Lecture #2: Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, Suboccipital Region, Thoracic Wall
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
31
myodural bridge associated with?
migraine headaches
How many pairs of cranial nerves are there?
12
The gray matter or the collection of nerve cell bodies in the CNS is called what?
Nucleus
The gray matter or the collection of nerve cell bodies in the PNS is called what?
Ganglion
The white matter or the collection of nerve cell bodies in the CNS is called what?
Tract
The white matter or the collection of nerve cell bodies in the PNS is called what?
Nerve
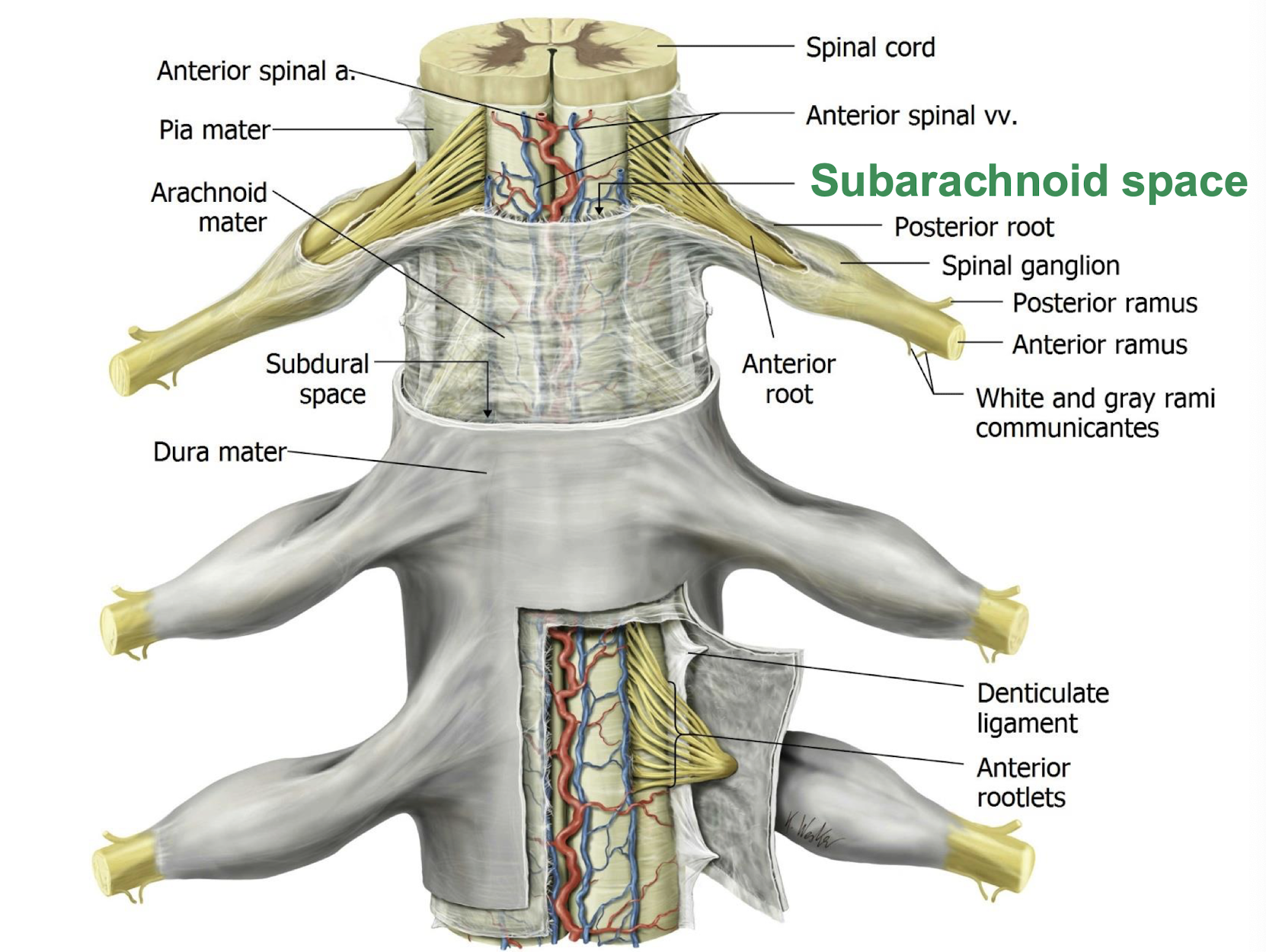
What surrounds the spinal cord as it passes through the Vertebral Canal?
Dural (thecal) Sac
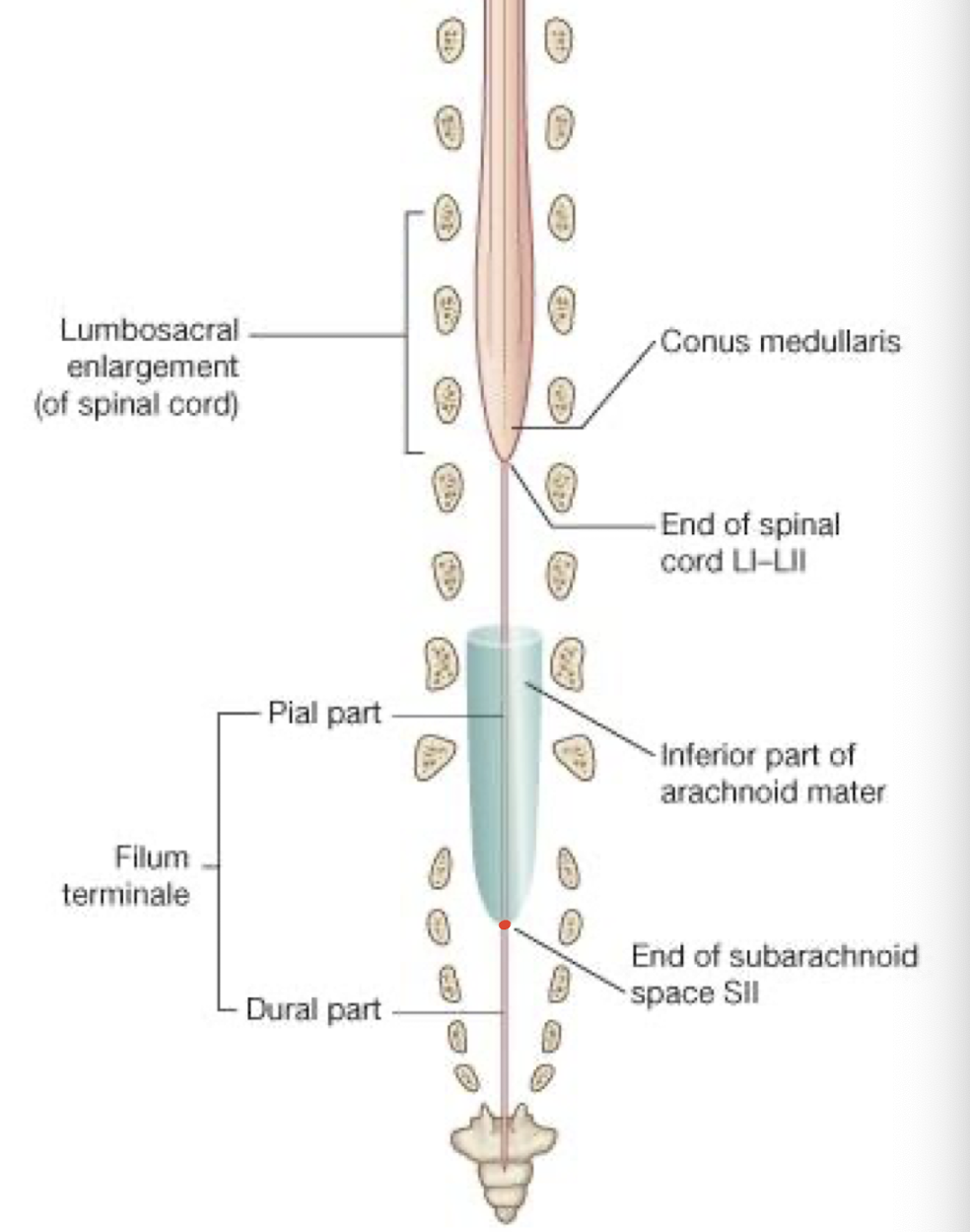
What purpose do the Lumbo-sacral enlargments serve along the spinal cord?
Gives rise to roots of spinal nerves for the brachial and lumbar plexuses (Upper and Lower extremities)
Where does the spinal cord end
L1-L2 in the conus medullaris
What nerve roots give rise to the Cauda Equina?
Lower lumbar, Sacral, and Coccygeal spinal nerves
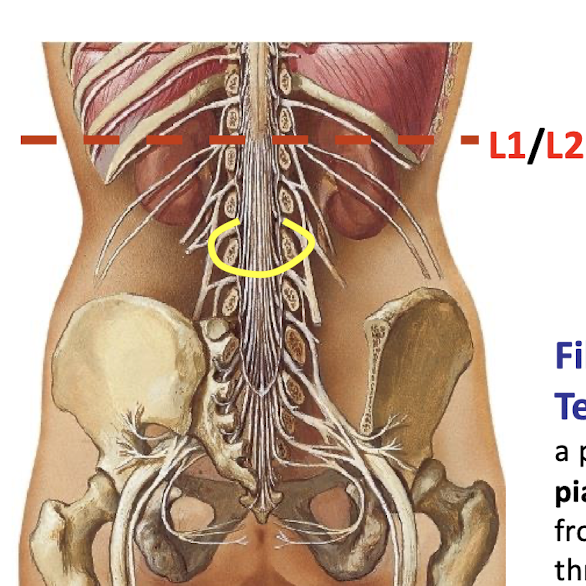
Filum Terminae
projection of the pia mater, extending from the conus medullaris to the coccyx
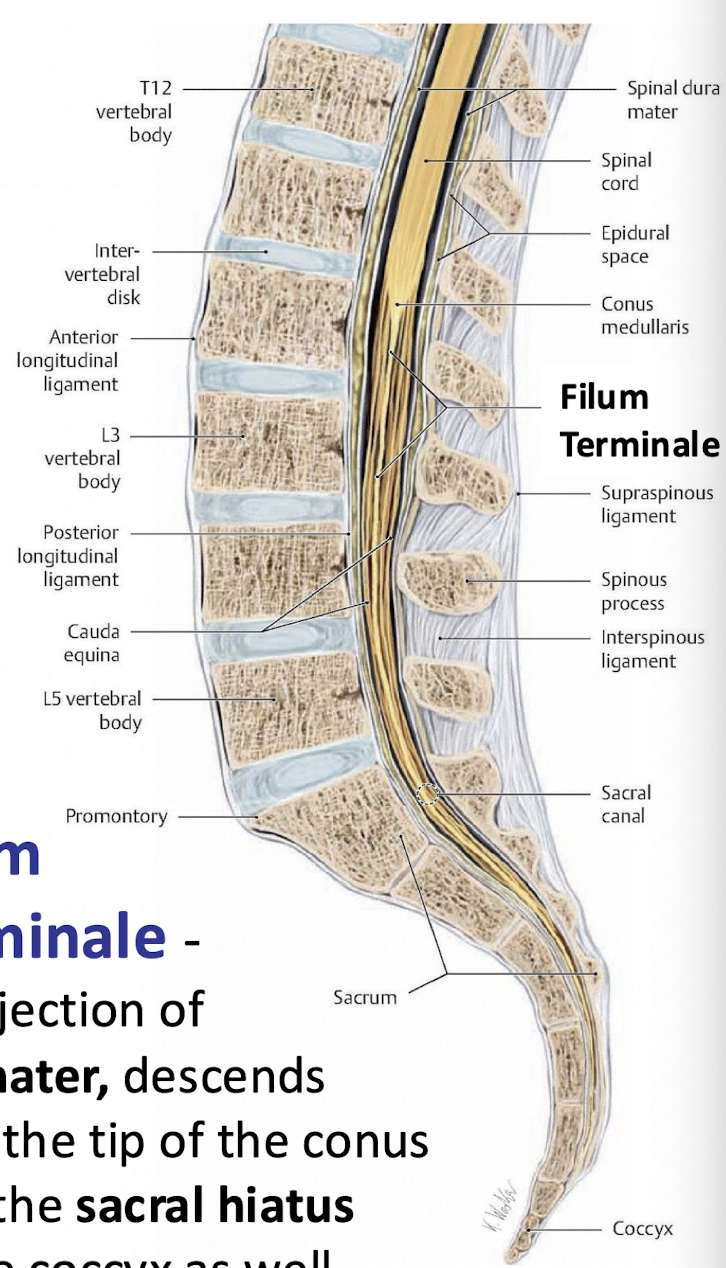
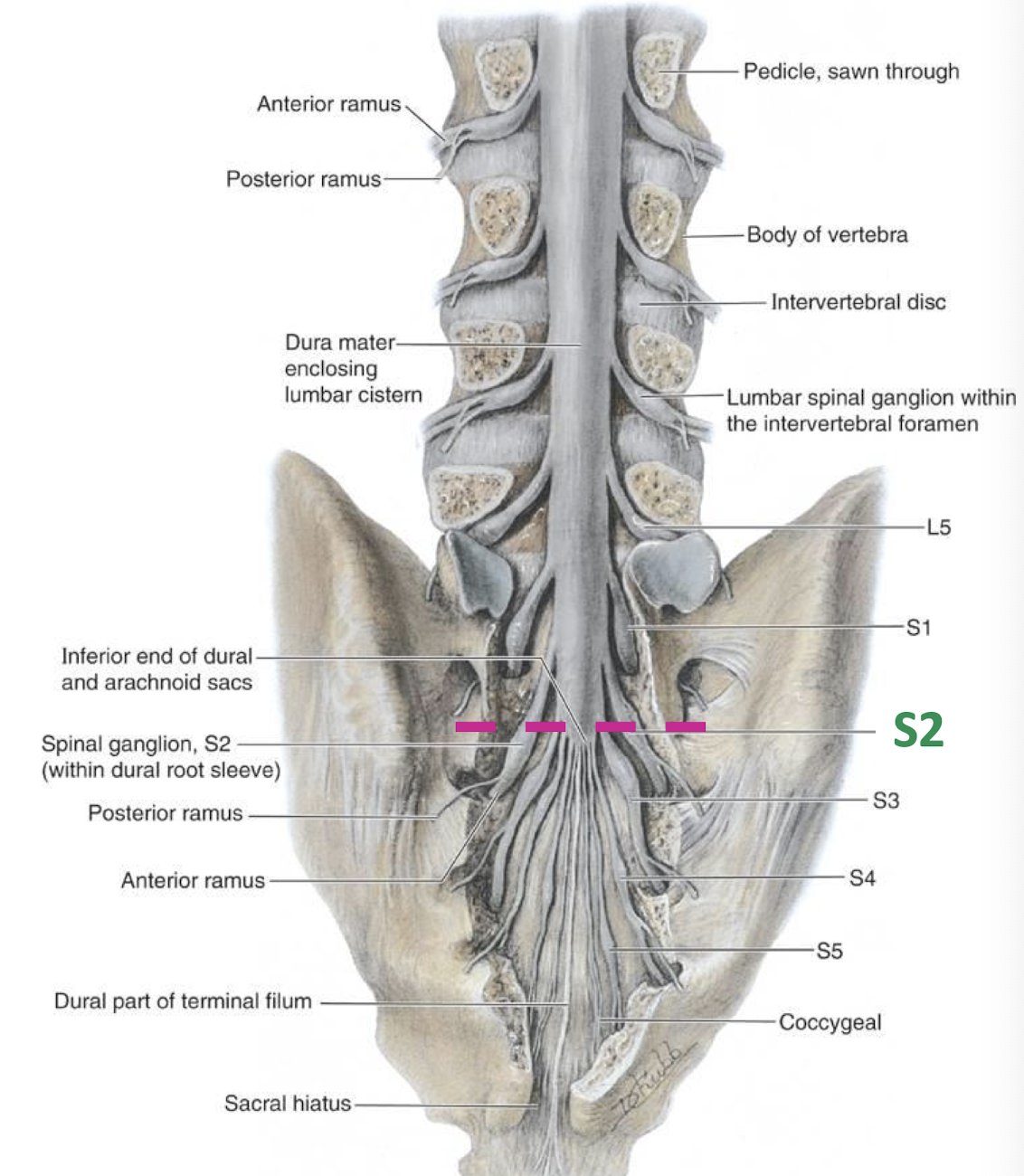
How far does the dural sac extend?
S2
Meninges - Dura function
Projects laterally at each intervertebral level to encompass roots of spinal nerves
What keeps the Arachnoid Mater in place?
Pressure of CSF keeps it attached to the Dura
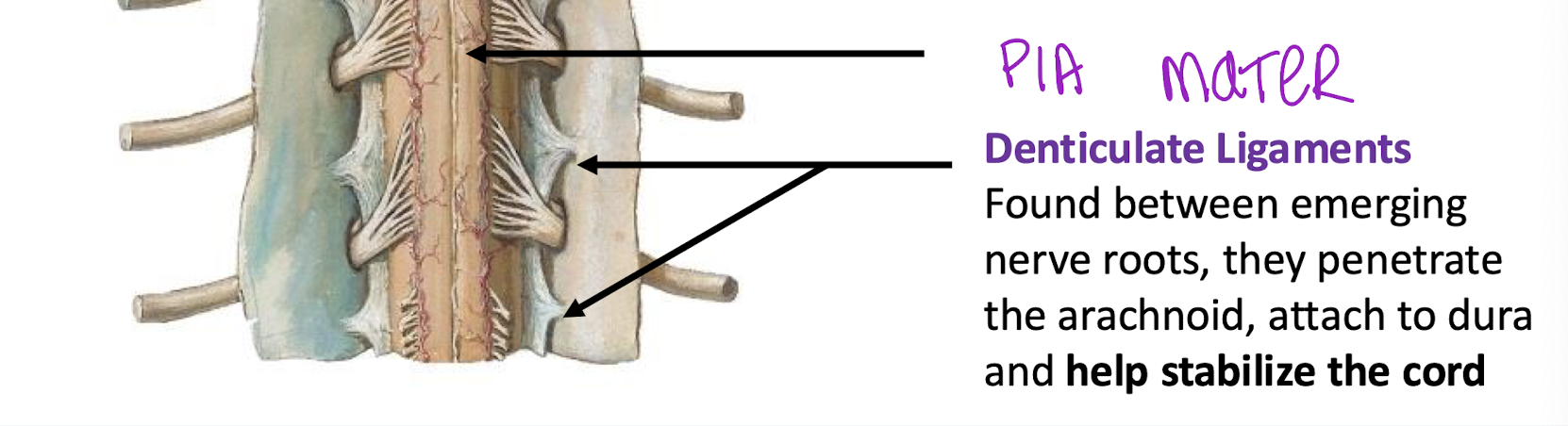
What keeps the pia mater attached to the arachnoid
Denticulate Ligaments - stabalize the cord within the minigial sac and subarachnoid space
Found between emerging nerve roots, and penetrate arachnoid, and attach to the dura to stabilize the cord
Where are the arteries and veins that supply the spinal cord found within?
the subarachnoid space
Where is CSF produced in the brain
Choroid Plexus in ventricles of the brain
what is CSF, function?
removes waste products of CNS metabolism.
adequate quantities of sleep → removal of waste products.
clear, colorless liquid that fills the ventricles and canals of CNS; functions as a shock absorber; creates bouyancy for spinal cord
Where does the subarachnoid space terminate caudally?
