BIO 168 Chapter 9 Muscular System Histology and Physiology
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
The structures that are predominantly composed of muscle tissue:
-the heart
-the walls of the small intestine
Voluntary movements such as raising your hand are produced by the contraction of ____ muscle cells.
skeletal muscle
Communication between cells is very, very rapid in smooth cardiac muscle. What cellular structure facilitates this communication?
gap junctions
the muscle that is responsible for changes in the diameter of blood vessels is ____ muscle.
smooth
what type of muscle tissue is responsible for propelling materials such as food through the body?
smooth muscle
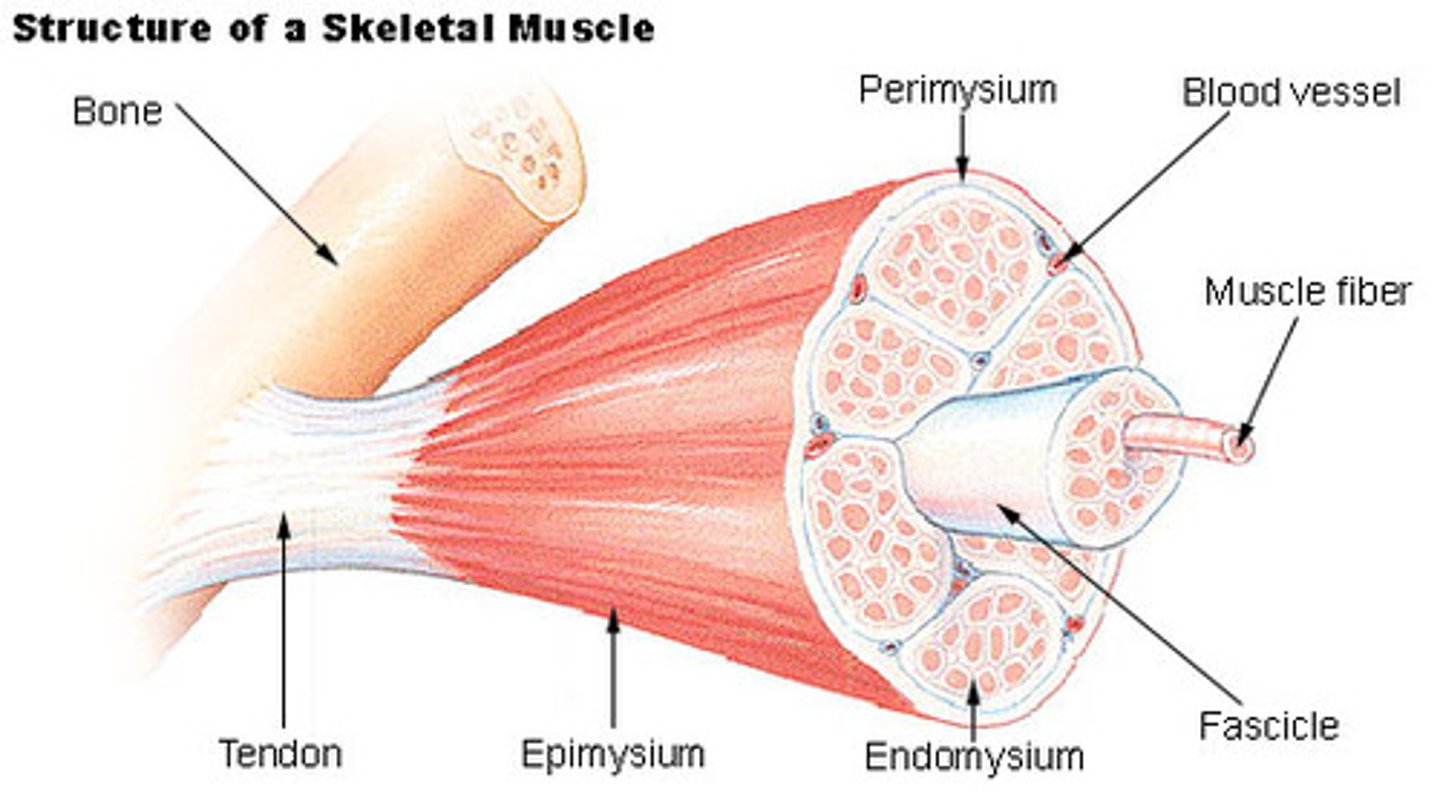
another name for a single skeletal muscle cell is a skeletal muscle ____.
fiber
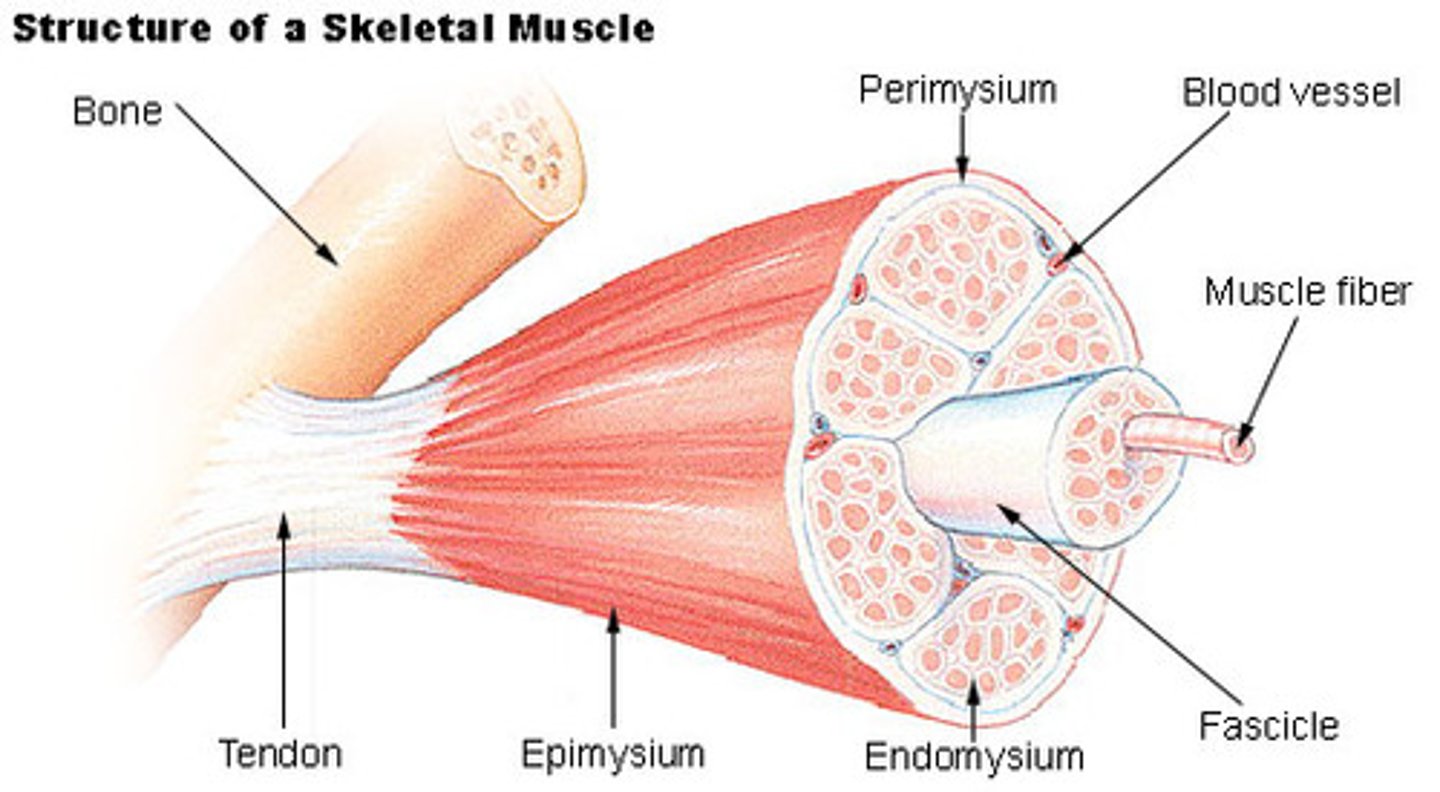
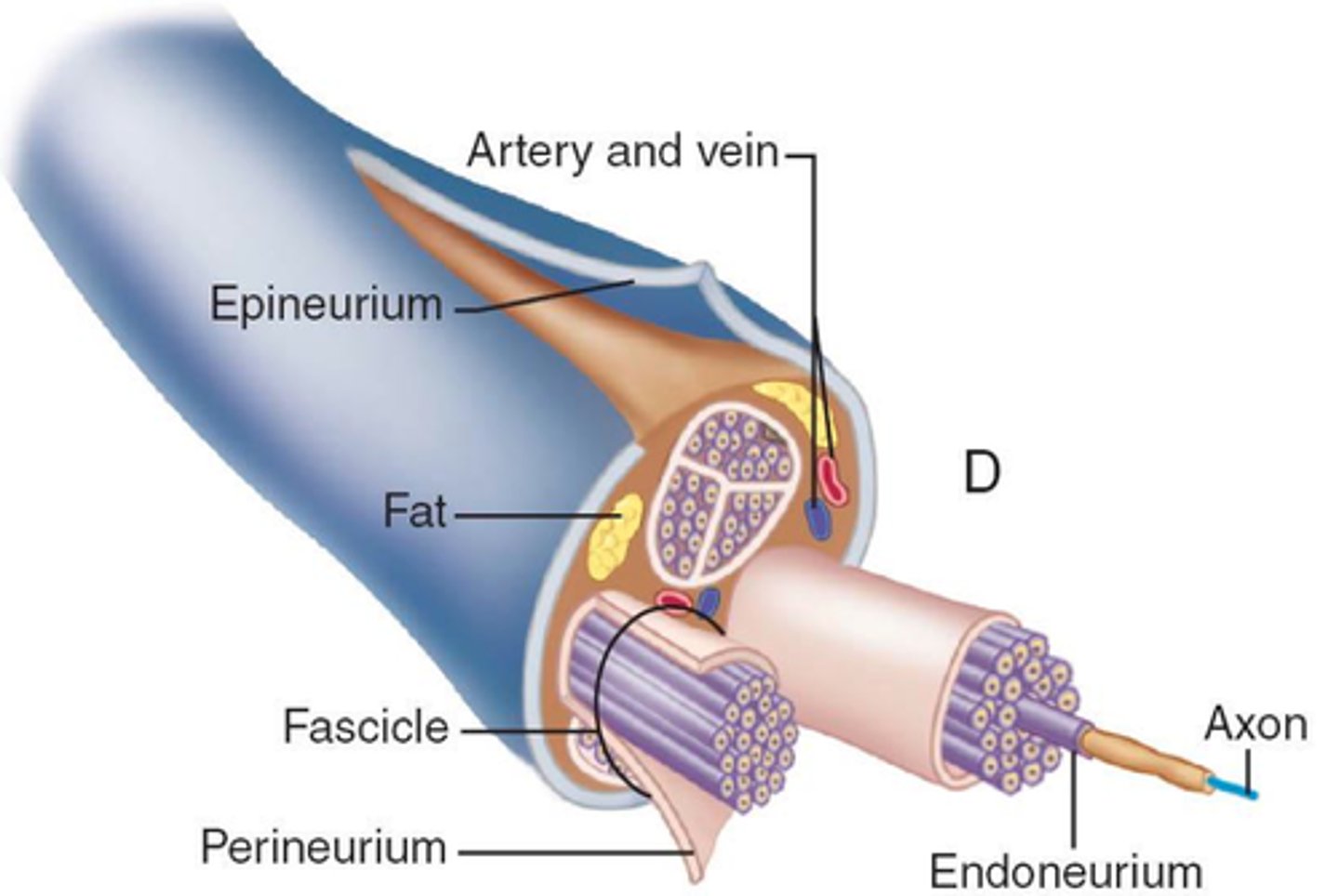
fasciculus
bundle of muscle fibers (D)
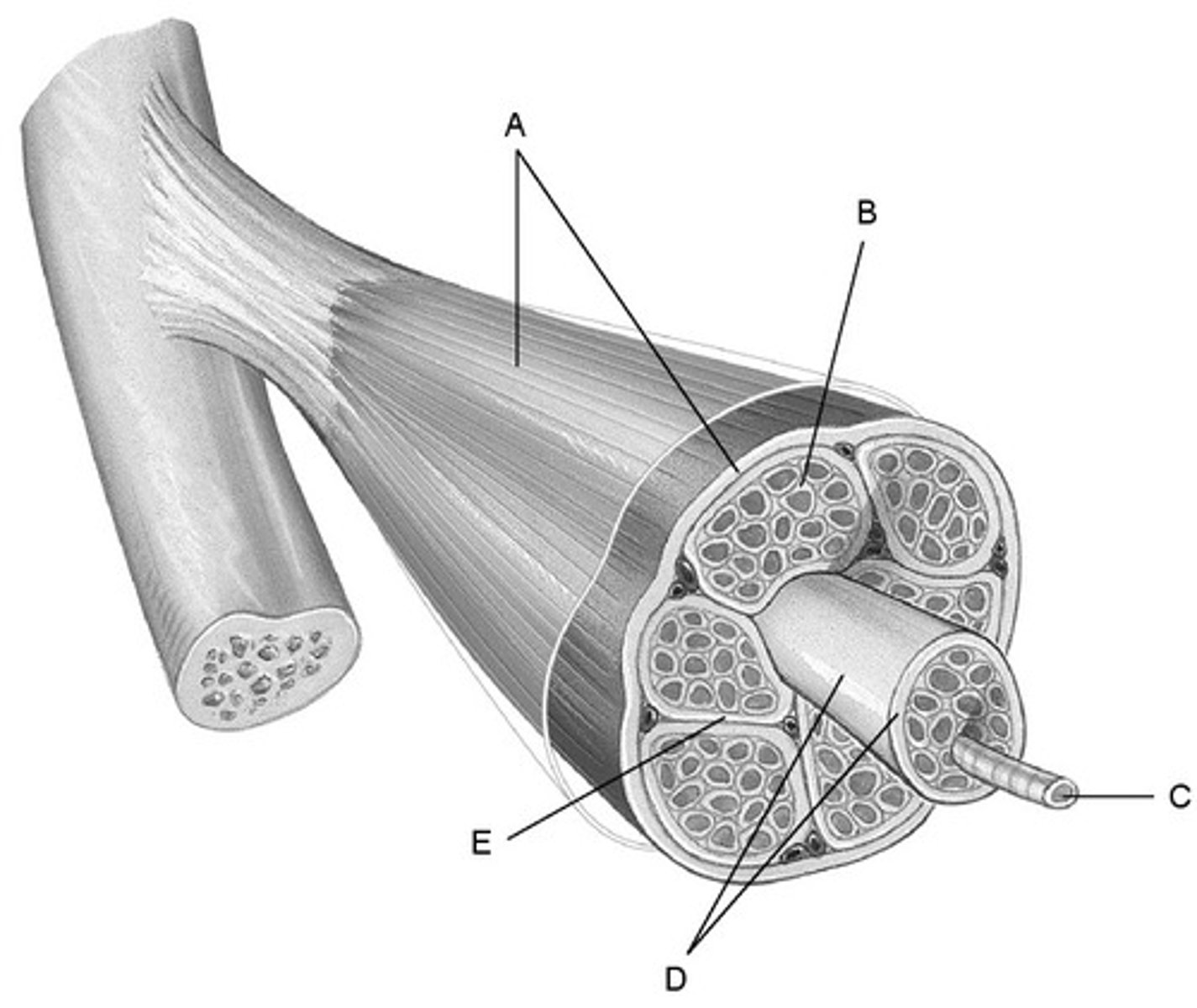
Perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding a fascicle
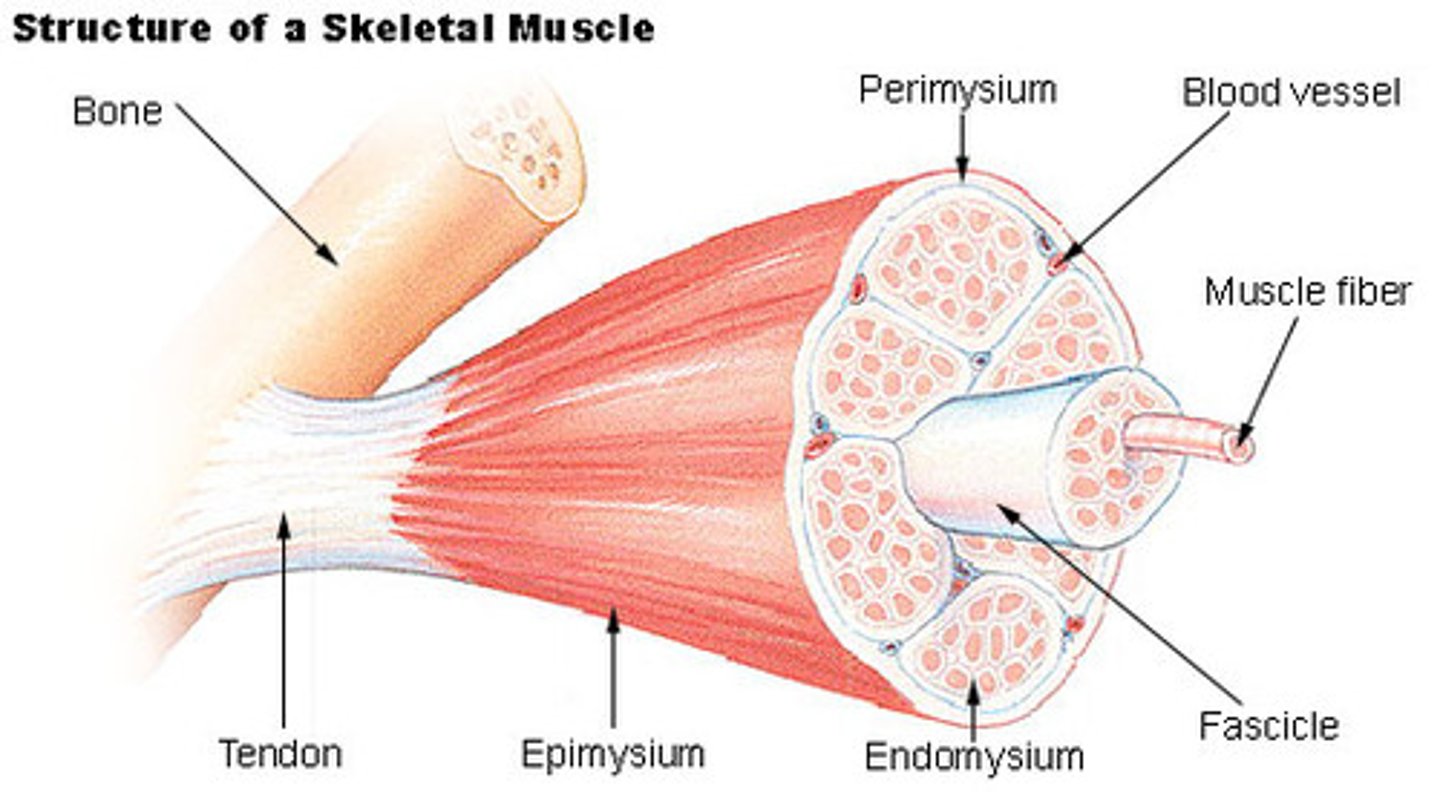
The arrangement of connective tissue layers from most superficial to deepest in a muscle.
the muscular fascia overlays the epimysium which overlays the perimysium which overlays the endomysium.
the general term for connective tissue sheets within the body is ____.
fascia
the cell bodies of motor neurons are located ____.
