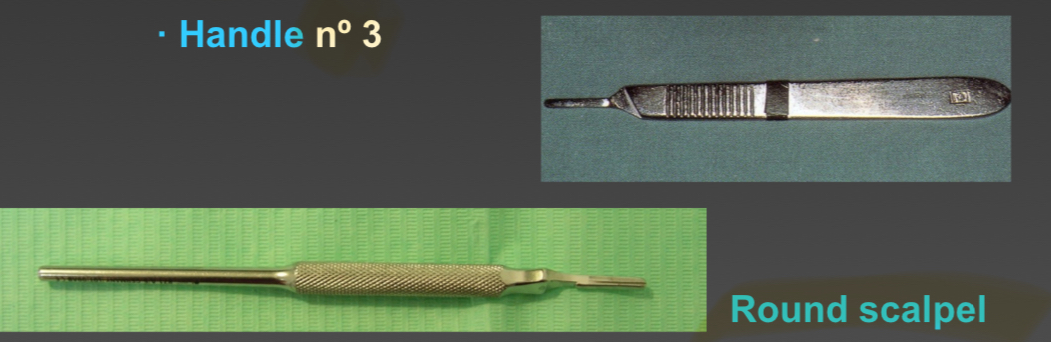
Blades are…
Disposable, removable, individual sterilised packages
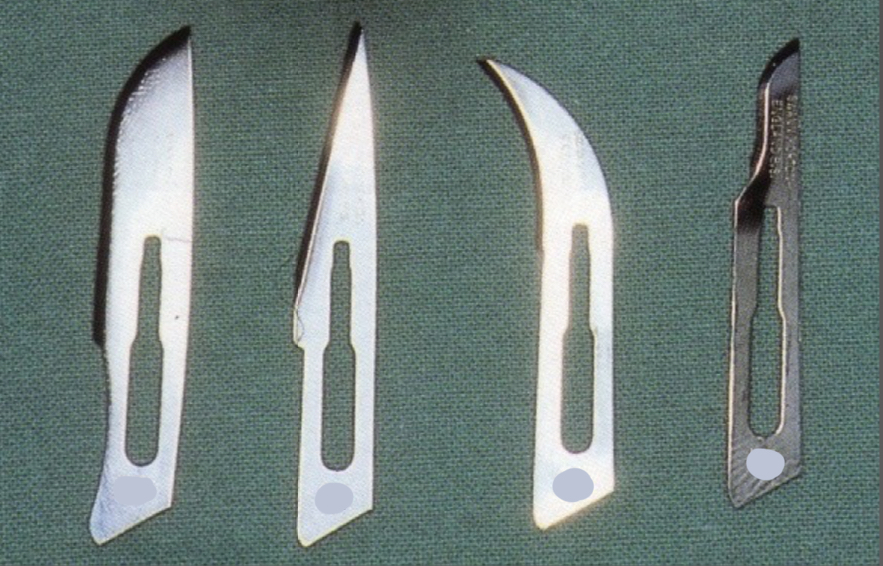
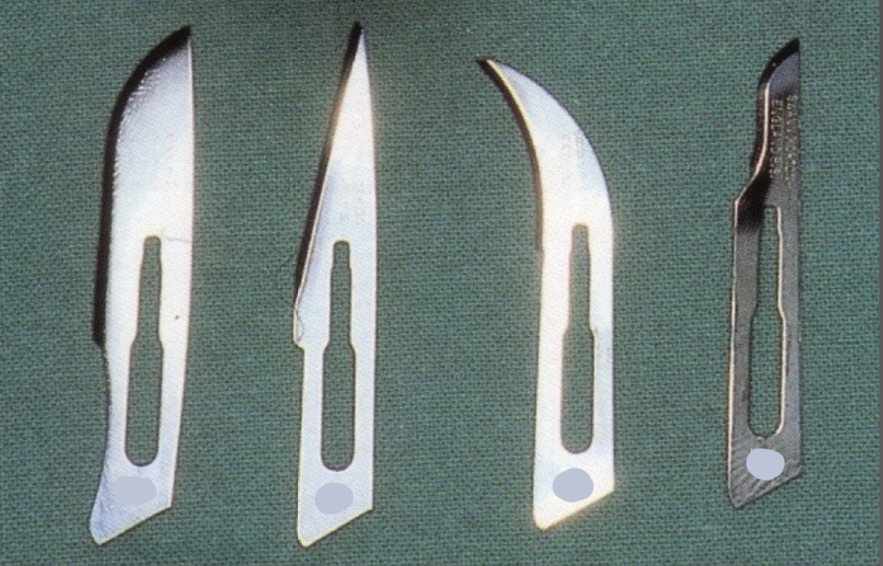
How can you tell the difference between blades used for scalpels?
10, 11, 12, 15
10, 15- curved
11- straight
12- hooked
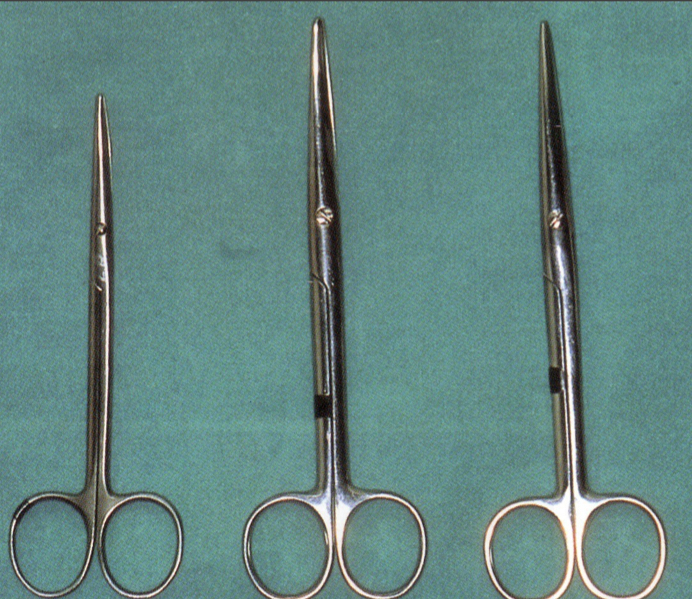
What are scissors and how does the appearance help?
Cutting instruments apply principles of 1st order lever
Blunt ends and medium sized curves for dissection of tissues
What are periosteal elevators used for?
Reflect and retract flap
Full thickness mucoperiosteal flap- detach buccal or palatal mucosa and periosteum from underlying bone
Partial thickness flap- leave underlying periosteum and bone
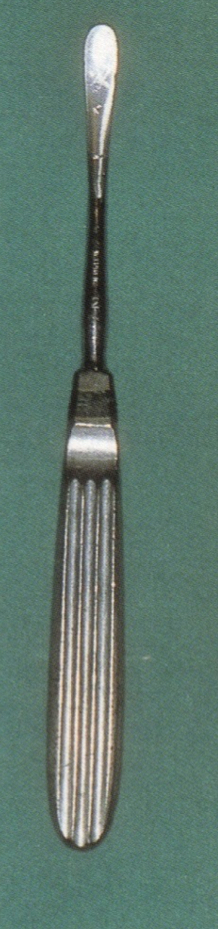
What’s this?
Obwegeser
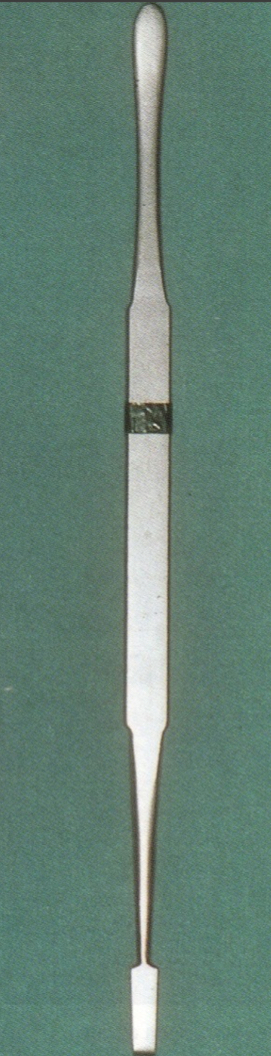
What’s this?
