Ocean Acidification
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Ocean Acidification
decreasing pH of ocean waters due to absorption of excess atmospheric CO2
pH Scale
the concentration of Hydrogen ions. 7 on the scale is neutral. Acids are below 7. Bases are above 7.

Base
A solution with very few H+
>7 on pH Scale; strong bases have a pH of 12, 13, 14.
FYI: the ocean is slightly basic.

Acid
The concentration of [H+] or Hydrogen Ions
<7 on pH Scale; strong acids have a pH of 1 or 2.
FYI: carbonic acid has a pH of 4.
![<p>The concentration of [H+] or Hydrogen Ions</p><p><7 on pH Scale; strong acids have a pH of 1 or 2.</p><p>FYI: carbonic acid has a pH of 4.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1b99c509-40b4-4bb4-aa73-2ed5f5e2a947.jpg)
Neutral pH
pH is equal to 7
contains equal numbers of hydrogen and hydroxide ions
[H+] = [-OH]
Example: WATER
![<p>pH is equal to 7</p><p>contains equal numbers of hydrogen and hydroxide ions</p><p>[H+] = [-OH]</p><p>Example: WATER</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4eb8c0f1-6270-4b2b-81a3-6fbec189b51e.jpg)
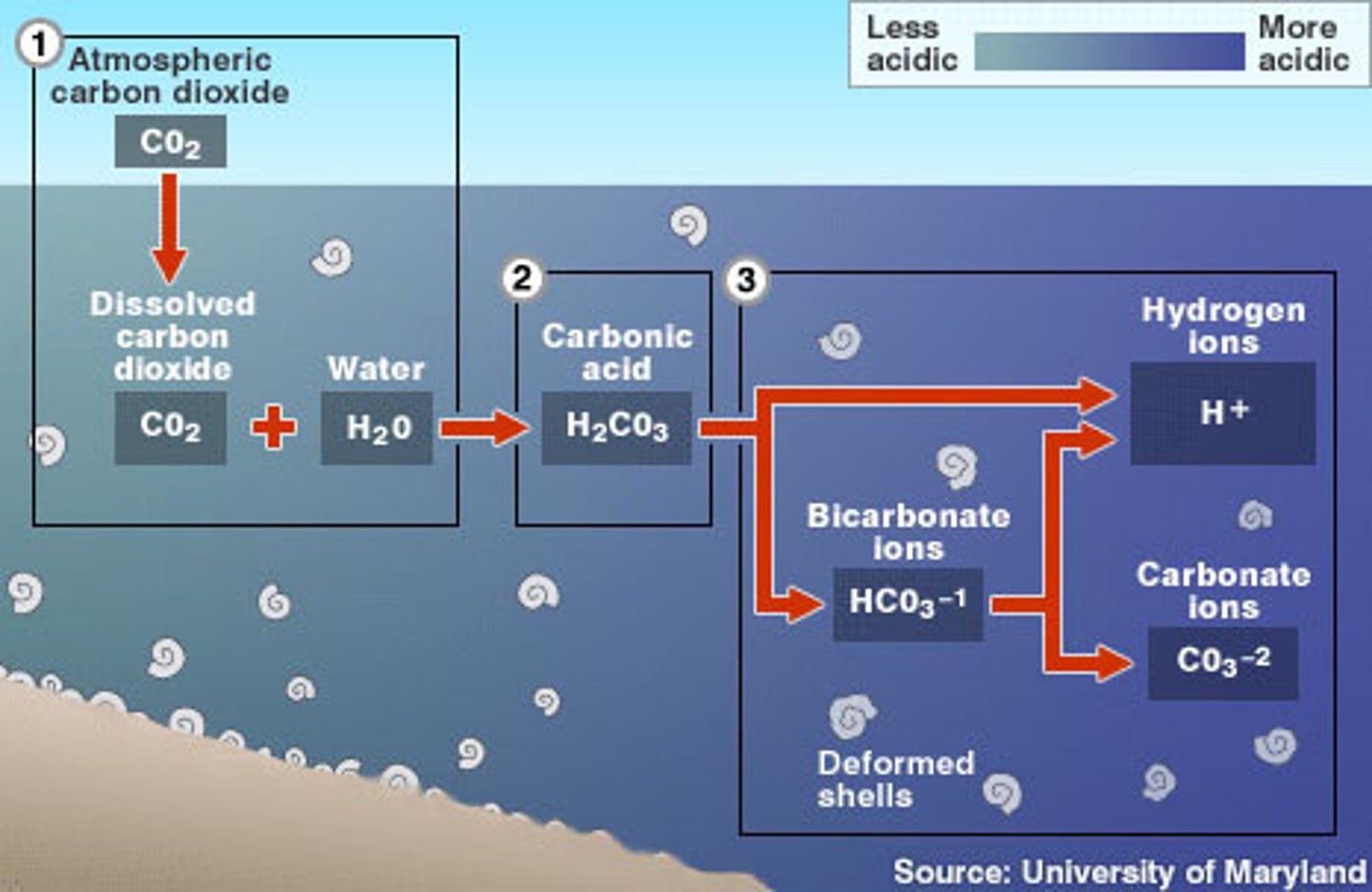
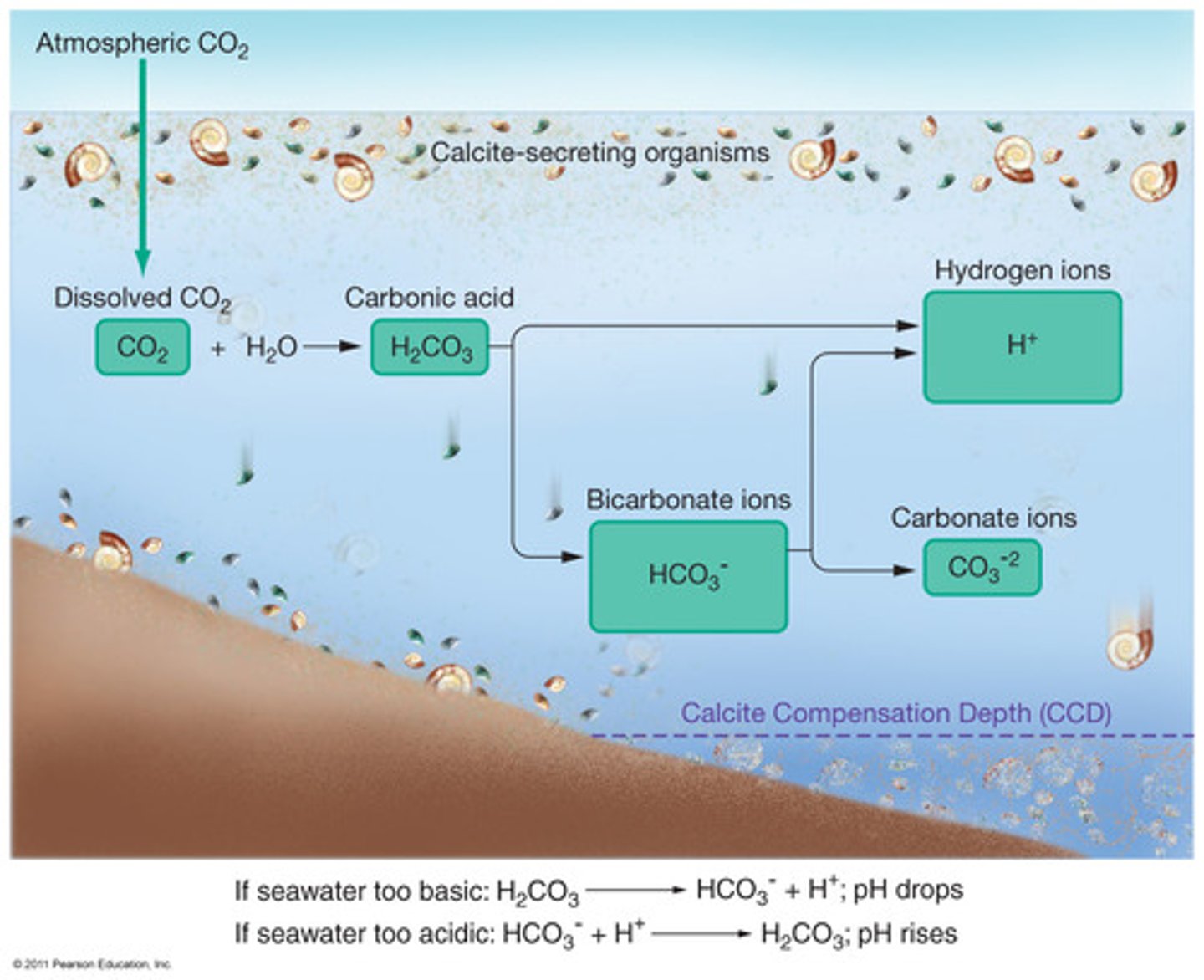
Carbonic Acid
CO2 + H2O --> H2CO3
The acid formed from carbon dioxide in water.
