Ancient Greece: Notable Places
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Cycladic Islands (All Facts)
Where Aegean civilization began to develop around 2800 BCE
Economic center of the eastern Mediterranean between Greece, Anatolia, and Crete
Produced an economy in which sea transport was more efficient than land transport
Cluster of islands that includes Delos, Melos, Paros, Naxos, Seriphos, and Siphnos
Their minerals were exported to the surrounding areas
Grew in trade with cities across Mesopotamia, the Levant, Egypt, and Anatolia
Traded in canoe-like vessels
Hopped from island to island
Cluster of islands that became
Very rich
Famous for their boat-building
A major trading culture
Cluster of islands whose inhabitants became skillful makers of
silver ornaments
lead model boats
marble figurines
Cluster of islands whose inhabitants
Benefited from trade between Greece, Crete, and Syria
Evolved an original style of painted pottery, with lively designs of birds and fish
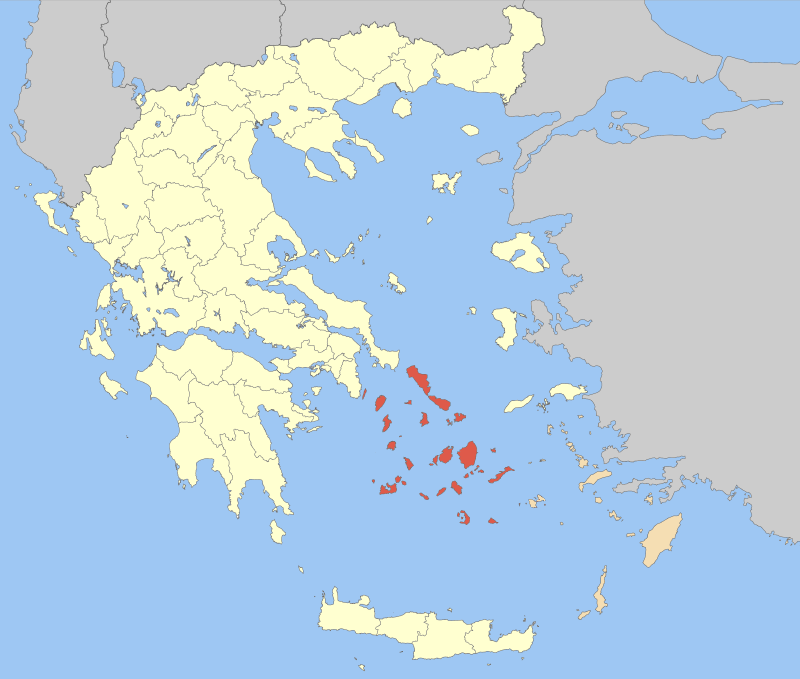
Dodecanese Islands (All Facts)
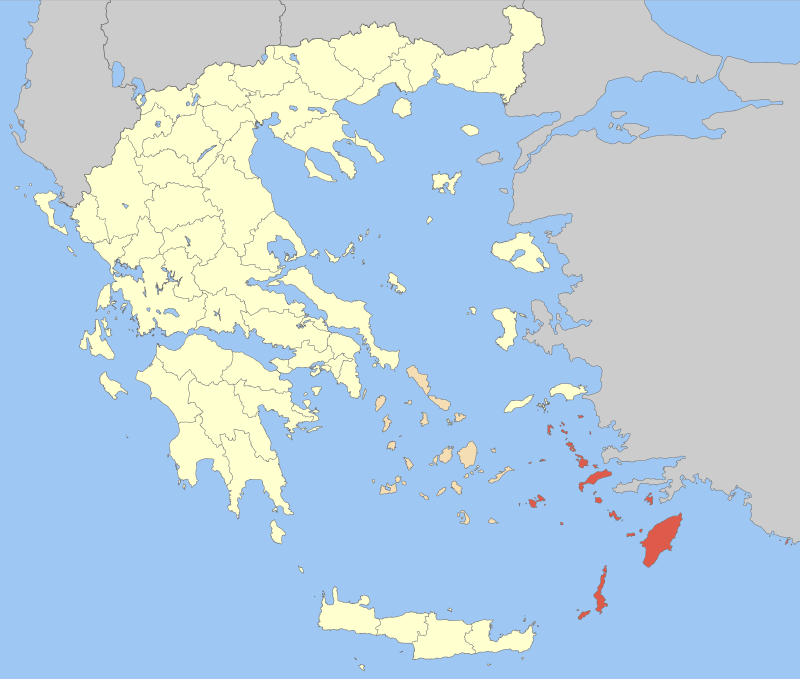
Delos (All Facts)
Cycladic Island of Greece
Smallest and most central of the Cyclades islands
All the other islands lie in a circle around it
Tiny city-state of the Aegean
Small island home of a religious community, it would be chosen as the administrative headquarters of the Delian League instituted by Aristides the Just of Athens
Was under direct control of Athens until Athens lost naval power
However, when it came under Rome, Rome decided to hand it back and declare it a free port for the inhabitants to continue to use
This substantially boosted the namesake island’s economic links with both Anatolia (Pergamum) and the far western Mediterranean
Accompanied by a new influx of seamen and merchants
Declared a free port by Rome in 167 BCE, it underwent an economic boom around 166 BCE
Became the pivot of east-west Mediterranean trade
Had a cosmopolitan population
Was administered by local officials, who promoted it as a center for the trade of corn and slaves
This, in turn, attracted a foreign colony, including financial firms
Island that was founded on the myth that it was the place where Leto gave birth to the divine twins Apollo and Artemis
Was the site of
a great Panhellenic shrine
a place of pilgrimage
Melos (All Facts)
Cycladic Island of Greece
Rich in volcanic glass
Paros (All Facts)
Cycladic Island of Greece
Rich in marble
Naxos (All Facts)
Cycladic Island of Greece
Rich in marble
Seriphos (All Facts)
Cycladic Island of Greece
Rich in copper, silver, and lead
Siphnos (All Facts)
Cycladic Island of Greece
Rich in copper, silver, and lead
Santorini (All Facts)
Cycladic Island of Greece
Also known as “Thera”
People living there had a that way of life was characterized by
A diet of vegetables, dried fish, cereals, oil, wine, and olives
People living there had homes that were characterized by having rooms in which
The bottom room served to store their food supplies in earthenware jars
The room above the bottom room was where they lived
One room in each house served as a shrine
The rooms were decorated with frescoes of landscapes showing animals, boats, growing lilies, growing papyrus, crocuses being picked, a small catlike animal stalking fucks and a fisherman with his arms full of fish
Severely damaged by a volcano now known as the “Minoan Eruption” around 1600 / 1500 BCE which left most of its inhabitants by that time buried under a huge layer of lava and debris with much of the island having disappeared and submerged under the sea
Akrotiri (All Facts)
City in Santorini
Where the people fled to when the island was destroyed by the “Minoan Eruption” in 1600 / 1500 BCE
