Psych Exam 10/3/25
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Psychology
scientific study of behavior and mental processes
Experimental psych
researchers who use scientific methods to study and understand fundamental aspects of human and animal behavior and mental processes, such as learning, memory, sensation, and perception.
Clinical psych
mental health professionals who specialize in the assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
Cognitive psych
professionals who study internal mental processes like memory, perception, and language to understand how people think, learn, and solve problems.
Developmental psych
professionals who study how humans change, grow, and adapt across their entire lifespan, from conception to old age
Theory
A broad explanation for a set of phenomena
Hypothesis
A specific, testable prediction derived from a theory
Operational definition
A precise definition of a variable in terms of how it will be measured
Survey research method
A type of descriptive research that uses questionnaires or interviews to gather data
Case study research method
A type of descriptive research that closely examines an individual or small group
Observational study research method
a scientist observes and collects data on subjects without intervening to influence the outcome, such as by administering a treatment
experimental research method
a type of research that manipulates a variable of interest (index. v) to uncover cause-and-effect relationships
meta-analysis research method
statistically combines and analyzes the results from multiple independent studies
Independent variable
the variable that is manipulated by the researcher
Dependent variable
the variable that is measured to see the effect of the Indep. v
Extraneous variable
any variable other than the Indep. v that could influence the DV
Cofounding variable
an extraneous variable that changed systematically along with the indep. v, making it impossible to determine the true cause of the outcome
Experimental group
The group that receives the treatment or manipulation
Control group
the group that does not receive the treatment, used as a baseline for comparison
What is a double-blind study and why is it used?
research design, where neither the participants nor the researchers know who is receiving the actual treatment and who is receiving a placebo, used to prevent bias.
What is a correlation?
a statistical measure of how two variables are linearly related
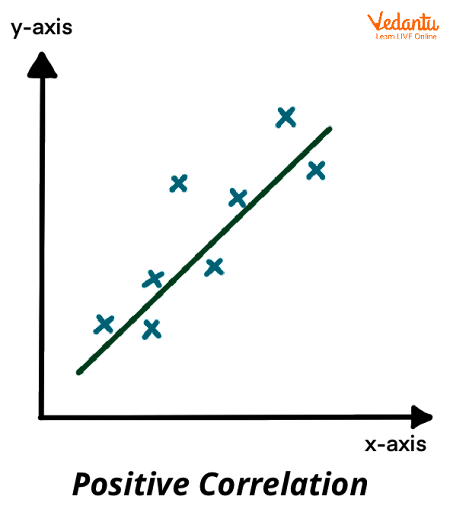
Positive correlation looks like? What are their corresponding coefficients?
Both increase together, Corresponding coefficient ranges +1 to 0

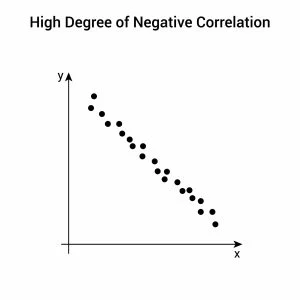
Negative correlation looks like? What are their corresponding coefficients?
One increases while the other decreases. Corresponding coefficients ranges -1 to 0
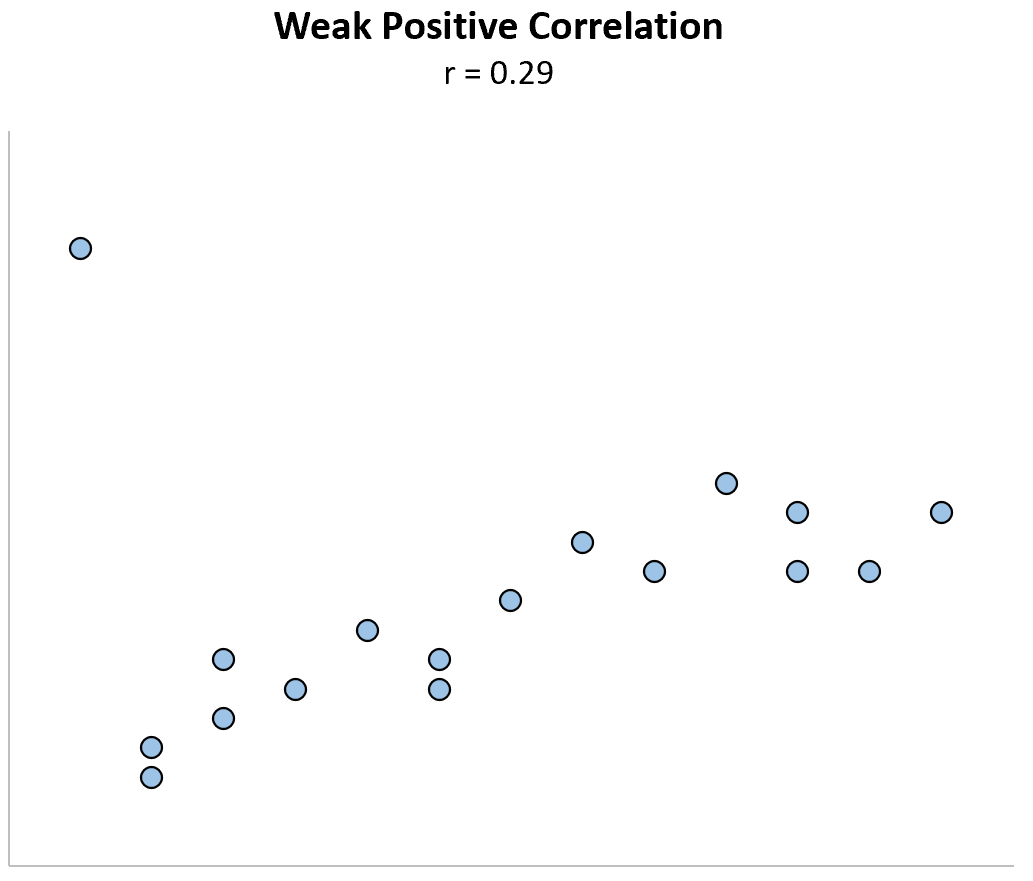
Weak correlation looks like? What are their corresponding coefficients?
