P431 Exam 2 Class 22,21,19,18,17
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
Efficiency (price)
Reducing operational costs across all functional areas
Responsiveness
Speed, order fulfillment, service level and customer satisfaction
Can you compete on both price and responsiveness?
No, you must make tradeoffs
Can a firm compete successfully on all dimensions of customer value?
No, a firm must make tradeoffs regarding innovation, choice, price, and experience.
What are the different areas a customer can perceive value?
Product Innovation: Speed to Market
Product selection and availability
Price and brand
Value added services
Relationships and experiences
What are the challenges with a single ops strategy?
Mismatches between the strategies
Identifying the strategy as customers, channels and products vary
Understanding drivers of ops strategy as they affect measures of cost, time and service levels
What items often have tradeoffs between each other?
Efficiency
Responsiveness
Cost
Flexibility
Risk
Inventory and Service Levels
Quality and Price
What are the operations rules for Chapter 3 covering the topic of matching products, markets, and strategies?
Rule 3.1: Aggregate forecasts are always more
accurate than individual forecastsRule 3.2: The appropriate SC strategy-push, pull, or
push-pull- is driven by demand uncertainty and
economies of scale.Rule 3.3: Lead times are drivers of the appropriate
SC strategyRule 3.4: The sales channel determines the
manufacturing and distribution strategies
Characteristics of push and pull strategies
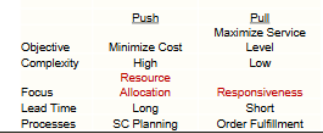
When do you use a push vs a pull strategy for production?
Push strategy: for certain demand
Pull strategy: for uncertain demand
What are the operations rules for chapter 5 covering risk mitigation strategies?
Rule 5.1: Integrate risks into operational and business decisions
Rule 5.2: SC cost is always flat around the optimal strategy.
Rule 5.3: Invest now, or pay later: firms need to invest in flexibility, or
they will pay the price later.
Resilient SC
the ability to recover quickly from SC disruptionsand adapt to changes in supply chain conditions.
What is the objective of a resiliency scorecard?
Identify gaps in the firm’s risk management strategies by analyzing the current state of the company’s risk management processes and comparing them to its goals
How do you quantify risk?
You can use a FMEA (failure modes and effects analysis) and analyze the significance of a risk by using an RPN (risk priority number).
The three areas an RPN evaluates regarding a risk is severity, occurrence, and detection.
What are some methods for managing SC risk?
Invest in capacity redundancy
Increase velocity in sensing and responding
Create flexible SC community
What are the operations rules for chapter 7 covering system flexibility?
Rule 7.1: A small investment in flexibility can significantly reduce total SC costs.
Rule 7.2: A long chain is preferred when designing the manufacturing network for flexibility
Rule 7.3: Variability degrades the performance of the SC while flexibility improves its performance
What is flexibility?
The ability to respond to change without increasing operational and SC costs and with little or no delay in response time. Change refers to demand volume and mix, commodity prices, labor costs, exchange rates, technology, equipment or any
other conditions to the market.
How do you make your SC flexible where you match supply/demand with little or no impact to customer?
Through manufacturing or distribution strategy or through capacity redundancy.
What do companies not understand about flexibility?
How to measure it
How much they need
Quantifying cost/benefit
A buzz word like agility and resilience
They can make an insight but not a strategic decision
What does a company need in order to integrate flexibility into their supply chains?
Need a holistic/interdisciplinary approach that integrates manufacturing, logistics/distribution, transportation, product design
What is analyzed when determining the extent of flexibility needed in a SC?
Determine cost/benefit
Determine level
Determine benefit of flexibility if demand differs
Why are long chains better then short chains?
Long chains perform better than many short chains because they pool plant/products to deal with uncertainty Investing in even a small degree of system flexibility requires changes to business processes, investments in information
sharing and rethinking org structure
What are the operations rules for chapter 9 covering product design flexibility?
Rule 9.1: Modular product architecture is important when flexibility is required
What are the different drivers of product design flexibility?
Include modular product architecture, standard components, standard processes, manufacturing flexibility and interfaces, postponement and component substitution.
What is the big advantage of product design flexibility for the SC?
Help to address changes in technology, demand mix and volume
What are the downsides of modularity in manufacturing?
longer development time, increased complexity and costs, performance and quality
challenges, higher coordination
What are the different SC characteristics that must be considered when implementing product design flexibility into a supply chain and operations strategy?