Its people were effectively entombed after the volcano
Troy (All Facts)
City in Anatolia whose citadel was famously destroyed around 2300 BCE
City which had much power and wealth by 2300 BCE due to the gold and silver products it contained
City in which people had bronze daggers, axes, silver ingots, and drinking vessels beaten out of gold and silver
Its craftsmen were skilled in the complex techniques of filigree and granulation and were clearly familiar with contemporary styles of craftsmanship in Mesopotamia
Enjoyed a period of great prosperity due to dominating over the important trading passage from the Aegean to the Sea of Marmara and the Bosporus Strait
Crete (All Facts)
Largest island of Greece, fifth largest island in the Mediterranean
Its most famous cities were Phaistos, Knossos, Malia, and Gournia
Around 2000 BCE
It took over as leader of Aegean trade
Palaces were built near the small towns that served as manufacturing centers across the island
Craftsmanship reached very high levels in which
Tiny seals in semi-precious stones were carved with great accuracy which showed plants, animals, birds, boats, shells, and geometric patterns
The walls of its palaces were covered in frescoes
It made fine pottery in bright colors on a dark background, echoing the patterns on the walls of its palaces
there was manufacture of stone vases and shapes that were first used in metalwork, particularly silver
Ships with sails carried these commodities along the coast of Anatolia to Syria where they were exchanged with traders from Egypt
Experienced a massive earthquake that brought ruin and desolation to the island around 1700 BCE
In response, its inhabitants built even more magnificent palaces compared to before including the Second Palace at Knossos
Had country houses, which were centers of estates that produced olive oil and wine and reared large flocks of sheep whose wool was the basis of its local textile industry
By 1450 BCE, all of its palatial complexes are destroyed, except for Knossos which was taken over by the Myceneans from the Greek mainland
By 1375 BCE, however, the palace at Knossos is destroyed by the Myceneans
Knossos (All Facts)
City in Crete
One of the first (and most important) cities of Minoan Civilization
Had a famous palace, built around 1700 BCE
Phaistos (All Facts)
City in Crete
Had a famous palace, built around 1900 BCE
Malia (All Facts)
City in Crete
Had a famous palace, built around 1900 BCE, for King Sarpidon
Gournia (All Facts)
City in Crete
Had a village of narrow winding streets and rough steps build on a hillside overlooking the sea
Its houses were furnished with materials brought over the mountains from Knossos, some 30 miles distant across the island
Chania (All Facts)
City in Crete
Characterized by its exports of painted inscriptions in the style of Mycenean script made on oil jars around 1450/1400 BCE
Pylos (All Facts)
City in the Peloponnese
One of the first (and most important) cities of Mycenean Civilization
Developed its own culture separate from that of Minoan Crete around 1650 BCE
Characterized by its craftsmen who made vases with figurative decorations
Characterized by its construction of tombs that were beehive-modeled called “Tholos”
Abandoned by 1200 BCE / 1050 BCE
Plain of Argos (All Facts)
Region in the Peloponnese
The Myceneans established a strategically-sited citadel there around 1300 BCE
Its citadel was surrounded by massive walls, which were rebuilt and incorporated some of the most recent novelties during that time of Hittite architecture
Tiryns (All Facts)
City in the Peloponnese, famous for its port and palace
