Brain Structure and Function
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Cerebrum
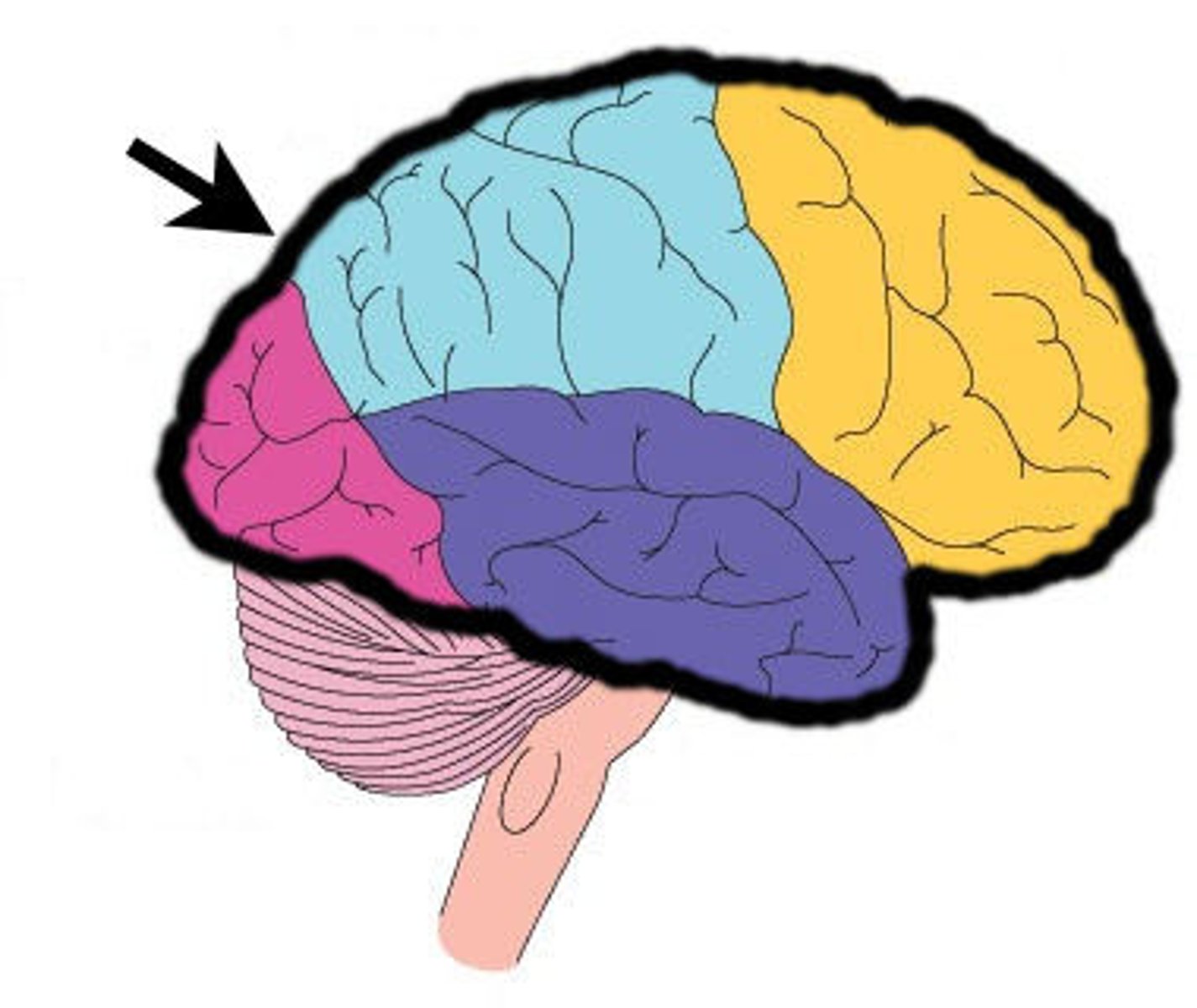
The largest area of the brain responsible for conscious thought and receiving sensory messages from parts of the body. Contains all the lobes.
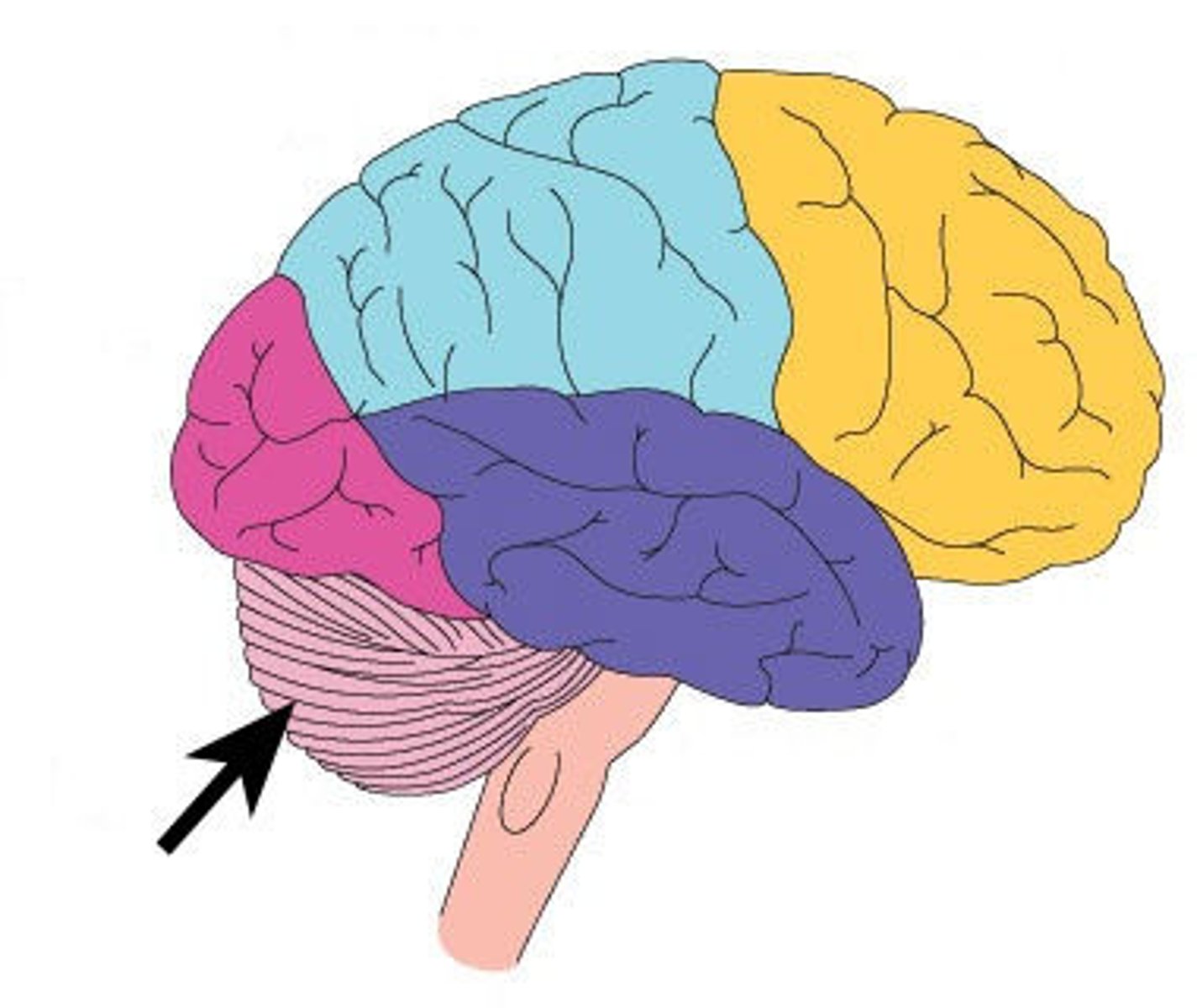
Cerebellum
Functions include processing sensory input from the eyes and ears for posture, balance, and coordination of movement
