IB Biology I Sem 2 Final
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
is water polar or non-polar? why?
polar because there is an uneven distribution of electrons between oxygen and hydrogen atoms
what are the 4 important properties of water based on hydrogen bonding?
1. cohesion
2. adhesion
3. capillary action
4. solvent properties
what is cohesion?
an attraction between molecules of the same substance
what is adhesion?
attraction between molecules of different substances
what is capillary action?
the attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid
what are solvent properties?
Water dissolves polar and ionic substances
what are the possible origins of water and why does it stay?
- asteroids collided with earth
- stays because of gravity and earth is the perfect distance from the sun
Name the function, monomer, and an example for carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (SHORT ANSWER)
CARBOHYDRATES
- function: short-term energy storage and structure
- monomer: monosaccharides
- ex: glucose
LIPIDS
- function: long term energy storage
- monomer: fatty acids
- ex: oil
PROTEINS
- function: catalyze reactions
- monomer: amino acids
- ex: hemoglobin
What are the characteristics of saturated fatty acids?
- carbons are carrying as many hydrogen atoms as they can
- solid at room temp
What are the characteristics of monounsaturated fatty acids?
- one double bond in the chain of hydrocarbons
- liquid at room temp
What are the characteristics of polyunsaturated fatty acids?
- have at least 2 double bonds in the carbon chain
- liquid at room temp
What are the characteristics of cis fatty acids?
- liquid at room temp
- low melting point
- hydrogens on the same side of the carbon double bond
What are the characteristics of trans fatty acids?
- higher melting point
- solid at room temp
- hydrogens on different sides of the carbon double bond
Why is carbon an important element for life?
allows for the formation of diverse compounds that life is based on
Peptide bonds connect_______ ________ to form ________ using a ________________ ____________
amino acids - proteins -condensation reaction
draw the basic structure of an amino acid (SHORT ANSWER)
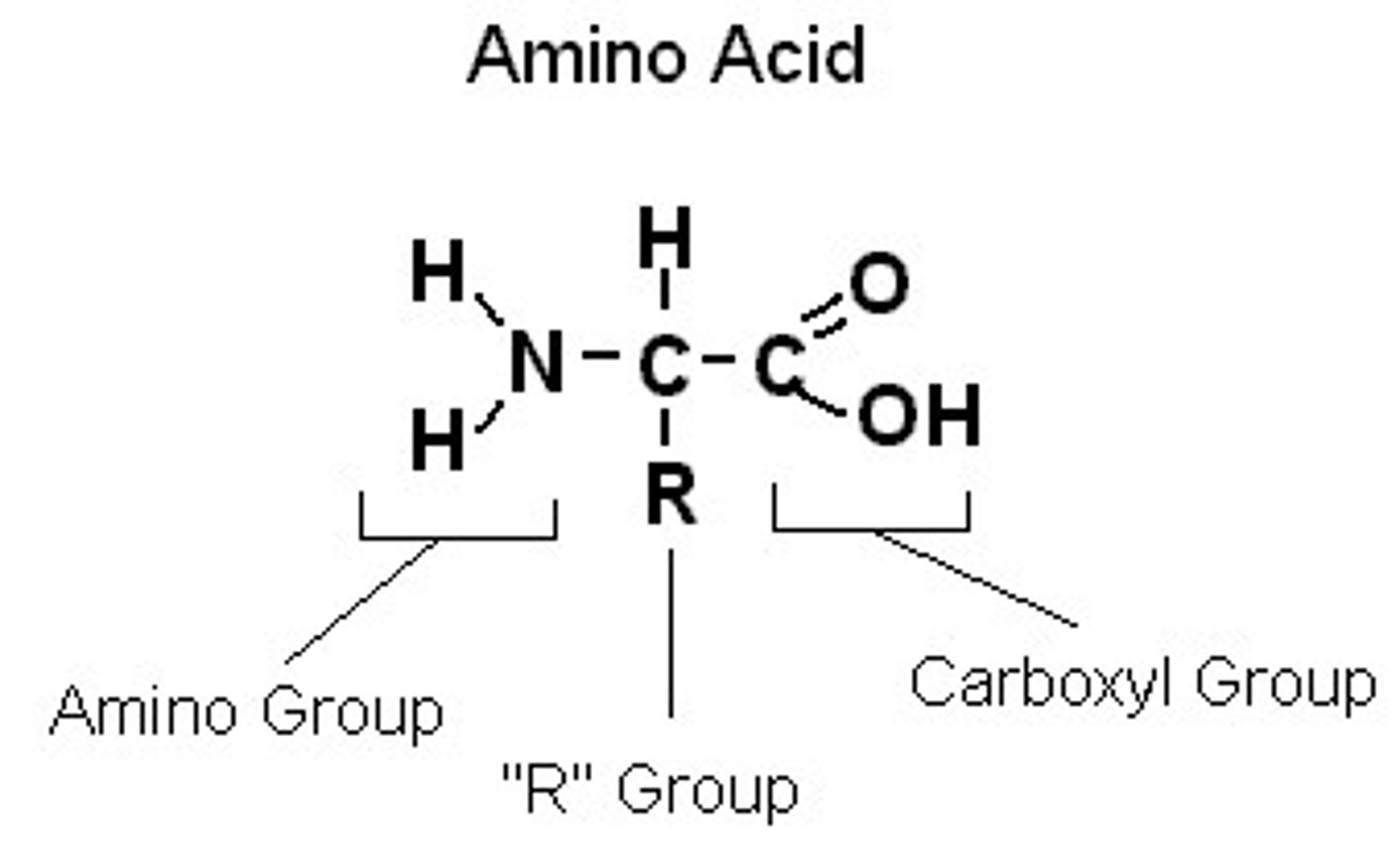
what is the effect of temperature on the action of the enzyme?
