Chapter 5: The Integumentary System Overview
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Integumentary System
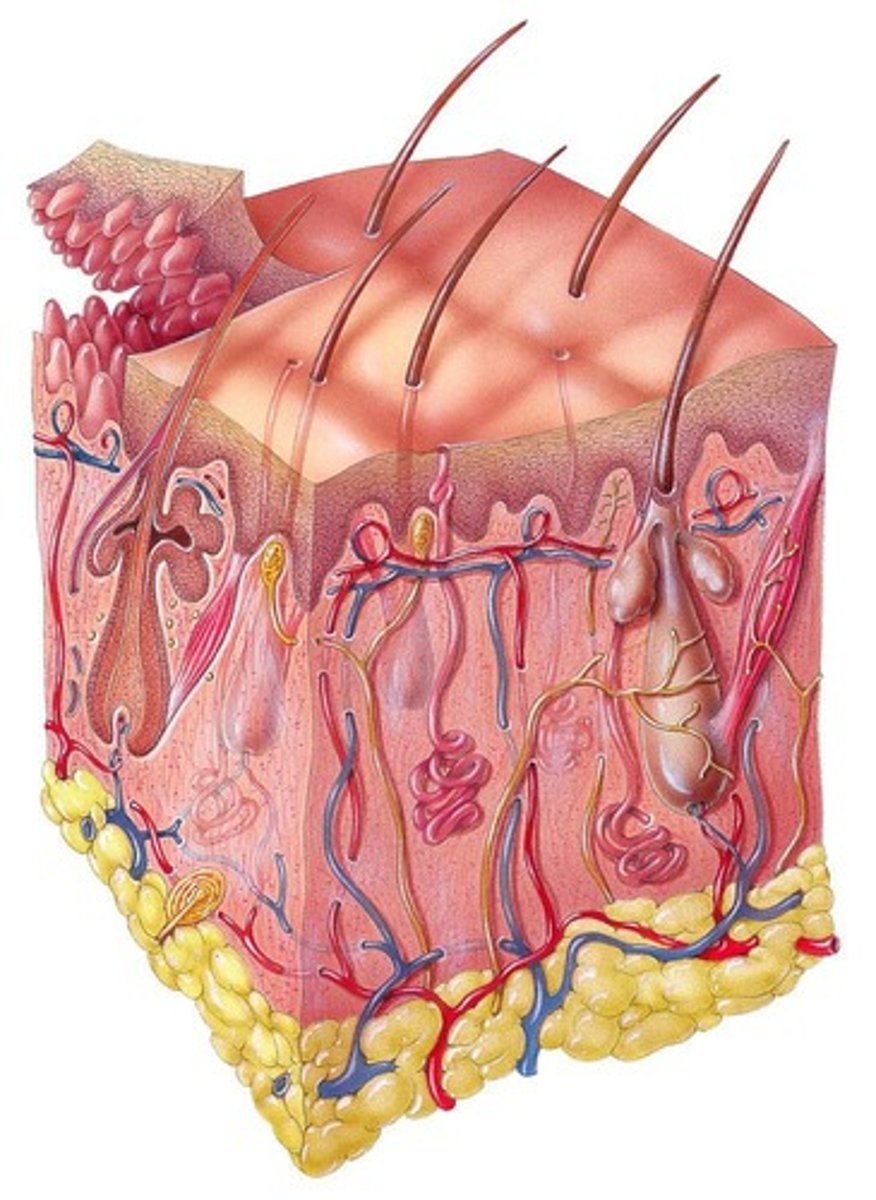
Includes skin and accessory structures.
Cutaneous Membrane
Another name for the integument.
Accessory Structures
Includes hair, nails, glands, blood vessels.
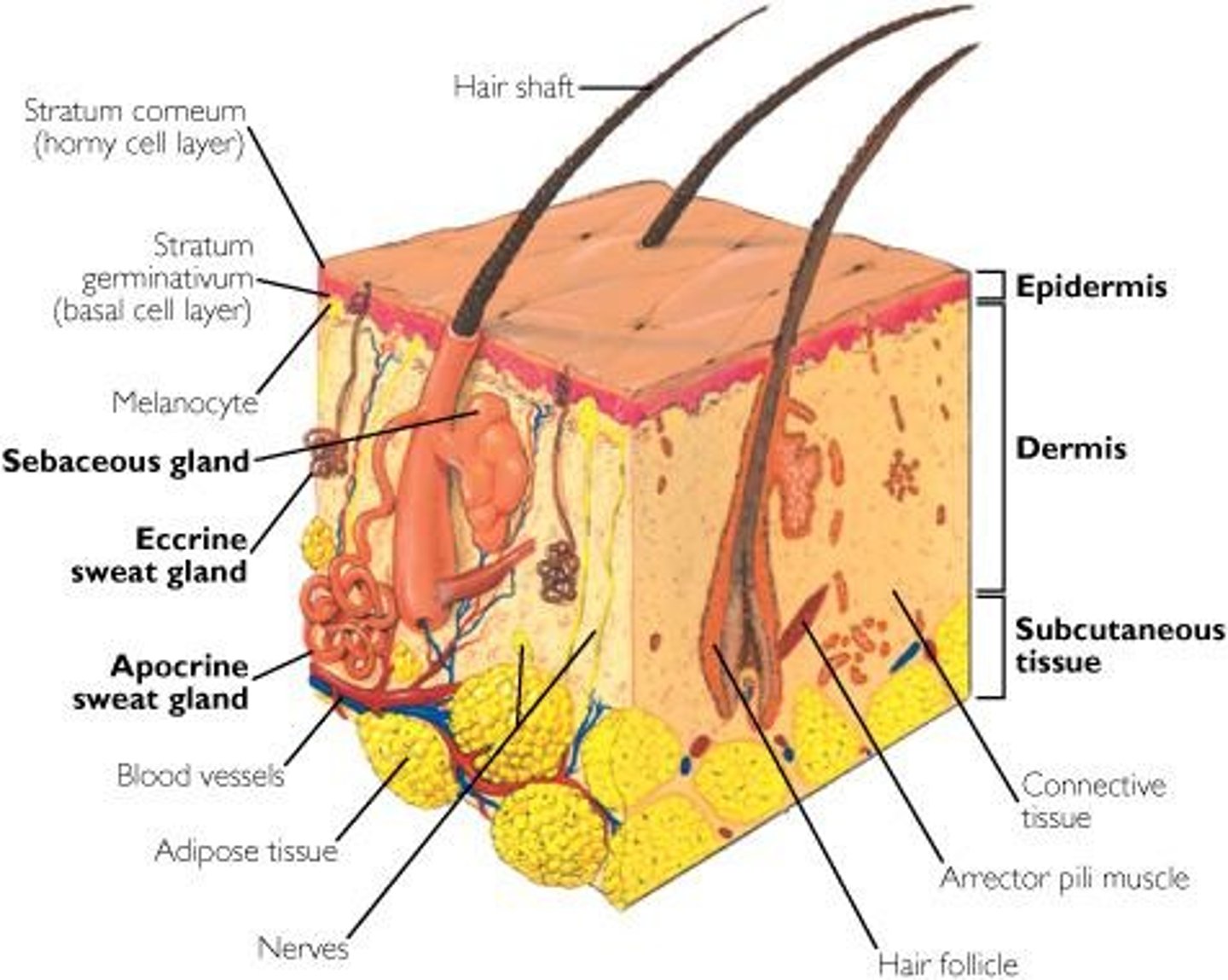
Epidermis
Outer layer of skin, contains epithelial tissue.