Famous for its citadel, constructed around 1600 BCE, which was heavily fortified and built in a style that was influenced by contemporary Hittite architecture
Argolis (All Facts)
City in the Peloponnese controlled by the Mycenean civilization but whose founding was around 5000 BCE
City in which, as Mycenean civilization began to collapse, peoples from Mycenae regrouped in the shelter of its citadel
Attica (All Facts)
City in the Peloponnese founded in Mycenean civilization around 1600 BCE
City in which, as Mycenean civilization began to collapse, peoples from Mycenae regrouped in the shelter of its citadel
Euboea (All Facts)
Second largest island of Greece, sixth largest island of the Mediterranean
Had a grave with a covering on it of a chief and his wife in Lefkandi which had a temple-like structure with a wooden colonnade
Sicily (All Facts)
Largest island in the Mediterranean
The “boot” of Italy, was eventually taken by the Greeks by the 700’s BCE but was made up of independent groups before that
Its local chiefs traded with Aegean traders and bartered local products for pottery and metalwork by 1500 BCE
Cyprus (All Facts)
Third-largest island in the Mediterranean
Had always been a crossroads for people and culture as it is situated between Europe, Africa, and the Levant in the Mediterranean
Its economic opportunities were opened up and its influence began to appear after the collapse of the Hittite and Mycenean Civilizations as well as the decline and eventual collapse of the Greeks at sea
Traded as far away as Egypt and Sardinia by 1075 BCE
Characterized by art which mixed Mycenean Greek styles with oriental and Egyptian ones
Characterized by Greek names having been written in its local script
Characterized by its development and spread of chambered tombs with long entrance passages, likely also influenced by the Greeks
Sardinia (All Facts)
Second largest island of the Mediterranean
Built fortresses on hilltops with blocks of roughly hewn stone around 1500 BCE
Corsica (All Facts)
Fourth largest island of the Mediterranean
Built fortresses on hilltops with blocks of roughly hewn stone around 1500 BCE
Characterized by its large number of Menhirs, which were tombs cut to form the shapes of noses, mouths and eyes; giving them a rudimentary human appearance
Gela (All Facts)
City in Sicily
Founded by the Dorians
Sparta (All Facts)
City in the Peloponnese in the far south of Greece
Established around 900 BCE - 700 BCE
Made up of the namesake group of people
Run along austere, disciplinarian lines
Commerce is forbidden
The possession of gold and silver are forbidden
People’s clothes do not vary much
Its male citizens are brought up as soldiers from the age of 7, live in dormitories, and eat together in communal mess halls, even when they are married
Experienced oriental-influenced luxury as well as a puritanic revival, with the ruling class giving itself over entirely to military training
Practiced infanticide
This was done amongst newborn babies who were judged to be too weak to be soldiers and were left to die in the wilderness
The strictness in their military discipline and conversion of city-states into armed camps likely stemmed from the fear of an uprising by the lower subject class
After the (Second) Peloponnesian War, it has become the major power in Ancient Greece until the rise of Thebes
Paros (All Facts)
Cycladic Island of Greece
Birthplace of Archilochus
Syracuse (All Facts)
City in Sicily
Colony of Corinth
Elis (All Facts)
City in the Peloponnese that contained Olympia
Its aristocratic inhabitants ran the festival that was the Olympic Games
Its aristocracy was responsible for overseeing the Olympics and whom presided over all religious ceremonies at Olympia
