ANAPHY: LESSON 1 - HUMAN ORGANISM
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
panahon na masayon pa :((
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
Anatomy
Scientific discipline that investigates the structure of the body
Anatomy
It means to dissect, or cut apart and separate, the parts of the body for study
Anatomy
Examines the relationship between structure of a body part and its function
Systemic Anatomy and Regional Anatomy
Two basic approaches to the study of anatomy
Systemic Anatomy
Study of the body by systems, such as the cardiovascular, nervous, skeletal, and muscular systems. It is the approach used in our books and most introductory textbooks.
Regional Anatomy
Study of the organization of the body by areas and all regions, such as the head, abdomen, or arm, all systems are studied simultaneously. It is an approach taken in many medical and dental schools.
Surface Anatomy and Anatomical Imaging
Two general ways to examine the internal structures of a living person
Surface Anatomy
Study of external features, such as bony projections, which serve as landmarks for locating deeper structures.
Anatomical Imaging
Involves the use of x-rays, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and other technologies to create pictures of internal structures.
Physiology
The scientific discipline that deals with the processes or functions of living things. It is important in here to recognize structures as dynamic rather than fixed and unchanging.
Examine the body’s responses to stimuli
Examine the body maintains of stable internal coonditions.
The major goals of physiology
Human Physiology
Study of humans
Cellular Physiology
Focuses on processes inside cells such as the manufacturing of substances, including proteins.
Systemic Physiology
Focuses on the functions of organ systems.
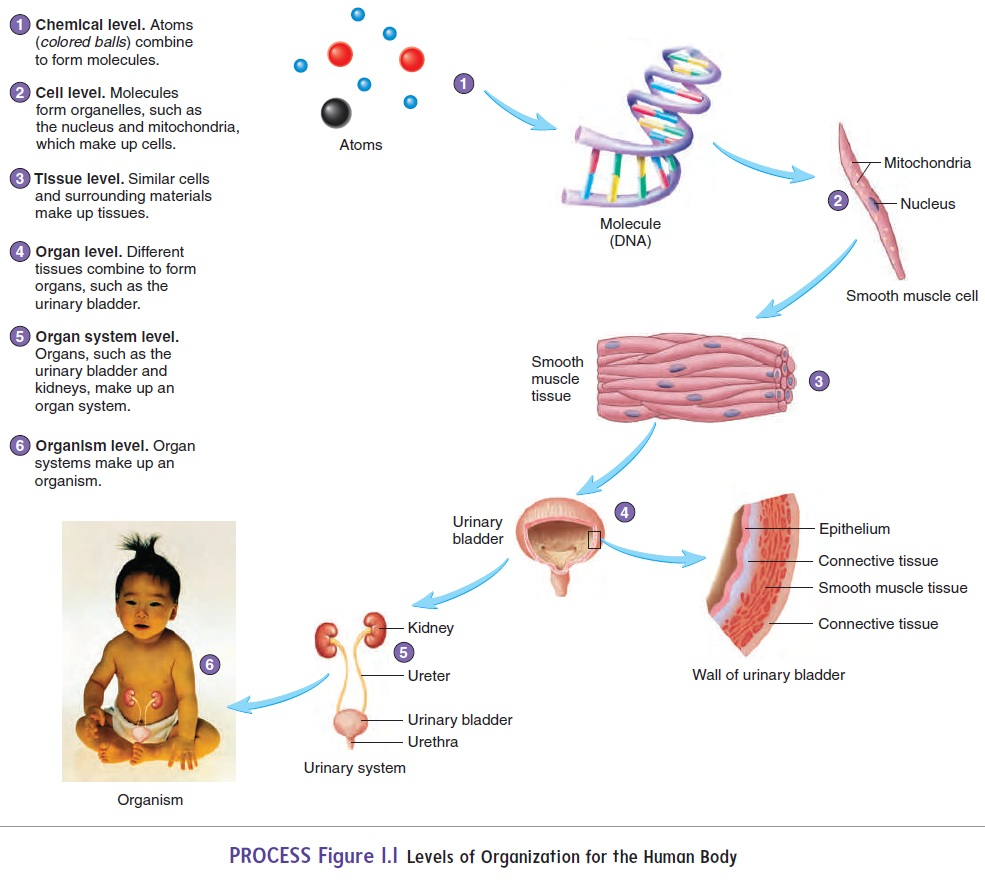
Chemical Level
Cell Level
Tissue Level
Organ Level
Organ System Level
Organism Level
Six Structural Levels of the Body
Chemical Level of Organization
Involves how atoms, such as hydrogen and carbon, interact and combine into molecules.