-in the brain
-in the spinal cord
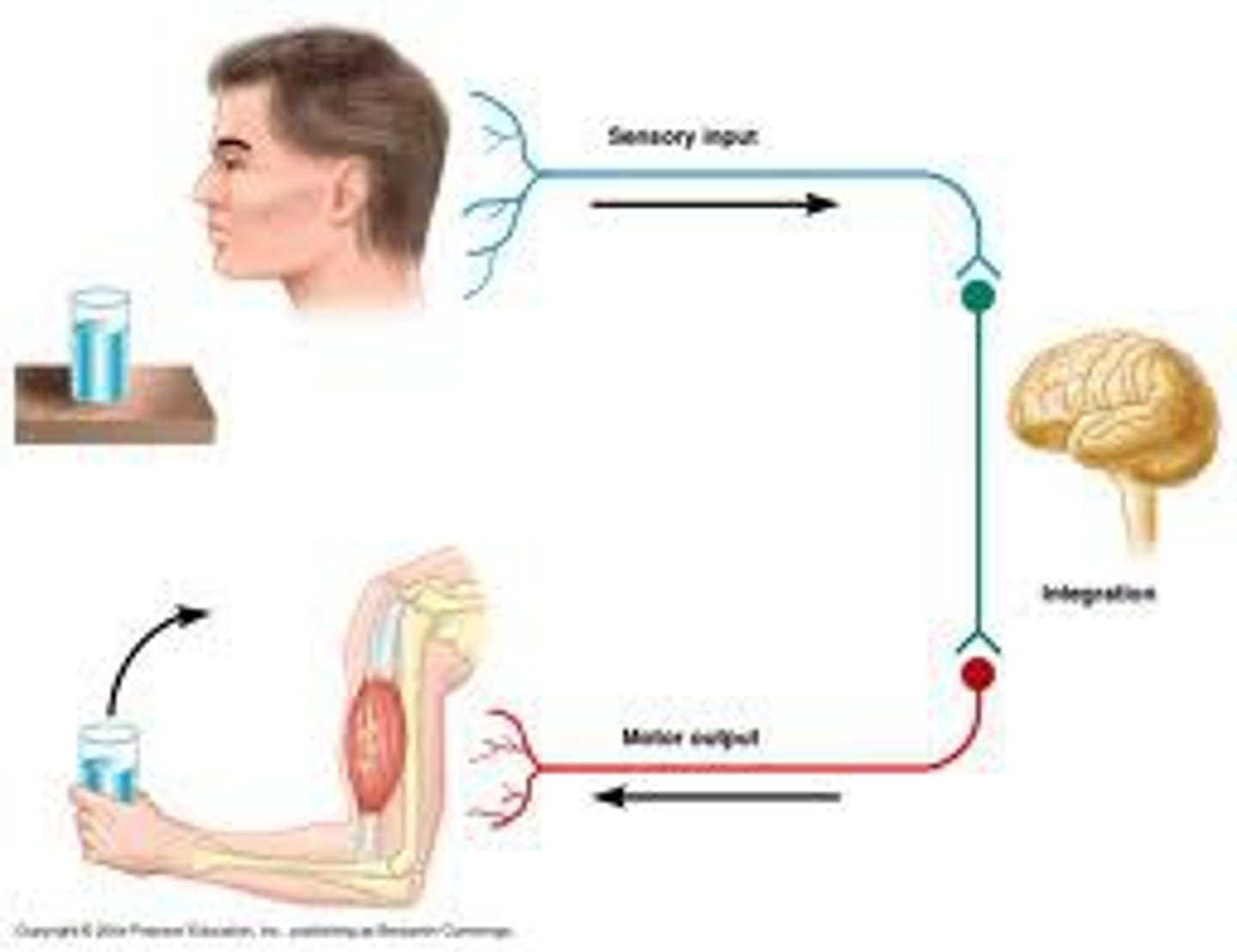
the cell bodies of motor neurons are located in _____ and the axons of the motor neurons extend to ____.
the brain and spinal cord; skeletal muscle fibers
**motor neurons originate in the brain and spinal cord and extend to skeletal muscle fibers through nerves.
specialized nerve cells that stimulate muscles to contract are called ____.
motor neurons
true or false: a whole muscle is usually innervated by more than one nerve.
TRUE
**the contact points between the axons and the muscle fibers, called synapses or neuromuscular junctions, are described later in this section. Each motor neuron innervates MORE THAN ONE muscle fiber. However, more than one motor neuron innervates most whole muscles.
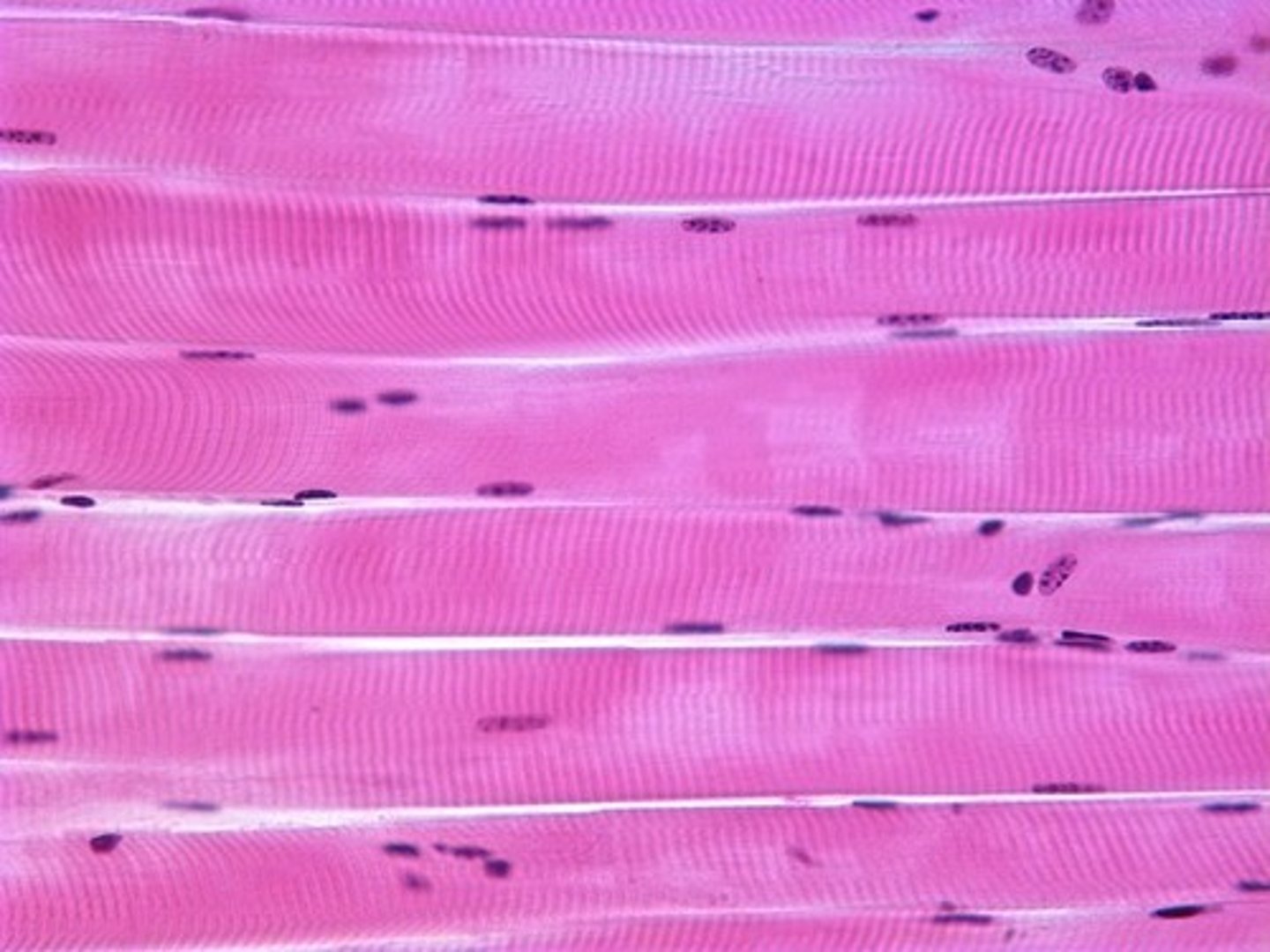
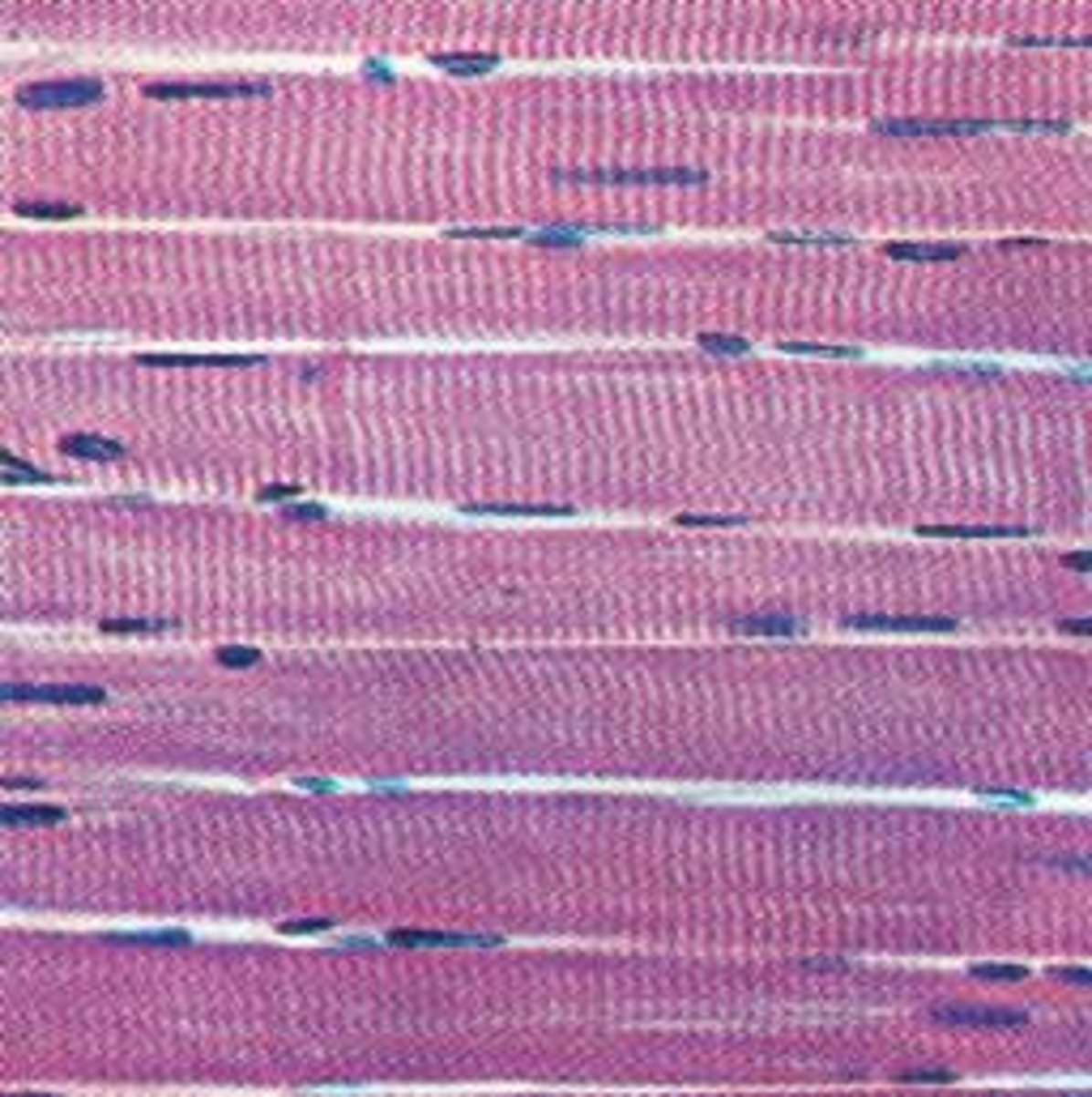
when examined in a longitudinal section, skeletal muscle has alternating light and dark bands producing a _____ appearance.
striated
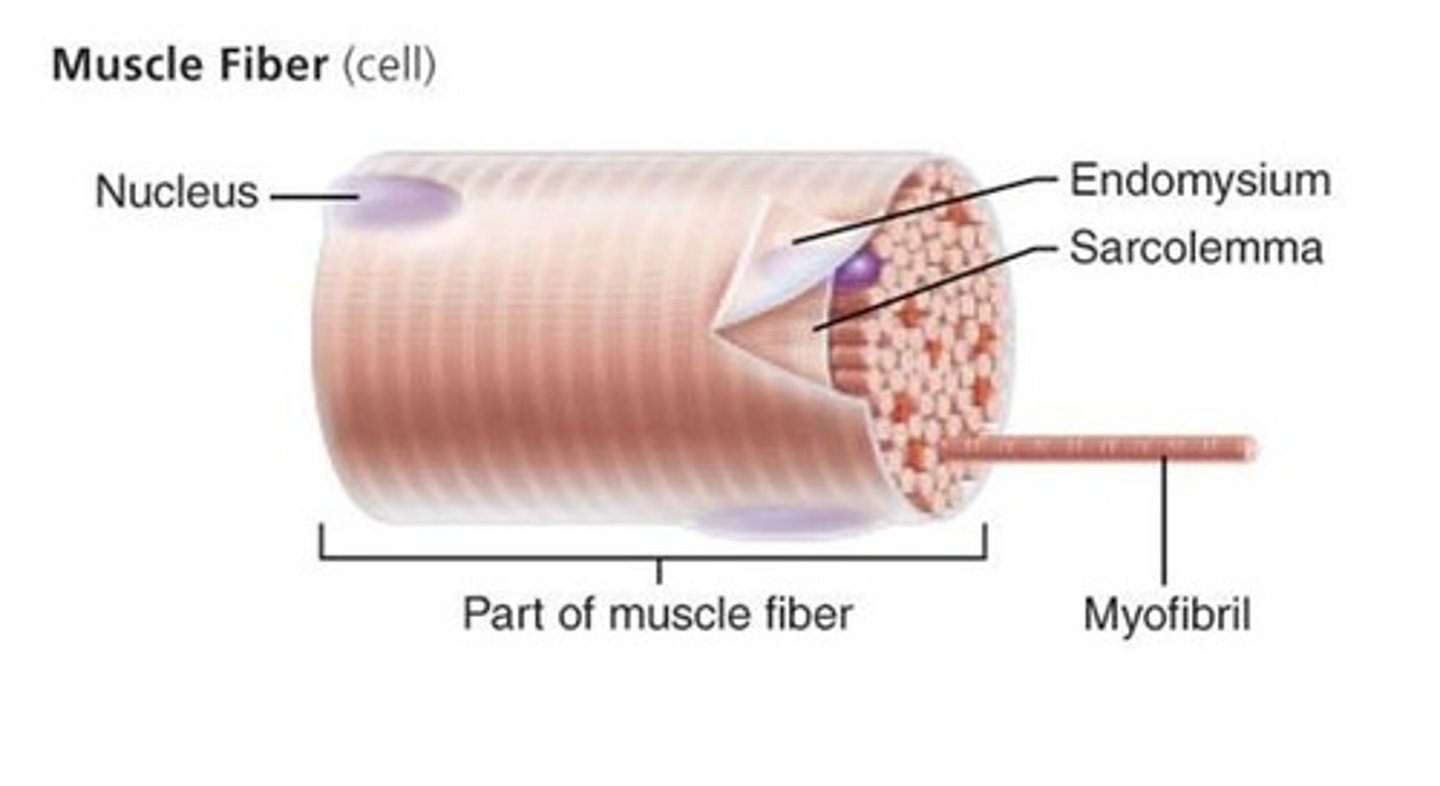
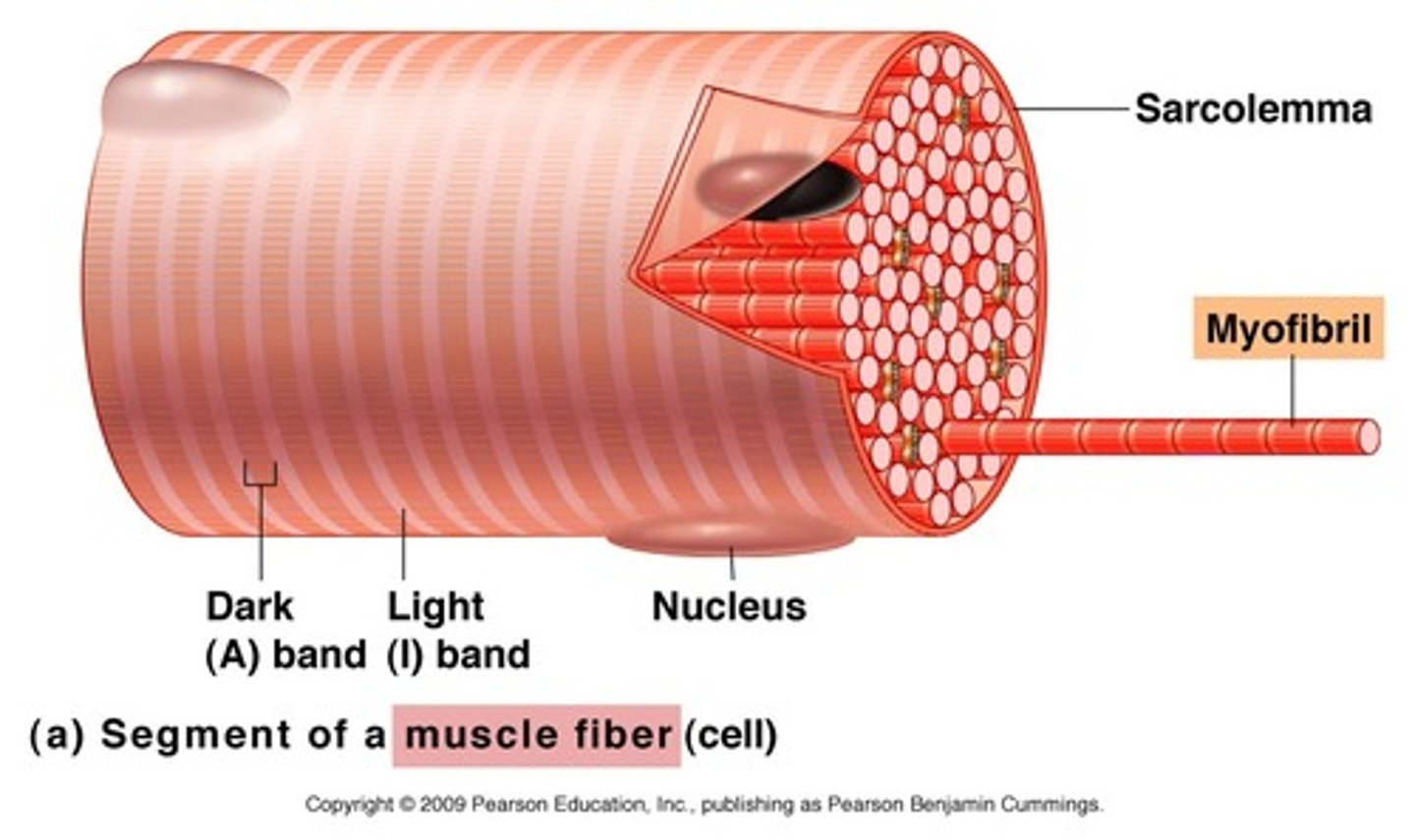
The plasma membrane of a muscle cell is called the ____.