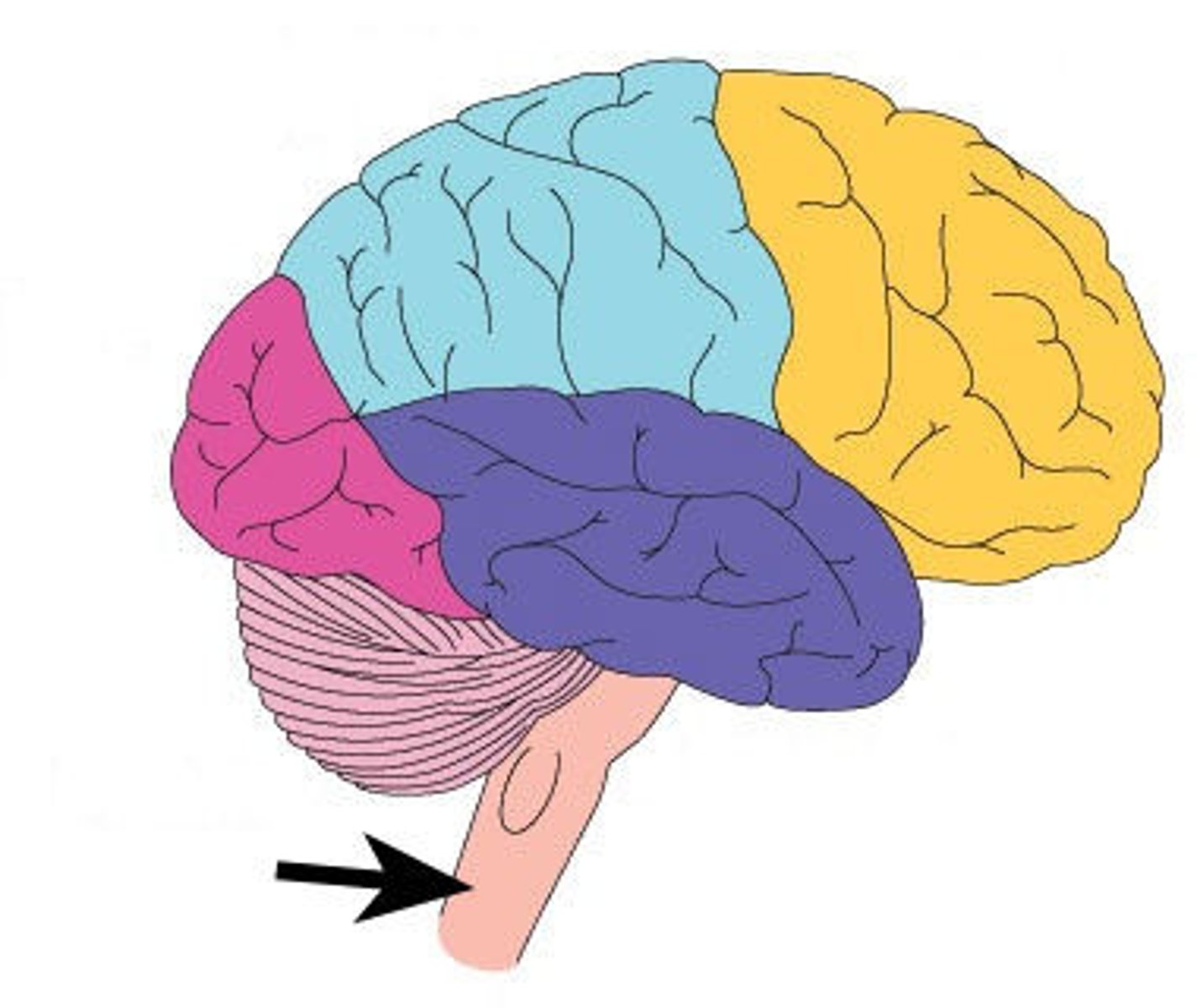
Brain Stem
Connects to the spinal cord, and controls/regulates unconscious actions like breathing and heartbeat
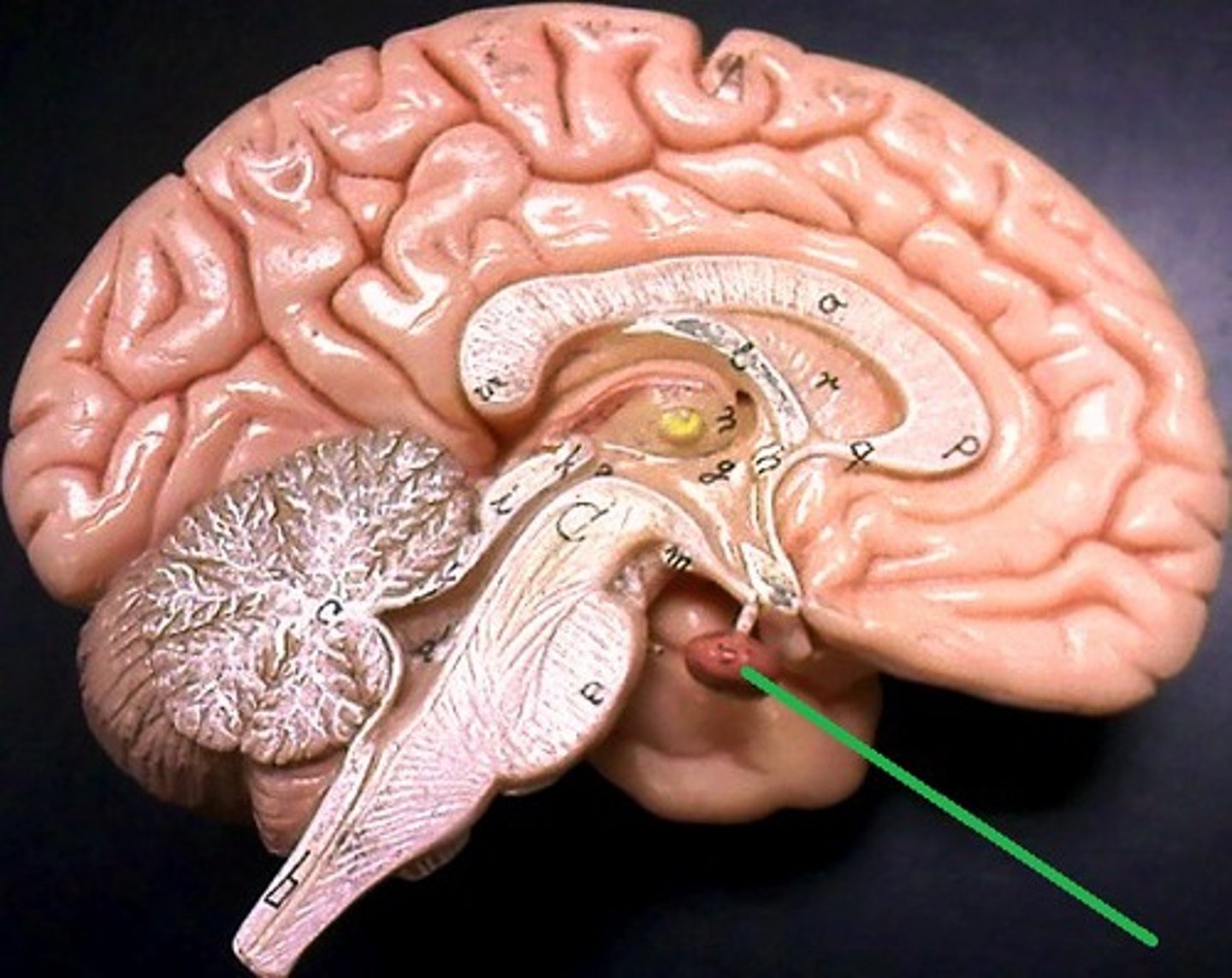
Pituitary Gland
Produces essential hormones for everyday living. Releases hormones that control other hormone glands in the body
Hypothalamus