Dermis
Inner layer of skin, consists of connective tissue.
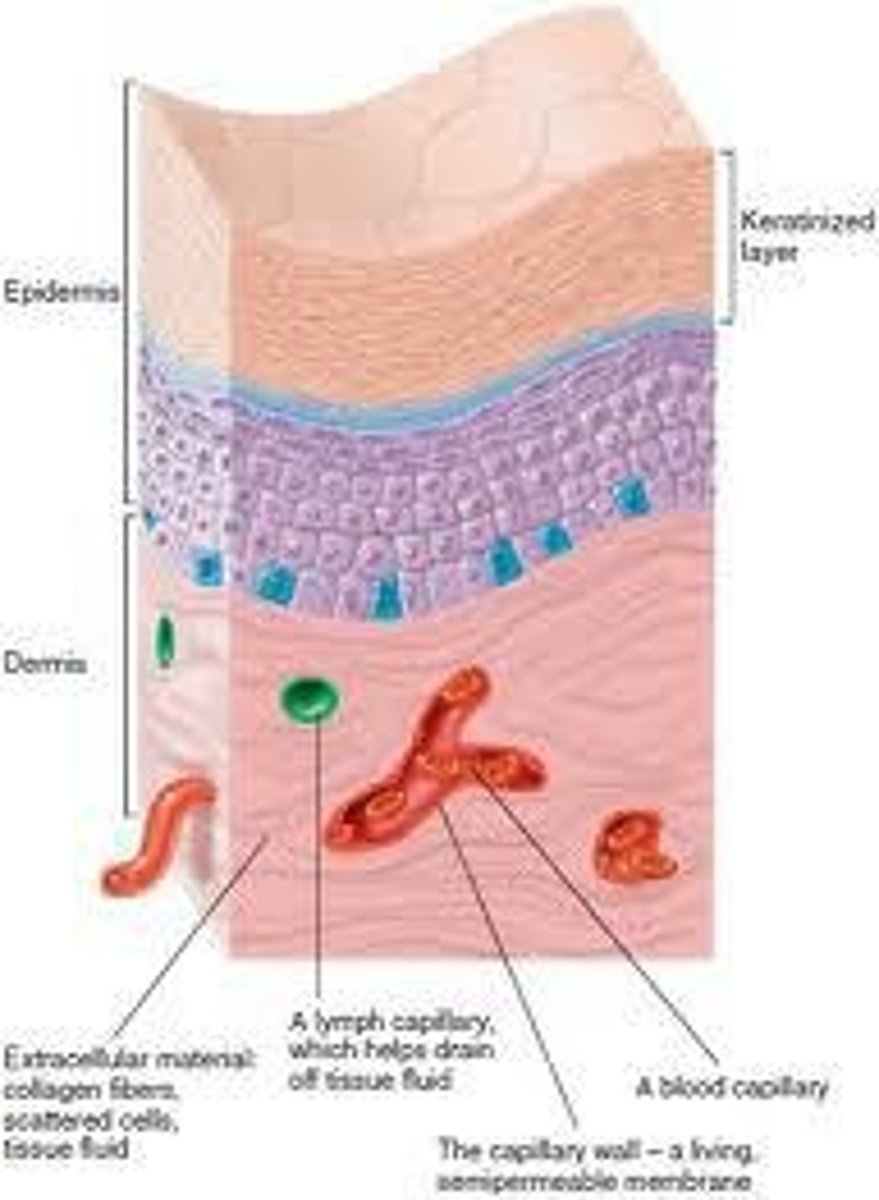
Subcutaneous Layer
Also called hypodermis, insulates and cushions.