Howarth

What’s this?
Molt

What’s this?
Willinger- elevator


What’s this?
Freer- elevator


What’s this?
Pritchard- elevator


What’s this?
Buser- elevator

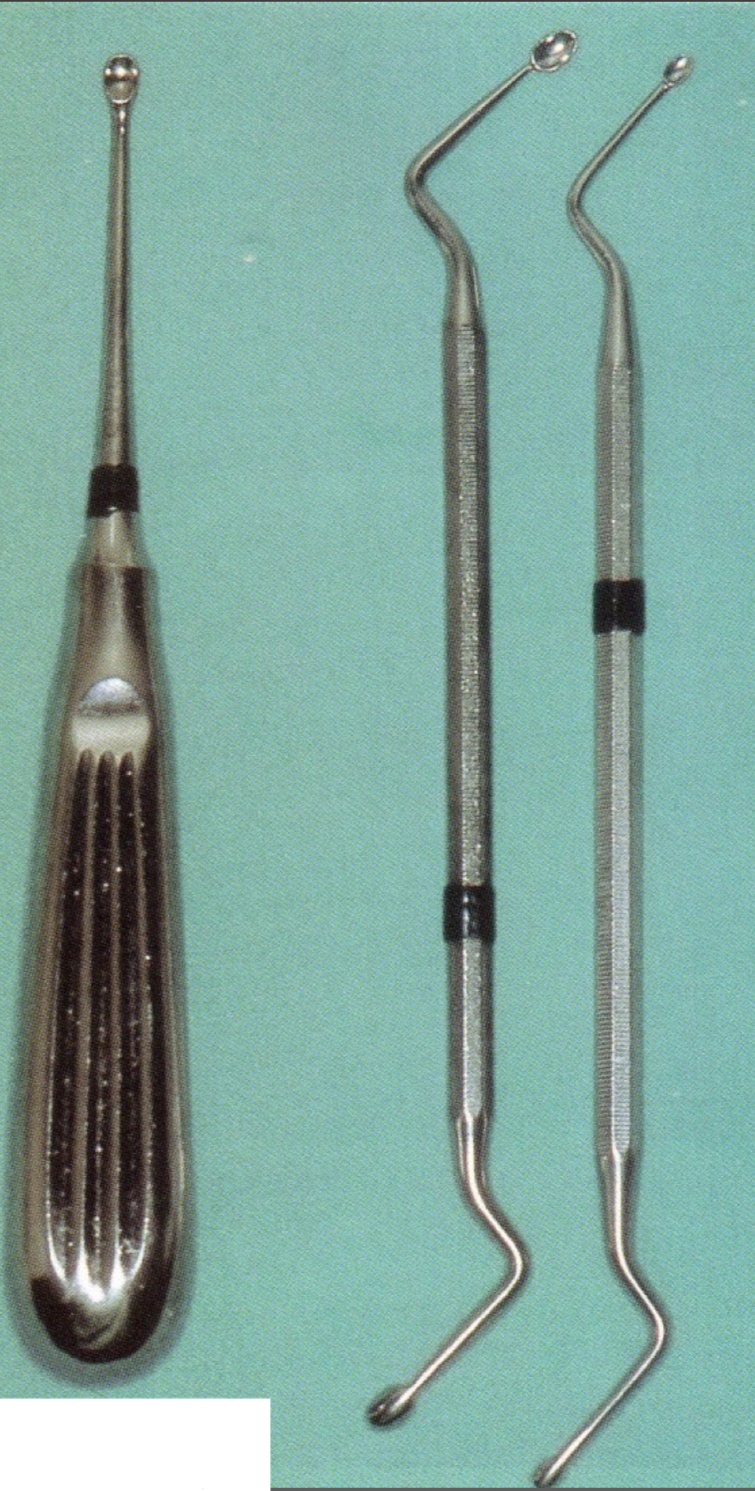
What are curettes?
Small scoop design- debride soft tissues
Straight/angles, varying length and concavity shape
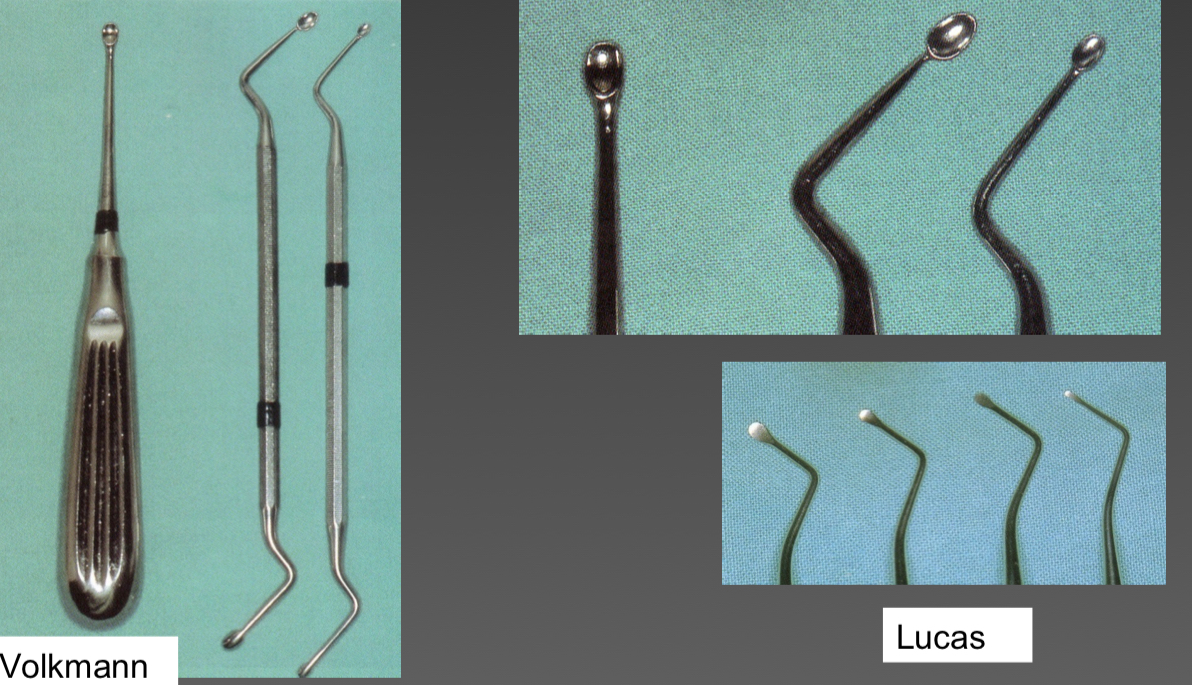
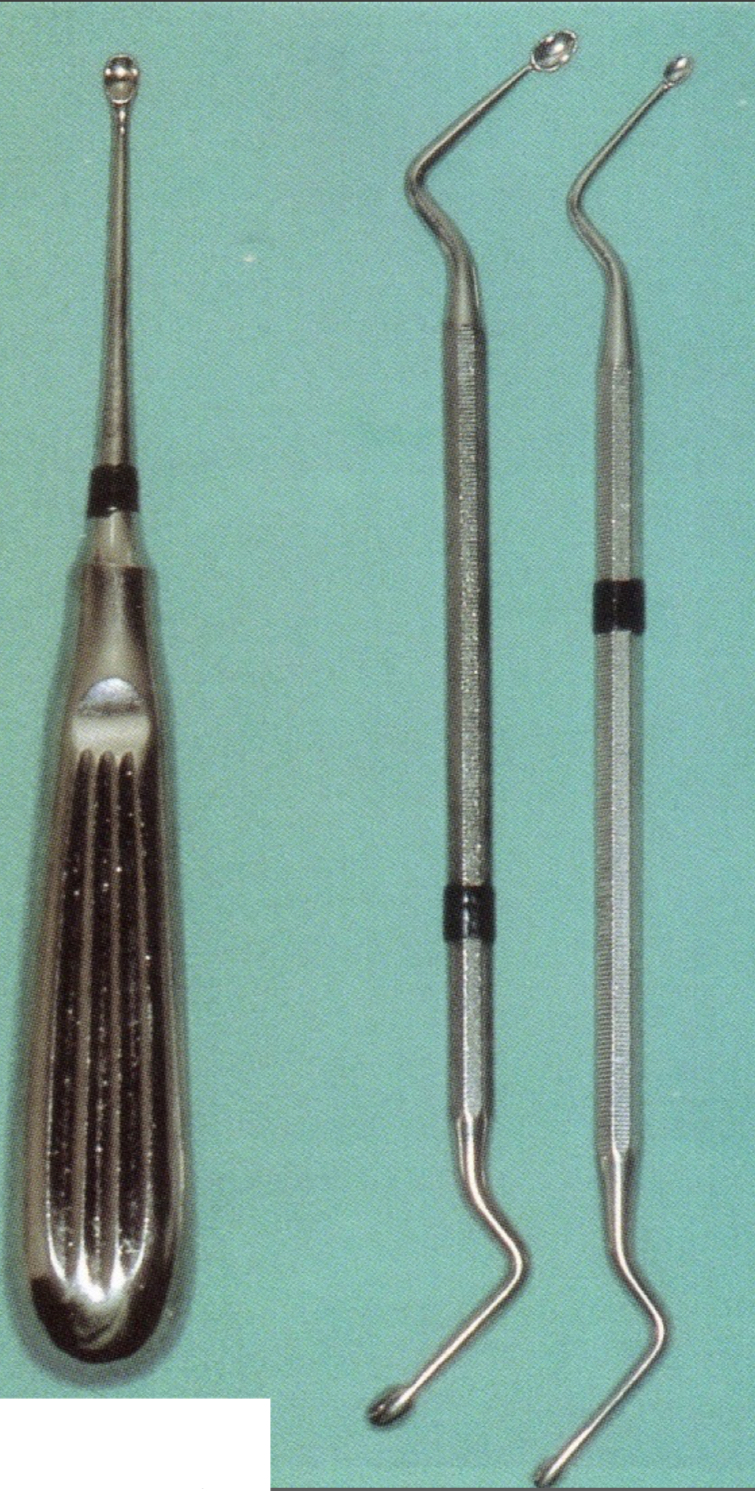
What type of instrument and its name?