sarcolemma
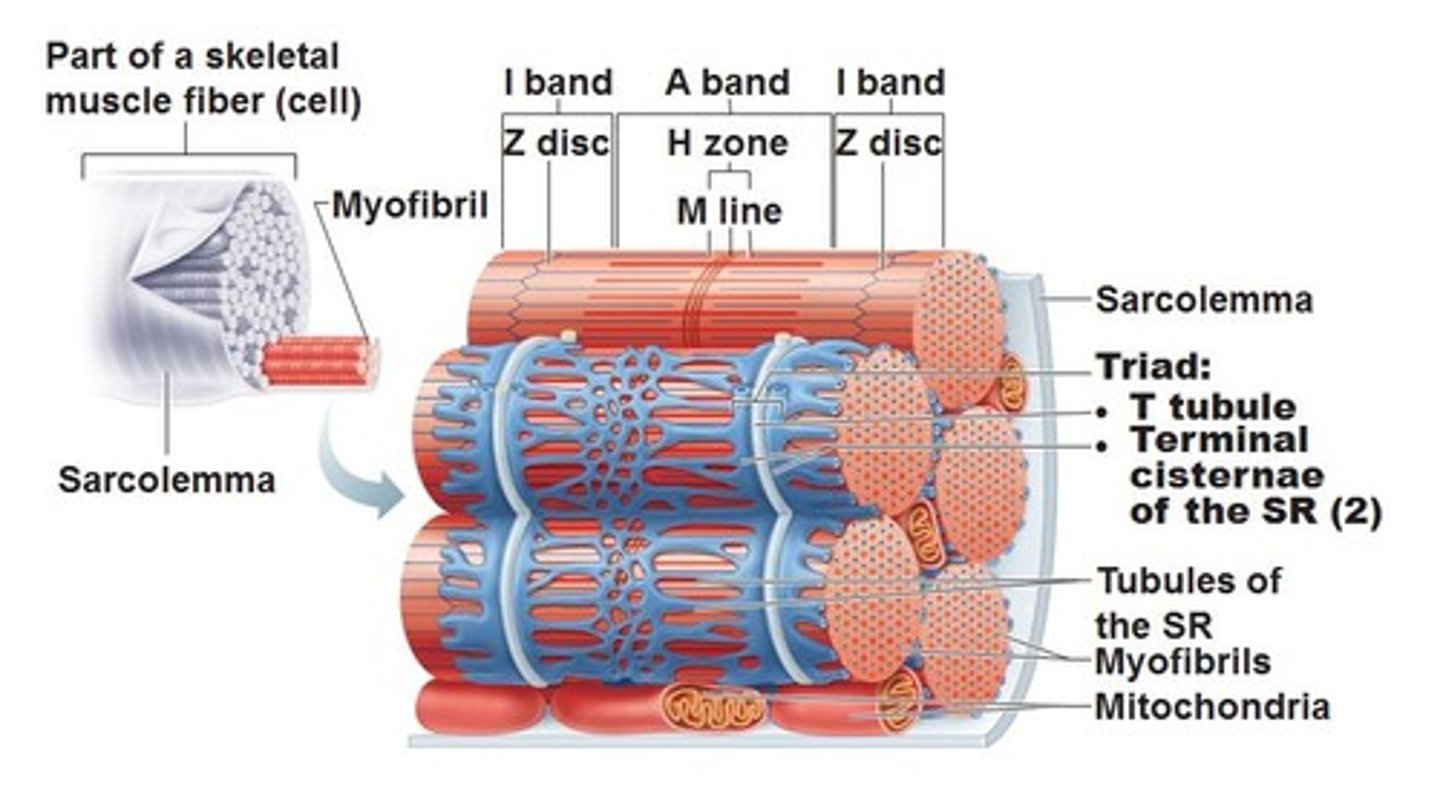
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Organelle of the muscle fiber that stores calcium.
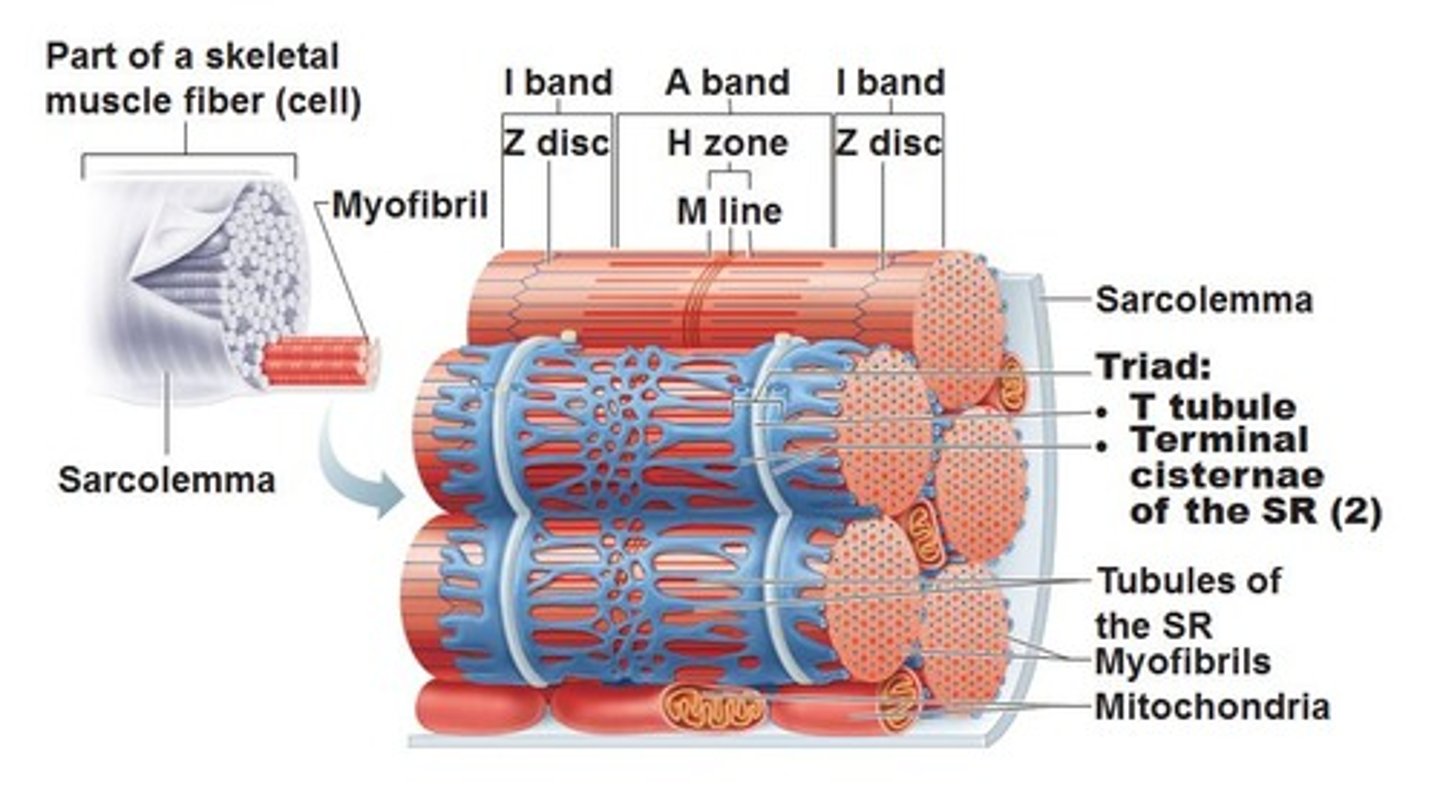
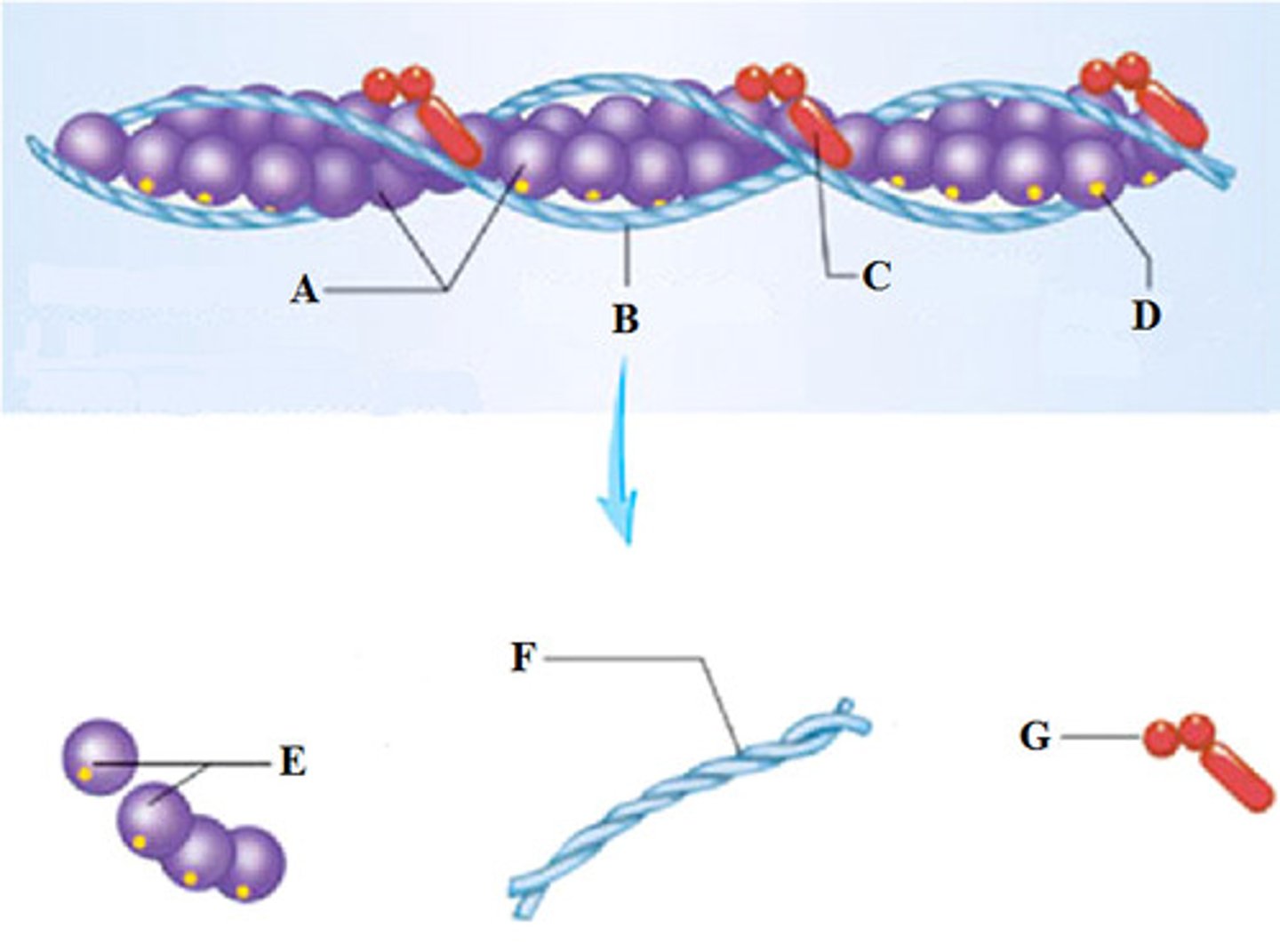
The sarcoplasmic reticulum is indicated by which of the labeled structures (A-D)?
B
The sarcoplasm of a muscle fiber is:
its cytoplasm
each ____ is a threadlike structure, approximately 1-3 micrometers in diameter, that extends from one end of the muscle fiber to the other.
myofibril
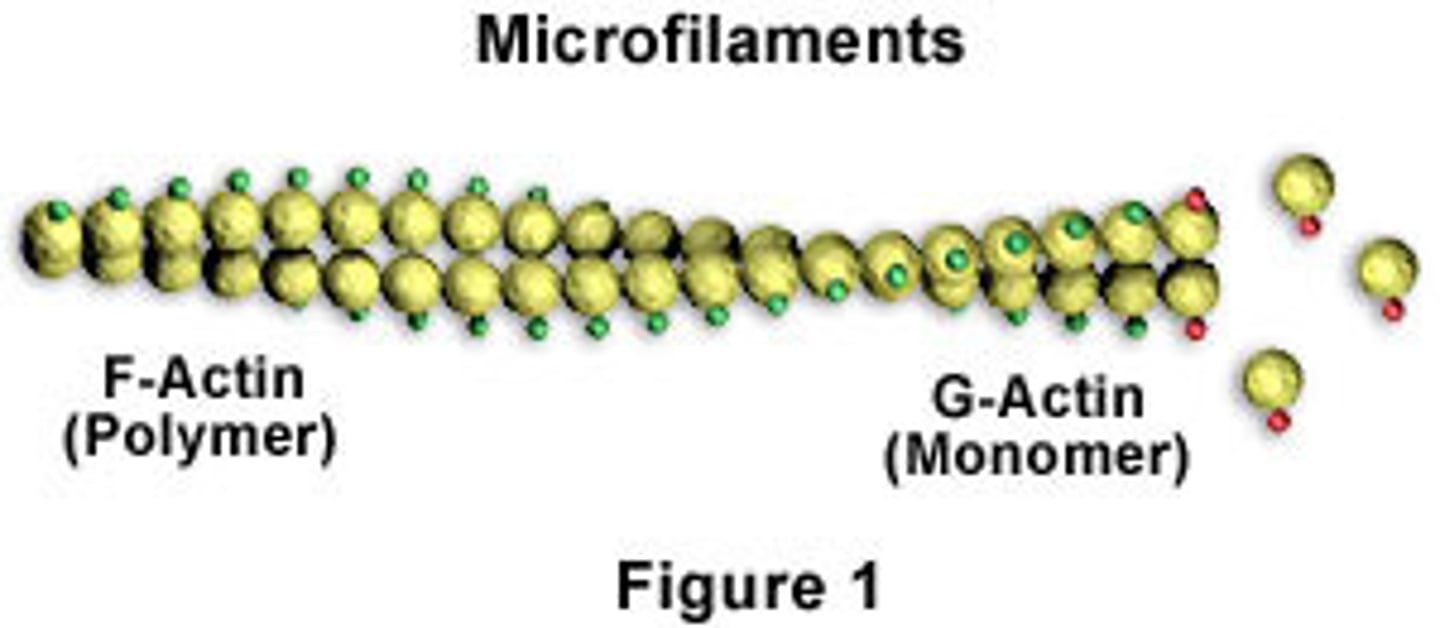
actin myofilament
thin myofilament which resembles two minute strands of pearls twisted together
Sarcomere
Contractile unit of muscle
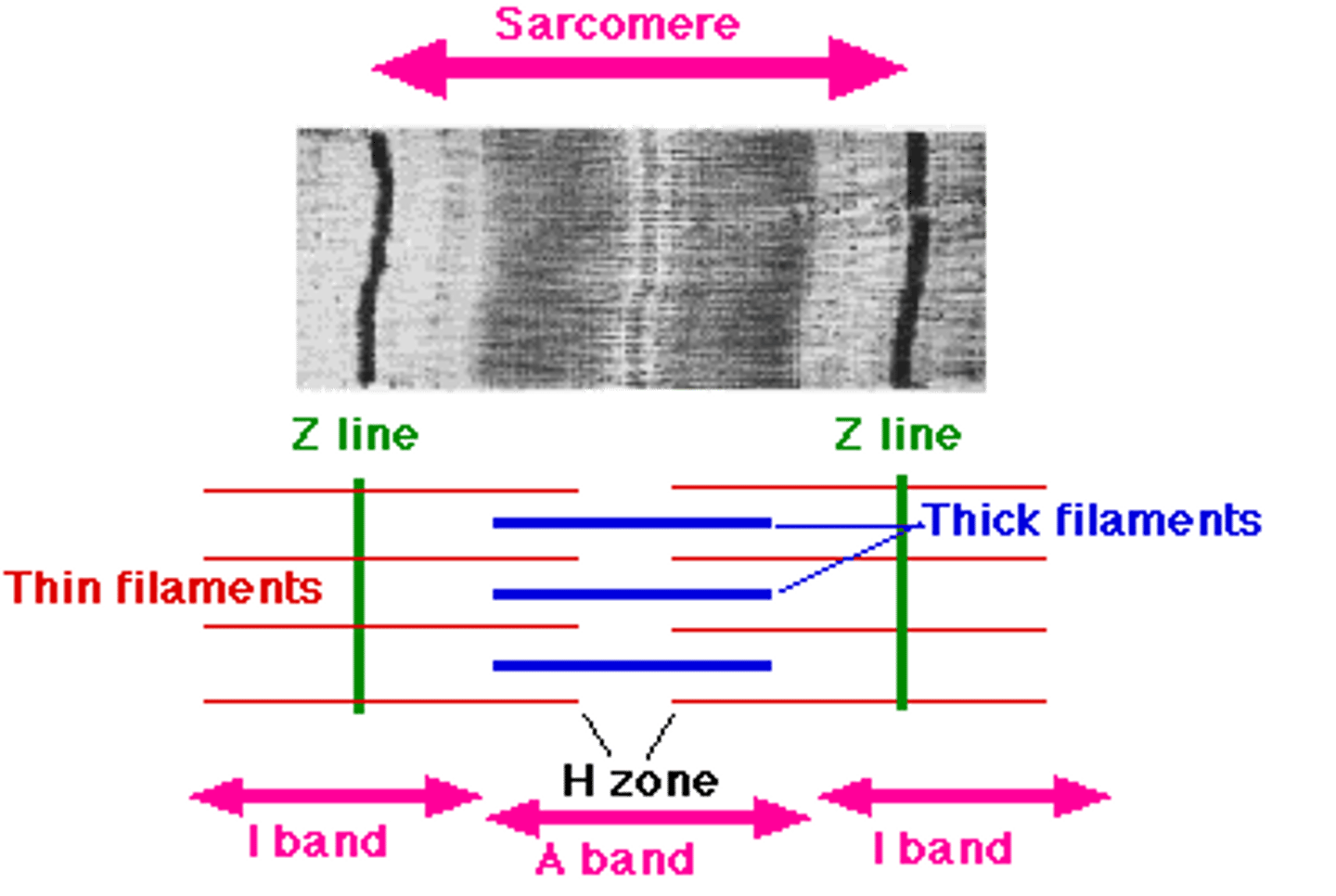
the sarcomere is called the basic functional unit of a muscle fiber because it is the smallest part of the fiber that is capable of ____.