S2 - Lumbar Cistern
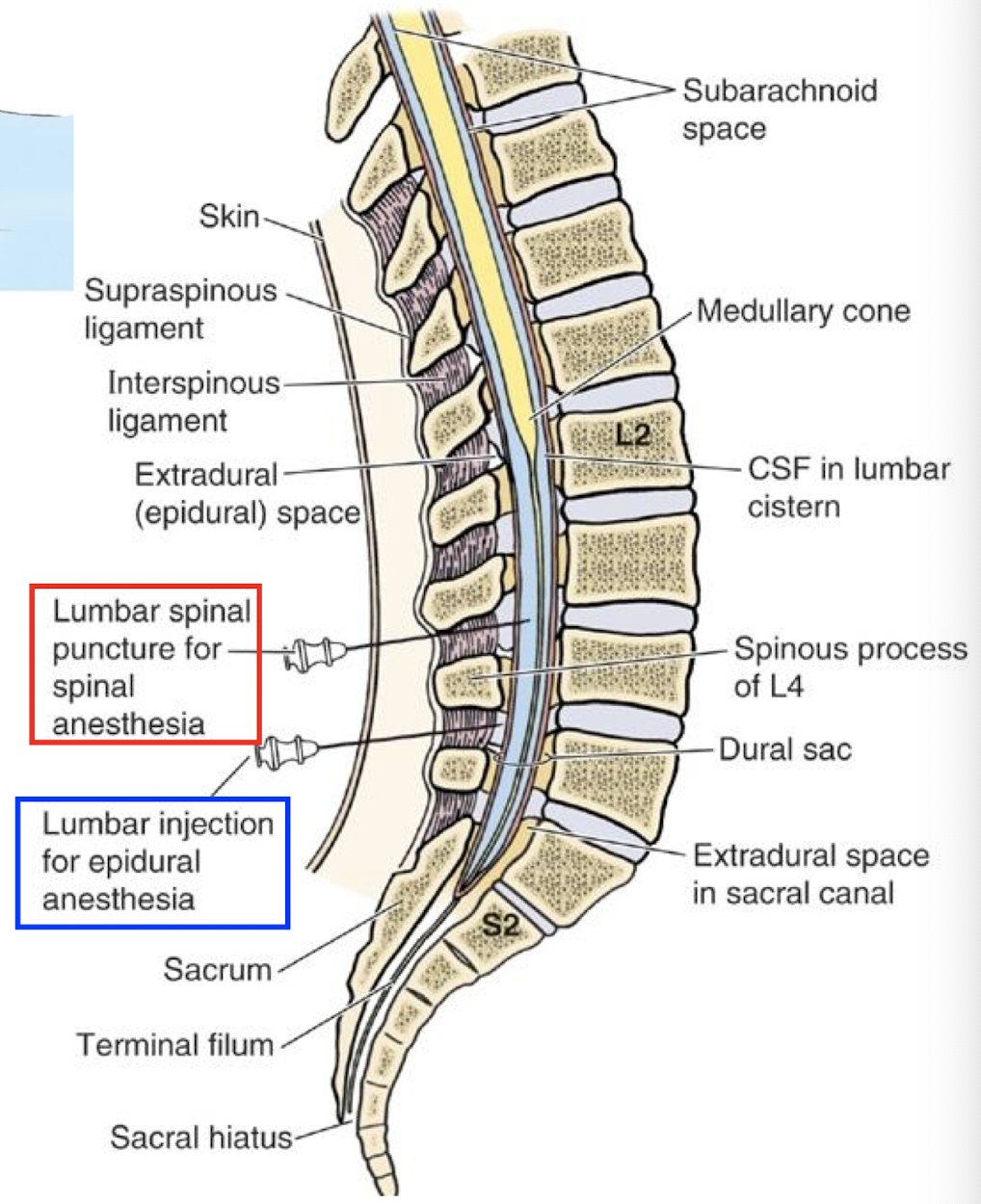
Describe a Lumbar Puncture
into subarachnoid space. lumbar cistern full of CSF
person in tightly flexed posture; allows for more space between spinous processes of lumbar vertebra
needle inserted at L3/L4 or L4/L5 below conus medullaris; needle may encounter cauda equina nerve roots but they will move out of the way
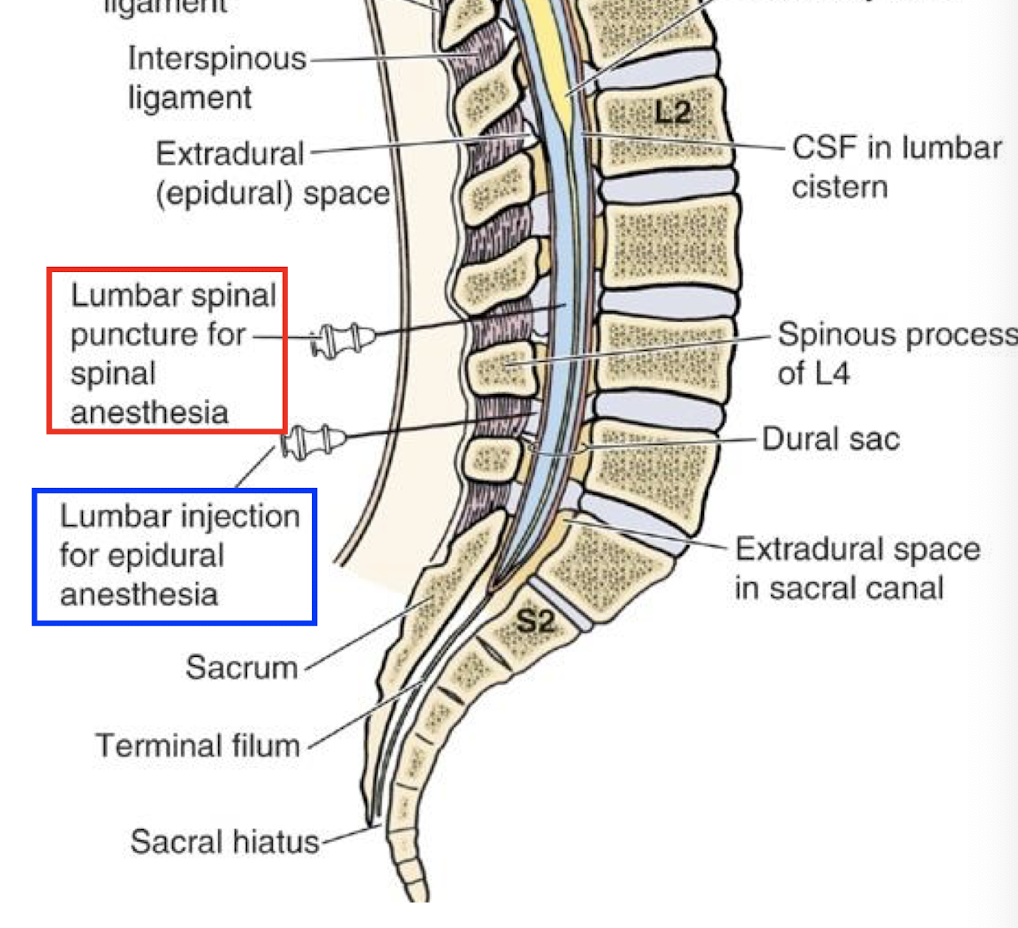
Epidural Anesthesia
tightly flexed posture, needle inserted into L3/L4 or L4/L5 however the needle does not go in as deep. numbs the cauda equina nerve roots and perineum.
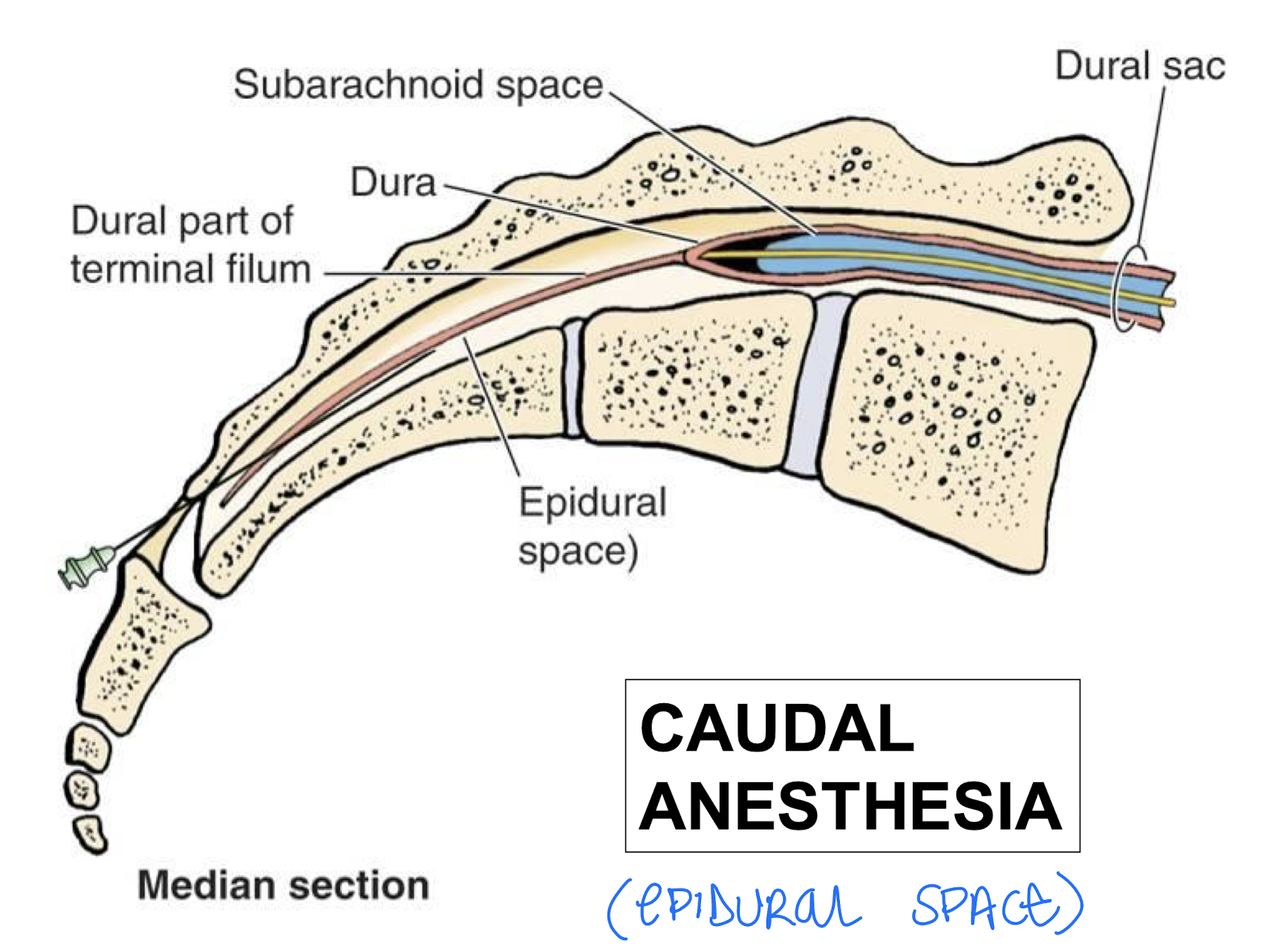
Caudal Anesthesia
Needle enters through the sacral foramina (sacral hiatus) and into the vertebral canal
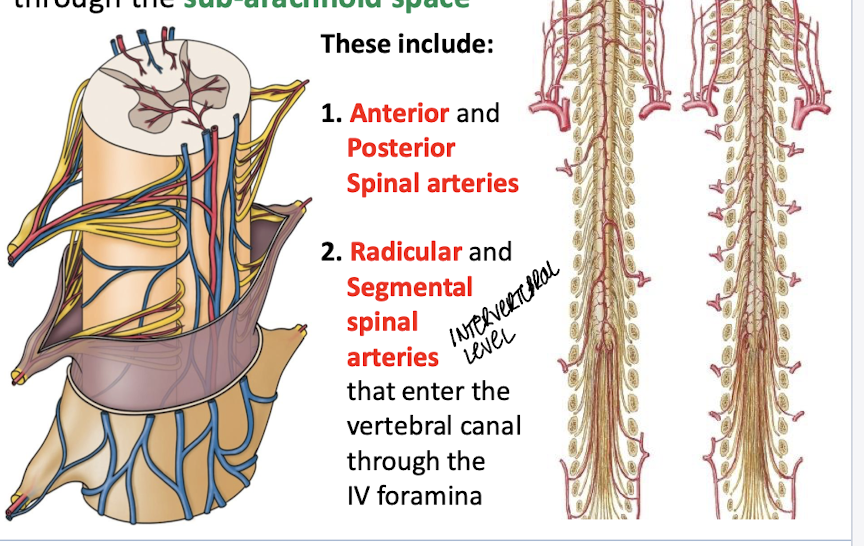
Arteries that supply the spinal cord
anterior and posterior spinal arteries;
Radicular (nerve roots) and medullar spinal arteries (entering the spinal cord) that enter through the intervertebral foramina
Anastomosis of vertical spinal vessels
communication between blood vessels.
provides collateral circulation. every tissue of the body has potential alternative blood supply if primary source is compromised.
exceptions: kidney, retina
aorta and spinal vessels through the segemtnal medullar arteries in the sub-arachnoid space
Somatic Nerves
Part of the PNS; includes motor and sensory nerves
Somatic Motor Nerves (GSE)
Part of the PNS; carries outputs efferently from CNS to stimulate tonic, reflexive, and voluntary contraction of skeletale muscle
Somatic Sensory Nerves (GSA)
sensory info to the CNS.
PNS; carries info afferently to the CNS through sensory ganglia for touch, pain, temperature from body wall;
and pain/proprioception from muscles, tendons, and joints
Visceral Efferent Nerves (GVE)
motor ANS;
innervate smooth muscles, regulate glands, innervate cardiac muscle
Visceral Sensory Nerves (GVA)
Part of the PNS, but make up the ANS; visceral reflexes, convey visceral sensations (hunger, nausea); poorly localized pain; also responsible for referred pain (think heart attack hurting left arm and heart. gall bladder pain in shoulder)
VERY VAGUE FEELINGS. POORLY LOCALIZED.
