Physiology 3051 unit 1
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
physiology
the study of normal functioning of humans throughout the whole body
function vs mechanism
why vs how
epithelial cells
separate internal and external environment
Extra cellular fluid in the body
14 liters
intracellular fluid in the body
28 liters
regulation of homeostasis
nervous system and endocrine system
endocrine system timing
slow response
endocrine system function
diffuse targets, entire tissues and organ systems impacted
nervous system timing
very fast response
nervous system function
negative feedback
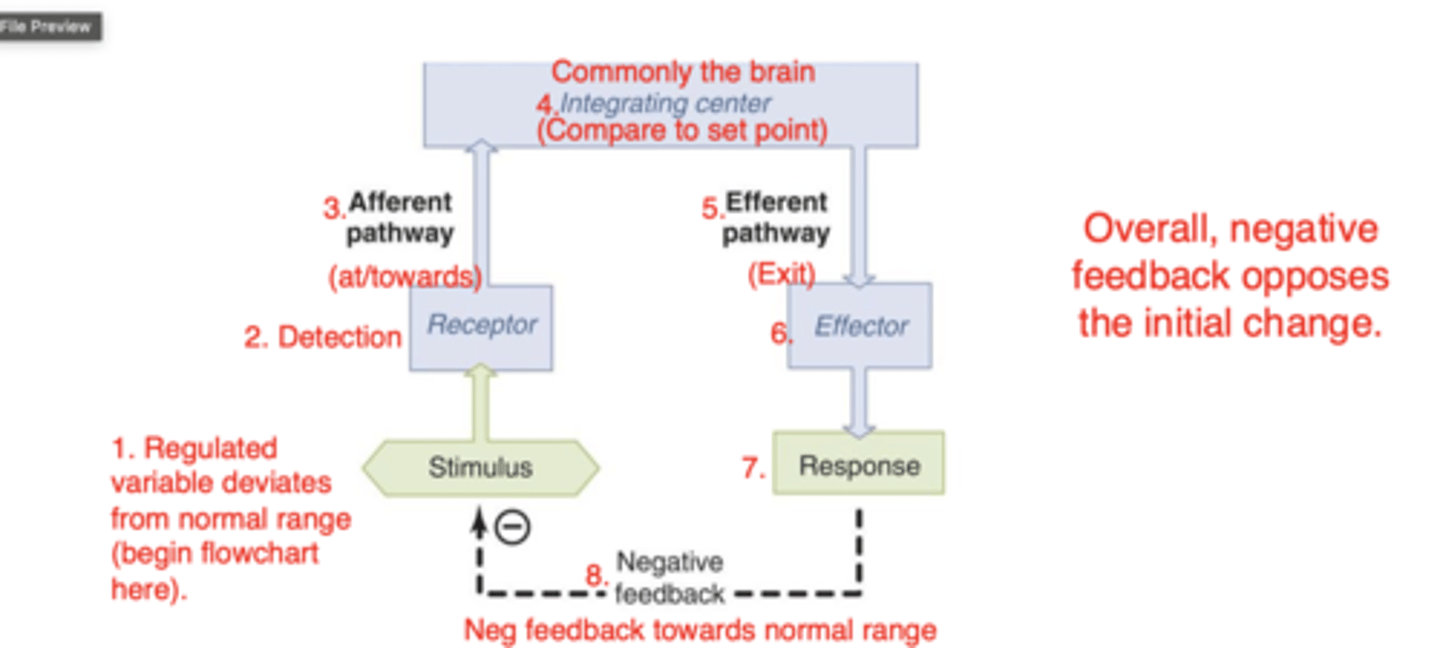
positive feedback loop
cause a rapid change in variable, reinforces stimulus rather than decreasing
breaking a positive feedback loop
requires a terminating event (childbirth)
anticipatory response
allows body to start response in anticipation of the change (Pavlov's dogs drooling)
Plasma membrane
selectively permeable phospholipid bilayer
hydrophilic
molecules CANT cross (water loving) fast