Cells
Are the basic structural and functional units of organisms, such as plants and animals.
Organelles
Are the small structures that make up some cells. It carry out particular functions, such as digestion and movement , for the cell.
Tissue
It is a group of similar cells and the materials surrounding them. The characteristics of the cells and surrounding materials determine the functions of it.
Epithelial
Connective
Muscle
Nervous
Tissues that make up the body are classified into four primary types
Organ
A tool. It is composed of two or more tissue types that together perform one or more common functions.
Organ System
A group of organs classified as a unit because of a common function or set of functions.
Integumentary System
Skeletal System
Muscular System
Lymphatic System
Respiratory System
Digestive System
Nervous System
Endocrine System
Cardiovascular System
Urinary System
Reproductive System (Female and Male)
Eleven Major Organ Systems
Integumentary System
Provides protection, regulates temperature, prevents water loss, and helps produce vitamin D. Consists of skin, hair, nails, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands.
Skeletal System
Provides protection and support, allows body movements, produces blood cells, and stores minerals and adipose tissue. Consists of bones, associated cartilages, ligaments, and joints
Muscular System
Produces body movements, maintains posture, and produces body heat. Consists of muscles attached to connective tissue sheets or the skeleton by tendons.
Nervous System
A major regulatory system that detects sensations and controls movements, physiological processes, and intellectual functions. Consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors.
Endocrine
A major regulatory system that influences metabolism, growth, reproduction, and many other functions. Consists of endocrine glands, including the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, gonads, and other tissues that secrete hormones.
Cardiovascular System
Transports nutrients, waste products, gases, and hormones throughout the body; plays a role in the immune response and the regulation of body temperature. Consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
Lymphatic System
Removes foreign substances from the blood and lymph, combats disease, maintains tissue fluid balance, and absorbs dietary fats from the digestive tract. Consists of the lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, thymus, spleen, and other lymphatic tissues.
Respiratory System
Exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and air and regulates blood pH. Consists of the lungs, diaphragm, and respiratory passages.
Digestive System
Performs the mechanical and chemical processes of digestion absorption of nutrients, and elimination of wastes. Consists of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, and other accessory organs.
Urinary System
Removes waste products from the blood and regulates blood pH, ion balance, and water balance. Consists of the kidneys, ureters, urethra, and urinary bladder.
Female Reproductive System
Produces oocytes and is the site of fertilization and fetal development: produces milk for the newborn; produces hormones that influence sexual function and behaviors. Consists of the ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina mammary glands, and associated structures.
Male Reproductive System
Produces and transfers sperm cells to the female and produces hormones that influence sexual functions and behaviors. Consists of the testes, accessory structures, ducts, and penis.
Organism
Is any living thing considered as a whole, whether composed of one cell, such as a bacterium, or of trillions of cells, such as a human.
Human Organism
Is a network of organ system that are mutual dependent upon one another.
Organization
Metabolism
Responsiveness
Growth
Development
Reproduction
Six Characteristics of Life
Life
The most important common feature of all organisms.
Organization
Refers to the specific interrelationships among the parts of an organism and how those parts interact to perform specific functions.
Metabolism
The is the ability to use energy to perform vital functions, such as growth, movement, and reproduction.
Responsiveness
The ability of an organism to sense changes in the external and internal environment and adjust to those changes.
Growth
Refers to an increase in size or number of cells, which produces an overall enlargement in all or part of an organism, cell size, or the amount of substance surrounding cells.
Development
Includes the changes an organism undergoes through time, beginning with fertilization and ending with death.
Differentiation
Involves changes in a cell’s structure and function from an immature, generalized state to a mature, specialized state.