They were considered the earthly guardians of Olympia
They united in the “Olympic Senate” where they elected nine Hellanodikai or judges
Its gymnasium was where the Olympians gathered for the final month of their ten months of training where they were forbidden any stimulants and were fed a diet of barley bread, wheat porridge, dried figs, nuts, and cheese
The opening ceremonies of the Olympics began here two days before the start of the games, where the competitors, selected by the Hellanodikai, began a two-day 35-mile long march to Olympia
Olympia (All Facts)
Sanctuary in Elis where the Olympic Games were held from 776 BCE - 394 BCE
Located in the Alpheus Valley in the northwest of the Peloponnese
Is a holy place and shrine dedicated to Zeus
Attracted thousands of pilgrims each year
Corinth (All Facts)
City in the Peloponnese located on the namesake isthmus
Established the colony of Syracuse in Sicily
Had much contact with the Near East, especially in the development of their commerce and colonial expansion
Was one of many places in Greece with well-established connections in the Levant
Characterized by its art, which was influenced by Eastern styles including its
Jewelry & Pottery - Eastern decorative motifs were common including friezes of
Animals - lions, tigers, and ibexes
Mythical beasts - sphinxes and griffins
Floral patterns - seen for the first time since the Mycenean Age in this city, they included
Assyrian-style lotuses
Palms
Buds
Pine Cones
These newer patterns replaced the more geometric patterns of earlier pottery
Dominated the ceramics market
Its colonies includes Corcyra and Potidaea
Rhodes (All Facts)
The largest of the Dodecanese islands
Had much contact with the Near East, especially in the development of their commerce and colonial expansion
Was one of many places in Greece with well-established connections in the Levant
When Delos became an economic powerhouse due to Rome deciding to give it back to Athens, the namesake island and city-state suffered since Rome did not give it back to the Greek people
This was because its inhabitants and leaders tried to negotiate a peace between Rome and Perseus of Macedonia, which greatly upset the Roman Senate
When the Macedonian War with Rome ended, the namesake city-state and island was stripped of their territories in Anatolia
It lost its position as a major trading nation in the region from there onwards
Greek Colonies (All Facts)
Needed to be established due to the social pressures and quarrels over distribution of land and fear of starvation occurring in mainland Greece around 650 BCE
Established upon Greek expeditions setting sail to all parts of the known world at the time, with each of the namesake having been founded by a particular city-state
Some city-states founded one or more of them
Were founded in Sicily and southern Italy, North Africa, and on the shores of the Black Sea as well as the Sea of Marmara and Bosporus Strait
Were settled by young men of fighting age who set out in bands of up to 200 and were led by an individual called an “Oikistes”
The settlers who founded them retain close links with their old homes, taking with them their traditional institutions and gods in the form of wooden statuettes when they arrive
Sometimes, the original inhabitants of the namesake lands welcomed the Greeks, who would give them grants of land
Other times, however, the Greeks had to fight their way ashore
If successful, they used the conquered natives as slave laborers in the fields
Once established, they became completely independent of the mother city that founded it
Were essentially agrarian, the land having been allotted equally among the settlers