The amount of nerves/neurons between the CNS and it’s peripheral structure
1 Nerve/1 neuron
either skeletal muscles innervated by GSE fibers OR sensory receptors innervated by GSA fibers
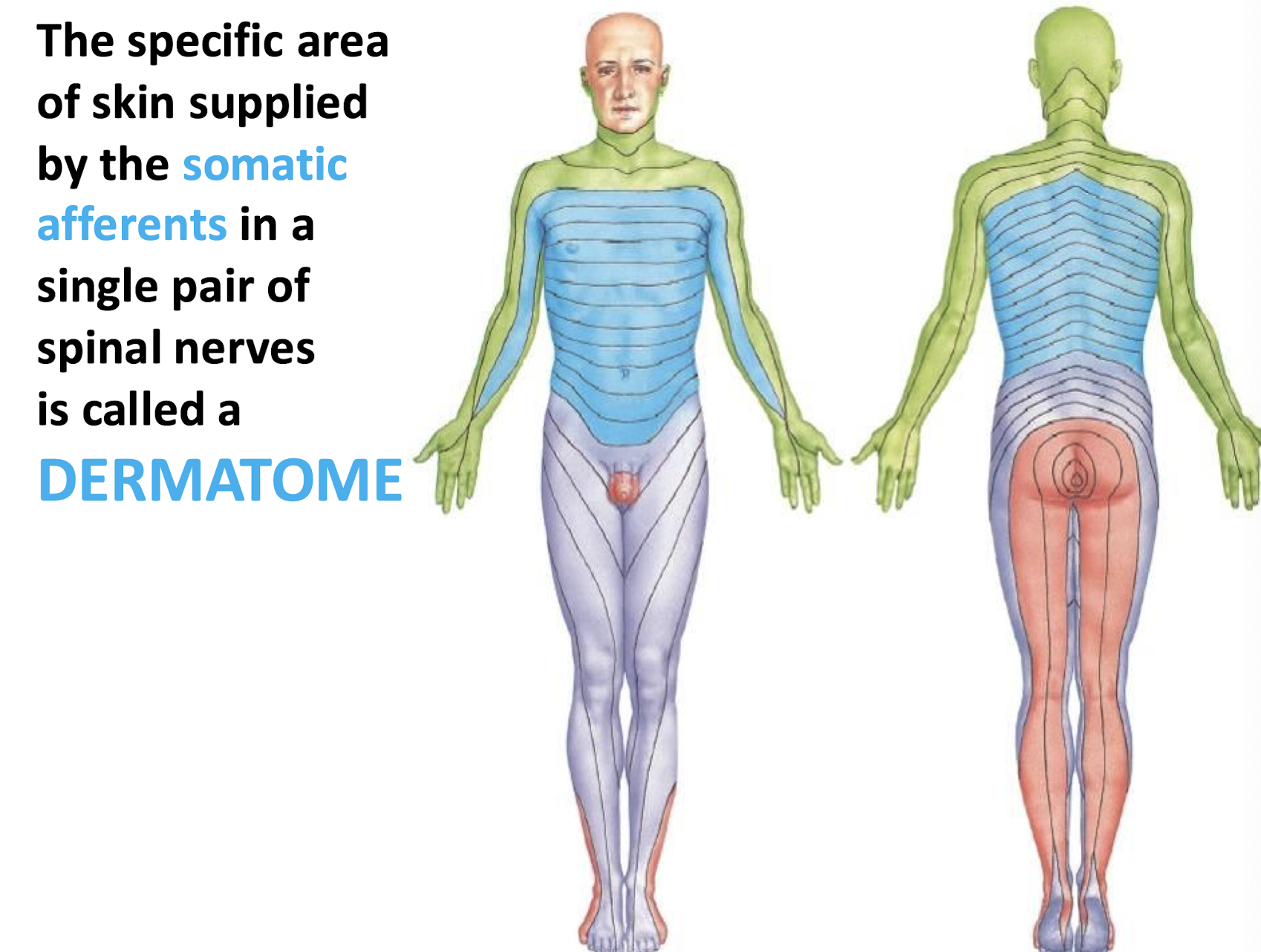
Dermatome
A specific area of the body wall that GSA and GSE supply; area of skin supplied by the somatic afferents in one pair of spinal nerves; these also overlap each other
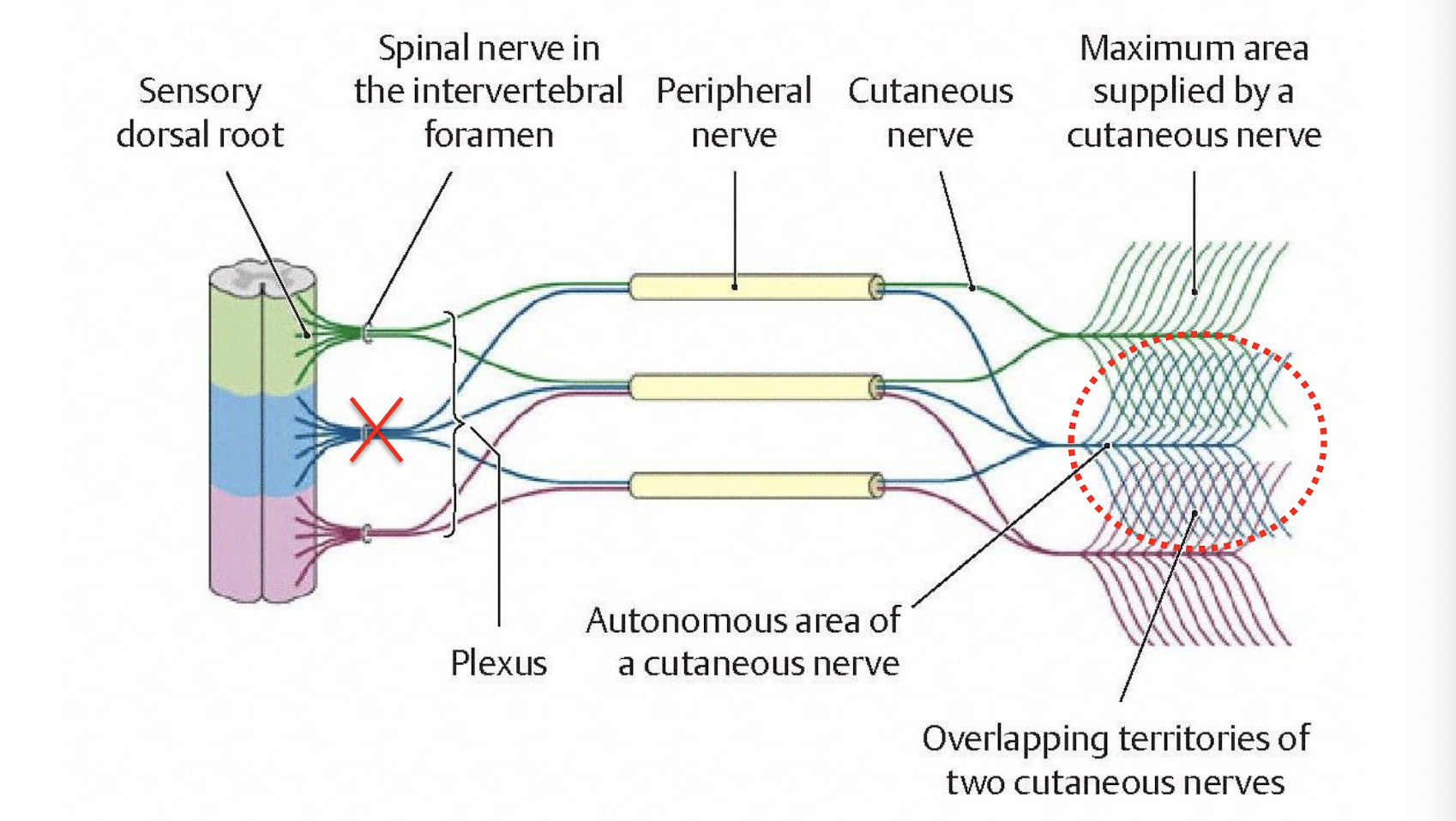
Why do dermatomes overlap?
loss of a single spinal nerve/dorsal root and their GSA don’t cause anesthesia
Myotome
A specific muscle mass in which the GSA and GSE fibers supply
Stimulus of a Lower Motor Neurons in the brainstem or spinal cord causes what in skeletal muscle?
Contraction of skeletal muscle
Lower motor neurons lie ______ to the muscle they intervate.
Ipsilateral
Where are the cell bodies of lower motor neurons found?
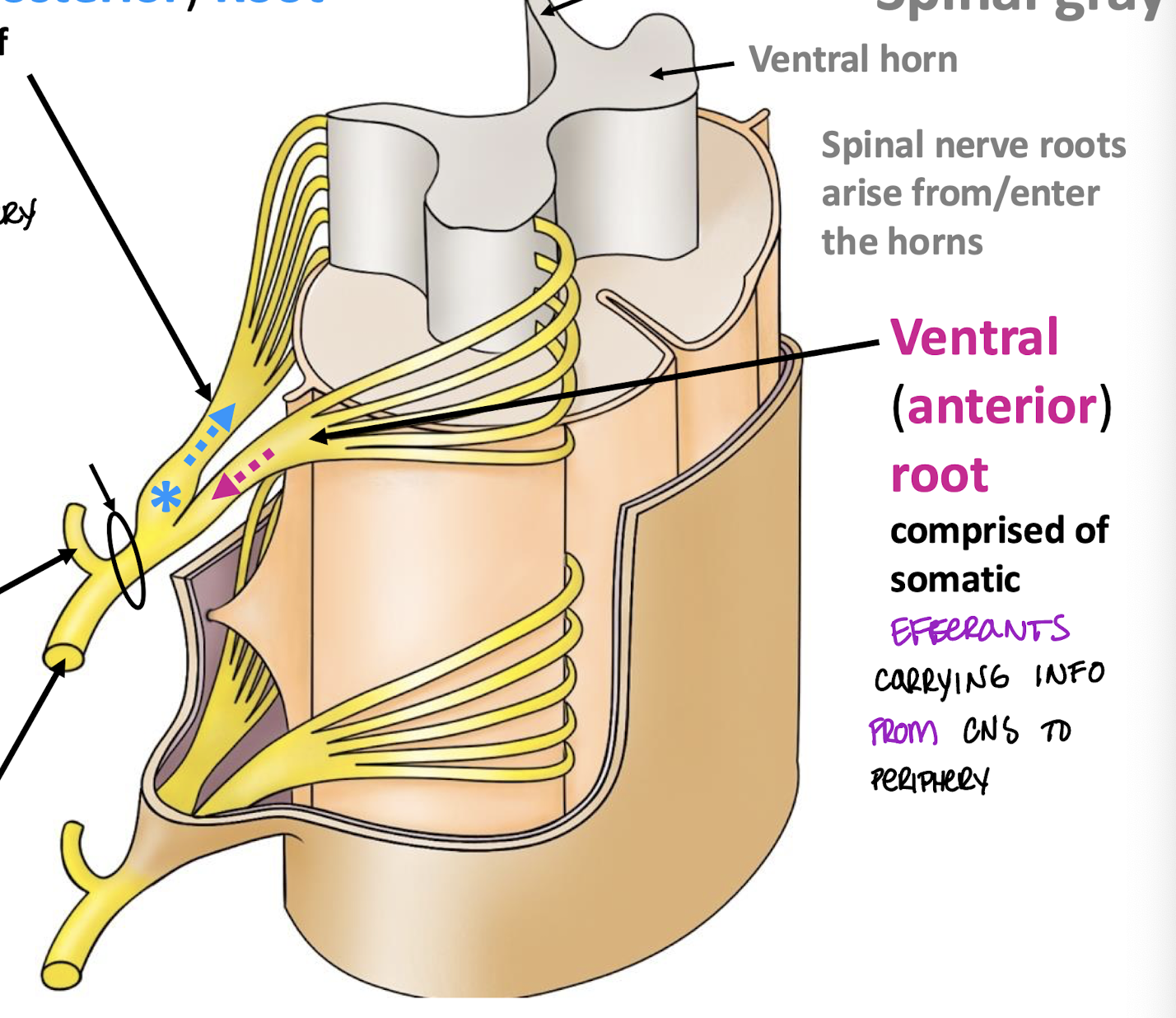
Ventral horns of spinal gray
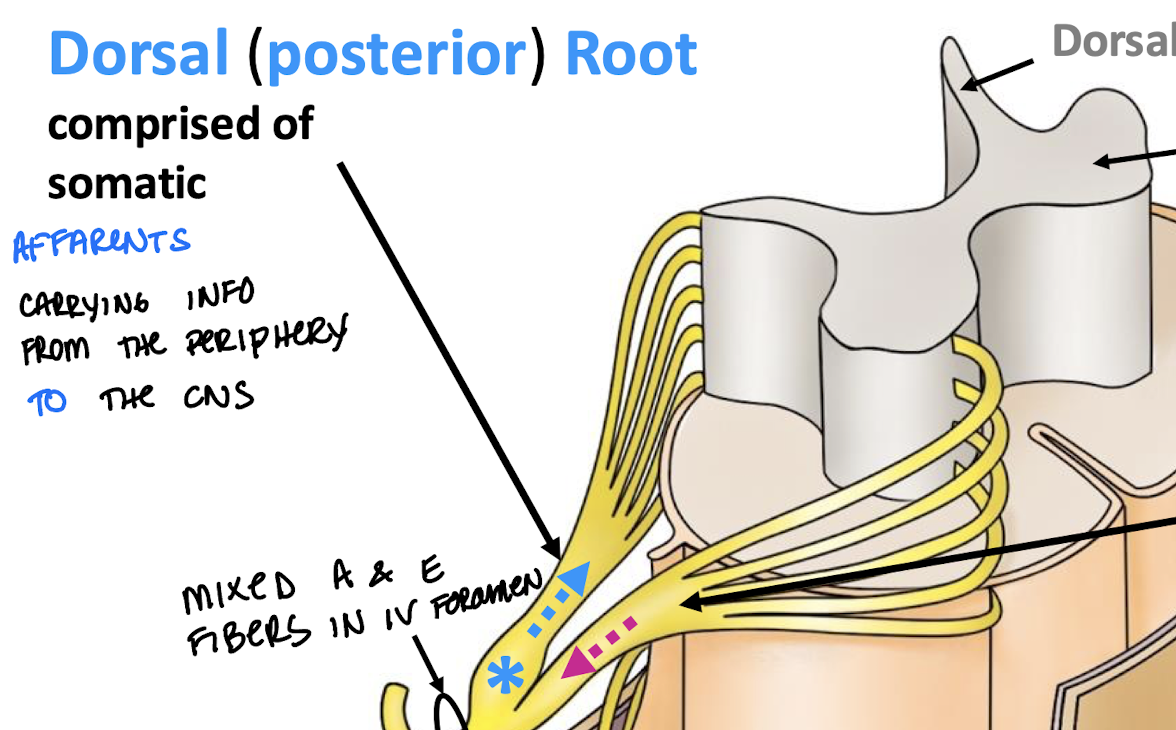
The Dorsal Root is comprised of?
Comprised of somatic afferents carrying info from periphery to CNS
Ventral Root
Comprised of somatic efferents carrying info from CNS to periphery
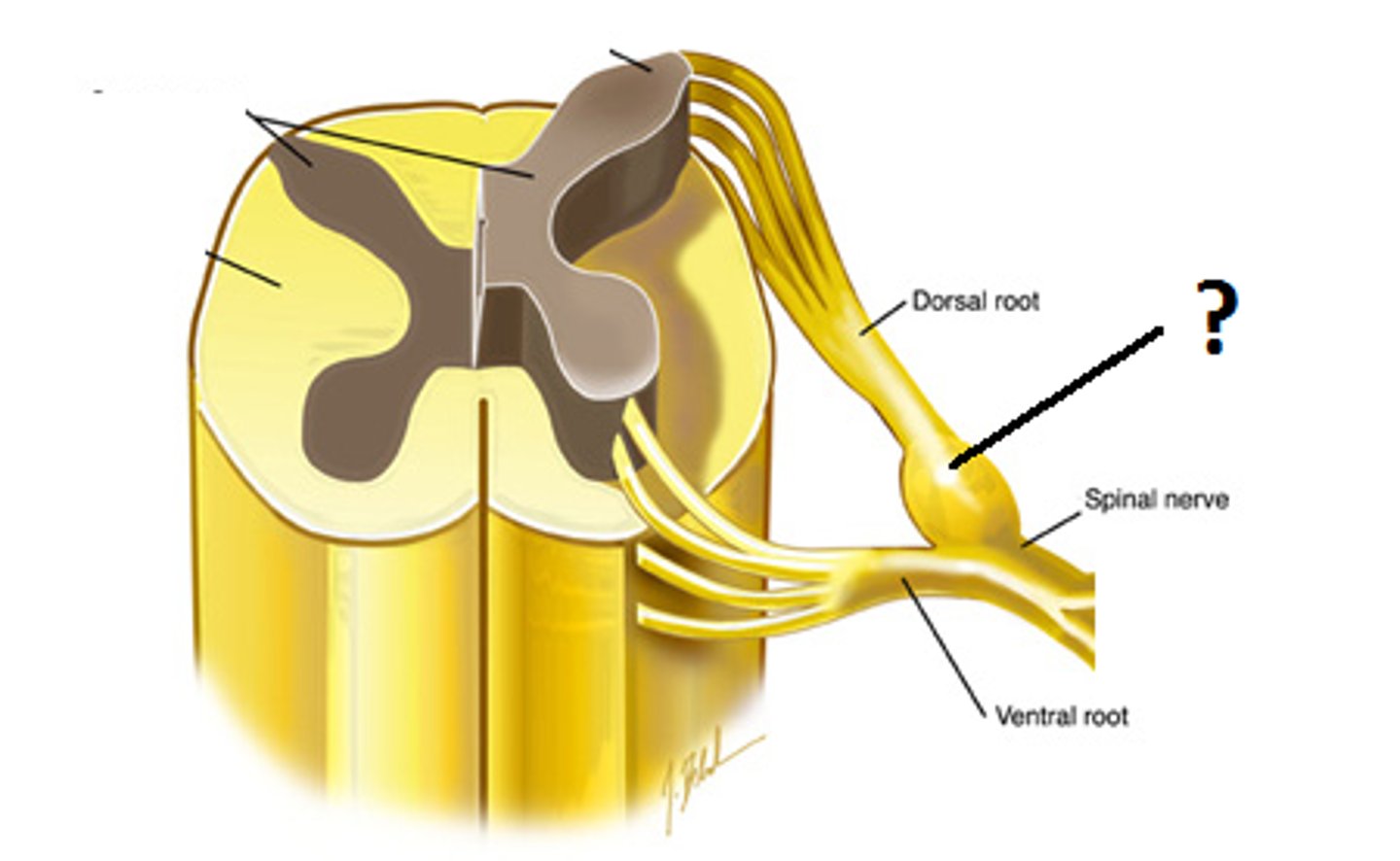
Dorsal and Ventral rami are made up of?
ventral and dorsal roots
Ganglion
collection of nerve cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system
Dorsal Ramus
MIXED spinal nerve in an Intervertebral foramen that splits into a smaller segment towards the back of the body
Ventral Ramus
MIXED spinal nerve in an intervertebral foramen that splits into a bigger segment towards the front of the body
Where are ganglions located?