Controls many bodily functions by sending messages for hormones to be released from the pituitary gland
Thalamus
Directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and other parts of the brain
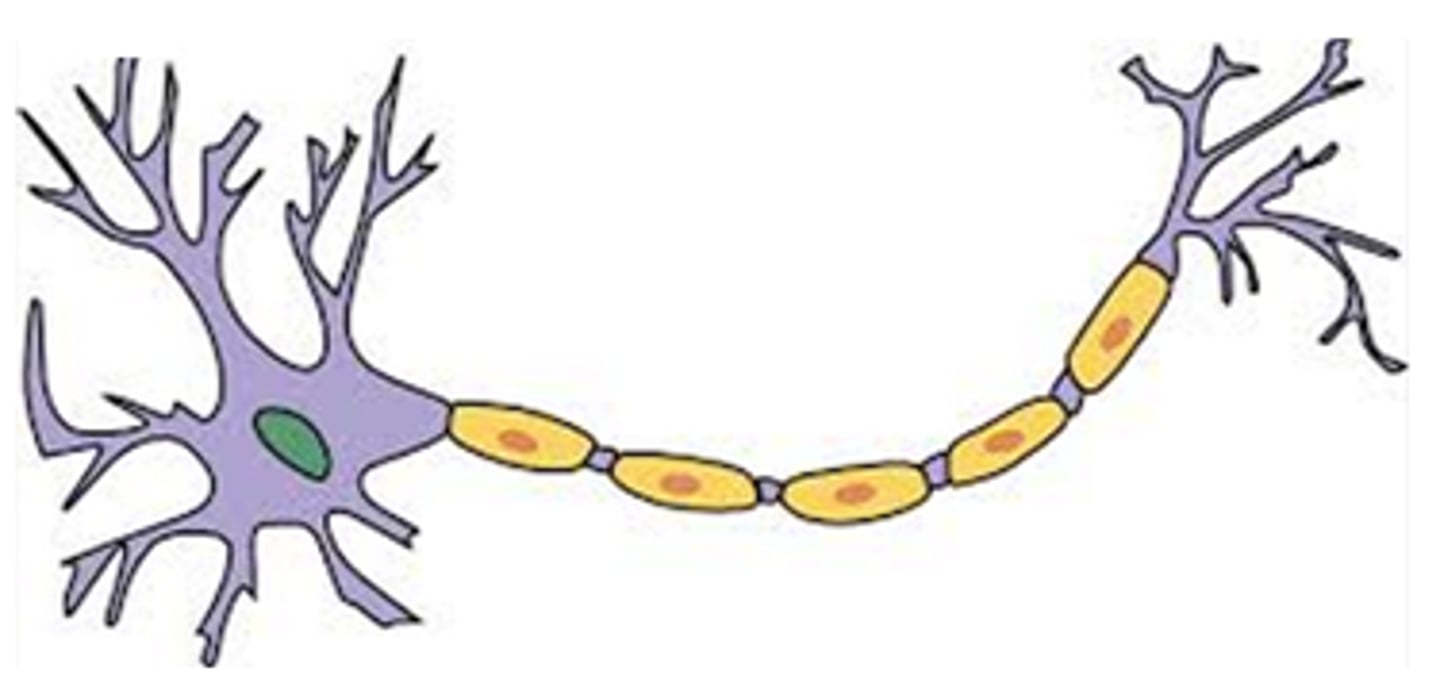
Neuron
The basic unit (cell) of the nervous system, particularly in the brain
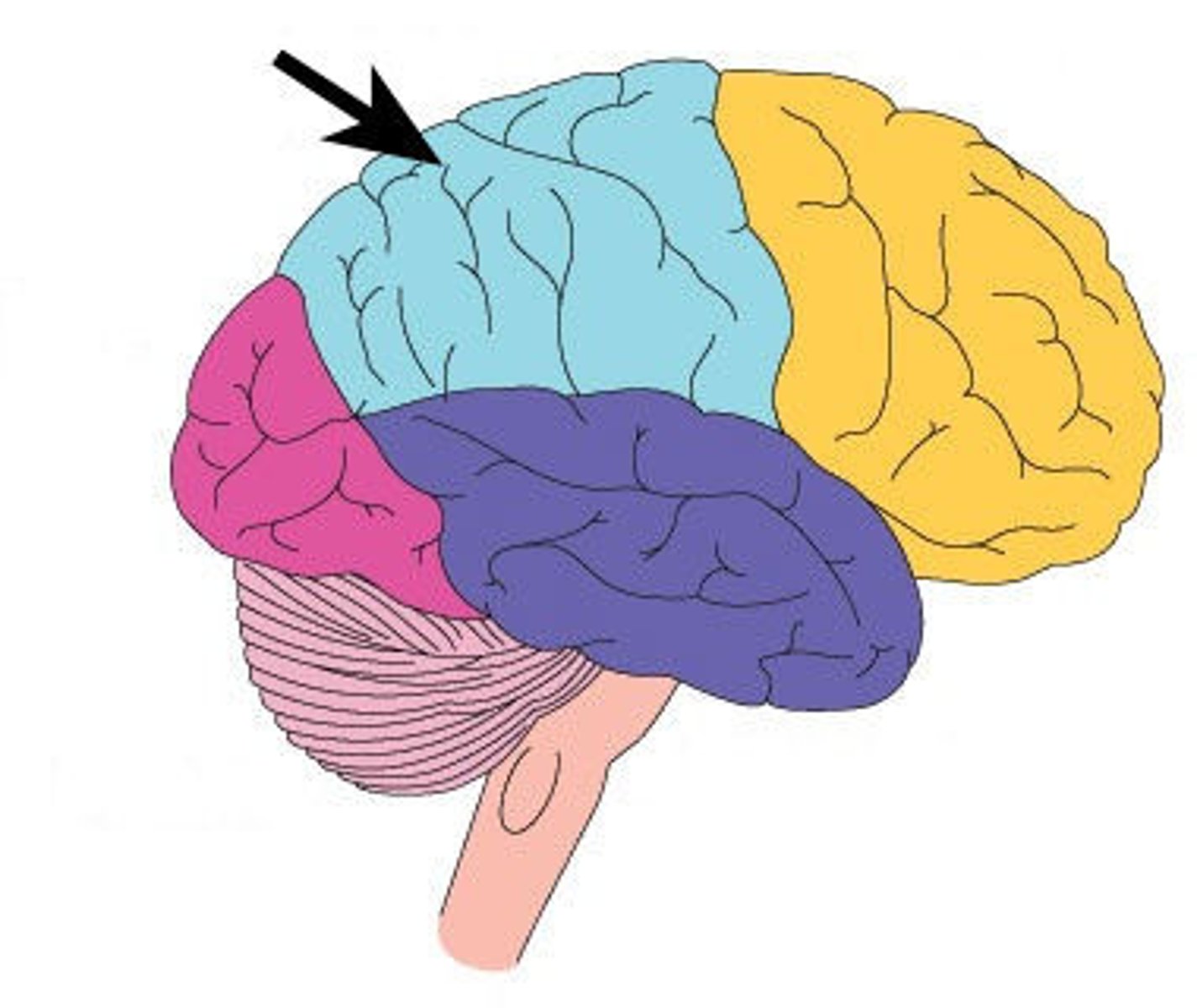
Parietal Lobe
A region of the cerebrum whose functions include processing information about touch and pain
