1. The Variability of Natural Populations
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Evo. Pop. Gen.
Last updated 9:47 AM on 5/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
1
New cards
Classical Hypothesis - Fisher and Muller
* Worked with single gene traits in natural populations
* Low population variability, low heterozygote frequency
* Alternative alleles are harmful
* Main evolutionary force- directional selection
* Species variability given mainly by between-population variation
* Low population variability, low heterozygote frequency
* Alternative alleles are harmful
* Main evolutionary force- directional selection
* Species variability given mainly by between-population variation
2
New cards
Balance hypothesis - Dobzhansky and Wright
* Examined the chromosomal polymorphisms in Drosophila populations
* Natural populations are generally variable w/ high heterozygosity
* Dominating force: Overdominant selection
* Species variability given within-population variation
* Natural populations are generally variable w/ high heterozygosity
* Dominating force: Overdominant selection
* Species variability given within-population variation
3
New cards
Phenotypic variation
Variability in phenotypes that exists in a population. (Ex: height, weight, and body shape, hair, eye color, and the ability to roll your tongue)

4
New cards
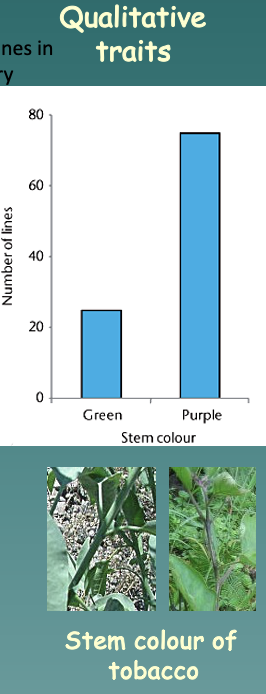
Qualitative Traits
A trait that can be described as a category (Ex: black or red coat color, horned or polled, coat color dilution)
Example: Stem color of tobacco
* Have 1 or 2 genes
* Have few genotypes