Calcium Carbonate
CaCO3
The white material in shells and limestone.

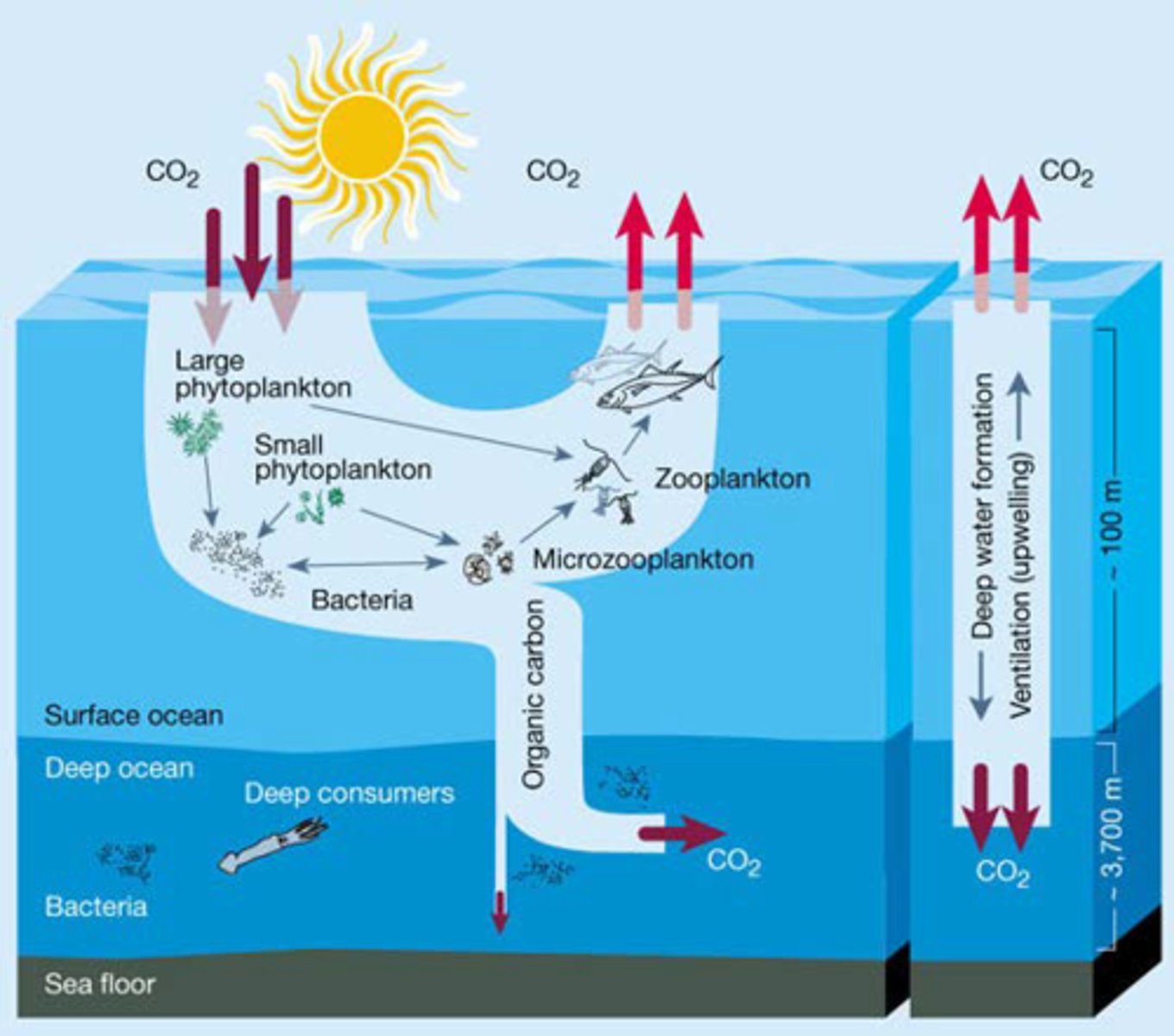
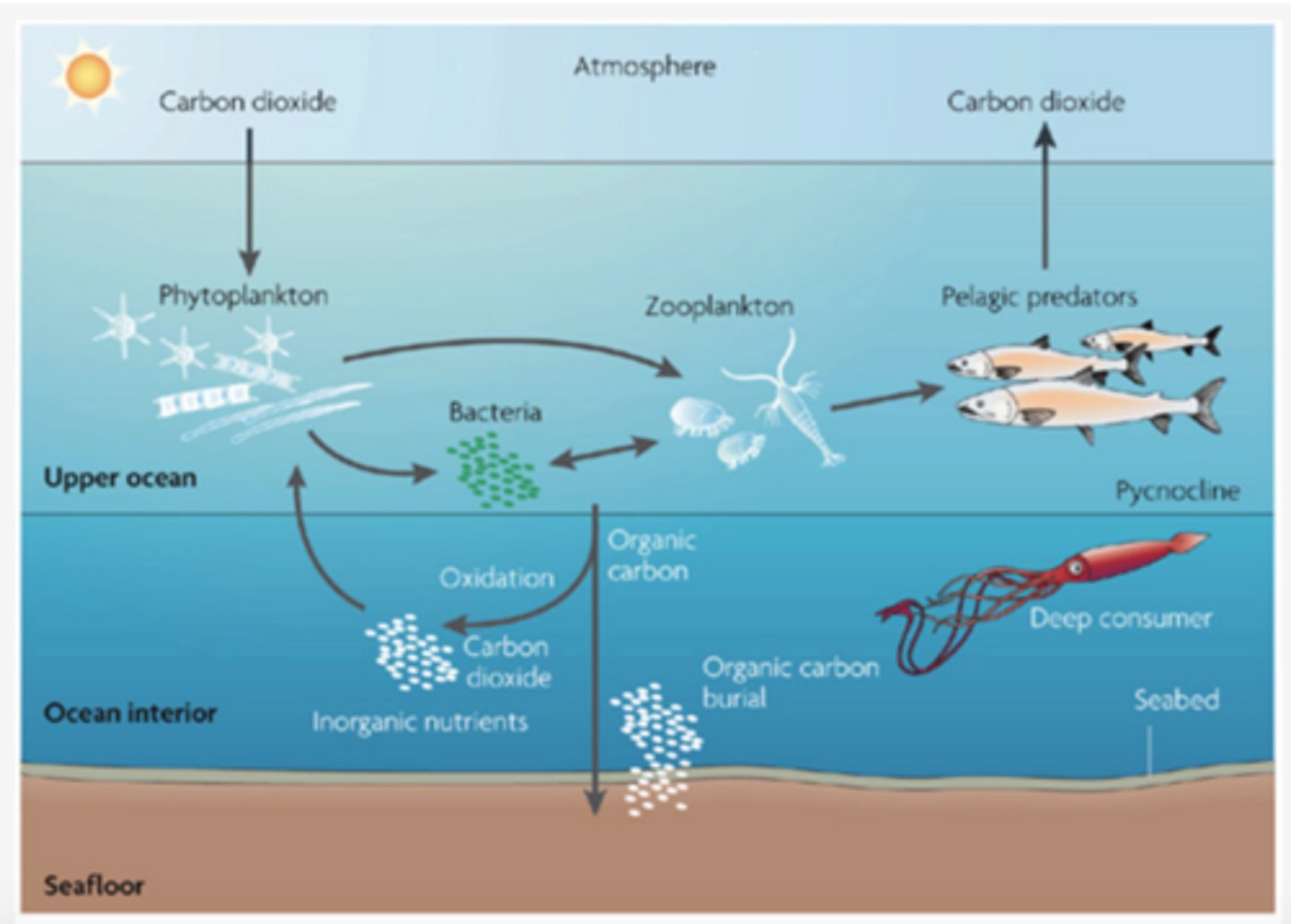
The carbonate pump
The cycling of calcium carbonate