Volkmann- more scooped
What type of instrument and its name?
Lucas- flatter
What are these and what are they used for, mode of action?
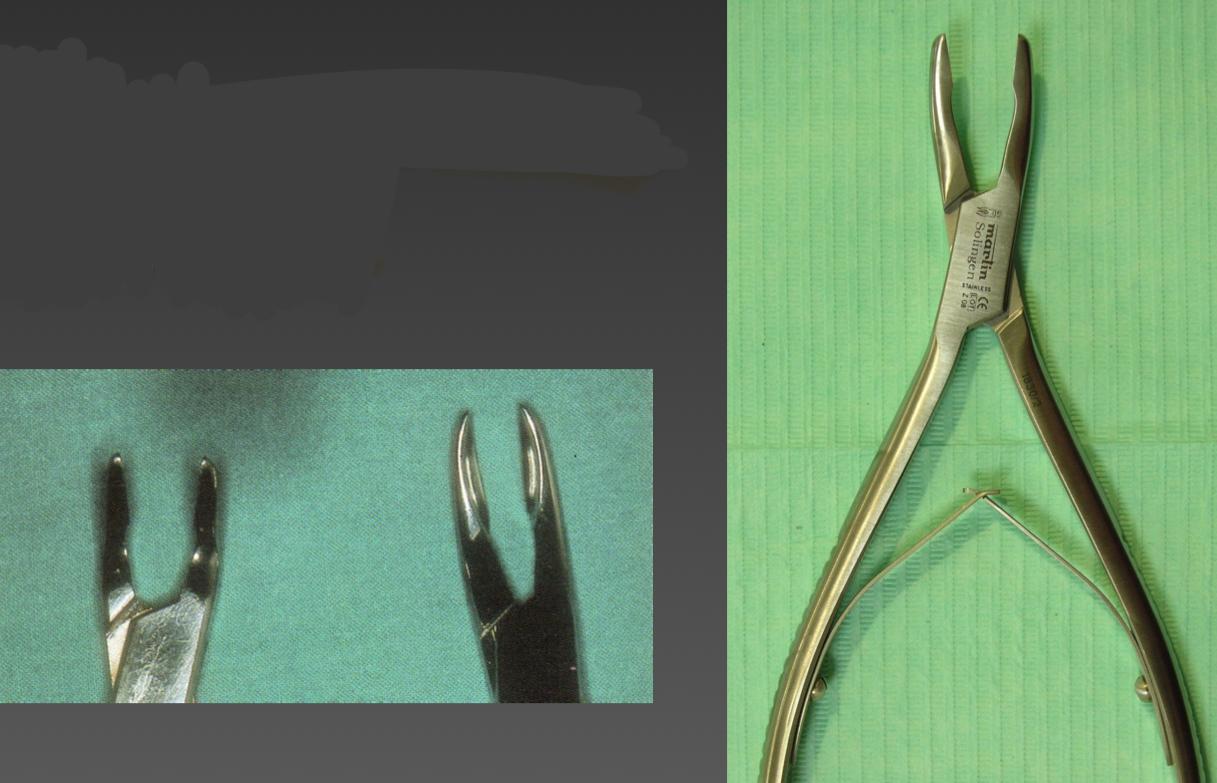
Rongeur forceps (bone nibblers)- for hard tissues
Remove bony tips from sharp alveolar edges, enlarge bone defects, initiate ostectomies
Lateral or frontal cutting action
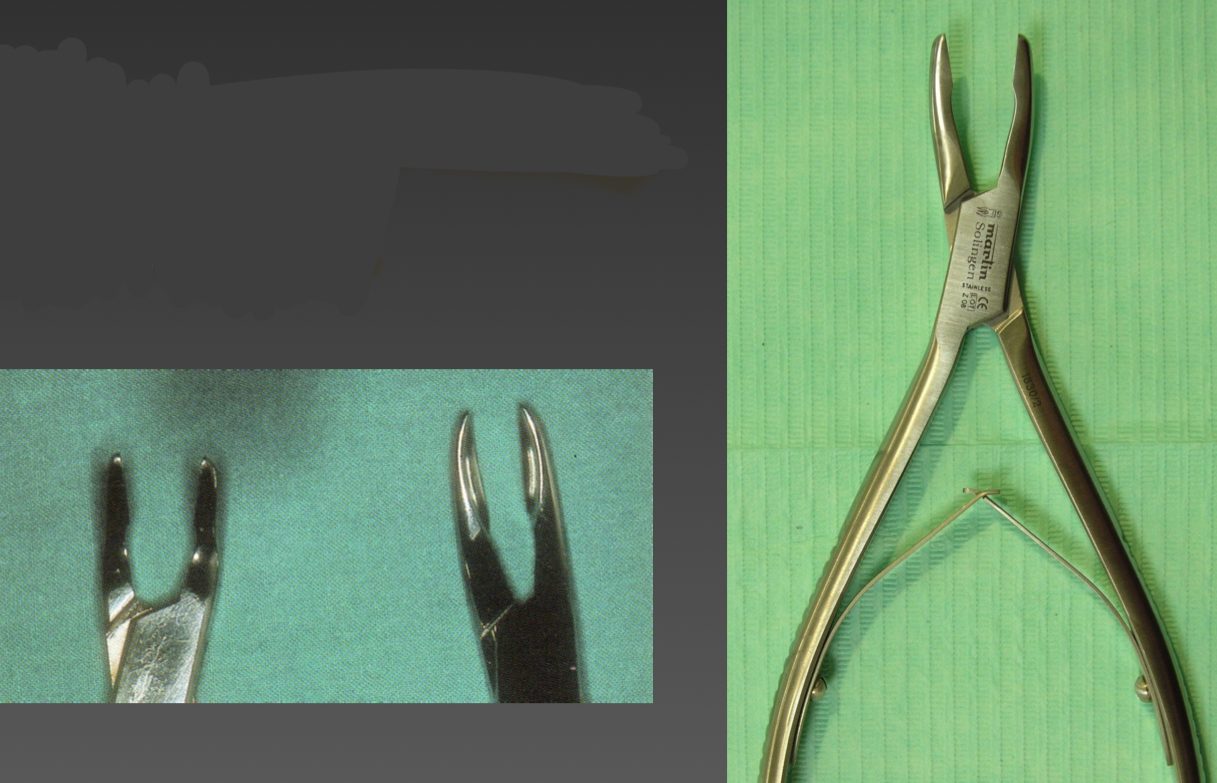
What are these and what are they used for?