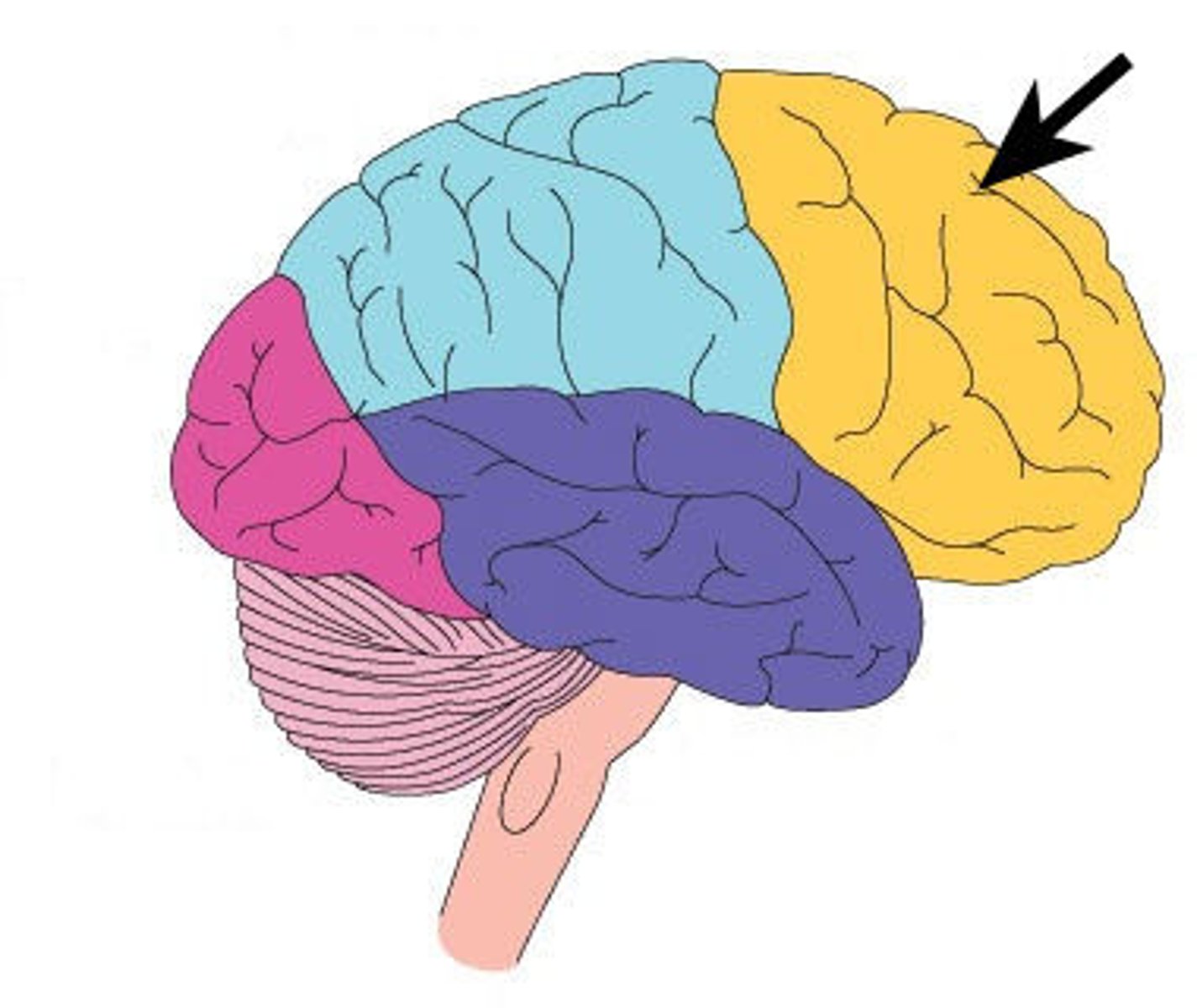
Frontal Lobe
A region of the cerebrum that has specialised areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement (executive functioning)
Occipital Lobe
A region of the cerebrum that processes visual information
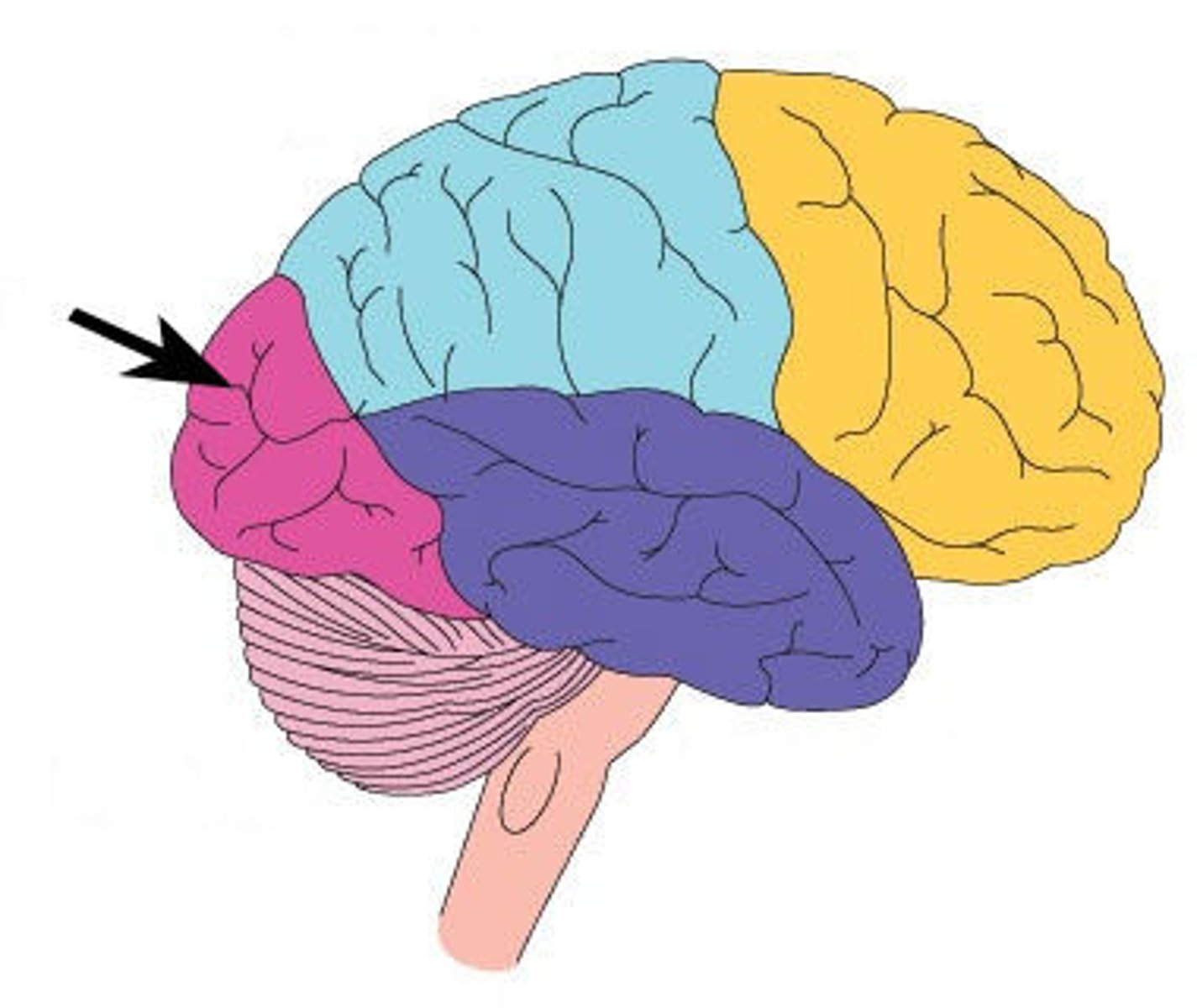
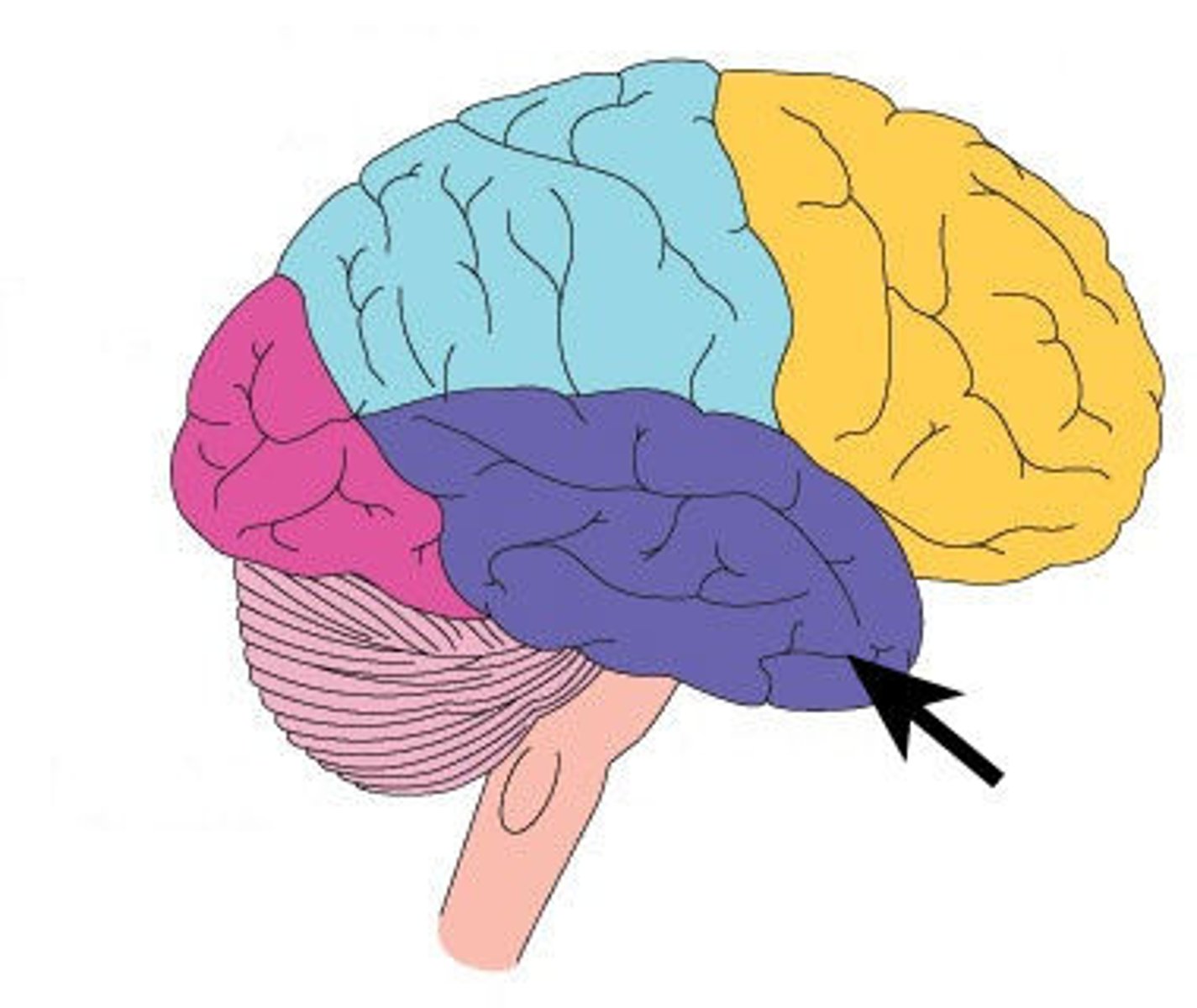
Temporal Lobe