Dorsal Root
Ventral Ramus Innervations
Anterolateral body wall; Hypaxial muscles; Extremities
Dorsal Ramus Innervations
Skin of back and posterior scalp; epaxial muscles (erector spinae muscles); Facet z joints; posterior spinal ligaments
Number of Cervical spinal nerves
8 pairs
Naming of cervical nerves
named according to inferior margin
C8 nerve goes through C7 and T1 space
Naming of thoracic, lumber, and sacral nerves
according to overlying vertebra.
has to do with the way that lumbar nerve roots go a bit vertically down before they actually leave the spinal cord
nerve L1 is between L1 and L2
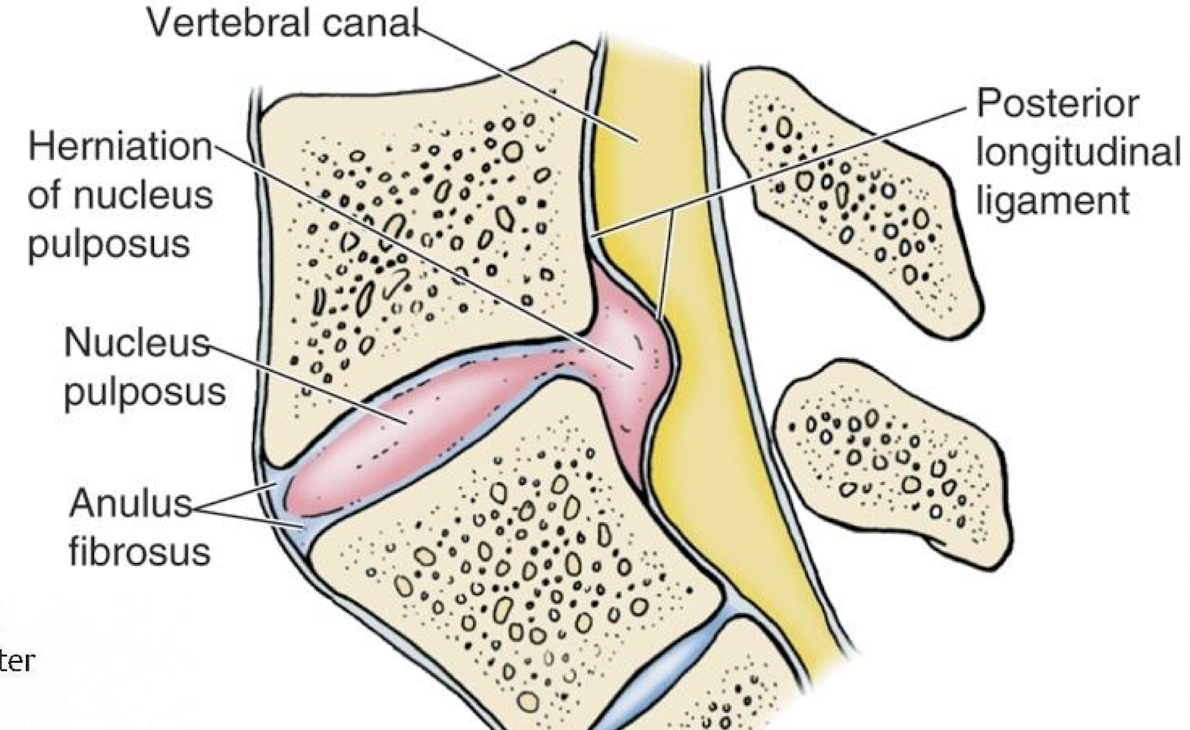
Where would the compression of a Posterolateral herniated Lumbar disc be?
will usually compress the roots of the spinal nerve emerging through the intervertebral foramen BELOW
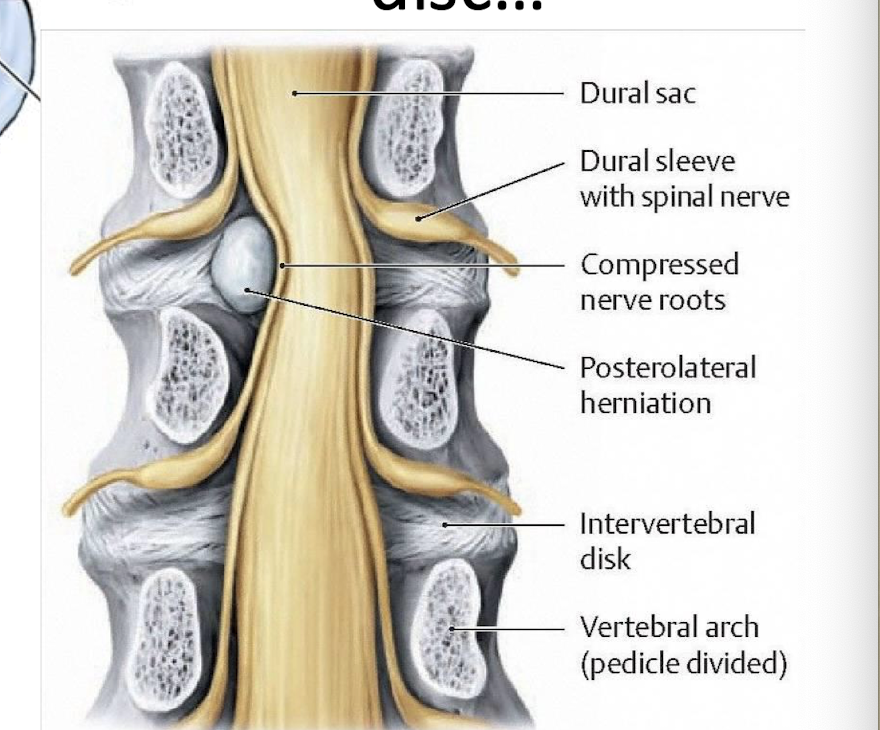
what nerve roots would a posterior herniation of a lumbar disc affect?
multiple nerve roots in the cauda equina
Irritative Peripheral Nerve Injuries: cause and motor/sensory symptoms
Caused by acute or chronic mechanical trauma or inflammation (impingement, entrapment, stretching)
These injuries may stimulate impulses in:
Sensory fibers stimulated: pain, or parasthesia (altered sensation);
Motor fibers stimulated: spasm, twitching of skeletal muscles
Destructive Peripheral Nerve Injuries cause and motor/sensory symptoms
Caused by trauma or neuropathy;
Motor symptoms: paralysis or paresis (weakness) of skeletal muscles;