* Phenotypic categories
Example: Stem color of tobacco
* Have 1 or 2 genes
* Have few genotypes
* Phenotypic categories
5
New cards
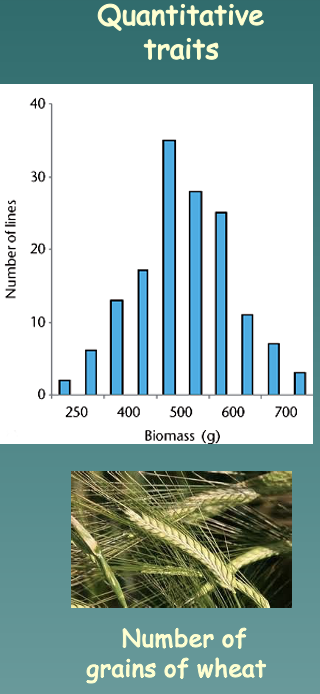
Quantitative traits
A characteristic controlled by multiple genes as well as the environment (Ex: IQ, blood pressure, height, and weight)
Example: Number of grains of wheat
* Have many genes
* Many genotypes
* Continuous distribution of the phenotypes
Example: Number of grains of wheat
* Have many genes
* Many genotypes
* Continuous distribution of the phenotypes
6
New cards
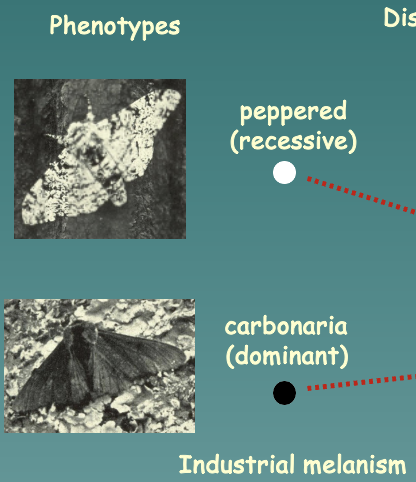
Peppered moth (biston betalaria)
* Example of a qualitative trait
* Involves two phenotypes: peppered (recessive), and carbonara (dominant)
* Involves two phenotypes: peppered (recessive), and carbonara (dominant)
7
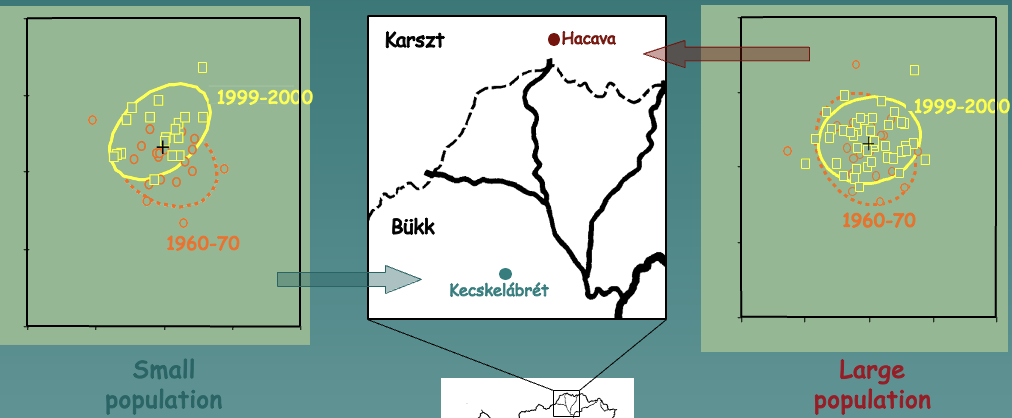
New cards
Wing traits of brown argus (Tricia artierxes issuekutzi)
* Example of a quantitative trait
* In small populations, evolutionary forces (ex: environmental changes) have a bigger effect, causing more drift and variation
* In small populations, evolutionary forces (ex: environmental changes) have a bigger effect, causing more drift and variation
8
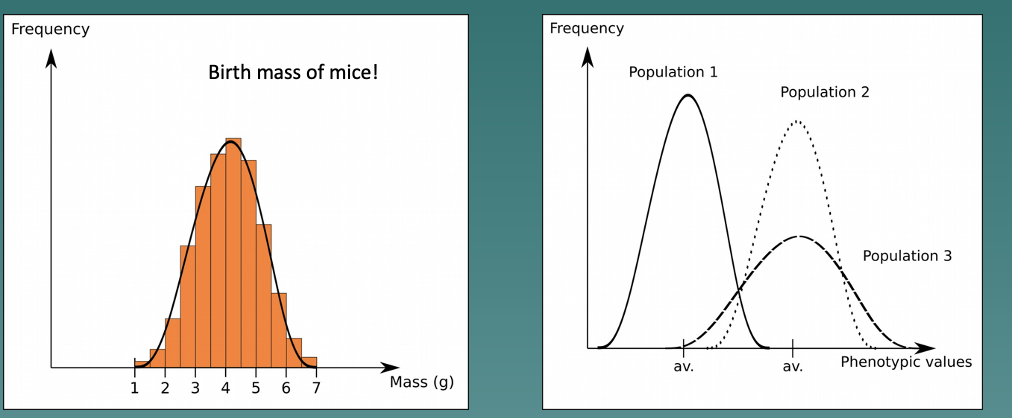
New cards
Birth mass of mice
* Example of a quantitative trait
* Each population was found to have its own phenotypic average, and its own variance (differences)
* Each population was found to have its own phenotypic average, and its own variance (differences)
9
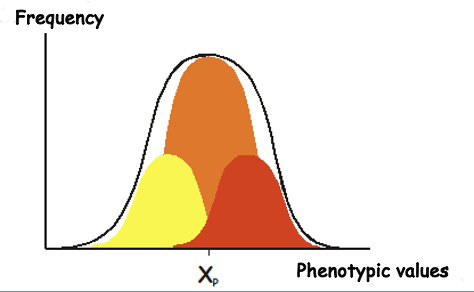
New cards
What makes up phenotypic variation?