as temperature increases, enzyme activity speeds up
what is the effect of pH on the action of the enzyme?
enzymes have an optimal pH where activity is the highest
what happens to the enzyme activity when the substrate or enzyme concentration increases?
the substrate-active site collisions happen more frequently and the rate of reaction increases
Explain the relationship between the structure of the active site, enzyme-substrate specificity, and denaturation
- the shape and chemical properties of the active site allow substrate molecules to bind
- when the enzyme denatures it changes the shape of the protein which prevents the substrate from binding
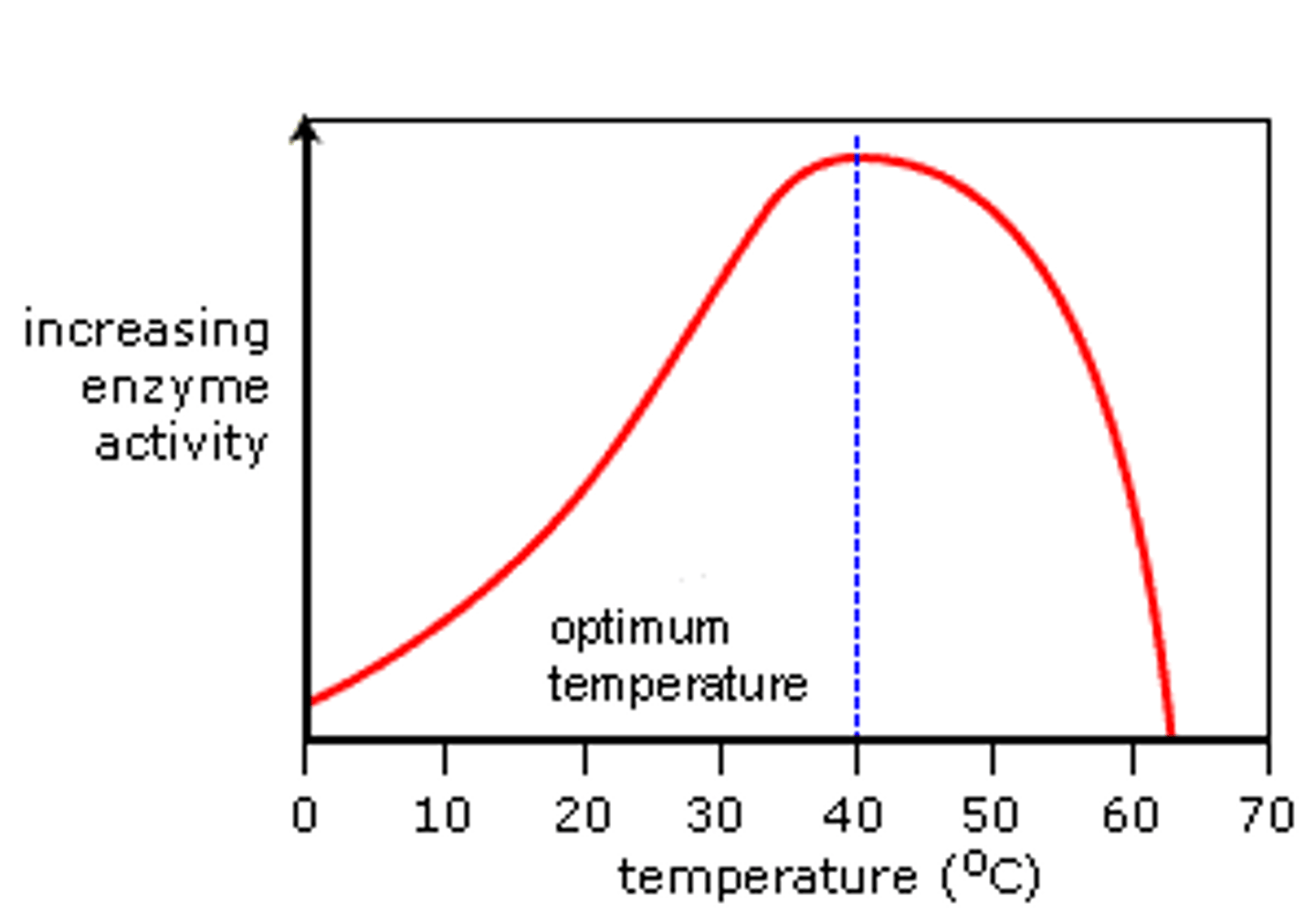
what is the effect on a graph of the relationship between temperature and enzyme activity?