contracting
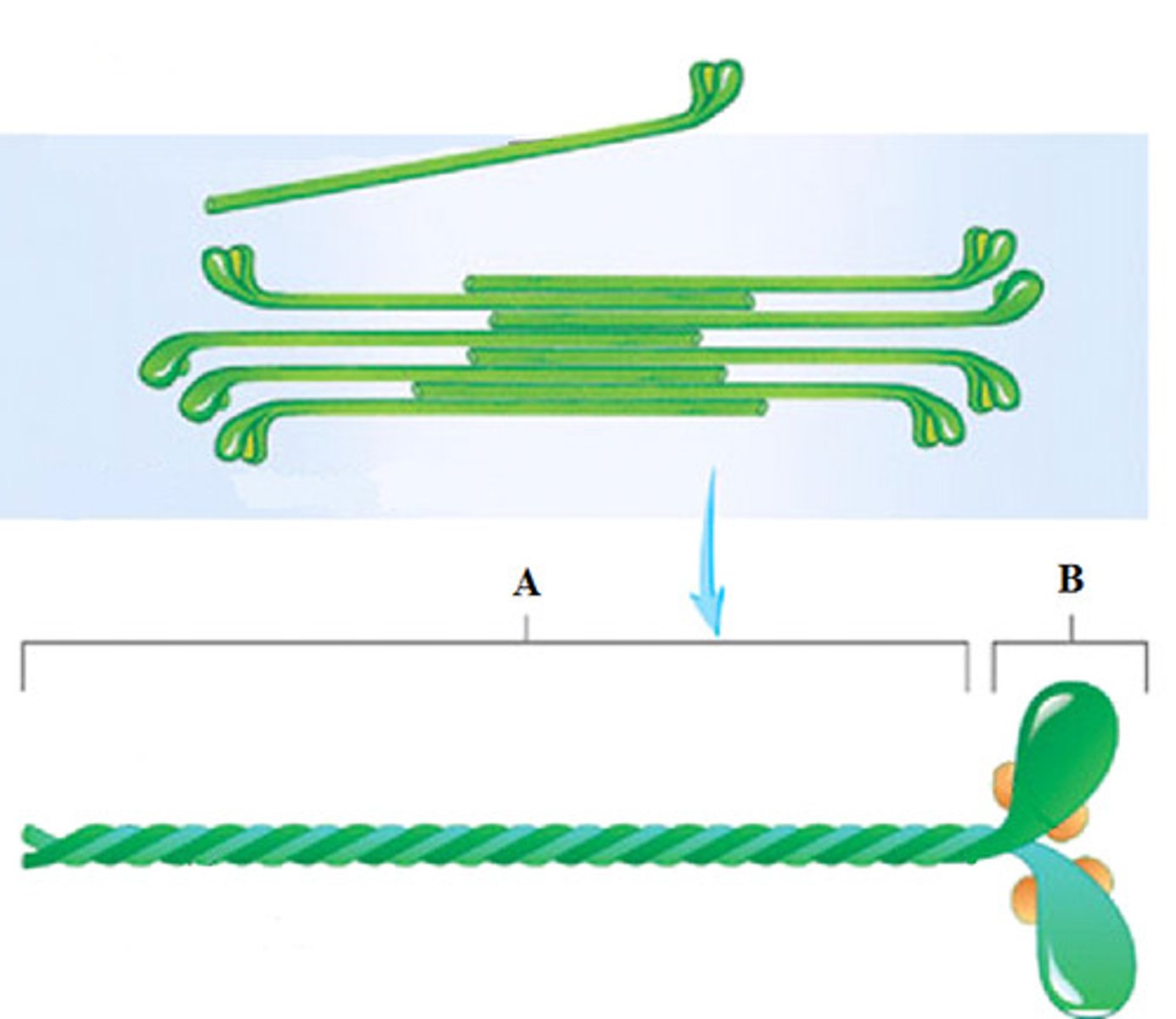
the myofilament composed of many elongated myosin molecules shaped like gold clubs is the _____ myofilament.
-thick
-myosin
each F actin strand is a polymer of approximately 200 small units called ____ actin monomers.
gobular
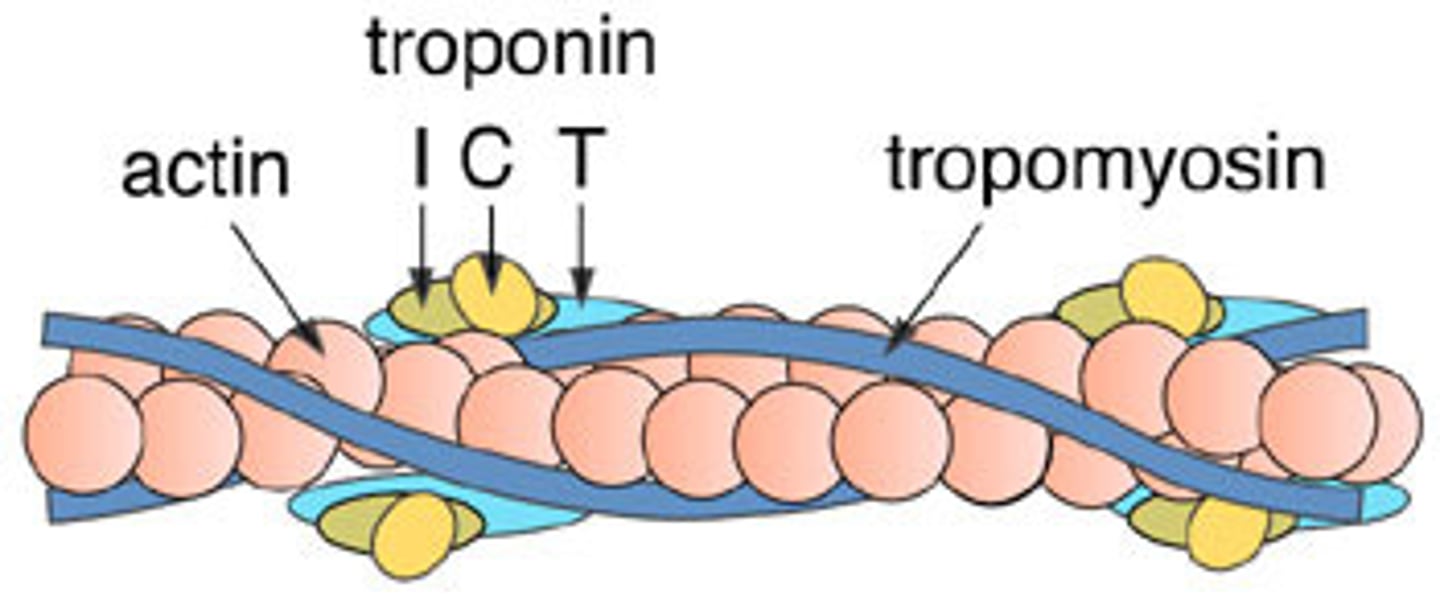
the fibrous protein that winds along the groove of the F actin double helix and blocks the myosin-binding sites on the actin filaments is called ____.
tropomyosin
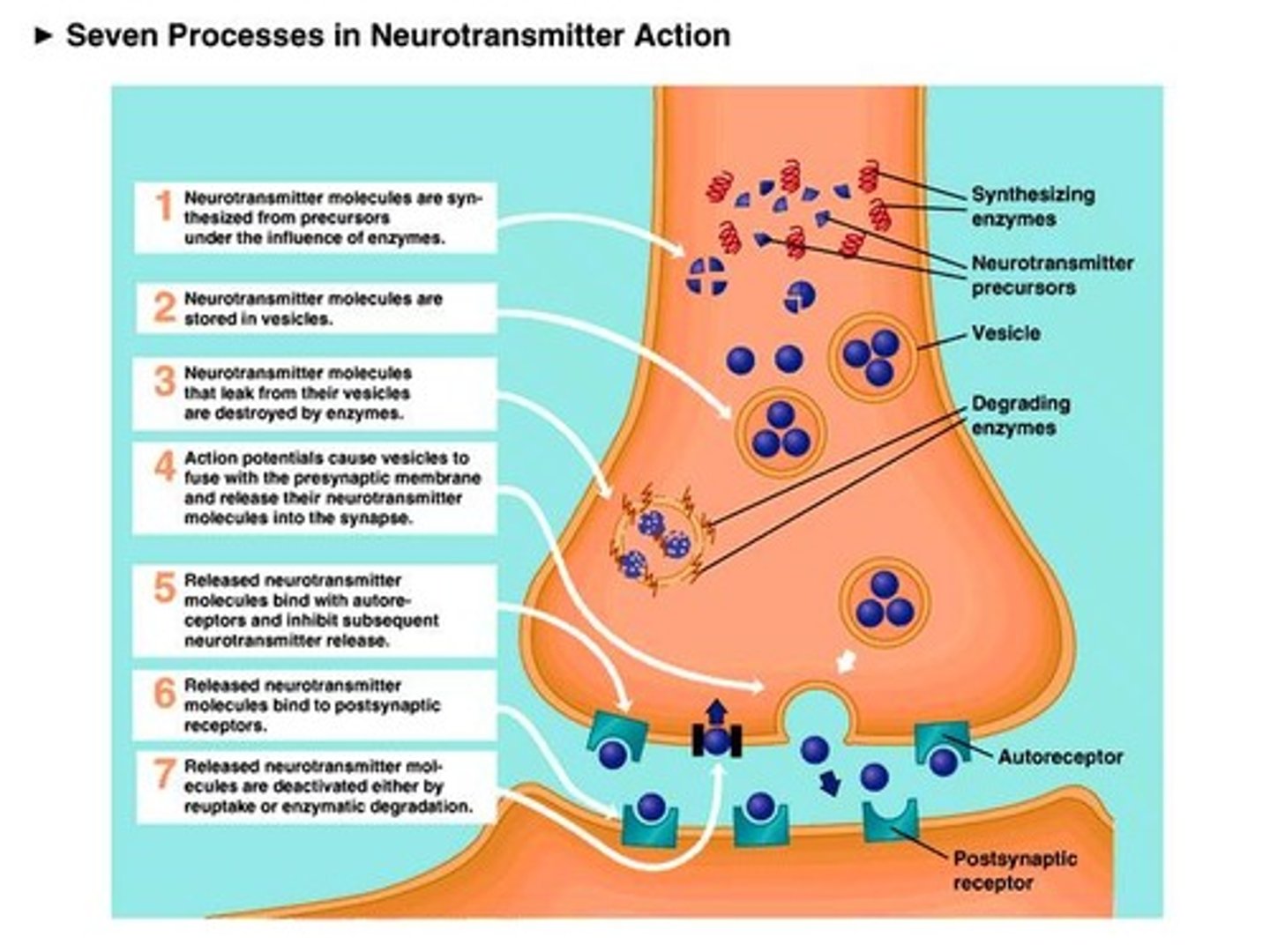
what is the neuromuscular junction?
it is the site where the nerve fiber innervates the muscle fiber
substances that are released from a presynaptic membrane and inhibit or stimulate the activity of an adjacent cell are called ____.
meurotransmitter
what is the synaptic cleft?
space between the presynaptic terminal and myofiber
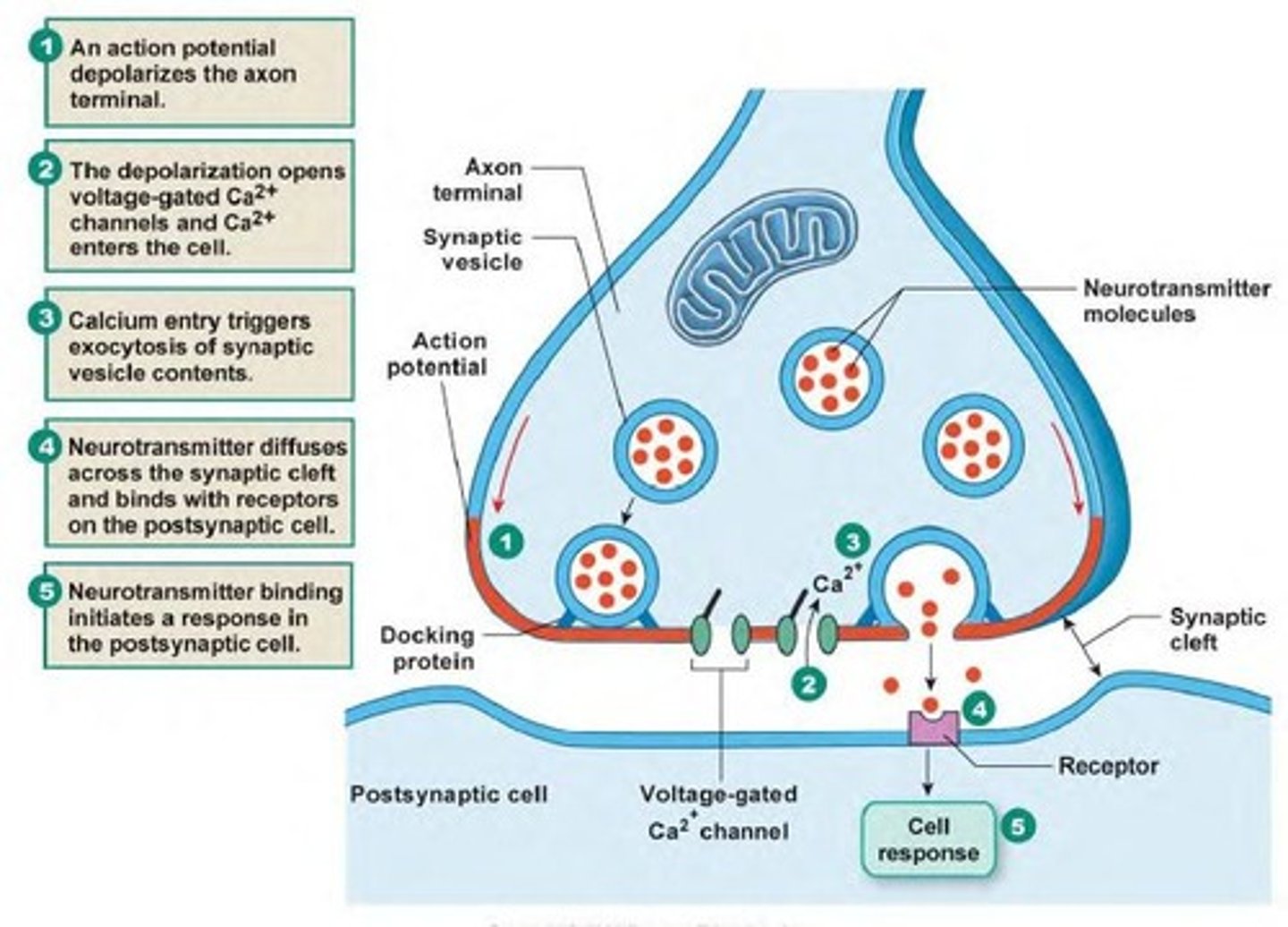
the muscle plasma membrane in the area of the neuromuscular junction is the ____.