– Demand uncertainty and variability
– Economies of scale in production and transport
– Lead Time
– Innovation speed
– Make/Buy decisions
– Product structure: Modularity and Integrality
What are the different operations and SC myths?
Myth 1: Reduce costs by all means
• Different products require different strategies (efficient / responsive)
Myth 2: Apply same operations strategy across all products, channels and customers
• Different products, channels, customers
Myth 3: Deploy the latest and best IT
• Must be driven by business needs
Myth 4: Ignore IT because it is just another commodity
• Combination of IT and business processes for integration and collaboration
Myth 5: Invest in a lot of redundancy and flexibility
• It’s not free. Need a cost/benefit
Myth 6: Treat CSR as a charity
• Many benefits
Myth 7: Leave operations to the functional areas of the company
• Ops needs equal seat as need integration/synergies
What reduces variability in the SC?
Information sharing, lead time reduction, & strategic partnering reduce variability in SC. SC transparency is a must.
Bullwhip effect
Increase in order variability (size) as we travel up in the SC. The bullwhip effect increases inventories and costs.
What are the main drivers of the bullwhip effect?
• Demand forecasting
• Lead Time
• Batch ordering
• Price fluctuation
• Inflated orders
• Lack of information sharing
What is the goal (objective) of the basic transportation model?
to Minimize Total Shipping Cost
What data is needed for the basic transportation model?
Plant Capacity
Regional Demands
Shipping Costs
What are the constraints for the basic transportation model?
Cannot exceed plant capacity
Must meet Region Demand
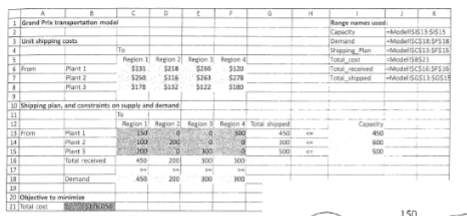
How do you interpret the capacity allocation graph for the basic transportation model?
Node: Indicated by a circle,
represents a geographical locationArc: Indicated by an arrow,
represents a route for getting a
product from one node to another
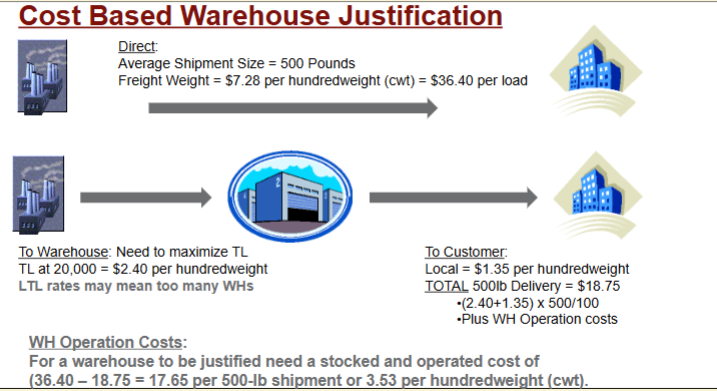
How do you decide when to build another warehouse in a SC?
You use a cost-based approach by comparing direct shipment costs to the costs of adding a warehouse between the manufacturer and customer. The stocked and operated cost per shipment of the warehouse needs to be less then what is calculated.
How does the number of facilities (warehouses) affect transportation cost?
Initially decreases with more facilities
• Financial savings from transportation consolidationReaches total cost minimization point then increases as the number
of facilities goes up
• Total facility costs increase, smaller inbound shipments
How does the number of facilities (warehouses) affect Inventory costs?
As the number of warehouse locations increases, total amount of
inventory increases (due to each facility needing its own safety stock)
What are some other considerations for determining number of needed facilities?
Customer Service Considerations
Postponement for high-value density product mfg
What must logistical strategies trade-off?
•Inventory
•Transportation
•Customer Service Performance
What is the threshold service level?
The overall level of customer service associated with the least-total-cost-system. The level considers:
Availability: Stock Service Level
Capability/Quality: Performance Cycle Time
What does the threshold service level ultimately trade-off?
Total Cost: Inventory & Transportation
Service: Availability & Capability
What is the least total cost network?
The network that has the “least total cost” is the one that has the right number of facilities to minimize transportation and inventory costs.