Reproduction
Formation of new cells or new organisms.
Homeostasis
Maintenance of a relatively constant environment.
Homeostasis
Condition in which body functions, body fluids, and other factors of the internal environment are maintained within a range of values suitable to support life.
Variables
Changes in conditions and these are values that are not constant.
Homeostatic Mechanisms
Such as sweating or shivering, normally maintain body temperature near an ideal normal value, or set point.
Negative-feedback Mechanisms
Regulates most systems of the body, which maintain homeostasis.
Negative-feedback Mechanisms
Means that any deviation from the set point is made smaller or is resisted.
Negative-feedback Mechanisms
It does not prevent variation but maintains variation within a normal range
Receptor
Control Center
Effector
Three components of negative-feedback mechanism
Receptor
Monitors the value of a variable by detecting stimuli.
Control Center
Determines the set point for the variable and receives input from the receptor about the variable.
Effector
Can adjust the value of the variable when directed by the control center, usually back toward the set point.
Changed Variable
Is a stimulus because it initiates a homeostatic mechanism
Positive-feedback Mechanisms
Occur when a response to the original stimulus results in the deviation from the set point becoming even greater.
Anatomical Position
Refers to a person standing erect with the face directed forward, the upper limbs hanging to the sides, and the palms of the hands facing forward.
Supine
When lying face upward
Prone
When lying face downward
Directional Terms
Describe parts of the body relative to each other
Inferior
Lower or below
Superior
Higher or above
Anterior
To go before or toward the front of the body
Posterior
Posterus, following, or toward the back of the body
Dorsal
Dorsum, back, or toward the back of the body (synonymous with posterior)
Ventral
Venter, belly, or toward the belly (synonymous with anterior)
Proximal
Proximus, near, or closer to a point of attachment
Distal
di + sto, to be distant, or farther from a point of attachment
Lateral
Latus, side, or away from the midline of the body
Medial
Medialis, middle, or toward the middle or midline of the body
Superficial
Superficialis, surface, or toward or on the surface
Deep
Deop, deep, away from the surface, or internal