Sensory symptoms: Anesthesia or hypesthesia (diminished sensation), also pain or dysesthesia (abnormal sensation)
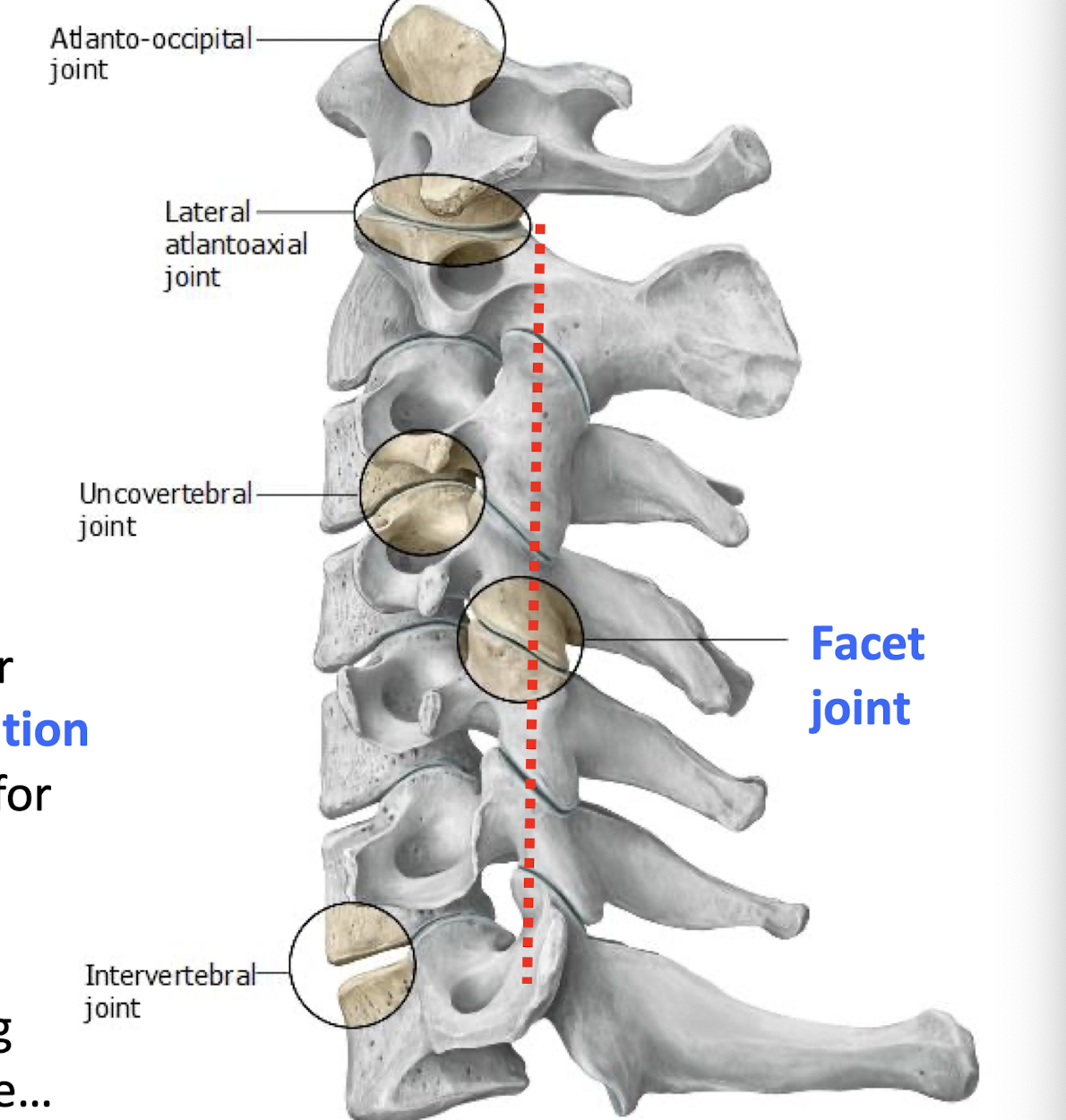
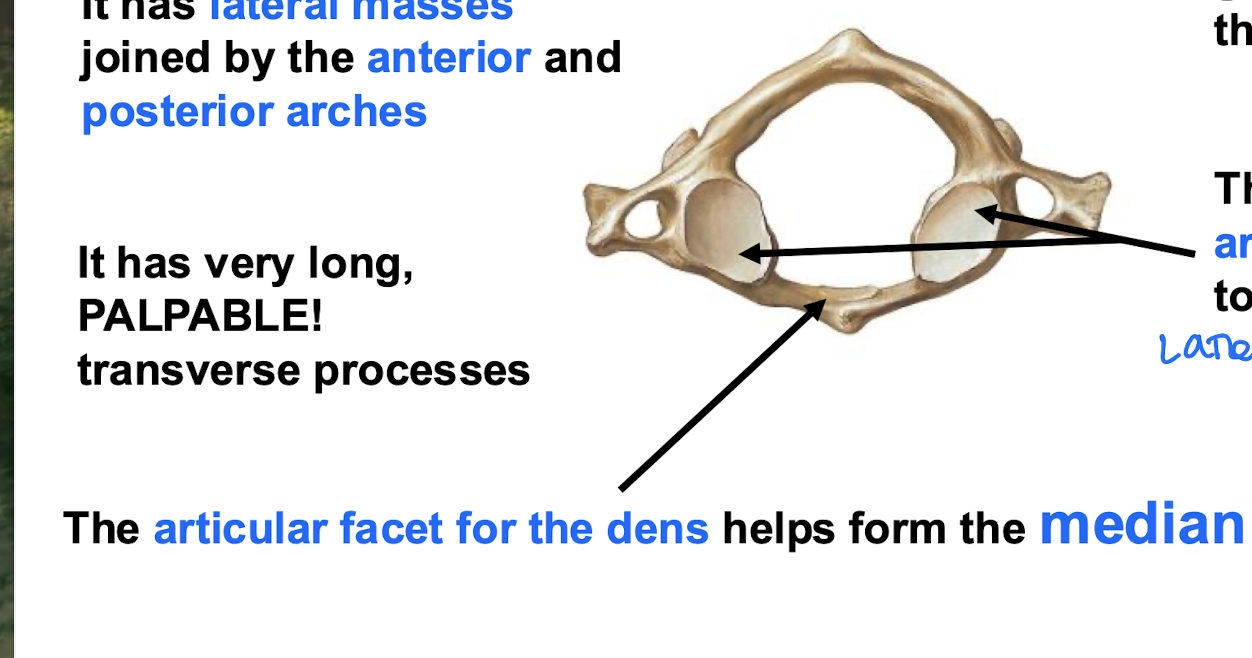
Articular Columns
Cervical facet z joints stacked on top of each other. make the c spine the most mobile
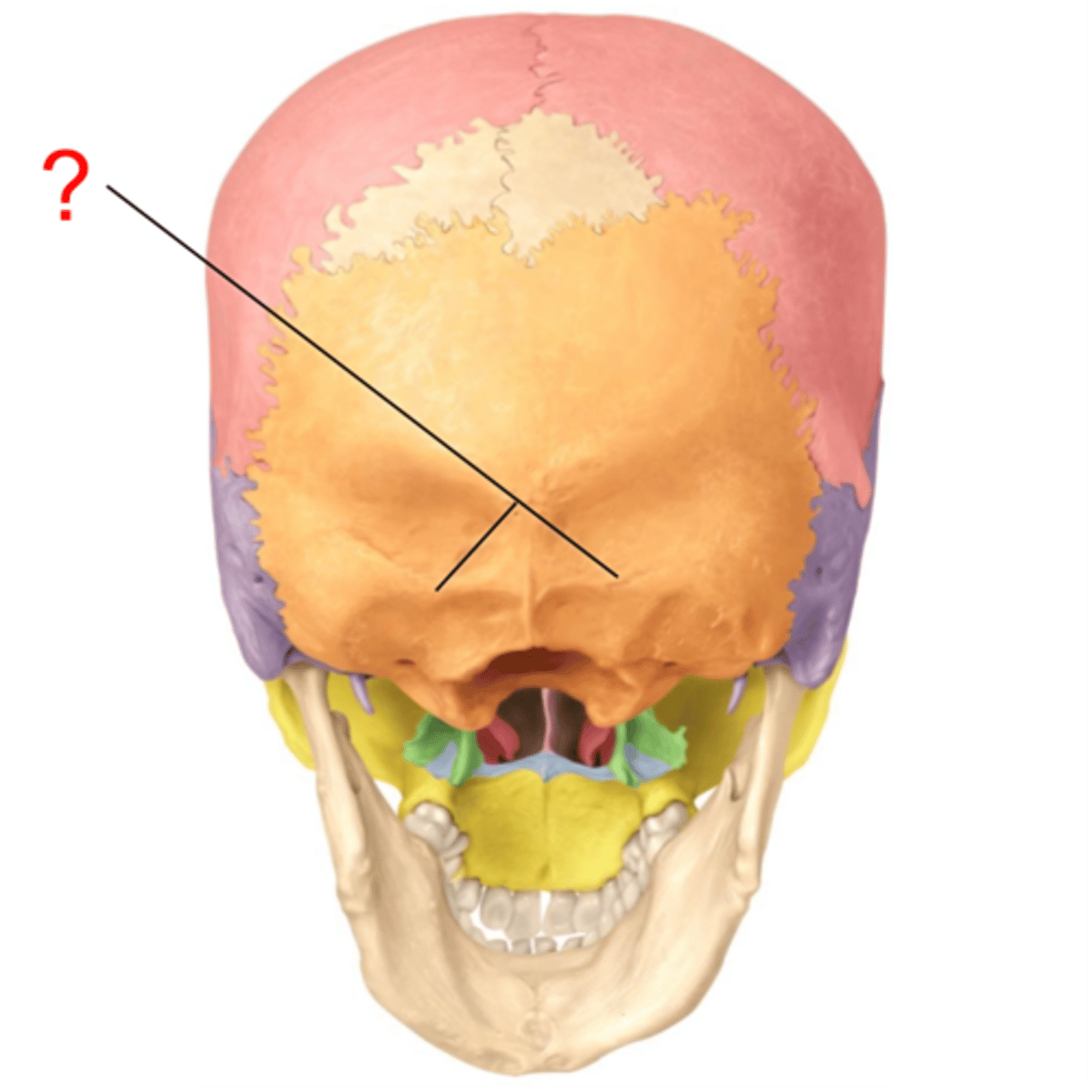
Nuchal Lines
site where muscles of the posterior neck and back attach to the skull
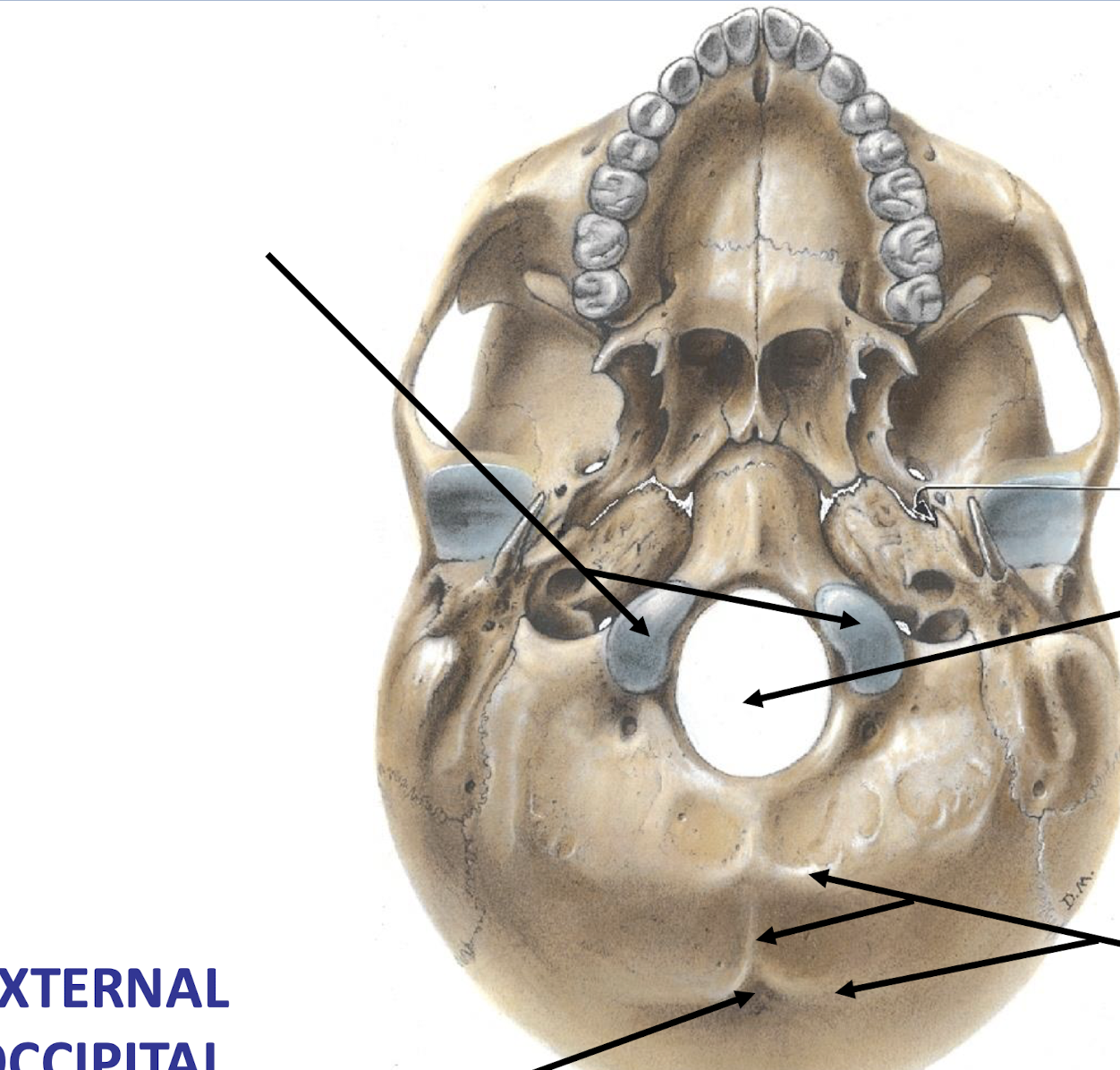
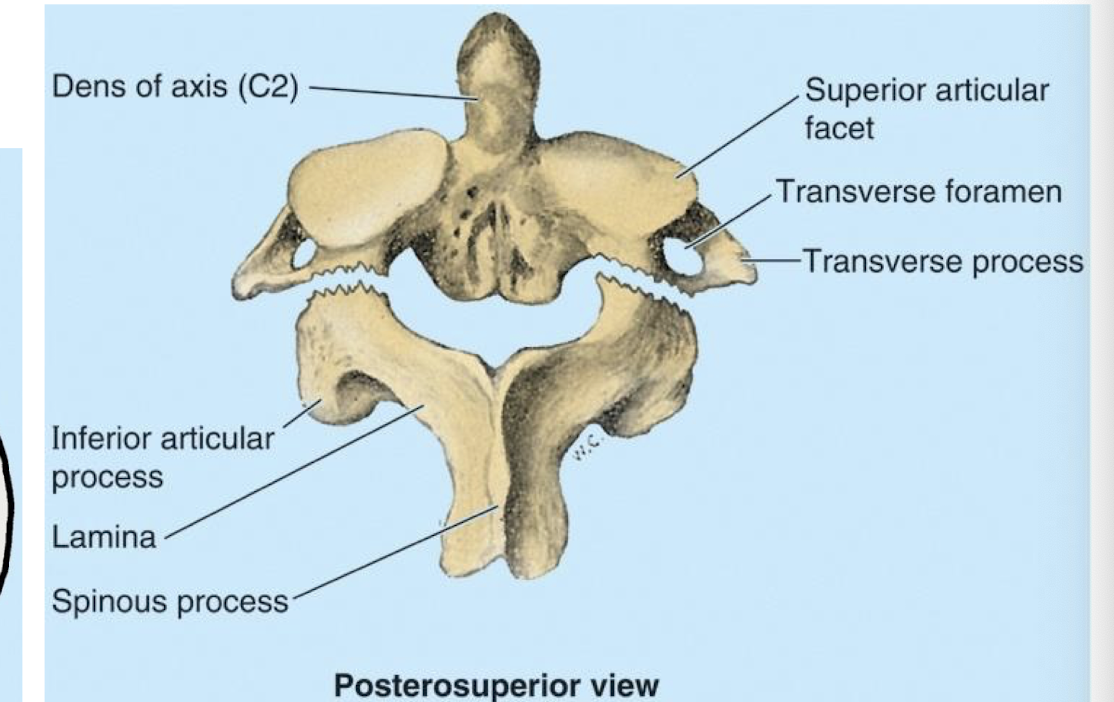
Occipital Condyles
Articulates with C1 (Atlas) which is why C1 has no body
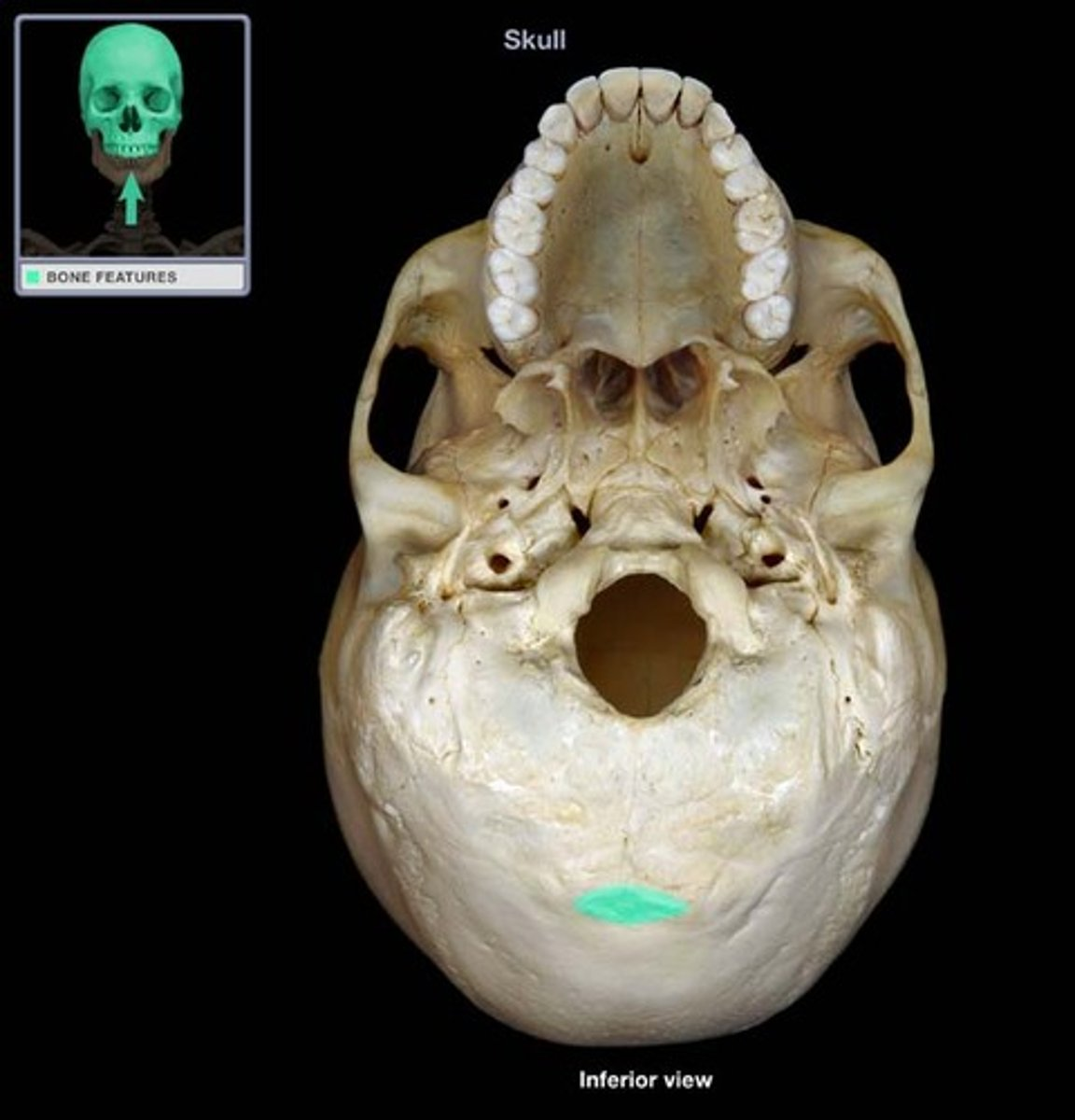
External Occipital Protuberance
superior origin of trap
attachment for neck and back muscles positioned most posteriorly

Atlanto-Occipital Joints
concave, waisted superior articular facets where occipaital condyles rest
the "Yes" joint; Jefferson Fracture (bursting of the atlas)
The “yes” joint
Atlanto-occipital joint
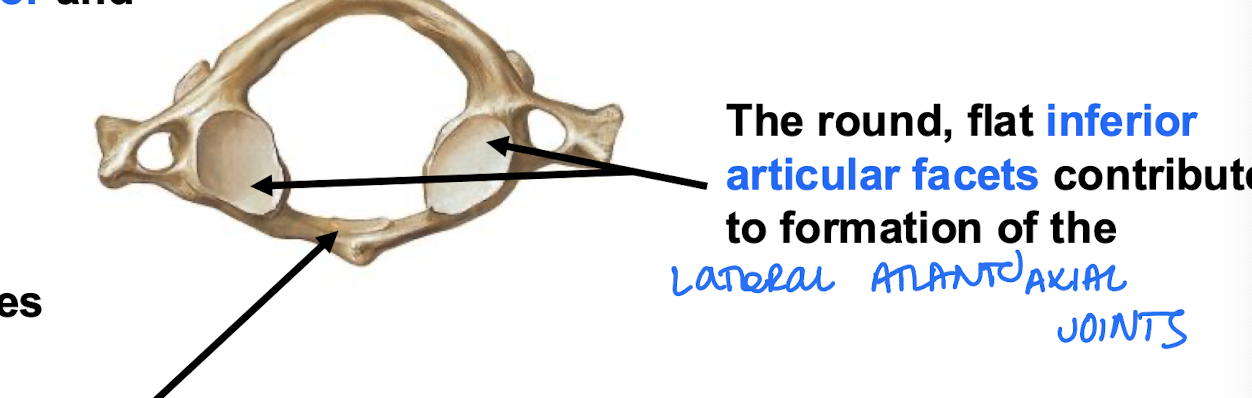
lateral atlantoaxial joint (Right and Left)
Inferior articular facets of the Atlas; Part of the "No" joints
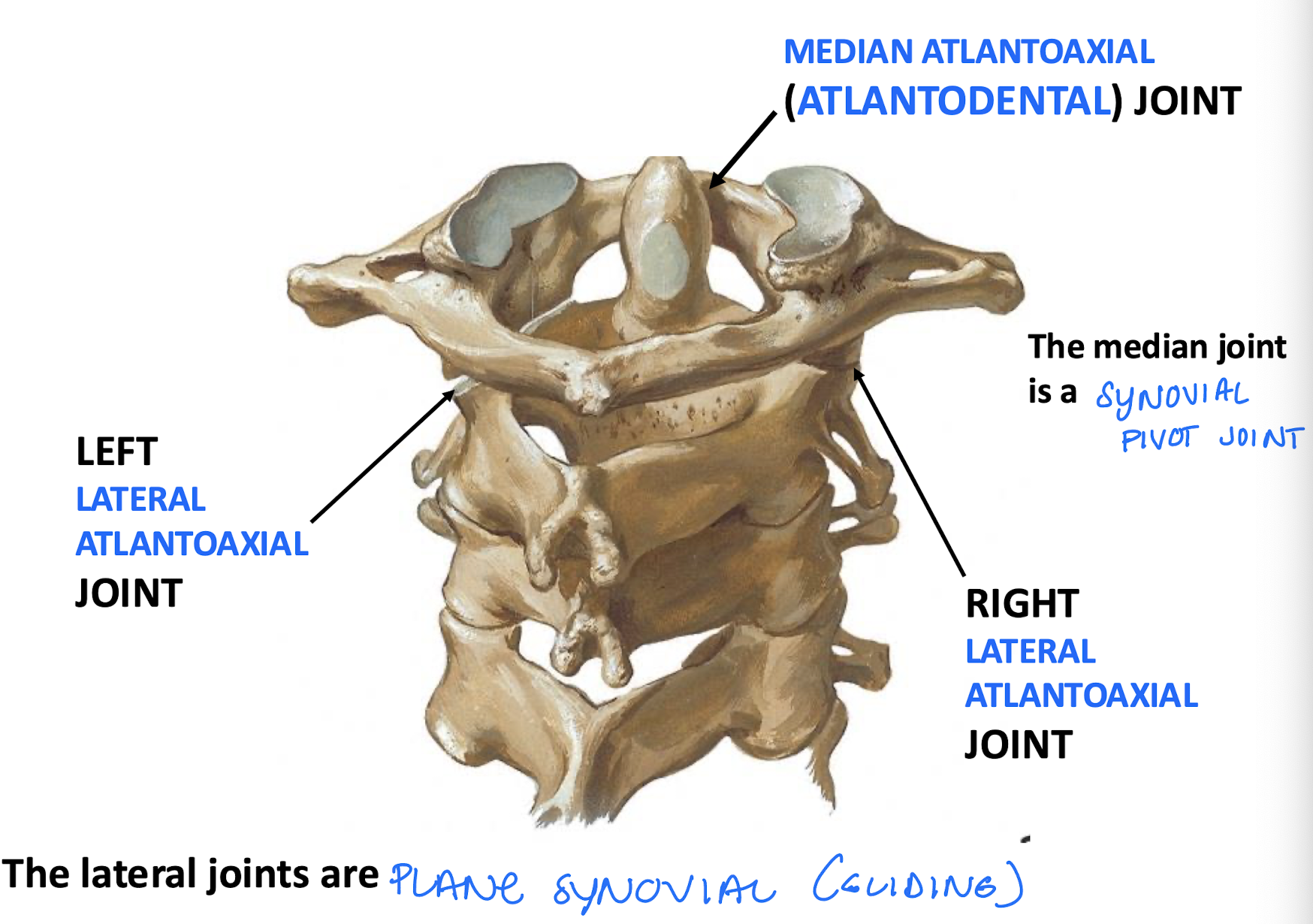
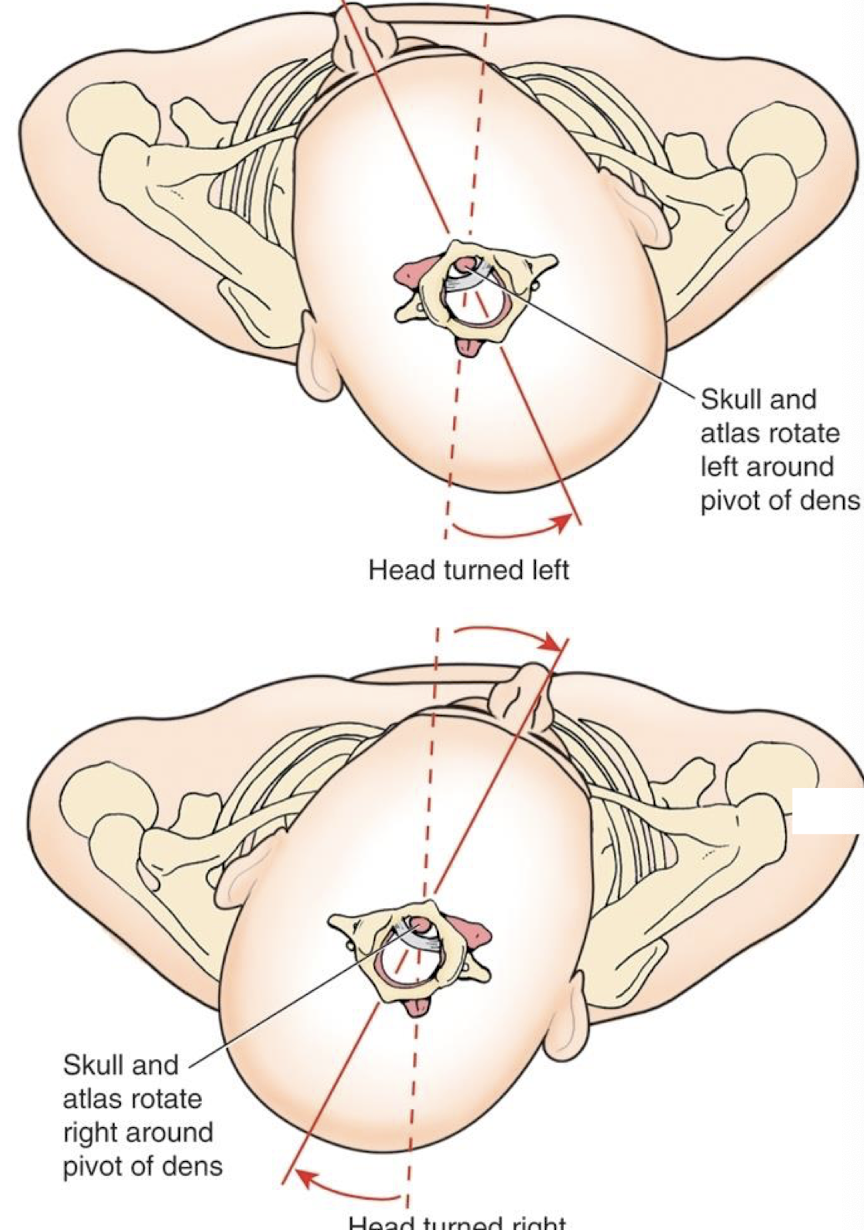
atlantoaxial joint function
“No” joints. head and atlas rotate together as a unit around the dens
median atlantoaxial joint
the Anterior articular facet on the Dens helps to form this joint; part of the "No" joints
Hangman’s fracture
fracture of C2 (axis)
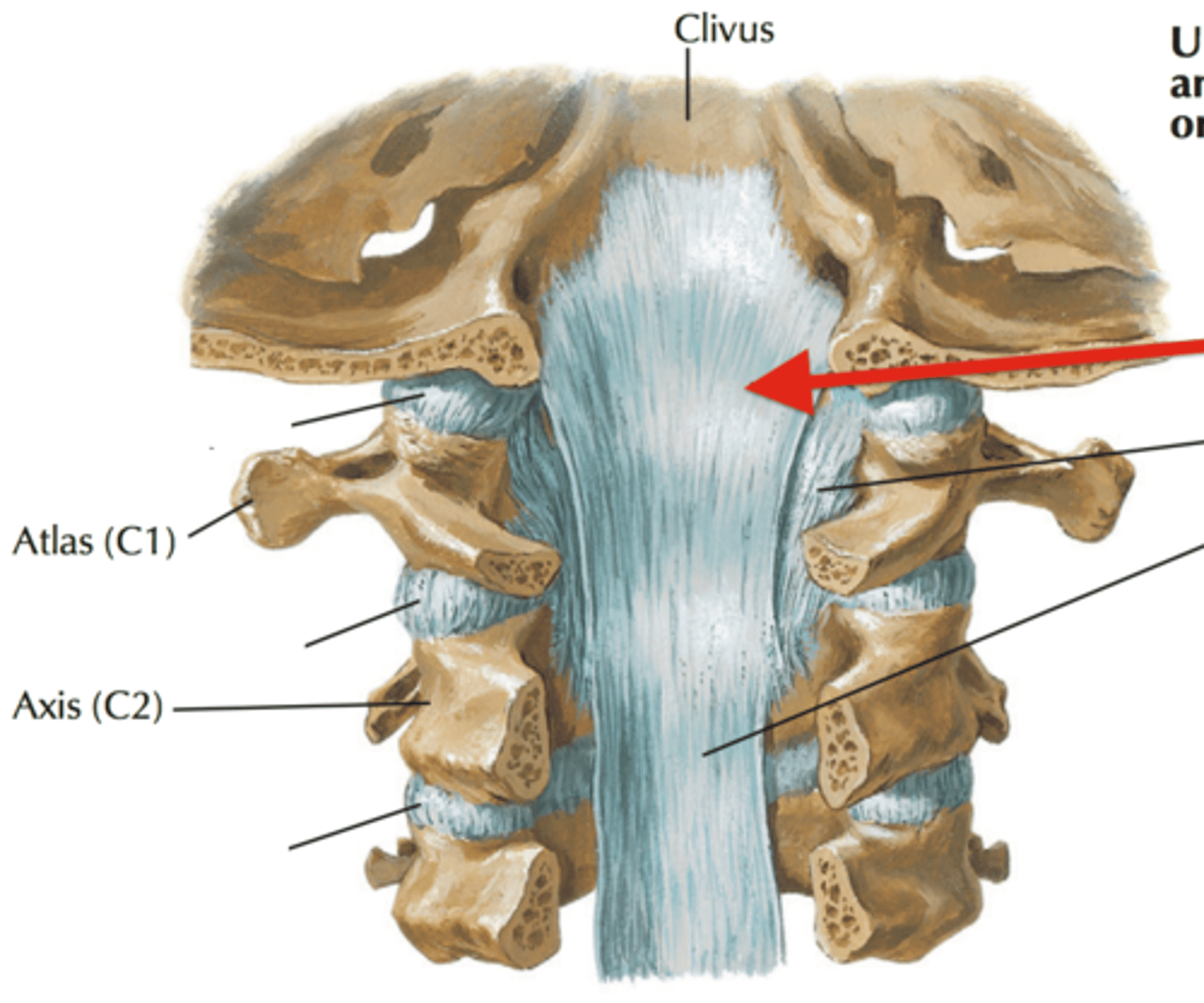
Tectorial Membrane
Continuation of PLL