increases, peaks, then decreases
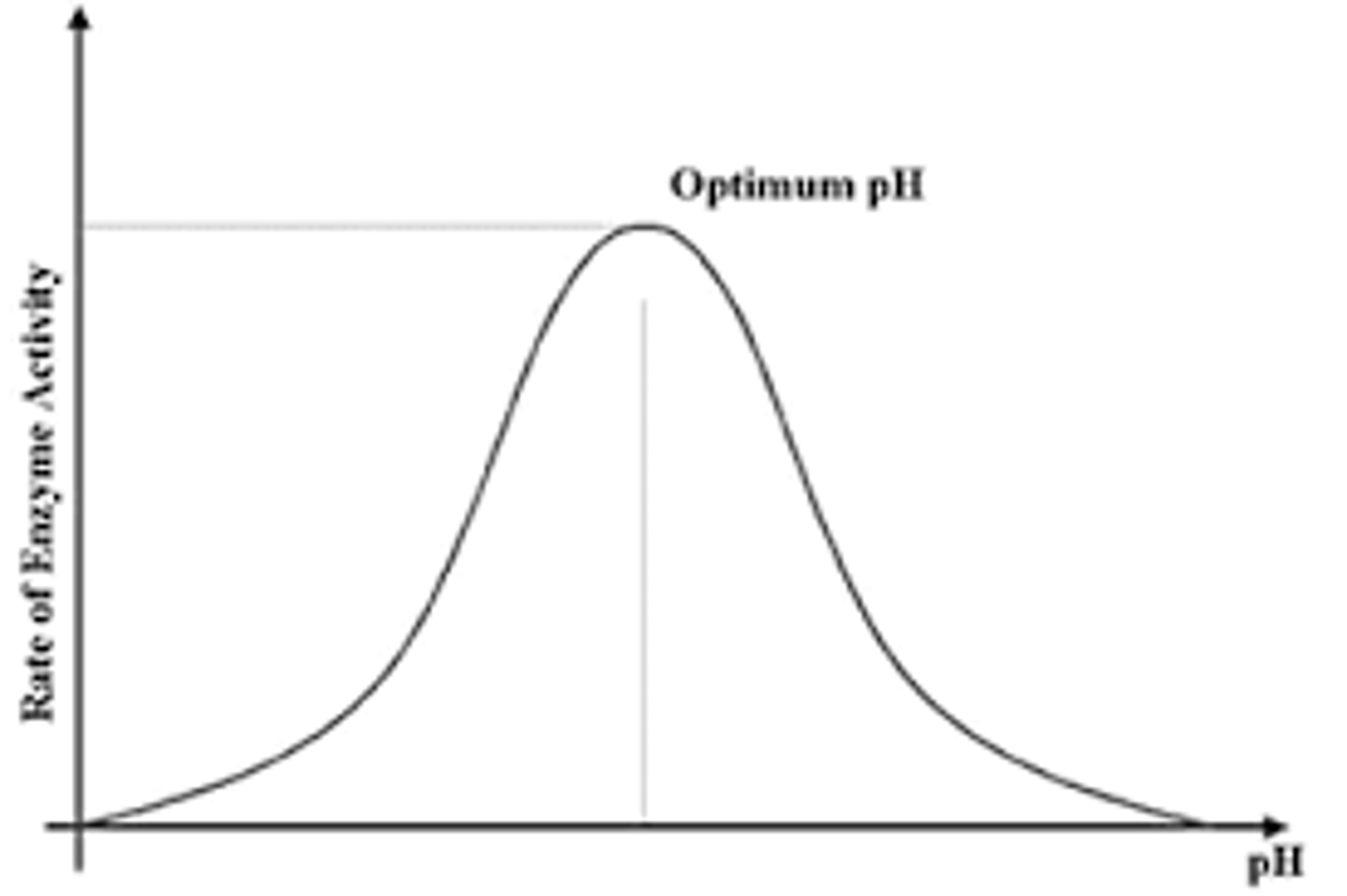
what is the effect on a graph of the relationship between pH and enzyme activity?
increases, peaks, and the, decreases
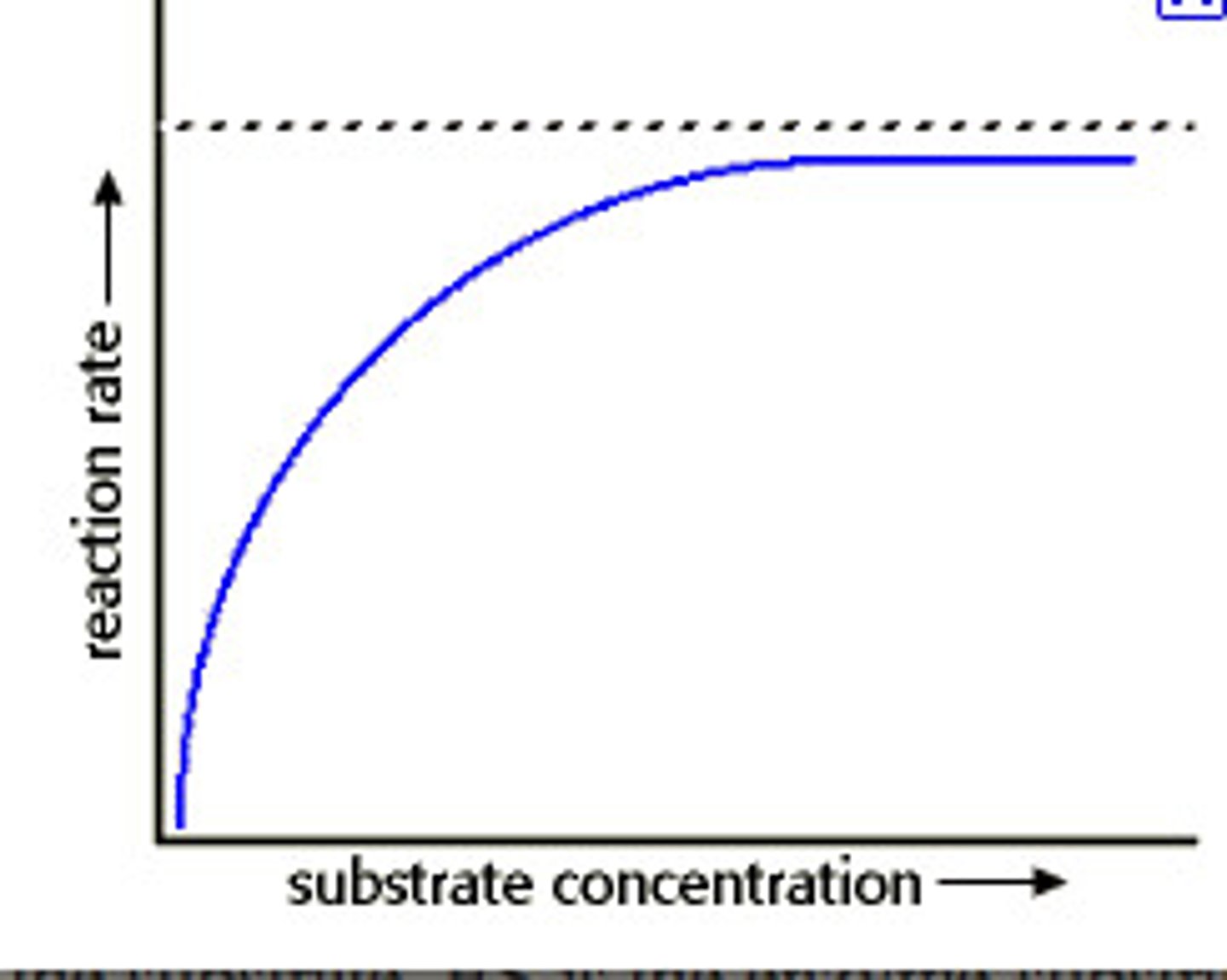
what is the effect on a graph of the relationship between substrate concentration and enzyme activity?