central region of the body
consists of the head, neck, and trunk.
Thorax
Abdomen
Pelvis
The trunk can be divided into 3 regions
Thorax
is the chest cavity where the heart and lungs are located
Abdomen
contains organs such as the liver, stomach, and intestines
Pelvis
Contains the bladder and reproductive organs
Arm
Forearm
Wrist
Hand
The upper limbs is divided into 4 parts
Thigh
Leg
Ankle
Foot
The lower limbs is divided into 4 parts
arm
extends from the shoulder to the elbow
forearm
extends from the elbow to the wrist
thigh
extends from the hip to the knee.
leg
extends from the knee to the ankle.
four sections or quadrants
abdomen is often subdivided superficially into two imaginary lines—one horizontal and one vertical—that intersect at the navel
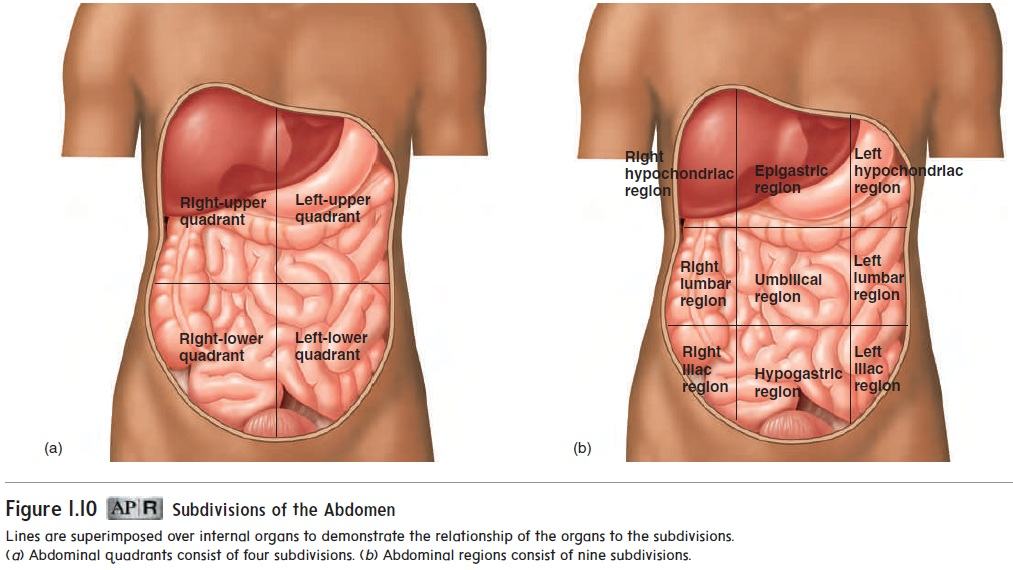
Right-upper Quadrant
Left-Upper Quadrant
Right-lower Quadrant
Left-lower Quadrant
Quadrants of the abdomen
Regions
Abdomen is sometimes subdivided into four imaginary lines—two horizontal and two vertical. These four lines create an imaginary tic-tac-toe figure on the abdomen
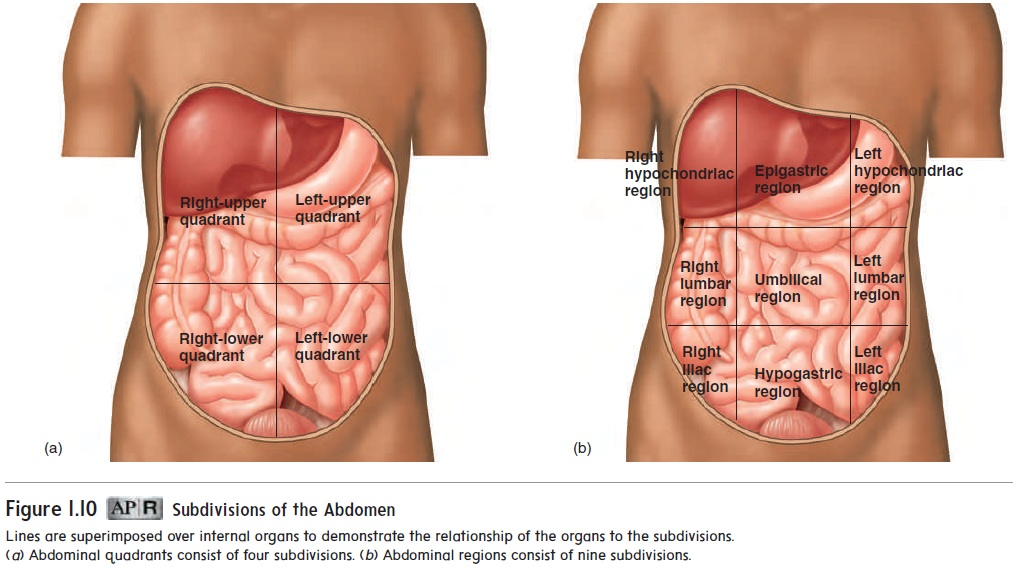
Right Hypochondriac Region
Epigastric Region
Left Hypochondriac Region
Right Lumbar Region
Umbilical Region
Left Lumbar Region
Right Iliac Region
Hypogastric Region
Left Iliac Region
Regions of the Abdomen
Planes
Useful to describe the body having imaginary flat surfaces
Plane
It divides or sections, the body, making it possible to “look inside” and observe the body’s structures.
sagittal plane
runs vertically through the body and separates it into right and left parts.
sagittal plane
literally means the flight of an arrow and refers to the way the body would be split by an arrow passing anteriorly to posteriorly.
median plane
is a sagittal plane that passes through the midline of the body, dividing it into equal right and left halves.
transverse plane or horizontal plane
runs parallel to the surface of the ground, dividing the body into superior and inferior parts.
frontal plane or coronal plane
runs vertically from right to left and divides the body into anterior and posterior parts.
longitudinal section
A cut along the length of a organ or through the long axis of the organ
transverse section or cross section
cuts completely through an organ or cuts at a right angle to the long axis
oblique section
it is a cut is made across the long axis at other than a right angle