People in business
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Communication
Sending and receiving information with feedback
Internal communication
Between people within a business
External communication
Between someone within a business and someone outside, like a customer
Types of internal communication
Downwards
Upwards
Horizontal
Formal communication
Using recognised channels to pass on information
Informal communication
Passing information using non approved methods to communicate
Importance of communication
Reduces mistakes
Costs could rise
Face- to face communication
When spoken information is exchanged between people who can see eachother
Advantages- Face to face communication
Allows immediate feedback
Encourages cooperation
Disadvantages- Face to face communication
No record of the message
Some people may not listen
Written communication
When businesses communicate using written information
Advantages- Written communication
Record of the message is kept
Can effectively convey data and graphs
Disadvantages- Written information
Takes time
Lack of direct feedback
Barriers to communication
Lack of clarity
Technological breakdown
Long chain of command
Overcoming communication barriers
Recruitment
Training
Chain of command
Recruitment
The process of finding and appointing new employees
Why do companies recruit
Replacing old workers
Growth of a business
Promotion
Types of employment
Full time
Part time
Job share
Casual employment
Seasonal employment
Advantages of full time employment
Loyalty
Commitment
Working efficiently
Disadvantages of full time employment
Cost
Benefits can be expensive
Recruitment process
Identify Job and and number of staff needed
Prepare a job description
Prepare a person specification
Advertise on suitable media
Shortlist for interview
Carry out interview
Appoint best candidate and provide feedback to unsuccessful applicants
Application form
Gathers information from job applicants
Curriculum Vitae
Provided by the job seeker and contains most information found on an application
Internal recruitment
Appointing someone who already work for the business
Advantages- Internal recruitment
Cheaper and quicker
Individuals are already familiar with the organisation
Motivation increases
External recruitment
Appointing someone from outside the business
Advantages- External recruitment
More responses and more choices
New candidates may have fresh ideas
Avoids resentment form unseucsessful candidates.
Attracting job applicants
Advertising
Headhunting
Employment agencies
Disability
Employees are obliged to make reasonable adjustments to accommodate disabled employees
Age discrimination
When a business decision based of a person’s age
Minimum wage
Governments have passed a legal minimum wage
Reduces poverty
Helps businesses
Benefits disadvantaged workers
Gender
Women should receive equal opportunity as men
Race and religion
Businesses must ensure they don’t discriminate on colour, race, religion and nationality
Training
The process of increasing the knowledge and skills of workers so that they can do their jobs effectively
Induction training
Helps new staff settle into the job
On the job training
Training while working, includes:
watching another worker
mentoring
job rotation
Advantages: On the job training
Output is being produced
Cheaper than other training
Easy to organise
Disadvantages- On the job training
Mistakes can be made
Staff might get stressed
Staff may get frustrated
Off the job training
Involves workers going to another place to receive training
Advantages- Off the job training
Output is not affected- mistakes