Examples include Naukratis, Syracuse, Byzantium, Sinope, Olbia, and Amisus
Emporia / Emporium (All Facts)
Commercial and/or agricultural settlements centered on trade established via Greek colonization who owed their existence not to a mother city, but to groups of businessmen who sought an opportunity for profitable trade
Naukratis (All Facts)
The only Greek colony in Egypt
Emporium in Egypt established via Greek colonization
Had a strictly commercial enterprise since the pharaoh there allowed the Greeks to worship their own gods but did not allow mixed marriages and maintained strict control over their activities
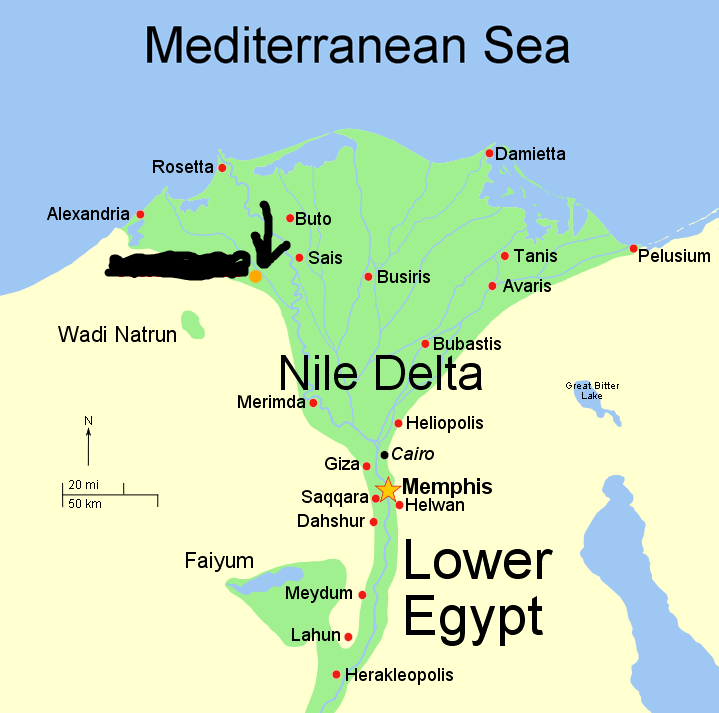
Byzantium (All Facts)
Greek Colony
City which eventually became Constantinople for the Romans and Istanbul for the Turks
Founded by the legendary “King Byzas” of Megara
Founded around 657 BCE
Sinope (All Facts)
Greek Colony
Founded by Ionians from the city of Miletus
Founded 756 BCE - 631 BCE
Olbia (All Facts)
Greek Colony in Sardinia
Founded around 325 BCE
Samsun / Amisus (All Facts)
Greek Colony
Founded 760 BCE - 750 BCE
Lesbos (All Facts)
Third largest island of Greece, eighth largest island of the Mediterranean
Birthplace of Alcaeus
Megara (All Facts)
City in Greece (on mainland in Attica District)
Controlled by the Corinthians, then by the Athenians
Athens (All Facts)
Most famous Greek city (on mainland), along with Sparta, Corinth, and Thebes
By the 400’s BCE
It became the judicial capital of the region and its focal point
Its currency was used in all trade throughout the empire
It bought wheat for everyone due to its rich silver mines and the business and craft skills of its citizens
Prior to the Peloponnesian War, it had
Consolidated its power after successful battles with the Persian invaders
Dominated several city-states in the Aegean in a loosely-structured empire
Power based on the biggest navy in the region, which included the 200 triremes built by Themistocles
This fleet enabled it to recover from invasion and win great naval battles during the Greco-Persian Wars
Benefited greatly from the Delian League, which it had originally created as an alliance of city-states against Persia but which made its own power grow considerably and which eventually allowed it to grow and become the head of an empire
Power still resided with old families, from which both Pericles and Cimon had come, but relied on their oratorical skills more so than a hereditary right to govern
After the Peloponnesian War, it had
All its fortifications destroyed
Its massive navy reduced to 12 ships
Its democracy transformed into an oligarchy
Its independence routed to be a subject ally to Sparta
Never again became a major political power in Ancient Greece
Massalia (All Facts)
Greek colony on the Mediterranean coast
Established by the Greeks of Phocaea (in Anatolia)
Site that sat on a small coastal plain alongside deep water and was protected by rocky hills
Was within easy reach of the Rhone river, which had opened up Greece to trade with Southern Gaul
Its founding is shrouded in legend:
The daughter of the local king, Princess Gyrtis, fell in love with one of the Phocaean leaders, Protis, and married him
The namesake land was her dowry
It was likely that the marriage was real but was part of an astute deal by the Phocaeans involving negotiations for property and trading rights which got them the namesake land
Outpost which happened to have lots of enemies, which attacked from the sea and from land
The tribes that attacked it from land were led by Grytis’s own brother according to the legend
Jealousy of the Phocaeans, who traded from men-of-war rather than merchantmen, increased their success in opening up silver supplies of Tartessos on the Atlantic coast of Iberia