-motor end plate
-postsynaptic membrane
the synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic cell of the neuromuscular junction contain:
acetylcholine
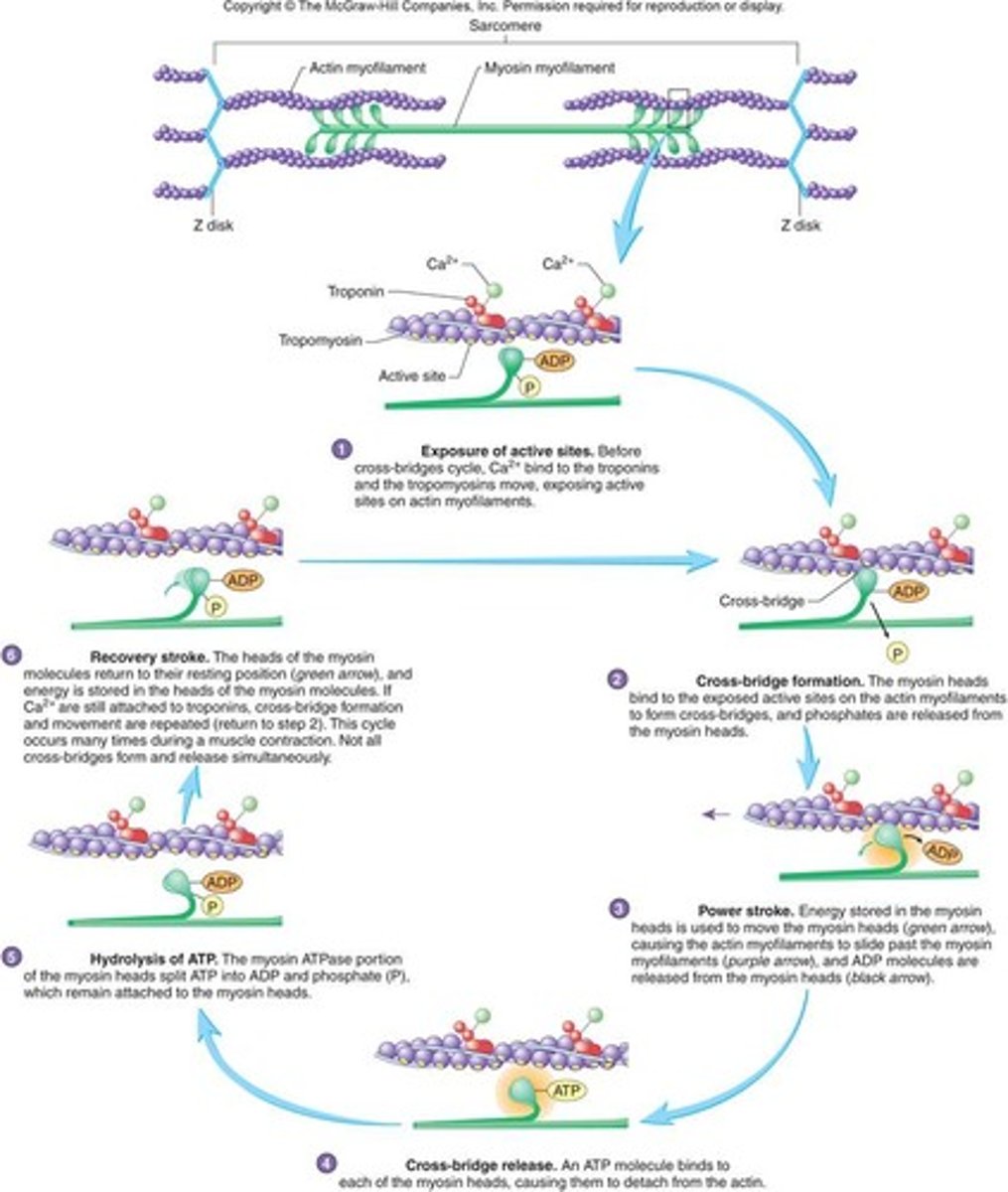
what does the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction predict about myofilaments and sarcomere length?
-during contracting, the thin myofilaments slide past the thick myofilaments
-during contraction, the total length of the sarcomere decreases.
**the primary function of skeletal muscle cells is to generate force by contracting, or shortening. the parallel arrangement of myofilaments in a sarcomere allows them to interact which causes contraction.
during a muscle fiber contraction, which decrease in size?
-entire sarcomere
-H zone
-I band
the charge difference across the plasma membrane in a cell at rest is called the ____ ____ potential.
resting membrane
describe the conditions in which there would be a net movement of Na+ through its ion channel and into the cell.
-if the cytoplasm was very negative (-70mV) white the extracellular fluid was very positive, then sodium ions would flow into the cell.
-if the concentration of Na+ is higher in the extracellular fluid than in the cytoplasm, sodium ions would flow into the cell.
typically the resting potential of a cell is between -70 and -90 mV. This means that the inside of the cell is more _____ than its surrounding environment.
negative
the voltage of a repolarizing neuron or muscle fiber is becoming more ____ with respect to the extracellular fluid around it.
negative
true or false: an action potential occurs in a very small area of the plasma membrane and does not affect the entire plasma membrane at one time.
true
when an action potential propagates, it:
Travels across the plasma membrane by stimulating the production of another action potential
Both fast twitch and slow twitch muscle fibers can increase in ______ as a result of exercise and training.
strength
efficiency
capacity
size
true or false: when muscles aren't used for a period of time they will atrophy
true
the rapid skeletal muscle contractions that produce shaking in response to reduced body temperature is called:
shivering
the energy required to produce ATP comes from
aerobic respiration
creatine phosphate
anaerobic respiration
the mechanism of atp production that requires oxygen is
aerobic respiration
does aerobic respiration produce more or less atp molecules per unit of glucose than anaerobic respiration?
more
list the end products of aerobic respiration
ATP
water
carbon dioxide
muscle fiber fatigue results from
calcium ion imbalances as ATP levels drop
fatigue can develop at three sites including
the muscle fiber
the central nervous system
the neuromuscular junction
the perimysium is ____.
a thick connective tissue layer around each fasciculus
myoblasts are
the precursors of muscle fibers
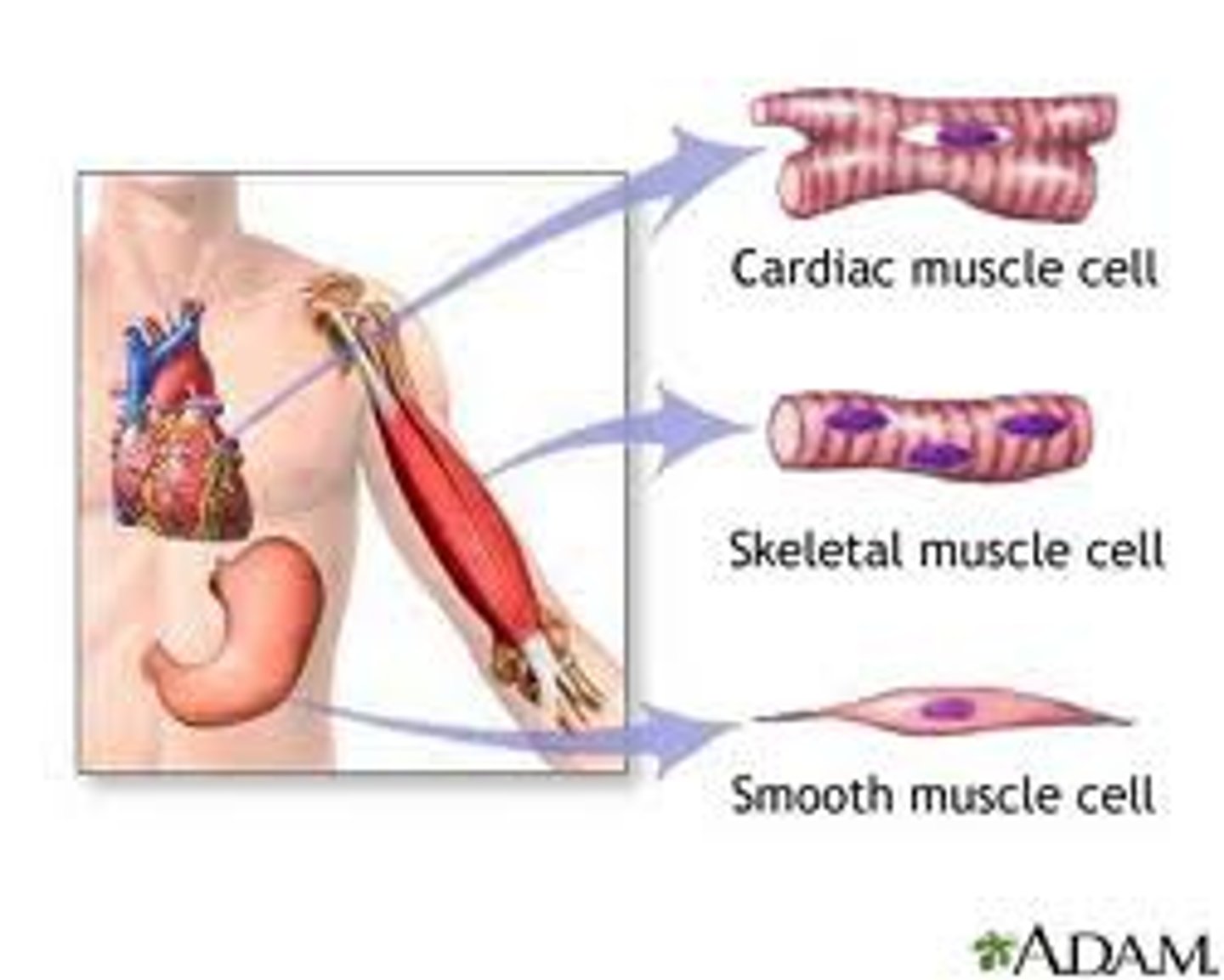
The types of muscle tissue
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
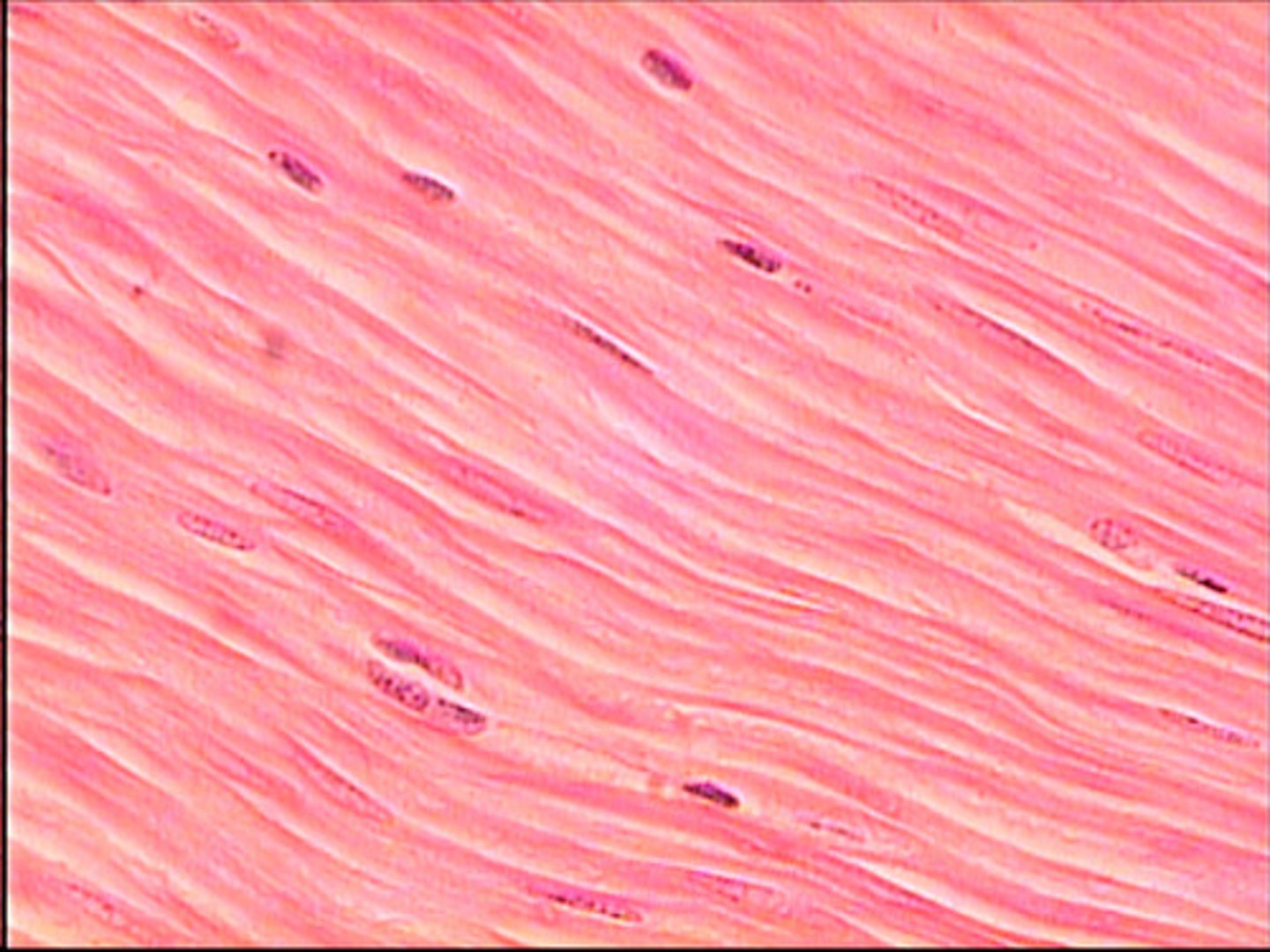
type of muscle tissue that is not striated and involuntary
smooth muscle tissue
protein channels connecting adjacent cardiac muscle cells which allow action potentials to pass from cell to cell are called _____
gap junctions
skeletal muscle is responsible for
locomotion, facial expressions, posture, respiratory functions and many other body movements
Comparison of muscle types (table 9.2, pg. 268)
skeletal muscle:
-attached to bones
-very long cylindrical cells
-multiple nuclei; peripherally located
-no special cell-to-cell attachments
-striated
-voluntary and involuntary (reflexes)
-function is body movement
-not capable of spontaneous contraction
smooth muscle:
-located in walls of hollow organs, blood vessels, eyes, glands, and skin
-spindle-shaped cells
-nucleus is single and centrally located
-gap junctions join some visceral smooth muscle cells together
-not striated
-involuntary
-function to move food through digestive tract, empty urinary bladder, regulate blood vessel diameter, change pupil size, contract many gland ducts, moves hair, and has many other functions
-some smooth muscle is capable of spontaneous contraction
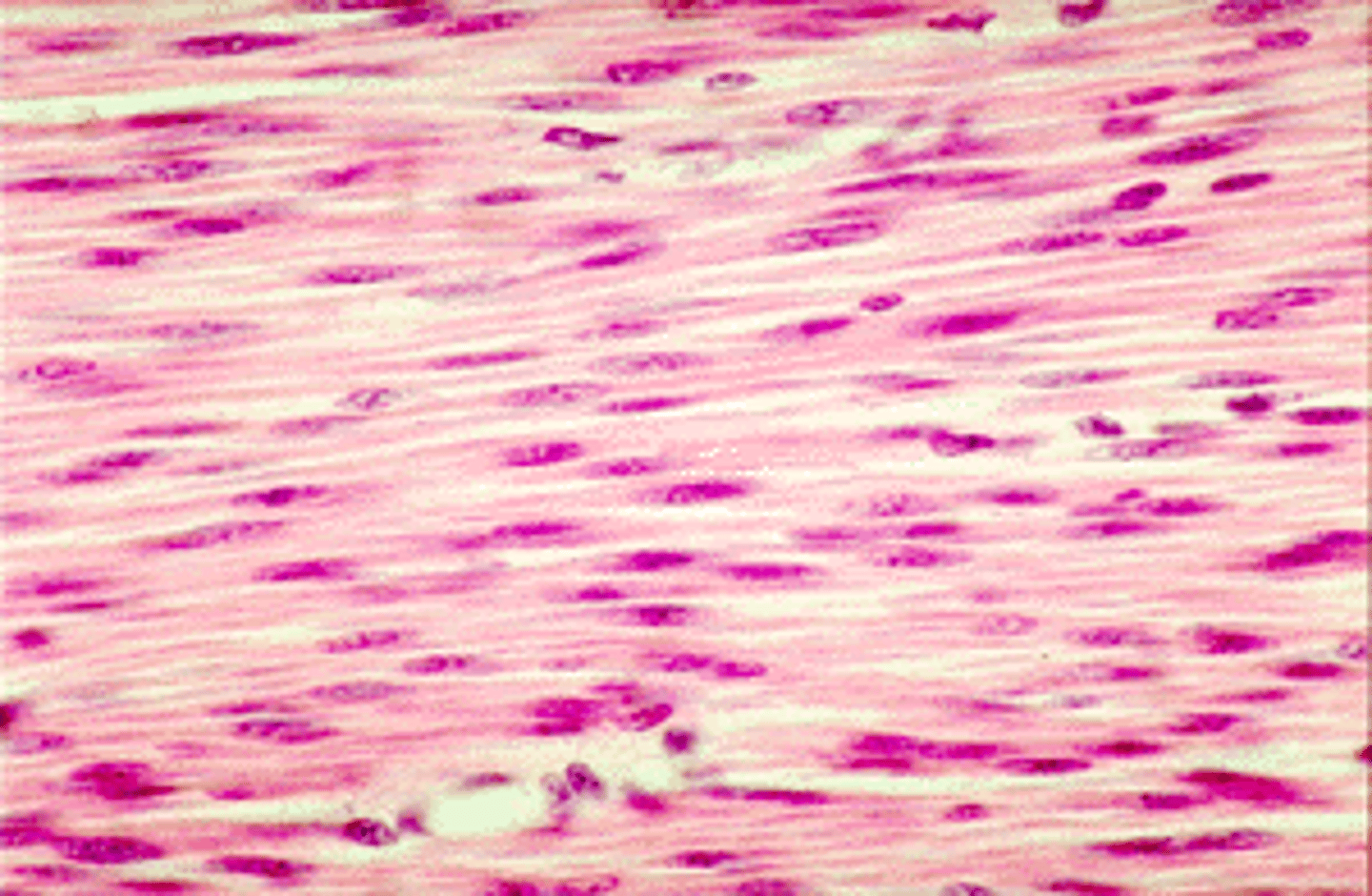
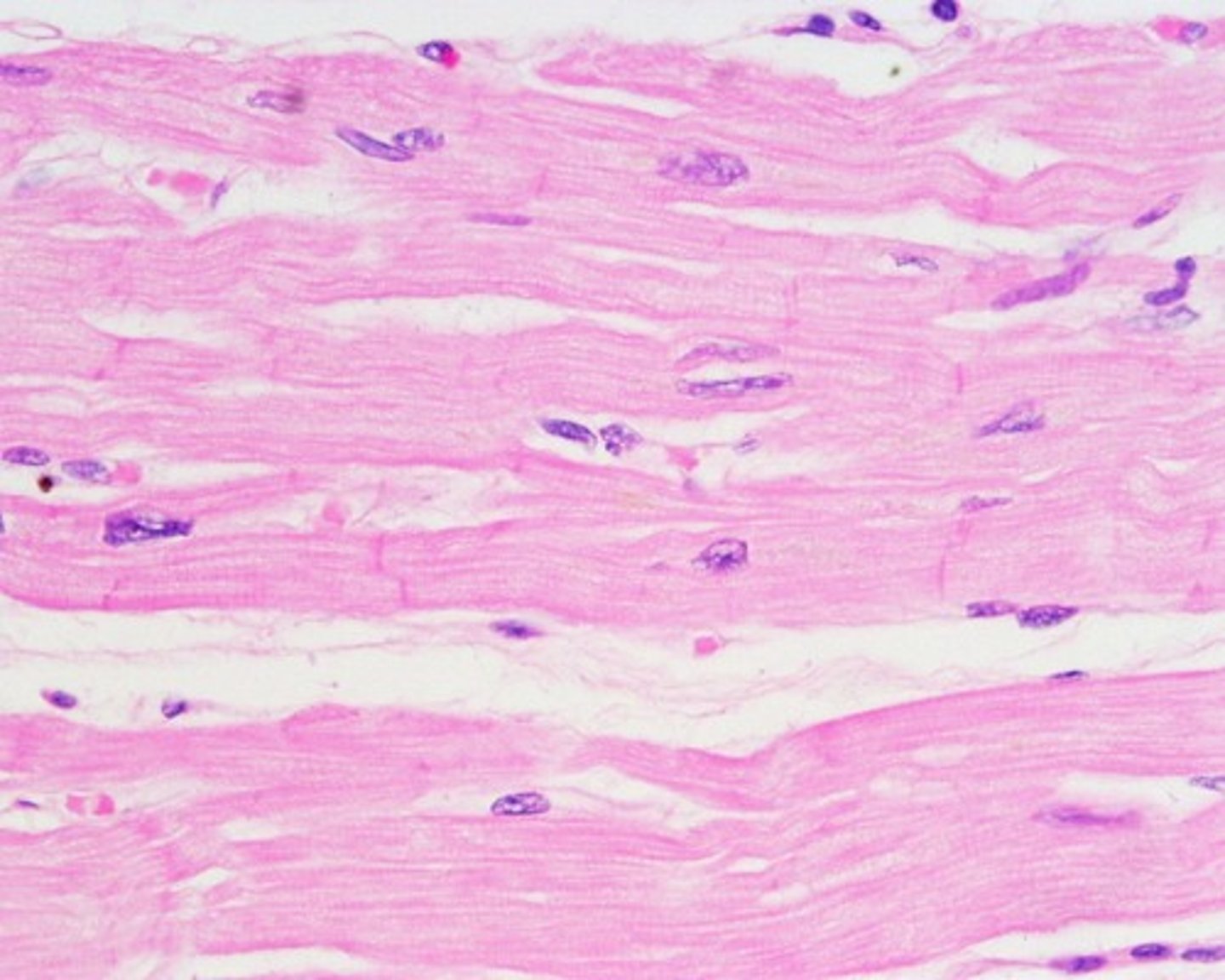
cardiac muscle:
-located in the heart
-cylindrical and branched cells
-nucleus is single and centrally located
-special cell-to-cell attachments: intercalated discs join cells to one another
-striated
-involuntary
-functions to pump blood; contractions provide the major force for propelling blood through blood vessels
-capable of spontaneous contraction
Perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding a fascicle
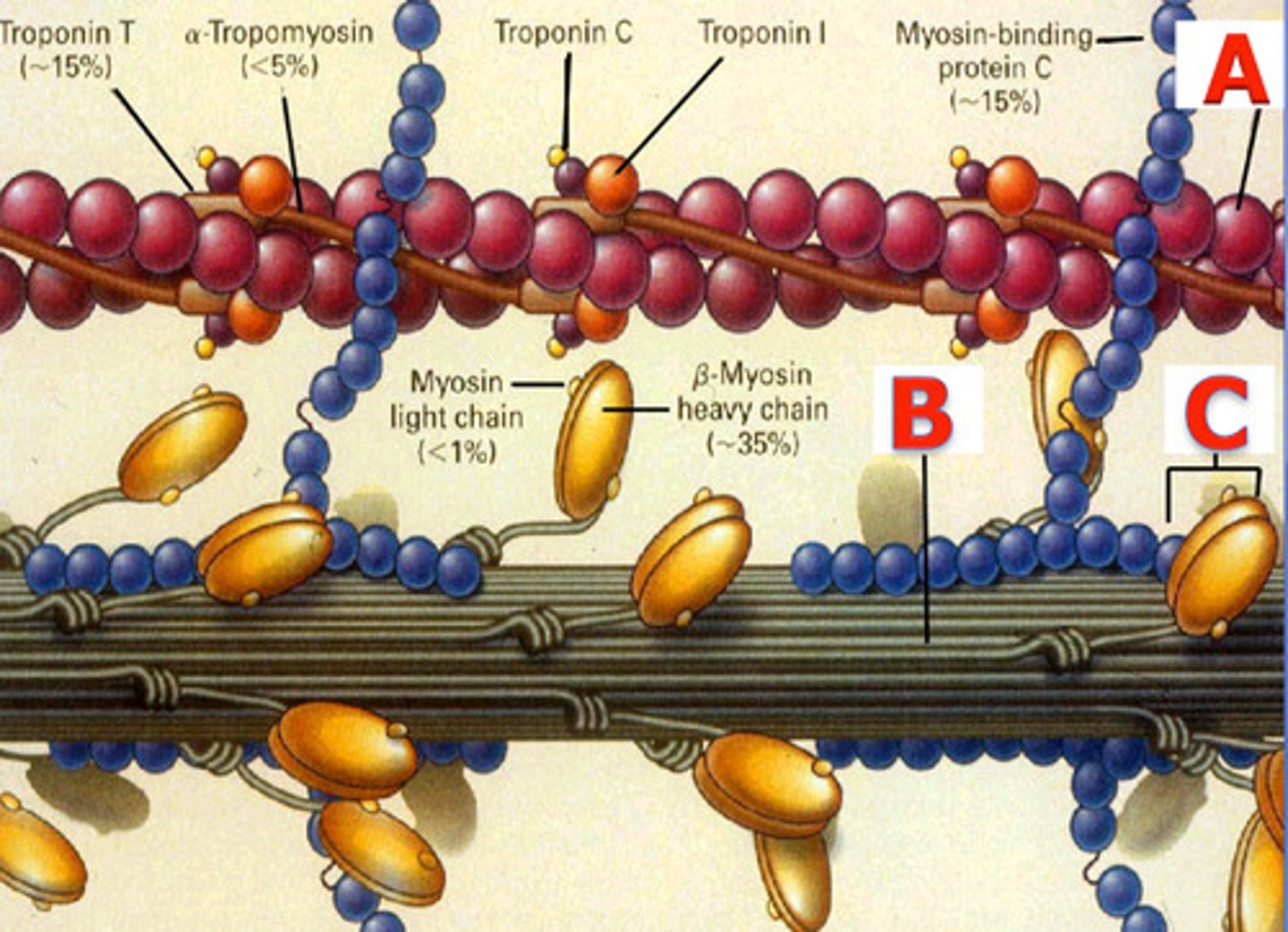
a skeletal muscle myofilament
contains either actin or myosin proteins
actin myofilaments - thin
myosin myofilaments - thick