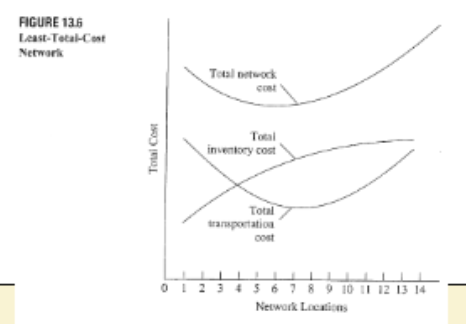
What is the center of gravity method for network design?
Finds the lowest cost based on demand and distance,
using X,Y coordinates to define a geographic position. (method uses weighted averages to make the facility closer to a location that has higher demand.
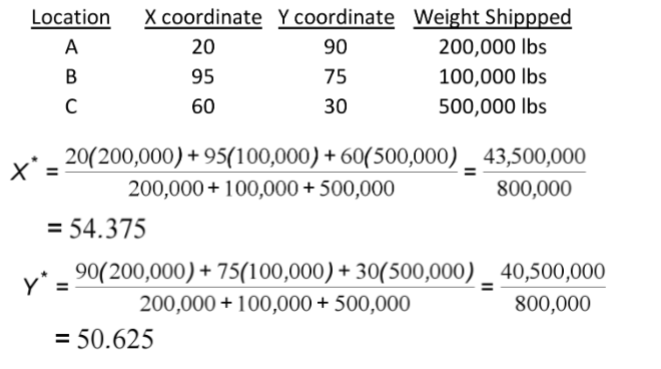
What are the calculations for the center of gravity method?
What does the final graph look like for the center of gravity method>
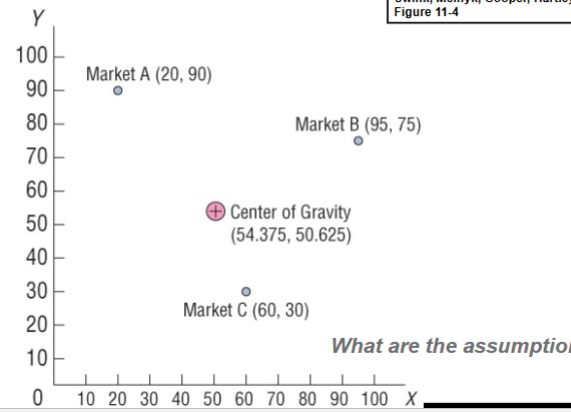
What are the assumptions for the center of gravity model?
1. Straight line distances between all locations
2. Amount of demand is a good proxy measure of
transportation cost
3. There are no qualitative factors included in the determination
What are some considerations when designing a network?
1. Data Collection & Aggregation
2. Transportation Rates
3. Mileage Estimation
4. WH Costs
5. WH Capabilities
6. WH Locations
7. Service Level Requirements
8. Future Demand with Uncertainty
9. Model and Data Validation
How do you aggregate data such as demand (customer) and products types into groups to create a SC network?
Customer Zone
– Aggregate using a grid network or other clustering technique for those in
close proximity.
– Replace all customers within a single cluster by a single customer
located at the center of the cluster
– Five-digit or three-digit zip code based clustering.
Product Groups
– Distribution pattern
• Products picked up at the same source and destined to the same customers
• Logistics characteristics like weight and volume.
– Product type
• Product models or style differing only in the type of packaging
Example of customer aggregation based on 3 digit zip codes to build a SC network.
Example of product aggregation to build a SC network.
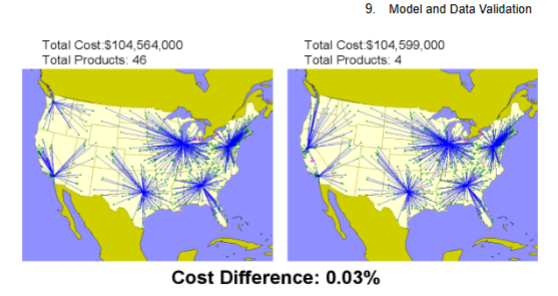
What are the tradeoffs due to an increase in the number of warehouses in a SC?
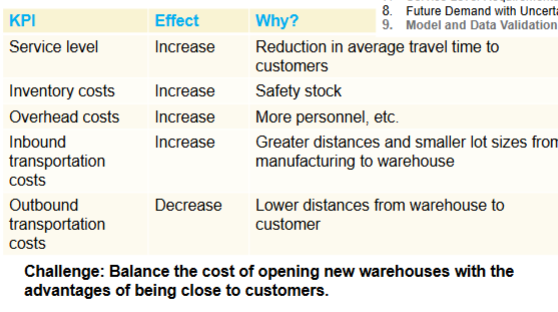
Why are warehouses needed?