Despite these problems, this colony thrived
The vine and olive took root in its Rhone Valley
Phocaea (All Facts)
Greek city in Anatolia
Its inhabitants founded the colony of Massalia (Marseilles in France)
Samos (All Facts)
Greek island in the Aegean Sea
Powerful city-state
Famous for its vineyards and wine production
Miletus (All Facts)
Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in Ionia
By the 500’s BCE, an intense intellectual life developed in which mathematicians, physicians, and philosophers imposed a new rationality upon matters once conceived in mythical terms
Birthplace of Thales, Anaximander, Anaximenes, Hecataeus, Hippodamus, and Aristagoras
City which inflicted heavy damage at the Battle of Lade during the Greco-Persian Wars, in which it was razed to the ground and its population was deported to Mesopotamia by the Persians
Catania (All Facts)
City in Sicily
Argos (All Facts)
Powerful Greek city-state in the Peloponnese
The Peloponnesian League was created to offset its power
Thessaly (All Facts)
Highest point in Ancient Greece
Where Mount Olympus was supposedly located
Aegina (All Facts)
Greek island located in the Saronic Gulf between Attica and the Peloponnese
There, the Greek goddess Aphaea was worshipped and a Temple was built in her honor
Britomartis, the Cretan nymph and daughter of Zeus, hid here when fleeing from Minos
Island which was at war with Athens during the rule of Themistocles
Piraeus (All Facts)
Historical Port of Athens
Modernized by Themistocles in his building program of the triremes in order to house them
Its “Middle Wall,” the third of the long walls which protected its roads, which was built by the Athenians
The Spartans argued that the old fortification walls should not be rebuilt since they could provide a defense for the Persians if the latter captured the city again
Their argument was ignored, however, by Athens, which would eventually be one of many things that would cause the First Peloponnesian War
Thasos (All Facts)
Greek island in the Aegean off the coast of Thrace
Wealthy
Formed an alliance with the “Delian League” of Greek maritime states
Provided the alliance with a strong contingent of ships
However, when they laid claim to the mines and markets on the Greek mainland, Athens got angry and so when they decided to leave the Delian League, Athens sent a fleet there and won the naval battle and laid siege to the city
After the battle, its city walls were demolished and the rebel islanders were forced to accept Athenian terms
They tried appealing to Sparta, but Sparta was dealing with an earthquake and helot revolts at this time so it could not help; this thus forced them to sue for peace with Athens
Pieria (All Facts)
Sacred spring on the frontier between Elis and Pisa
Was where the Olympians washed themselves and sacrificed a pig during their two-day 35-mile long march from Elis to Olympia
Letrini (All Facts)
Was where the Olympians rested the night before arriving in Olympia during their two-day 35-mile long march from Elis to Olympia
Cerameicus (All Facts)
Potters' quarter of the city of Athens, from which the English word "ceramic" is derived
Part of the city of Athens upon which the huge procession of the Panathenaea set off towards the Acropolis
The Acropolis at Athens (All Facts)
Historical religious, political, and civic center of Athens, dedicated to Athena; it contained Greece’s most well-known architectural structures; most of which were overseen during their construction by Pericles during the Golden Age of Greece
Was a fortress for many years
Characterized by its steep cliffs on three sides