arranged in highly ordered units called sarcomeres which join end to end to form the myofibrils
each f actin strand is a polymer of approximately 200 small units called ____ monomers
globular (G) actin monomers
substances that are released from a presynaptic membrane and inhibit or stimulate the activity of an adjacent cell are called _____.
neurotransmitters.
describe the conditions in which there would be a net movement of Na+ through its ion channel and into the cell
- if the concentration of Na+ is higher in the extracellular fluid than in the cytoplasm, sodium ions would flow into the cell
- if the cytoplasm was very negative (-70mV) while the extracellular fluid was very positive, then sodium ions would flow into the cell.
sodium (Na+) is more abundant in which fluid compartment?
outside the plasma membrane
list the characteristics of the sodium-potassium ion pump
Answer:
- pumps sodium out of the cell against its concentration gradient
- pumps potassium along its concentration gradient
- uses ATP
Note: in a resting cell, the sodium potassium pump transports K+ from the outside of the cell to the inside and transports the Na+ from inside the cell to the outside.
a negative membrane potential indicated that the area with a more negative charge is on the ____ of the membrane.
inside
note: the potential difference is reported as a negative number because the inner surface of the plasma membrane is negative compared with the outside.
the voltage-gated ion channels in the sarcolemma are ___ until it is stimulated by a motor neuron
closed
the method of atp production that can produce up to 36 atp molecules for each glucose molecule is
aerobic respiration
in regards to atp production which is more efficient
aerobic respiration is more efficient than anaerobic respiration
during rest condition the energy from aerobic respiration is used to produce
creatine phosphate
creatine phosphate is used to store energy that can be used to synthesize
ATP (adenine triphosphate)
Fatigue is a temporary state of reduced work capacity. Muscle fiber fatigue results from:
Acidosis and ATP depletion due to either an increased ATP consumption or a decreased ATP production
Oxidative stress, which is characterized by the build-up of excess reactive oxygen species (ROS; free radicals)
Local inflammatory reactions
answer: calcium ion imbalances as atp levels drop
psychological fatigue
involved the central nervous system
occurs when the muscle are capable of functioning but the individual perceives that additional muscular work is not possible
the perimysium is
a thick connective tissue layer around each fasciculus
Transverse tubules (T-tubules)
Transmit action potential through cell
Allow entire muscle fiber to contract simultaneously
Have same properties as sarcolemma
the purple fibrous structures are called
actin myofilaments
Myosin myofilament
thick myofilaments which resemble bundles of golf clubs
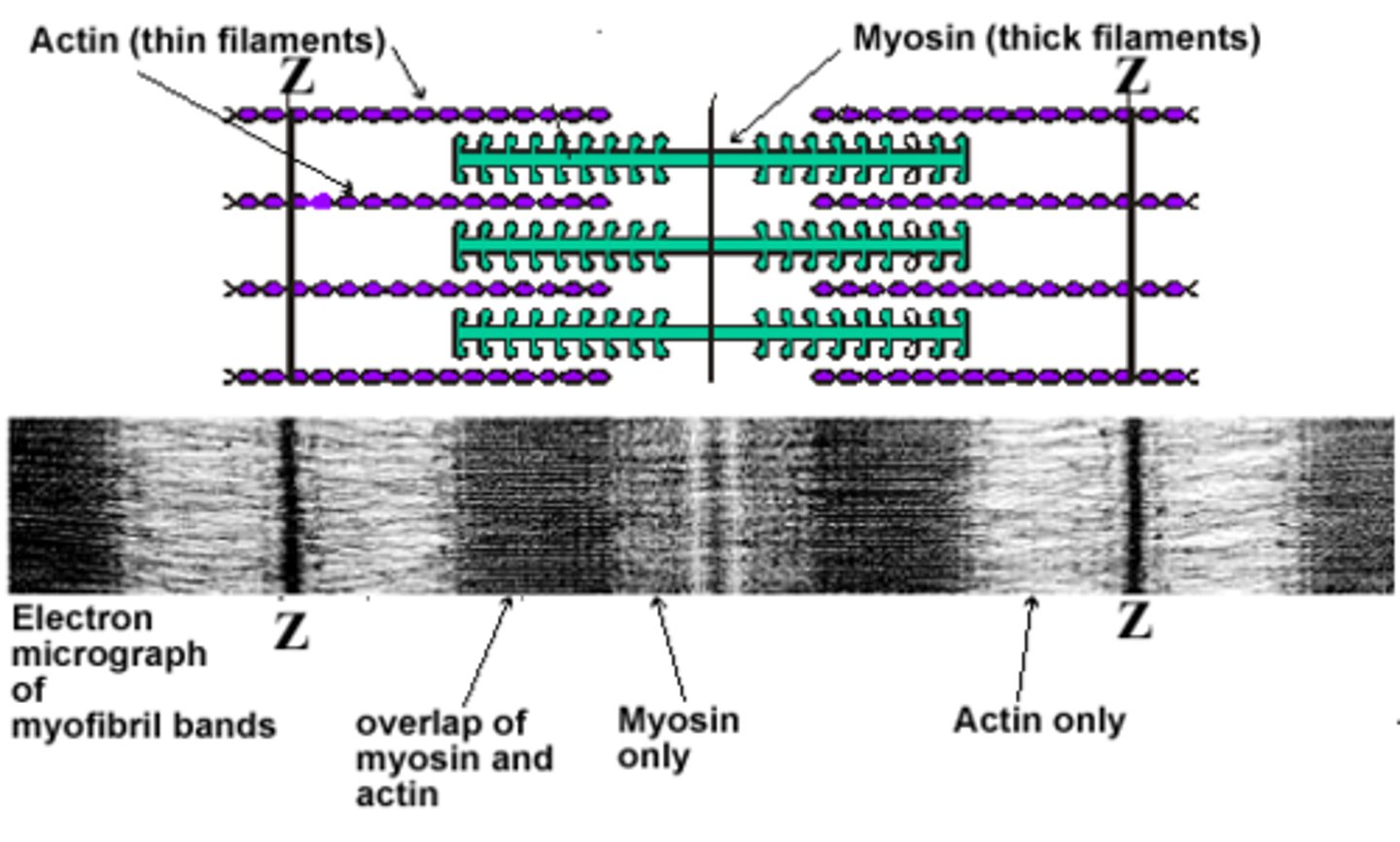
each ___ includes a Z disk and extends from each side of the z disk to the ends of the myosin myofilaments
isotropic band or I band
sarcomere lengthening involves
an external force applied to a muscle by other muscle or by gravity
the recoil of the elastic elements of the cell
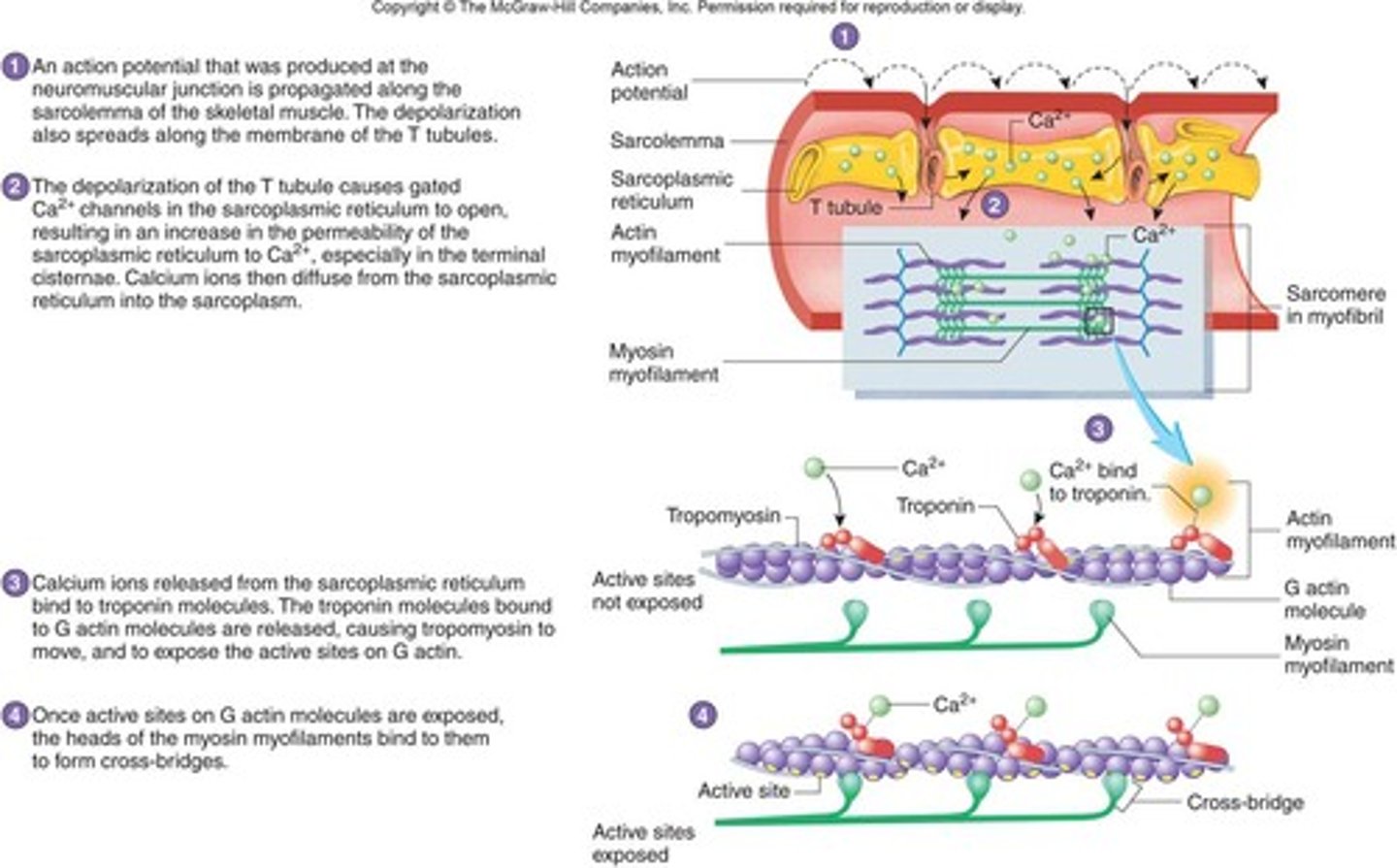
in order for the excitation-contraction coupling to occur, the production of an action potential must occur within the _____ of a muscle fiber
sarcolemma
what triggers the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
the depolarization of the adjacent transverse tubule
the role of calcium ions in muscle fiber contraction
cause the movement of tropomyosin
binds to troponin, freeing up the myosin binding actin site on the thin myofilament
cross bridge cycling
Answer:
-power stroke
-cross-bridge formation
-recovery stroke
-cross-bridge release
Note:
-Myosin head attaches to actin binding site, forming cross-bridge
-Myosin cross-bridge pulls thin filament toward center of sarcomere
-ADP and phosphate are released from myosin
-New ATP binds to myosin
-Linkage between actin and myosin cross-bridge break
-ATP splits
-Myosin cross-bridge goes back to original position
describe cross bridges and what conditions are needed for their formation
can only form when the myosin head is cocked or energized
they can only form when calcium is present in the sarcoplasm
they form when myosin binds to its active site of actin
functions of the muscular system
body movement
maintenance and posture
respiration
production of body heat
communication
constriction or organs and vessels
heart beat
properties of muscle
contractility- ability of a muscle to shorten with force
excitability- capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus
extensibility- muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond to a limited degree
elasticity- ability of muscle to recoil to original resting length after stretched.