Positioned between suppliers, mfg and
customers. Established to lower total cost
and/or to improve customer service.
What is the purpose of a supply facing (inbound) warehouse?
Procurement: Consolidate and smoothing of material flow
•Must balance purchase price, quantity discount, payment terms, and logistical support to achieve lowest delivered cost.Traditional Role: Stockpile parts
Evolving Role: Sorting, Sequencing and eliminating multiple handling and storage
What is the purpose of a demand-facing (outbound) warehouse?
Manufacturing Strategies: Store, sort and sequence FG for customers
•Full Line product assortments (multi-products) at TL transport rates
•MTO requires more Supply Facing Warehouses
•MTP requires more Demand Facing StrategiesCustomer Accommodation (Marketing Strategies): Store, sort, sequence and consolidate to
customers. Provides customized inventory assortments
•Rapid Replenishment: Common in food and mass merchandise
•Market-Based ATO: Postponement value-add performed at WH
What is a point-to-point transportation system?
Transportation system that travels directly to a destination
What are the pros and cons of a point-to-point transportation system?
Pros: May minimize connections and travel time.
Cons:
1) If a city pair is not served, passengers are out of luck, as there is no way to
get to a destination using that airline's route network.
2) The frequency of flights may be reduced because requires a large number
of combinations and flights to be full
What is the hybrid approach to a point-to-point transportation system?
Some heavily hub-oriented carriers operate a limited number of point-to-point
routes that do not connect with either a hub or focus city.
What is the hub and spoke transportation system?
System of connections in which all traffic moves along spokes connected to the hub at the center
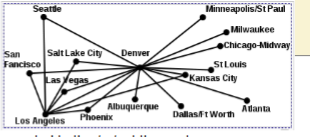
What are the pros of a hub and spoke transportation system?
Pros:
1) Less Routes: With 10 destinations, hub-spoke requires 9 routes to connect all destinations, while
point-to-point would require 45 routes.
2) Generally more efficient use of transportation resources. Aircraft are more likely to fly at full
capacity, and can often fly routes more than once a day.
3) Complicated operations can be carried out at the hub, rather than at every node.
4) Spokes are simple, and new ones can be created easily.
5) Scheduling is convenient for customer since there are few routes, with frequent service.
What are the cons of a hub and spoke transportation system?
Cons:
1) Since centralized, day-to-day ops inflexible. Changes may vibrate throughout the network.
Hub constitutes bottleneck. Delays at the hub can result in delays throughout the network.
Delays at a spoke can also affect the network too.
2) Route scheduling is complicated. Careful traffic analysis and precise timing are required.
3) Cargo must pass through the hub before reaching its destination, requiring longer journeys.
Desirable for freight, which can benefit from sorting and consolidating operations at the hub
Undesirable for time-critical cargo and passengers.
What are the 5 logistical functions?
1. Order Processing
2. Inventory
3. Transportation
4. Warehousing
5. Materials Handling & Packaging
What are the different types of risks at each step in the SC?
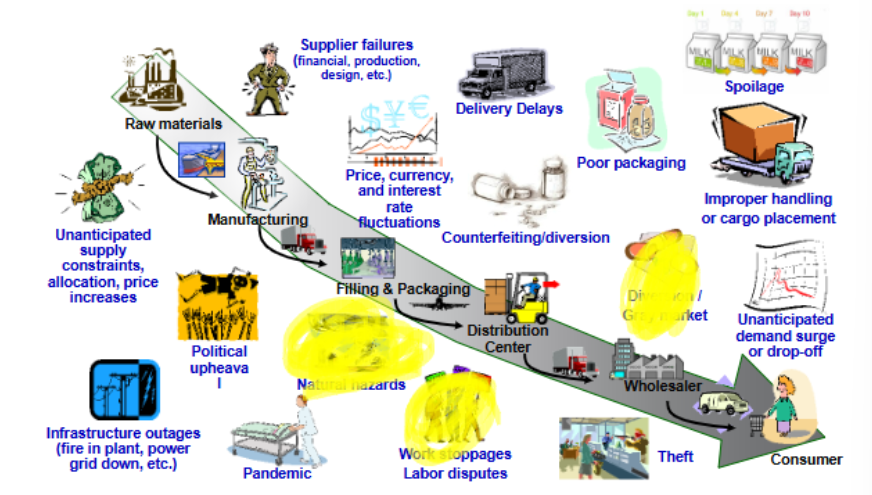
What are some strategic risks in a SC?