Genotypic variation and Environmental variation
10
New cards
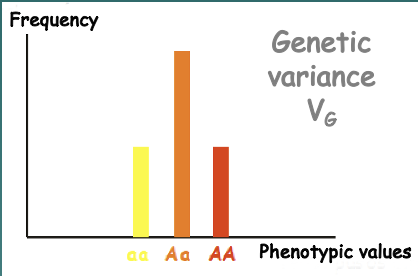
Genotypic variance
The final phenotypes of heterozygous offspring (Example: AA, Aa, aa)
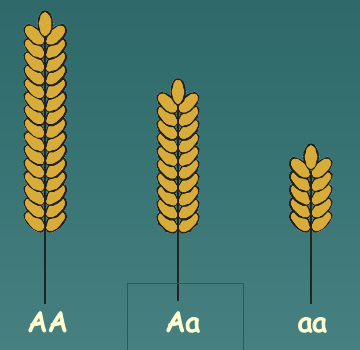
11
New cards
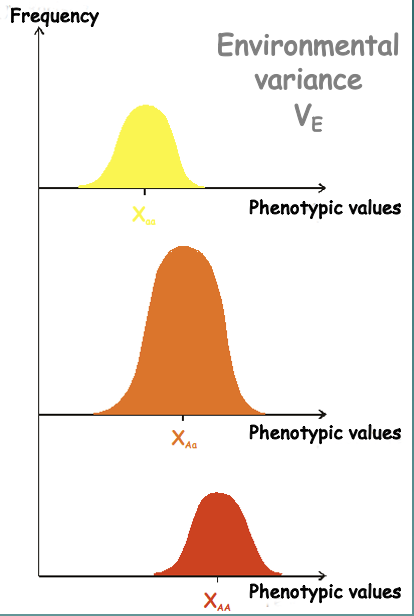
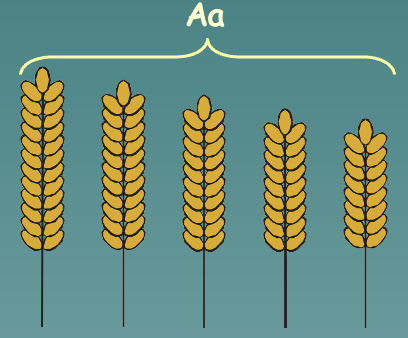
Environmental variance
Causes continuous distribution in final phenotypes of heterozygous offspring (Example: all the different varieties of Aa)
12
New cards
Phenotypic Variance equation:
Vp = Vg + Ve + Vge
Phenotypic variance= genotypic+ environmental+interaction
Phenotypic variance= genotypic+ environmental+interaction
13
New cards
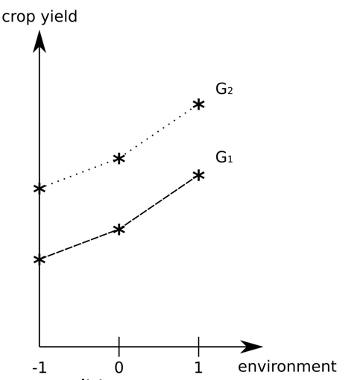
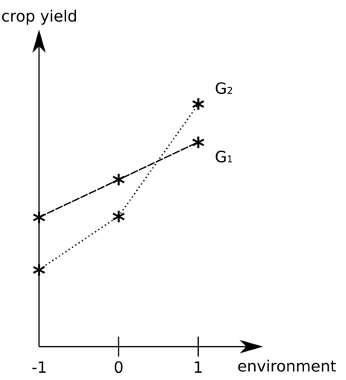
If Vge = 0
Genes and the environment do not interact
14
New cards
If Vge > 0
There is interaction between genes and the environment
15
New cards
Genetic variance equation
Vg = Va + Vd + Vi
* Interactions between genes
* Interactions between genes
16
New cards
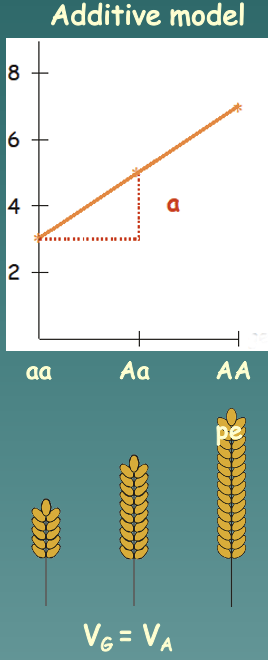
Additive model
Deviation from the avg. phenotype due to inheriting a particular allele
* Additive interaction between alleles: heterozygous individuals are a mid-point between the alleles
* Additive interaction between alleles: heterozygous individuals are a mid-point between the alleles
17
New cards
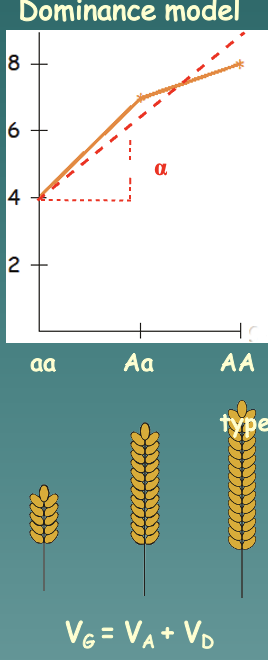
Dominance model
Deviation due to the interactions between alternative alleles at a specific locus (location on a chromosome)
* Heterozygous individuals resemble each other more
* Heterozygous individuals resemble each other more