Biology 1001 unit 2: Carbon Atoms and Large Biological Molecules
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
carbon
an element with Atomic number 6 (=> 6 protons + 6 electrons)
The dominant isotope C-12 has ALSO 6 neutrons
all life on earth is ______ based
all the large molecules
Ability to form 4 bonds makes carbon a good material to form the
backbone of ________________ that living
organisms are made of
inorganic compounds
non-living origin, subject to the laws of physics and chemistry
organic compounds
considered impossible to produce because they were imbued with a “life force”
Fredrich wohler
trying to make ammonium cyanate using ammonium ions and cyanate ions
however was shocked to see urea crystals form
paved the way for synthesis of organic compounds
stanley miller
Tried to recreate conditions of Earth’s early environment.
produced a variety of organic
compounds including:
amino acids and oily hydrocarbons
Conclusion: Organic molecules, CAN be formed abiotically (in the
absence of life) IF conditions are right
why carbon?
it is small, allowing other atoms to get close enough to share electrons
it has 6 electrons- 4 in the outer shell
therefore it can connect up to 4 different atoms (takes 8 to fill its outer shell)
carbon can bond covalently with…
hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, Sulphur, phosphorus and other carbons.
junction
carbon acts as a ______ from which a molecule can branch off in 4 directions
share single electrons- forming tetrahedrons
or two electrons - double covalent bond
shapes of 3 simple carbon based molecules:
a) methane
b) ethane
c) ethene
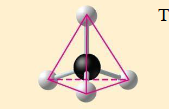
methane
tetrahedron
CH4
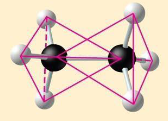
ethane
two overlapping
C2H6
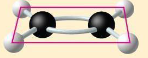
ethene
double bonds- flat/in the same plane
C2H4
carbon skeletons
molecular diversity arises from variation in ____________
carbon skeleton variations:
a) length
b) branching
c) double bond position
d)presence of rings
isomers
compounds that have the same numbers of atoms of the same elements but different structures and hence different properties.
structural, cis-trans, enantiomers
structural isomers
differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms
have same molecular formula but different arrangement of carbon skeletons
may also differ in the location of double bonds
cis-trans isomers
differ in arrangement around a double bond- due to inflexibility of double bonds
cis- xs are on the same side
trans- xs are on opposite sides

enantiomers
differ in spatial arrangement around an asymmetric carbon- mirror images, like left and right hands
cannot be superimposed on each other
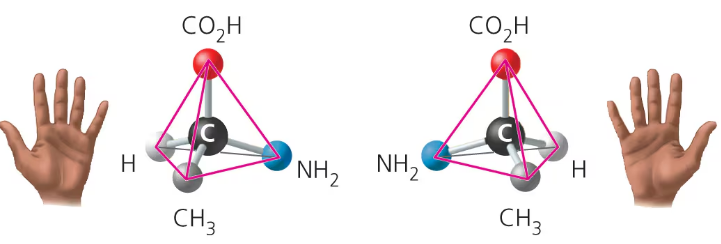
left handed enantiomers
L or S
100 times more effective in ibuprofen
ineffective in albuterol (counteracts)
right handed enantiomers
D or R
more effective in albuterol
ineffective ibuprofen
thalidomide tragedy
Marketed from 1957 -1961
Sedative and drug for morning sickness in pregnancy
24,000 children born with severe birth defects
Probably >120,000 babies died before birth due to teratogenic (affecting embryo or fetus) effects of the S enantiomer
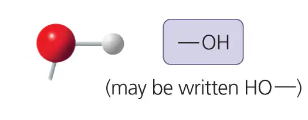
hydroxyl group properties
-OH
is polar due to electronegative oxygen
forms hydrogen bonds with water, helping dissolve compounds suchas sugars
compound name: Alcohol
hydroxyl group form
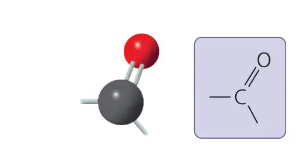
carbonyl group
>C=O
sugars with ketone groups are called ketoses
those with aldehydes are aldoses
compound name: ketone- within a carbon skeleton
aldehyde- at the end of a carbon skeleton
carbonyl group form
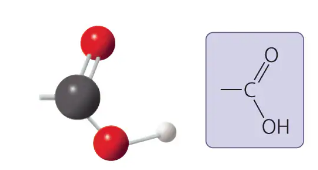
