Biology; membranes and enzymes
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Meaning of the compartmentalization and its advantages.
Under compartmentalization is meant, that the cell is divided into "rooms" to allow different conditions for each compartment. Examples: cytosol, membranes, organelles.
plasmatic and non-plasmatic phases
Plasmatic: water and proteins, thicker
Non-plasmatic: watery, not many or even none proteins
organelles with two, one and no membranes
Double membrane: nucleus, mitochondria, plastids
Single membrane: Golgi apparatus, vacuole, vesicles, endoplasmic reticulum (rough and smooth), lysosomes
No membrane: ribosomes, nucleolus, cytoskeleton -> composed of proteins and nucleic acids
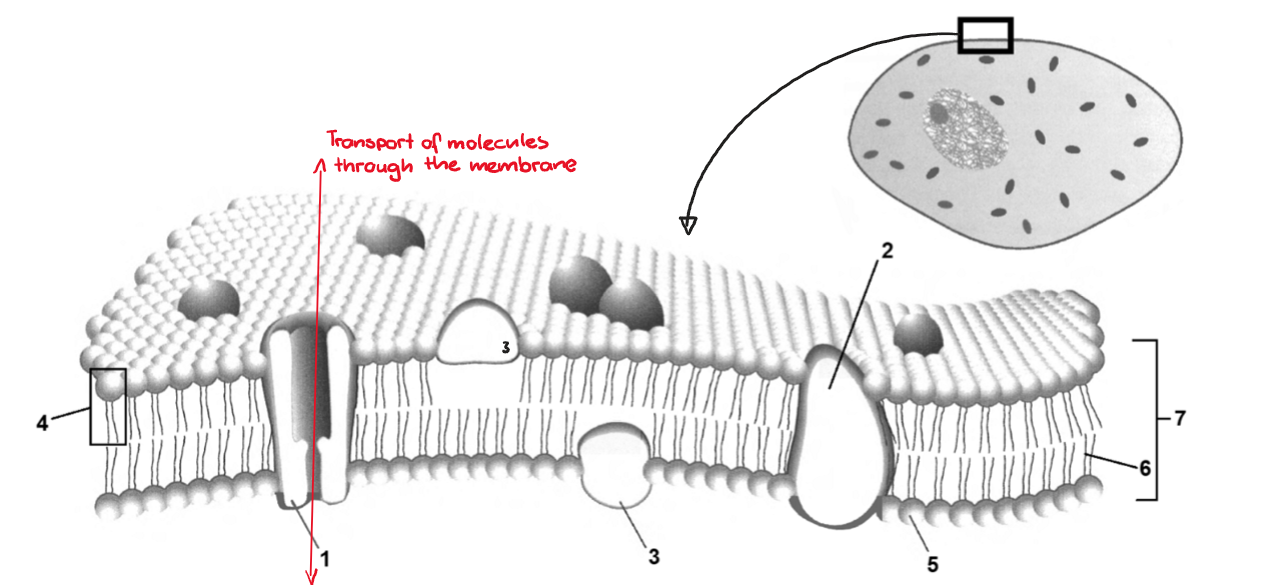
1: channel, pump or carrier
2: integral protein
3: peripheral protein
4: phospholipid
5: phosphate group / hydrophilic side of phospholipids
6: non-polar tails of phospholipid / hydrophobic end on phospholipids
7: phospholipid bilayer = membrane
definition of fluid mosaic for biological membranes
Fluid because the molecules can move freely, mosaic because of the diversity of molecules.
process of simple diffusion
solutes from the side with higher concentration to the side with lower concentration of the membrane
process of facilitated diffusion
solutes pass through the membrane with the help of channel proteins
process of active transport
molecules are pumped from the side with lower concentration to the side with higher concentration → process requires energy from ATP
process of endocytosis and exocytosis
endocytosis: cell membrane buds inwards creating a pouch and fills with solutes / pouch grows, closes and separates from the membrane / outer solutes now in vesicle inside the cell
exocytosis: molecules to be exported packed in a pouch moving towards the cell membrane / membrane and vesicle fusing / content spilled out outside
examples for transport types (simple diffusion, etc.)
simple diffusion: fatty acids
facilitated diffusion: H2O
active transport: K+
exocytosis / endocytosis: proteins, particles
definition of phagocytosis
Cellular eating: particle is taken into the cell through endocytosis → in a vesicle, fuses with a lysosome → smaller cell broken down
examples: white blood cells, enzymes
definition metabolism
total of chemical reactions in an organism both inside and in between the cells
definition activation energy
certain amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction, it lowers some kind of barrier around the cell to make it more likely for the reaction to take place
definition active site and induced fit
active site: site of an enzyme (pouch) with the right shape and chemistry (right amino acids in the right places) for the substrate
induced fit: the active site changes slightly to the substrate
steps of an enzyme catalyzing a reaction
substrate binds to the active site / induced fit started by substrate → catalyzing the reaction / products released from active site / new substrate binds the enzyme
(enzymes are reusable)
5 factors affecting the activity of the enzymes
product concentration (own product binds enzyme in case of overproduction)
availability of cofactors (cofactors = chemical compounds; low availability → low activity)
substrate concentration (fewer substrates → fewer substrates, fewer products)
temperature (best activity around body temperature → 36.5°C)
pH (preferred pH range)
2 ways of the cell changing its concentration
increased enzyme concentration → more products
increased rate of breaking down enzymes (high → low)
2 enzymes with their substrates and products
lactase → lactose → glucose + galactose
amylase → starch → maltose
2 ways of inhibitors inhibiting enzymes
binding the enzyme outside its active site, altering the active site
substrate imposter blocking the active site from “real” substrate