Nuc. Med Exam 3
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Scintillator
Material that emits a UV or visible-light photon (scintillation photon) when an electron transitions from a higher to a lower orbital
Calibration
Adjustment of the output of a radiation detector in order to match a known value.
Precision
How close several measured values are to each other
accuracy
How close a measured value is to the true value of a sample
Peak broadening
the relatively wide width of a gamma ray photopeak – the gamma rays come out of the nucleus with a single energy, but the scintillation detector with its variability produces a wide range of electrical pulse sizes
Energy resolution
the measure of the peak broadness or width of the energy spectrum
FWHM (Full width at heigh maximum)
quantification or unit of measurement of the width at half maximum of a energy spectrum. Correlating with the energy resolution of the spectrum.
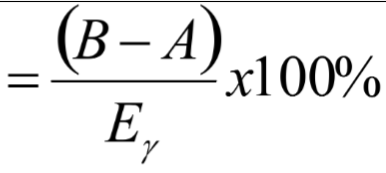
non-paralyzable dead time
count rate reaches the maximum and then plateaus. Events happening during dead time do not add more dead time.
paralyzable dead time
count rate reaches a maximum and then decreases. Events occurring during dead time add more dead time.
Cyclotron
proton travels through a spiral, the spiral has electrical and magnetic force on it that alternates to move the proton through, while accelerating it, then it’s diverted towards the target atom.
Because the nucleon added to the nucleus is a proton, the target becomes a new element. Produces chemically distinct product atoms, is carrier free. The radionuclides produced are neutron-deficient and decay via electron capture and positron/beta plus decay.
Cost: High
Quality: Good
neutron-deficient radionuclides
Neutron activation
using a neutron to irradiate a non-radioactive target that produces a radioactive product.
Produces proton-deficient radionuclides that decay via beta minus decay. Produces many radionuclides that aren’t chemically separable, carrier is present.
Cost: Low
Quality: Poor
proton-deficient radionuclides
Fission
a neutron being aimed at a U-235 atom, which it absorbs and due to instability splits into two atoms, releasing gamma rays, and further emissions of beta minus and gamma. The product radionuclides are proton-deficient.
Radionuclides produced are carrier free and usually in pure forms. Can be used for other uses other than nuclear medicine.
Cost: Medium
Quality: good
proton-deficient radionuclides
Compton edge: formula
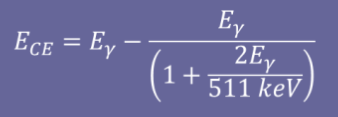
Iodine escape peak formula
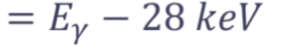
Poisson coefficient of variation formula
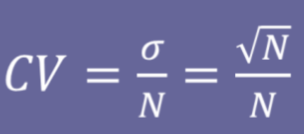
What does Poisson’s model predict?
the frequency distribution of all possible true values of m.
the shape of the frequency distribution if m is greater than 30
⭐ that the standard deviation of the frequency distribution is the square root of m.