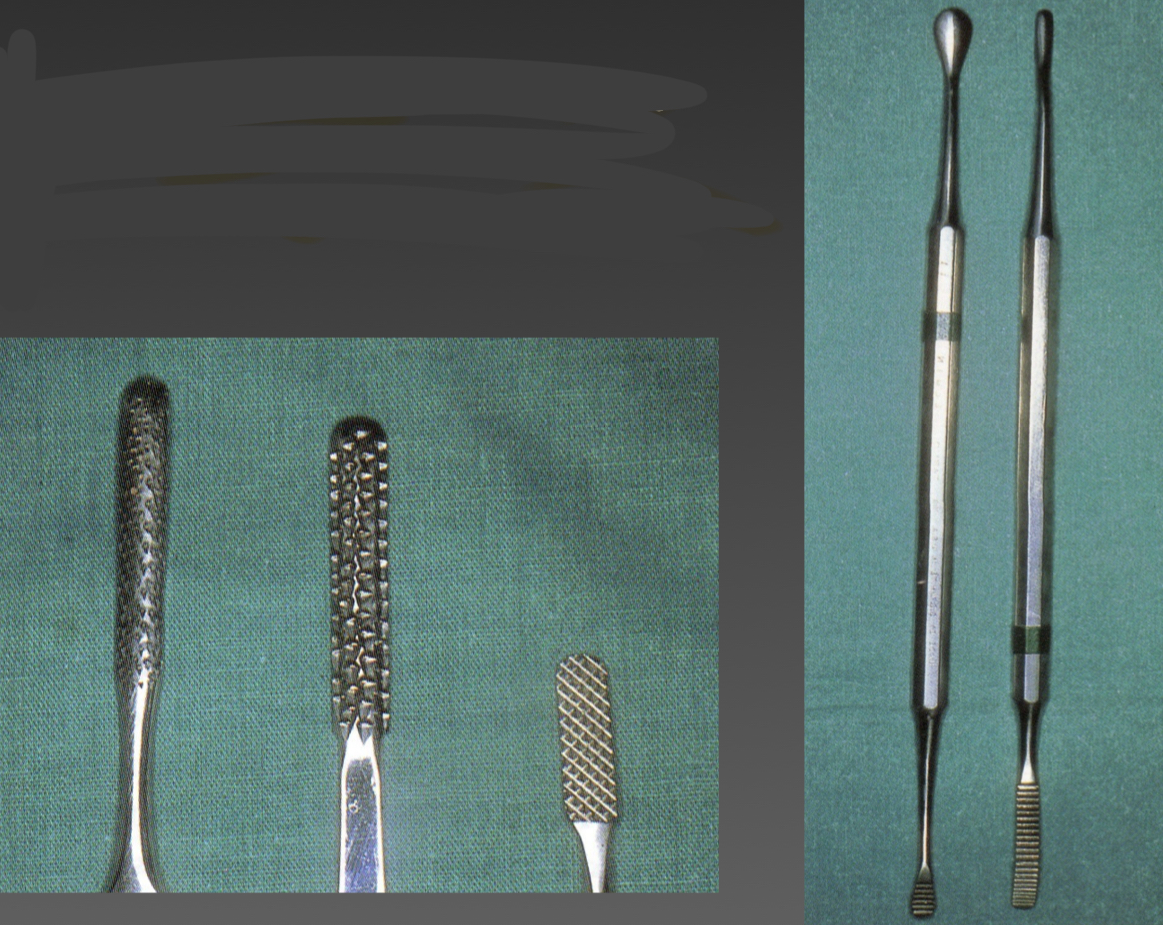
Bone files- have 2 active areas with diff inclination and orientation
File and smooth sharp or compressed bone edges- use after rongeur forceps with irrigation
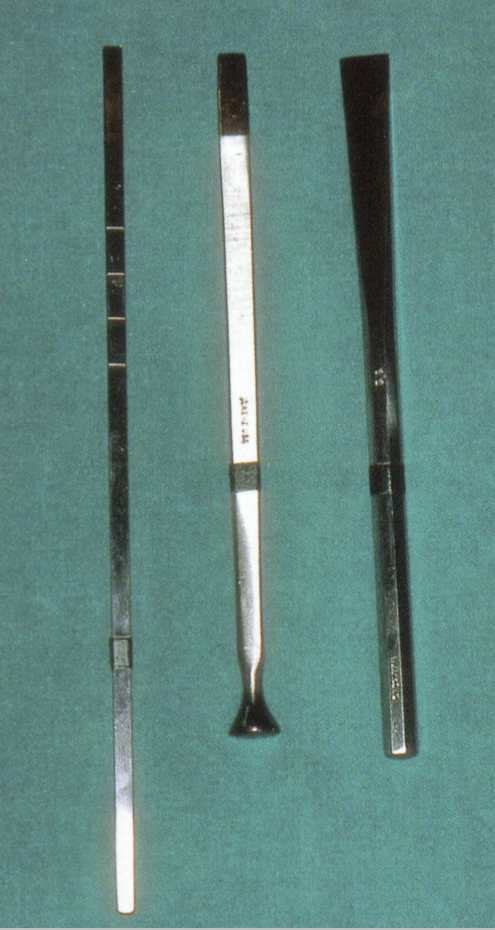
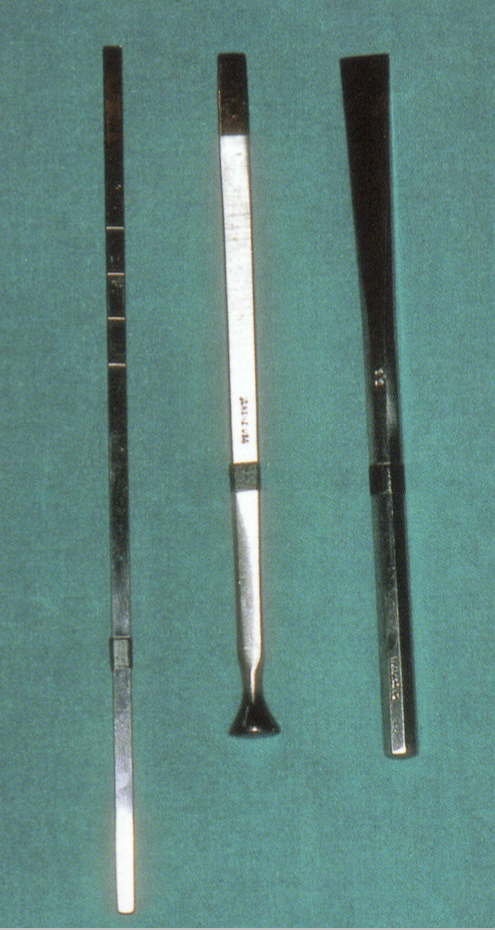
What are these and the types?