carboxyl group
-COOH
acts as an acid (can donate H+) because the covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen is so polar
compound name: carboxylic acid or organic acid
carboxyl group form
amino group
-NH2
acts as a base- can pick up an H+ from the surrounding solution
compound name: amine
amino group form
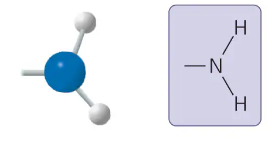
sulfhydryl group
-SH
two- SH groups can react, forming a “cross-link” that helps stabilize protein structure
maintain straightness or curliness of hair
compound name: thiol
sulfhydryl group form

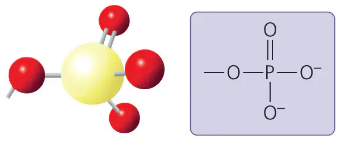
phosphate group
-OPO32-
contributes negative charge (1- inside, 2- when at the end)
when attached , confers on a molecule the ability to react with water, releasing energy
compound name: organic phosphate
phosphate group form
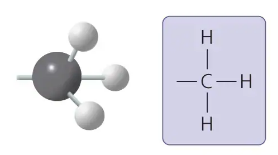
methyl group
-CH3
affects the expression of genes when on DNA or in proteins bound to DNA
affects the shape and function of male and female sex hormones
compound name: methylated compound
methyl group form
organic molecule categories
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
momomers
small molecules
building blocks of big molecules
can polymerize- link up to form macromolecules
polymers
big molecules
polymerized
linked together
carried out by dehydration reaction
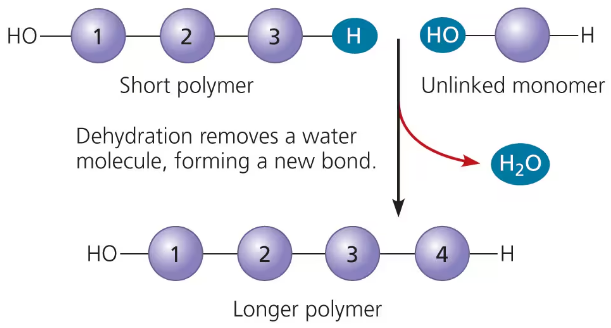
dehydration reaction
two molecules become covalently bonded with the removal of water
how a polymer is produced:
monomers are lined by enzymes
enzymes remove a hydroxyl (-OH) group from one monomer and a hydrogen (-H) from the other
then link the two monomers together and release a water molecule (H2O)
process repeated over and over
dehydration reaction: synthesizing a polymer
hydrolysis: breaking down a polymer
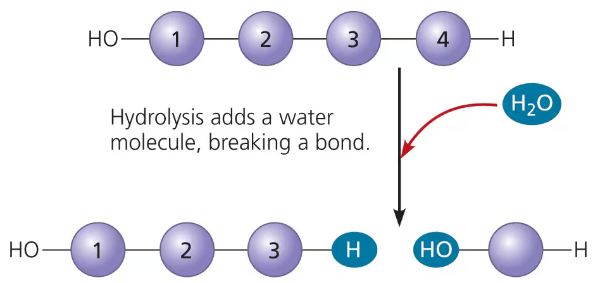
hydrolysis
to break down large polymers to monomers
breaks bond between two molecules by the addition of H2O
example: digestion
carbohydrates
serve as fuel and building material
include sugars and polymers of sugars
monosaccharides/simple sugars
disaccharides- double sugars
macromolecules- polysaccharides
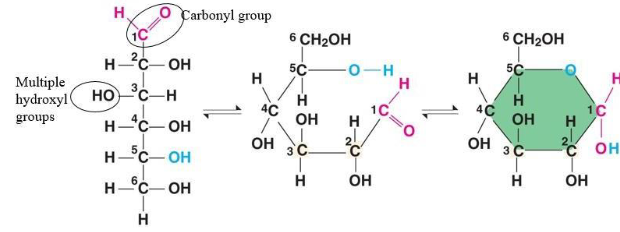
monosaccharide
the simplest carbohydrate
simple sugars
monomers from which more complex carbohydrates are built
all isomers of C6H12O6
ex. glucose, fructose, galactose
disaccharides
two monosaccharides joined by a dehydration reaction- glycosidic linkage
ex. maltose, sucrose, lactose
monosaccharide structure
can be linear or ring
tend to form rings in a solution- more stable
polysaccharides
macromolecules- built from monomers
energy store- storage material, hydrolyzed as needed to provide sugar for cells- ex. starch
structural molecules- building material for structure that protect the cell- ex. cellulose
functions of sugars (little carbs):
energy supply
sugars→ major energy source for cells
glucose= fuel for cellular respiration →ATP production
carbon skeletons
provide raw materials for carbon framework, and synthesis of other small molecules
ex. amino acids, fatty acids, and polysaccharides
starch
the energy storing polysaccharide found in plants
made up of glucose monomers linked together
molecules are helical (spiral)
different forms- amylose (branched) vs. amylopectin (unbranched)
glycogen
the energy storing polysaccharide of animals
polymerized glucose with extensive branching
→ stored in liver, muscle, etc
→ hydrolysis releases glucose on demand
short term energy store
cellulose
structural polysaccharide
polymer of glucose
essential component of plant cell walls
leaves, wood
most abundant organic compound on earth
indigestible by most organisms
starch vs. cellulose- why the difference?