Consisted of a magnificent complex of temples which towered over the city of Athens
Consisted of three temples - the Erectheum, the Temple of Athena Nike; the Propylaea; and the Parthenon with its huge Doric columns, were constructed and completed in just over 40 years, making this site one of the architectural feats of the age
The whole structure was a monument to the recovery of Athens from the devastation of the Greco-Persian Wars and Persian invasion of 480 BCE
In the Bronze Age, it was topped by a Mycenaean palace
Brauron Sanctuary (All Facts)
Place near Philaidai, on the east coast of Attica, upon which Ancient Greek young girls of marriageable age flocked to in increasing numbers
Place where the “Arkteia” was performed
Thebes (All Facts)
City-state located in Boeotia in Central Greece
Rose to power after Athens and Sparta, around the mid-300’s BCE
After Athens was ruined by the (Second) Peloponnesian War and Sparta became decadent, it took these ancient rivals’ place as the dominant power in Greece
Megalopolis (All Facts)
Comprised of an amalgam of 40 villages in south-west Arcadia on the Greek mainland
Messene (All Facts)
Capital of the reborn nation of Sparta’s former helot serfs
Was once Ithome of Bronze Age Greece
Restored by the Thebans after the Battle of Leuctra
Pella (All Facts)
Hub of the growing Macedonian-Greek Empire under Philip II of Macedonia and Alexander the Great in Macedonia
Was developed in the late 400’s BCE by King Archelaus
Athenian propaganda created by Demosthenes asserted it as nothing more than a “puny little village” but this assertion was contradicted by the testimony of contemporary travelers who visited the area, who stated that it
Was approached by a well-engineered road 30 feet wide
Was on a vast fertile plain flanked by the sea, with a thriving port
In this city
Were elegant buildings, with 6-foot-thick walls that were decorated with
Rare pebble mosaics
Ionic and Doric colonnades
3-foot roof tiles stamped with the city’s name on it
Palaces contained murals by the great Macedonian artist Zeuxis
Standards of public hygiene, water supply, and drainage matched its aesthetic quality
Euripides’s plays were performed
Aristotle tutored Alexander the Great (as a visiting tutor)
Alexandria (All Facts)
Named after the ruler who built it, it was founded in 331 BCE
Was the scientific capital of the Hellenistic world, largely owing to the support and encouragement of Egypt’s Ptolemaic rulers
Built on the Egyptian coast in the west of the Nile River Delta
Was set on the crossroads between the Hellenistic World of Greece and Anatolia, the rich Nile River Valley, and the markets of the east
Having inherited the trading links of Phoenician Tyre in Lebanon after the siege by the city’s namesake founder, the city acquired great wealth and fine public buildings
Thus, it became a great trading center or entrepot
Consisted of a great harbor, being created by constructing a mole linking the mainland with the island of Pharos, which was to be used as a naval base for the ruler’s war against the Persian Empire
Designed by the architect Dinocrates, who marked out the city in a grid pattern of straight streets intersecting each other at right angles
Demographics
A substantial Jewish quarter grew up in the northeastern part of the city
Egyptian fishermen had settled in the southwestern parts of the city
Greeks had settled in the central sectors around the royal palaces and surrounding gardens of the city
Its inhabitants
Quarried porphyry stone for export to Rome for buildings by 50 BCE
Its sailors sailed down the east coast of Africa and reached Rhapta (the Rufifi river mouth in Tanzania) on the Indian Ocean