more global extended supply chains, over-stretched supply base, suppliers moving into other businesses, talent erosion , scarcity of materials
What are some hazard risks in a SC?
terrorism, weather, natural disasters
What are some financial risks in a SC?
supplier insolvency, fluctuating exchange rates, escalating commodity prices, corruption
What are some operational risks in a SC?
transportation equipment capacity, key bottleneck throughput, escalating fuel costs
What are the risks associated with each of the four categories of risk (hazard, operations, financial, strategic)?
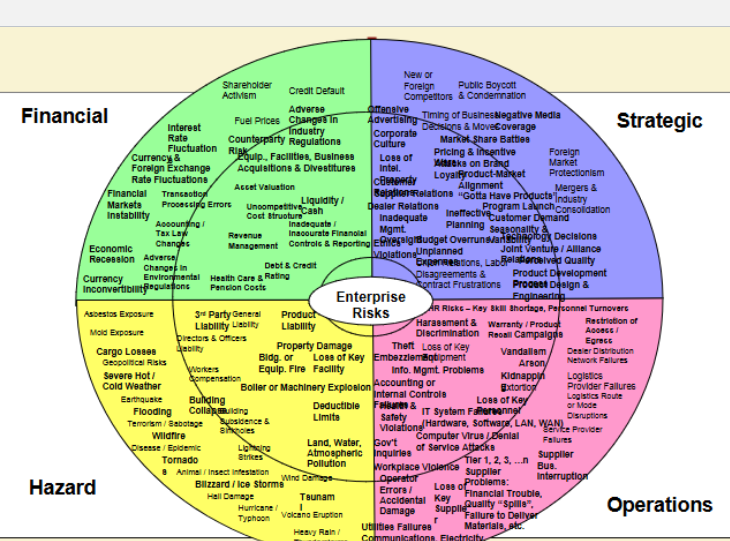
What are some top strategies for risk mitigation by large enterprises?

What makes a SC sustainable?
A sustainable SC reflects the firm’s ability to plan for, mitigate, detect, respond to, and recover from likely risks.
What is the SC risk area of product complexity?
Product Complexity: Refers to the number of product design variations that the firm decides to offer and correspondingly support including:
• Product Development
• Sourcing
• Manufacture
• Delivery
• Aftermarket Support
What is the SC risk area of Regulation?
Regulation: SCM involves many interactions with external parties
• Environmental
• Financial and Taxation
• Minimizing total SC cost
• Value Added Taxation (VAT)
What is the SC risk area of resource availability?
Resource Availability
• Expertise
• Transport Capability
What is the SC risk area of security?
Security:
• Protect Firm
• Protect Product
• Protect Reputation
How do you balance product complexity with SC risk?
need to build and maintain the most profitable product portfolio
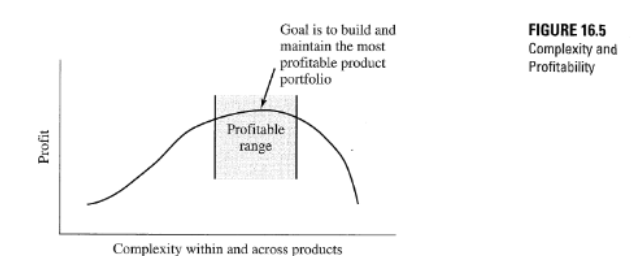
What are some benefits for the SC of low-complexity products?

What are some characteristics of high complexity products?

What are the key facts regarding contingent business interruption insurance?
1. Moving from a physical event such as a fire, flood or natural
disaster (Focus around you)
2. Moving to pandemic, strikes, ash clouds, cyber risks, insolvent
suppliers, political, strikes, transportation
3. Moving below the Tier-1
4. Insurance companies requiring a better understanding of their
SC with risks identified and contingency plans
5. Cannot insure reputational damage to firm
6. Prevention is better than the cure
What is contingent business interruption insurance?
a type of coverage that protects a business from financial losses when a third-party supplier, customer, or other key entity experiences a disruption.
How can transportation be used in risk management?