formed into shells by certain organisms such as plankton and mollusks
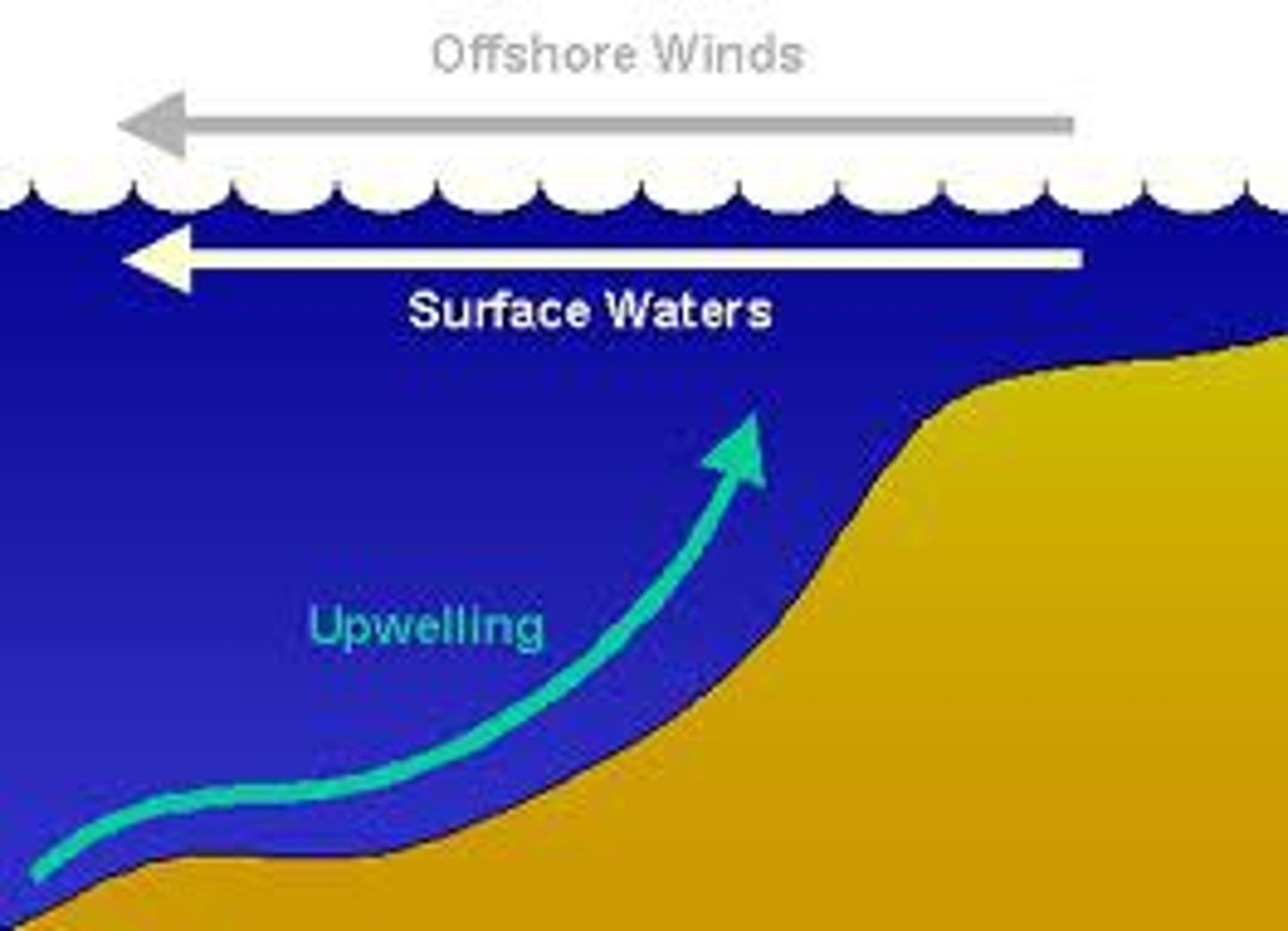
Upwelling
The movement of deep, cold, and nutrient-rich water to the surface
marine snow