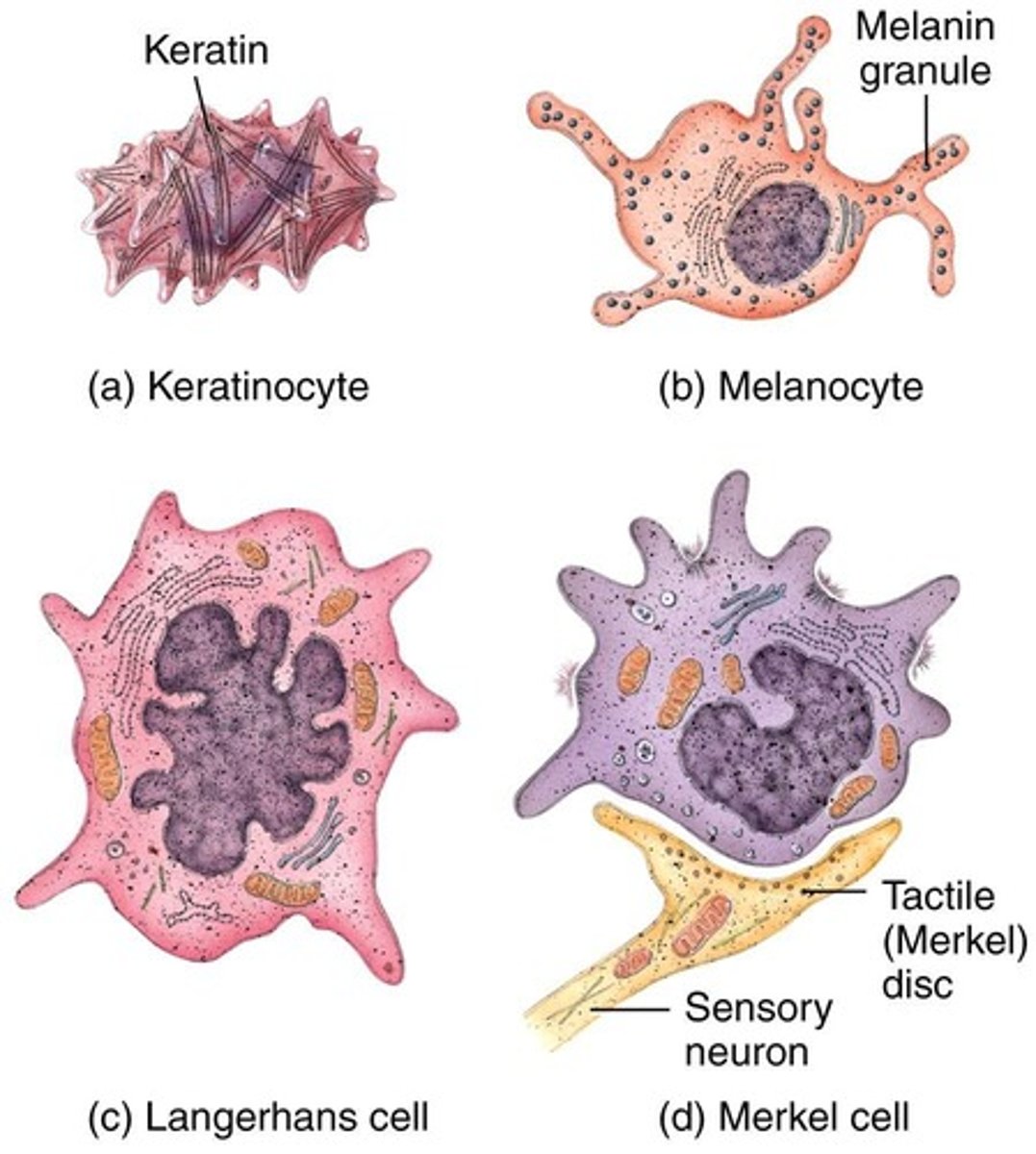
Keratinocytes
Cells producing keratin, make up 90% of epidermis.
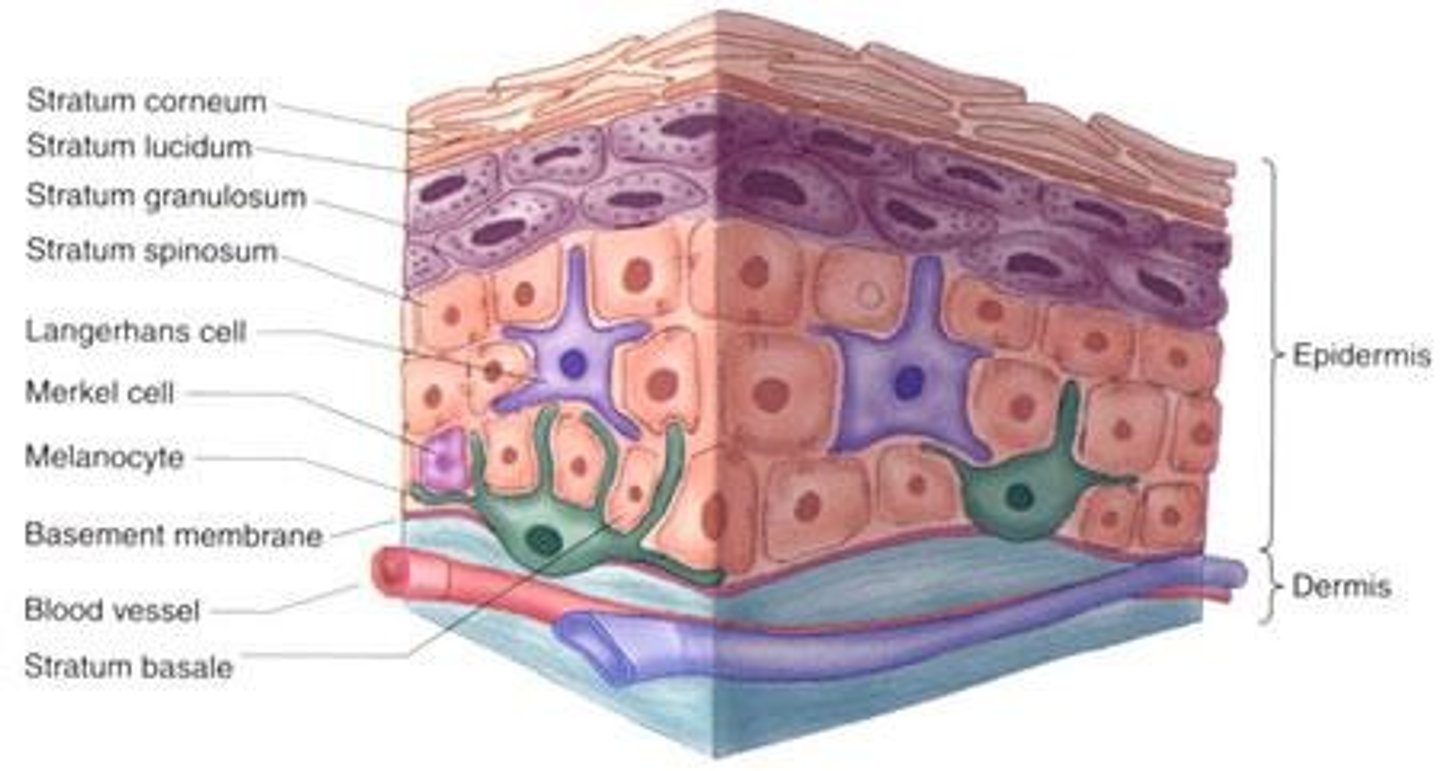
Melanocytes
Cells producing melanin, protect against UV damage.