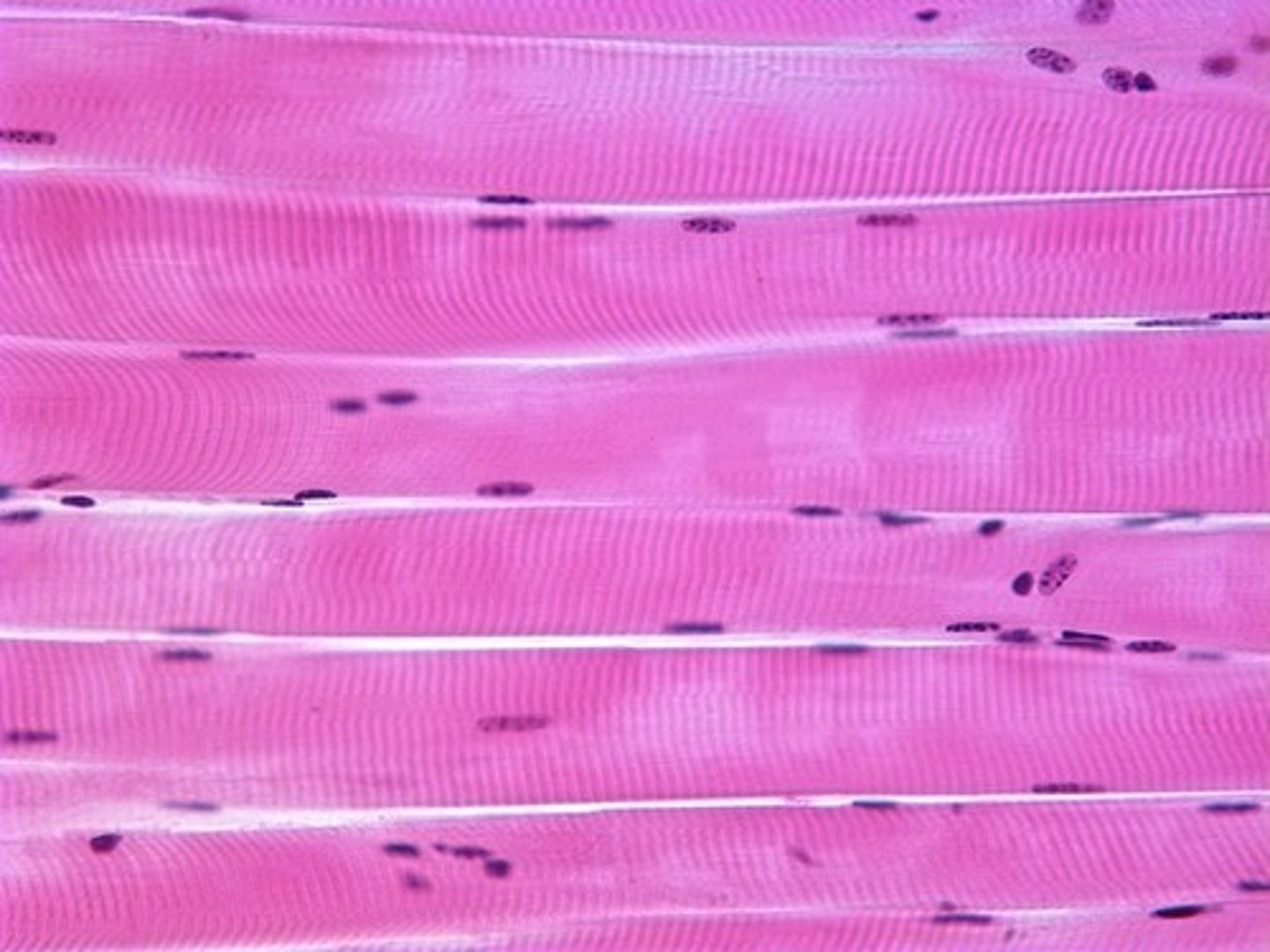
skeletal muscle
Attached to bones
Nuclei multiple and peripherally located
Striated, Voluntary and involuntary (reflexes)
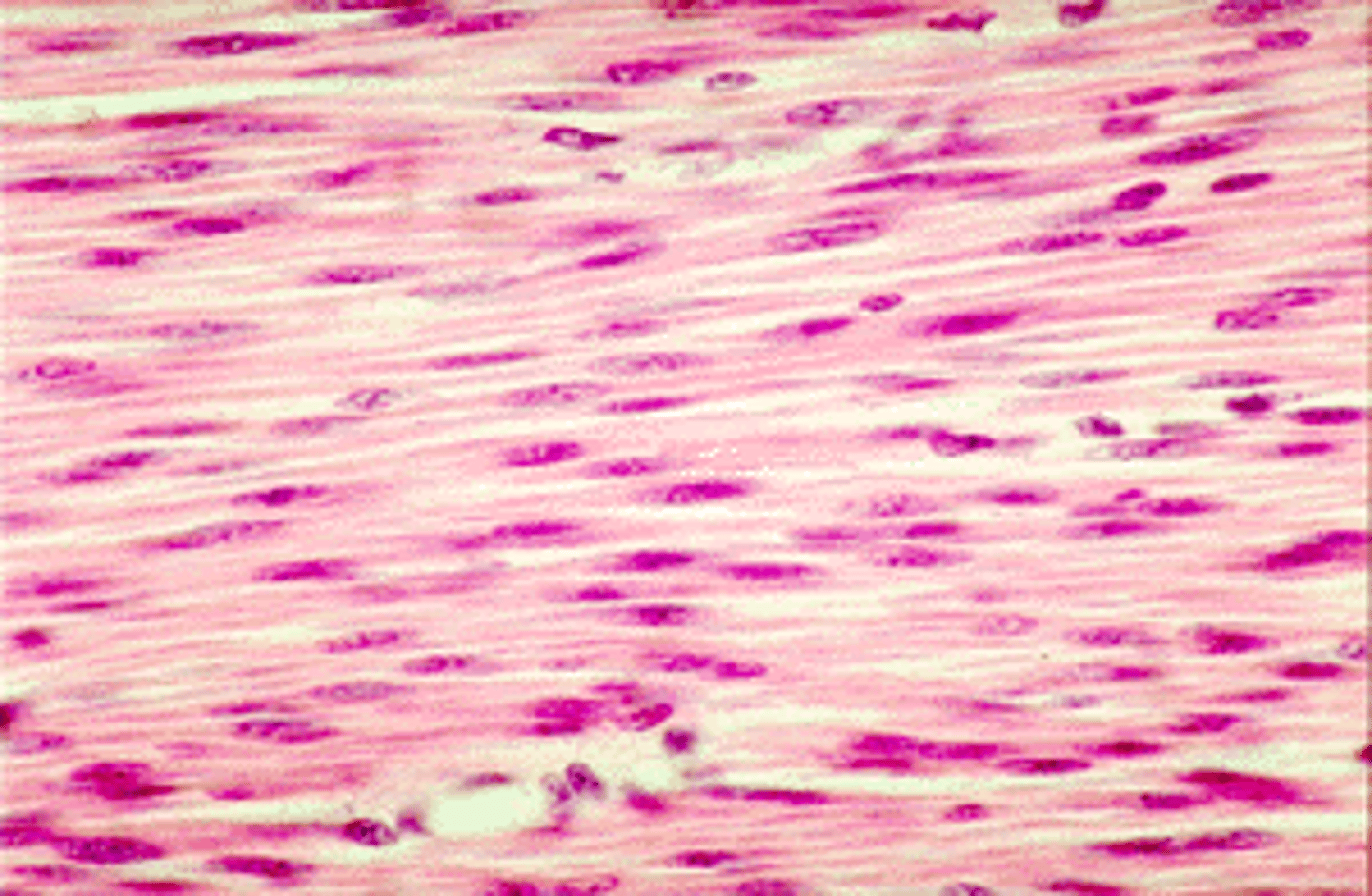
smooth muscle
Walls of hollow organs, blood vessels, eye, glands, skin
Single nucleus centrally located
Not striated, involuntary, gap junctions in visceral smooth
cardiac muscle
Heart
Single nucleus centrally located
Striations, involuntary, intercalated disks
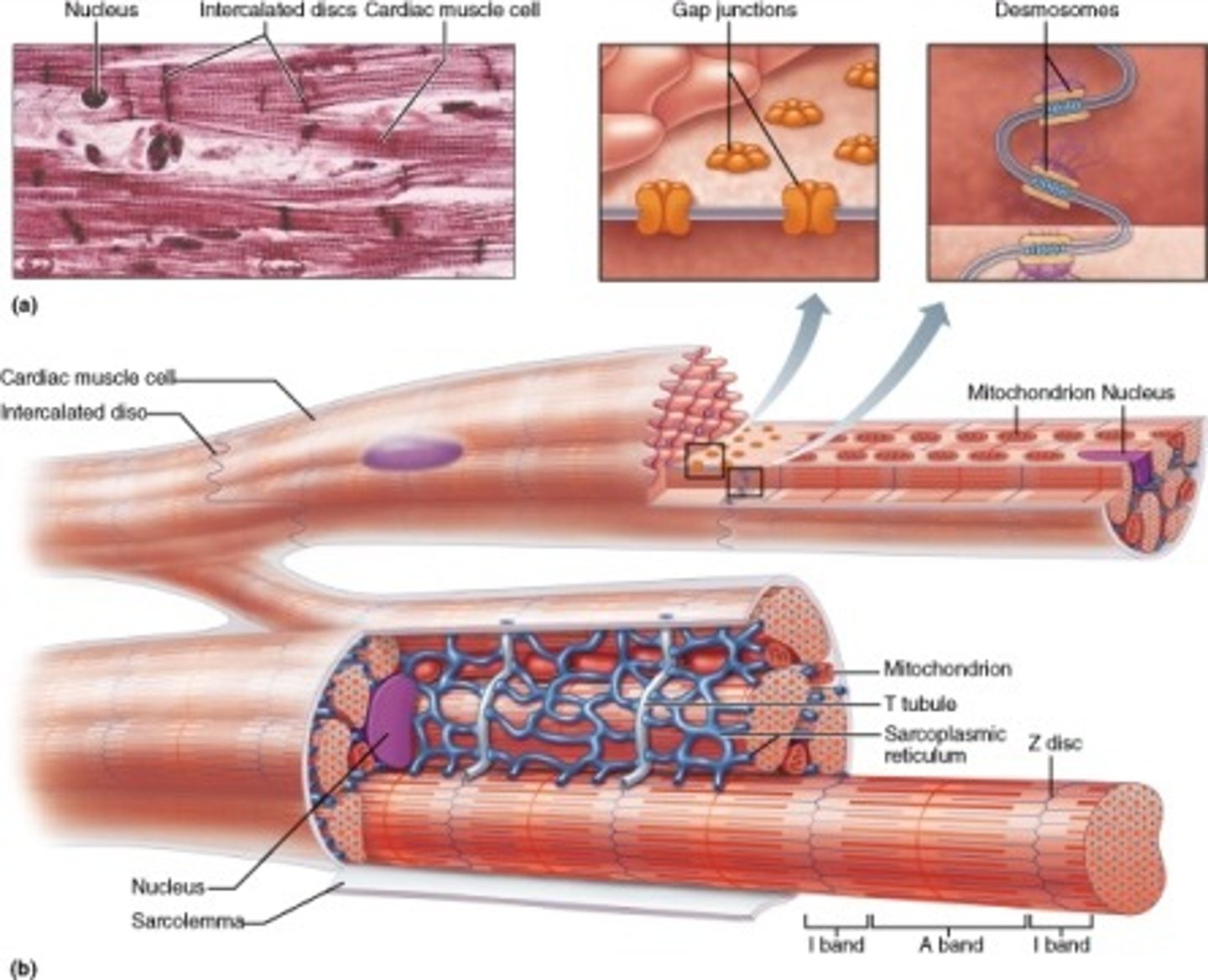
Skeletal Muscle Structure
Muscle fibers or cells
--Develop from myoblasts
--Numbers remain constant
Connective tissue
Nerve and blood vessels

Tendons
Attach muscles to bones
Aponeurosis: A very broad tendon
Muscles
Origin or head: Muscle end attached to more stationary of two bones
Insertion: Muscle end attached to bone with greatest movement
Belly: Largest portion of the muscle between origin and insertion
Synergists: Muscles that work together to cause a movement
Parts of a Muscle
Sarcolemma- Cell Membrane of muscle fiber
Sarcoplasm- cytoplasm of muscle cell
Mitochondria- many nuclei
Sarcomeres- contractile unit b/n z lines
--Contain thick & thin myofilaments
Actin- (thin); 2 strands twisted together
Myosin- (thick); made of protein
Structure of Actin and Myosin
Components of Sarcomeres
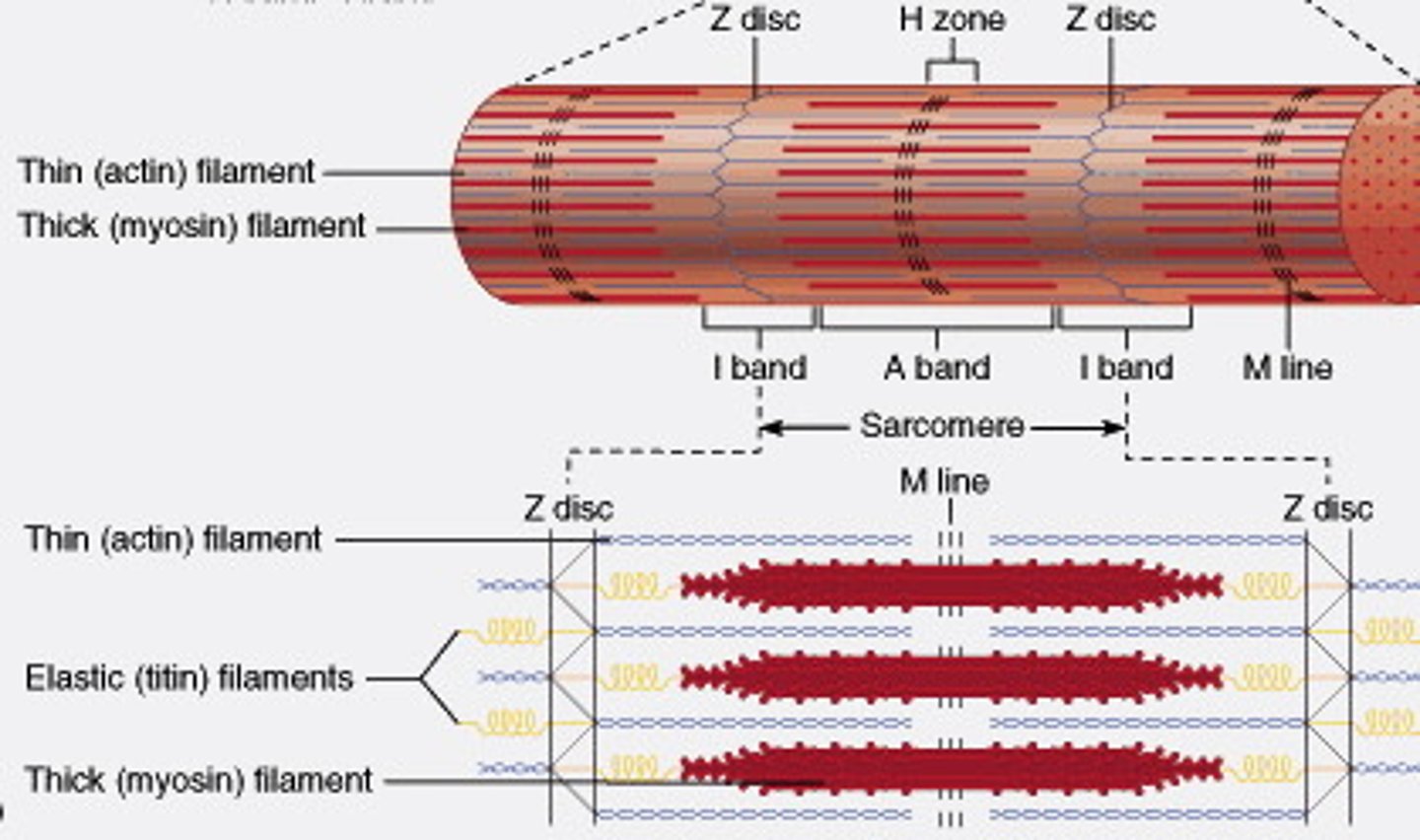
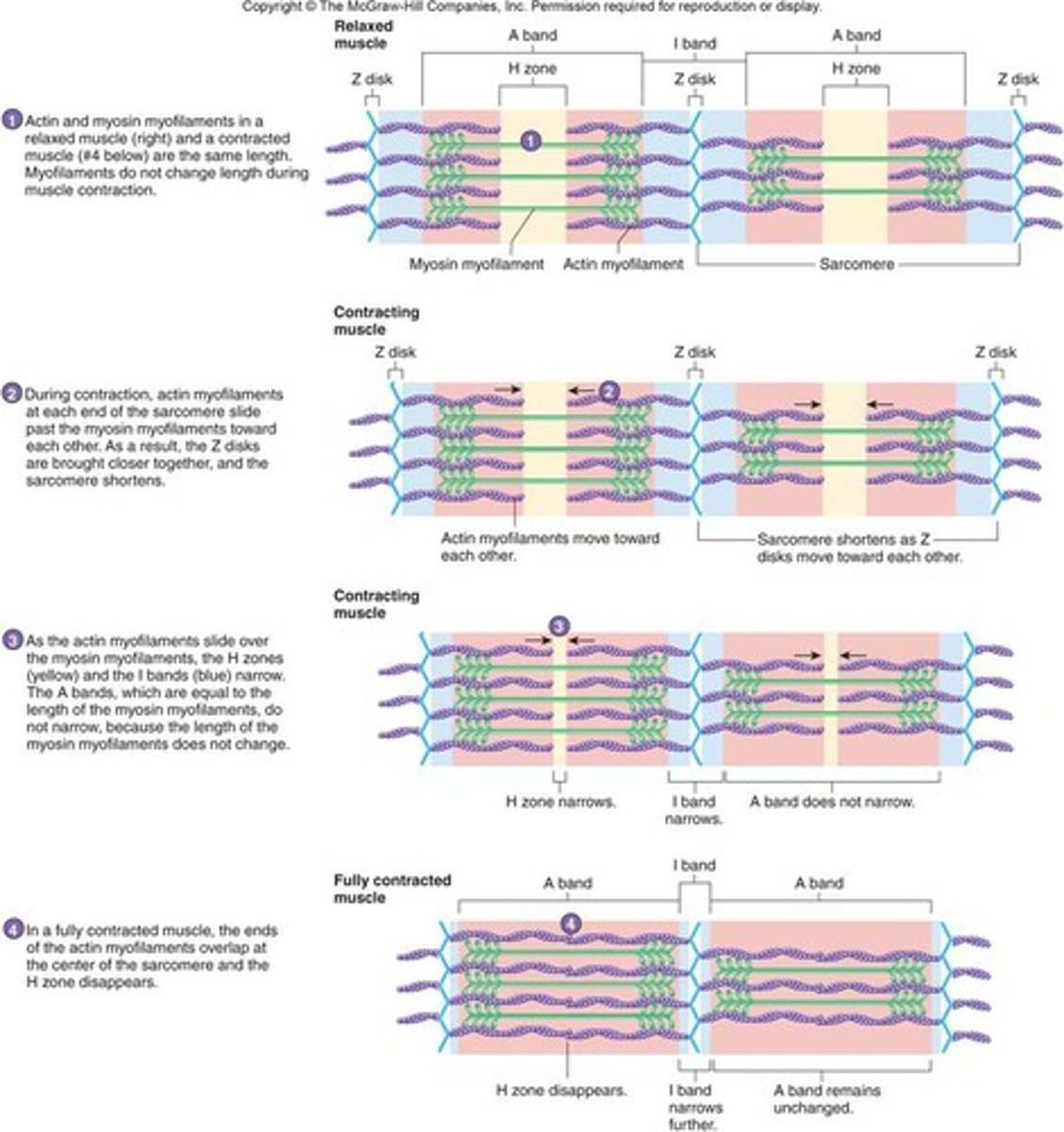
sliding filament model
Actin myofilaments sliding over myosin to shorten sarcomeres
-Actin and myosin do not change length
-Shortening sarcomeres responsible for skeletal muscle contraction
During relaxation, sarcomeres lengthen
Sarcomere Shortening
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum releases Ca2+