connects the Atlas to the Occipital bone along the anterior side of foramen magnum
Cruciform Ligament
stabilizing ligament of the atlantoaxial joint
has transverse and Longitudinal portions;
lies deep to the Tectorial membrane
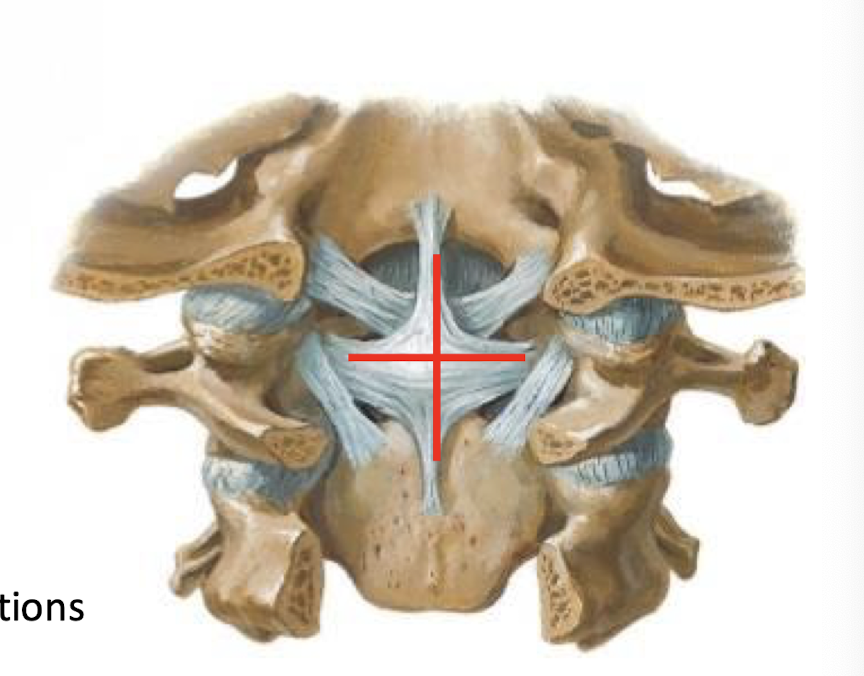
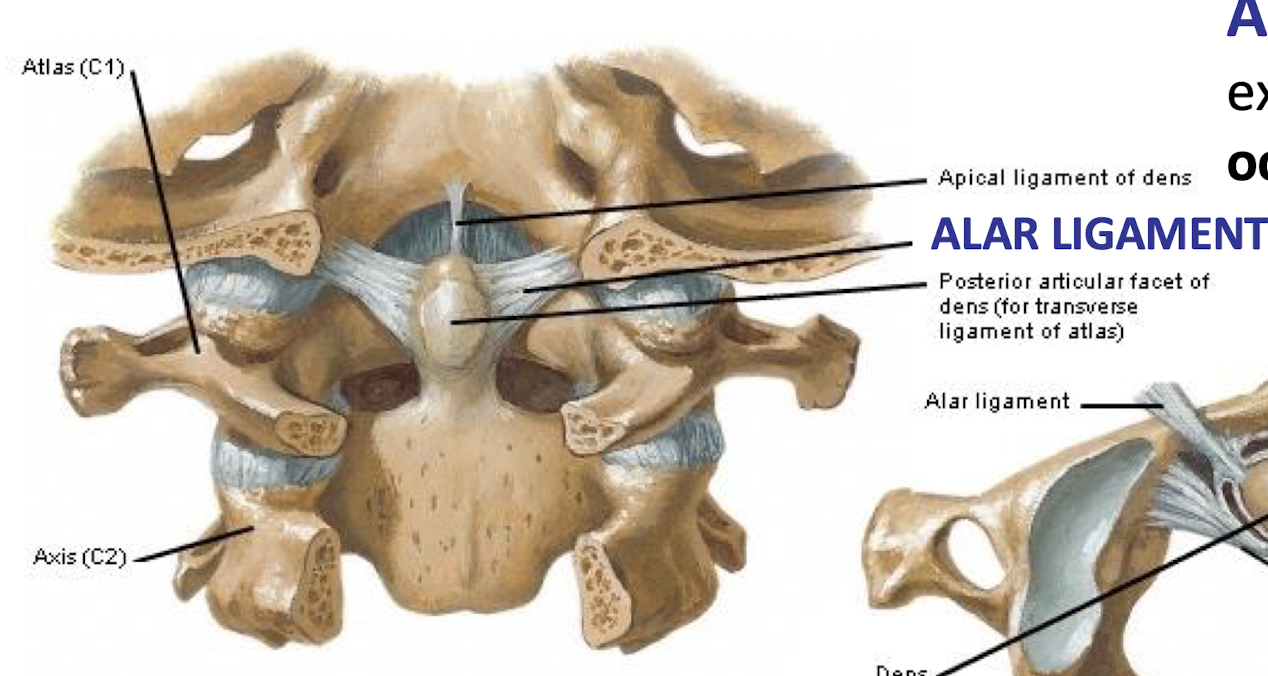
Transverse Ligament of the Atlas (What would happen if it ruptured?)
Forms a collar around the Dens; maintains the median atlantodental joint; Rupture may lead to injury of spinal cord by wandering Dens
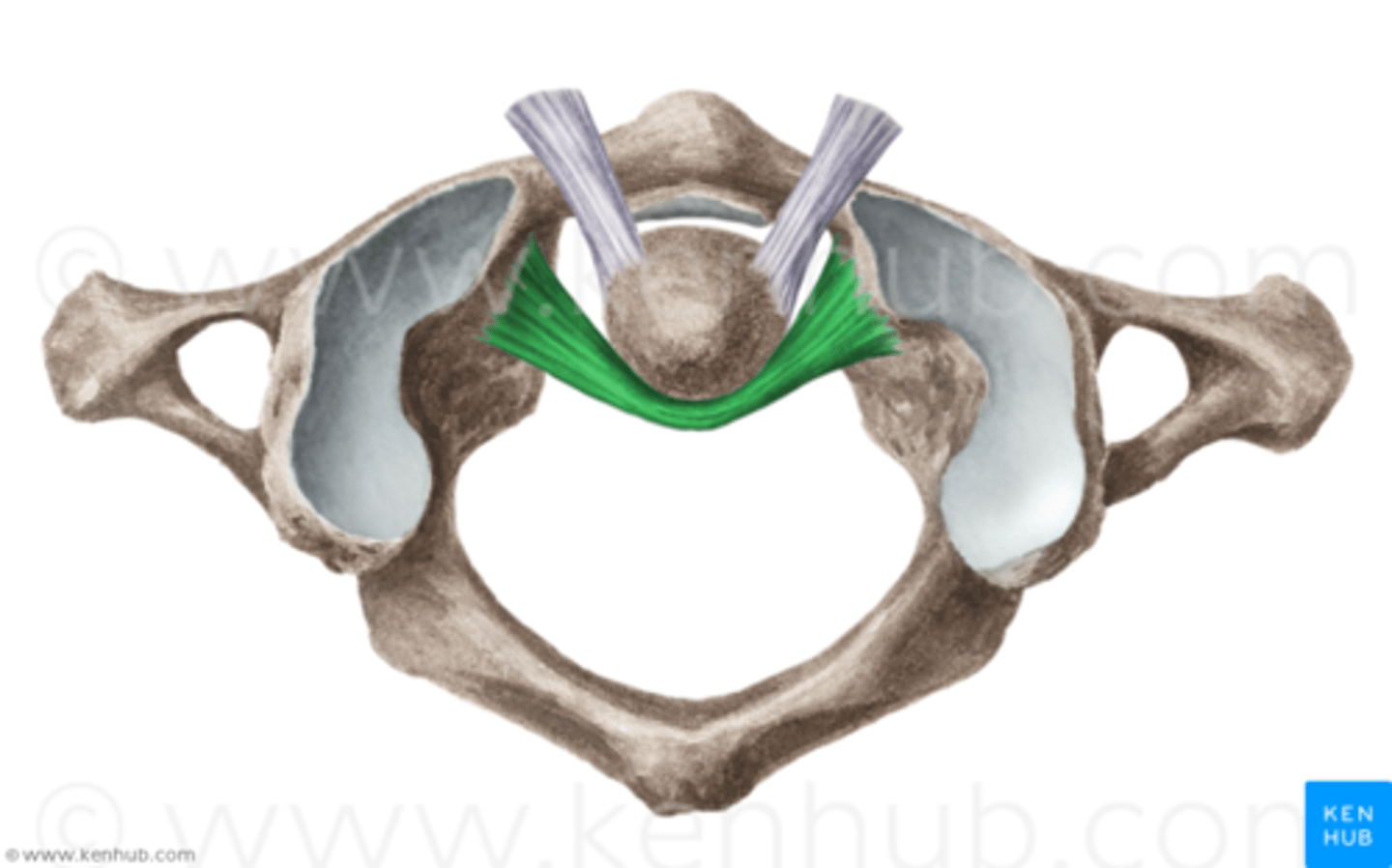
Alar Ligaments
Extend from Dens to occipital condyles;
limits rotation and lateral bending of the head;
think football tackling wrong* →
Hyperflexion injury produces instability of the head on the atlas. indicates an alar ligament tear (along w fracture of the dens)
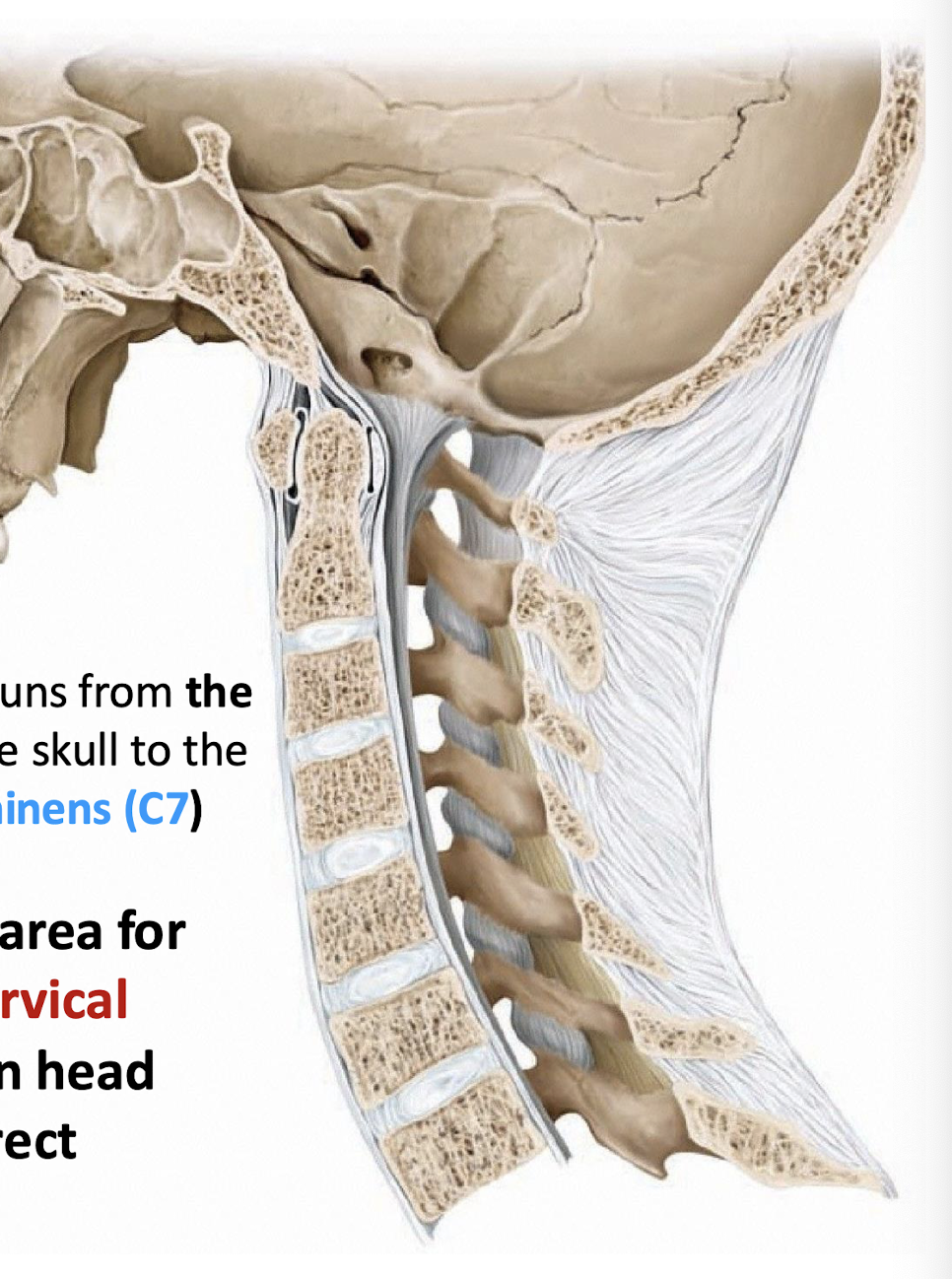
Ligamentum Nuchae
Runs from External Occipital Protuberance down to C7; provides surface for attachment of posterior cervical muscles that maintain head position
Actions of Posterior Neck Muscles (Nuchal Musculature)
Resist flexion of the head; maintain head upright
repositions sense organs in the skull
rapid, precise movements. some reflexive movements.
C1 Dorsal Ramus Innervations
Sub occipital muscles (obliquus capitis superior, Obliquus capitis inferior, Rectus capitis posterior major, and Rectus capitis posterior minor
functions and contents of the suboccipital muscles
help to resist the pull of gravity on the head
the capitis muscles form the subboccipital triangle.
