ProSales Exam 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
value
relationship between costs and benefits
question
(technique for handling objections)
turn customer concern into question and refocus on strengths
get customer thinking in a new way
direct denial
(technique for handling objections)
confrontational strategy
customers may react negatively
use when customers statement is clearly false
indirect denial
(technique for handling objections)
agree, validate objection and explain why untrue
less threatening
feel-felt-found
(technique for handling objections)
acknowledge customer’s feelings, extend feelings, counter
technique has been around for awhile
3rd party endorsements
(technique for handling objections)
use of outside parties to bolster statements
using referrals, reference other companies
adds credibility
bounce back
(technique for handling objections)
turns concern into reason for action
more aggressive
effective with objections about time or price
revisit something else in conversation
defer
(technique for handling objections)
address later in agenda
postpone until later
suggest customer listen to entire presentation
trial offer
(technique for handling objections)
calms objects by testing products
define terms
no commitment to purchase
sales call planning
strongest tool is preparation
formalize your presentation
closing
achievement of sales call goals
natural progression of dialogue
adopt buyer’s perspective to work towards solutions
direct close
ask for order
straight forward
effective if buyer is driver
assumptive close
assumes next steps
communicate like they will buy
minor point close
something small that indicates a larger agreement
ex: What color do you prefer?
alternative choice close
choosing between viable choices
ask multiple choice questions
summary of benefits close
review benefits, ask direct close
formal method of closing
buy now close
creates urgency
must be honest
"standing room” close
common mistakes in closing
bad attitude
ineffective preapproach
talking instead of listening
“one size fits all”
negotiation
occurs anytime two or people need to resolve a difference of opinion
need to come to agreement
does not mean conflict
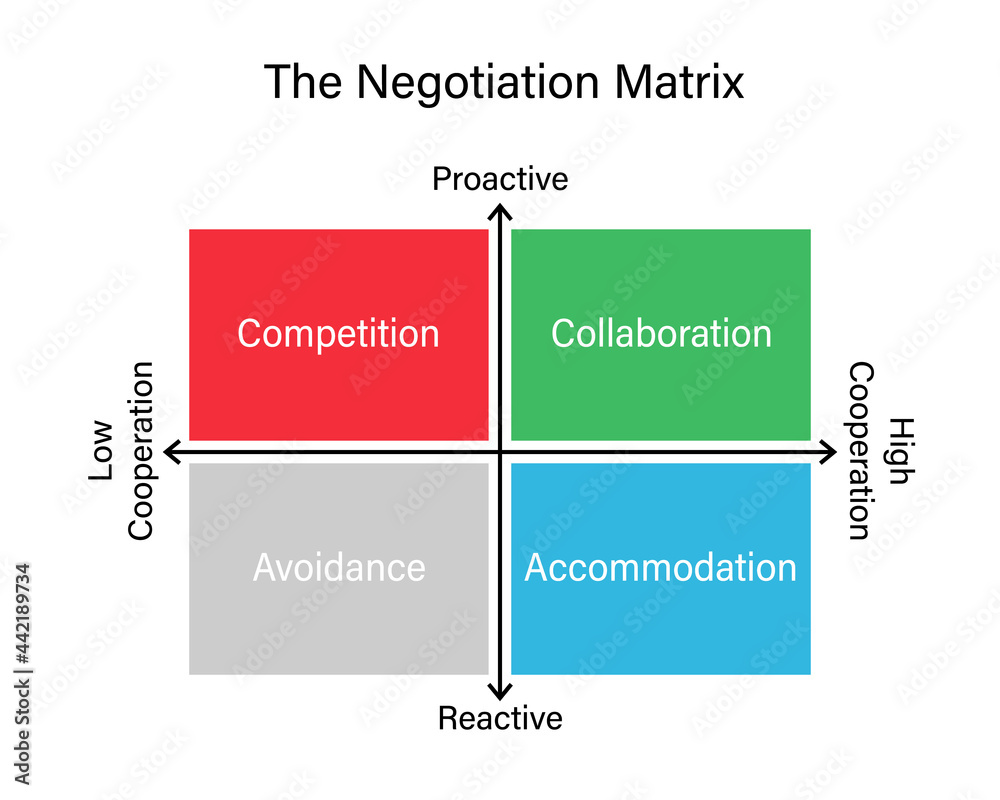
avoiding
(technique for negotiations)
postpone to win
low-low
emotionally charged situations
stronger alternative to consider
compromising
(technique for negotiations)
split the difference
collaborating is not possible but goals must be achieved
use facets of different styles
start with small solutions
accommodating
(technique for negotiations)
lose to win
relationship > outcome
good to let other party “win”
delay bigger negotiation
short term loss for long term gain
competing
(technique for negotiations)
win-lose
outcome > relationship
need to win over expense of relationship
collaborating
(technique for negotiations)
win-win
high-high
both parties must achieve goal
fairness, honest, creative
negotiation matrix
business ethics
principles and standards that guide behavior in world of business
right-wrong
externally derived
ethics
principles governing behavior of an individual or group
morals
standards of behavior or beliefs concerning what is acceptable or not
internally derived
very personal
“good” or “bad” component
laws
system of rules that a particular country or community recognizes as regulating actions, enforceable with penalties
not always right-wrong
utilitarian theory
no act in itself is right or wrong, based on results they yield
duty ethics
not concerned with consequences of act
morally obligated to act a certain way
ex: child labor
virtue ethics
desirable characteristics and promote in others
emphasize individual character
rightness or wrongness of individual actions
market orientation
all actions taken by the firm are meant to maximize success in competitive market
ultimate focus on customer
relationship business model
retention, acquisition, profitability
customer value
customer weighs the cost of relationship with the seller, benefits outweigh the cost
enhanced by CRM
360 degree view of customer
phases of relationship development
awareness
exploration
expansion
commitment
dissolution
prospecting- MAD
M- money
A- authority
D- desire
initiator
starts buying process
gatekeeper
controls flow of information
users
influence steps, don’t have buying power
influencers
directly or indirectly provide information
economic
technical
coach
buyer
contacts seller to place order
decider
makes final decision
controller
sets budget
two way communication
both parties are senders and receivers
encoding
translation of thoughts into words
decoding
interpreting meaning of message
feedback
information given back to indicate understanding
persuading
sales persons primary objective
influencing buyer’s decision
manipulation
eliminating or reducing buyer’s choice
key follow up
customer satisfaction
customer retention and loyalty
reexamine value added
reset customer expectations