A region of the cerebrum responsible for hearing and language. It also houses areas related to memory and responsive emotions (hippocampus and amygdala, respectively)
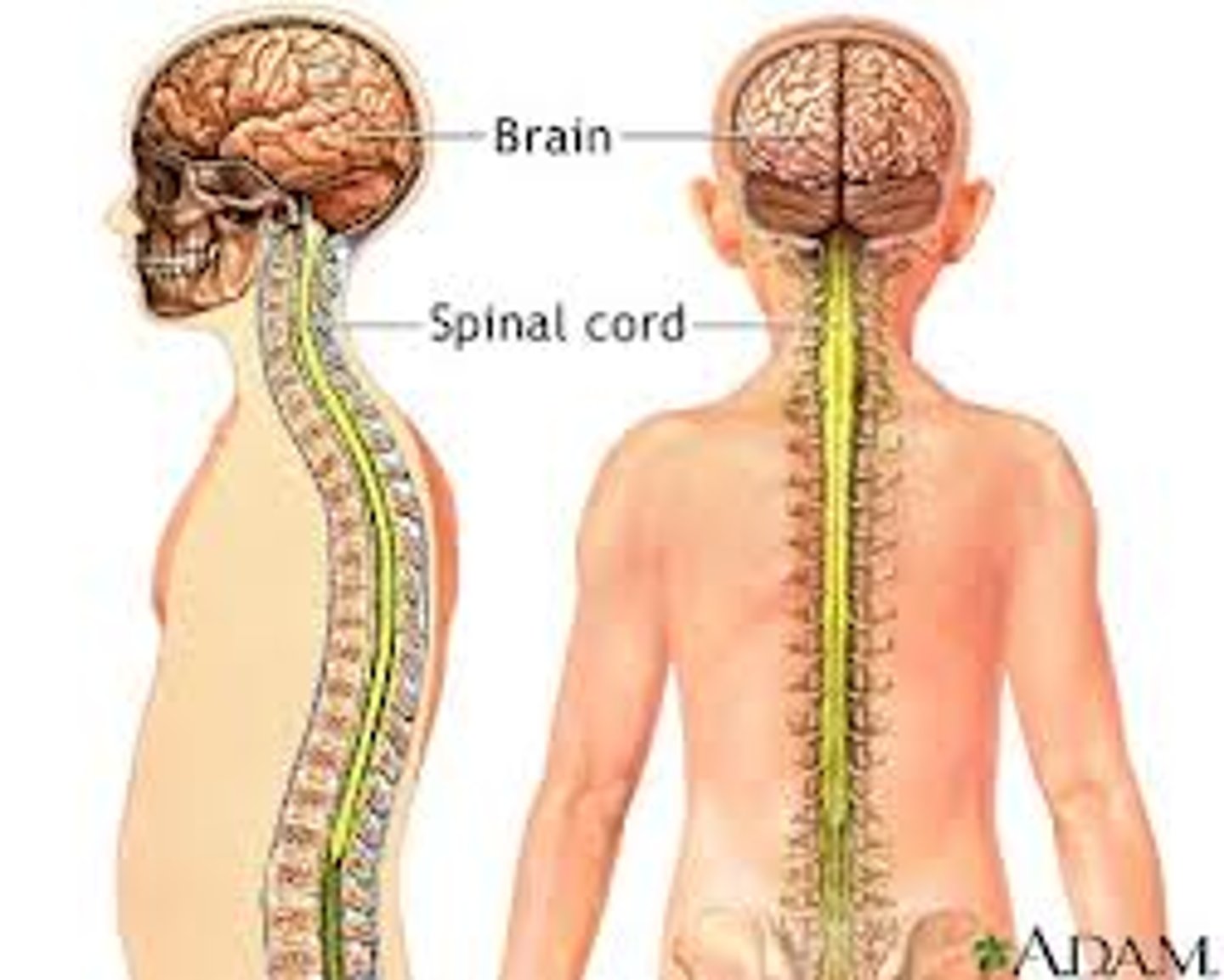
Nervous System
A body system consisting of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves in the body
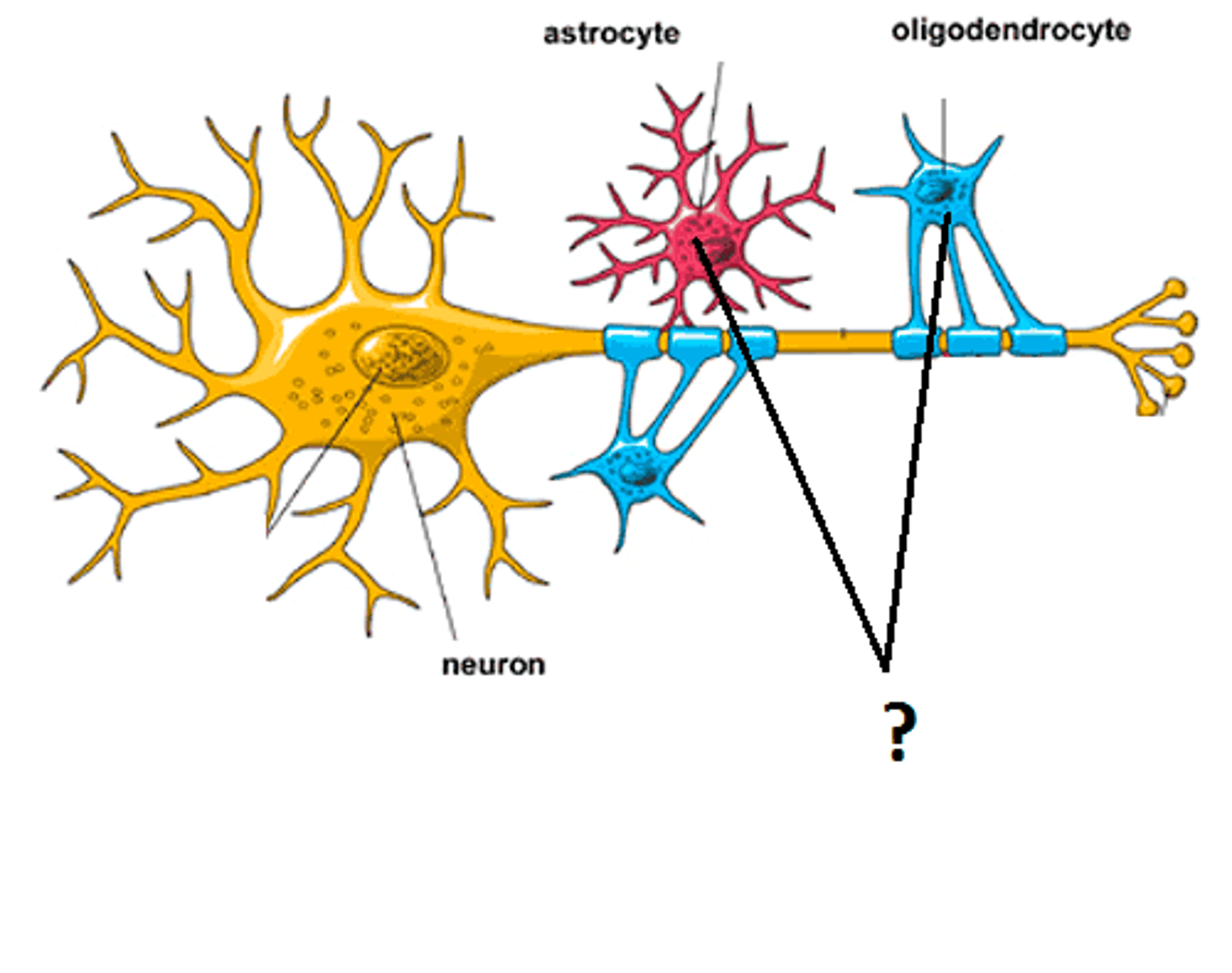
Glial Cell (Glia)
Cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
Blood-Brain Barrier