Tarentum (All Facts)
Leading Greek city in Southern City, it fell to the Romans in 272 BCE
Antioch (All Facts)
Capital of the Seleucid Empire
Famous for its park at Daphne
Was mostly well-managed, with local magistrates
responsible for
the condition of the streets
the water supply
public sanitation
having the powers to fine people for breaking the laws
Its population
shows a mix of Greek, Macedonian, and oriental influences
depends mostly on agriculture
Seleuceia-in-Pieria (All Facts)
Seleucid city famous for its harbor
Was mostly well-managed, with local magistrates
responsible for
the condition of the streets
the water supply
public sanitation
having the powers to fine people for breaking the laws
Its population
shows a mix of Greek, Macedonian, and oriental influences
depends mostly on agriculture
Apamea (All Facts)
Seleucid city that was a big military center on the middle Orontes
Was where the Seleucids kept their war animals
Was mostly well-managed, with local magistrates
responsible for
the condition of the streets
the water supply
public sanitation
having the powers to fine people for breaking the laws
Its population
shows a mix of Greek, Macedonian, and oriental influences
depends mostly on agriculture
Museum of Alexandria (All Facts)
Building in which the Ptolemies made it into the leading Greek university, with schools of medicine, mathematics, astronomy, and geography
University of Alexandria (All Facts)
Building in which the Ptolemies supported the administration of schools of medicine, mathematics, astronomy, and geography
Scholars from all over the Greek world were
Attracted to it
Paid by the Ptolemaic Kings
Ptolemies encouraged the study of biology in this building by providing it with convicted criminals who were cut open while they were still alive, in which much knowledge about the brain and other organs, including the reproductive system, was acquired
Library of Alexandria (All Facts)
Part of the Museum of the same name, it was founded by Ptolemy II (or possibly Ptolemy I, his predecessor)
Was the greatest in the world at the time, an unrivalled intellectual center
It held around 120,000 individual books
The staff there worked under a chief of the namesake vocation where they carried out the enormous task of cataloging new acquisitions which arrived continually; each catalogued according to
Their origins
Former owner
Edition
Author
Subject-matter
Often works were recopied by hand or deviant editions were corrected
Ephesus (All Facts)
One of the oldest and most important Greek cities on the Anatolian coast
Was built around a temple dedicated to Artemis
Sybaris (All Facts)
Greek city located in southern Italy
Was one of the wealthiest Greek cities
It was razed to the ground and its inhabitants were massacred around 510 BCE
Had become infamous for its decadent lifestyle
The cities of Old Greece, under the guide of a religious crusade beat down the upstart
Alexandria of Sogdia (All Facts)
Greek city built by the Greeks on the shores of the Oxus (Amu Darya)
On the pattern of a Greek town, it included an acropolis, public monuments, lower town, and outer wall
Pergamum (All Facts)
Capital of the Attalid Dynasty, it had the same name as the general name of the kingdom it belonged to
Became the cultural center that competed with Ptolemaic Alexandria, especially by the 150’s BCE
Library of Pergamum (All Facts)
Had difficulty obtaining books, for they almost all were bought by its Ptolemaic Egyptian rival
Ptolemias Epitheras (All Facts)
Port city of Egypt founded on the Ethiopian coast of the Red Sea in 264 BCE
From this port, the Egyptians conducted a flourishing trade in ivory and skins