increases then plateaus
what is competitive inhibition?
An inhibitor competes with the substrate for binding to the active site
what is noncompetitive inhibition?
inhibitor binds at a site different from substrate, the allosteric site
List evidence for the last universal common ancestor and where it evolved (SHORT ANSWER)
the genetic code is the same for all species and it evolved in the vicinity of hydrothermal vents
what is the cell theory?
All living things are made up of cells, cells are the most basic units of life, new cells are produced from existing cells
compare and contrast eukaryotes and prokaryotes
eukaryotes - large, complex, nucleus
prokaryotes - small, simple, no nucleus
both have DNA
what are the differences between plant and animal cells?
plants have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large vacuole
function of the plasma membrane
controls the entry and exit of substances
function of cytoplasm
where metabolism and enzyme reactions occur
function of free ribosomes
proteins that stay in cytoplasm or enter the nucleus
function of ribosomes on rough er
make proteins that will leave the cell
function of the nucleus
holds the cell's chromosomes
function of the mitochondria
carries out aerobic respiration to make ATP energy
function of the rough er
transport proteins to the golgi apparatus
function of the smooth er
allows molecules to move throughout the cell
function of the golgi apparatus
processes and packages substances for export from the cell
function of the vacuoles
storage area
function of the lysosomes
contains strong enzymes used for digestion
function of the cholorplast
produces glucose through photosynthesis
function of the cytoskeleton
gives the cell its shape
function of the microtubules
moving chromosomes during cell division
function of the centrioles
anchor points for microtubules during cell division
function of the cillia
hair-like structures used to move the cell
function of the flagella
whip-like structure that allows a cell to move
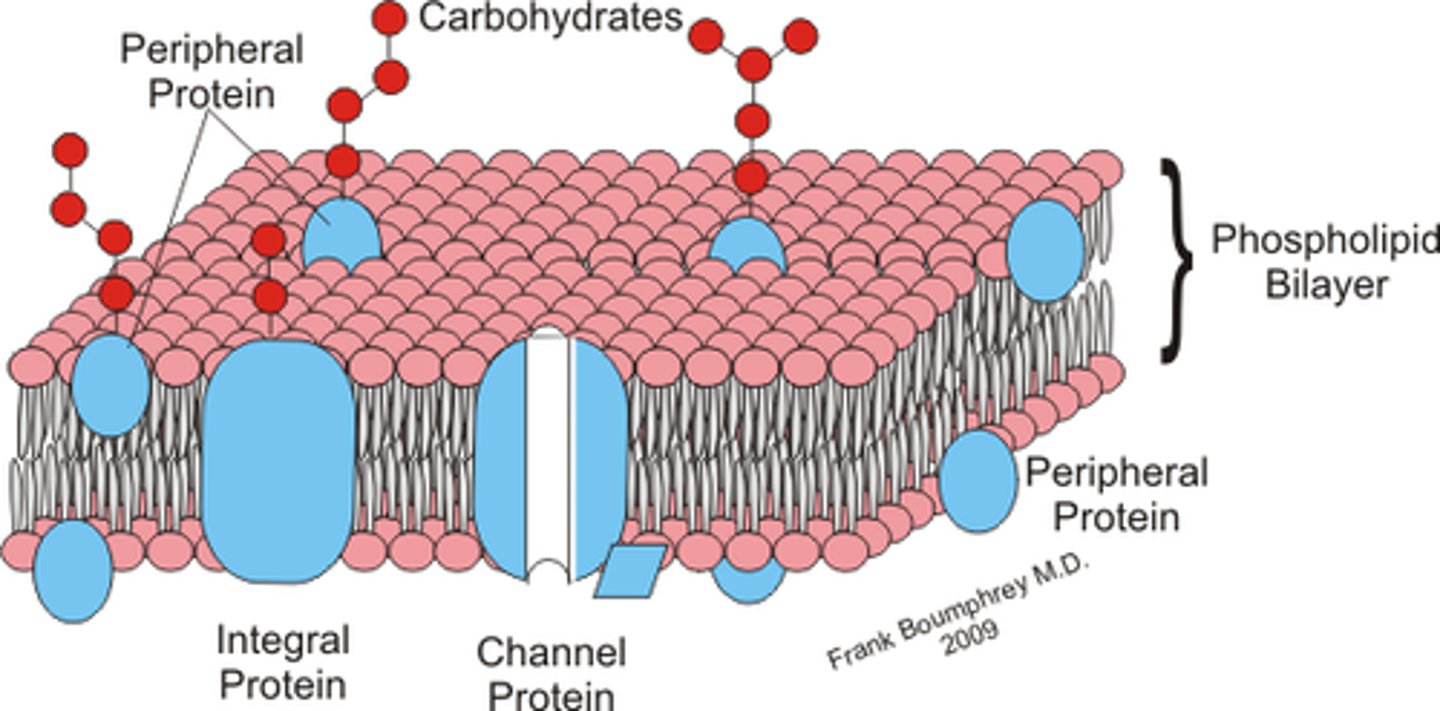
draw a lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane (SHORT ANSWER)
polar (hydrophilic) head and two non-polar (hydrophobic) tails
define active transport and give an example
movement of particles against the concentration gradient using ATP energy - ex: pump proteins
define passive transport and give an example
movement of particles with the concentration gradient (no ATP needed) - ex: osmosis, facilitated diffusion
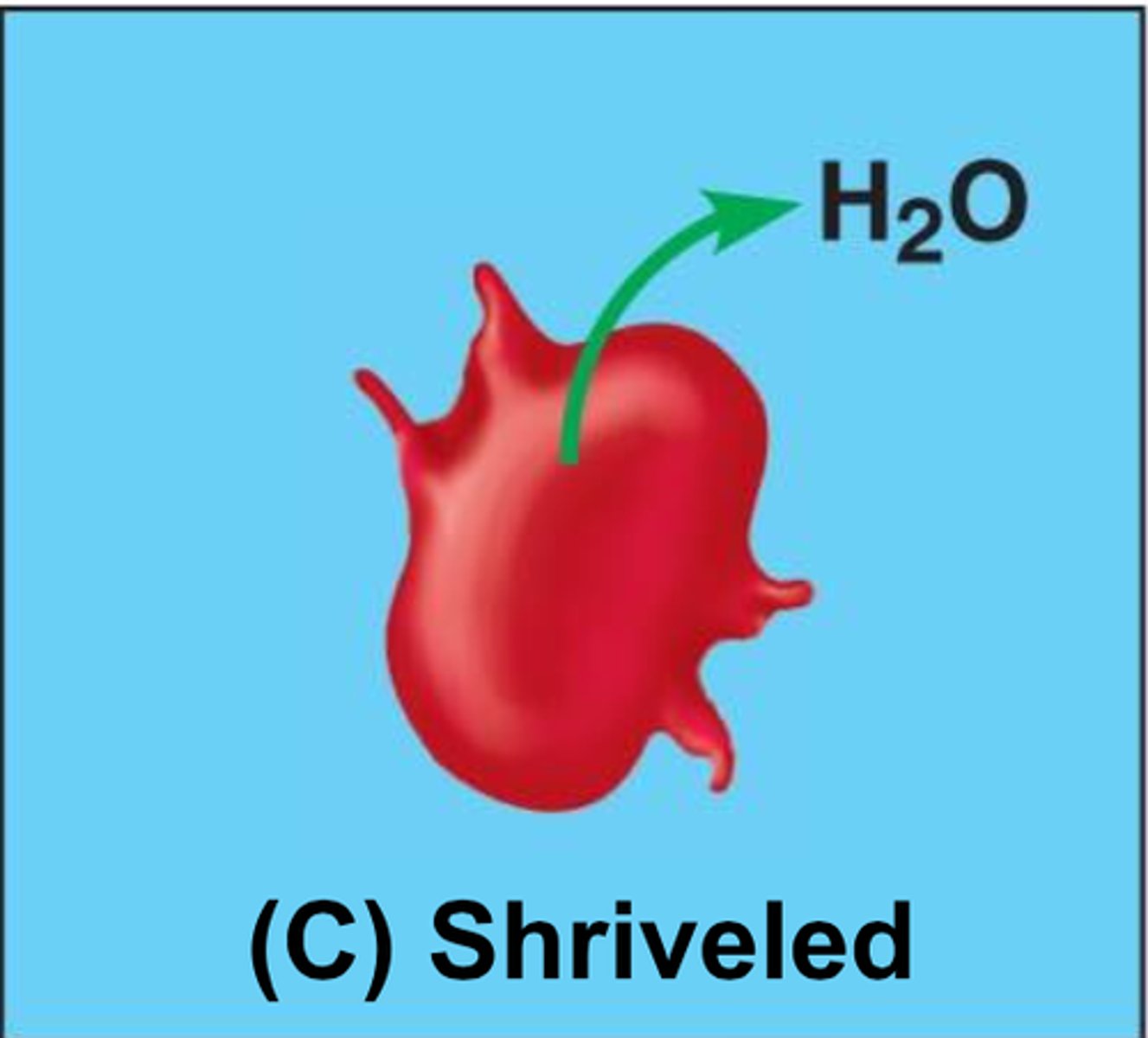
what does it mean to say a cell is HYPERtonic?