A protective system that prevents certain molecules from entering the brain, but allows others to cross
Axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body
Soma
The cell body of a neuron, which contains the nucleus
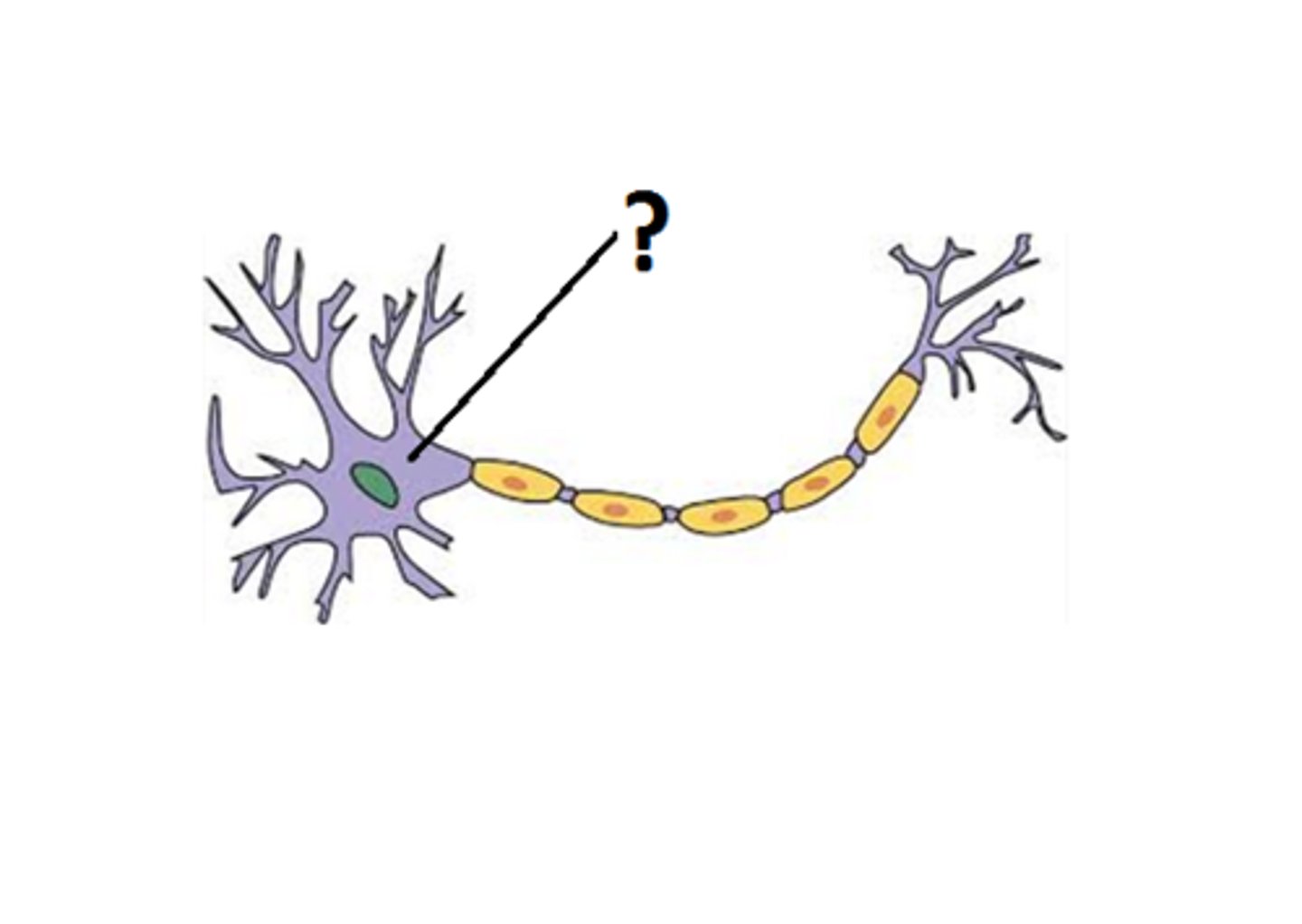
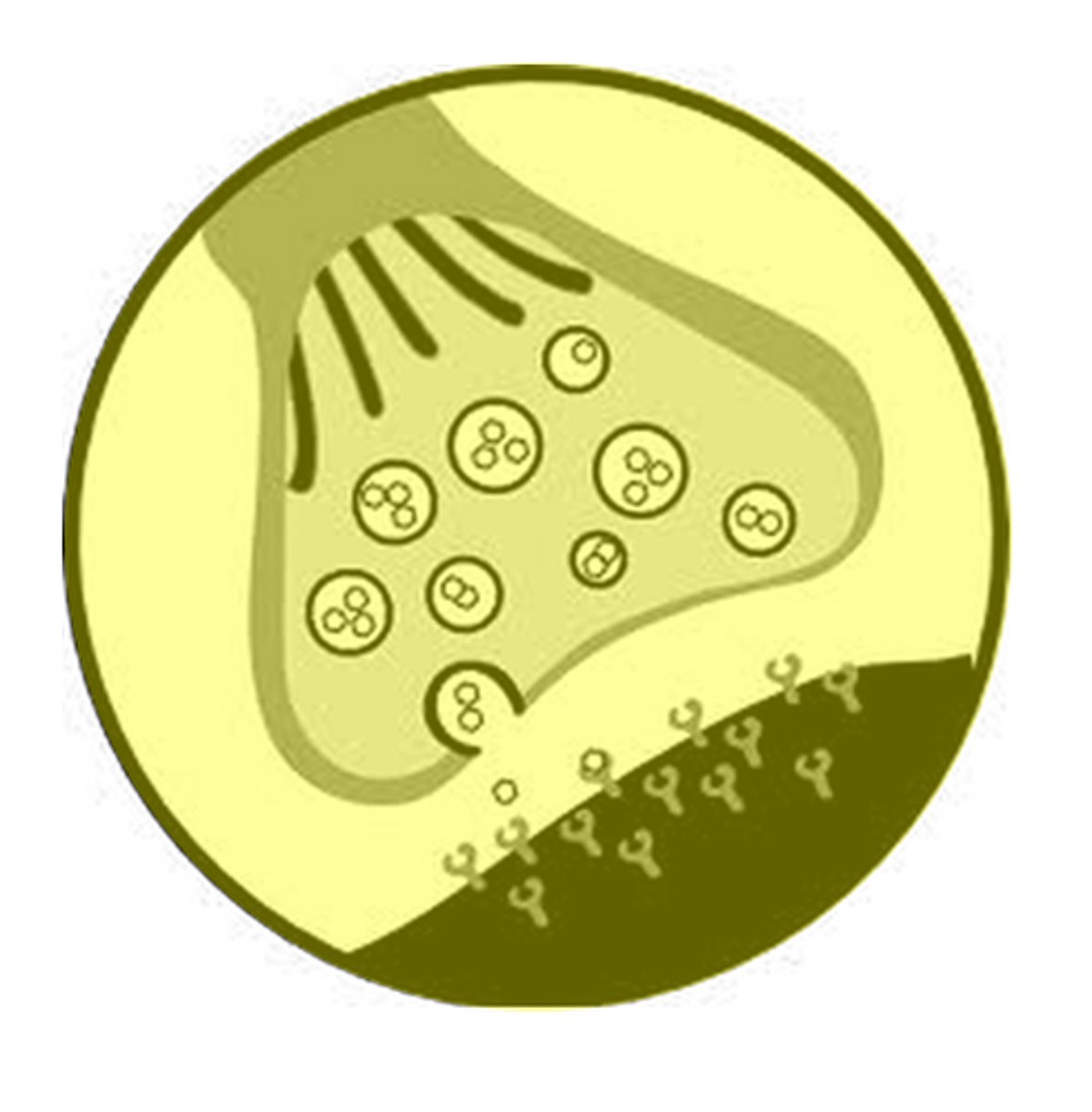
Synapse
A junction where information (electrochemical signals) is transmitted from one neuron to the next.