- Ca2+ binds to troponin on the actin filament
-Tropomyosin shifts, exposing myosin-binding sites
- Myosin binds, and ATPase activity allows myosin to pull thin filaments towards the center at the H zone and then ATP causes dissociation
Physiology of Skeletal Muscle
Nervous system
-Controls muscle contractions through action potentials
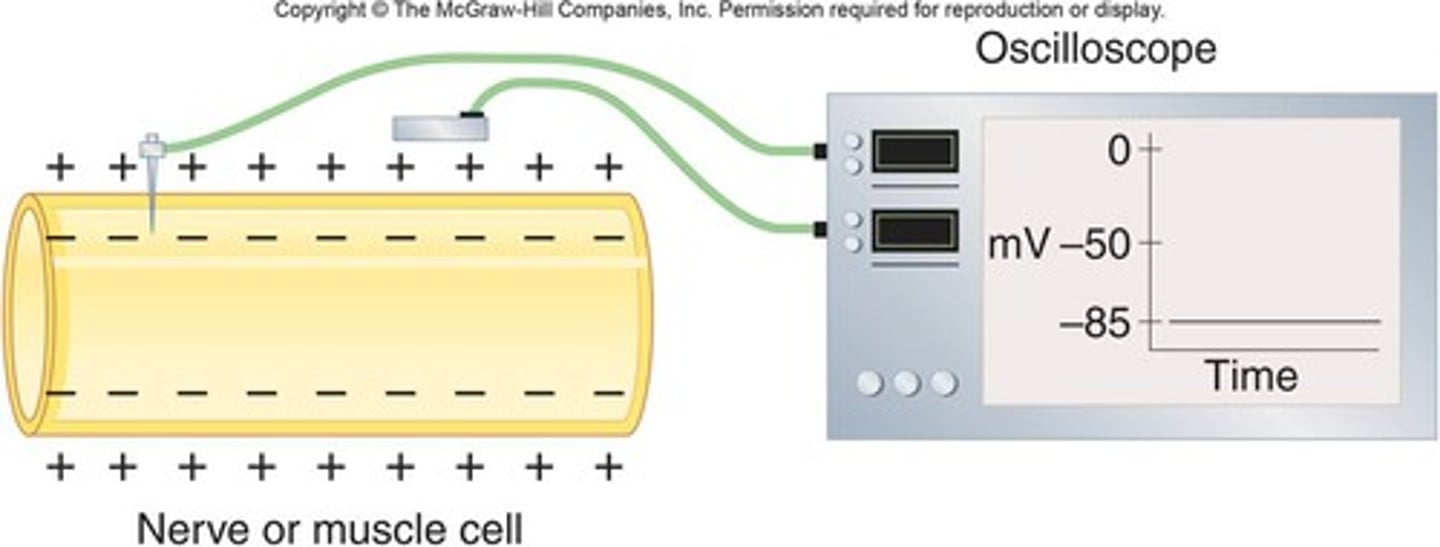
Resting membrane potentials
-Membrane voltage difference across membranes (polarized)
--Inside cell more negative and more K+
--Outside cell more positive and more Na+
Must exist for action potential to occur
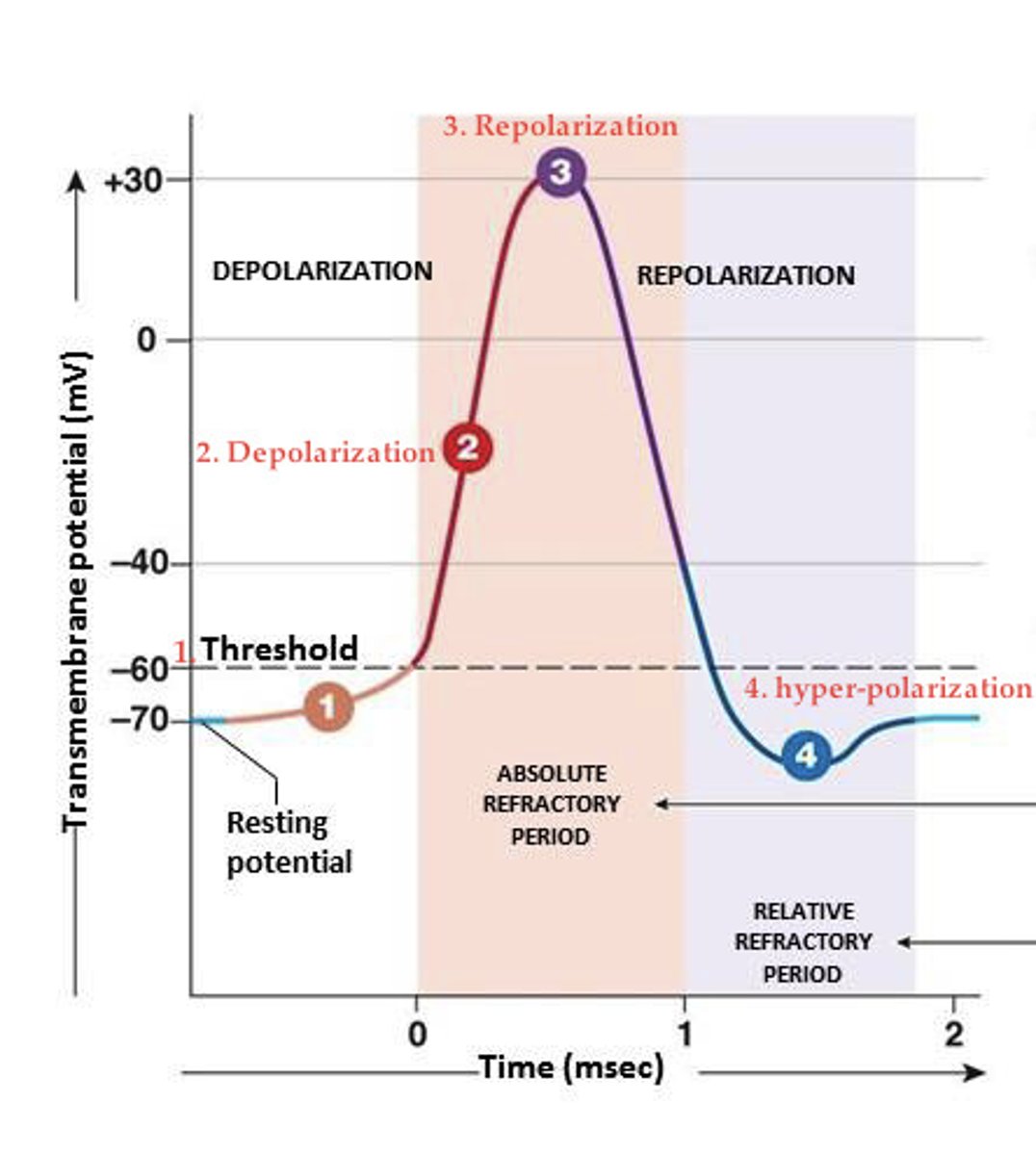
Action Potentials
Phases
-Depolarization
---Inside plasma membrane becomes less negative
-Repolarization
---Return of resting membrane potential
All-or-none principle
-Like camera flash system
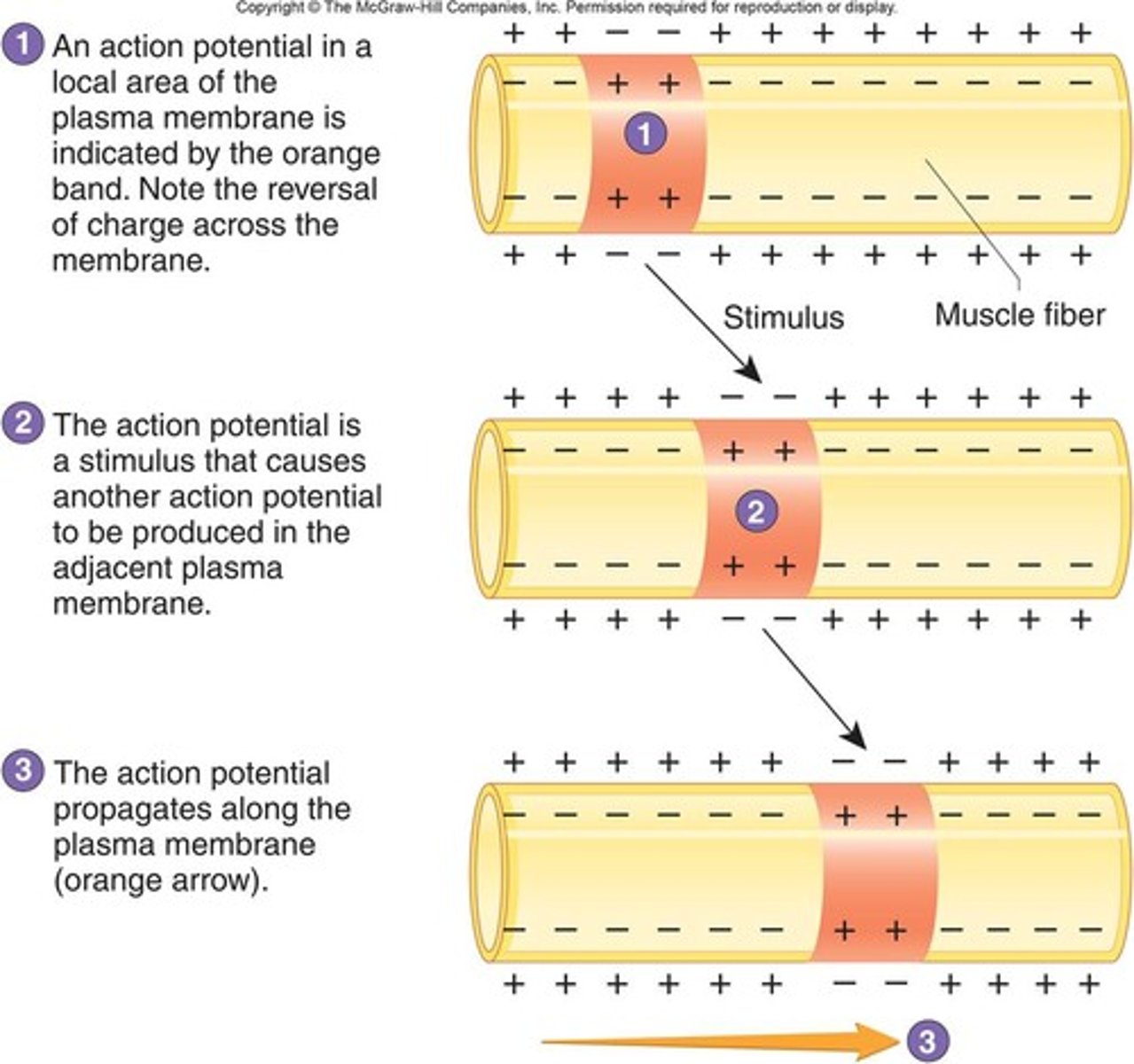
action potential propagation
the movement of an action potential along an axon; in myelinated axons, it occurs via saltatory conduction
Neuromuscular Junction
Synapse or NMJ
Synaptic vesicles
--Acetylcholine: Neurotransmitter (stimulates or inhibits the production of an action potential)
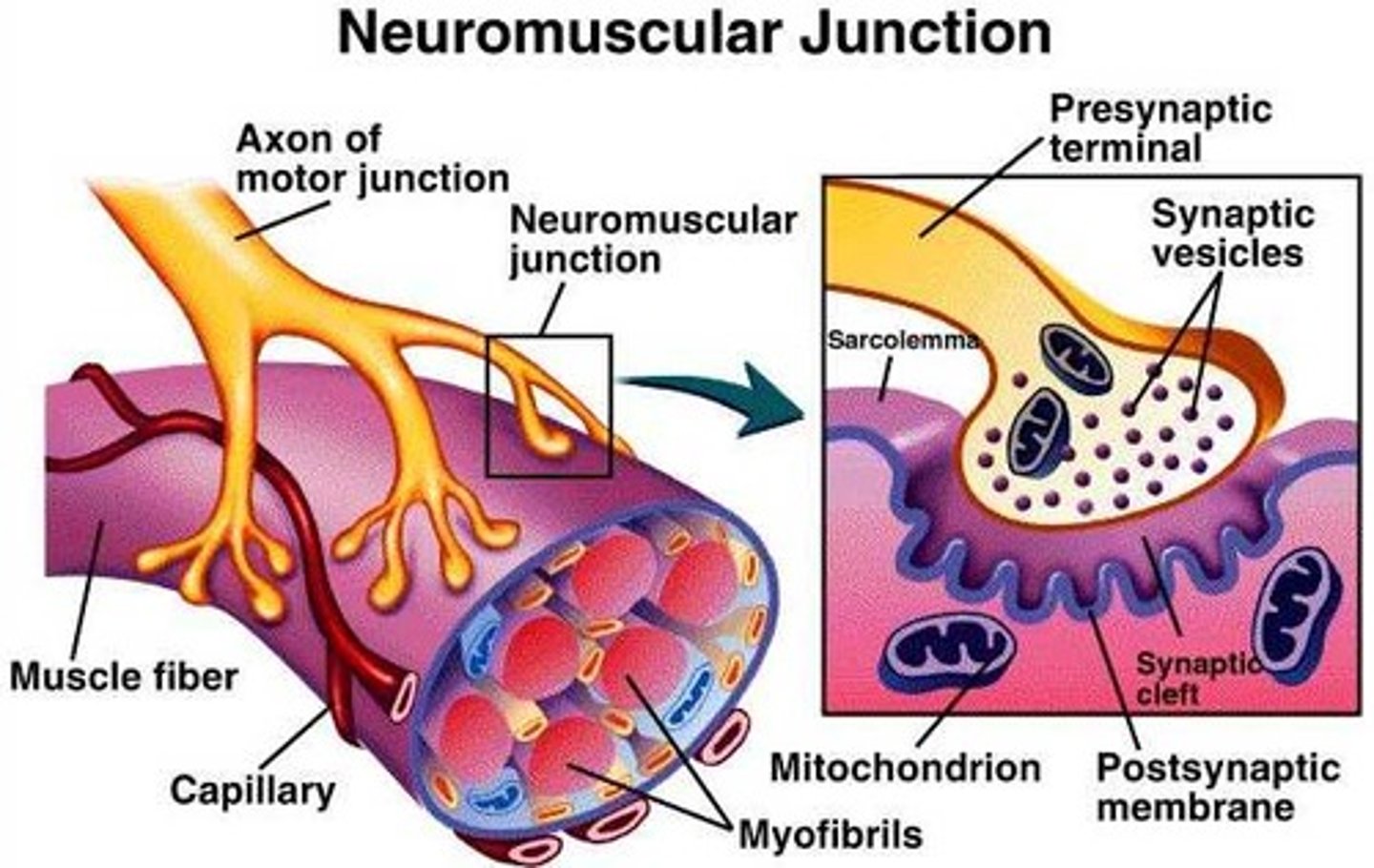
Action Potentials and Muscle Contraction
Steps for Contraction
1. Neuron sends impulse releasing acetylcholine
2. Ca+ ions are released & actin exposes active sites
3. Myosin cross-bridges attaches to actin & sarcomeres shorten
4. The muscle shortens & contracts
cross bridge movement
1) Exposure of active sites, 2) Cross-bridge formation, 3) Power stroke, 4) cross-bridge releases, 5) Hydrolysis of ATP, 6) Recovery stroke, then back to #2 - how actin moves across myosin and contracts