hydrophobic
molecules CAN cross (water fearing) slow
facilitated diffusion
no energy needed, needs transmembrane protein, moves down the concentration gradient, ion channels allow charged ions to cross membrane
simple diffusion
substance can freely enter the cell
primary active transport
directly uses ATP, needs transmembrane proteins, pumps AGAINST concentration gradient
secondary active transport
pumps AGAINST concentration gradient, uses energy indirectly
endocytosis
molecules enter through vesicles formed from the plasma membrane
exocytosis
intracellular vesicle attaches to the plasma membrane and releases contents into the ECF
Hydrophilic signaling molecule
bind to the extracellular receptors on the surface of the plasma membrane, initiate 2nd message or cascade, alter ion channel conformations
hydrophobic signaling molecule
bind to intracellular receptors and alter transcription an protein synthesis
hydrophobic signaling molecule speed
slow effect, metabolized slowly
hydrophilic signaling molecule speed
fast effect, metabolized quickly
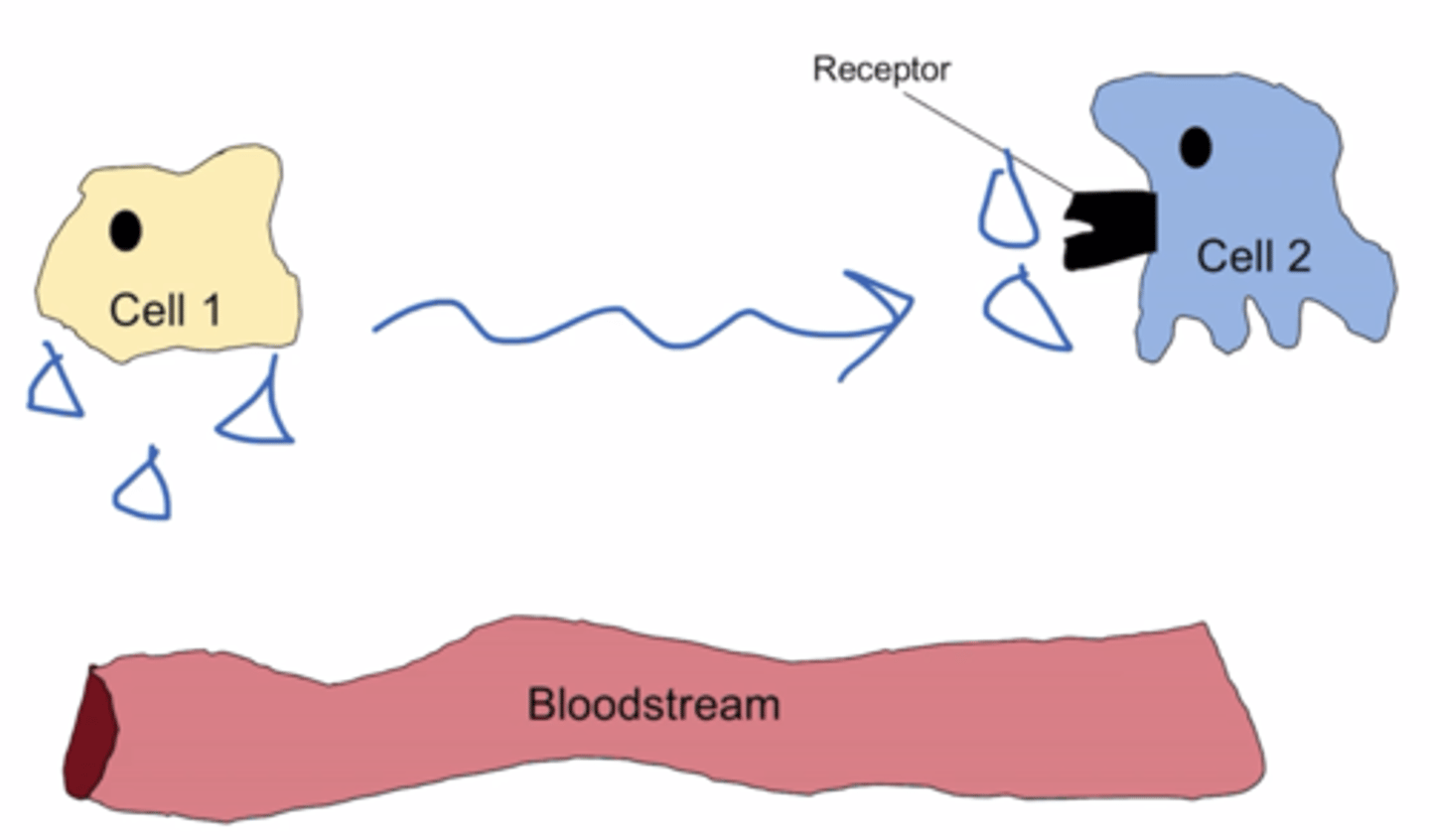
Autocrine signaling
the target cell is also the secreting cell
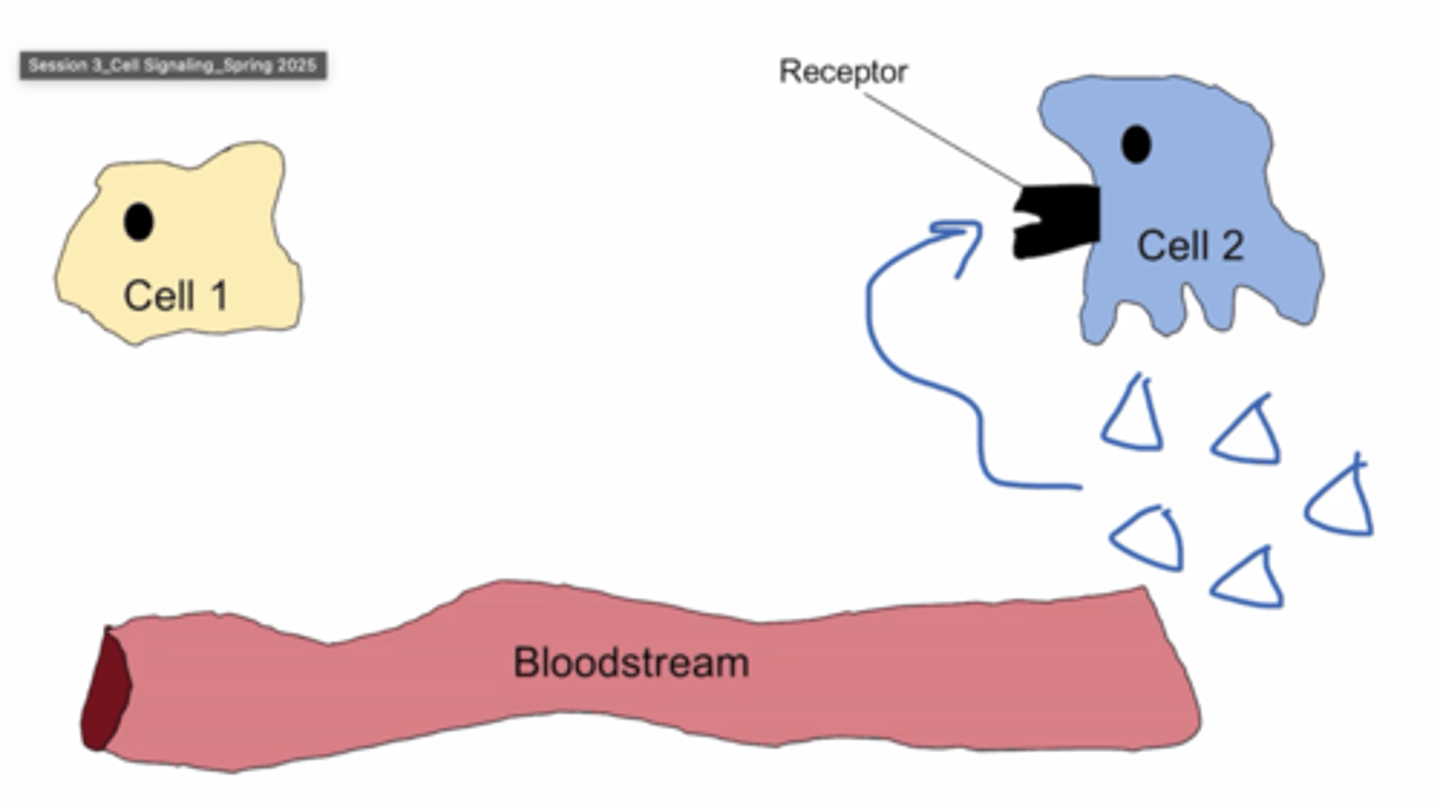
paracrine signaling
signal released from cell A binds to neighboring cell B
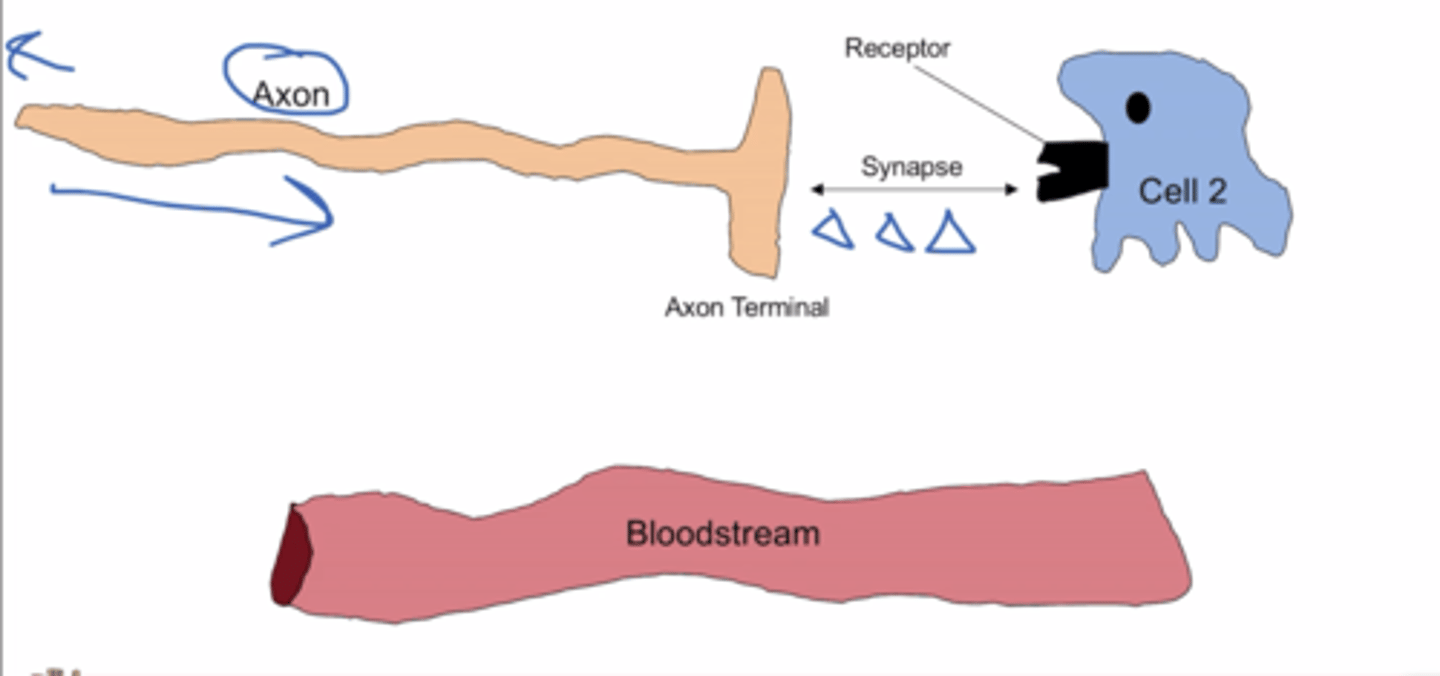
Neurotransmitter signaling
signal released from axon terminal into synapse, signals bind to nearby cell receptor
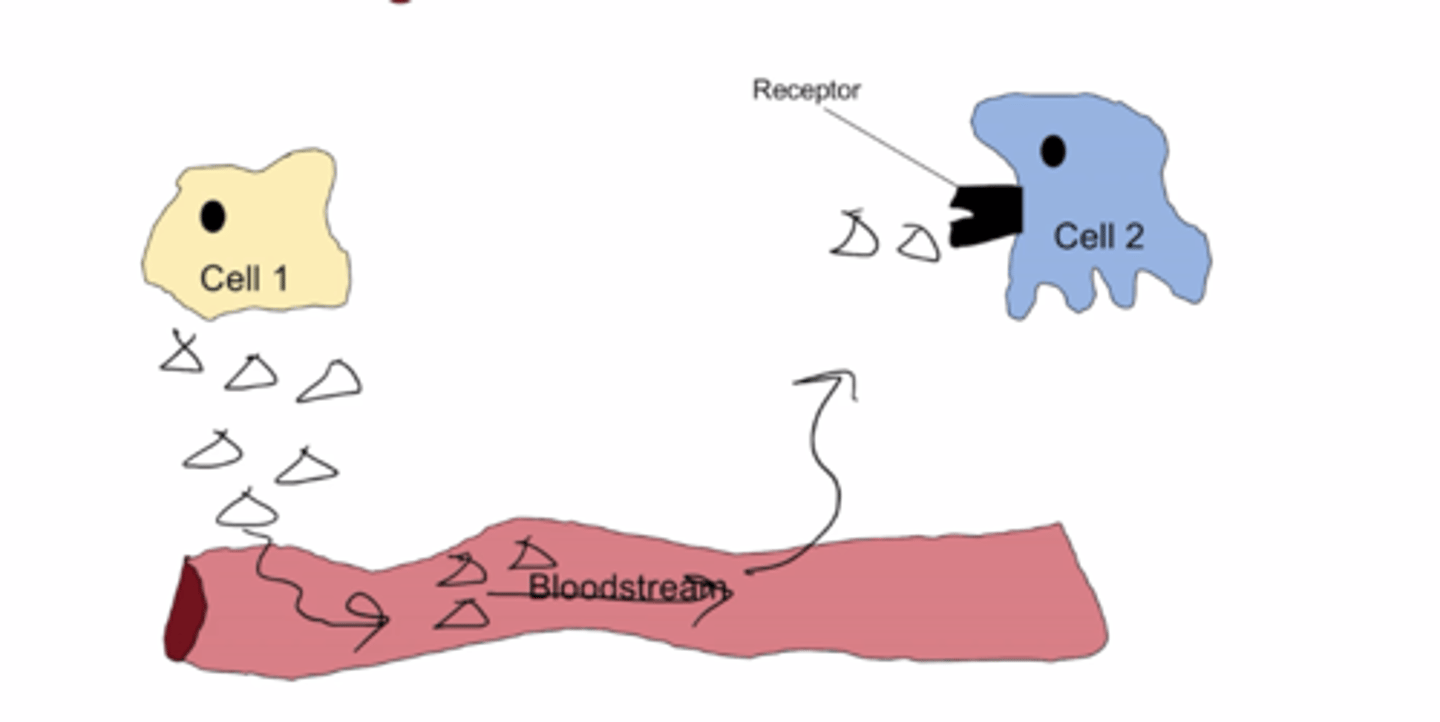
Endocrine signaling