Corresponding coefficients ranges +1 to +3.
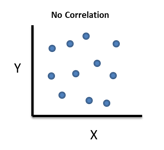
No correlation looks like? What are their corresponding coefficients?
There is no linear relationship between two variables, no corresponding coefficients
Descriptive statistics: What are they used for?
Summarize and organize data
Hindsight bias: What is it?
That “I knew it all along” phenomenon
Neuronal Communication
They communicate via electrochemical signals
Myelin: what is it and what disorder is its breakdown implicated in?
the fatty, protective coating that insulates nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord, multiple sclerosis (MS)
Acetylcholine
Enables muscle action, learning and memory. With Alzheimers disease, ACh-producing neurons deteriorate.
Dopamine
Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion. Oversupply linked to schizophrenia. Undersupply linked to tremors and decreased mobility in Parkinson’s disease.
Seratonin
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal. Undersupply linked to depression. Some drugs that raise
Endorphins
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter; involved in memory. Your brain releases endorphins during excersize, laughing, eating chocolate, or when your stressed or in pain.
Glutamate
A major excitatory neurotransmitter
GABA
Inhibits neurotransmitter firing; contributes to motor control, vision.
Narcolepsy
a chronic neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and involuntary sleep episodes, known as sleep attacks.
Insomnia
a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep, despite having adequate time and opportunity for sleep
Sleep apnea
a sleep disorder characterized by repeated episodes of pauses in breathing during sleep.
Somnambulism (Sleepwalking)
undesirable actions, such as walking, that occur during sleep, limited arousals from non-rapid eye movement (NREM) slow-wave sleep
Sleep terrors
episodes of intense fear and panic that occur during deep sleep, typically in the first half of the night
REM sleep behavior disorder
a sleep disorder characterized by acting out dreams during REM sleep, the stage of sleep when rapid eye movements and vivid dreaming occur.
Frontal lobe
Located in the front of the brain, responsible for higher-level cognitive activities like language, emotions, and decision making.
Parietal lobe
located below the frontal lobe, over the occipital lobe, responsible for integration of sensory info like touch and temp.
Occipital lobe
located under the parietal lobe, responsible for processing visual info.
Temporal lobe
Located under the frontal lobe, responsible for processing hearing info, memories, and language comprehension,
Broca’s area
language production, damage would cause difficulty speaking
Wernickes Area
Critical for language comprehension, damage would cause fluent but meaningless speech
Manifest Content
the actual storyline or events of a dream that a person remembers upon waking, including images, sounds, and plot
Latent content
the hidden psychological meaning behind the dream, representing unconscious thoughts, fears, desires, or repressed impulses that the dream's manifest content disguises.
What are the various stages of consciousness?
conscious, preconscious, and unconscious levels of awareness
Selective attention
the ability to concentrate on one specific task or stimulus while ignoring other, competing information in your environment.
Inattentional blindness
the failure to see an unexpected object or event because your attention is focused on something else, even though the object is in plain sight
Automatic Processing
the effortless, unconscious, and automatic way the brain handles information and performs tasks
Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT)
Using X-rays, a scanner creates multiple cross-sectional images of the brain
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Electrodes placed on the scalp record electrical activity from the area directly below.
Position Emission Tomography (PET)
A radioactively labeled substance called a tracer is injected into the bloodstream and tracked while the participant performs a task.
Evolutionary Psychology
Focus: How behavior and mental processes have developed over time through natural selection.
Usage:
Explains behaviors in terms of survival and reproductive advantages.
Example: A psychologist might study why humans have fear responses (e.g., fear of snakes) as an evolved trait to avoid danger.
Cognitive Neuroscience
Focus: The biological processes underlying cognition, linking brain activity with mental functions.
Usage:
Uses tools like fMRI and EEG to study how the brain supports thinking, memory, language, and attention.
Example: A cognitive neuroscientist may investigate which brain areas are active during decision-makingor memory recall.