Langerhans Cells
Macrophages involved in immune responses.
Merkel Cells
Cells functioning in touch sensation.
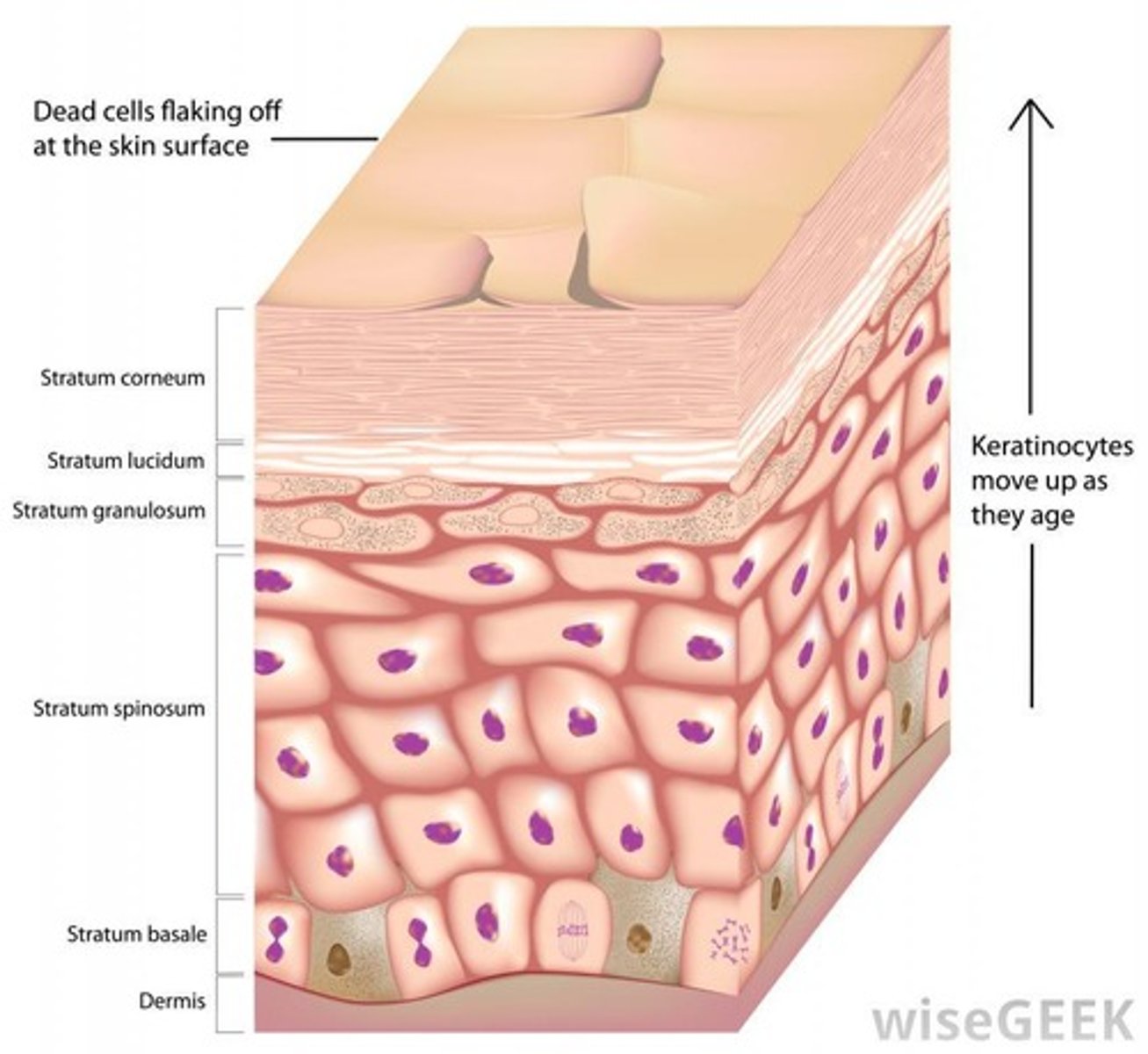
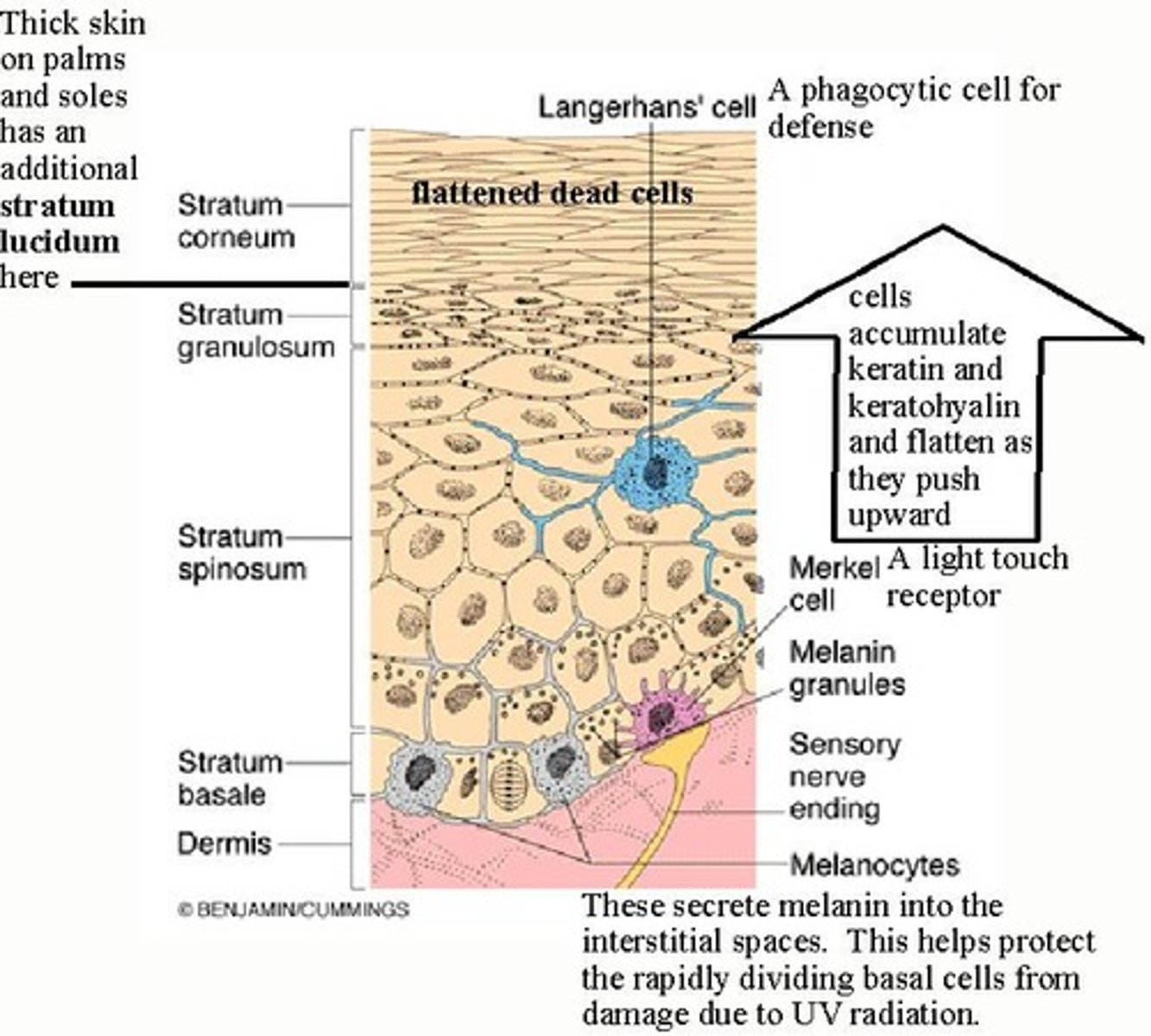
Stratum Basale
Deepest epidermal layer, site of cell division.
Stratum Spinosum
Layer with 8-10 keratinocytes, provides strength.
Stratum Granulosum
Layer with non-dividing cells filled with keratin.
Stratum Lucidum
Only present in thick skin, like palms.
Skin Thickness Range
1-5 mm, thinnest at eyelids, thickest at heels.
Skin Weight
Weighs 4.5-5 kg, about 16% of body weight.
Skin Functions
Protection, temperature regulation, sensory perception.
Vitamin D Synthesis
Occurs from cholesterol due to sunlight exposure.
Sloughing Off
Natural loss of skin layers, contributes to dust.
Epidermal Cell Types
Includes keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans, Merkel cells.
Connective Tissue in Dermis
Provides structural support and elasticity.

Epidermal Layer Composition
Composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
Stratum Corneum
Outermost epidermal layer of dead keratinocytes.
Keratinization
Process of replacing cells with keratin protein.
Callus
Thickened skin from constant friction stimulation.
Dandruff
Excess keratinized cells shed from the scalp.
Thin Skin
Covers all body regions except palms and soles.
Thick Skin
Covers palms, digits, and soles; hairless.
Melanin
Pigment produced by melanocytes in stratum basale.
Eumelanin
Brown to black skin pigment variant.
Pheomelanin
Yellow to red skin pigment variant.
Freckles
Clusters of melanin triggered by sunlight exposure.
Nevi
Benign chronic skin lesions, also known as moles.