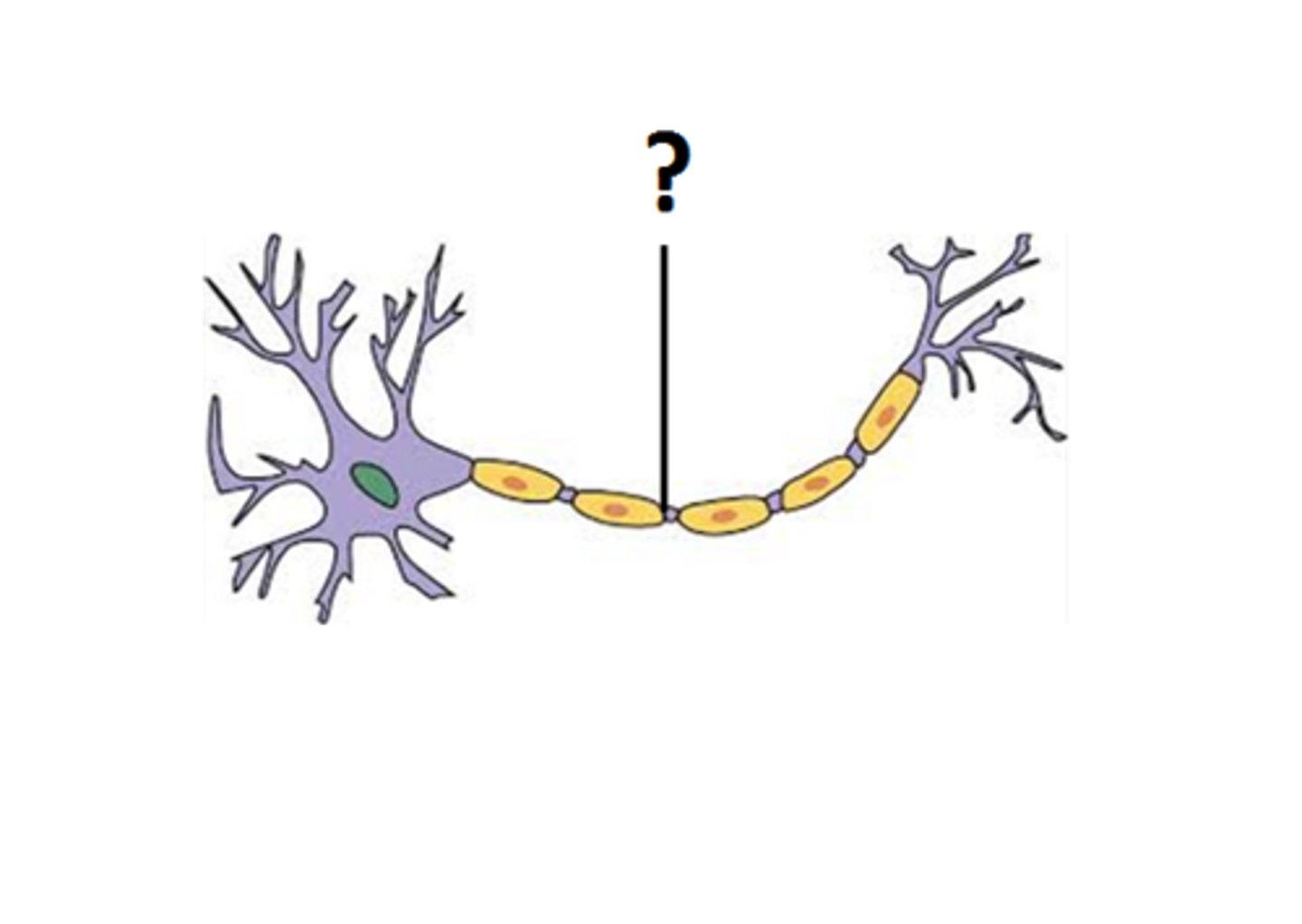
Myelin
A layer of fatty tissue covering the fibers (axons) of many neurons, which enables faster transmission speed of signals
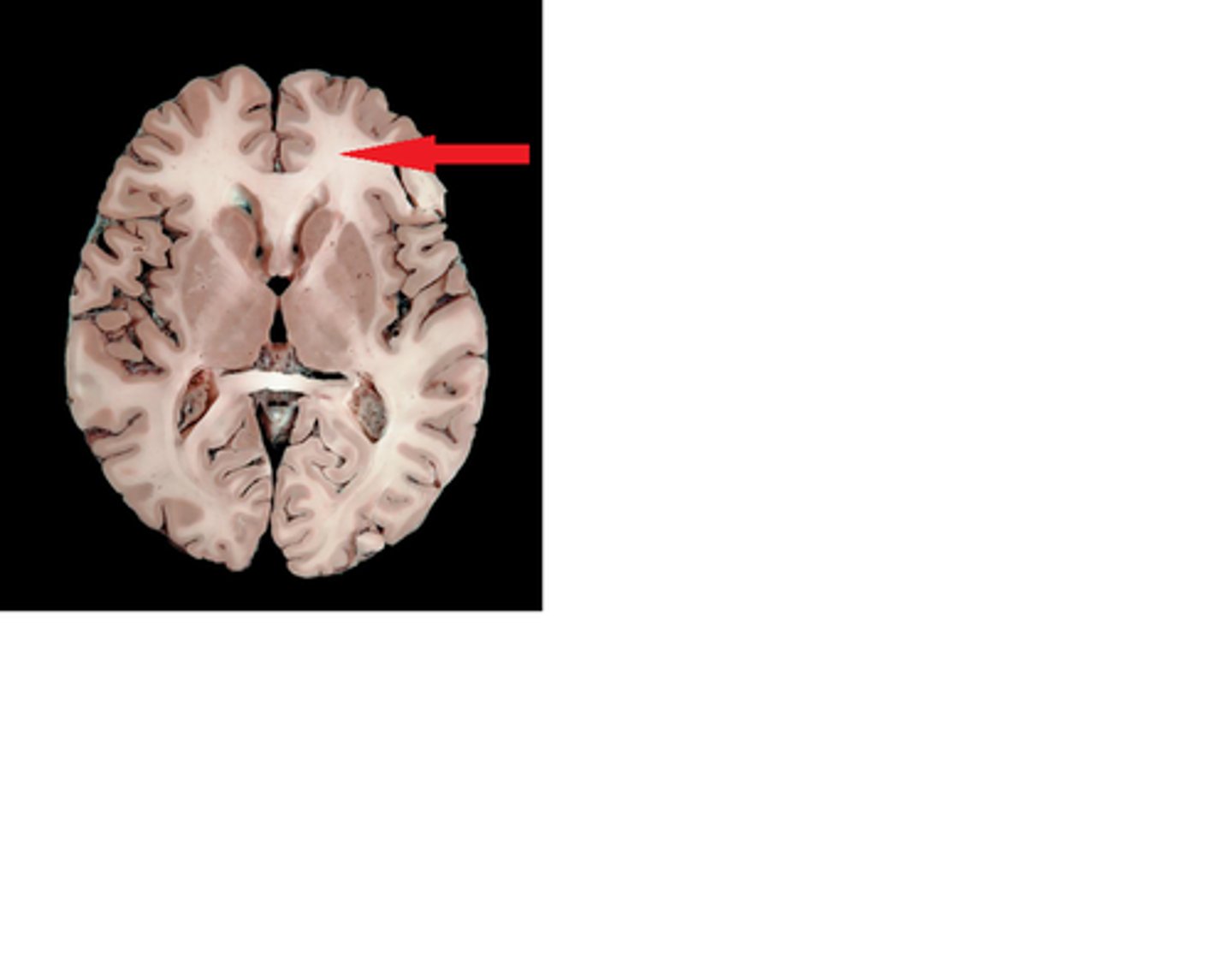
White Matter
Light-coloured conntective tissue of the brain and spinal cord consisting of the axons of neurons and their myelin sheaths. Connects parts of the brain to each other.
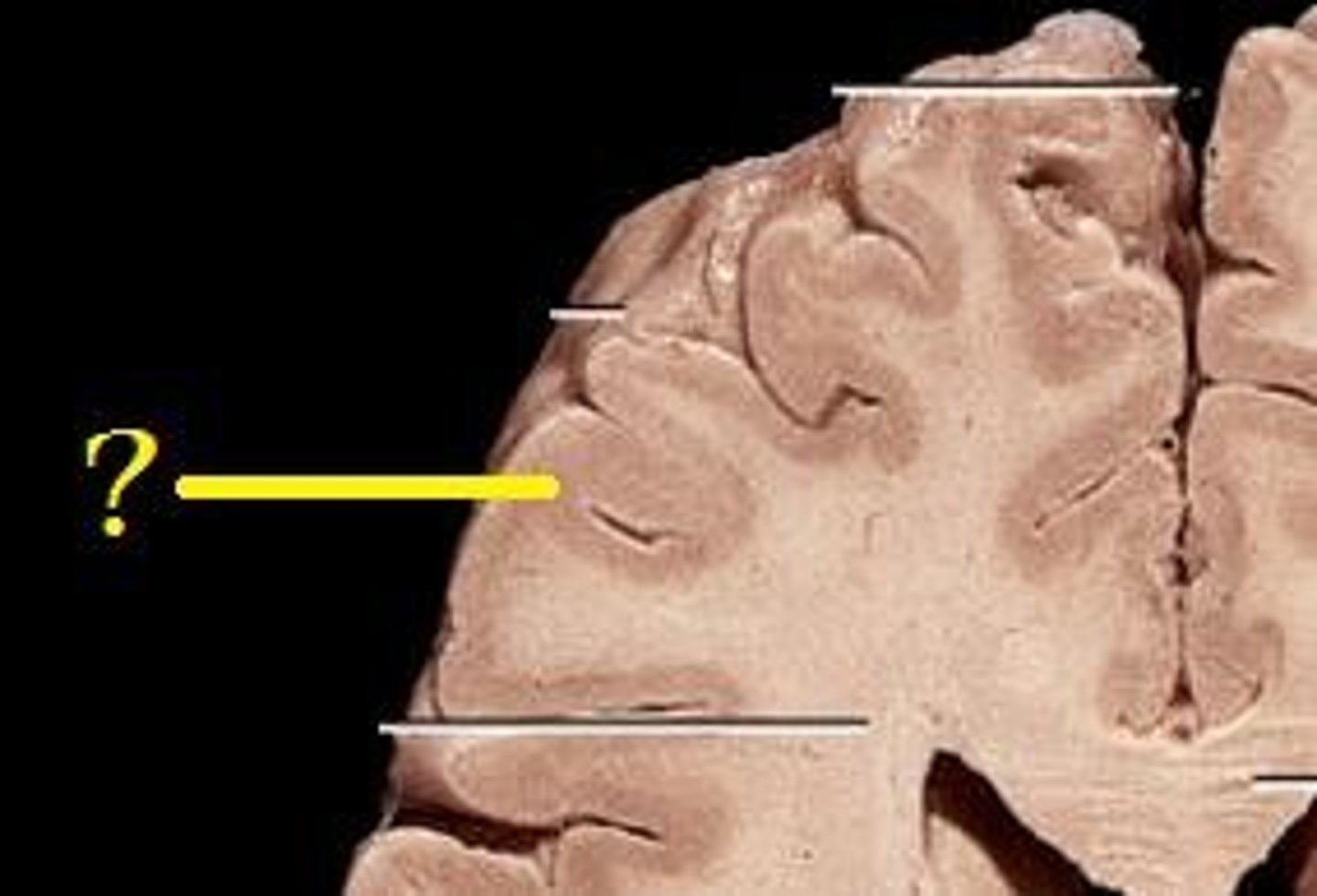
Grey Matter
Tissue in the central nervous system that is abundant in cell bodies of neurons. Responsible for "thoughts" (producing the electrochemicals to transmit).