Customers will not be at risk
Learning cannot be distracted by work
Disadvantages- Off the job training
No output will be produced
Can be expensive
Takes time to organise
Herzberg’s theory
2 factors lead to employee motivation and job satisfaction-
Hygiene factors- Without these factors- Job dissatisfaction
Motivators- Lead to job satisfaction
Hygiene factors
Pay
Working conditions
Job supervision
Policies & rules
Motivators
Achievement
Recognition
Responsibility
Interesting work
Growth
Advantage and Disadvantage- Herzberg’s theory
Advantage- Improves motivation and work enrichment
Disadvantage- All employees do not have the same needs
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
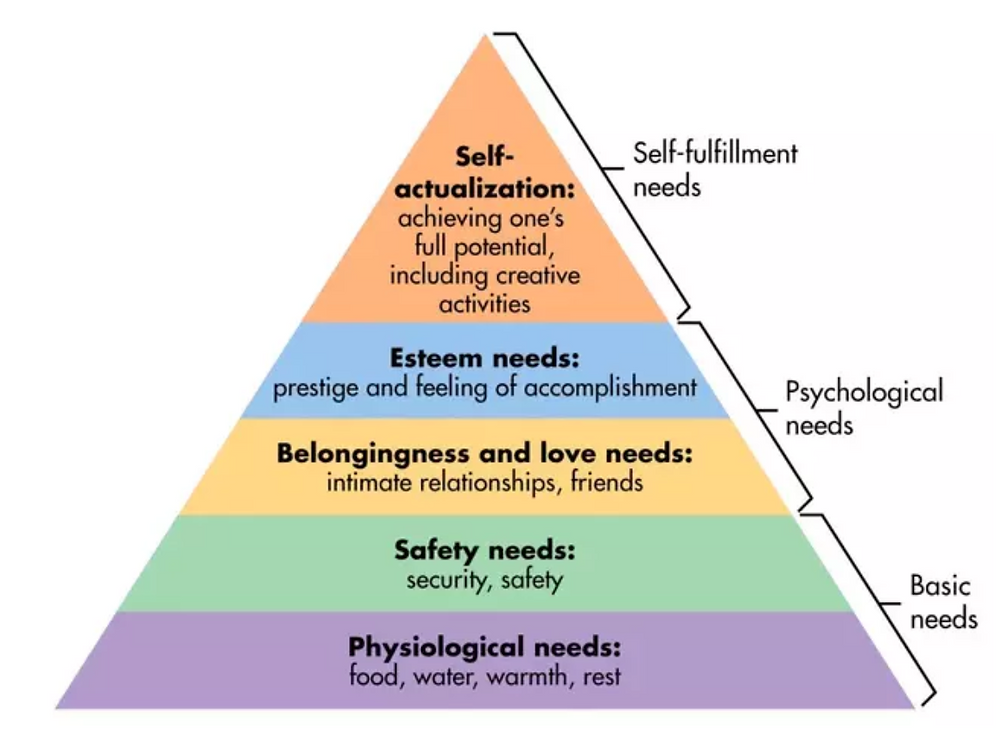
Advantage and disadvantage- Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
Advantage- Easy to follow- Step by step
Disadvantage- Difficult to find worker’s level
Taylor’s theory of scientific management
Piece rate- Paying workers according to what they produce
Use specialist tools & equipment
Follow a strict working procedure
Proper training
Advantage and Disadvantage- Taylor’s theory
Advantage- Increased labour productivity
Disadvantage- Not flexible- Treats workers like machines.
2 methods of communication
Financial reward
Non- Financial reward
Time rates
Pay according to the number of hours the staff worked
Advantage and Disadvantage- Time rates
Advantage- Easy to calculate
Disadvantage- Rewards lazy workers
Piece rate
Pay according to amount of output produced
Advantage and Disadvantage- Piece rate
Advantage- More output
Disadvantage- Mistakes and poor quality
Performance related pay (PRP)
Rewarding non-financial workers
Advantage and Disadvantage- PRP
Advantage- Clear targets
Disadvantage- Targets may be unrealistic
Bonus payment
Additional payments along with salary
Advantage and Disadvantage- Bonus payment
Advantage- Only paid if targets are met
Disadvantage- Disagreements between workers
Promotion
Moving to a higher postion
Advantage and Disadvantage- Promotion
Advantage- More salary
Disadvantage- Depends on the superiors
Job enrichment
Adding more challenging or meaningful tasks to the job
Job enrichment
Allowing employees to work different jobs of the same field
Autonomy
Giving staff authority to make decisions and take action
Organisational chart
A diagram that shows different job roles and how they relate to each other
Chain of command
Route of which orders are passed down through the heierarchy
Span of control
Number of workers a person directly controls
Flat structure
Few layers of management, wide span of controls and short chain of command
Advantages- Flat structure
Better communication
Low management costs
Disadvantages- Flat structure
Less chance of promotion
Less formality
Tall structure
Lots of leaders and layers of management, long chain of command
Advantages- Tall structure
More control
Clear route of promotion
Disadvantages- Tall structure
Long chain of command
High management costs
Delegation
The authority given to subordinates to carry out certain tasks
Centralisation
When decisions are made at the highest level of management
Advantages-Centralisation
Communication and control is easier
Prevents workers from being independent as they may make mistakes
Disadvantages- Centralisation
Less creativity and more ideas
Staff may get demotivated
Decentralisation
When decisions are made at lower levels of management
Advantages- Decentralisation
Workers have more motivation
Decisions are made faster
Disadvantages- Decentralisation
Senior mangers loose control
Costs may rise