detritus originating in the photic zone that sinks to the abyss, serving as the primary source of energy for deep- sea organisms
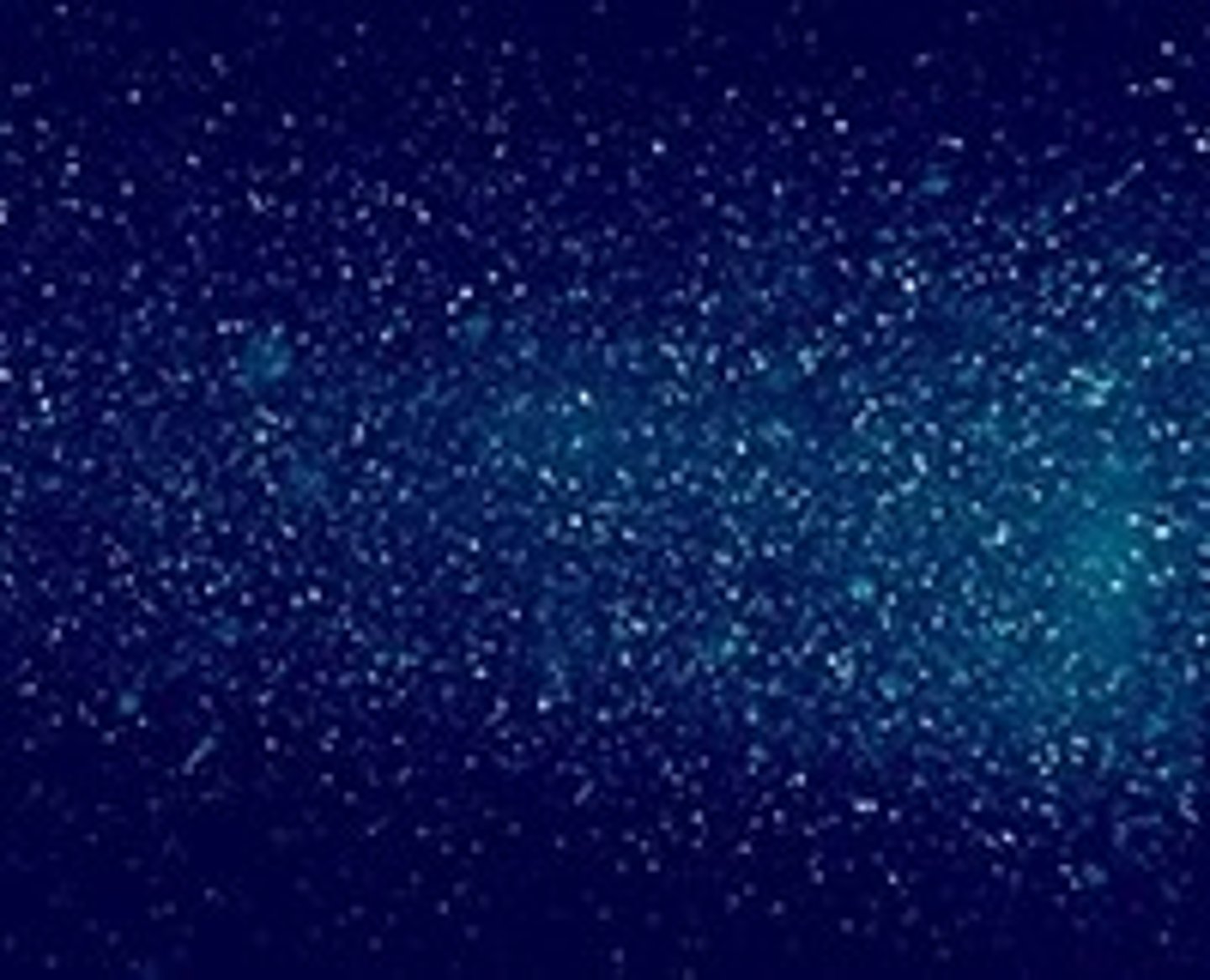

Ocean buffering system
Calcium Carbonate in the ocean prevents the ocean from experiencing large pH changes
biological pump
transport of organic carbon and nutrients from the surface ocean to the deep ocean which are then upwelled to the surface