Signals enter bloodstream and bind to a receptor that is far away (travels long distances)
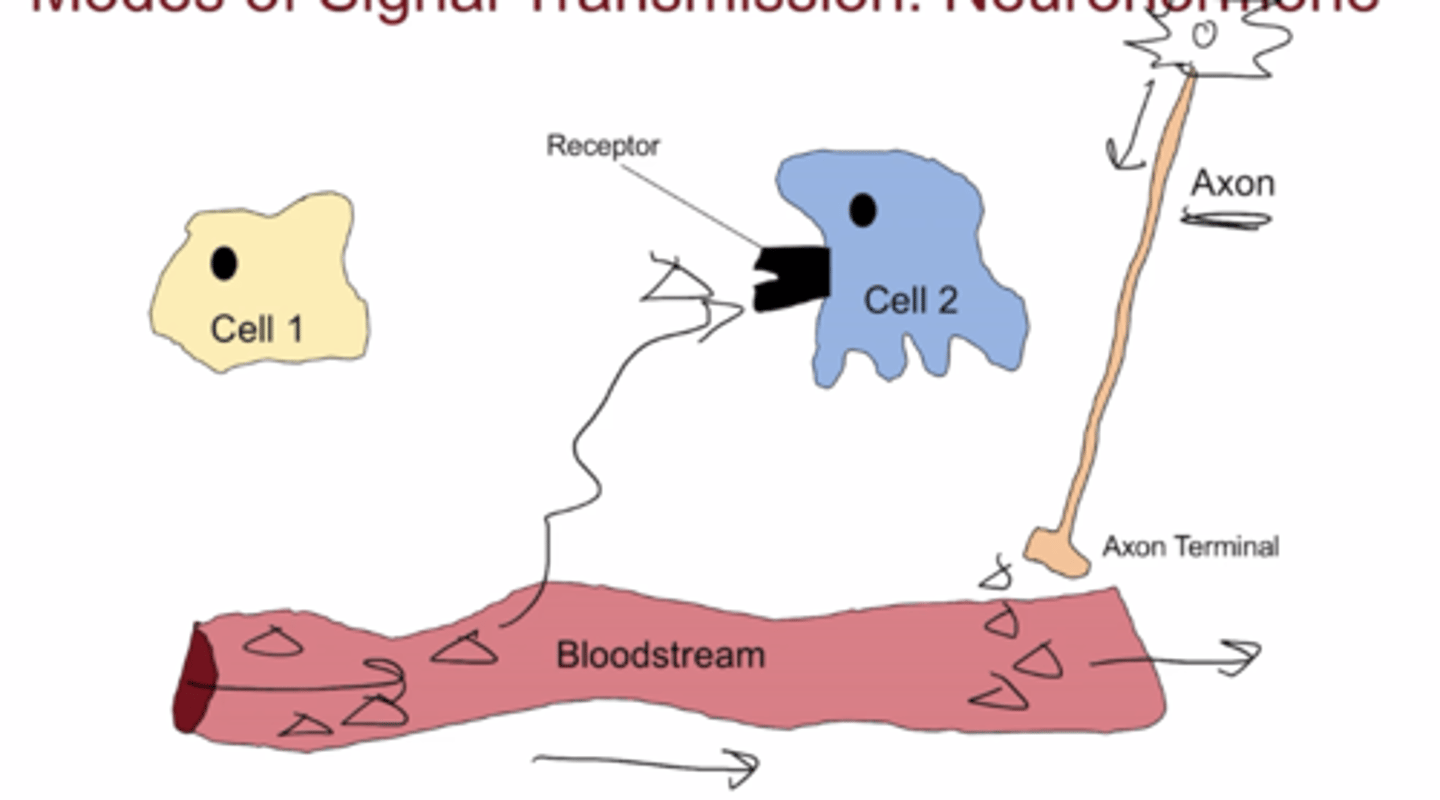
neuro hormone signaling
Signal exits axon terminal, goes through he bloodstream and binds to cell receptor
how does water cross cell membranes
aquaporin channels
what mode of transportation does water use
passive transport, always down its concentration gradient
osmolarity
total solute concentration of a solution per unit volume
if water concentration goes down, the solute concentration...