Psychoanalytic (Psychodynamic)
Focus: Unconscious drives, early childhood experiences, and internal conflicts.
Usage:
Therapists might explore a client’s dreams, slips of the tongue, or childhood memories to uncover unconscious motives.
Often used in long-term talk therapy to resolve deep-seated emotional issues.
Sociocultural Psychology
Focus: How behavior and thinking vary across situations and cultures.
Usage:
Researches how social norms, ethnicity, gender roles, and culture influence behavior.
A psychologist might study how parenting styles differ across cultures or how cultural values affect mental health stigma.
Cognitive Psychology
Focus: Internal mental processes like thinking, memory, problem-solving, and perception.
Usage:
Psychologists design experiments to understand how we learn, remember, and process information.
Helpful in areas like education, therapy, and AI development.
Behavioral Psychology
Focus: Observable behaviors and how they are learned through interaction with the environment.
Usage:
Emphasizes learning through reinforcement and punishment.
Common in behavior therapy (e.g., treating phobias with exposure therapy or using rewards for behavior change in children).
Biological Psychology (Neuroscience/Biopsychology)
Focus: How biology (genes, neurotransmitters, hormones, brain structures) influences behavior.
Usage:
Explains mental disorders in terms of brain chemistry and genetics.
Psychologists might study the effects of medications, brain injuries, or genetic predispositions.
Positive Psychology
Focus: The study of strengths, well-being, happiness, and what makes life worth living.
Usage:
Helps individuals and organizations improve resilience, optimism, and life satisfaction.
Often used in coaching, therapy, and workplace interventions to enhance quality of life.
Stages and brain waves
There are two main types of sleep:
NREM (Non-Rapid Eye Movement) – Stages 1–3
REM (Rapid Eye Movement)
Awake: Alpha waves
S1: Light sleep, theta waves
S2: light sleep, theta waves
S3: deep sleep, delta waves
REM sleep: dream sleep, similar to beta waves
Progression
One full sleep cycle = ~90 minutes
Sleep cycles repeat 4–6 times per night
Typical progression:
Awake → NREM Stage 1 → Stage 2 → Stage 3 → Stage 2 → REM → repeatEarly in the night: More time in deep NREM (Stage 3)
Later in the night: More time in REM sleep
Theories: What are the theorized purposes and activities of each sleep stage?
Stage | Theorized Purpose & Activities |
|---|---|
Stage 1 | Transition into sleep; may involve muscle twitches; light sensory disconnection |
Stage 2 | Memory consolidation begins; sleep spindles may help with learning and processing motor skills |
Stage 3 (Deep Sleep) | Physical restoration; boosts immune function; growth hormone released; essential for feeling rested |
REM Sleep | Emotional regulation, dreaming, memory consolidation (especially emotional/creative); brain development in infants |
REM Sleep: What is the theorized functional purpose of REM sleep?
crucial for brain health, despite the body being paralyzed (to prevent acting out dreams).
Key functions:
🧠 Memory consolidation – Especially emotional and procedural memories (like learning a new skill).
🎭 Emotional processing – Helps manage stress and regulate mood.
💡 Creativity & problem-solving – Brain connects unrelated ideas.
👶 Brain development – Especially high in infants and young children.
Thalamus
acts like a relay station. It takes in sensory information from your body (except for smell) and sends it to the right parts of the brain to be processed. It also plays a role in alertness and sleep.
Hypothalamus
helps keep your body in balance. It controls things like hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sleep cycles. It also connects the brain to the hormone system through the pituitary gland. It’s important for survival and emotional responses.
Hippocampus
is mainly involved in memory. It helps form new long-term memories, especially memories about facts and events. Without it, you’d have trouble learning new information.
Amygdala
processes emotions, especially fear and anger. It helps you react to threats and also plays a role in forming emotional memories.
brain stem
regulating various essential bodily functions
Cerebellum
coordinating and fine-tuning movements
Sympathetic nervous system
initiates the "fight or flight" response to stress, increasing heart rate, dilating pupils, and diverting energy to muscles.
parasympathetic nervous system
activates the "rest and digest" state, conserving energy by slowing heart rate, constricting pupils, and promoting digestion and other restorative bodily functions.
how do Adrenal glands affect an individual
producing crucial hormones like cortisol, aldosterone, and adrenaline, which regulate essential functions such as stress response, blood pressure, salt/water balance, and metabolism
corpus callosum
a structure in the middle of your brain that connects the right and left hemispheres (sides)
How Neurons Talk to Each Other
A neuron gets a message.
It sends an electric signal down its body (this is called an action potential).
The signal reaches the end of the neuron and jumps across a tiny gap (called a synapse) to the next neuron.
To do this, it uses special chemicals called neurotransmitters.
The next neuron picks up the message and keeps it going.
What is Myelin?
is a fatty coating that covers parts of a neuron.
It helps the message travel faster and smoothly, like insulation on a wire.
If it breaks down, the messages get slower or confused.
This happens in a disease called Multiple Sclerosis (MS), which can make it hard to move or think clearly.