Vertebral Artery, Sub-Occipital Nerve, Posterior arch of atlas
C2 nerve innervates the skin over this triangle
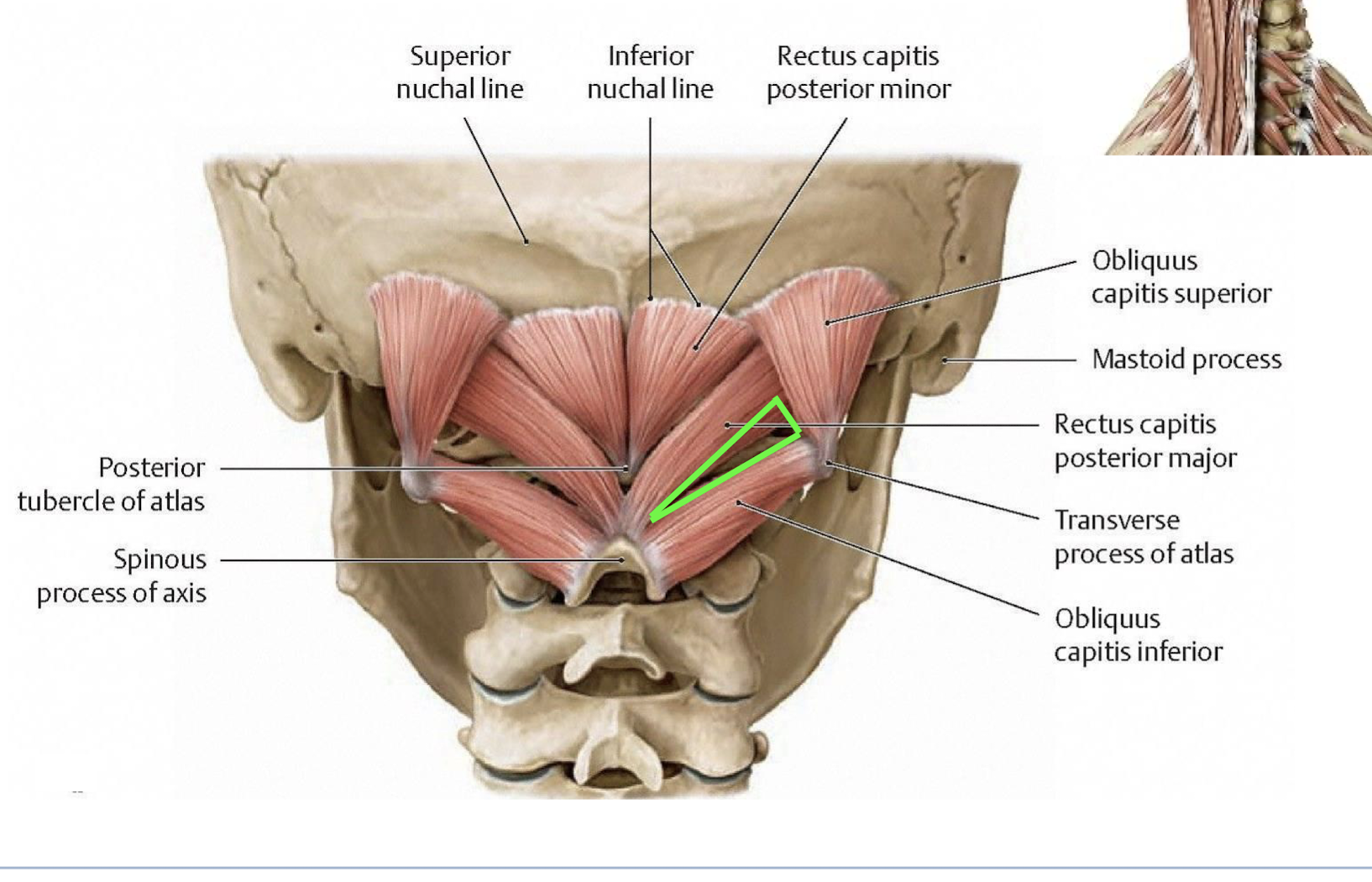
The Greater Occipital Nerve
Supplies the skin overlaying the triangle and posterior scalp
Atlanto-Occipital membrane ossification
more ossification can cause compression of vertebral artery flow → can lead to loss of consciousness in elderly patients with their head back
think of washing an old lady’s head*
Mediastinum
Mid-line soft tissue that separates pulmonary cavities
Sub-occipital spasms
chronic headache (migraine) due to constant traction of the dura
Superior Thoracic Aperture
Transmits abundant neurovascular between thorax and neck
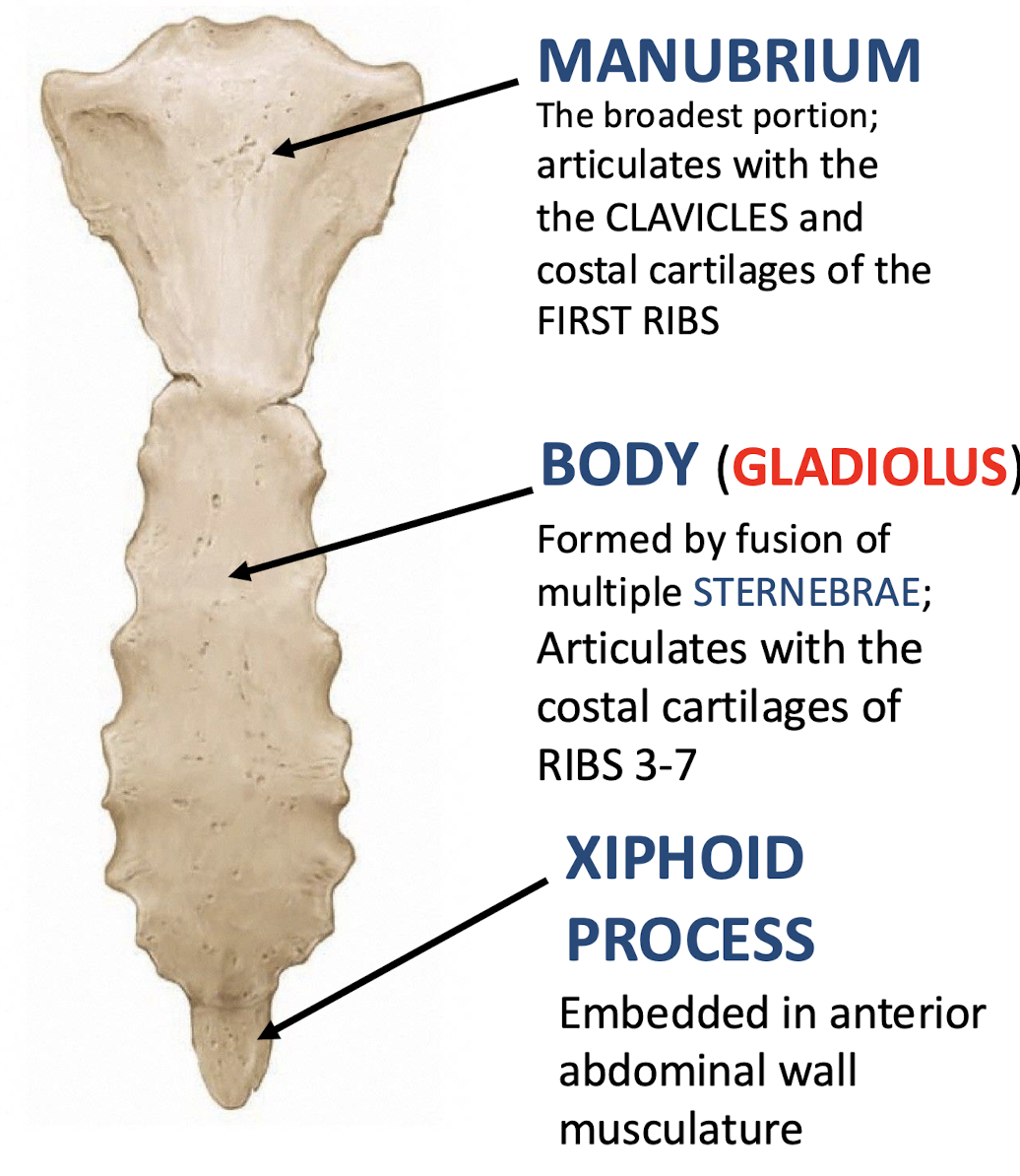
Manubrium
Literally meaning "Handle"; top portion of the sternum; articulates with the clavicles and costal cartilages of the first ribs
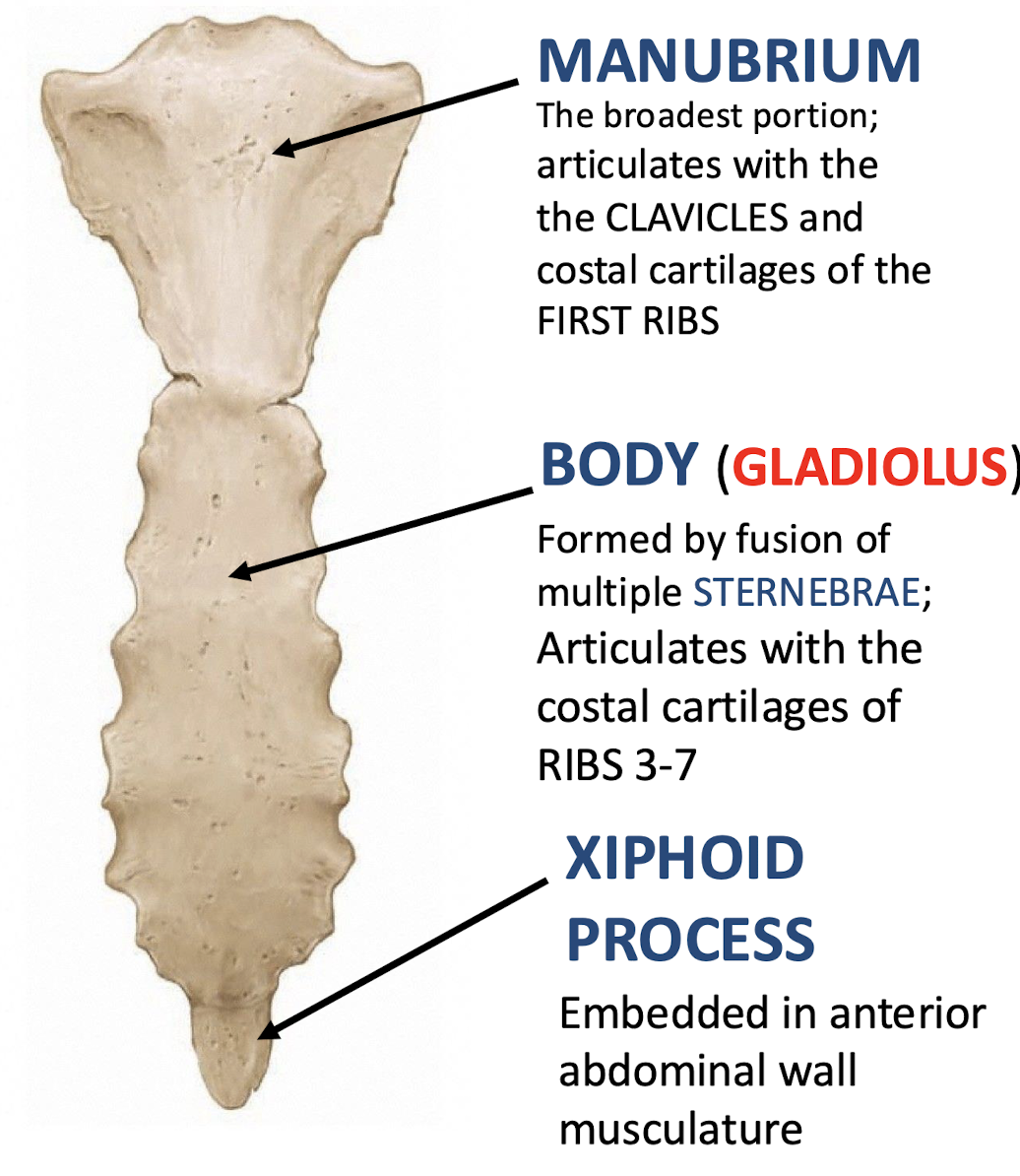
Body (Gladius)
Articulates with costal cartilages of ribs 3-7; middle portion of sternum
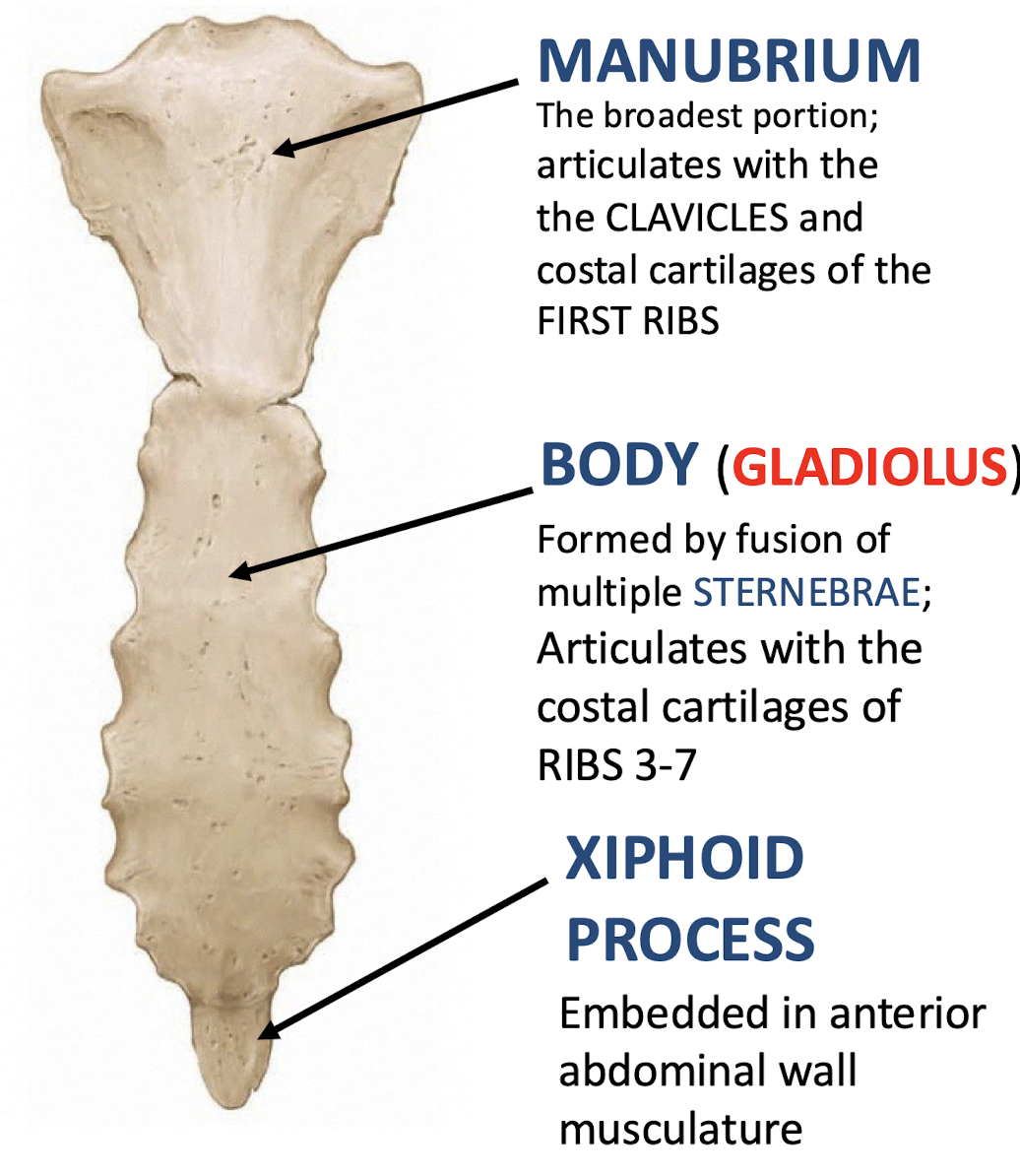
Xiphoid Process
Embedded in anterior abdominal wall musculature; inferior tip of sternum
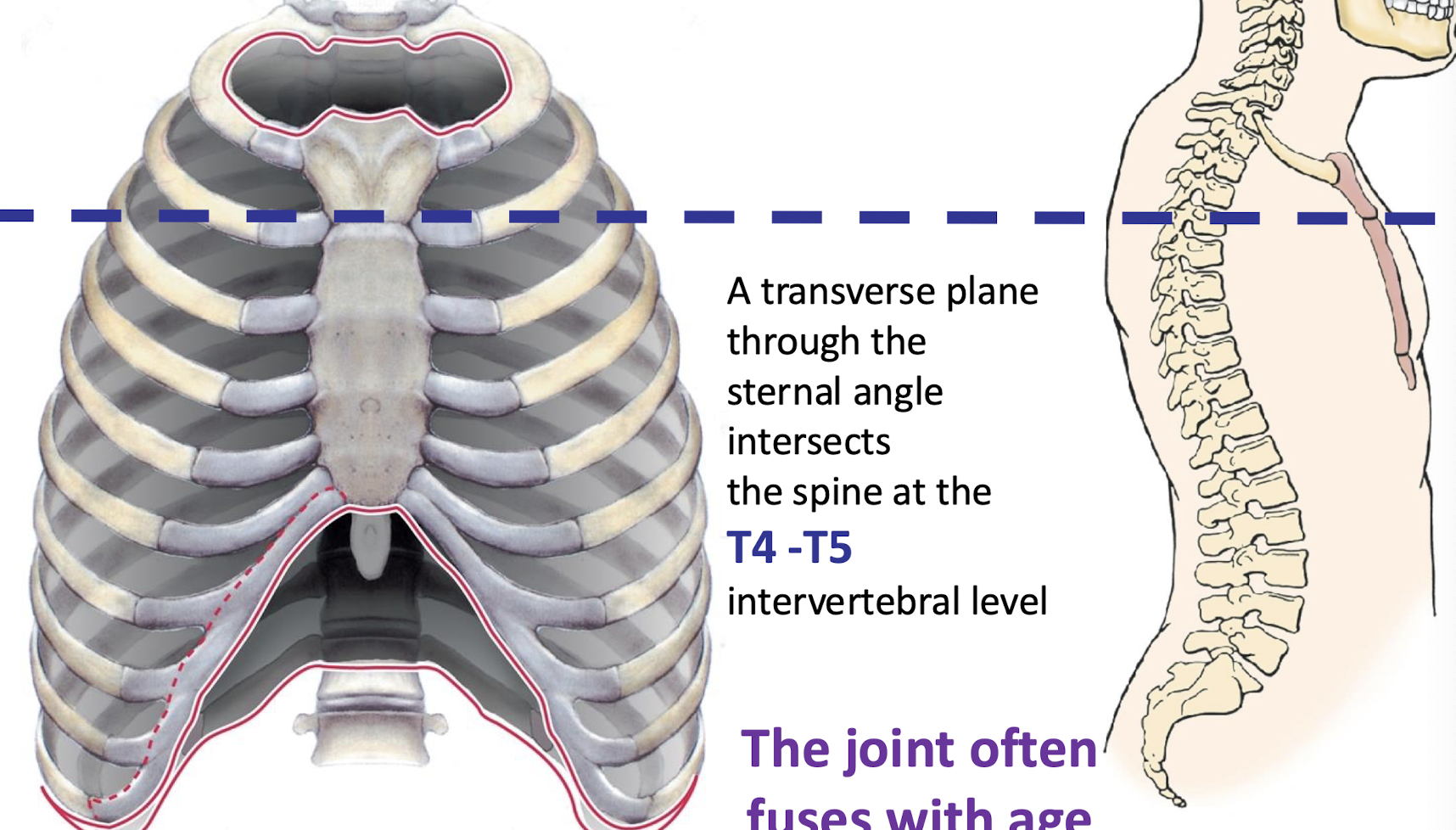
Sternal Angle/Manubriosternal joint
firbocartilagional joint. (bones held together by cartilage)
Ridge between manubrium and body at second rib (Palpable); in line with spine at T4-T5 vertebrae
True Ribs
Ribs 1-7; articulate with sternum via their own costal cartilages
False Ribs
Ribs 8-10; have cartilages that articulate with the next highest costal cartilage
floating ribs
Ribs 11-12; No sternal articulation. Articulate with only one vertebral body.