Chisels- straight with single, double or half round bevel
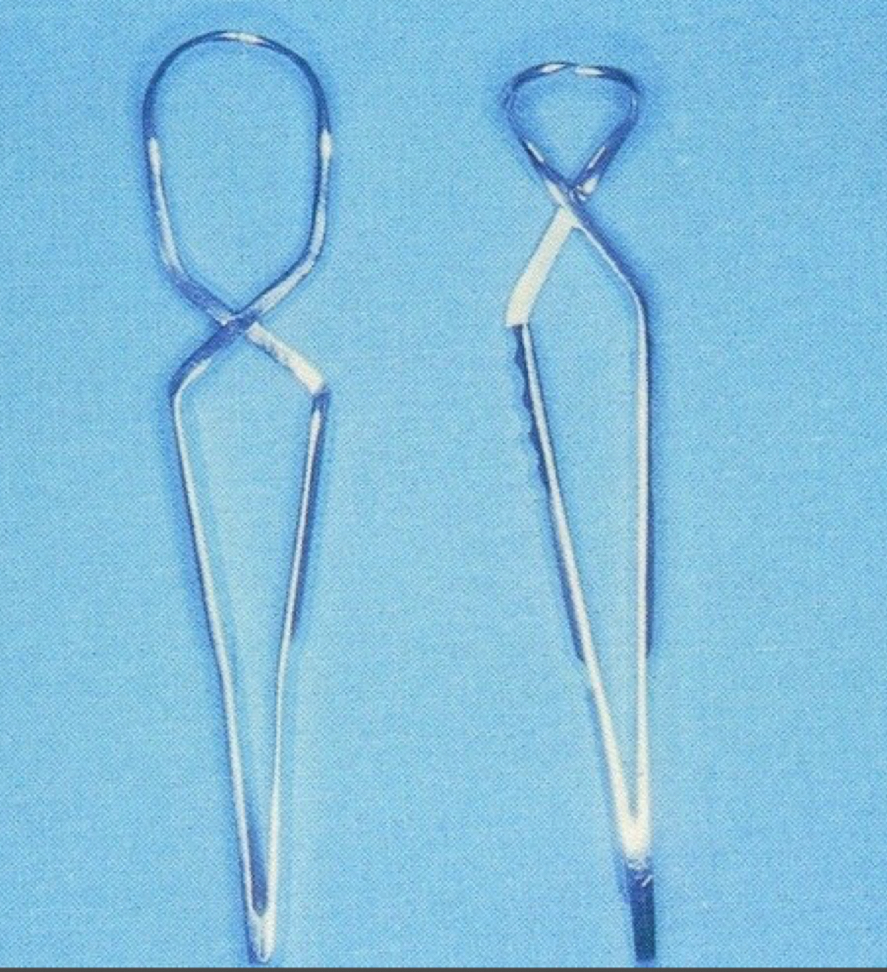
What are these?
Field tweezers or pincers
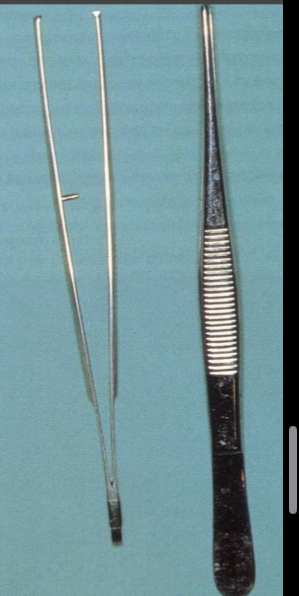
What are these?
Dissecting tweezers- long/short, with/out teeth, thick/thin
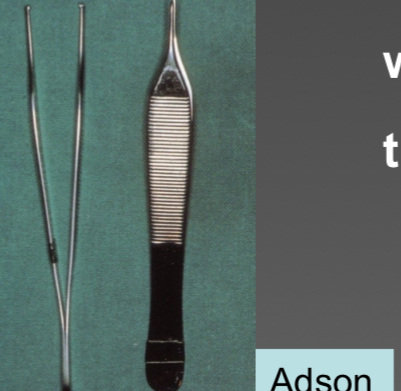
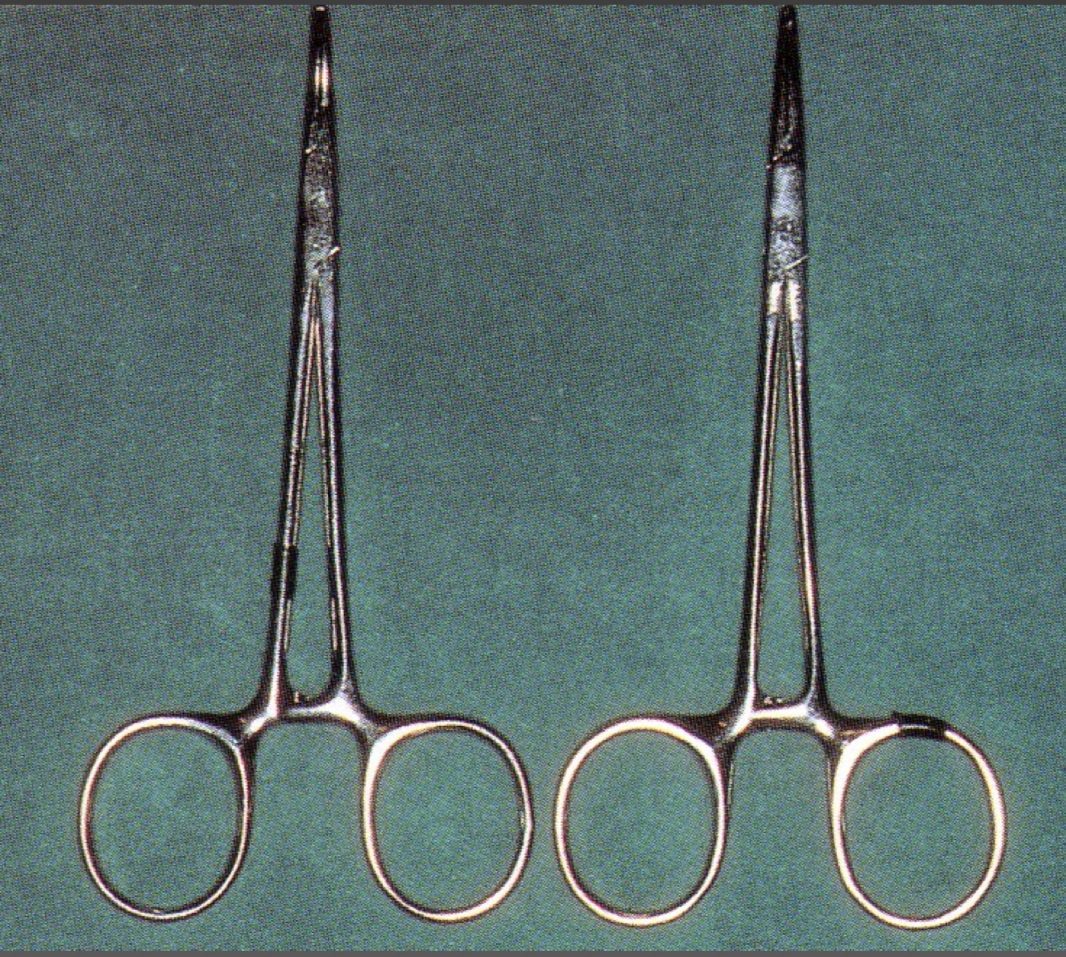
What are these, characteristics and what is it used for?