1. Air for high value
• 2-3% of world trade by air yet accounts for 40% of
value
2. Reliability can trump both cost and speed
3. Beyond value calculation there is element of panic
• Driving-down stock levels
• Issues with increased demand or slight problems
4. Sea is better with avoiding boarder crossings
5. Within US rail is better with reduced fuel
What are the requirements for a cold chain?
1. Temperature Control: Keeping and documenting that products stayed at a
consistent temperature from origin to final destination.
2. Packaging: Using insulated and refrigerated containers to protect products
during transit.
3. Monitoring Systems: Employing real-time tracking and temperature
monitoring devices.
4. Effective Transportation: Ensuring that vehicles are equipped with
refrigeration units.
5. Storage Facilities: Utilizing refrigerated warehouses for storage.
What departments oversee food safety?
US Dept of Agriculture (USDA)
US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Why should we emphasize food safety and oversight in a SC?
Changing market conditions: Increased imports and exports
Complicated SC
Recent outbreaks of foodborne illness
Risk Mgmt Approach
SC Optimization Approach
loss of inventory from produce going bad
What are some important things to consider with inventory management of fresh food products?
Weeks/days/hours of freshness
Hot points in transport process
Intermittent and gradual reduction in quality may be more dangerous as undetectable
What percentage of food products use coldchain?
70 percent
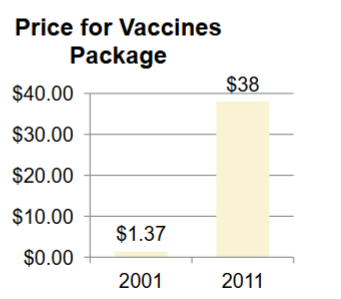
What temperature must vaccines stay at?
2 and 8 degrees celsius (35-46 degrees F)
What happens when vaccines are outside the recommended storage temperature?
If vaccine temperature is outside of this range at
any point in the supply chain it becomes less viable
and its effectiveness is not reversible
How do vaccines not stored at the right temperature effect the end user?
Compromised vaccines may result in increased
mortality rates and the re-emergence or occurrence
of preventable infectious diseases
Why can you get a coke everywhere but not a vaccine?
What is the trend for vaccines package price?
Going up
What are the highest costs within a cold chain?
The highest costs within a cold chain include:
energy costs, fuel costs, transportation costs
and labor costs. (highest being labor and
second being energy)
How much does the power cost to run cold chains annually?
consume about
$30 billion of power each year and that is
rising with rising energy costs.
How much is spent to manufacture and transport and dispose of food that is never eaten?
$218 billion
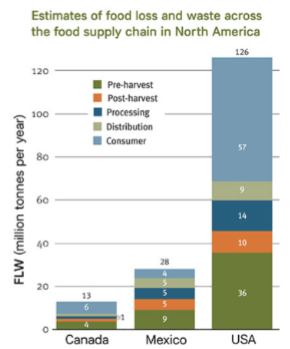
How much food waste do supply chains cause in north america?
Supply chains cause about 40% of food
waste in North America
What step in the supply chain is food lost or wasted the most?
Consumer step
What are the most important points of the FSMA (food safety modernization act)?
1. Gives FDA new authority
• Granting expedited “Green Lane” clearance
• Authority to collect fees for re-inspections.
2. Shift in responsibility from government to industry (self-audits)
3. Food companies to implement preventative controls
develop control systems
corrective actions
training
4. Under more scrutiny for temperature control and sanitation conditions
5. Supplier Approval and Verification
6. Risk management in their facility and SC
7. Recall Program
What tracking and tracing takes place due to the FSMA?
1. Electronic Traceability for both regulations & customer expectations
• Farm to Table
2. Accurately and quickly
3. Identify all ingredients
4. All production and inventory records
5. Ability to initiate a recall: Need for speed too
• Pulling Product from shelves
• Communication (everyone)
• Reverse Logistics
• Process, storage, disposal (will not get back into SC)
• Product Replacement
• Goodwill
What are the important steps in tracing compromised food in the cold chain?
1. The food industry uses the process of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP)
2. Documenting both the production and distribution chains of products
3. In the case of contaminated food a product can be traced back to a common source or
forward through distribution channels
4. Ability to take action quickly thus preventing illness
5. Removing product and notifying people
6. Must be made available to FDA within 24-hours of a request
What is an “unbroken” cold chain?
uninterrupted series of storage and distribution activities which maintain a given temperature range.
what is “cool cargo”?
products that must be maintained at a certain temperature during transport