water is moving out of the cell - cell shrivels up
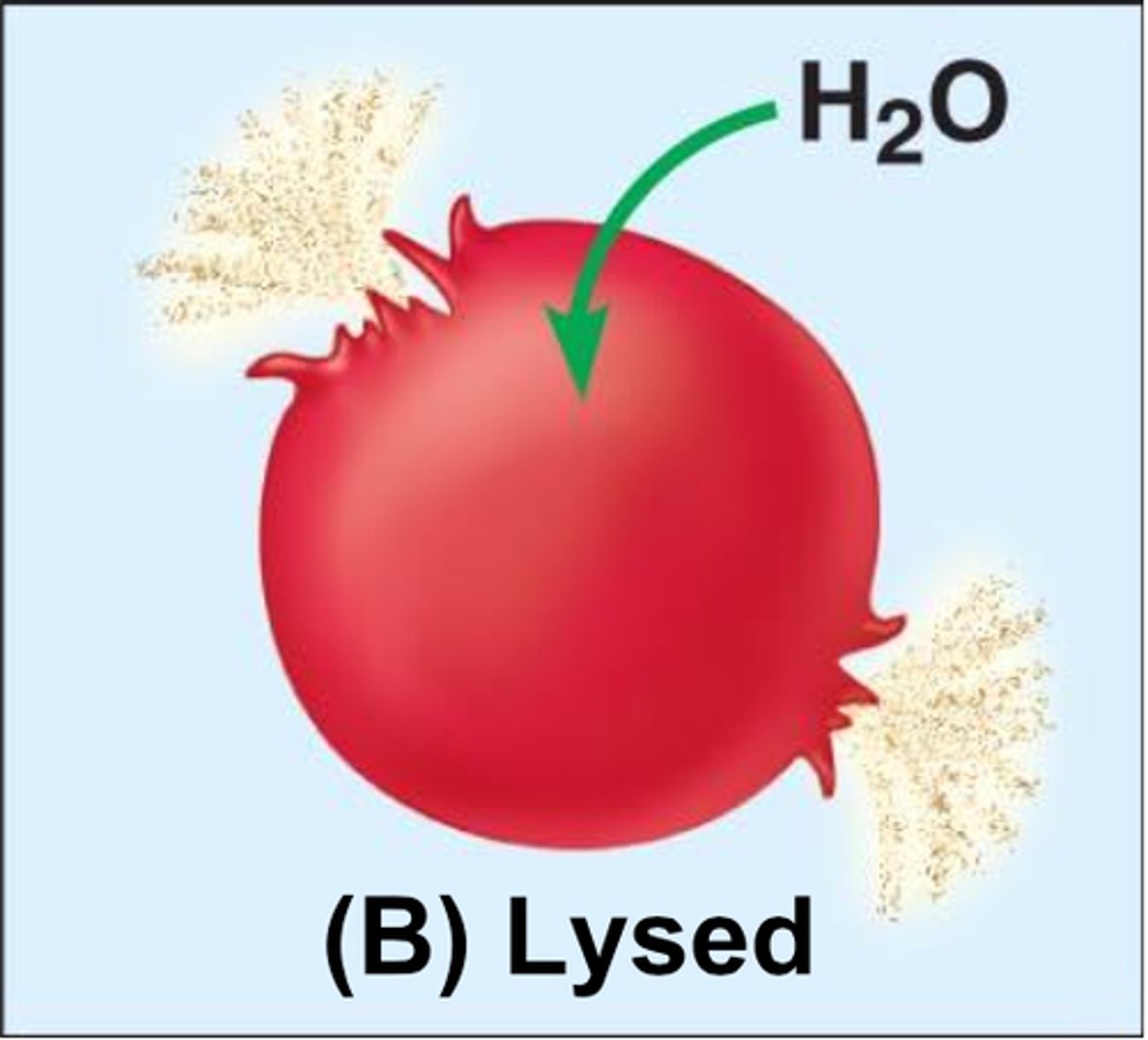
what does it mean to call a cell HYPOtonic?
water is moving into the cell - cell swells up
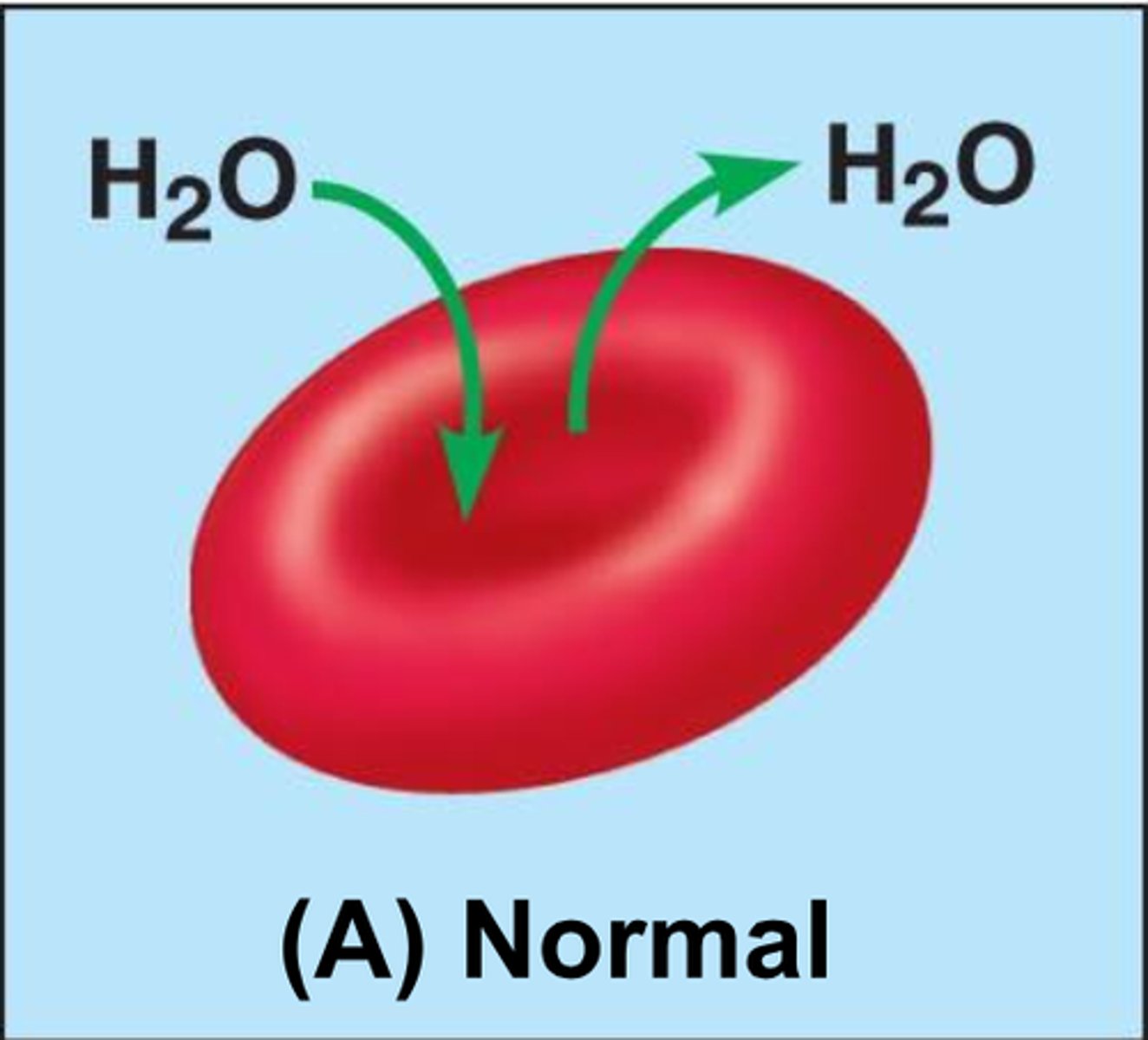
what does it mean to call a cell isotonic?