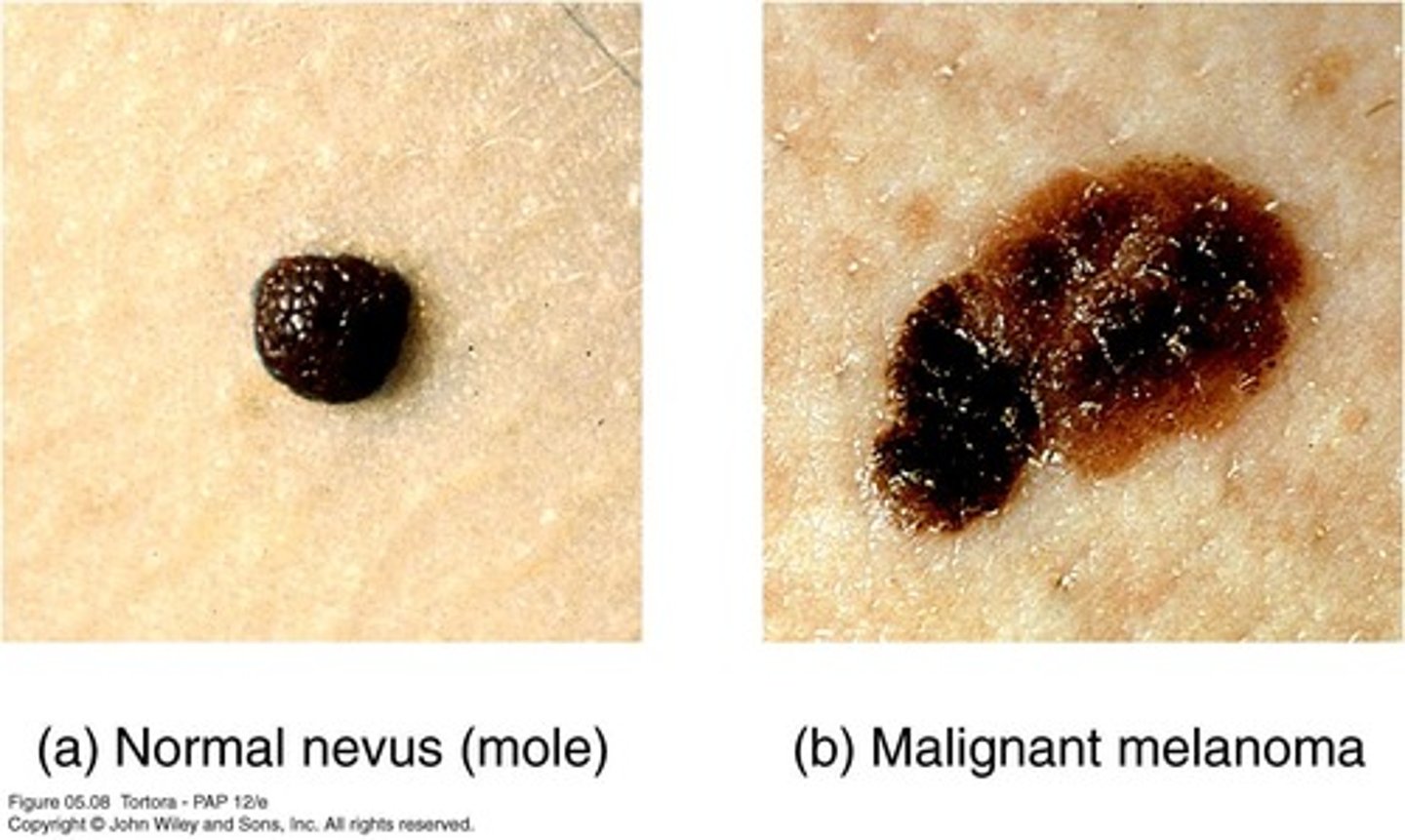
Malignant Melanoma
Cancer of melanocytes, aggressive skin cancer.
Vitiligo
Chronic disorder causing depigmentation patches.
Albinism
Congenital absence of pigment in skin and hair.
Dermis
Layer beneath epidermis, composed of connective tissue.
Papillary Region
Upper dermis with areolar connective tissue and touch receptors.
Reticular Region
Lower dermis with dense irregular connective tissue.
Stretch Marks
Tears in dermis from excessive stretching.
Lines of Cleavage
Tension lines indicating collagen fiber direction.
Sebaceous Glands
Oil glands in the dermis associated with hair follicles.
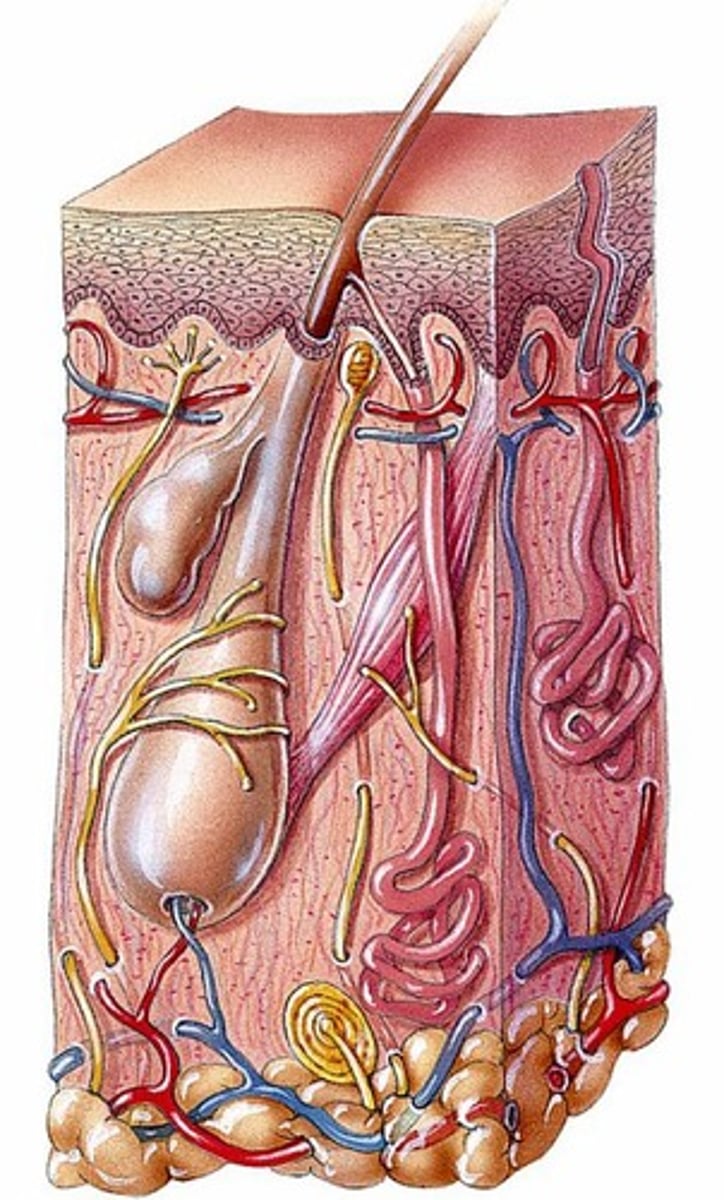
Sudoriferous Glands
Sweat glands located in the dermis.