glucose exists as two isomers- alpha and beta
Starch and glycogen are polymers of a glucose→ helical form
Cellulose is a polymer of β glucose monomers→ linked together- able to form straight close packed chains
cellulose strong and tough, chemically stable
chitin
structural polysaccharide
found in animal exoskeletons and fungal cell walls
long chain polymer of β glucose- with N-containing side group
lipids
large (not macro) molecules
not polymers- more diverse in structure
commonly hydrophobic (water hating)- have large hydrocarbon regions
types of lipids:
fats- energy storage
phospholipids- structure
steroids and cholesterol- hormonal
fats
energy storage
more commonly known as triacylglycerols
→ glycerol’s with 3 fatty acid side groups
TAGs or triglycerides
consist of fatty acids joined at one end to glycerol
main long term energy store in animals
animal fat vs. plant oils
animal fat is solid because it doesn’t have double bonds meaning it can pack closer together
plant oils are liquid at room temp because they have double bonds and cant pack as closely together- the fatty acid chains kink
saturated fats
has no double bonds between C atoms
all H positions filled
chains are straight
ex. dairy
mono-unsaturated fatty acid
has one double bond in the chain
chain is bent
ex. plant oils
poly-unsaturated fatty acid
more than one double bond
very bendy
ex. plant and fish oils
hydrogenation
the process that makes plant oils solid at room temp- margarine
take unsaturated fat
bubble H through it in the presence of a catalyst
double bonds will break, hydrogen will form covalent bonds with carbon
all chains will straighten out, making it solid
other functions of fats:
padding- for internal organs
insulation
buoyancy in marine mammals
phospholipids
structural lipid made up of glycerol joined to two fatty acids and phosphate group
hydrocarbon chains act as nonpolar, hydrophobic tails
and rest acts as a polar hydrophilic head
form bilayers
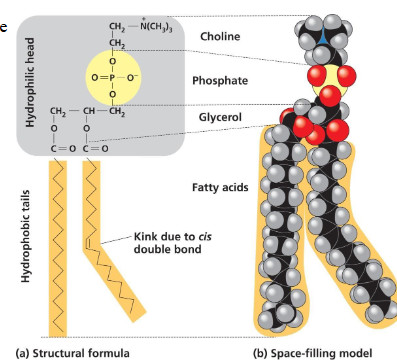
phospholipids self aggregate into a bilayer because…
they have hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts
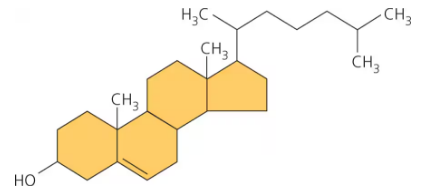
steroids
lipid characterized by carbon skeleton with 4 fused carbon rings
ex. cholesterol
cholesterol
steroid
common component of animal cell membranes
molecule from which other steroids, including sex hormones are synthesized ex. progesterone, testosterone, estrogen
proteins
=>50% of dry mass of most cells
are all polymers of amino acids
linked in unbranched chains
made up of one or more polypeptides, each folded and coiled into a specific 3d structure
=completed sweater
amino acids
an organic molecule with both an amino group and carboxyl group
general formula for amino acids:
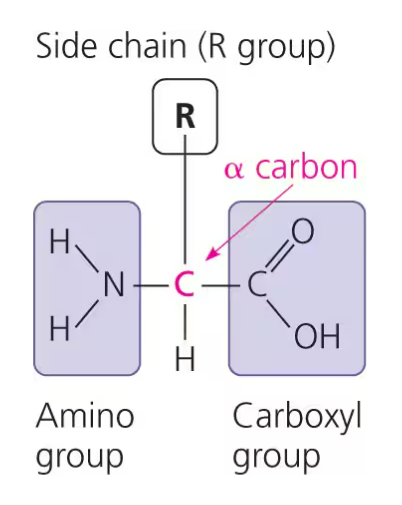
making a polypeptide:
amino acids are linked together in dehydration reactions
a peptide pair is formed between each AA pair
result- polypeptide with amino end and carboxyl end
polypeptide
a chain of amino acids
linked together by peptide bonds
=strand of yarn
four levels of protein structure:
primary= AA sequence
secondary= hydrogen bonding in the backbone
tertiary= overall shape due to interaction of side chains
quaternary= applies to proteins made up of 2 or more polypeptides
correct shape is critical to function
when polypeptides are produced inside cells, correct folding is achieved by:
the intrinsic order of amino acids
the environment in the cell (pH, concentration, temp)
other proteins
misfolded proteins are no longer functional- can cause disease.
nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
polymers
built up of monomers called nucleotides
linked by dehydration reactions that form
phosphodiester bonds
nucleotide
=molecule in 3 parts
nitrogenous base
pentose sugar
phosphate group
five nitrogenous bases:
pyrimidines
cytosine
thymine -DNA
uracil- RNA
purines
adenine
guanine