water is moving equally in and out of the cell - cell is normal sized
what is solvation?
a solute dissolving in water
what are the steps of the cell cycle?
G1, S, G2, Mitosis
what happens during the G1 phase of the cell cycle?
cell growth
what happens during the S phase of the cell cycle?
DNA replication
what happens during the G2 phase of the cell cycle?
cell growth and preparation for mitosis
what is crossing over and when does it occur?
The exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes during prophase I
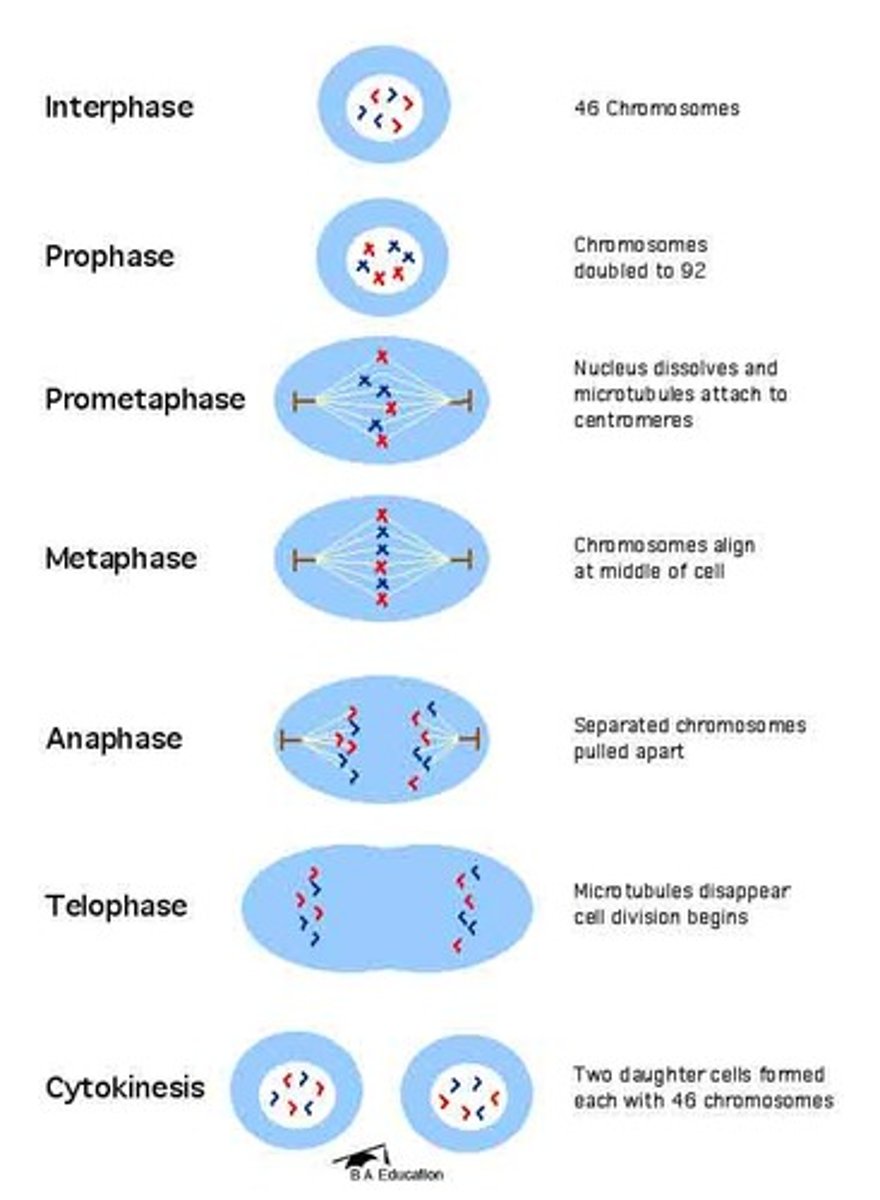
what are the steps of mitosis?
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
what happens during prophase?
chromosomes condense
what happens during metaphase?
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
what happens during anaphase?
sister chromatids separate
what happens during telophase?
new nuclear membranes form
what is the purpose of mitosis?
cell reproduction
Label the steps of mitosis and cytokinesis (SHORT ANSWER)
prometaphase not needed
what are the steps of meiosis?