Dermal Papillae
Small projections in papillary region containing capillaries.
Epidermal Ridges
Contours from dermal papillae; form fingerprints.
Collagen Ridges
Accumulated collagen fibers creating epidermal speed bumps.
Dermis
Skin layer primarily composed of collagen fibers.
Fibroblasts
Cells producing collagen; active during skin injury.
Subcutaneous Layer
Hypodermis; attaches skin to underlying tissues.
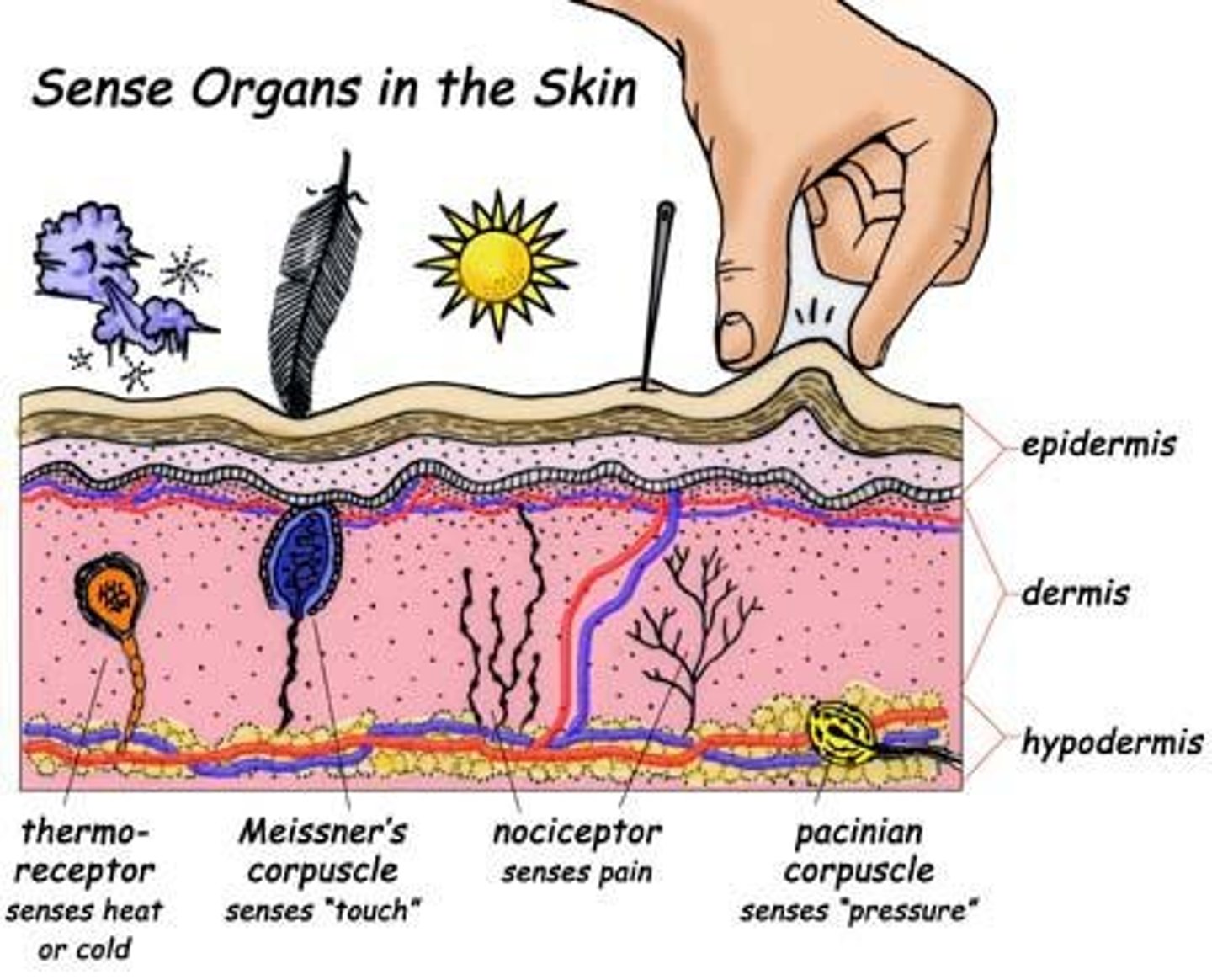
Pacinian Corpuscles
Sensory receptors detecting pressure in skin.
Specialization of Layers
Multiple skin layers allow for functional adaptations.
Temperature Stability
Dermis maintains body temperature through regulation.
Sensory Receptors
Detect various tactile sensations in skin.
Merkel Discs
Receptors for light touch located superficially.
Meissner Corpuscles
Sensory receptors for light touch in dermis.
Hair
Composed of dead keratinized epidermal cells.