Hemostatic tweezers- mosquito
straight/curved, blunt end with/out teeth
used to hold continuous pressure and clamp blood vessels
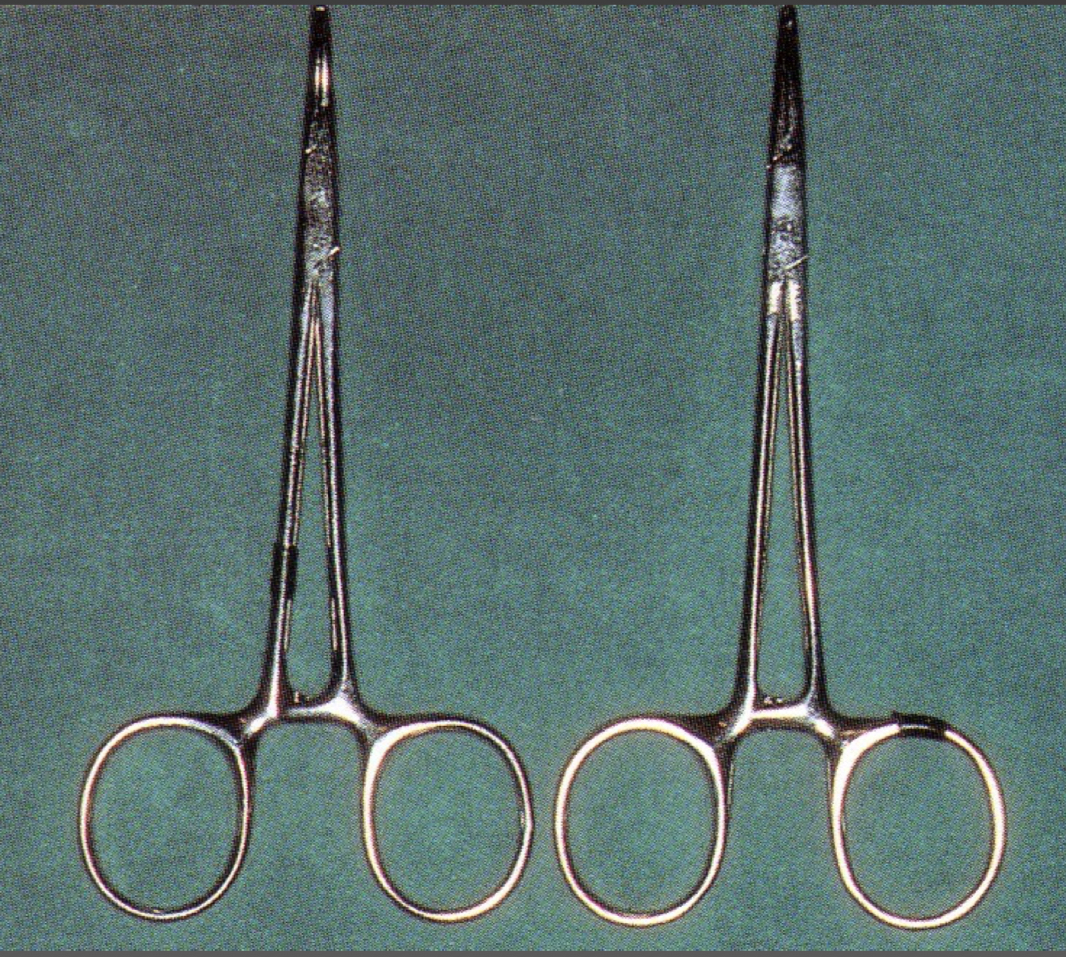
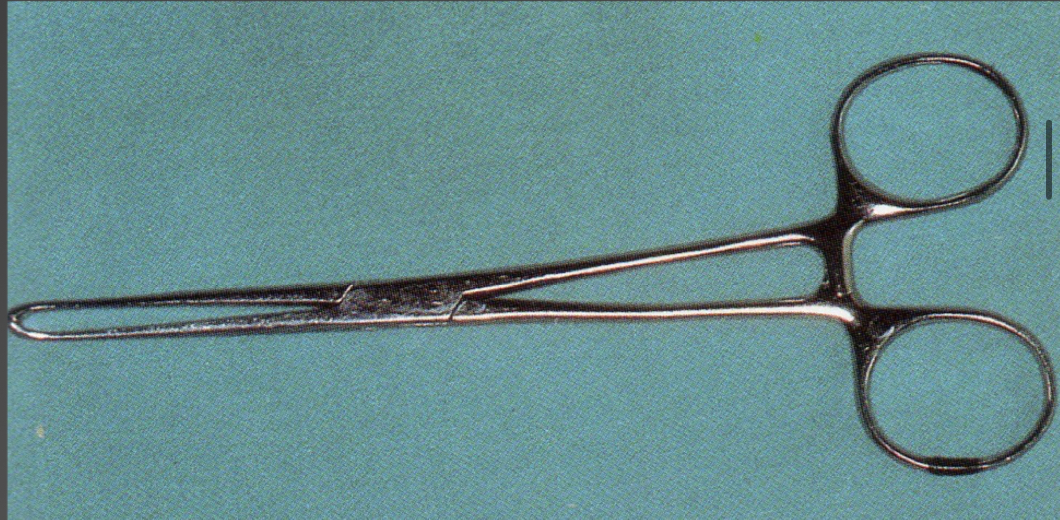
What are these?
Forcipression tweezers- Allis- holds tissues together
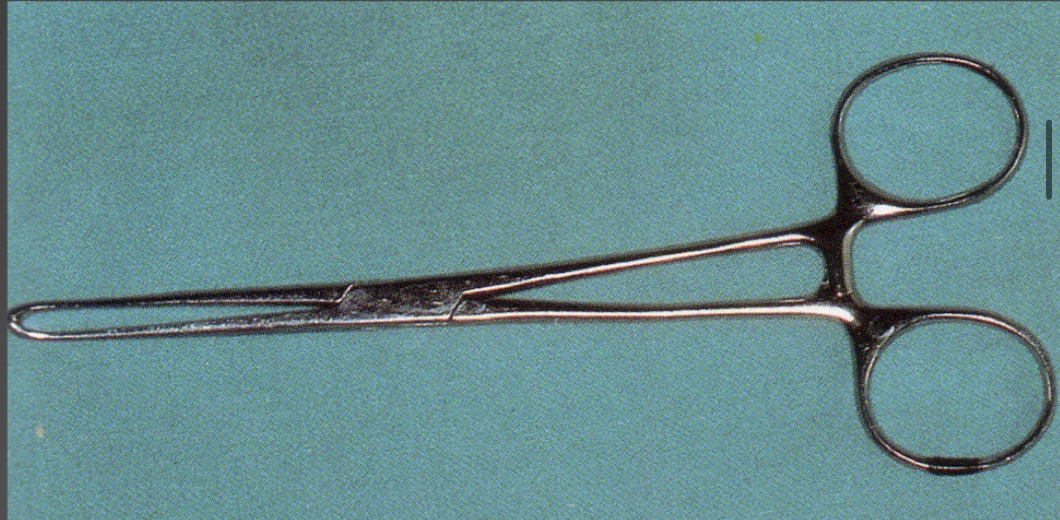
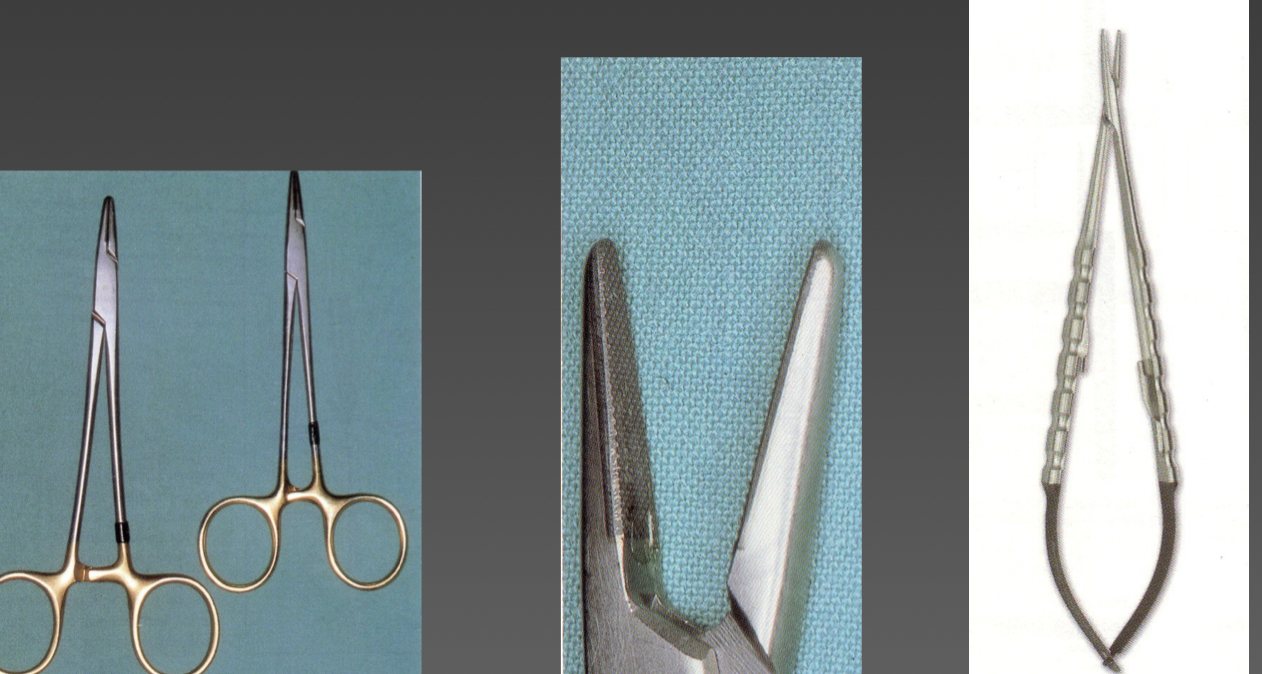
What’s this?