goes up
2 multiple choice options
Tonicity
describes behavior, no units, determined by osmolarity and penetrating vs non penetrating solutes
hyperosmotic
greater than 300 mosm
2 multiple choice options
hypoosmotic
less than 300 mosm
2 multiple choice options
isosmotic
equal to 300 mosm
2 multiple choice options
penetrative solution
urea and ethanol
non penetrative solution
Glucose, Na+, Cl-, K+, and other ions
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
pheral nervous system
afferent and efferent divisions
astrocytes
monitor and regulate ECF of the CNS, supply metabolic fuel to neurons, important for blood-brain barrier
Oligodendrocytes
synthesize myelin in the CNS
Schwann cells
synthesize myelin in the PNS
microglia
proliferate following neuronal injury, remove cell debris, have immune function
synapse
Gap between neurons
convergence
multiple presynaptic neurons communicate with ONE postsynaptic neuron
Divergence
one presynaptic neuron communicates with MULTIPLE postsynaptic neurons
at rest, membrane potential is...
negative (-70mV)
chemical driving force
concentration gradients
electrical driving force
opposites attract, like charges repel
volume in a cell only changes when...
water enters the cell
resting membrane potential is generated by...
the Na+/K+ATP-ase pump
Na+ leak channels
always leaking IN but a SMALL amount
K+ leak channels
always leaving the cell
Equilibrium potential equation
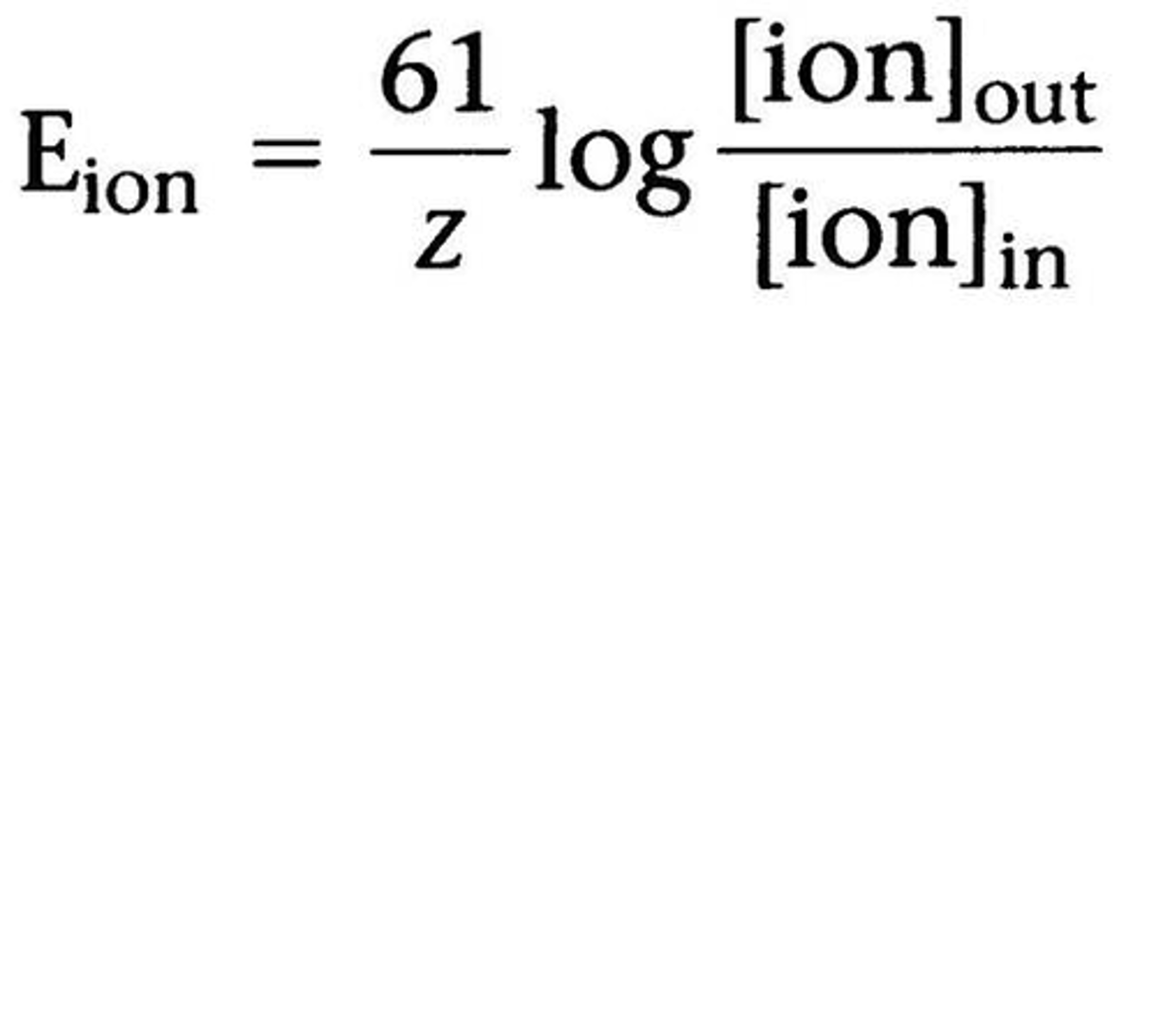
neurons communicate by...
changes in membrane potential
ligand gated channels
chemicals
leak channels
always open
voltage-gated channels
open and close in response to changes in membrane potential
mechanically-gated channels
open in response to physical deformation of the receptor
graded potentials
summation, initiated by depolarizing and hyperpolarizing, mediated by ligand-gated channels, amplitude varies with stimulus intensity
action potentials
amplitude is all or nothing, initiated by depolarization only, no summation, mediated by voltage-gated channels
action potentials phase 1
threshold reached, Na+ channels open and membrane rapidly depolarizes as the Na+ enters the cell, K+ channels DONT open