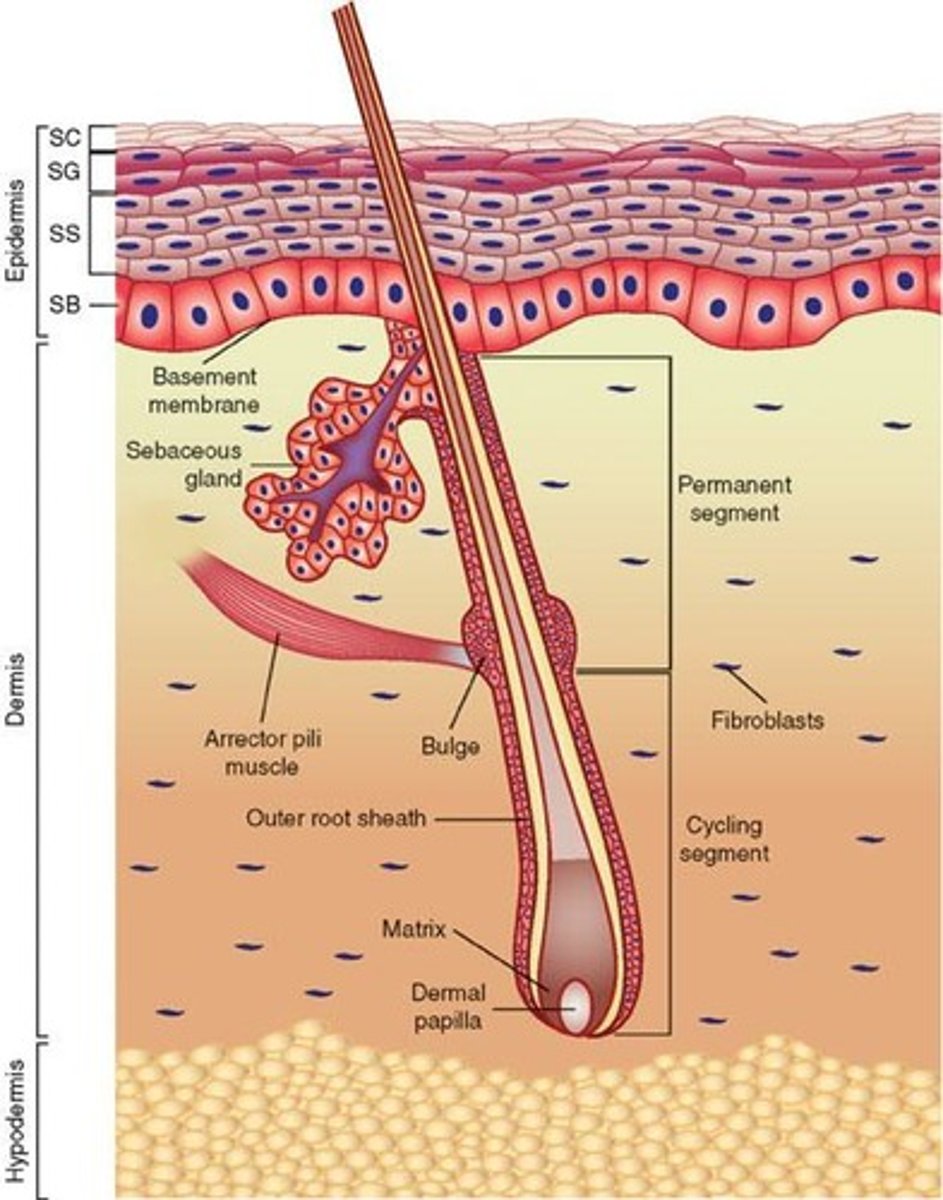
Keratinization
Process where hair cells become keratinized.
Hair Shaft
Part of hair above the skin surface.
Hair Follicle
Structure below skin level housing hair root.
Sebaceous Gland
Oil gland merging with hair follicle for hydration.
Hair Root
Deepest part of hair; living epithelial cells.
Epithelial Sheath
Partially keratinized cells protecting hair root.
Dermal Sheath
Fully keratinized layer; tough protective covering.
Types of Hair
Includes lanugo, vellus, and terminal hair.
Lanugo
Fine, nonpigmented hair covering fetal body.
Terminal Hairs
Coarse, pigmented hair; visible as facial hair.
Exocrine Glands
Epithelial cells secreting substances like oil.
Sebum
Oily substance preventing dehydration and inhibiting bacteria.
Eccrine sweat glands
Most common sweat glands, cover most body areas.
Apocrine sweat glands
Sweat glands in axilla and groin, secrete viscous sweat.
Thermoregulation
Body cooling process via sweat secretion.
Emotional sweating
Sweating due to stress, fear, or embarrassment.
Ceruminous glands
Modified sweat glands producing earwax in ear canal.
Nail structure
Includes free edge, body, root, and cuticle.
Keratinization
Process of cell death as nails grow.
Physical barrier
Skin's dense tissue and keratin protect against injury.
Biological barrier
White blood cells provide immune defense in skin.
Chemical barrier
Water, acids, and oils protect skin from pathogens.
Microbe protection
Non-pathogenic bacteria occupy space to prevent infections.
Langerhans cells
Skin white blood cells involved in immune response.
Melanin
Pigment blocking UV rays, secreted by melanocytes.
Adipose tissue
Insulates body, protecting against cold temperatures.
Burn
Tissue damage from heat, chemicals, or electricity.
First-degree burn
Affects epidermis, causing mild pain and redness.
Second-degree burn
Destroys epidermis and part of dermis, losing functions.
Homeostasis
Skin's role in maintaining internal stability.
Sweat composition
Eccrine sweat contains water and salt (NaCl).
Cerumen
Waxy secretion from ceruminous glands, protects ear.
Second-degree burn
Destroys epidermis and part of dermis.
Third-degree burn
Full-thickness burn affecting all skin layers.
Epidermis
Outer skin layer, involved in first-degree burns.
Dermis
Middle skin layer, involved in second-degree burns.
Subcutaneous layer
Deepest skin layer, affected in third-degree burns.
Fibroblasts
Cells that secrete collagen for tissue repair.
Basal cells
Epithelial stem cells in the epidermis.
Growth factors
Substances secreted by fibroblasts to recruit cells.
Scar formation
Collagen deposition leading to permanent tissue change.
Epidermal wound healing
Occurs with superficial wounds, no blood vessel damage.
Deep wound healing
Involves dermis, blood vessels, and scar tissue.
Provisional matrix
Temporary scab formed during deep wound healing.