Head of Ribs
Part of the rib that connects to the vertebrae at costal facets
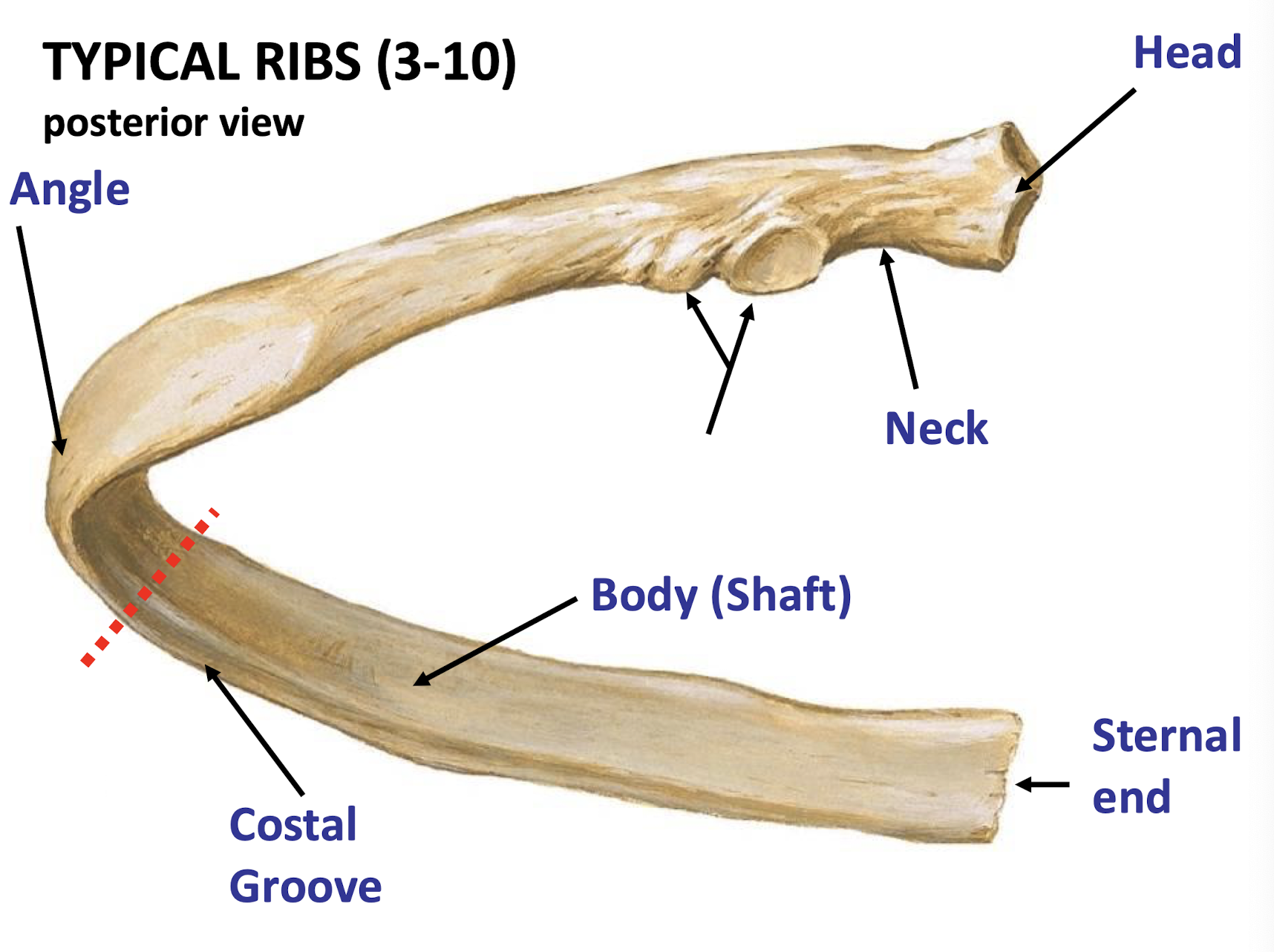
Costal Groove
Contains and Protects intercostal neurovasculature bundle
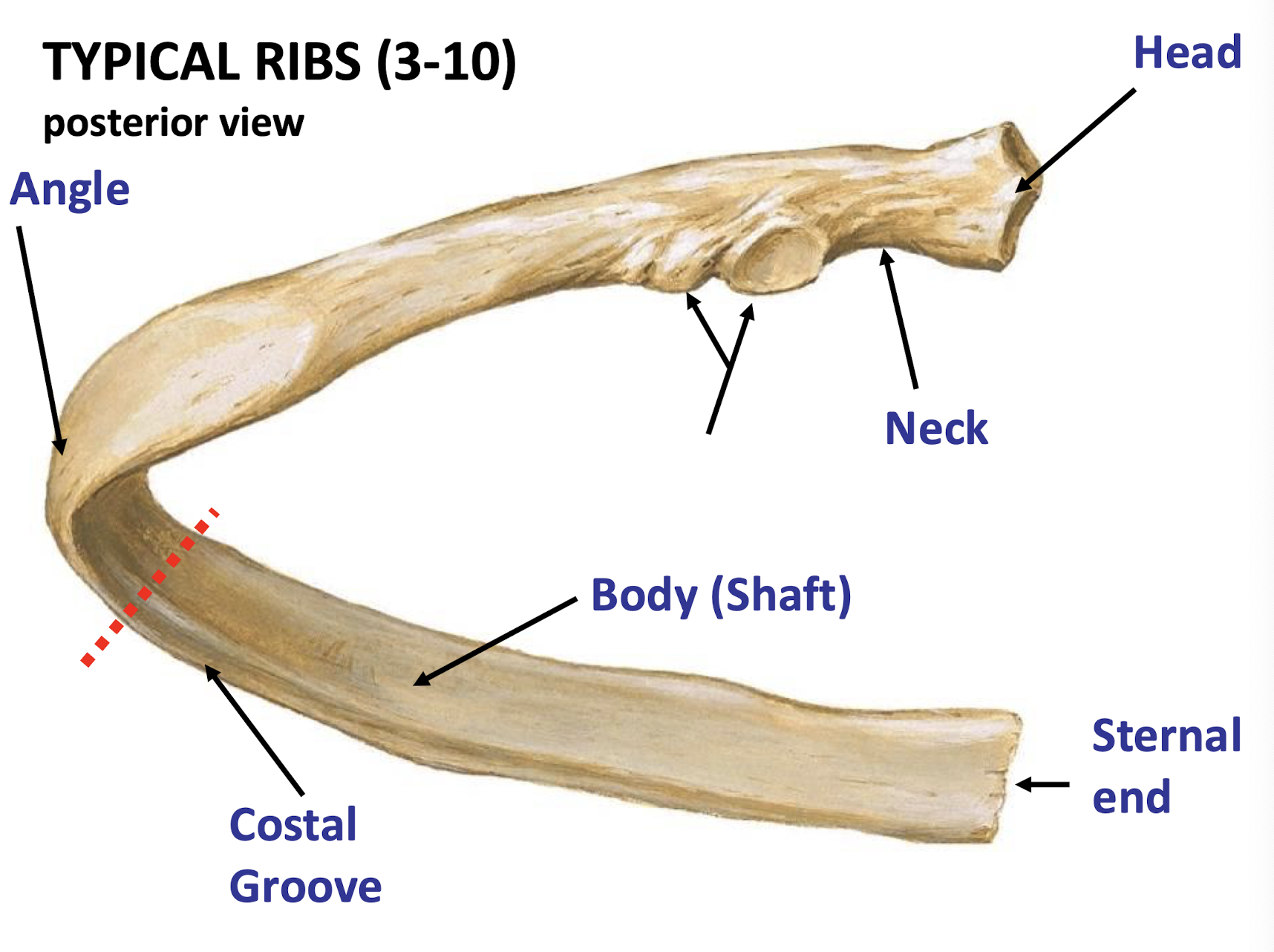
The atypical ribs, describe rib 1
Very short and broad
Rib 1: Surface features of this rib includes scalene tubercle and grooves for subclavian vessels
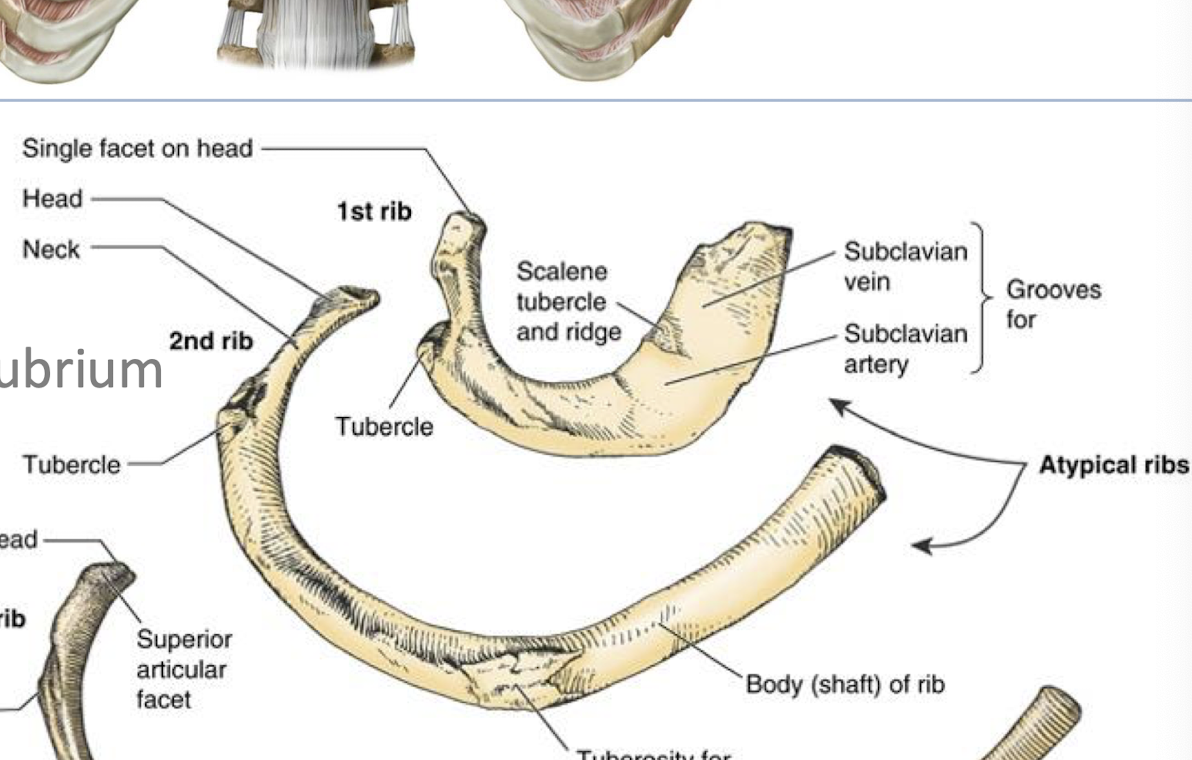
Scalene Muscles
run between cervical spine and upper ribs; serve as accessory muscles for breathing. also help to bend and rotate cervical spine.
contraction: elevates rib cage during inspiration.
Primary Cartilaginous joint (Joint 1)
immobile, thin layer of hyaline cartilage; closer to the midline of the body
Costochondral Joints (Joints 2-7 on the rib cage)
Allows gliding of the ribs to assist in breathing; plane synovial joints
External interocostals
Run Anteroinferiorly from the rib above to the rib below; most active during inspiration to ELEVATE the ribs
they run in direction fingers would if putting hands in pockets
tonic contractions keep intercostal walls rigid while we breathe.
internal intercostals
Run between consecutive ribs. tonic contractions keep intercostal walls rigid while we breathe.
run perpendicular to external intercostals
Inferoposteriorly from floor of costal grooves to ribs below; most active during expiration to DEPRESS the ribs
innermost intercostals
Same action as internal intercostals; helps to house the neurovasculature bundle between it and the muscle layer above it
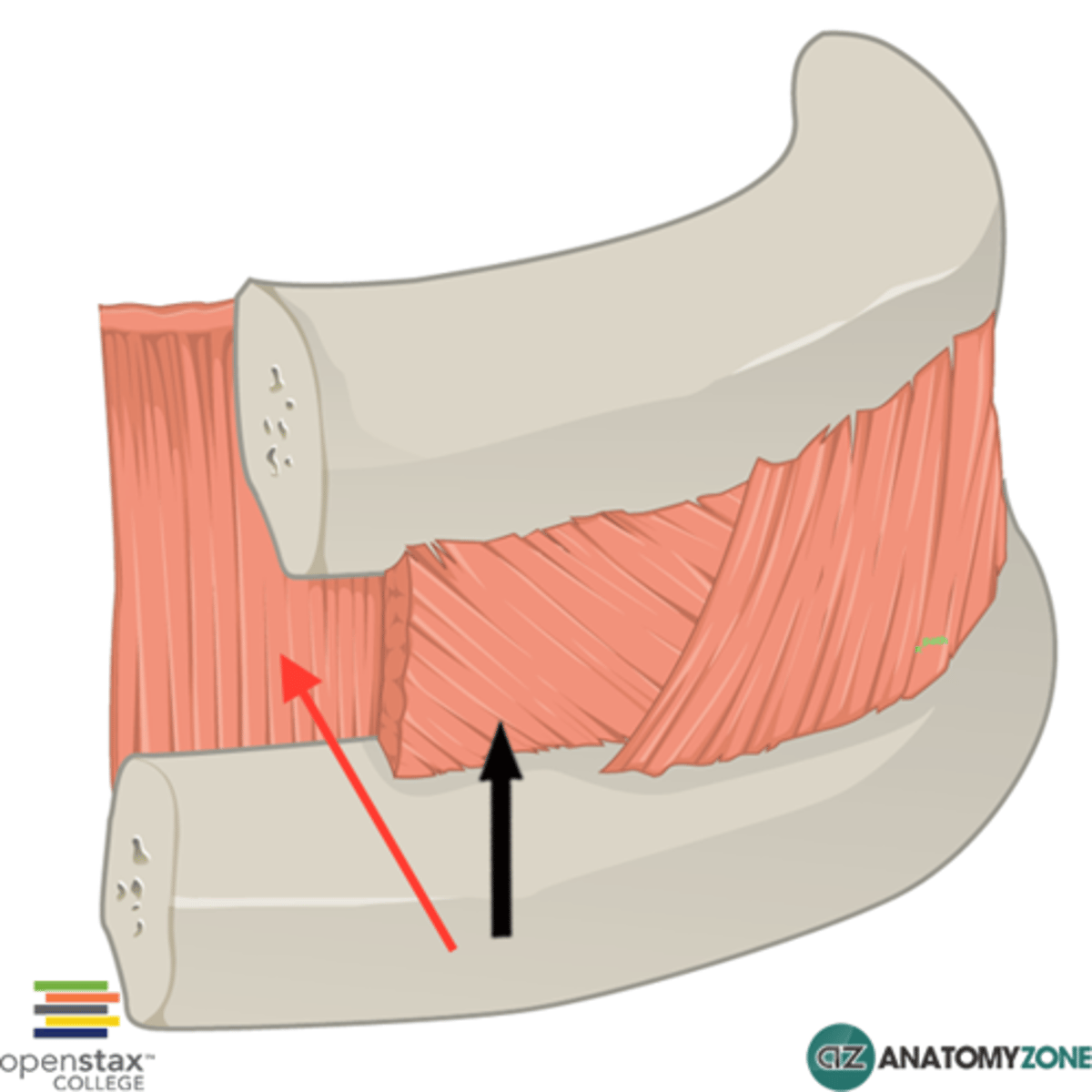
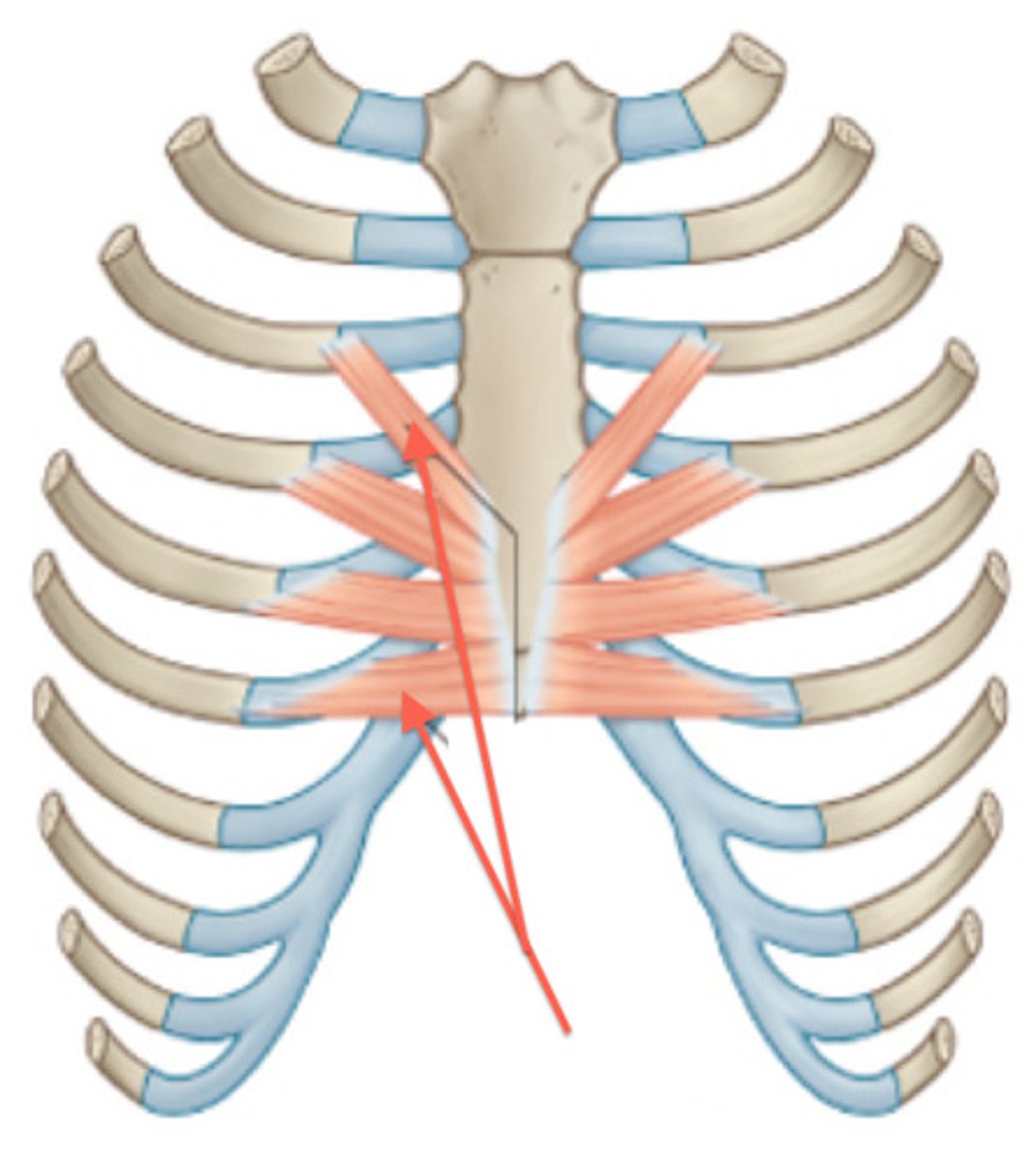
Transversus Thoracis
Limited to the anterior chest wall;
Origin: ribs 2-6 inner layer of intercostal cartilage;
Insertion: surface of sternum and xiphoid process;
Action: depression of ribs;
Innervation: 2-7th intercostal nerves
Direction of neurovasculature bundle Superior to Inferior
Veins, Arteries, nerves