Needle holder- forcipression tweezer to hold suture needles
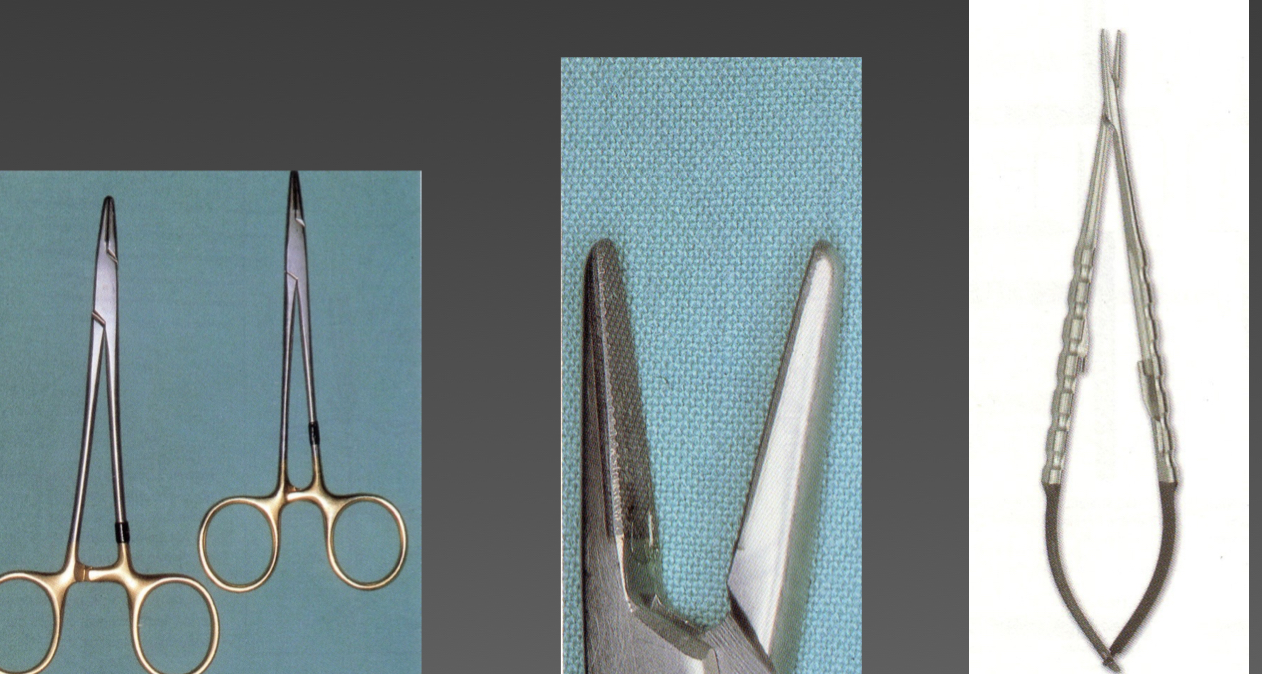
What are the elements of a rotary instrument?
Engine
Surgical handpiece
Bur
What are the types of engines of a rotary instrument and its characteristics?
Conventional
Electric or compressed air- low speed- up to 40,000rpm
Turbine- high speed- 300,000-400,000rpm- risk of bone necrosis and subcutaneous emphysema
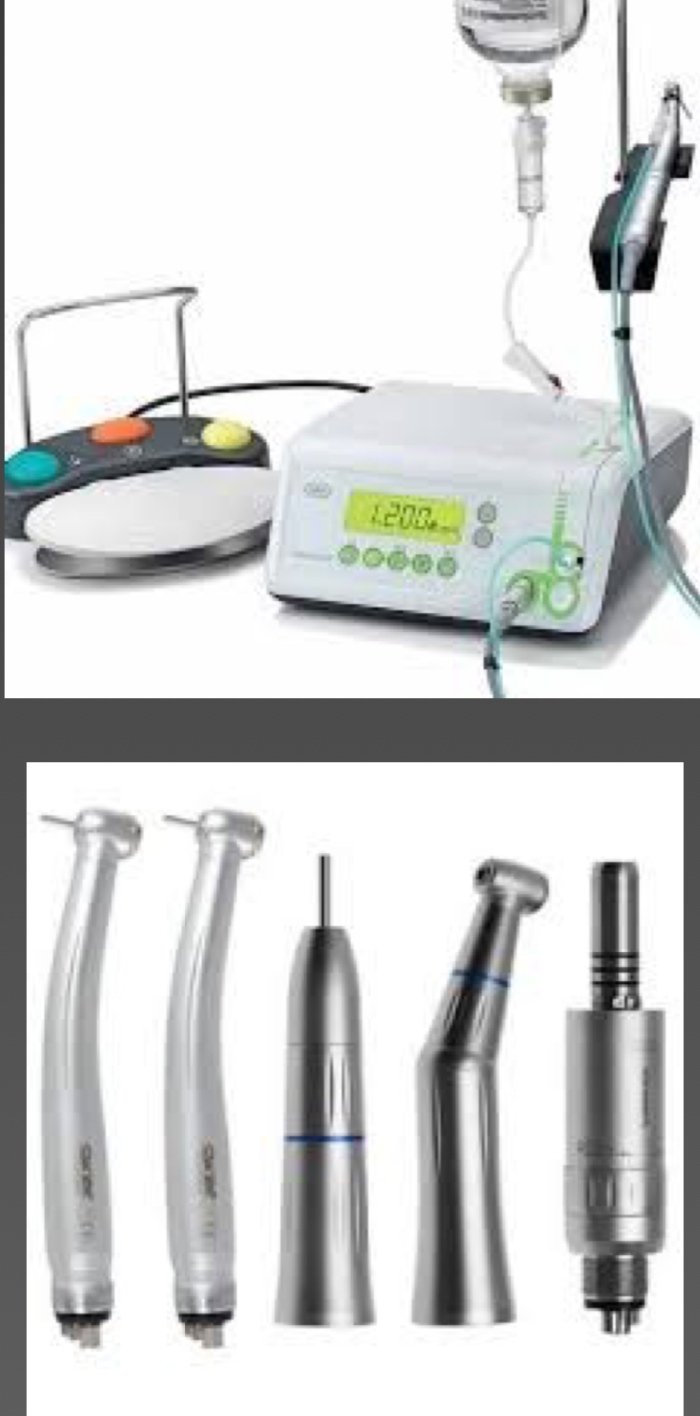
How does irrigation improve the use of a surgical handpiece?