action potentials phase 2
sudden decrease in Na+ permeability, sudden increase in K+ permeability
action potentials phase 3
Na+ channels close, K+ channels close slowly so the cell hyper polarizes so it becomes more negative than its RMP, then everything closes and Leak channels bring cell back to RMP
refractory periods
an action potential, the membrane is less excitable than at rest
absolute refractory
not possible for a cell to generate a 2nd action potential voltage-gated Na+ channels CANT open
relative refractory
possible to generate a 2nd action potential, bit needs a larger stimulus than normal, SOME Na+ channels have entered the close state
Unmyelinated neurons
action potential begins at trigger zone and propagates to the axon terminal, propagation is slow (cheaper)
myelinated neurons
myelin creates membrane resistance so ions flow towards the middle of the axon, faster (expensive)
Node of ranvier
brief breaks in the myelin segments
electrical synapse
multiple cells "behave as one"
chemical synapse
slow, allow for more complexity and modifications
pre-synaptic event 1
Action potential propagates to axon terminal
pre-synaptic event 2
voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open
pre-synaptic event 3
rapid influx of Ca2+ actives vesicle exocytosis, vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane
pre-synaptic event 4
neurotransmitter diffuses across synaptic cleft onto post synaptic cell
Excitatory post-synaptic event 1
neurotransmitter binds to post-synaptic receptor
Excitatory post-synaptic event 2
ligand-gated channels open
Excitatory post-synaptic event 3
cations flow through channel into cell
Excitatory post-synaptic event 4
net effect is depolarization (very small), summation is key!
Inhibitory post-synaptic event 1
Neurotransmitter binds to post-synaptic receptor
inhibitory post-synaptic event 2
ligand-gated channels open
inhibitory post-synaptic event 3
EITHER K+ flows out of the cell OR Cl- flows in
inhibitory post-synaptic event 4
net effect is hyper polarization or inhibits further depolarization