Prophase 1, Metaphase 1, Anaphase 1, Telophase 1, Prophase 2, Metaphase 2, Anaphase 2, Telophase 2
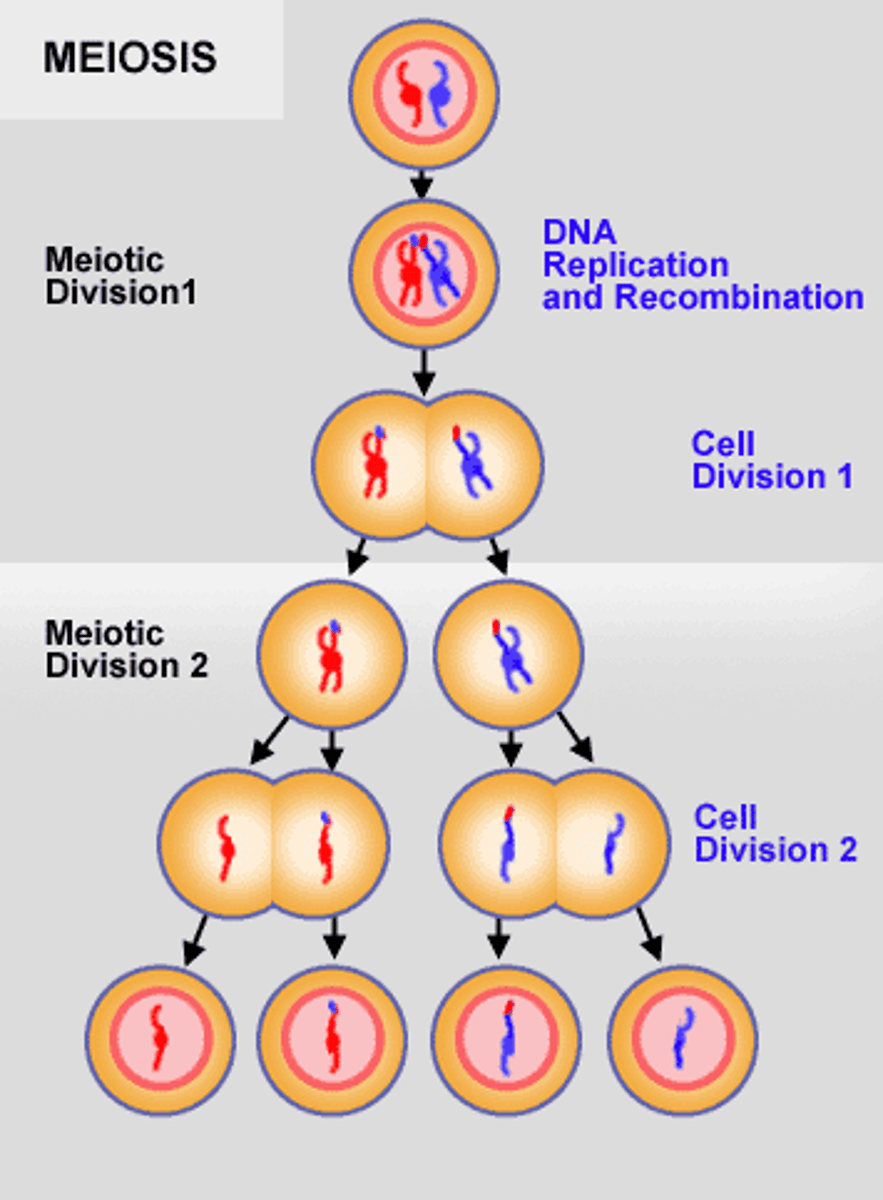
what is the purpose of meiosis?
produce gametes for sexual reproduction
how many chromosomes are present after mitosis?
46
how many chromosomes are present after meiosis?
23
State and draw the structure of nucleotides (SHORT ANSWER)
sugar, phosphate, base

what is the shape of DNA called?
double helix
what are complementary base pairings?
Adenine + Thymine, Cytosine + Guanine
how are DNA and RNA similar?
They are both nucleic acids
how are DNA and RNA different?
DNA is double stranded, has thymine, and is deoxyribose sugar
RNA is single stranded, has uracil, and is ribose sugar
is DNA replication conservative or semi-conservative?
semi-conservative
what are the steps of DNA replication?
1. original strand of DNA is unzipped by an enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds between the bases.
2. Free nucleotides attach to their complementary base
3. Another type of enzyme connects these nucleotides into a chain
4. This process continues until the entire strand of DNA has been unzipped and copied.
- always in 5'-3' direction
what are the steps of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
Melting, Annealing, Elongation
what is gel electrophoresis?
lab method that separates DNA by length
what is transcription?
The process of making RNA from DNA
what are the steps of transcription?
- promoter (section of DNA) starts the process and allows transcription factors to bind
- RNA polymerase binds to DNA and unwinds into 2 strands
- RNA polymerase moves along the template strand adding nucleotides
what is translation?
the decoding of an mRNA message into a protein
what are the steps of translation?
initiation, elongation, translocation, termination
what is the complementary base pairing of DNA to RNA? (SHORT ANSWER)
A-U, T-A, G-C, C-G
what is tRNA?
transfer RNA - transfers one specific amino acid to the ribosome
what is rRNA?
ribosomal RNA - combines with proteins to make the ribosomes where proteins will be make
what is mRNA?
messenger RNA - carries genetic information in DNA from nucleus to cytoplasm
what are anticodons?
Three bases on tRNA that match to codons on mRNA
what are codons?
mRNA triplets that code for an amino acid
what is splicing?
Removal of introns and joining of exons.
what is a haploid cell?
cell with half the number of chromosomes (23)
what is a diploid cell?
cell that has both sets of chromosomes (46)
what are homologous chromosomes?
two genetically similar chromosomes, one from each parent
what does homozygous mean?
two of the same alleles
what does heterozygous mean?
two different alleles
what is phenotype?
physical characteristics of an organism
what is genotype?
genetic makeup of an organism
what is a gene?
segment of DNA that codes for a protein
what is an allele?
an alternative version of a gene
what is a recessive trait?
A trait that will only appear in the offspring if both parents give it
what is a dominant trait?
a trait that will appear in the offspring if one of the parents contributes it