Limbic System
A system made of several brain parts that is associated with emotions and drives
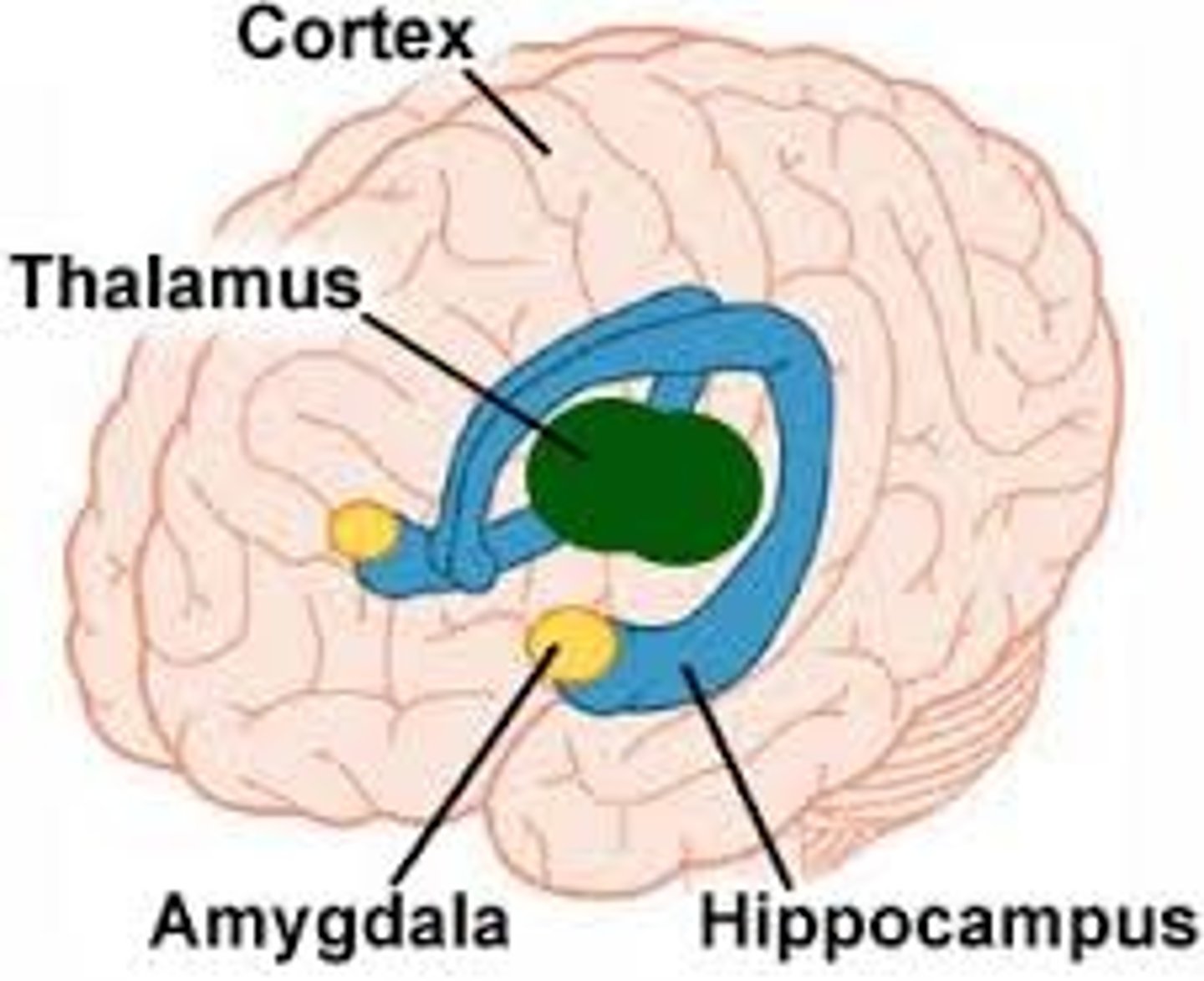
Dienchephalon
A region at the centre of the brain containing the thalamus and hypothalamus
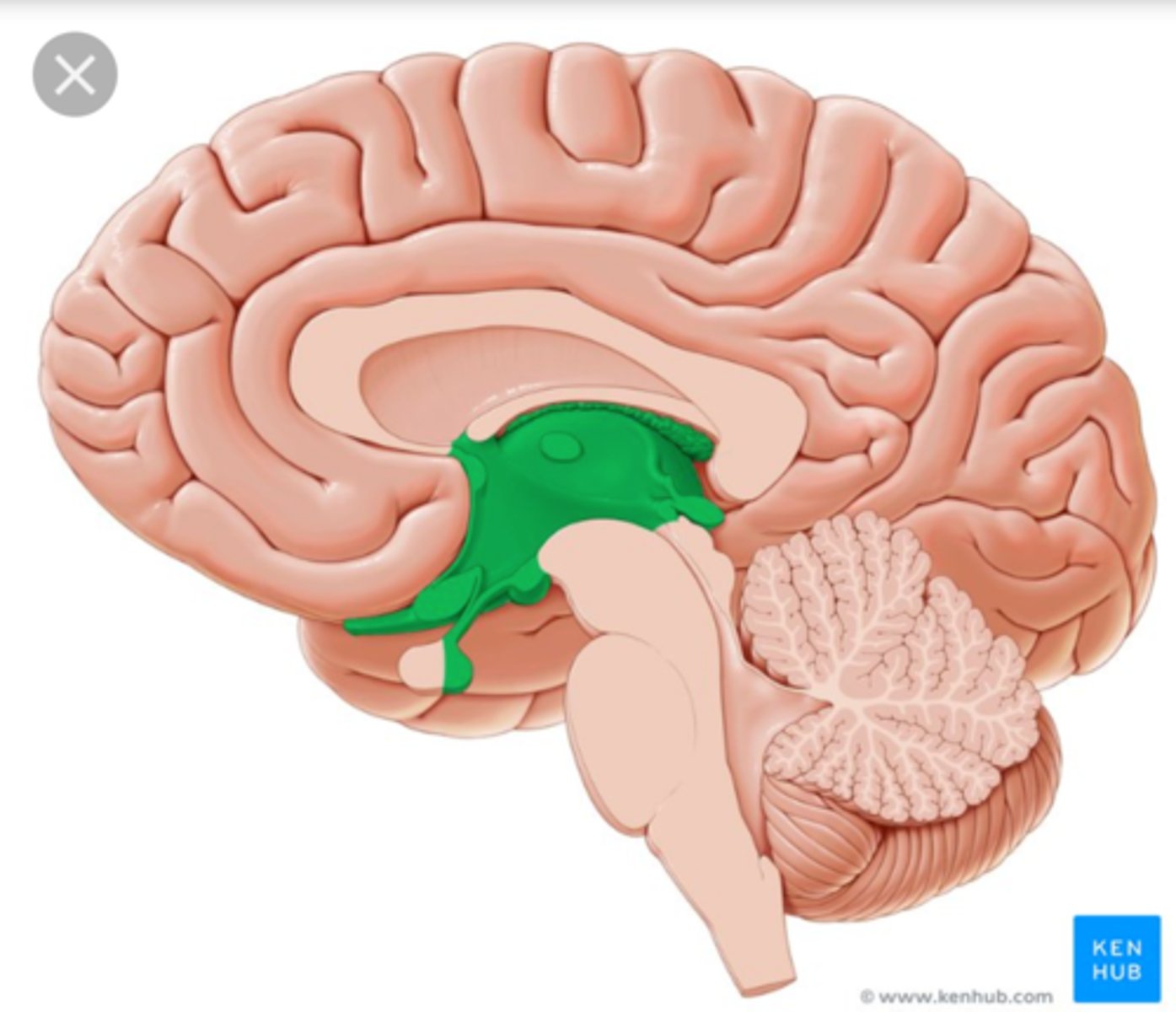
Hippocampus
A small brain part located in the temporal lobe that helps process and store memories
Neurodivergence
An umbrella term covering all conditions involving the brain working in a different way from the statistical norm
Autism
A condition, present from early childhood, characterised by difficulty in communicating and forming relationships, advanced memory, and focused interest in specific areas
ADHD
A condition marked by some of the following traits: inability to focus, hyperfocus in areas of interest, difficulty organising or planning ahead, chronic lateness, inability to finish tasks, etc.
Dyslexia
A condition marked most obviously by a difficulty reading text
Dementia
A slowly progressive decline in mental abilities, usually in old age, including declines in memory, thinking, judgment, and personality changes