Irrigated with water to preserve vitality of tissues without overheating
Keeps site clear of debris
Can see consistency of tissue
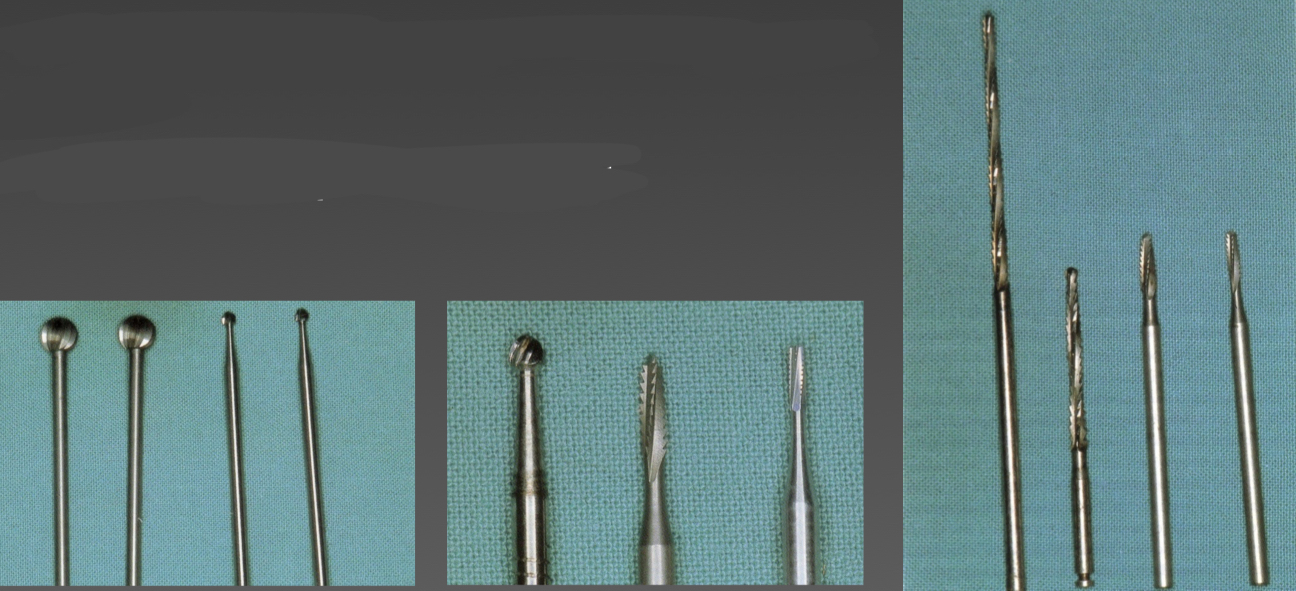
What can burs be made of and give two types?
Tungsten carbide- round, different calibers, for osteotomy and ostectomy
Steel- thick to smooth bone edges
Lindemann burs- elongated for hard to reach areas
Fissure burs- tapered or straight
How does an electric scalpel work, when is it used?
High freq alternating current into electrode- active and passive
To dissect tissues, electrocoagulation, desiccate
4 advs of electric scalpel
Sterile accurate incision, high speed
Doesn’t compress or cause tissues to bleed
Good healing
Multiple uses
Disadvs of electric scalpel
Unpleasant smell and smoke
Can’t use in pacemaker carriers
Risk of explosion
What does laser stand for?
Light amplification by stimulation emission of radiation
What are the uses of low vs high power lasers?
Analgesia and anti inflammatory
Incisions, vaporise or ablate hard tissues
What are the characteristics of lasers?
Amplification- aggregating effect
Monochromatic- uniform wavelength
Unidirectional
Coherence
What are the features of a suture needle?
Straight/curved
Triangular or cyclindrical crossection tip
Atraumatic
Diff length and radius- 1/2, 1/4, 3/8, 5/8
What are the diff types of suture thread?
Absorbable- synthetic, natural
Non absorbable- metallic, synthetic, natural
What are the characteristics of 3/0 black braided silk?
Easy handling and knot tying (resistant to unravelling)
Foreign body reaction, retention of bacterial plaque, expansion due to liquid absorption
What are the 4 types of hemostatics for hemorrhage control?
Hemostatic medications- with compresses/gauze
Sponges- resorbable filler material
Bone wax
Surgical cements
What are the methods for drainage?
Tubes (penrose)- when there’s an extraoral route of bone, skin or for large cystic lesions
Gauze (capillarity)
Glove finger
Puncture
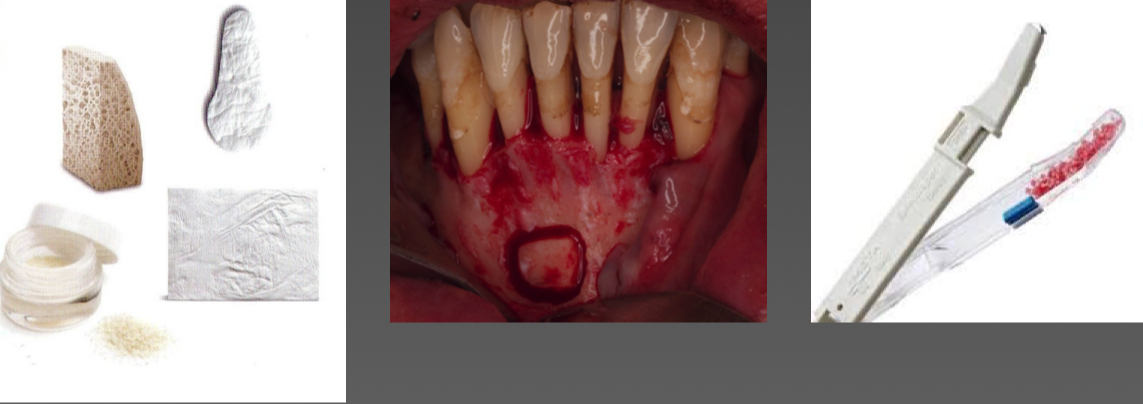
What are materials for bone regeneration/substitution? (3)
Regeneration membranes (barrier for bone growth instead of ct)
Artificial bone substitutes
Autologous bone
What is disinfection?
Destroys pathogenic organisms vegetative or non-sporulant state- Chemical (includes ultrasonic tanks)
What is sterilization?
Elimination of all microorganisms including sporulated forms
Chemical or physical
What is the preferred method of sterilization and why?
Pressurised water vapour (in autoclave)-
Destroys all microorganisms and spores
Doesn’t deteriorate instruments
Corrosion avoided with 0.1% cyclohexylamine
What are the disadvantages of dry heat like flame treatments and hot air vs wet heat like boiling?
harms instruments
requires long time for bactericidal effect
Sensitive to water hardness and altitude, ca precipitates in instruments, doesn’t destroy spores or microorganisms
What is the correct procedure for instruments sterilisation? (7)
Wash and brush
If highly contaminated, bath of 2% glutaraldehyde, 0.5% chlorexidine with 70% alcohol
Disassemble multi component instruments
Ultrasonic treatment of surgical instruments and burs
Dry and place in sealable bags
Put in autoclave trays
Use indicator strips to confirm correct sterilization cycle completed
What are the uses of antiseptic liquids?
Disinfect of skin or mucosa
Rinse oral cavity to reduce no of microorganisms
Local treatment of oral lesions
Treat of clinical surfaces
What is the most used antiseptic liquids?
0.5% chlorhexidine solution with 70% alcohol
2% glutaraldehyde solution
30 mins immersion- disinfects
10h immersion- sterilises
What are the features of formaldehyde gas as an antiseptic?
Good bactericide
Slow 48h action
formalin or trioxymethylene tablets
What are the features of ethylene oxide gas as an antiseptic?
Great efficiency in 2-6hrs
Flammable in contact with air
Instruments must be aired for 48hrs
What are the features of non-saturated chemical steam as antiseptic?
Effective in 10 minutes
Avoids corrosion and loss of cutting edges in sharp
instruments, turbines and handpieces
How is gamma vs beta vs UV radiation for sterilization?
Highly effective, need to protect personnel, expensive, cold method
less, strict rules, for slightly dense material
Least effect- germicide, used in operating rooms